Assessing the Impact of Climatic Factors and Air Pollutants on Cardiovascular Mortality in the Eastern Mediterranean Using Machine Learning Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Feature Selection
2.3. CVD Mortality Modelling
2.4. Evaluation Metrics and Feature Importance
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of PM2.5 and PM10 Models Across Lags
3.2. Seasonal Analysis of Model Performance
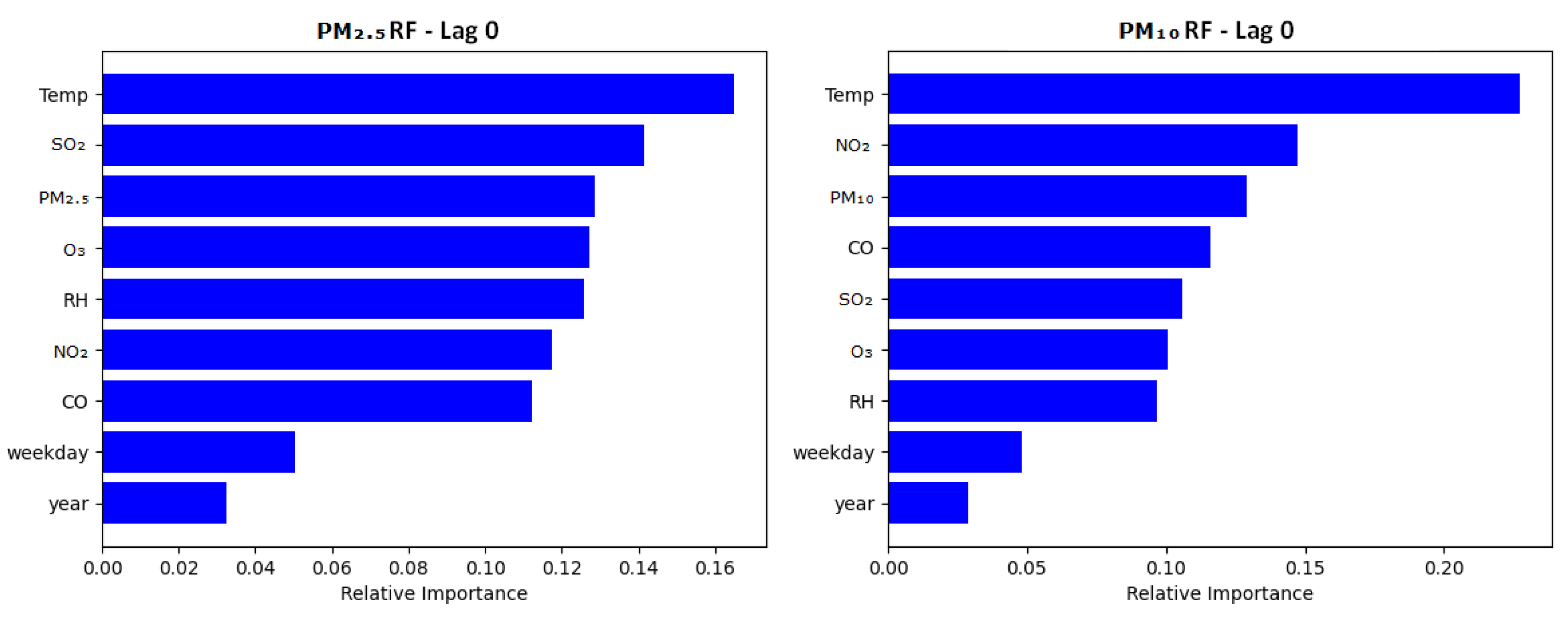
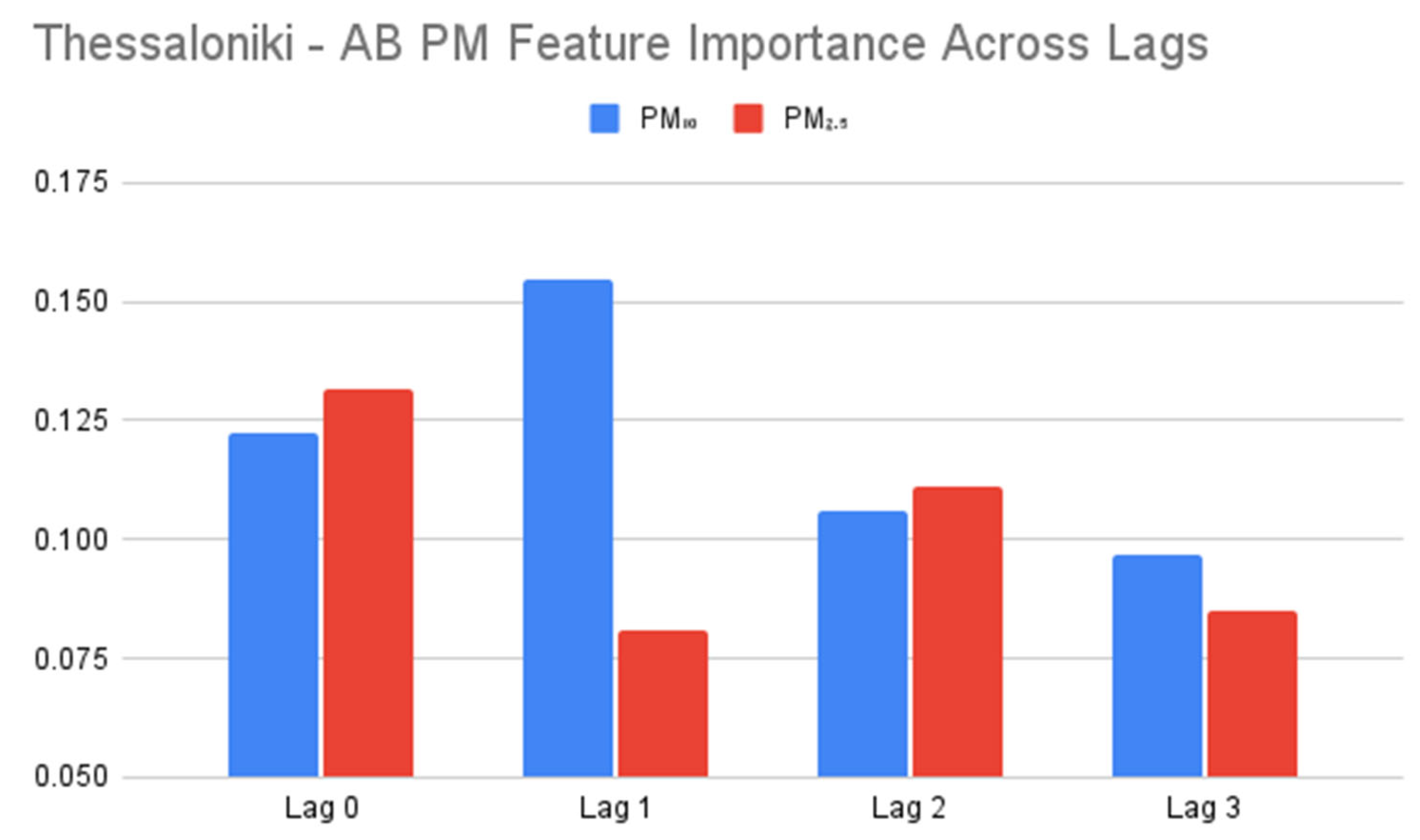
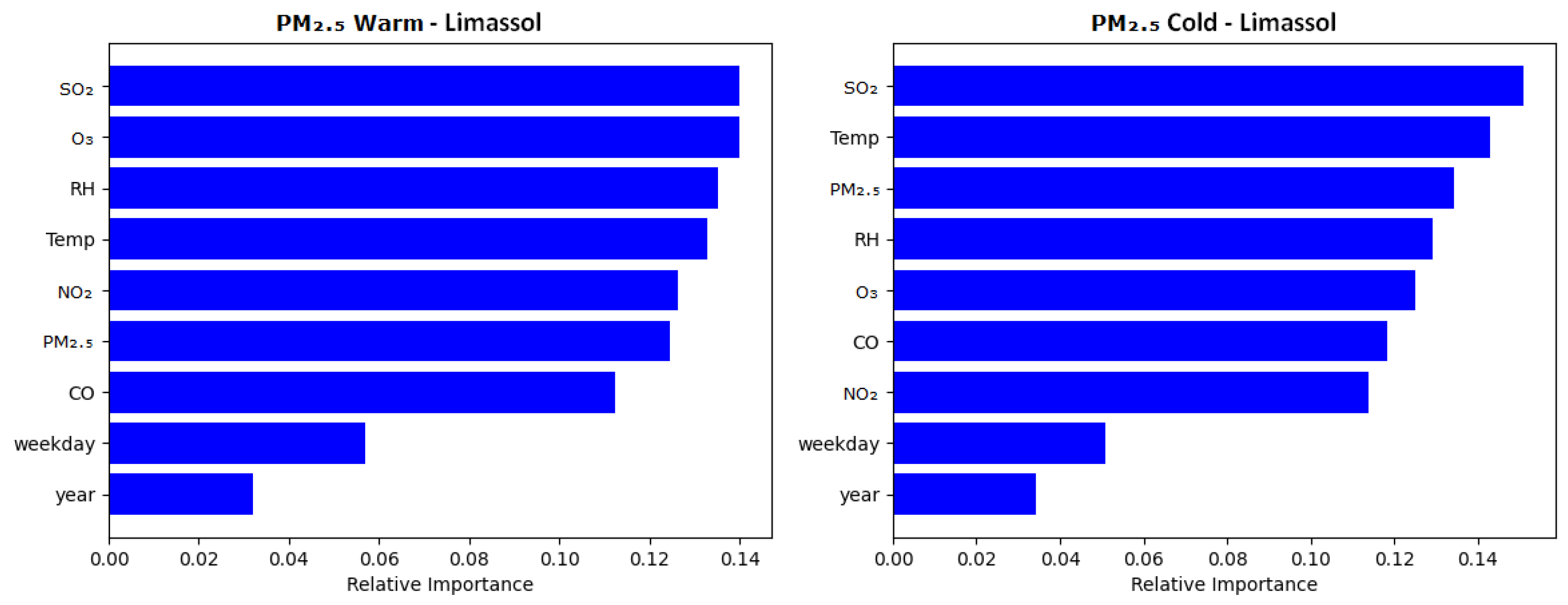
3.3. Feature Importance
3.3.1. Comparison Across Lags
3.3.2. Seasonality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Heart Federation. World Heart Report 2023: Confronting the World’s Number One Killer. Available online: https://world-heart-federation.org/resource/world-heart-report-2023/ (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Fuster, V. The global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risks: A compass for global action. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2980–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodruff, R.C.; Tong, X.; Khan, S.S.; Shah, N.S.; Jackson, S.L.; Loustalot, F.; Vaughan, A.S. Trends in cardiovascular disease mortality rates and excess deaths, 2010–2022. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2024, 66, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Mensah, G.A.; Turco, J.V.; Fuster, V.; Roth, G.A. The global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk: A compass for future health. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 2361–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilleos, S.; Al-Ozairi, E.; Alahmad, B.; Garshick, E.; Neophytou, A.M.; Bouhamra, W.; Yassin, M.F.; Koutrakis, P. Acute effects of air pollution on mortality: A 17-year analysis in Kuwait. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellano, P.; Reynoso, J.; Quaranta, N.; Bardach, A.; Ciapponi, A. Short-term exposure to particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and ozone (O3) and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo-Ojo, T.C.; Wichmann, J.; Arowosegbe, O.O.; Probst-Hensch, N.; Schindler, C.; Künzli, N. Short-term effects of PM10, NO2, SO2, and O3 on cardio-respiratory mortality in Cape Town, South Africa, 2006–2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bont, J.; Jaganathan, S.; Dahlquist, M.; Persson, Å.; Stafoggia, M.; Ljungman, P. Ambient air pollution and cardiovascular diseases: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 291, 779–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Liu, F.; Yu, H.; Wu, S.; Xiang, H. Association between exposure to ambient air pollution and hospital admission, incidence, and mortality of stroke: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of more than 23 million participants. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2021, 26, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellano, P.; Kasdagli, M.I.; Pérez Velasco, R.; Samoli, E. Long-term exposure to particulate matter and mortality: An update of the WHO global air quality guidelines systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Public Health 2024, 69, 1607683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmad, B.; Li, J.; Achilleos, S.; Al-Mulla, F.; Al-Hemoud, A.; Koutrakis, P. Burden of fine air pollution on mortality in the desert climate of Kuwait. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2023, 33, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, H.W.L.; Ng, D.C.Y. Spatial and Socio-Classification of Traffic Pollutant Emissions and Associated Mortality Rates in High-Density Hong Kong via Improved Data Analytic Approaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2021 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden and strength of evidence for 88 risk factors in 204 countries and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2162–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.H.; Bo, Y.C.; You, J.; Liu, S.F.; Liu, M.J.; Zhu, Y.J. Spatiotemporal trends of cardiovascular disease burden attributable to ambient PM2.5 from 1990 to 2019: A global burden of disease study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- European Environment Agency. Air Quality in Europe—2020 Report; (EEA Report No. 09/2020); 2020. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/air-quality-in-europe-2020-report (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- World Health Organization. Exposure & Health Impacts of Air Pollution. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/environment-climate-change-and-health/air-quality-energy-and-health/health-impacts/exposure-air-pollution (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Liu, C.; Yavar, Z.; Sun, Q. Cardiovascular response to thermoregulatory challenges. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H1793–H1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, H.; Ban, J.; Gong, J.; Li, T. Cardiovascular mortality risks during the 2017 exceptional heatwaves in China. Environ. Int. 2023, 172, 107767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatana, S.A.M.; Werner, R.M.; Groeneveld, P.W. Association of Extreme Heat and Cardiovascular Mortality in the United States: A County-Level Longitudinal Analysis From 2008 to 2017. Circulation 2022, 146, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Sun, Z.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Miao, S.; Zheng, C.; Tong, S. Impacts of Urbanization on the Temperature-Cardiovascular Mortality Relationship in Beijing, China. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellei, M.; Herrera, M.; Fosas, D.; Natarajan, S. The influence of relative humidity on adaptive thermal comfort. Build. Environ. 2017, 124, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H.; Tsai, H.-H.; Chen, H.-C. Influence of weather factors on thermal comfort in subtropical urban environments. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, J.; Liu, J. Effects of elevated air speed on thermal comfort in hot-humid climate and the extended summer comfort zone. Energy Build. 2023, 287, 112953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavcová, E.; Kyselý, J. Effects of sudden air pressure changes on hospital admissions for cardiovascular diseases in Prague, 1994–2009. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2014, 58, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussoussou, N.; Boussoussou, M.; Merész, G.; Rakovics, M.; Entz, L.; Nemes, A. Complex effects of atmospheric parameters on acute cardiovascular diseases and major cardiovascular risk factors: Data from the CardiometeorologySM study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrignani, M.G.; Lombardo, A.; Braschi, A.; Renda, N.; Abrignani, V. Climatic influences on cardiovascular diseases. World J. Cardiol. 2022, 14, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Li, A.; Zhao, M.; Xu, J.; Li, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Q.; Ge, X.; Xu, Q. Associations and burdens of relative humidity with cause-specific mortality in three Chinese cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 3512–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouis, P.; Kakkoura, M.; Ziogas, K.; Paschalidou, A.K.; Papatheodorou, S.I. The effect of ambient air temperature on cardiovascular and respiratory mortality in Thessaloniki, Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, R.; Sera, F.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Guo, Y.; Tong, S.; Coelho, M.S.Z.S.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; Lavigne, E.; Matus, P.; et al. Ambient particulate air pollution and daily mortality in 652 cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; He, J.; Ponsawansong, P.; Jin, J.; Xu, Z.; Yang, T.; Pan, X.; Prapamontol, T.; et al. The mortality effect of apparent temperature: A multi-city study in Asia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, L.d.S.V.; de Oliveira, B.F.A.; Schneider, R.; Gasparrini, A.; Hacon, S.d.S. Mortality risk from respiratory diseases due to non-optimal temperature among Brazilian elderlies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Santana, P.; Rocha, A. Modelling of temperature-attributable mortality among the elderly in Lisbon metropolitan area, Portugal: A contribution to local strategy for effective prevention plans. J. Urban Health 2021, 98, 516–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parliari, D.; Cheristanidis, S.; Giannaros, C.; Keppas, S.C.; Papadogiannaki, S.; de’Donato, F.; Sarras, C.; Melas, D. Short-term effects of apparent temperature on cause-specific mortality in the urban area of Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psistaki, K.; Achilleos, S.; Middleton, N.; Paschalidou, A.K. Exploring the impact of particulate matter on mortality in coastal Mediterranean environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psistaki, K.; Dokas, I.M.; Paschalidou, A.K. Analysis of the heat- and cold-related cardiovascular mortality in an urban Mediterranean environment through various thermal indices. Environ. Res. 2023, 216 Pt 4, 114831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psistaki, K.; Dokas, I.M.; Paschalidou, A.K. The impact of ambient temperature on cardiorespiratory mortality in northern Greece. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Schwartz, J.D.; O’Neill, M.S. What weather variables are important in predicting heat-related mortality? A new application of statistical learning methods. Environ. Res. 2014, 132, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, Q.; Du, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Du, Z.; Li, T. A random forest model to predict heatstroke occurrence for heatwave in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650 Pt 2, 3048–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Luo, L.; Su, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y. Machine learning approaches to predict peak demand days of cardiovascular admissions considering environmental exposure. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2020, 20, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marien, L.; Valizadeh, M.; zu Castell, W.; Nam, C.; Rechid, D.; Schneider, A.; Meisinger, C.; Linseisen, J.; Wolf, K.; Bouwer, L.M. Machine learning models to predict myocardial infarctions from past climatic and environmental conditions. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 3015–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreault, J.; Campagna, C.; Chebana, F. Machine and deep learning for modelling heat-health relationships. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.; Patel, D.; Xiao, J.; Jansz, J.; Yun, G.; Lin, T.; Robertson, A. Can we use a machine learning approach to predict the impact of heatwaves on emergency department attendance? Environ. Res. Commun. 2023, 5, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, F.; Castronuovo, G.; Grimaldi, S.; Telesca, V. Random forest and feature importance measures for discriminating the most influential environmental factors in predicting cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Wu, C.H.; Luo, K.H.; Chang, H.C.; Wu, S.C.; Chuang, H.Y. Use of Machine Learning Algorithms to Determine the Relationship Between Air Pollution and Cognitive Impairment in Taiwan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 284, 116885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, H.W.L. Improved Remote Sensing Algorithms and Data Assimilation Approaches in Solving Environmental Retrieval Problems. Ph.D. Thesis, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong, China, 2019. Available online: https://lbezone.hkust.edu.hk/bib/991012752564803412 (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Pozzer, A.; Steffens, B.; Proestos, Y.; Sciare, J.; Akritidis, D.; Chowdhury, S.; Burkart, K.; Bacer, S. Atmospheric health burden across the century and the accelerating impact of temperature compared to pollution. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.-Y.; Liu, J.C.; Bell, M.L. Temperature-related mortality: A systematic review and investigation of effect modifiers. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 073004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anenberg, S.C.; Haines, S.; Wang, E.; Nassikas, N.; Kinney, P.L. Synergistic health effects of air pollution, temperature, and pollen exposure: A systematic review of epidemiological evidence. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorieva, E.; Lukyanets, A. Combined effect of hot weather and outdoor air pollution on respiratory health: Literature review. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafoggia, M.; Michelozzi, P.; Schneider, A.; Armstrong, B.; Scortichini, M.; Rai, M.; Achilleos, S.; Alahmad, B.; Analitis, A.; Åström, C.; et al. Joint effect of heat and air pollution on mortality in 620 cities of 36 countries. Environ. Int. 2023, 181, 108258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Breitner, S.; Stafoggia, M.; Donato, F.D.; Samoli, E.; Zafeiratou, S.; Katsouyanni, K.; Rao, S.; Diz-Lois Palomares, A.; Gasparrini, A.; et al. Effect modification of air pollution on the association between heat and mortality in five European countries. Environ. Res. 2024, 263 Pt 1, 120023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionello, P.; Scarascia, L. The relation between climate change in the Mediterranean region and global warming. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2018, 18, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zittis, G.; Almazroui, M.; Alpert, P.; Ciais, P.; Cramer, W.; Dahdal, Y.; Fnais, M.; Francis, D.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Howari, F.; et al. Climate change and weather extremes in the Eastern Mediterranean and Middle East. Rev. Geophys. 2022, 60, e2021RG000762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochman, A.; Marra, F.; Messori, G.; Pinto, J.G.; Raveh-Rubin, S.; Yosef, Y.; Zittis, G. Extreme weather and societal impacts in the eastern Mediterranean. Earth Syst. Dynam. 2022, 13, 749–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, U.; Ricaud, P.; Zbinden, R.; Dulac, F. Atmospheric pollution over the eastern Mediterranean during summer—A review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 13233–13263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulac, F.; Sauvage, S.; Hamonou, E. (Eds.) Atmospheric Chemistry in the Mediterranean Region: Volume 2—From Air Pollutant Sources to Impacts; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsangari, H.; Paschalidou, A.; Vardoulakis, S.; Heaviside, C.; Konsoula, Z.; Christou, S.; Georgiou, K.E.; Ioannou, K.; Mesimeris, T.; Kleanthous, S.; et al. Human mortality in Cyprus: The role of temperature and particulate air pollution. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2016, 16, 1905–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmad, B.; Yuan, Q.; Achilleos, S.; Salameh, P.; Papatheodorou, S.I.; Koutrakis, P. Evaluating the temperature-mortality relationship over 16 years in Cyprus. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2024, 74, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stapleton, A.; Eichelmann, E.; Roantree, M. A framework for constructing machine learning models with feature set optimisation for evapotranspiration partitioning. Appl. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 16, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londschien, M.; Bühlmann, P.; Kovács, S. Random forests for change point detection. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2023, 24, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujon, K.M.; Hassan, R.B.; Towshi, Z.T.; Othman, M.A.; Samad, M.A.; Choi, K. When to Use Standardization and Normalization: Empirical Evidence from Machine Learning Models and XAI. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 135300–135314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrar, D. Cross-Validation. In Reference Module in Life Sciences Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology; Ranganathan, S., Gribskov, M., Nakai, K., Schönbach, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.; Gunn, S. Identifying feature relevance using a random forest. In Subspace, Latent Structure and Feature Selection; Saunders, C., Grobelnik, M., Gunn, S., Shawe-Taylor, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wang, D.; Niu, X.; Sun, J.; Xu, H.; Cao, J.; Shen, Z. Application of machine learning in atmospheric pollution research: A state-of-art review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 910, 168588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahakalkar, A.U.; Gianquintieri, L.; Amici, L.; Brovelli, M.A.; Caiani, E.G. Geospatial analysis of short-term exposure to air pollution and risk of cardiovascular diseases and mortality—A systematic review. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, R.; Sera, F.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Milojevic, A.; Guo, Y.; Tong, S.; Coelho, M.S.Z.S.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; et al. Short-term associations of ambient nitrogen dioxide with daily total, cardiovascular, and respiratory mortality: Multilocation analysis in 398 cities. BMJ 2021, 372, n534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castronuovo, G.; Favia, G.; Telesca, V.; Vammacigno, A. Analyzing the Interactions between Environmental Parameters and Cardiovascular Diseases Using Random Forest and SHAP Algorithms. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 24, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alahmad, B.; Khraishah, H.; Royé, D.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Guo, Y.; Papatheodorou, S.I.; Achilleos, S.; Acquaotta, F.; Armstrong, B.; Bell, M.L.; et al. Associations between extreme temperatures and cardiovascular cause-specific mortality: Results from 27 countries. Circulation 2023, 147, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, E.; Masselot, P.; Sera, F.; Roye, D.; Breitner, S.; Ng, C.F.S.; de Sousa Zanotti Stagliorio Coelho, M.; Madureira, J.; Tobias, A.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; et al. Short-term association between sulfur dioxide and mortality: A multicountry analysis in 399 cities. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 037002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaran, K.; Gasparrini, A.; Hajat, S.; Smeeth, L.; Armstrong, B. Time series regression studies in environmental epidemiology. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henschel, S.; Querol, X.; Atkinson, R.; Pandolfi, M.; Zeka, A.; Le Tertre, A.; Analitis, A.; Katsouyanni, K.; Chanel, O.; Pascal, M.; et al. Ambient air SO2 patterns in 6 European cities. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Thessaloniki PM2.5 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE 0 | MAE 1 | MAE 2 | MAE 3 | RMSE 0 | RMSE 1 | RMSE 2 | RMSE 3 | |
| AB | 2.851 | 2.837 | 2.837 | 2.825 | 3.589 | 3.572 | 3.568 | 3.558 |
| DT | 4.061 | 4.157 | 4.108 | 4.226 | 5.145 | 5.214 | 5.200 | 5.368 |
| ET | 2.869 | 2.862 | 2.866 | 2.864 | 3.628 | 3.615 | 3.617 | 3.620 |
| RF | 2.875 | 2.852 | 2.842 | 2.857 | 3.626 | 3.609 | 3.593 | 3.609 |
| XGB | 3.180 | 3.112 | 3.116 | 3.093 | 4.007 | 3.928 | 3.939 | 3.916 |
| Thessaloniki PM10 | ||||||||
| AB | 2.833 | 2.849 | 2.834 | 2.862 | 3.576 | 3.582 | 3.575 | 3.592 |
| DT | 4.125 | 4.176 | 4.149 | 4.129 | 5.199 | 5.275 | 5.217 | 5.240 |
| ET | 2.892 | 2.897 | 2.882 | 2.908 | 3.646 | 3.646 | 3.629 | 3.648 |
| RF | 2.872 | 2.882 | 2.853 | 2.872 | 3.626 | 3.629 | 3.596 | 3.611 |
| XGB | 3.178 | 3.168 | 3.141 | 3.179 | 4.011 | 3.983 | 3.944 | 3.990 |
| Limassol PM2.5 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE 0 | MAE 2 | MAE 1 | MAE 3 | RMSE 0 | RMSE 1 | RMSE 2 | RMSE 3 | |
| AB | 1.070 | 1.110 | 1.056 | 1.071 | 1.307 | 1.357 | 1.290 | 1.306 |
| DT | 1.372 | 1.382 | 1.406 | 1.395 | 1.809 | 1.825 | 1.848 | 1.808 |
| ET | 1.042 | 1.047 | 1.039 | 1.031 | 1.307 | 1.321 | 1.294 | 1.283 |
| RF | 1.027 | 1.032 | 1.028 | 1.020 | 1.286 | 1.299 | 1.282 | 1.276 |
| XGB | 1.125 | 1.099 | 1.110 | 1.119 | 1.416 | 1.404 | 1.398 | 1.410 |
| Limassol PM10 | ||||||||
| AB | 1.142 | 1.133 | 1.090 | 1.093 | 1.385 | 1.375 | 1.330 | 1.335 |
| DT | 1.406 | 1.405 | 1.412 | 1.414 | 1.863 | 1.855 | 1.849 | 1.833 |
| ET | 1.050 | 1.041 | 1.038 | 1.037 | 1.318 | 1.304 | 1.296 | 1.291 |
| RF | 1.043 | 1.038 | 1.031 | 1.032 | 1.304 | 1.294 | 1.284 | 1.285 |
| XGB | 1.141 | 1.125 | 1.121 | 1.132 | 1.440 | 1.421 | 1.414 | 1.420 |
| Thessaloniki PM2.5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE Warm | MAE Cold | RMSE Warm | RMSE Cold | |
| AB | 2.786 | 2.955 | 3.492 | 3.691 |
| DT | 3.934 | 4.457 | 4.952 | 5.558 |
| ET | 2.863 | 3.023 | 3.587 | 3.809 |
| RF | 2.836 | 2.957 | 3.557 | 3.716 |
| XGB | 3.100 | 3.408 | 3.922 | 4.254 |
| Thessaloniki PM10 | ||||
| AB | 2.761 | 2.954 | 3.461 | 3.724 |
| DT | 3.855 | 4.345 | 4.890 | 5.468 |
| ET | 2.839 | 3.021 | 3.548 | 3.801 |
| RF | 2.776 | 2.972 | 3.482 | 3.743 |
| XGB | 3.060 | 3.297 | 3.843 | 4.179 |
| Limassol PM2.5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE Warm | MAE Cold | RMSE Warm | RMSE Cold | |
| AB | 1.066 | 1.145 | 1.280 | 1.432 |
| DT | 1.475 | 1.459 | 1.876 | 1.910 |
| ET | 1.029 | 1.130 | 1.271 | 1.418 |
| RF | 0.998 | 1.105 | 1.231 | 1.390 |
| XGB | 1.083 | 1.192 | 1.344 | 1.506 |
| Limassol PM10 | ||||
| AB | 1.018 | 1.173 | 1.221 | 1.455 |
| DT | 1.347 | 1.559 | 1.738 | 2.056 |
| ET | 0.999 | 1.129 | 1.239 | 1.428 |
| RF | 0.981 | 1.134 | 1.218 | 1.430 |
| XGB | 1.064 | 1.242 | 1.337 | 1.577 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Psistaki, K.; Richardson, D.; Achilleos, S.; Roantree, M.; Paschalidou, A.K. Assessing the Impact of Climatic Factors and Air Pollutants on Cardiovascular Mortality in the Eastern Mediterranean Using Machine Learning Models. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030325
Psistaki K, Richardson D, Achilleos S, Roantree M, Paschalidou AK. Assessing the Impact of Climatic Factors and Air Pollutants on Cardiovascular Mortality in the Eastern Mediterranean Using Machine Learning Models. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(3):325. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030325
Chicago/Turabian StylePsistaki, Kyriaki, Damhan Richardson, Souzana Achilleos, Mark Roantree, and Anastasia K. Paschalidou. 2025. "Assessing the Impact of Climatic Factors and Air Pollutants on Cardiovascular Mortality in the Eastern Mediterranean Using Machine Learning Models" Atmosphere 16, no. 3: 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030325
APA StylePsistaki, K., Richardson, D., Achilleos, S., Roantree, M., & Paschalidou, A. K. (2025). Assessing the Impact of Climatic Factors and Air Pollutants on Cardiovascular Mortality in the Eastern Mediterranean Using Machine Learning Models. Atmosphere, 16(3), 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030325











