Energy Dependence of Solar Energetic Protons and Their Origin in Solar Cycles 23 and 24
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) (since Oct-1975): a network of satellites in geosynchronous orbit, providing fluxes of SEPs in specific energy ranges, e.g., via the Energetic Particle Sensor, https://www.swpc.noaa.gov/products/goes-proton-flux, (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO), since Dec-1995:
- Charge, Element, and Isotope Analysis System: designed to study the composition of the solar particles in the solar wind and IP space http://www2.physik.uni-kiel.de/SOHO-CELIAS/ (accessed on 19 July 2024);
- Comprehensive Suprathermal and Energetic Particle Analyzer http://www2.physik.uni-kiel.de/et/ag-heber/costep/ (accessed on 19 July 2024), which consists of two detectors: Electron Proton Helium Instrument (EPHIN) and Low Energy Ion and Electron Instrument;
- Energetic and Relativistic Nuclei and Electron (ERNE) [16] consisting of low and high energy detector (HED), https://srl.utu.fi/projects/erne/ (accessed on 19 July 2024);
- Wind (since Nov-1994): https://wind.nasa.gov/inst_info.php (accessed on 19 July 2024):
- Wind 3D Plasma Analyzer (Wind 3DP)
- Wind SMS Suprathermal Particle Data
- Energetic Particles: Acceleration, Composition and Transport (EPACT) [17]
- STEREO (since Oct-2006), https://izw1.caltech.edu/STEREO/, https://sprg.ssl.berkeley.edu/impact/ (accessed on 19 July 2024):
- High-Energy Telescope,
- Low-Energy Telescope,
- Solar Electron Proton Telescope,
- Suprathermal Ion Telescope.
The launch of the two STEREO spacecraft ahead and behind the Earth along its orbit around the Sun leads to a different vantage point. This is why their data will not be considered for the comparative study performed here. Catalogs of STEREO SEP events have been already compiled, e.g., [18,19] and a stereoscopic perspective is required to detect the so-called wide-longitude SEPs, e.g., [20]. - Parker Solar Probe (since Aug-2018) https://parkersolarprobe.jhuapl.edu/ (accessed on 19 July 2024) and Solar Orbiter (since Feb-2020) https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Space_Science/Solar_Orbiter (accessed on 19 July 2024) are the most recent additions to the fleet of solar-dedicated missions. Due to their specific fly-by orbital motion and thus, partial temporal coverage, data from their respective particle instruments are not considered in this study.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Proton Catalogs
- 1973–2013 (250): Solar Energetic Particle Environment Modelling (SEPEM) reference event list, 7.23–10.45 MeV, DPFU, [31] http://www.sepem.eu/help/event_ref.html (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- 1976–now: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) proton list, GOES, >10 MeV, >10 pfu, ftp://ftp.swpc.noaa.gov/pub/indices/SPE.txt (https://umbra.nascom.nasa.gov/SEP/) (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- 1997–now: Coordinated Data Analysis Workshop (CDAW) major SEP events, GOES, >10 MeV, >10 pfu (based on the NOAA list but corrected for ESPs), https://cdaw.gsfc.nasa.gov/CME_list/sepe/ (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- 1997–2006 (280): International Monitoring Platform (IMP)-8, GOES, SOHO, 25–30 MeV, DPFU, [32],
- 1996–2019 (434): Wind/EPACT, 19–28 MeV and 28–72 MeV, DPFU, [33] http://www.stil.bas.bg/SEPcatalog/ (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- 1997–2014 (52): GOES MeV, pfu, [34]
- 1997–2014 (42): SOHO/EPHIN MeV, DPFU, [35].
- HED01: 14–17 (15.5) MeV
- HED02: 17–22 (19.5) MeV
- HED03: 21–28 (24.5) MeV
- HED04: 26–32 (29.0) MeV
- HED05: 32–40 (36.0) MeV
- HED06: 40–51 (45.5) MeV
- HED07: 51–67 (59.0) MeV
- HED08: 64–80 (72.0) MeV
- HED09: 80–101 (90.5) MeV
- HED10: 101–131 (116) MeV
2.2. Solar Origin Identification
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
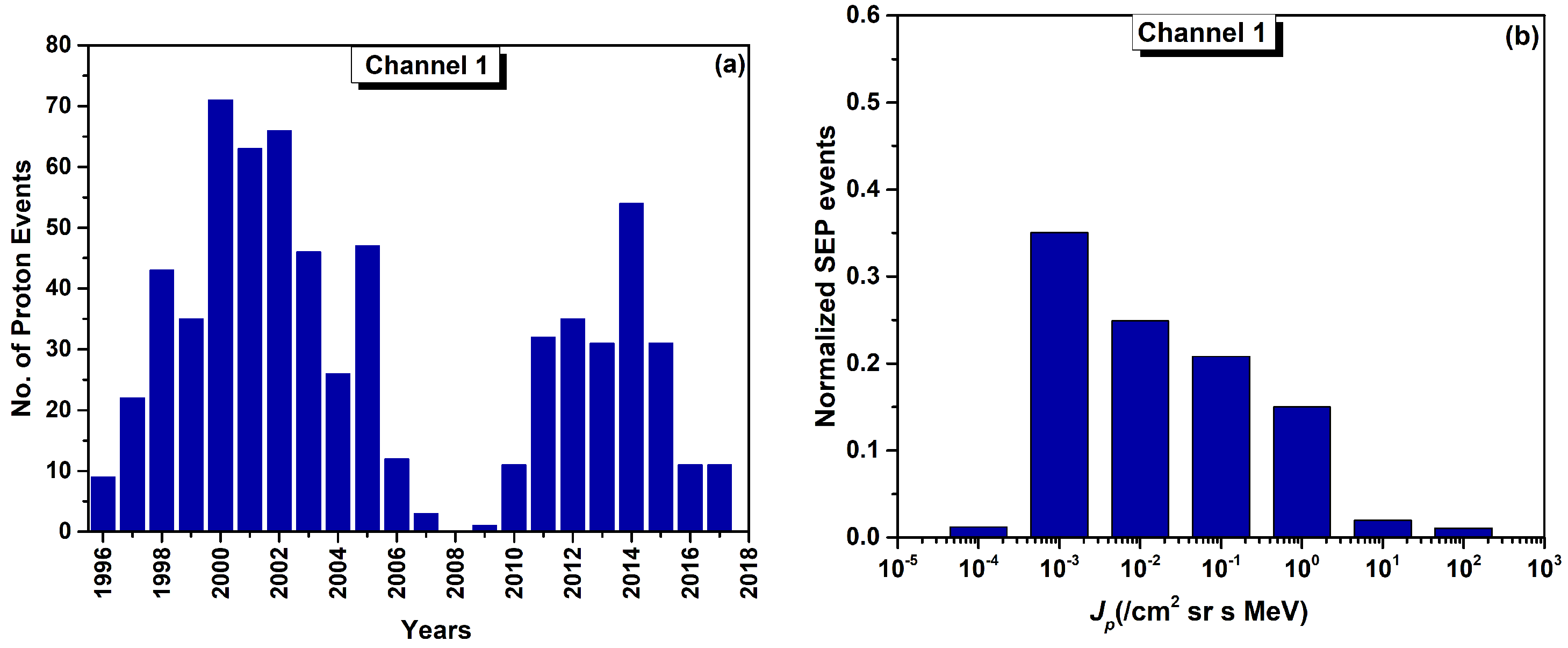
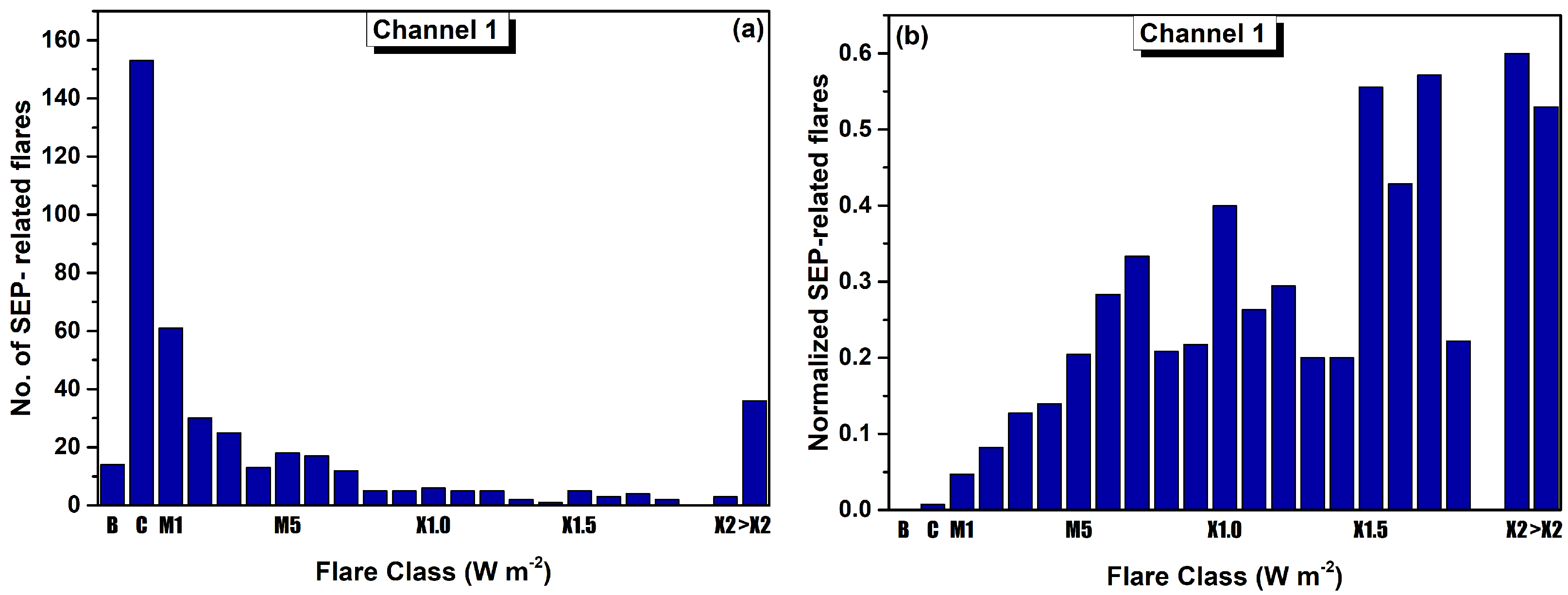
3.1. Distributions
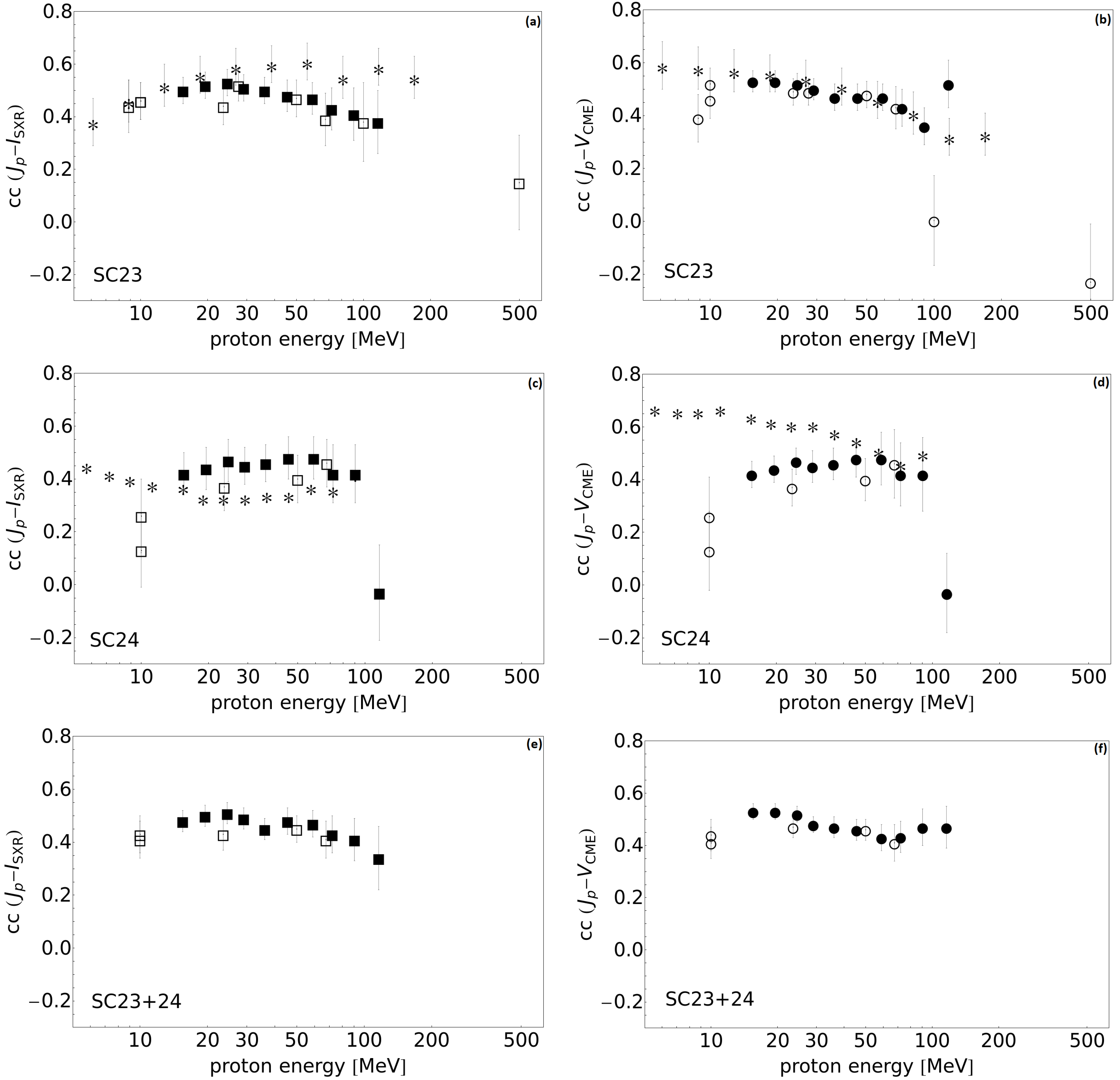
3.2. Pearson Correlations
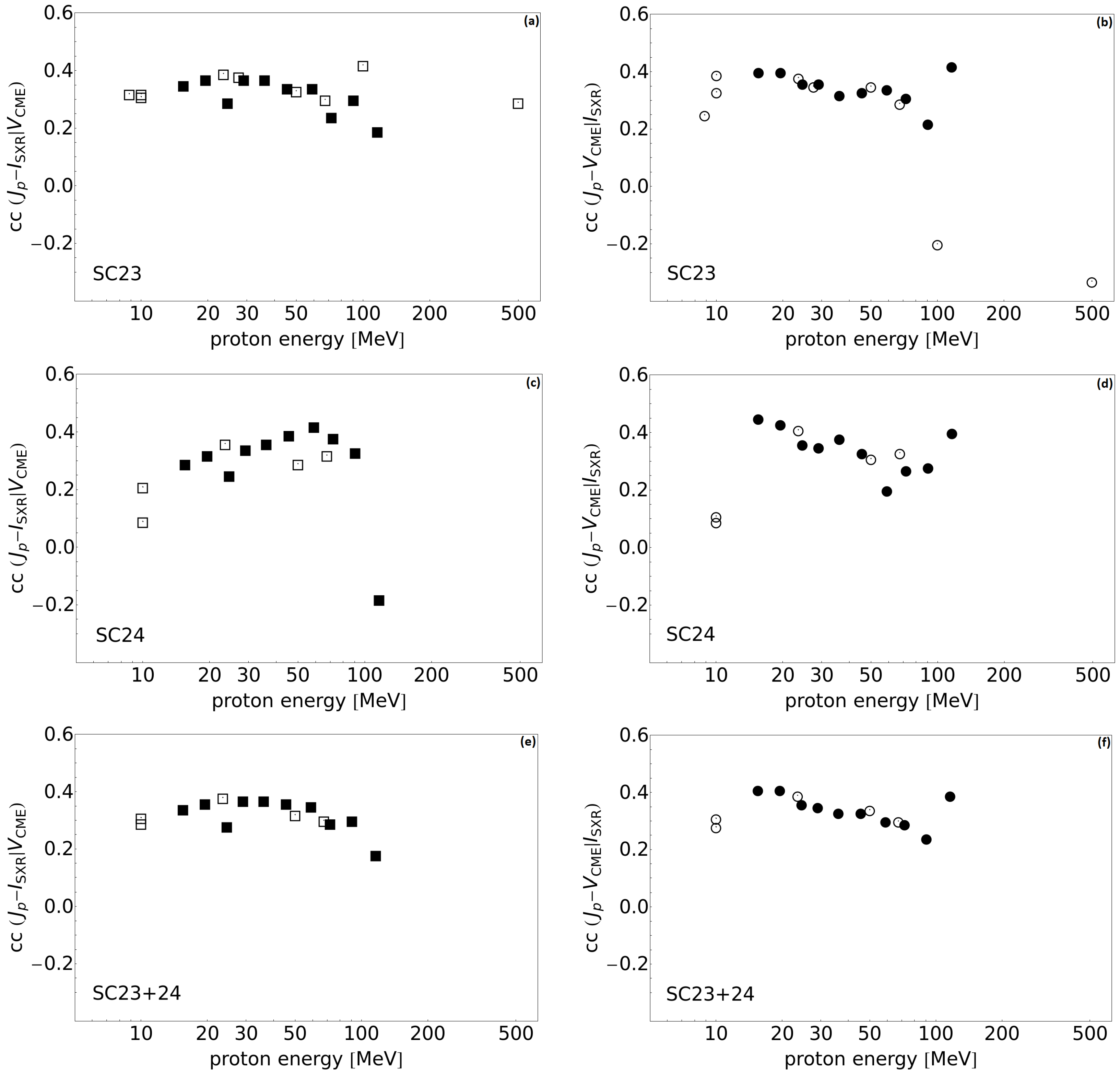
3.3. Partial Correlations
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | active region |
| AW | angular width |
| CDAW | Coordinated Data Analysis Workshop |
| CME | coronal mass ejection |
| DPFU | differential proton flux unit |
| EM | electromagnetic |
| EPACT | Energetic Particles: Acceleration, Composition and Transport |
| EPHIN | Electron Proton Helium Instrument |
| ERNE | Energetic and Relativistic Nuclei and Electron |
| ESP | energetic storm particle |
| GOES | Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite |
| GLE | ground level enhancement |
| HED | high-energy detector |
| IMP | International Monitoring Platform |
| IP | interplanetary |
| NOAA | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
| SC | solar cycle |
| SEP | solar energetic proton |
| SEPEM | Solar Energetic Particle Environment Modelling |
| SF | solar flare |
| SOHO | Solar and Heliospheric Observatory |
| SXR | soft X-ray |
| SW | space weather |
Appendix A. Properties of the Solar Origin of SEP Events
| Channel/ MeV Range | SEP Intensity | SF Class | CME Speed | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC23 | SC24 | SC23+24 | SC23 | SC24 | SC23+24 | SC23 | SC24 | SC23+24 | |
| HED01/ 14–17 | 4.6/0.03 (442) | 0.58/0.032 (217) | 3.3/0.03 (659) | M9.8/M1.7 (295) | M5.0/M1.6 (130) | M8.3/M1.6 (447) | 1030/899 (340) | 992/919 (171) | 1017/901 (511) |
| HED02/ 17–22 | 0.57/0.02 (437) | 0.36/0.010 (217) | 0.5/0.02 (653) | M9.8/M1.7 (294) | M5.0/M1.7 (129) | M8.3/M1.7 (423) | 1032/899 (339) | 994/920 (170) | 1019/903 (509) |
| HED03/ 21–28 | 0.27/0.008 (421) | 0.17/0.007 (211) | 0.24/0.007 (632) | M9.9/M1.7 (289) | M5.1/M1.7 (126) | M8.5/M1.7 (415) | 1041/906 (330) | 1003/923 (167) | 1028/916 (497) |
| HED04/ 26–32 | 0.18/0.008 (365) | 0.11/0.005 (185) | 0.16/0.006 (550) | X1.1/M2.2 (260) | M5.4/M1.8 (116) | M9.0/M1.9 (376) | 1086/957 (292) | 1023/948 (152) | 1064/953 (444) |
| HED05/ 32–40 | 0.12/0.006 (330) | 0.09/0.005 (154) | 0.12/0.006 (484) | X1.2/M2.4 (236) | M6.0/M2.0 (100) | X1.0/M2.2 (336) | 1122/1042 (268) | 1051/975 (132) | 1098/991 (400) |
| HED06/ 40–51 | 0.09/0.005 (289) | 0.06/0.004 (137) | 0.09/0.004 (426) | X1.3/M3.0 (211) | M6.4/M2.1 (93) | X1.1/M2.6 (304) | 1152/1081 (239) | 1084/997 (124) | 1128/1053 (363) |
| HED07/ 51–67 | 0.06/0.004 (223) | 0.05/0.004 (100) | 0.06/0.004 (323) | X1.5/M3.8 (174) | M7.8/M2.4 (69) | X1.3/M3.5 (243) | 1203/1136 (189) | 1142/1119 (92) | 1183/1120 (281) |
| HED08/ 64–80 | 0.04/0.003 (144) | 0.02/0.003 (52) | 0.03/0.003 (196) | X2.1/M6.0 (117) | X1.1/M5.1 (42) | X1.8/M5.6 (159) | 1314/1199 (129) | 1190/1159 (50) | 1279/1199 (179) |
| HED09/ 80–101 | 0.02/0.002 (114) | 0.007/0.002 (41) | 0.02/0.002 (155) | X2.3/M7.5 (94) | X1.2/M5.3 (33) | X2.1/M7.1 (127) | 1383/1267 (104) | 1279/1261 (40) | 1354/1261 (144) |
| HED10/ 101–131 | 2.42/0.009 (55) | 0.006/0.002 (20) | 1.8/0.003 (75) | X3.6/X1.4 (52) | X1.9/M7.9 (17) | X3.2/X1.1 (69) | 1566/1444 (52) | 1431/1418 (19) | 1530/1443 (71) |
Appendix B. Pearson Correlation Coefficients with the Projected Value of the CME Speed
| Channel/MeV Range | Difference (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC23 | SC24 | SC23+24 | SC23 | SC24 | SC23+24 | |
| SEPEM/7–10 | - | - | 2 | - | - | |
| NOAA/>10 | 3 | 1 | 3 | |||
| CDAW/>10 | 3 | 0 | 3 | |||
| HED01/14–17 | 4 | 0 | 3 | |||
| HED02/17–22 | 3 | 1 | 3 | |||
| EPACT-l/19–28 | 4 | 2 | 4 | |||
| HED03/21–28 | 3 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Cane-list/25–30 | - | - | 3 | - | - | |
| HED04/26–32 | 4 | 3 | 4 | |||
| HED05/32–40 | 4 | 2 | 3 | |||
| HED06/40–51 | 4 | 3 | 4 | |||
| EPACT-h/28–72 | 4 | 3 | 4 | |||
| HED07/51–64 | 4 | 3 | 3 | |||
| SEPServer/55–80 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||
| HED08/64–80 | 1 | 4 | 1 | |||
| HED09/80–101 | 0 | 2 | 0 | |||
| HED10/101–131 | 2 | 5 | 1 | |||
| GOES/>100 | - | - | 5 | - | - | |
| EPHIN/>500 | - | - | 6 | - | - | |
References
- Charbonneau, P. Dynamo models of the solar cycle. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2020, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathaway, D.H. The Solar Cycle. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2015, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miteva, R.; Samwel, S.W.; Costa-Duarte, M.V.; Malandraki, O.E. Solar cycle dependence of Wind/EPACT protons, solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Sun Geosph. 2017, 12, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, L.; Dennis, B.R.; Hudson, H.S.; Krucker, S.; Phillips, K.; Veronig, A.; Battaglia, M.; Bone, L.; Caspi, A.; Chen, Q.; et al. An Observational Overview of Solar Flares. Space Sci. Rev. 2011, 159, 19–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, D.F.; Howard, T.A. Coronal Mass Ejections: Observations. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2012, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, A.O. Flare Observations. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2017, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Moon, Y.J.; Kim, R.S.; Lee, H.; Cho, K.S. Comparison between 2D and 3D Parameters of 306 Front-side Halo CMEs from 2009 to 2013. Astrophys. J. 2016, 821, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, C.; Mays, M.L.; Kay, C.; Riley, P.; Palmerio, E.; Dumbović, M.; Mierla, M.; Scolini, C.; Temmer, M.; Paouris, E.; et al. Quantifying errors in 3D CME parameters derived from synthetic data using white-light reconstruction techniques. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 72, 5243–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontin, D.I.; Priest, E.R. Magnetic reconnection: MHD theory and modelling. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2022, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhina, G.S.; Tsurutani, B.T. Geomagnetic storms: Historical perspective to modern view. Geosci. Lett. 2016, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Giacalone, J. Large gradual solar energetic particle events. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2016, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpua, E.; Koskinen, H.E.J.; Pulkkinen, T.I. Coronal mass ejections and their sheath regions in interplanetary space. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2017, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, K.L.; Dalla, S. Acceleration and Propagation of Solar Energetic Particles. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 212, 1107–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, K.L. Radio astronomical tools for the study of solar energetic particles I. Correlations and diagnostics of impulsive acceleration and particle propagation. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2021, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samwel, S.W.; Miteva, R. Catalogue of in situ observed solar energetic electrons from ACE/EPAM instrument. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 505, 5212–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torsti, J.; Valtonen, E.; Lumme, M.; Peltonen, P.; Eronen, T.; Louhola, M.; Riihonen, E.; Schultz, G.; Teittinen, M.; Ahola, K.; et al. Energetic Particle Experiment ERNE. Sol. Phys. 1995, 162, 505–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Rosenvinge, T.T.; Barbier, L.M.; Karsch, J.; Liberman, R.; Madden, M.P.; Nolan, T.; Reames, D.V.; Ryan, L.; Singh, S.; Trexel, H.; et al. The Energetic Particles: Acceleration, Composition, and Transport (EPACT) investigation on the WIND spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 1995, 71, 155–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, I.G.; von Rosenvinge, T.T.; Cane, H.V.; Christian, E.R.; Cohen, C.M.S.; Labrador, A.W.; Leske, R.A.; Mewaldt, R.A.; Wiedenbeck, M.E.; Stone, E.C. > 25 MeV Proton Events Observed by the High Energy Telescopes on the STEREO A and B Spacecraft and/or at Earth During the First ∼ Seven Years of the STEREO Mission. Sol. Phys. 2014, 289, 3059–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, A.; Malandraki, O.E.; Dresing, N.; Heber, B.; Klein, K.L.; Vainio, R.; Rodríguez-Gasén, R.; Klassen, A.; Nindos, A.; Heynderickx, D.; et al. SEPServer catalogues of solar energetic particle events at 1 AU based on STEREO recordings: 2007–2012. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 569, A96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paassilta, M.; Papaioannou, A.; Dresing, N.; Vainio, R.; Valtonen, E.; Heber, B. Catalogue of {>}55 MeV Wide-longitude Solar Proton Events Observed by SOHO, ACE, and the STEREOs at {≈} 1 AU During 2009–2016. Sol. Phys. 2018, 293, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroshnichenko, L.I.; Nymmik, R.A. Extreme fluxes in solar energetic particle events: Methodological and physical limitations. Radiat. Meas. 2014, 61, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veselinović, N.; Savić, M.; Dragić, A.; Maletić, D.; Banjanac, R.; Joković, D.; Knežević, D.; Udovičić, V. Correlation analysis of solar energetic particles and secondary cosmic ray flux. Eur. Phys. J. D 2021, 75, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenn, R. Space Weather: The Solar Perspective. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2006, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulkkinen, T. Space Weather: Terrestrial Perspective. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2007, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmer, M. Space weather: The solar perspective. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2021, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semkova, J.; Koleva, R.; Benghin, V.; Dachev, T.; Matviichuk, Y.; Tomov, B.; Krastev, K.; Maltchev, S.; Dimitrov, P.; Mitrofanov, I.; et al. Charged particles radiation measurements with Liulin-MO dosimeter of FREND instrument aboard ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter during the transit and in high elliptic Mars orbit. Icarus 2018, 303, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitman, K.; Egeland, R.; Richardson, I.G.; Allison, C.; Quinn, P.; Barzilla, J.; Kitiashvili, I.; Sadykov, V.; Bain, H.M.; Dierckxsens, M.; et al. Review of Solar Energetic Particle Prediction Models. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 72, 5161–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainio, R.; Valtonen, E.; Heber, B.; Malandraki, O.E.; Papaioannou, A.; Klein, K.L.; Afanasiev, A.; Agueda, N.; Aurass, H.; Battarbee, M.; et al. The first SEPServer event catalogue ˜68-MeV solar proton events observed at 1 AU in 1996–2010. J. Space Weather. Space Clim. 2013, 3, A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paassilta, M.; Raukunen, O.; Vainio, R.; Valtonen, E.; Papaioannou, A.; Siipola, R.; Riihonen, E.; Dierckxsens, M.; Crosby, N.; Malandraki, O.; et al. Catalogue of 55–80 MeV solar proton events extending through solar cycles 23 and 24. J. Space Weather. Space Clim. 2017, 7, A14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biji, M.S.; Prince, P.R. A study of the characteristic properties of SEP events observed by SOHO ERNE during solar cycle 24. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 2902–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosby, N.; Heynderickx, D.; Jiggens, P.; Aran, A.; Sanahuja, B.; Truscott, P.; Lei, F.; Jacobs, C.; Poedts, S.; Gabriel, S.; et al. SEPEM: A tool for statistical modeling the solar energetic particle environment. Space Weather 2015, 13, 406–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cane, H.V.; Richardson, I.G.; von Rosenvinge, T.T. A study of solar energetic particle events of 1997-2006: Their composition and associations. J. Geophys. Res. (Space Phys.) 2010, 115, A08101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miteva, R.; Samwel, S.W.; Costa-Duarte, M.V. The Wind/EPACT Proton Event Catalog (1996 - 2016). Sol. Phys. 2018, 293, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, G.M.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.F. Dependence of E ≥ 100 MeV protons on the associated flares and CMEs. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 17, 073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühl, P.; Dresing, N.; Heber, B.; Klassen, A. Solar Energetic Particle Events with Protons Above 500 MeV between 1995 and 2015 Measured with SOHO/EPHIN. Sol. Phys. 2017, 292, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierckxsens, M.; Tziotziou, K.; Dalla, S.; Patsou, I.; Marsh, M.S.; Crosby, N.B.; Malandraki, O.; Tsiropoula, G. Relationship between Solar Energetic Particles and Properties of Flares and CMEs: Statistical Analysis of Solar Cycle 23 Events. Sol. Phys. 2015, 290, 841–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miteva, R.; Samwel, S.W.; Zabunov, S.; Dechev, M. On the flux saturation of SOHO/ERNE proton events. Bulg. Astron. J. 2020, 33, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Paassilta, M.; Vainio, R.; Papaioannou, A.; Raukunen, O.; Barcewicz, S.; Anastasiadis, A. Magnetic connectivity and solar energetic proton event intensity profiles at deka-MeV energy. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 71, 1840–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miteva, R. On the solar origin of in situ observed energetic protons. Bulg. Astron. J. 2019, 31, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, J.V.; Jenkins, C.R. Practical Statistics for Astronomers; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Miteva, R. On extreme space weather events: Solar eruptions, energetic protons and geomagnetic storms. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 1977–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottet, G.; Samwel, S.; Klein, K.L.; Dudok de Wit, T.; Miteva, R. Statistical Evidence for Contributions of Flares and Coronal Mass Ejections to Major Solar Energetic Particle Events. Sol. Phys. 2015, 290, 819–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, A.; Sandberg, I.; Anastasiadis, A.; Kouloumvakos, A.; Georgoulis, M.K.; Tziotziou, K.; Tsiropoula, G.; Jiggens, P.; Hilgers, A. Solar flares, coronal mass ejections and solar energetic particle event characteristics. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2016, 6, A42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Channel/MeV Range | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC23 | SC24 | SC23+24 | SC23 | SC24 | SC23+24 | |
| SEPEM/7–10 | (66) | - | - | (67) | - | - |
| NOAA/>10 | (77) | (32) | (109) | (77) | (37) | (114) |
| CDAW/>10 | (90) | (34) | (124) | (91) | (39) | (130) |
| HED01/14–17 | (295) | (130) | (425) | (340) | (171) | (511) |
| HED02/17–22 | (294) | (129) | (423) | (339) | (170) | (509) |
| EPACT-l/19–28 | (176) | (79) | (255) | (196) | (109) | (305) |
| HED03/21–28 | (289) | (126) | (415) | (329) | (167) | (496) |
| Cane-list/25–30 | (193) | - | - | (213) | - | - |
| HED04/26–32 | (260) | (116) | (376) | (292) | (152) | (444) |
| HED05/32–40 | (235) | (100) | (335) | (267) | (132) | (399) |
| HED06/40–51 | (210) | (93) | (303) | (238) | (124) | (362) |
| EPACT-h/28–72 | (168) | (71) | (239) | (186) | (97) | (283) |
| HED07/51–67 | (174) | (68) | (242) | (189) | (91) | (280) |
| SEPServer/55–80 | (91) | (45) | (136) | (100) | (58) | (158) |
| HED08/64–80 | (117) | (42) | (159) | (129) | (50) | (179) |
| HED09/80–101 | (95) | (33) | (128) | (105) | (40) | (145) |
| HED10/101–131 | (52) | (17) | (69) | (52) | (19) | (71) |
| GOES/>100 | (37) | - | - | (37) | - | - |
| EPHIN/>500 | (24) | - | - | (22) | - | - |
| Channel/MeV Range | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC23 | SC24 | SC23+24 | SC23 | SC24 | SC23+24 | |
| SEPEM/7–10 | 0.32 | - | - | 0.25 | - | - |
| NOAA/>10 | 0.31 | 0.21 | 0.31 | 0.39 | 0.09 | 0.31 |
| CDAW/>10 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 0.28 |
| HED01/14–17 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.41 |
| HED02/17–22 | 0.37 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.41 |
| HED03/21–28 | 0.39 | 0.36 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.39 |
| EPACT-l/19–28 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 |
| Cane-list/25–30 | 0.38 | - | - | 0.35 | - | - |
| HED04/26–32 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.35 | 0.35 |
| HED05/32–40 | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.37 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.33 |
| HED06/40–51 | 0.34 | 0.39 | 0.36 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| EPACT-h/28–72 | 0.33 | 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.31 | 0.34 |
| HED07/51–64 | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.35 | 0.34 | 0.20 | 0.30 |
| HED08/64–80 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.33 | 0.30 |
| SEPServer/55–80 | 0.24 | 0.38 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.29 |
| HED09/80–101 | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.22 | 0.28 | 0.24 |
| HED10/101–131 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.42 | 0.40 | 0.39 | |
| GOES/>100 | 0.42 | - | - | - | - | |
| EPHIN/>500 | 0.29 | - | - | - | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miteva, R.; Samwel, S.W.; Dechev, M. Energy Dependence of Solar Energetic Protons and Their Origin in Solar Cycles 23 and 24. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15081016
Miteva R, Samwel SW, Dechev M. Energy Dependence of Solar Energetic Protons and Their Origin in Solar Cycles 23 and 24. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(8):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15081016
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiteva, Rositsa, Susan W. Samwel, and Momchil Dechev. 2024. "Energy Dependence of Solar Energetic Protons and Their Origin in Solar Cycles 23 and 24" Atmosphere 15, no. 8: 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15081016
APA StyleMiteva, R., Samwel, S. W., & Dechev, M. (2024). Energy Dependence of Solar Energetic Protons and Their Origin in Solar Cycles 23 and 24. Atmosphere, 15(8), 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15081016






