Assessing the Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Health Impacts of Surface Ozone Pollution in Beijing, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
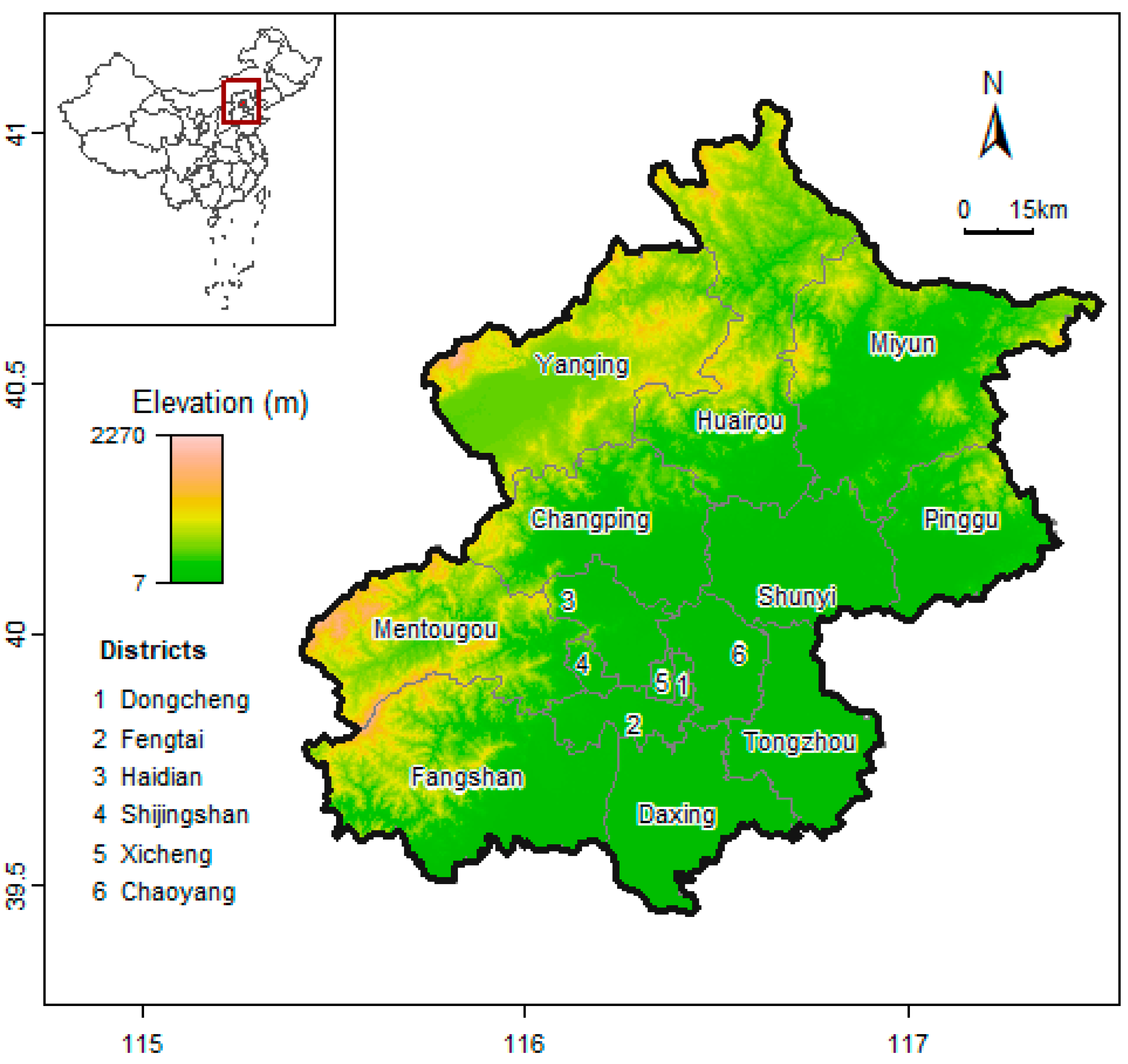
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
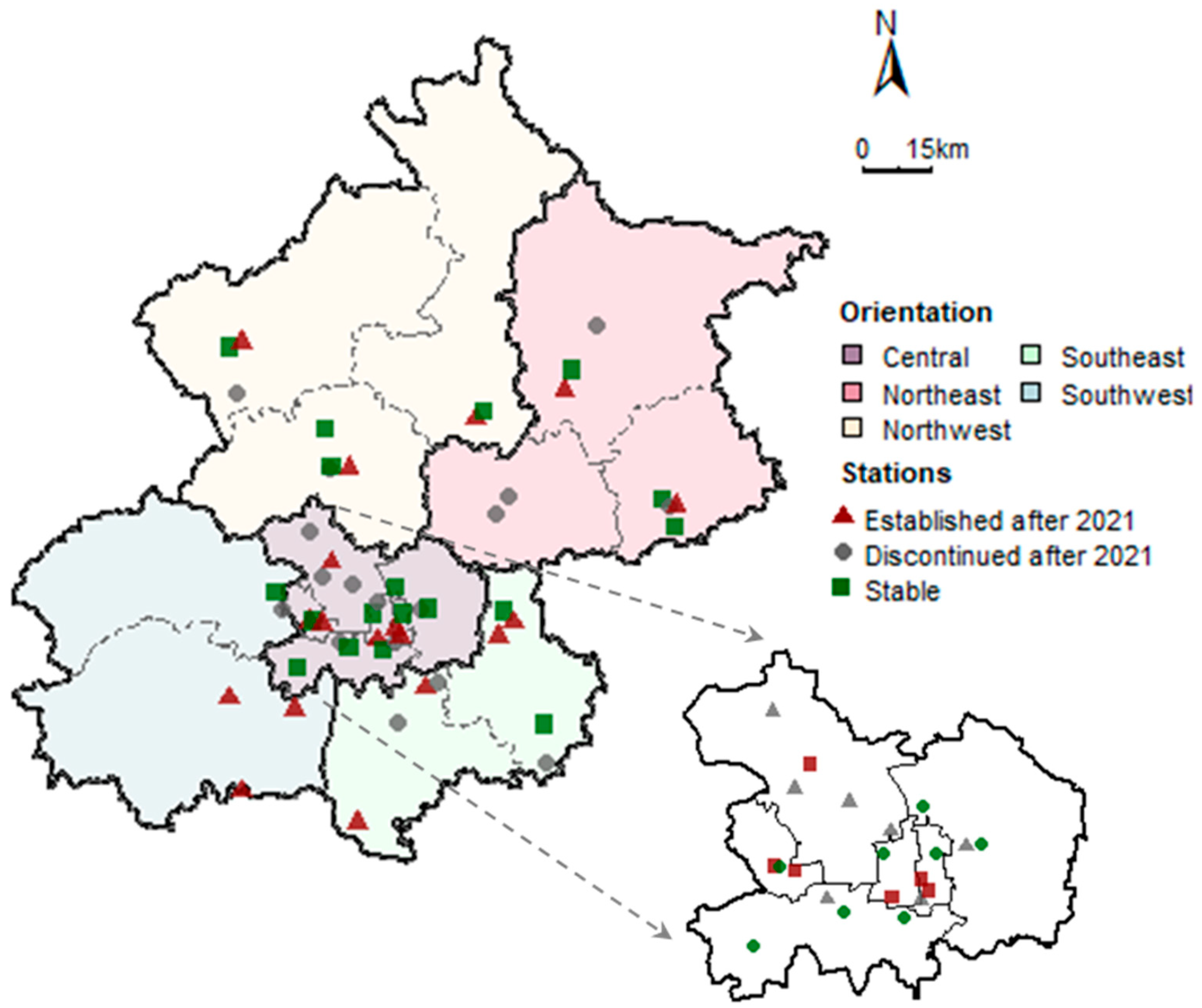
2.2.1. Ground-Level Ozone Concentration
2.2.2. Satellite-Derived Ozone Concentration
2.2.3. Population Data
2.2.4. Baseline Mortality Data
2.2.5. Concentration–Response Relationship Data
2.3. Ozone Metric Determination
2.4. Ozone Exposure Estimates
2.5. Ozone Health Impact Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Temporal Patterns of Ozone
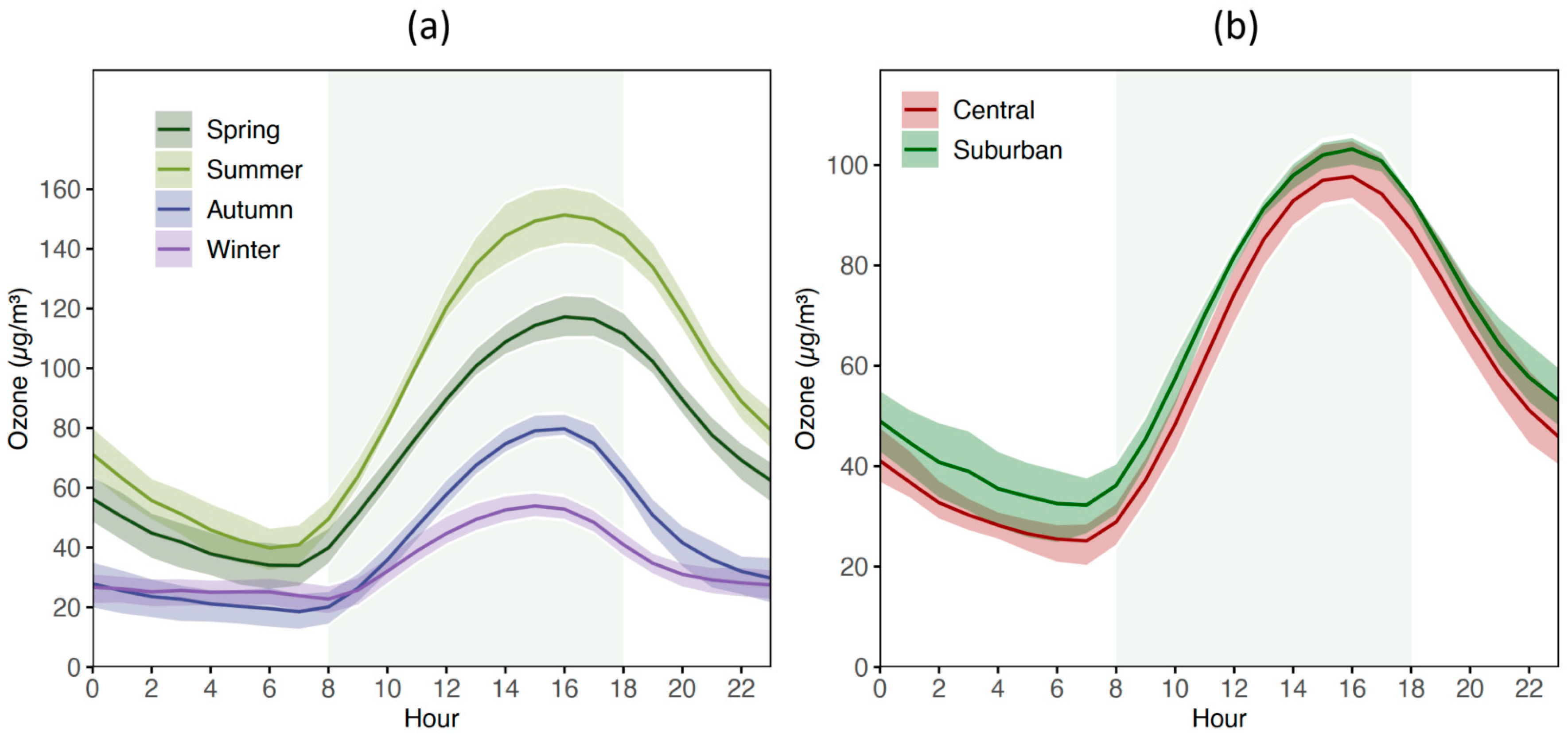
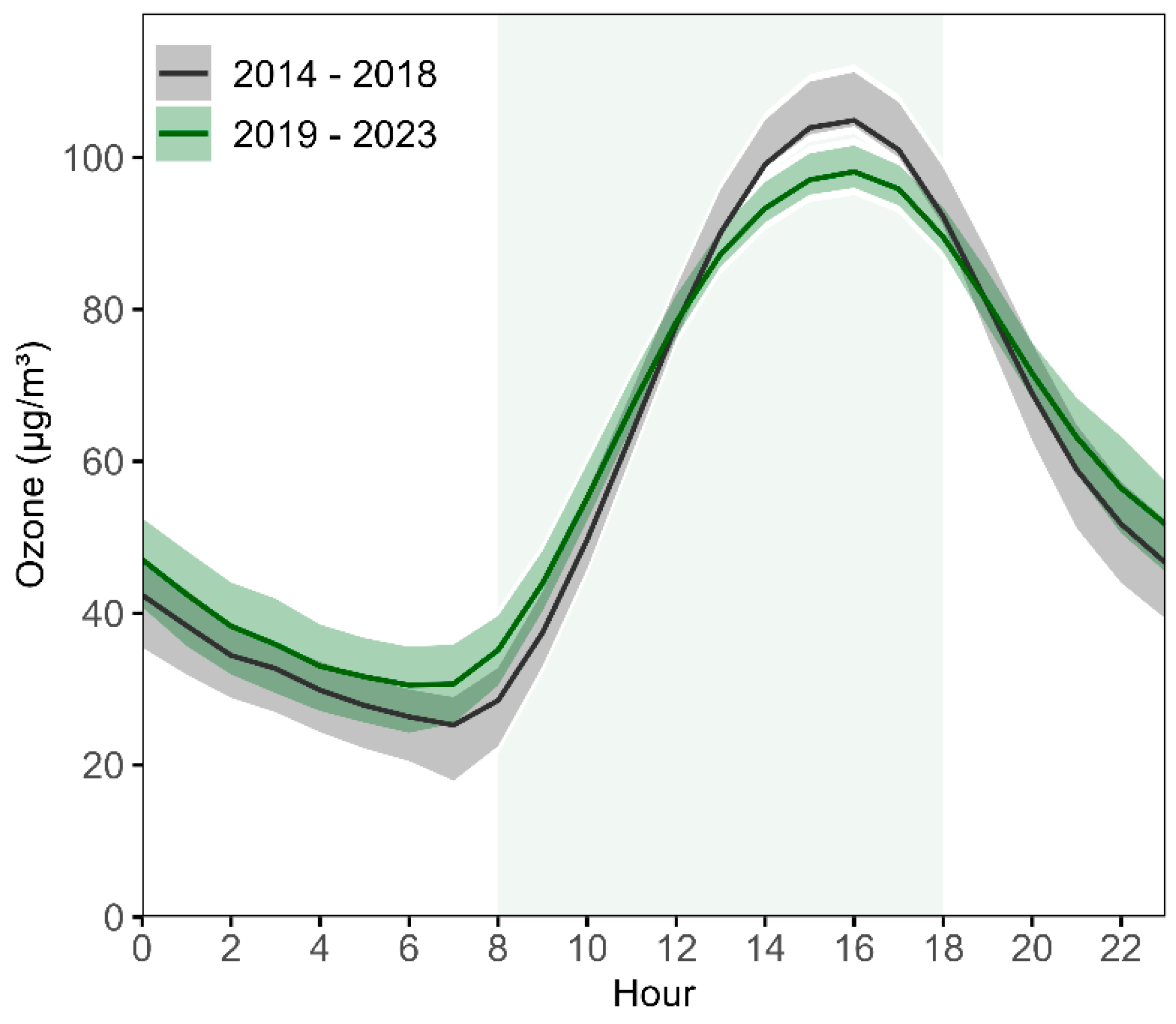
3.1.1. Diurnal Variations in Hourly Ozone Concentration
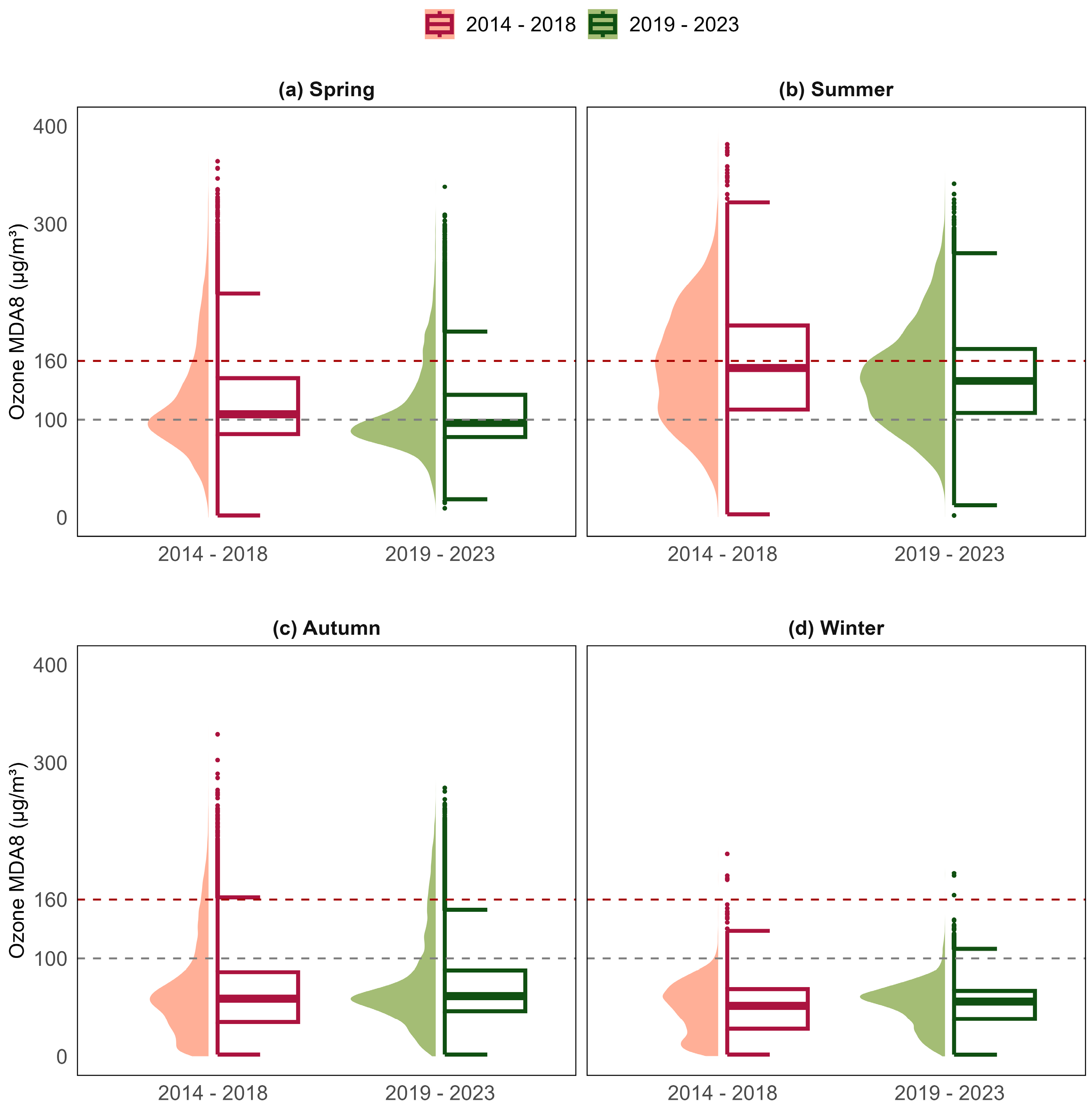
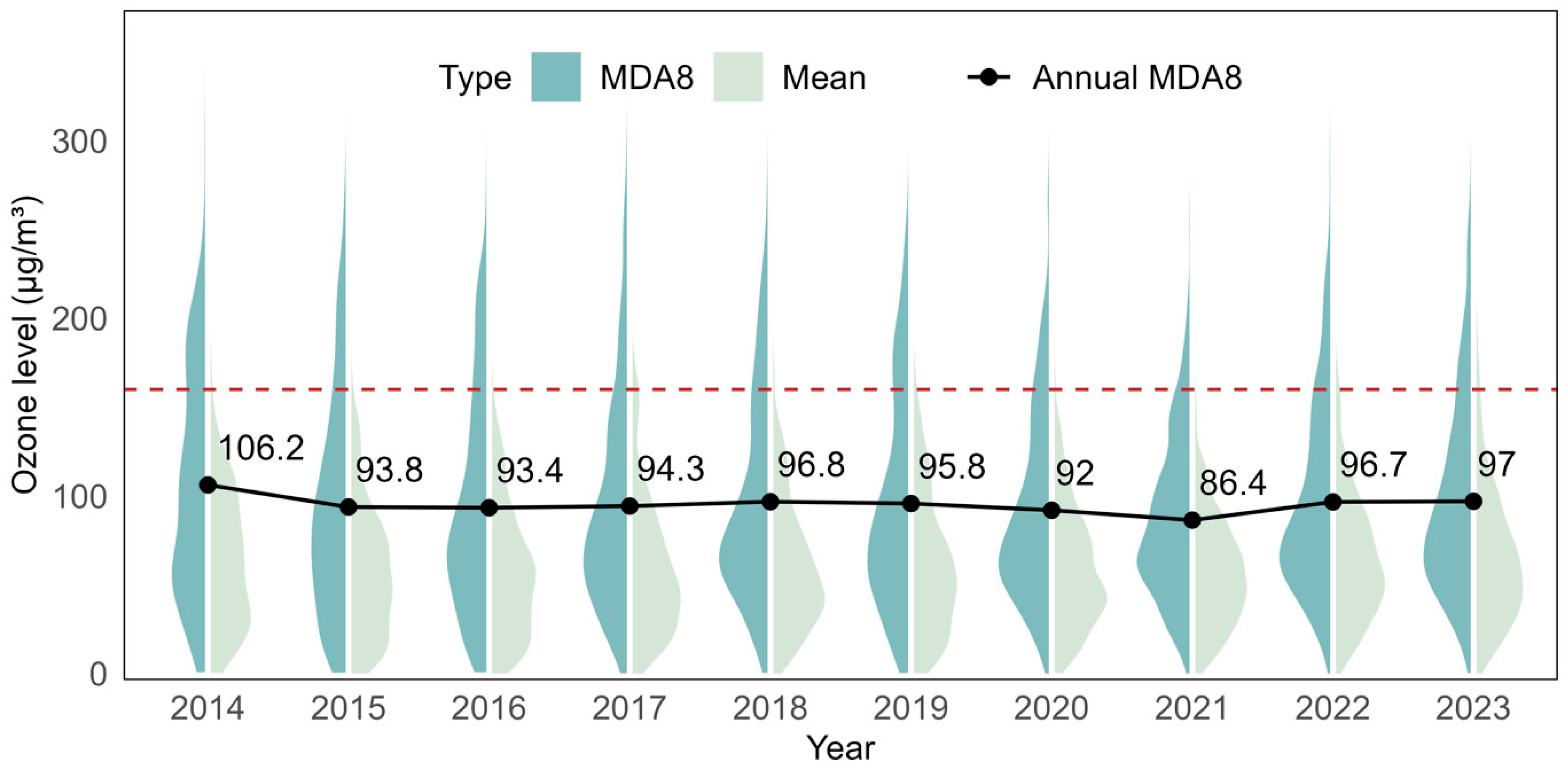
3.1.2. Seasonal and Annual Variations in Daily Ozone Concentrations
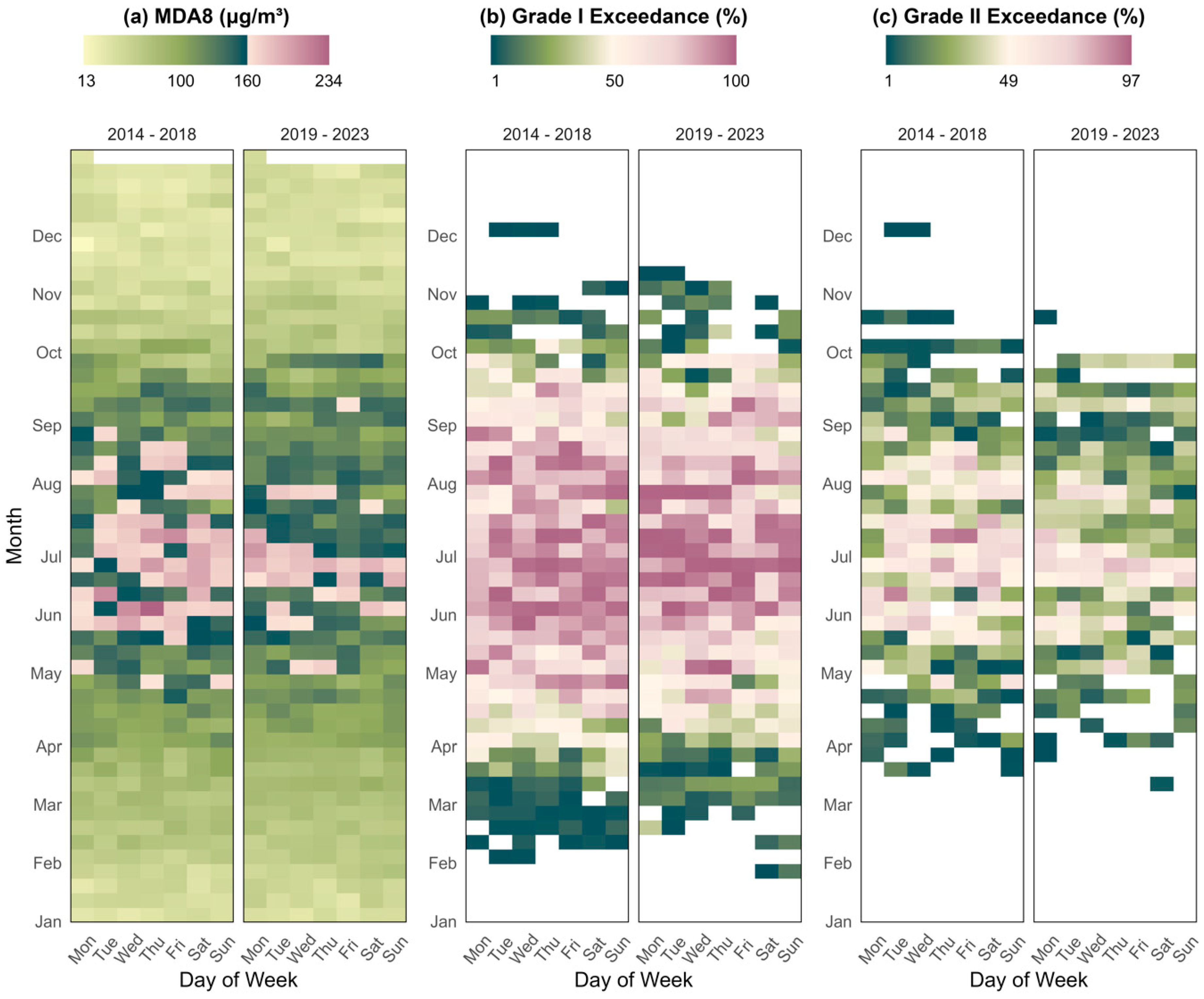
3.1.3. Compliance with Air Quality Standards
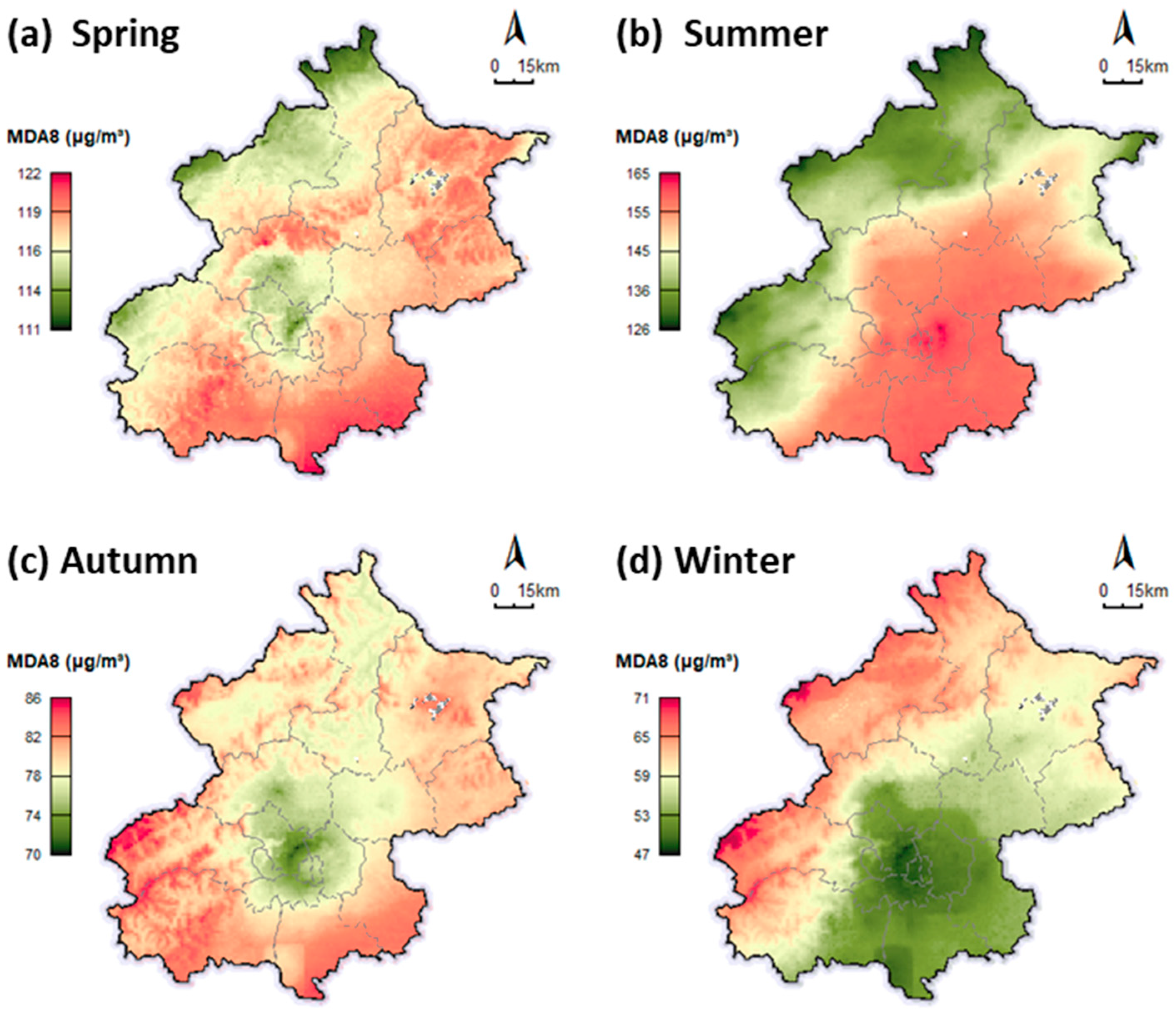
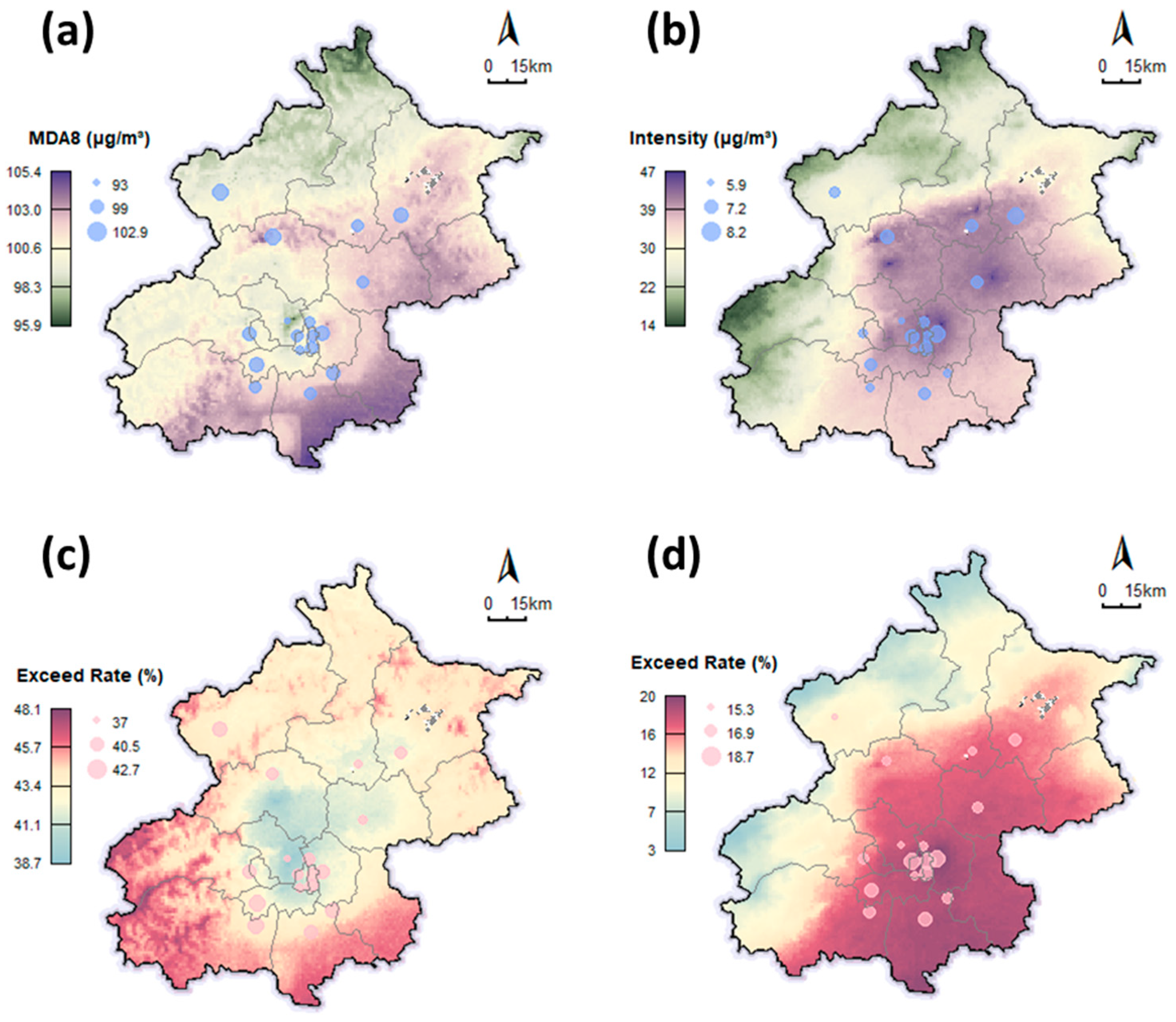
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Ozone Pollution
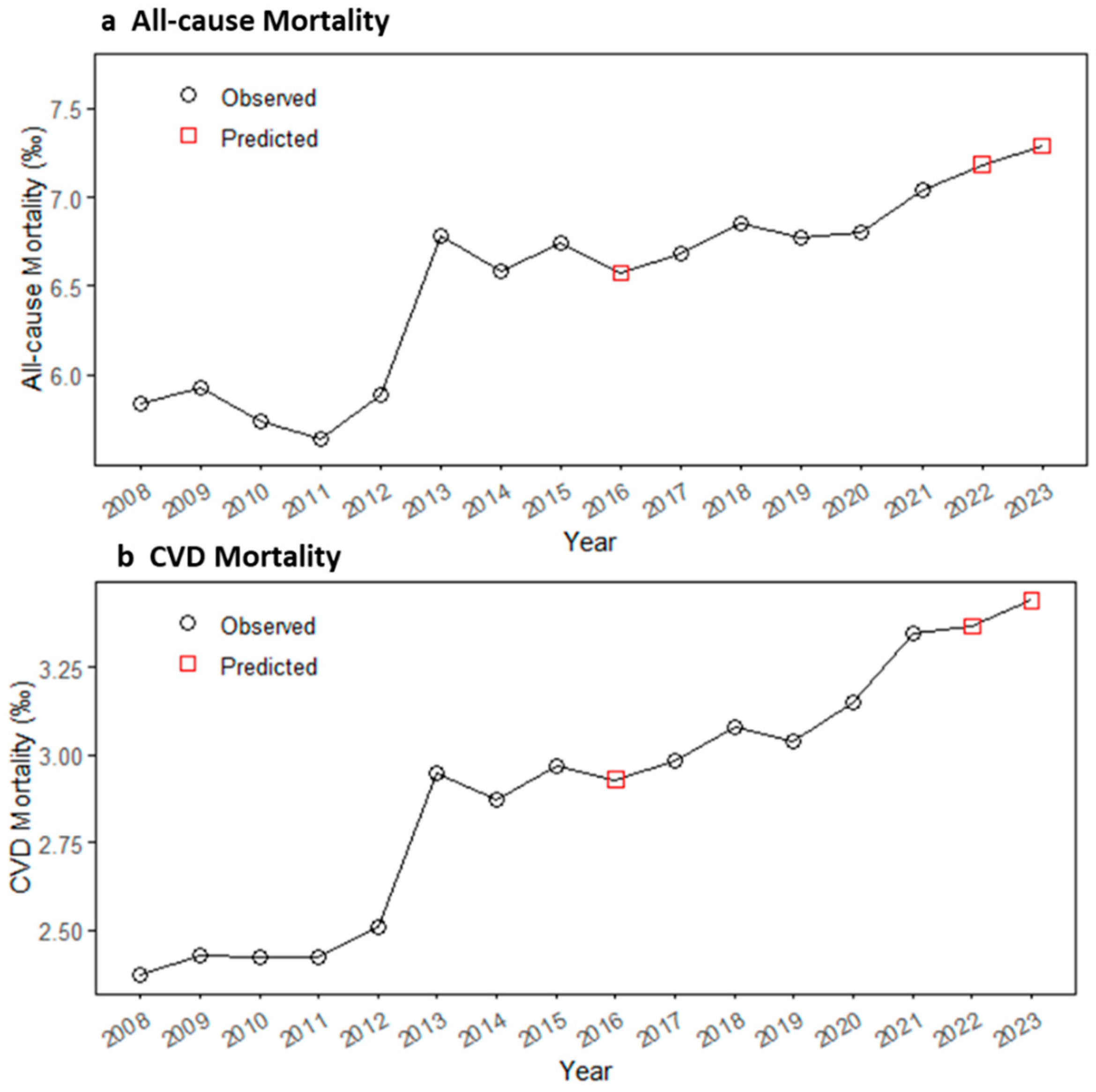
3.3. Avoidable Mortality Under Tiered Air Quality Standards
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brauer, M.; Roth, G.A.; Aravkin, A.Y.; Zheng, P.; Abate, K.H.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasgholizadeh, R.; Abbasi, M.A.; Abbasian, M.; et al. Global Burden and Strength of Evidence for 88 Risk Factors in 204 Countries and 811 Subnational Locations, 1990–2021: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2162–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; Agathokleous, E.; Anenberg, S.C.; De Marco, A.; Paoletti, E.; Calatayud, V. Trends in Urban Air Pollution over the Last Two Decades: A Global Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, B.; Du, C.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, H. Quantifying the Interactive Effects of Meteorological, Socioeconomic, and Pollutant Factors on Summertime Ozone Pollution in China during the Implementation of Two Important Policies. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; Khaniabadi, Y.O.; Leca, S.; De Marco, A. Relationships between Ozone and Particles during Air Pollution Episodes in Arid Continental Climate. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Peng, L.; Bi, F.; Li, L.; Bao, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Chai, F. Strategy of Coordinated Control of PM2.5 and Ozone in China. Res. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 1763–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Wang, P.; Zhu, J.; Li, K.; Liao, H. Summer Ozone Pollution in China Affected by the Intensity of Asian Monsoon Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntourou, K.; Fameli, K.M.; Moustris, K.; Manousakis, N.; Tsitsis, C. Trends of the Global Burden of Disease Linked to Ground-Level Ozone Pollution: A 30-Year Analysis for the Greater Athens Area, Greece. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-Year Trends of the Global Burden of Disease Attributable to Ambient Air Pollution: An Analysis of Data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawahda, A.; Yamashita, K.; Ohara, T.; Kurokawa, J.; Yamaji, K. Evaluation of Premature Mortality Caused by Exposure to PM 2.5 and Ozone in East Asia: 2000, 2005, 2020. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 3445–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N.; Noone, K. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change. Phys. Today 1998, 51, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; De Marco, A.; Anav, A.; Gualtieri, M.; Sicard, P.; Tian, H.; Fornasier, F.; Tao, F.; Guo, A.; Paoletti, E. Economic Losses Due to Ozone Impacts on Human Health, Forest Productivity and Crop Yield across China. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, A.D.; Anav, A.; Sicard, P.; Feng, Z.; Paoletti, E. High Spatial Resolution Ozone Risk-Assessment for Asian Forests. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 104095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, A.; Garcia-Gomez, H.; Collalti, A.; Khaniabadi, Y.O.; Feng, Z.; Proietti, C.; Sicard, P.; Vitale, M.; Anav, A.; Paoletti, E. Ozone Modelling and Mapping for Risk Assessment: An Overview of Different Approaches for Human and Ecosystems Health. Environ. Res. 2022, 211, 113048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; You, J.; Lin, Y.; Duan, X.; Zhao, X.; Fang, X.; Campen, M.J.; Li, S. Air Pollution Intervention and Life-Saving Effect in China. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.; Yuan, L.; A Perlin, S. Comparison of Spatial Interpolation Methods for the Estimation of Air Quality Data. J. Expo. Anal. Env. Epid. 2004, 14, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Davis, J.M.; Liu, C.; Gao, W. Spatial Interpolation of Surface Ozone Observations Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the of SPIE The International Society for Optical Engineering, San Diego, CA, USA, 19–23 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, H.O.; Sunil, T.; Alamgir, H.; Jospeph, J. Application of Validation Data for Assessing Spatial Interpolation Methods for Eight-Hour Ozone or Other Sparsely Monitored Constituents. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, R.; O’Lenick, C.R.; Monaghan, A.; Wilhelmi, O.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Hayden, M.; Estes, M. Application of Geostatistical Approaches to Predict the Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Summer Ozone in Houston Texas. J. Exposure Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 806–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Jacob, D.J.; Liu, X.; Huang, G.; Li, K.; Liao, H.; Wang, T. An Evaluation of the Ability of the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) to Observe Boundary Layer Ozone Pollution across China: Application to 2005–2017 Ozone Trends. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6551–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collet, S.; Kidokoro, T.; Karamchandani, P.; Jung, J.; Shah, T. Future Year Ozone Source Attribution Modeling Study Using CMAQ-ISAM. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 2018, 68, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Pinault, L.; Toyib, O.; Vanos, J.; Tjepkema, M.; Cakmak, S. Long-Term Ozone Exposure and Mortality from Neurological Diseases in Canada. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson-Pitts, B.J.; Pitts, J.N. Tropospheric Air Pollution: Ozone, Airborne Toxics, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, and Particles. Science 1997, 276, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, R.W.; Yu, D.; Armstrong, B.G.; Pattenden, S.; Wilkinson, P.; Doherty, R.M.; Heal, M.R.; Anderson, H.R. Concentration-Response Function for Ozone and Daily Mortality: Results from Five Urban and Five Rural U.K. Populations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuvolone, D.; Petri, D.; Voller, F. The Effects of Ozone on Human Health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 8074–8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Hollander, H.A. den et al, V.Z.R. European Characterization Factors for Human Health Damage of PM10 and Ozone in Life Cycle Impact Assessment. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Wilson, J.G.; Zhan, F.B.; Zeng, Y. Air Pollution Exposure Assessment Methods Utilized in Epidemiological Studies. J. Environ. Monit. 2009, 11, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, K.; Liu, X.; Shi, L.; Tao, G.; Loftus, C.T.; Lange, S.; Goodman, J.E. Concentration-Response of Short-Term Ozone Exposure and Hospital Admissions for Asthma in Texas. Environ. Int. 2017, 104, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Lim, Y.H.; Kashima, S.; Yorifuji, T.; Honda, Y.; Kim, H.; Hong, Y.C. Non-Linear Concentration-Response Relationships between Ambient Ozone and Daily Mortality. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.L.; Goldberg, R.; Hogrefe, C.; Kinney, P.L.; Knowlton, K.; Lynn, B.; Rosenthal, J.; Rosenzweig, C.; Patz, J.A. Climate Change, Ambient Ozone, and Health in 50 US Cities. Clim. Change 2007, 82, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerckhoffs, J.; Wang, M.; Meliefste, K.; Malmqvist, E.; Fischer, P.; Janssen, N.A.H.; Beelen, R.; Hoek, G. A National Fine Spatial Scale Land-Use Regression Model for Ozone. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, S.; Naja, M.; Subbaraya, B.H. Seasonal Variations in Surface Ozone and Its Precursors over an Urban Site in India. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2713–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Xue, B.; Lv, Z.; Meng, Z.; Yang, X.; Xue, T.; Yu, Q.; He, K. Ground-Level Ozone Pollution and Its Health Impacts in China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 173, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, K.J.; Li, V.O.; Lam, J.C. Effects of China’s Current Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan on Air Pollution Patterns, Health Risks and Mortalities in Beijing 2014–2018. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Song, Y.; Cai, X. A Health-Based Assessment of Particulate Air Pollution in Urban Areas of Beijing in 2000–2004. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 376, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China: Population Density in Beijing by District 2023. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1083082/china-population-density-in-beijing-by-district/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Ren, J.; Hao, Y.; Simayi, M.; Shi, Y.; Xie, S. Spatiotemporal Variation of Surface Ozone and Its Causes in Beijing, China since 2014. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 260, 118556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yang, X.; Xu, J. Spatio-Temporal Variation and Influencing Factors of Ozone Pollution in Beijing. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Liang, L. Spatio-Temporal Evolution of Ozone Pollution and Its Influencing Factors in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; Xie, X.; Chen, D.; Cheng, N.; Yang, L.; Li, R. Understanding Long-Term Variations of Meteorological Influences on Ground Ozone Concentrations in Beijing During 2006–2016. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dong, J.; Guo, J.; Cai, P.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Q.; Song, X. Understanding Temporal Patterns and Determinants of Ground-Level Ozone. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3095-2012; Ambient Air Quality Standards. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Lu, X.; Hong, J.; Zhang, L.; Cooper, O.R.; Schultz, M.G.; Xu, X.; Wang, T.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Severe Surface Ozone Pollution in China: A Global Perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Dickerson, R.R.; Pinker, R.T.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Xue, W.; Cribb, M. Full-Coverage Mapping and Spatiotemporal Variations of Ground-Level Ozone (O3) Pollution from 2013 to 2020 across China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 270, 112775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Cheng, F.; Lv, Q.; Li, K.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, B.; Xue, W.; Wei, J. Two-Decade Surface Ozone (O3) Pollution in China: Enhanced Fine-Scale Estimations and Environmental Health Implications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 317, 114459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Chen, R.; Wang, L.; Meng, X.; Liu, C.; Niu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Qi, J. Ambient Ozone Pollution and Daily Mortality: A Nationwide Study in 272 Chinese Cities. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 117006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, D.Q.; Balmes, J.R.; Frampton, M.W.; Zareba, W.; Stark, P.; Arjomandi, M.; Hazucha, M.J.; Costantini, M.G.; Ganz, P.; Hollenbeck-Pringle, D.; et al. Cardiovascular Function and Ozone Exposure: The Multicenter Ozone Study in oldEr Subjects (MOSES). Environ. Int. 2018, 119, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD). 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/standards/classifications/classification-of-diseases (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Gao, Q.; Zang, E.; Bi, J.; Dubrow, R.; Lowe, S.R.; Chen, H.; Zeng, Y.; Shi, L.; Chen, K. Long-Term Ozone Exposure and Cognitive Impairment among Chinese Older Adults: A Cohort Study. Environ. Int. 2022, 160, 107072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Huang, W.; Huang, X.; Zhong, L.; Lu, S.E.; Li, Y.; Dai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, T. Estimated Acute Effects of Ambient Ozone and Nitrogen Dioxide on Mortality in the Pearl River Delta of Southern China. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaniyazi, L.; Nagashima, T.; Guo, Y.; Pan, X.; Tong, S. Projecting Ozone-Related Mortality in East China. Environ. Int. 2016, 92, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhong, L.; Bi, X.; Li, H.; Liu, W.; Zhu, T.; Huang, W. Systematic Review of Chinese Studies of Short-Term Exposure to Air Pollution and Daily Mortality. Environ. Int. 2013, 54, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, L.; Chen, X.; Bi, J.; Kinney, P.L. Acute Effect of Ozone Exposure on Daily Mortality in Seven Cities of Jiangsu Province, China: No Clear Evidence for Threshold. Environ. Res. 2017, 155, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.J.; Chen, B.H.; Kan, H.D. Health Impact Assessment of Surface Ozone Pollution in Shanghai. China Environ. Sci. 2010, 30, 603–608. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, X.; Qiao, Z.; Ji, K.; Zeng, J.; Luo, B.; et al. Using Rush Hour and Daytime Exposure Indicators to Estimate the Short-Term Mortality Effects of Air Pollution: A Case Study in the Sichuan Basin, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.M.; Qian, Z.; Vichit-Vadakan, N.; Kan, H. Public Health and Air Pollution in Asia (PAPA): A Multicity Study of Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Mortality. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lei, R.; Ding, R.; Zhu, F.; Cheng, H.; Liu, J.; Shen, C.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, C.; Li, X.; et al. Short-Term Effect of PM2.5/O3 on Non-Accidental and Respiratory Deaths in Highly Polluted Area of China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, M.; Saikawa, E.; Chen, F. Sensitivity of Projected PM2.5-and O3-Related Health Impacts to Model Inputs: A Case Study in Mainland China. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 256–264. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhang, X.-Y. Ozone Spatial-Temporal Distribution and Trend over China since 2013: Insight from Satellite and Surface Observation. Huanjing Kexue/Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 1132–1142. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lefohn, A.S.; Malley, C.S.; Smith, L.; Wells, B.; Hazucha, M.; Simon, H.; Naik, V.; Mills, G.; Schultz, M.G.; Paoletti, E.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Global Ozone Metrics for Climate Change, Human Health, and Crop/Ecosystem Research. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2018, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapina, O.; Schultz, M.G.; Hense, A. Cluster Analysis of European Surface Ozone Observations for Evaluation of MACC Reanalysis Data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 6863–6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoder, M.I. Diurnal, Seasonal and Weekdays–Weekends Variations of Ground Level Ozone Concentrations in an Urban Area in Greater Cairo. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 149, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsydypov, V.V.; Zayakhanov, A.S.; Zhamsueva, G.S.; Balzhanov, T.S.; Dementeva, A.L. Diurnal Variation of Surface Ozone Concentration in the Atmosphere of the Arid Territory of Mongolia, Station Sainshand, in the Warm Period 2005–2014. In Proceedings of the 26th International Symposium on Atmospheric and Ocean Optics, Atmospheric Physics, Moscow, Russia, 6–10 July 2020; Volume 11560, pp. 1377–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Awang, N.R.; Elbayoumi, M.; Ramli, N.A.; Yahaya, A.S. Diurnal Variations of Ground-Level Ozone in Three Port Cities in Malaysia. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2016, 9, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomer, B.J.; Vinnikov, K.Y.; Dickerson, R.R. Changes in Seasonal and Diurnal Cycles of Ozone and Temperature in the Eastern U.S. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2543–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Stavrakou, T.; Elguindi, N.; Doumbia, T.; Granier, C.; Bouarar, I.; Gaubert, B.; Brasseur, G.P. Diverse Response of Surface Ozone to COVID-19 Lockdown in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Liu, Y.; Meng, Y.; Dai, X.; Huang, L.; Luo, W.; Yang, M.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, J.; Xiao, H. Surface Ozone Changes during the COVID-19 Outbreak in China: An Insight into the Pollution Characteristics and Formation Regimes of Ozone in the Cold Season. J. Atmos. Chem. 2023, 80, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Cheng, X.; Yang, M.; Shu, L. Stratospheric Influences on Surface Ozone Increase during the COVID-19 Lockdown over Northern China. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; De Marco, A.; Agathokleous, E.; Feng, Z.; Xu, X.; Paoletti, E.; Rodriguez, J.J.D.; Calatayud, V. Amplified Ozone Pollution in Cities during the COVID-19 Lockdown. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Health Endpoints | RR (95% CI, 10 μg/m3) | Study Areas | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| All cause | 1.0064 (1.0042–1.0086) | PRD cities | [49] |
| 1.0036 (1.0012–1.0060) | East China | [50] | |
| 1.0048 (1.0038–1.0058) | Megacities | [51] | |
| 1.0055 (1.0034–1.0076) | Jiangsu | [52] | |
| 1.0024 (1.0013–1.0035) | 272 cities | [45] | |
| 1.0045 (1.0016–1.0730) | Shanghai | [53] | |
| 1.0019 (1.0001–1.0004) | Sichuan | [54] | |
| 1.0038 (1.0023–1.0053) | Wuhan | [55] | |
| 1.0005 (0.9958–1.0053) | Anhui | [56] | |
| 1.0056 (1.0042–1.0074) | Xian | [57] | |
| Cardiovascular | 1.0098 (1.0061–1.0135) | PRD cities | [49] |
| 1.0060 (1.0022–1.0097) | East China | [50] | |
| 1.0045 (1.0029–1.0060) | Megacities | [51] | |
| 1.0027 (1.0010–1.0044) | 272 cities | [45] | |
| 1.0098 (1.0058–1.0137) | Jiangsu | [58] | |
| 1.0018 (1.0001–1.0053) | Sichuan | [54] | |
| 1.0050 (1.0014–1.0104) | Shanghai | [53] | |
| 1.0037 (1.0001–1.0073) | Wuhan | [55] |
| Parameters | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 h ozone | (μg/m3) | Hourly ozone concentration obtained from the observation |
| MDA8 | (μg/m3) | Daily maximum 8 h running averages, calculated from hourly data |
| Exceedance day | (d) | The number of days when MDA8 ozone concentrations exceed the Grade I (100 μg/m3) or Grade II standard (160 μg/m3) over a specific period |
| Intensity | (μg/m3) | The amount of MDA8 ozone concentrations exceeding the Grade I (100 μg/m3) or Grade II standard (160 μg/m3) |
| Exceedance rate | (%) | The proportion of MDA8 ozone concentrations exceeding the Grade I (100 μg/m3) or Grade II standard (160 μg/m3) |
| Parameters | Concentration Limits | Applicability Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 h values | Grade I: 160 μg/m3 Grade II: 200 μg/m3 | Grade I limits apply to natural reserves and other areas requiring special protection. Grade II limits apply to residential zones, commercial and traffic-mixed residential areas, industrial zones, and rural areas. |
| 8 h values | Grade I: 100 μg/m3 Grade II: 160 μg/m3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, F.; You, J.; Gao, L. Assessing the Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Health Impacts of Surface Ozone Pollution in Beijing, China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040397
Yin F, You J, Gao L. Assessing the Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Health Impacts of Surface Ozone Pollution in Beijing, China. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(4):397. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040397
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Fangxu, Jiewen You, and Lu Gao. 2025. "Assessing the Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Health Impacts of Surface Ozone Pollution in Beijing, China" Atmosphere 16, no. 4: 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040397
APA StyleYin, F., You, J., & Gao, L. (2025). Assessing the Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Health Impacts of Surface Ozone Pollution in Beijing, China. Atmosphere, 16(4), 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040397








