The Correlation Between Surface Temperature and Surface PM2.5 in Nanchang Region, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
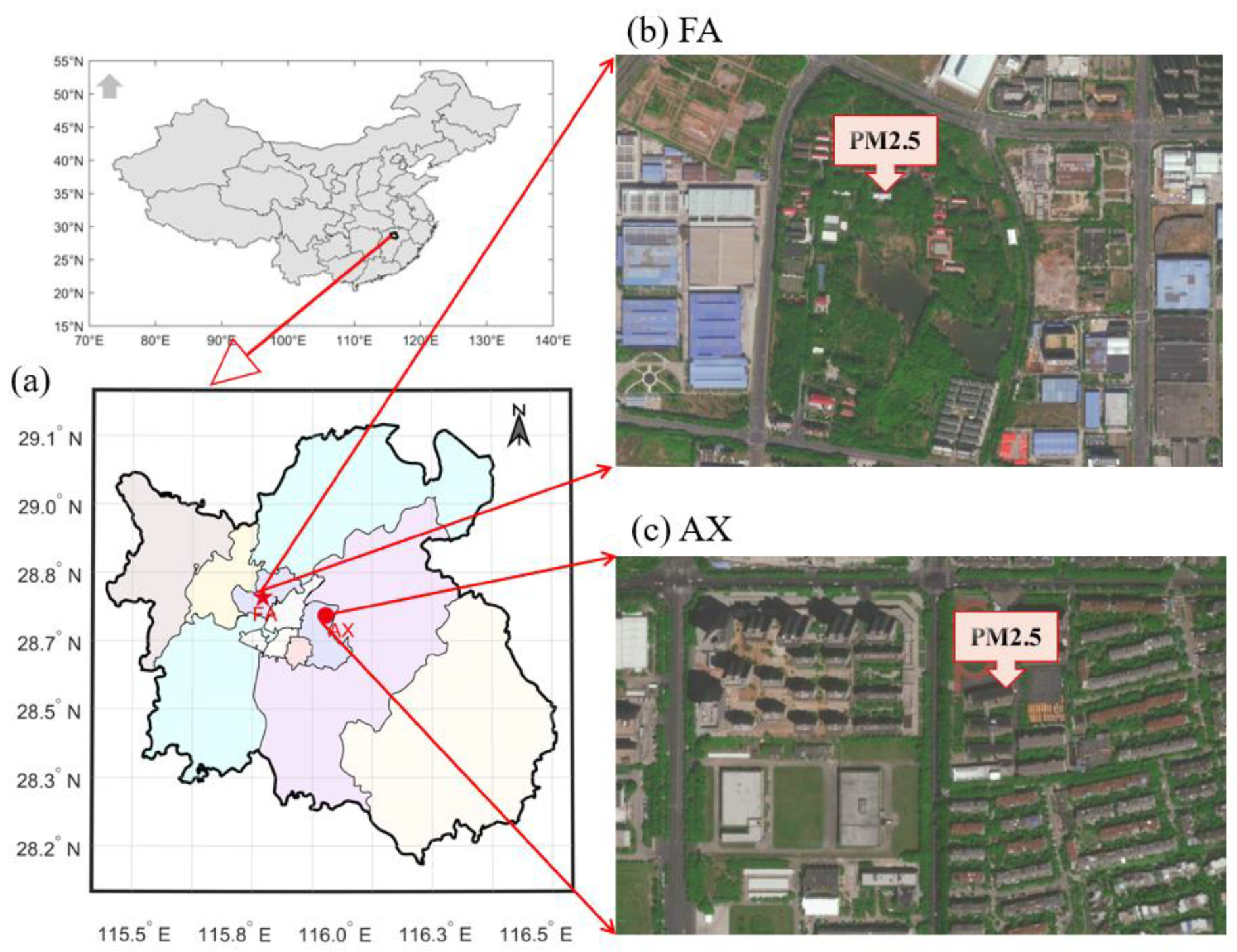
2.1. PM2.5 Observations
2.2. Meteorological Data
2.3. PM2.5 Data Quality
2.4. Linear Regression and Regression Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
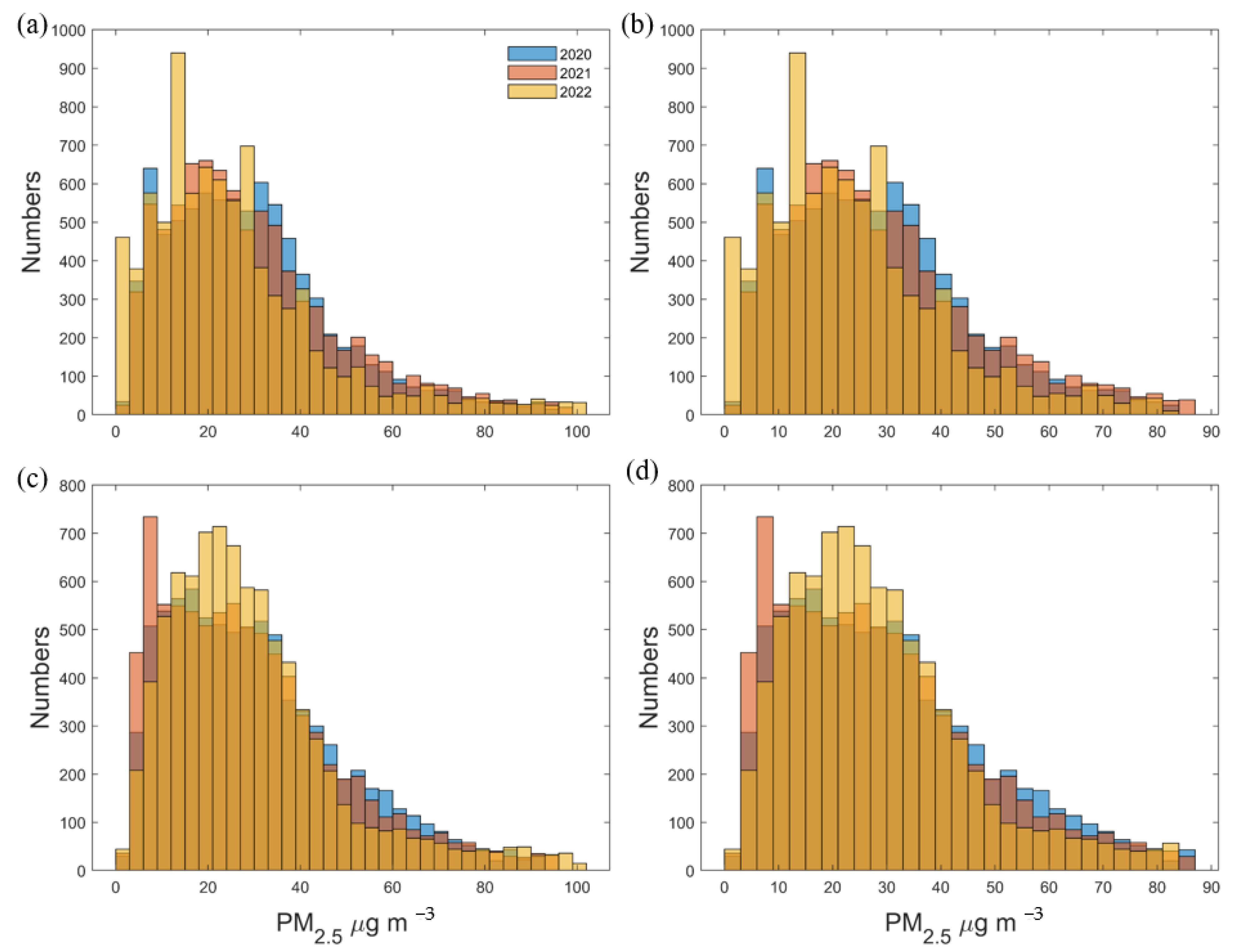
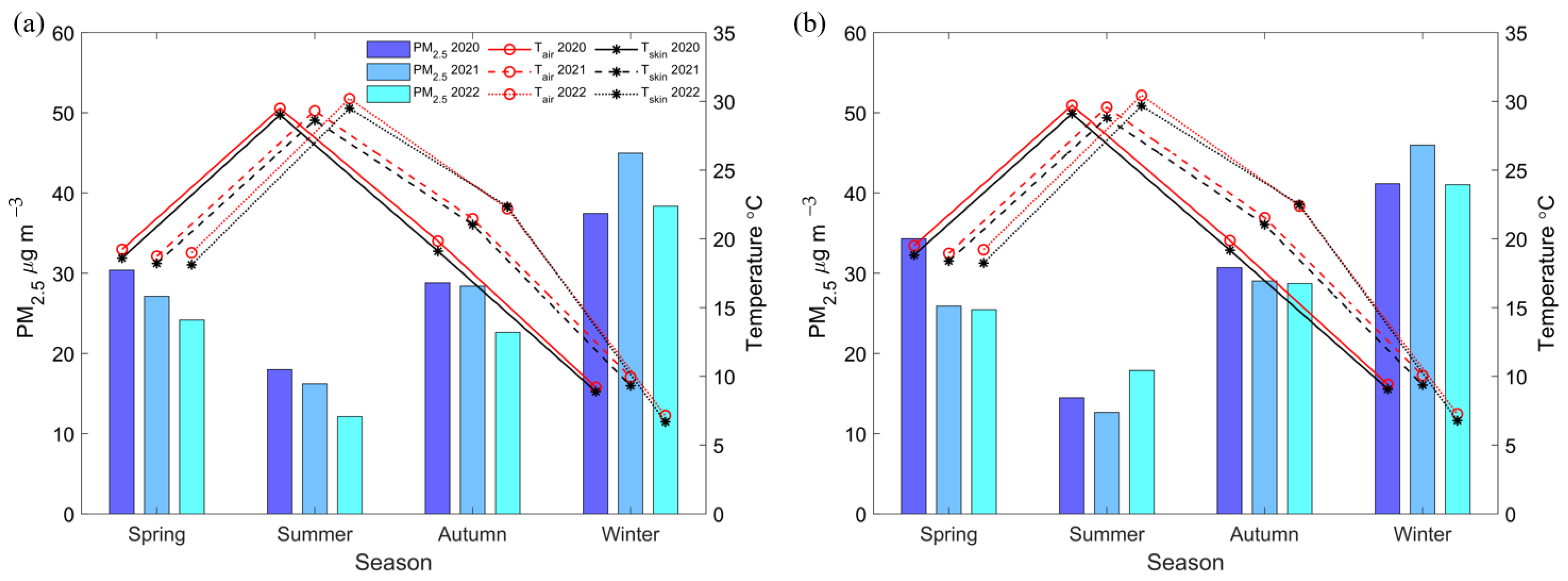
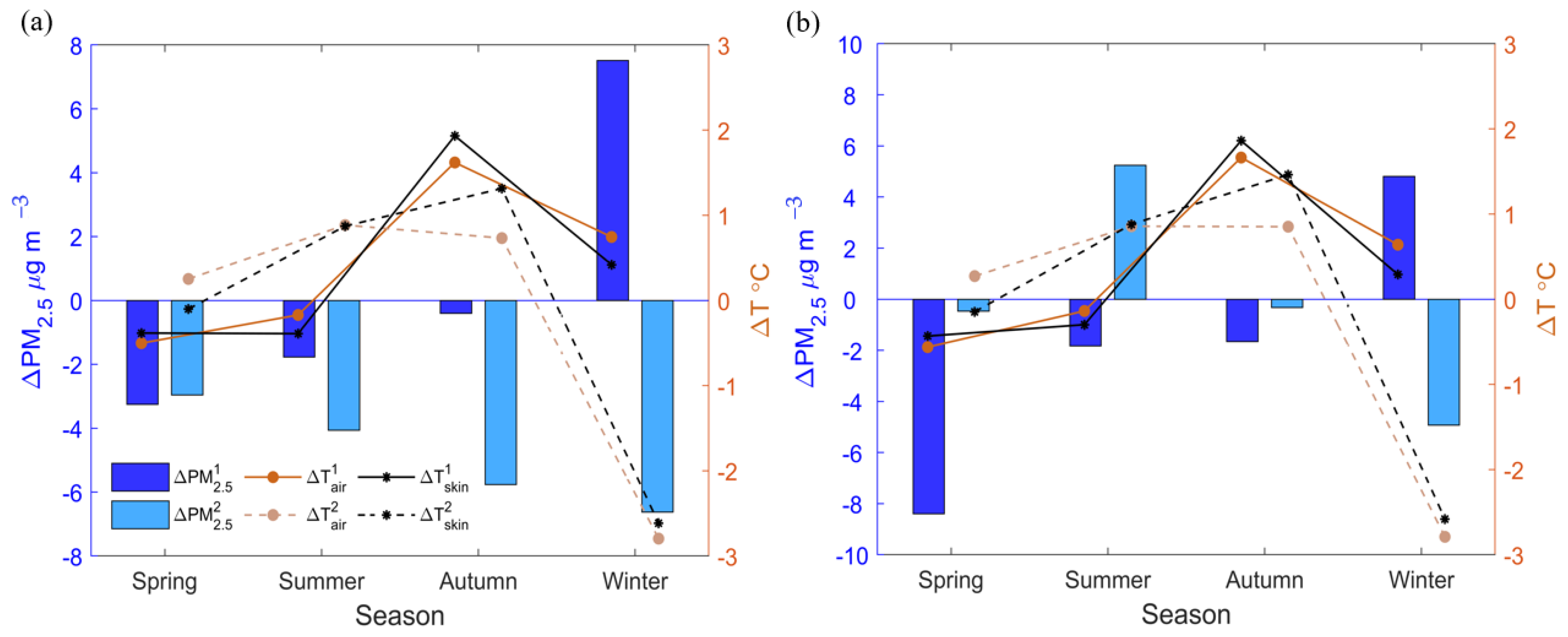
3.1. Seasonal Variations of Surface PM2.5 and Surface Temperature
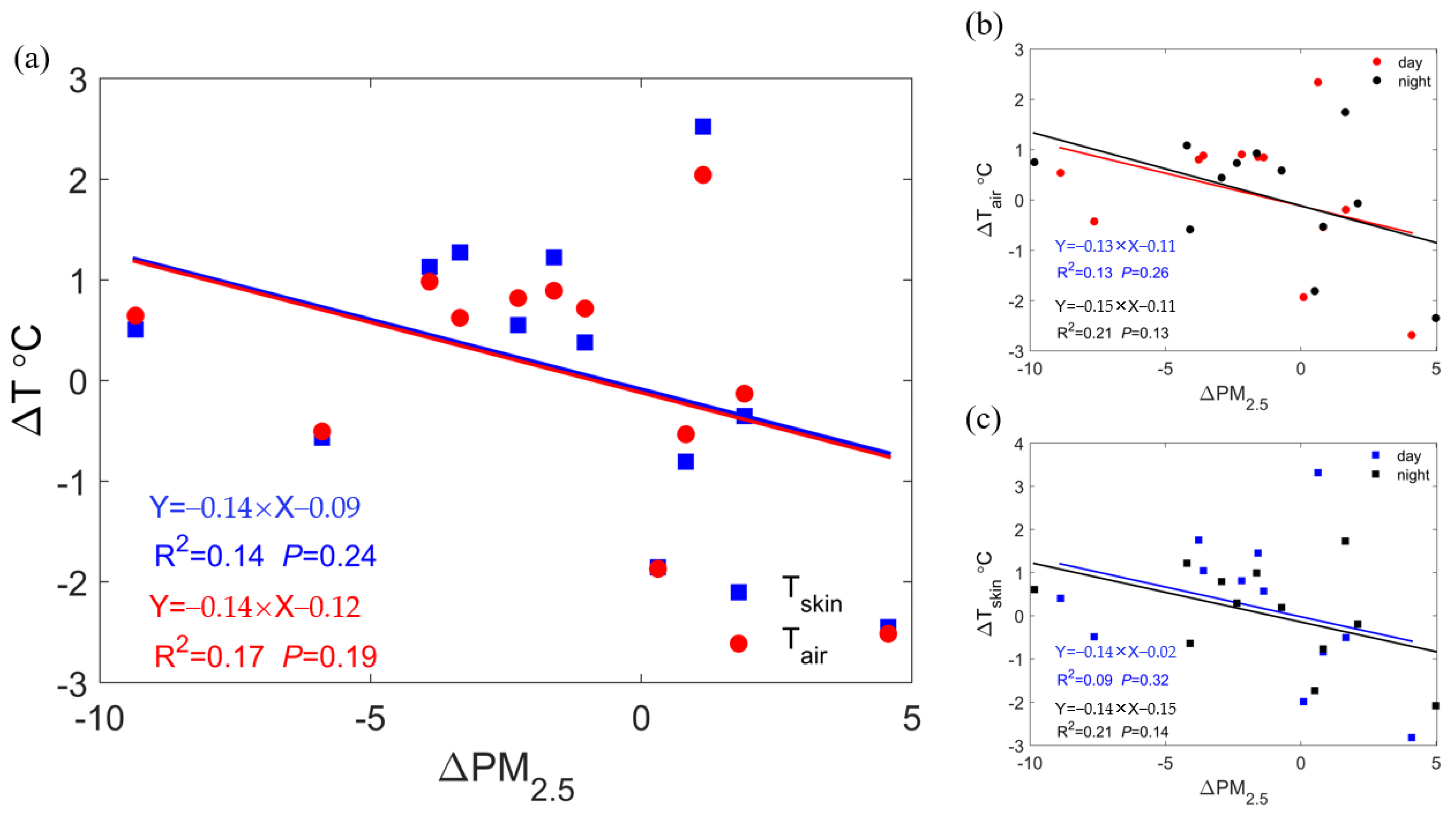
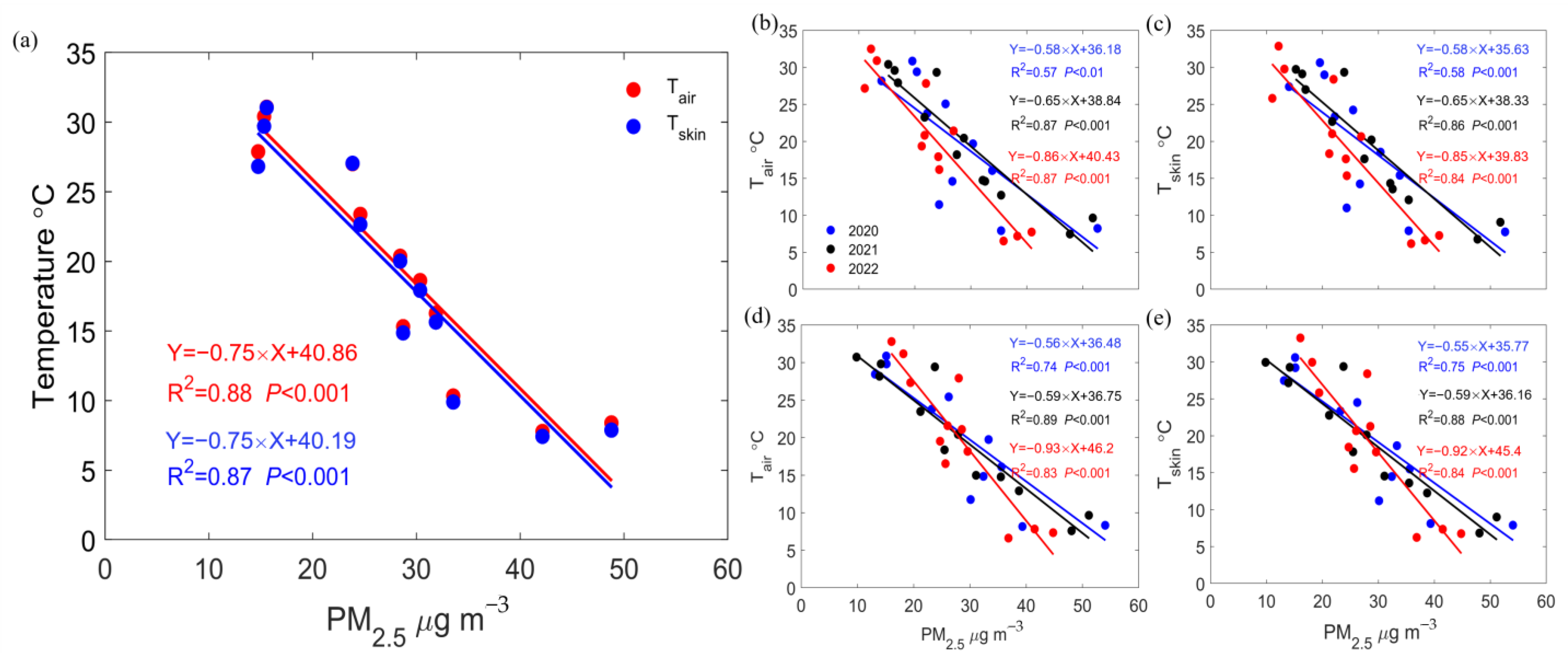
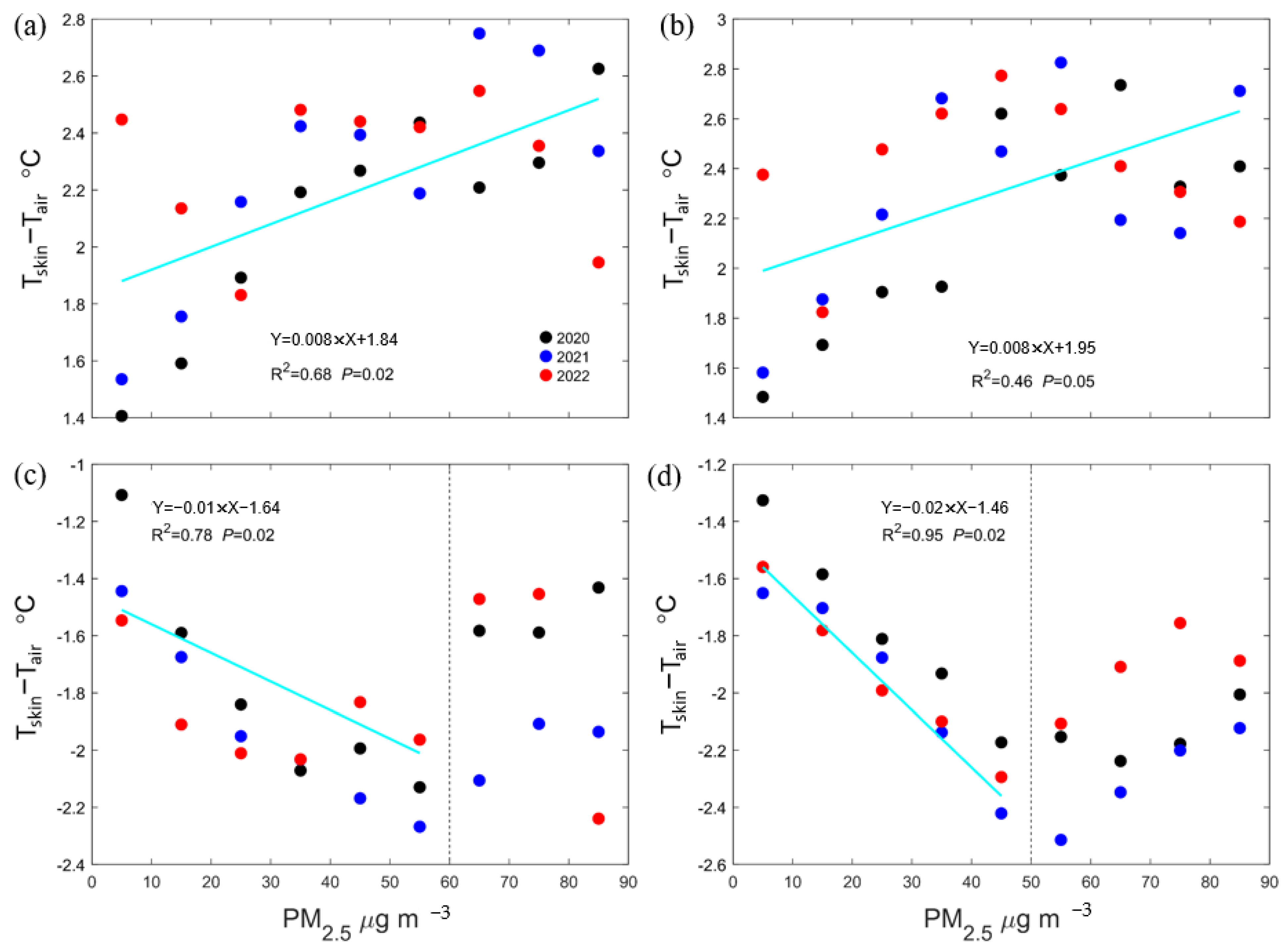
3.2. Response of Local Surface Temperature to PM2.5 Concentrations
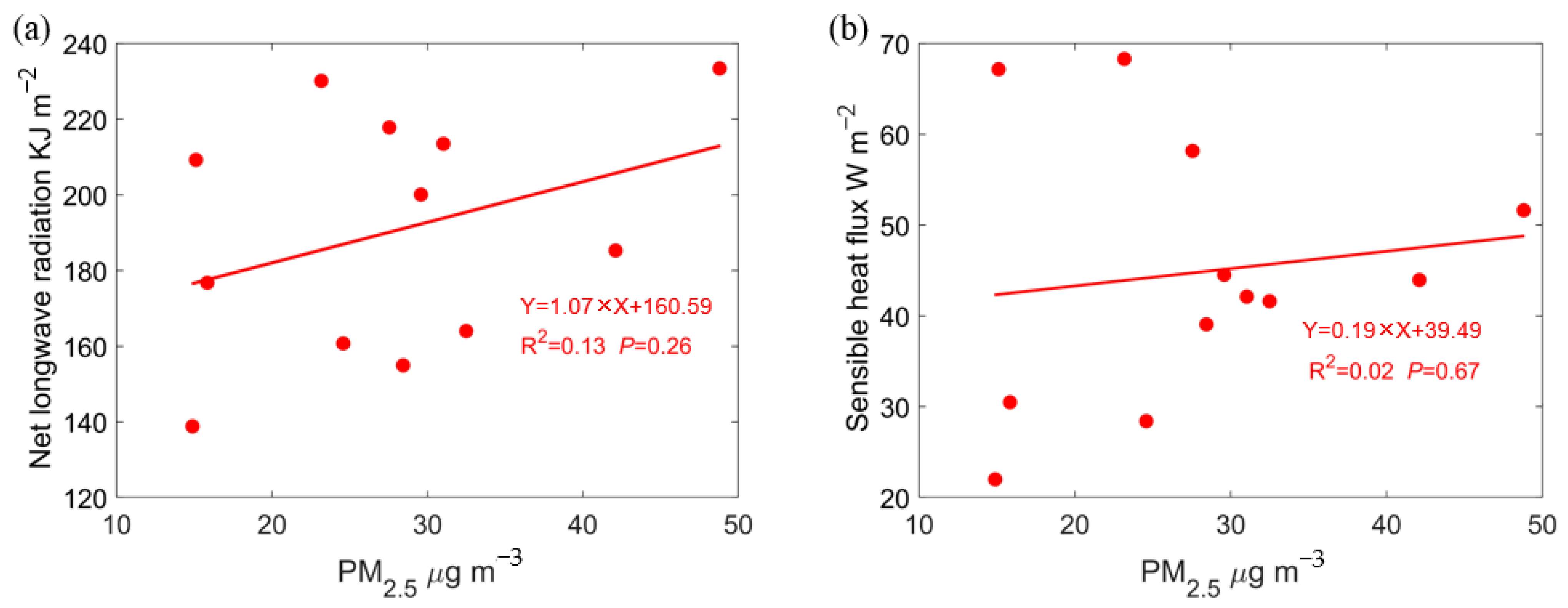
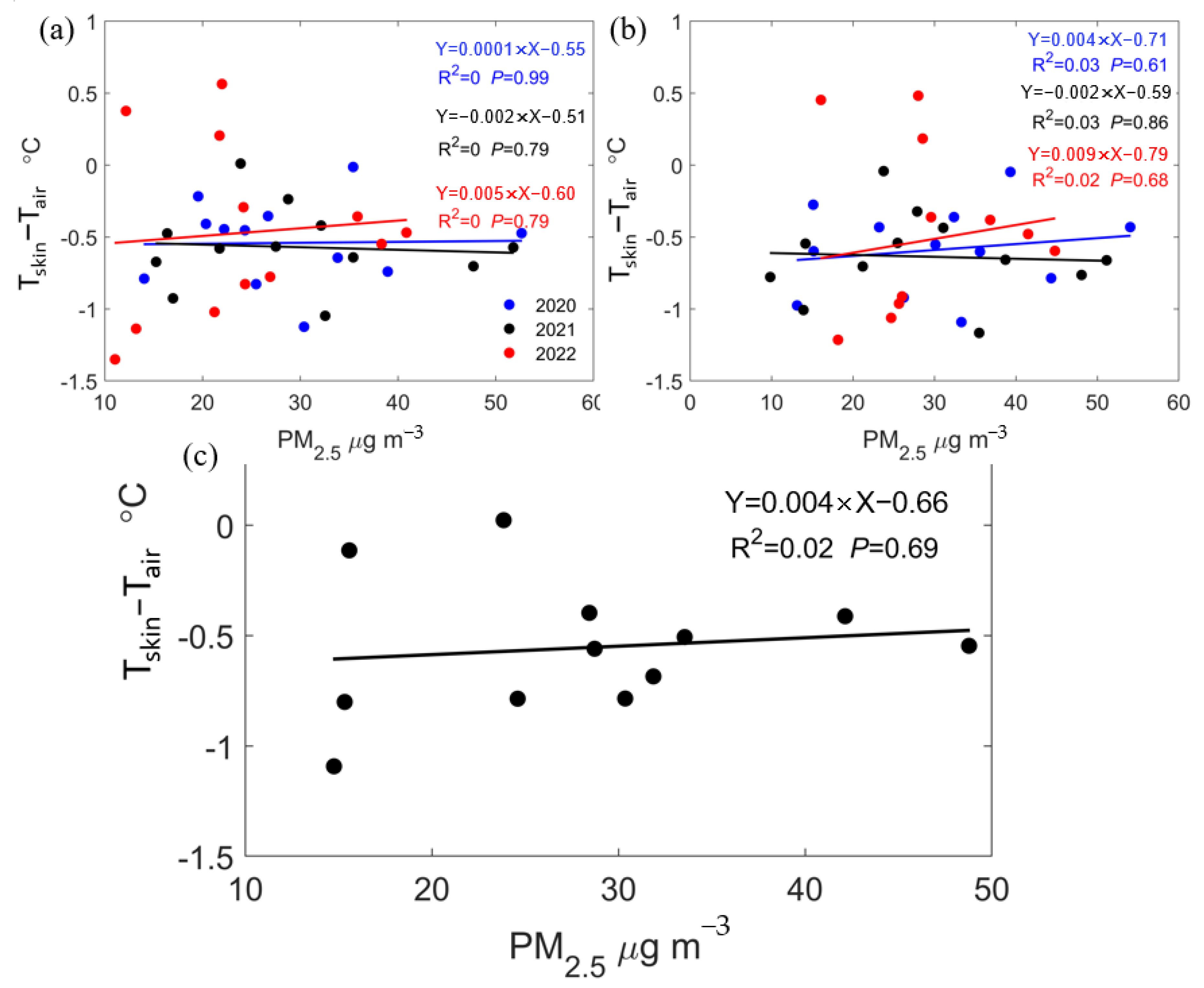
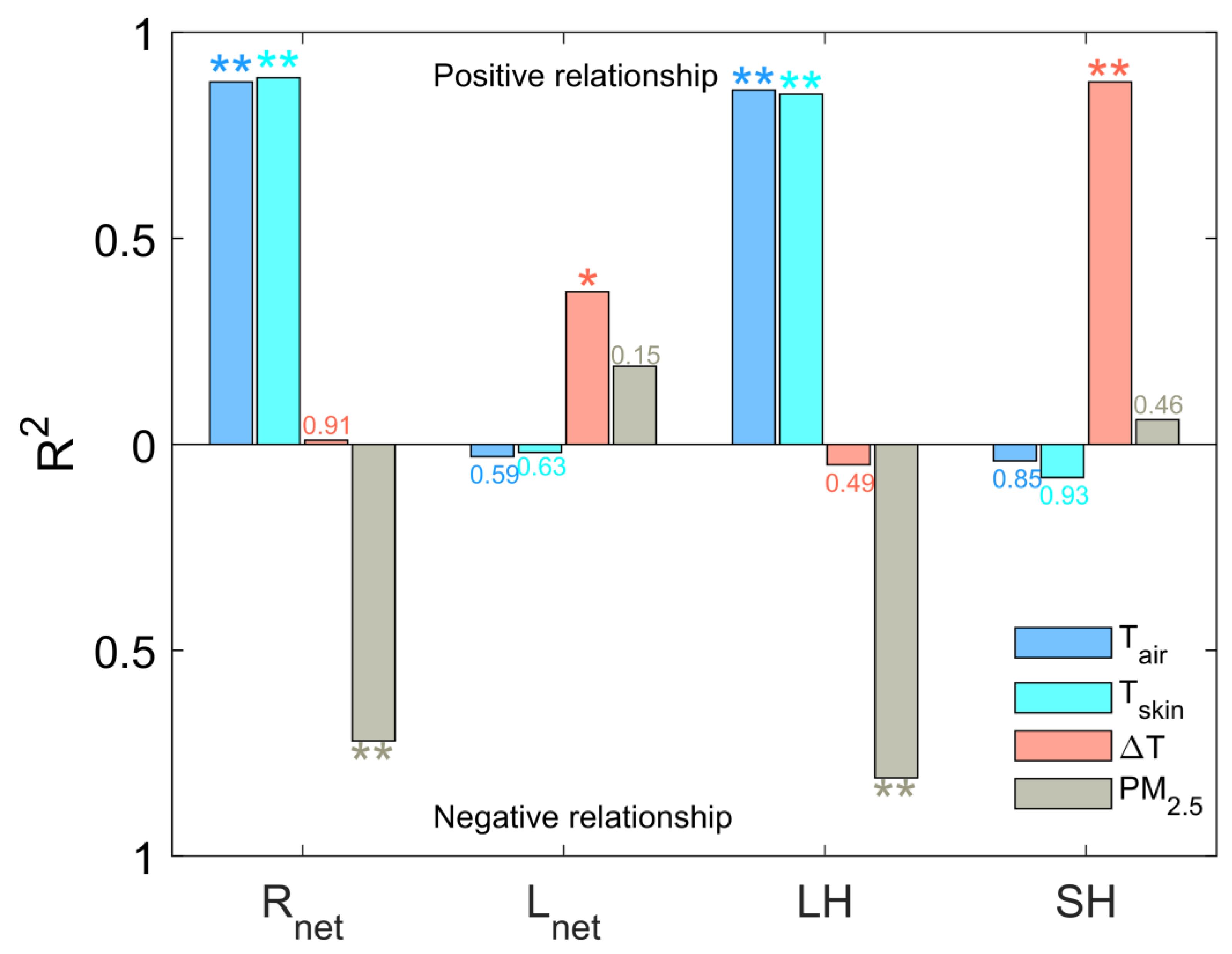
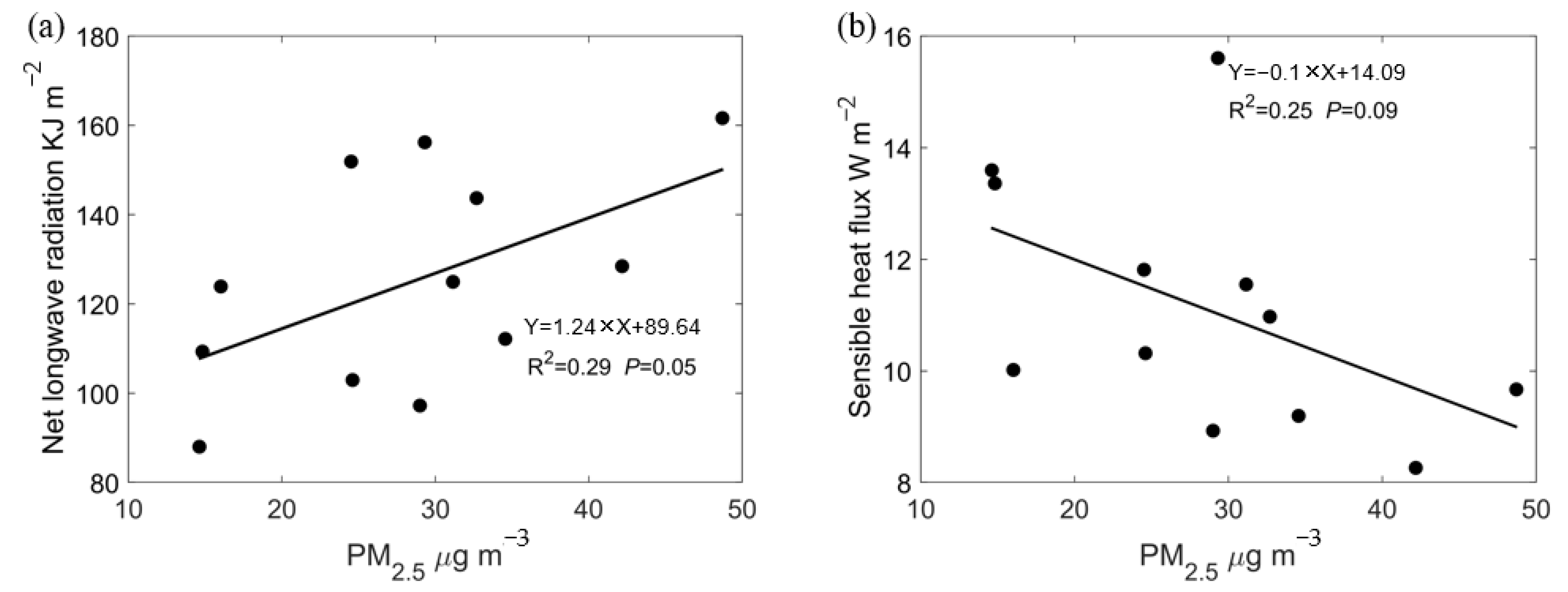
3.3. Mechanistic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Jenamani, K.R. Alarming rise in fog and pollution causing a fall in maximum temperature over Delhi. Curr. Sci. 2007, 93, 314–322. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/24099461 (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Twomey, S. The influence of pollution on the shortwave albedo of clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1977, 34, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.D.; Sodoudi, S.; Liu, J.F.; Tao, W. Temporal variation of urban aerosol pollution island and its relationship with urban heat island. Atmos. Res. 2020, 241, 104957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Jana, S.; Maitra, A. Dominance of pollutant aerosols over an urban region and its impact on boundary layer temperature profile. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Zou, J.L.; Yang, W.; Li, C.-Q. A review of recent advances in research on PM2.5 in China. Int. J. Envion. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Gao, J.Q.; Wang, B.; Ouyang, F. Statistical Analysis of Weather Effects on PM2.5. Adv. Mat. Res. 2013, 610–613, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chao, C.; Ping, W.; Chen, Z.; Cao, S.; Wang, Q.; Xie, G.; Wan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, B. Influence of atmospheric fine particulate matter (PM2.5) pollution on indoor environment during winter in Beijing. Build. Environ. 2015, 87, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megaritis, A.G.; Fountoukis, C.; Charalampidis, P.E.; Denier van der Gon, H.A.C.; Pilinis, C.; Pandis, S.N. Linking climate and air quality over Europe: Effects of meteorology on PM2.5 concentrations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 10283–10298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, Z.F.; Gao, S.H. Effect of cold wave on winter visibility over eastern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 2394–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, Z.Q.; Fast, J.; Ban, J.M. Simulations of sulfate–nitrate–ammonium (SNA) aerosols during the extreme haze events over northern China in October 2014. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10707–10724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.F.; Xu, G.R.; Li, Q.C.; Chen, C.L.; Li, J.B. Effect of precipitation on reducing atmospheric pollutant over Beijing. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Yao, L.; Wang, L.L.; Liu, Z.R.; Ji, D.S.; Tang, G.Q.; Zhang, J.K.; Sun, Y.; Hu, B.; Xin, J.Y. Mechanism for the formation of the January 2013 heavy haze pollution episode over central and eastern China. Sci. China 2014, 57, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Xia, X.G.; Cribb, M.; Mi, W.; Holben, B.; Wang, P.C.; Chen, H.B.; Tsay, S.C.; Eck, T.F.; Zhao, F.S.; et al. Aerosol optical properties and their radiative effects in northern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhao, X.J.; Chen, D.; Fan, S.Y.; Guo, J.P.; Ai, S. Impacts of aerosol–radiation interaction on meteorological forecasts over northern China by offline coupling of the WRF-Chem-simulated aerosol optical depth into WRF: A case study during a heavy pollution event. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 12527–12547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, J.Z.; Wang, Y.Q.; Liu, H.L.; Sun, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.M. Changes in chemical components of aerosol particles in different haze regions in China from 2006 to 2013 and contribution of meteorological factors. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 12935–12952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Tripathi, S.N.; Mishra, S.K. Probable mixing state of aerosols in the Indo-Gangetic Basin, northern India. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L03808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, U.; Markakis, K.; Koçak, M.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Daskalakis, N.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Poupkou, A.; Kındap, T.; Unal, A.; Kanakidou, M. Summertime aerosol chemical composition in the Eastern Mediterranean and its sensitivity to temperature. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 50, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Lee, X.H.; Liu, S.D.; Schultz, N.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, L. Urban heat islands in China enhanced by haze pollution. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, T.J.; Fang, H.; Ma, Y.P.; Han, Y.Q.; Huang, S.; Yao, Y.A.; Shi, J.Q. Impact of aerosol on the urban heat island intensity in Nanjing. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 37, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, T.J.; Riemer, N.; Chen, P.L.; Li, M.M.; Li, S. Urban heat island impacted by fine particles in Nanjing, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaro, E.; de Arellano, J.V.G.; Ouwersloot, H.G.; Schröter, J.S.; Donovan, D.P.; Krol, M.C. Aerosols in the convective boundary layer: Shortwave radiation effects on the coupled land-atmosphere system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 5845–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wong, C.H.; Cheung, T.F.; Blake, D.R.; Arimoto, R.; Baumann, K.; Tang, J.; Ding, G.A.; Yu, X.M.; Li, Y.S.; et al. Relationships of trace gases and aerosols and the emission characteristics at Lin’an, a rural site in eastern China, during spring 2001. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Gao, Z.Q.; Miao, S.G.; Guo, X.F.; Sun, T.; Liu, M.F.; Li, D. Contrasting characteristics of the surface energy balance between the urban and rural areas of Beijing. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Liu, S.; Yu, X.; Li, X.M.; Chen, C.; Peng, Y.; Dong, Y.; Dong, Z.P.; Wang, F.Q. Urban boundary layer height characteristics and relationship with particulate matter mass concentrations in Xi’an, central China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xue, M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Zhou, C.H.; Tan, S.C.; Che, H.Z.; Chen, B.; Li, T. Mesoscale modeling study of the interactions between aerosols and PBL meteorology during a haze episode in Jing-Jin-Ji (China) and its nearby surrounding region-Part 1: Aerosol distributions and meteorological features. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 3257–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wu, D.; Fan, Q.; Wang, B.M.; Li, H.W.; Fan, S.J. Observational studies of the meteorological characteristics associated with poor air quality over the Pearl River Delta in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10755–10766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo Scientific. TEOM 1405-DF: Dichotomous Ambient Particulate Monitor with FDMS Option; 42-010815 Revision, A.003; Thermo Scientific: Franklin, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretherton, C.; Widmann, M.; Dymnikov, V.; Wallace, J.; Bladé, I. The effective number of spatial degrees of freedom of a time-varying field. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 1990–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louie, P.K.K.; Chow, J.C.; Chen, L.W.A.; Watson, J.G.; Leung, G.; Sin, D.W.M. PM2.5 chemical composition in Hong Kong: Urban and regional variations. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 338, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.S.; Dong, F.; He, D.; Zhao, X.J.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, W.Z.; Yao, Q.; Liu, H.Y. Characteristics of concentrations and chemical compositions for PM2.5 in the region of Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4631–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Jing, J.; Tao, J.; Hsu, S.C.; Wang, G.; Cao, J.; Lee, C.S.L.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Beijing: Seasonal perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7053–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Chang, W.; Yang, Y. Climatic effects of air pollutants over China: A review. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 115–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.J.; Li, R.H.; Qiu, R.Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Tan, C.; Li, Q.P.; Ge, W.; Han, X.J.; Tang, X.G.; Shi, W.Y.; et al. Global land surface temperature influenced by vegetation cover and PM2.5 from 2001 to 2016. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Xia, X.; Tao, M.; Zhu, L. Modeling the feedback between aerosol and meteorological variables in the atmospheric boundary layer during a severe fog-haze event over the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 4279–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.-K.; Tignor, M.M.B.; Allen, S.K.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, V.; Midgley, P.M. (Eds.) Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of IPCC the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, P.; Eliasson, I.; Holmer, B.; Grimmond, C.S.B. Longwave incoming radiation in the Tropics: Results from field work in three African cities. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2006, 85, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresne, J.L.; Gautier, C.; Ricchiazzi, P.; Fouquart, Y. Longwave scattering effects of mineral aerosols. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 1959–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Dai, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.F.; Xu, J.; Huangfu, Y.Q.; Feng, Y.C. Air humidity affects secondary aerosol formation in different pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.W.; Hu, M.; Tan, Q.W.; Feng, M.; Qu, Y.; An, J.L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Liu, X.G.; Cheng, N.L.; Deng, Y.J.; et al. Key role of atmospheric water content in the formation of regional haze in Southern China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 216, 116918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, T.J.; Wang, Q.G.; Cao, Y.; Qu, Y.W.; Nie, D.Y. Radiative effects and chemical compositions of fine particles modulating urban heat island in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 247, 118201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Yao, X. Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.T.; Heese, B.; McFarlane, S.A.; Chazette, P.; Jones, A.; Bellouin, N. Vertical distribution and radiative effects of mineral dust and biomass burning aerosol over West Africa during DABEX. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavelle, F.; Pont, V.; Mallet, M.; Solmon, F.; Johnson, B.; Leon, J.F.; Liousse, C. Simulation of aerosol radiative effects over West Africa during DABEX and AMMA SOP-0. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaro, E.; de Arellano, J.V.G.; Krol, M.C.; Holtslag, A.A.M. Impacts of aerosol shortwave radiation absorption on the dynamics of an idealized convective atmospheric boundary layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2013, 148, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Che, H.; Qi, B.; Wang, Y.Q.; Dong, Y.S.; Xia, X.G.; Wang, H.; Gui, K.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, H.J.; et al. Characterization of vertical distribution and radiative forcing of ambient aerosol over the Yangtze River Delta during 2013–2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1846–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, S.C.; Dickinson, R.E. Radiative effects of aerosols on the evolution of the atmospheric boundary layer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos 2002, 107, AAC 3-1–AAC 3-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Zhang, G.; Luo, Y.; Liang, X.; Liu, L.; Luo, K.; Xiao, Y. The Correlation Between Surface Temperature and Surface PM2.5 in Nanchang Region, China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040411
Wang W, Zhang G, Luo Y, Liang X, Liu L, Luo K, Xiao Y. The Correlation Between Surface Temperature and Surface PM2.5 in Nanchang Region, China. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(4):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040411
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Weihong, Gong Zhang, Yong Luo, Xuan Liang, Linqi Liu, Kunshui Luo, and Yuexin Xiao. 2025. "The Correlation Between Surface Temperature and Surface PM2.5 in Nanchang Region, China" Atmosphere 16, no. 4: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040411
APA StyleWang, W., Zhang, G., Luo, Y., Liang, X., Liu, L., Luo, K., & Xiao, Y. (2025). The Correlation Between Surface Temperature and Surface PM2.5 in Nanchang Region, China. Atmosphere, 16(4), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040411




