Spatiotemporal Evolution of Regional Air Pollution Exposure and Health Effects Assessment in Jiangsu Province, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
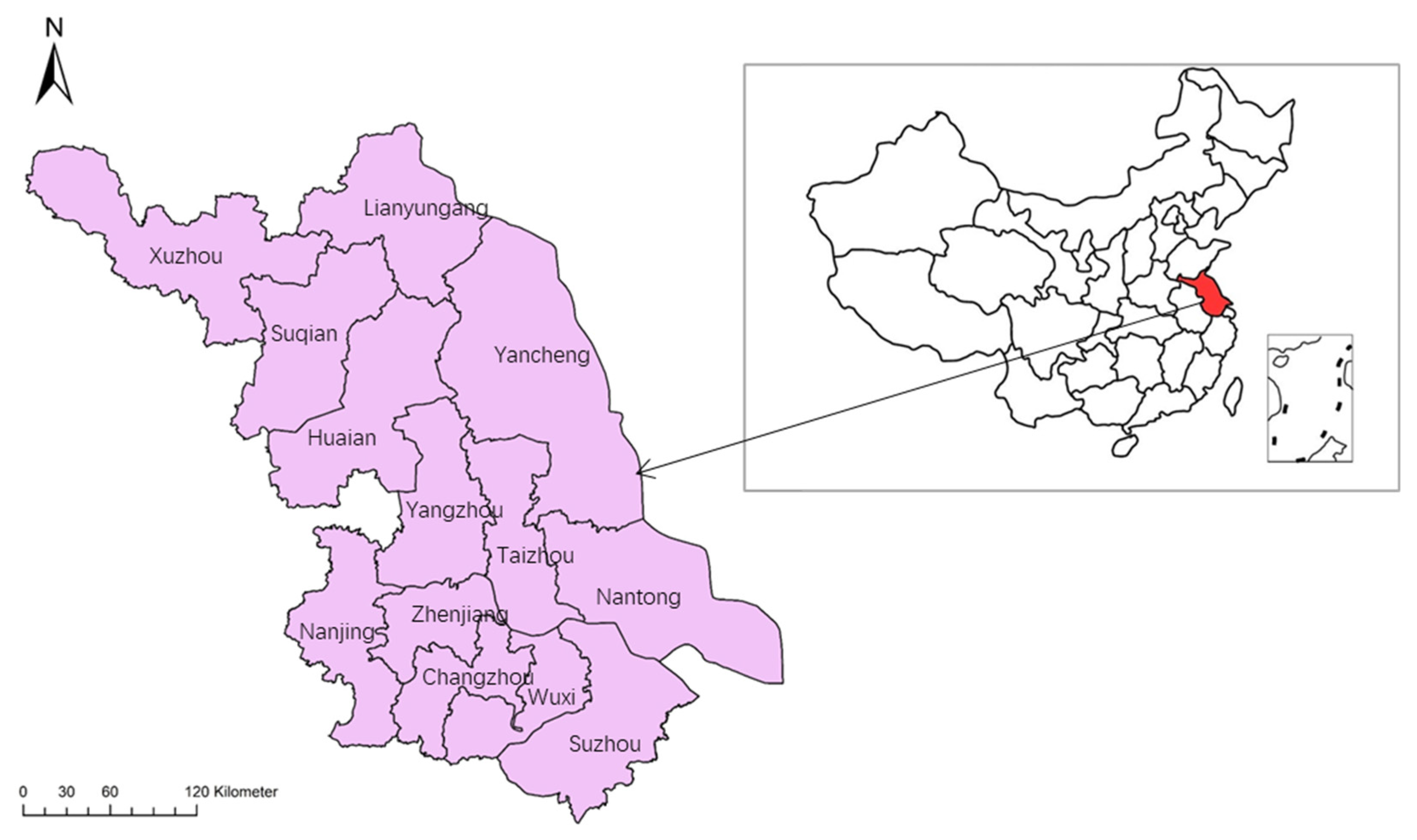
2.1. Research Scope
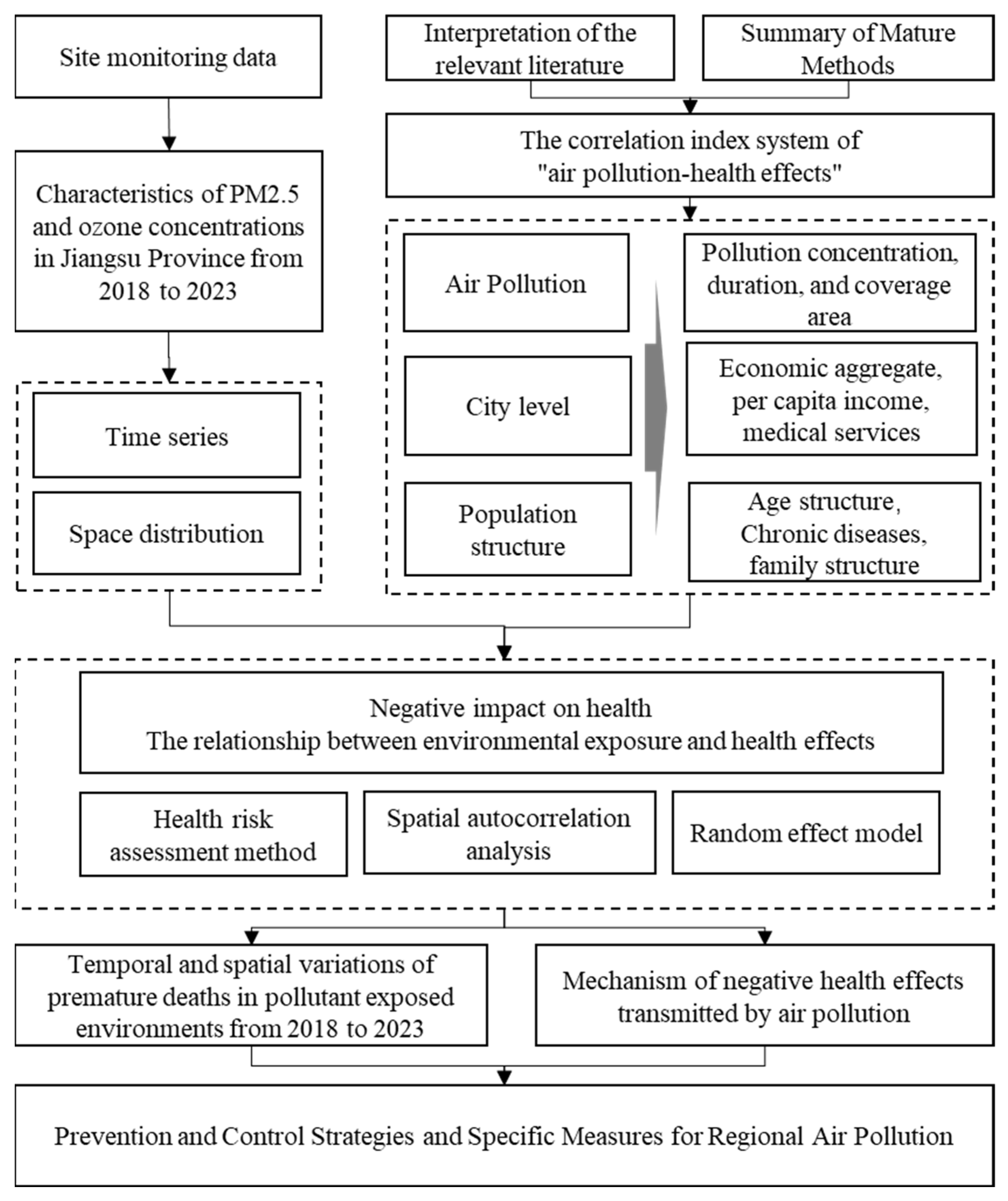
2.2. Research Framework
2.3. Variables and Indicators
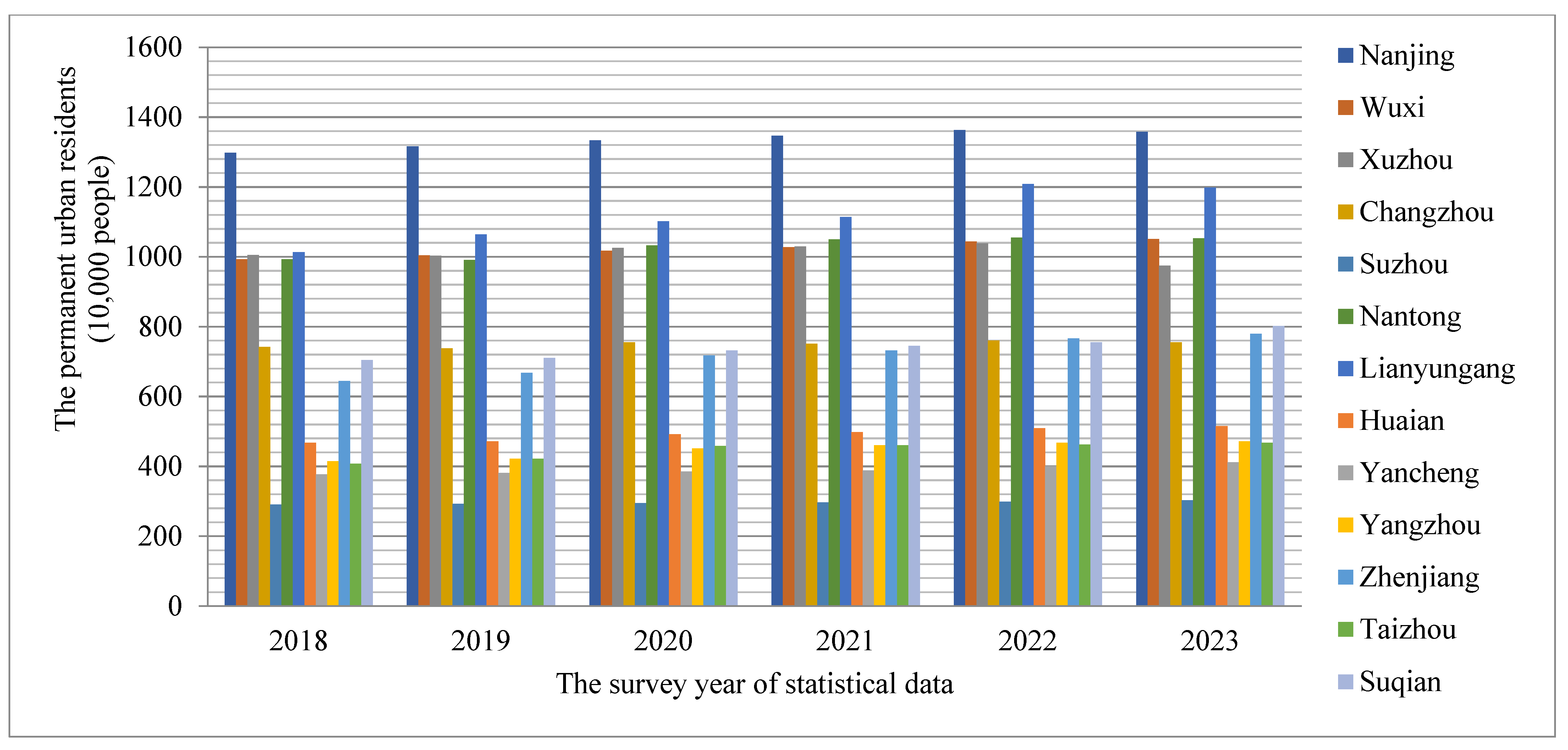
2.3.1. Statistical Yearbook Data
2.3.2. Air Quality Data
2.3.3. Indicator Variable System
2.4. Research Methods
2.4.1. Random Effects Model
2.4.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
2.4.3. Health Risk Assessment Methods
3. Results
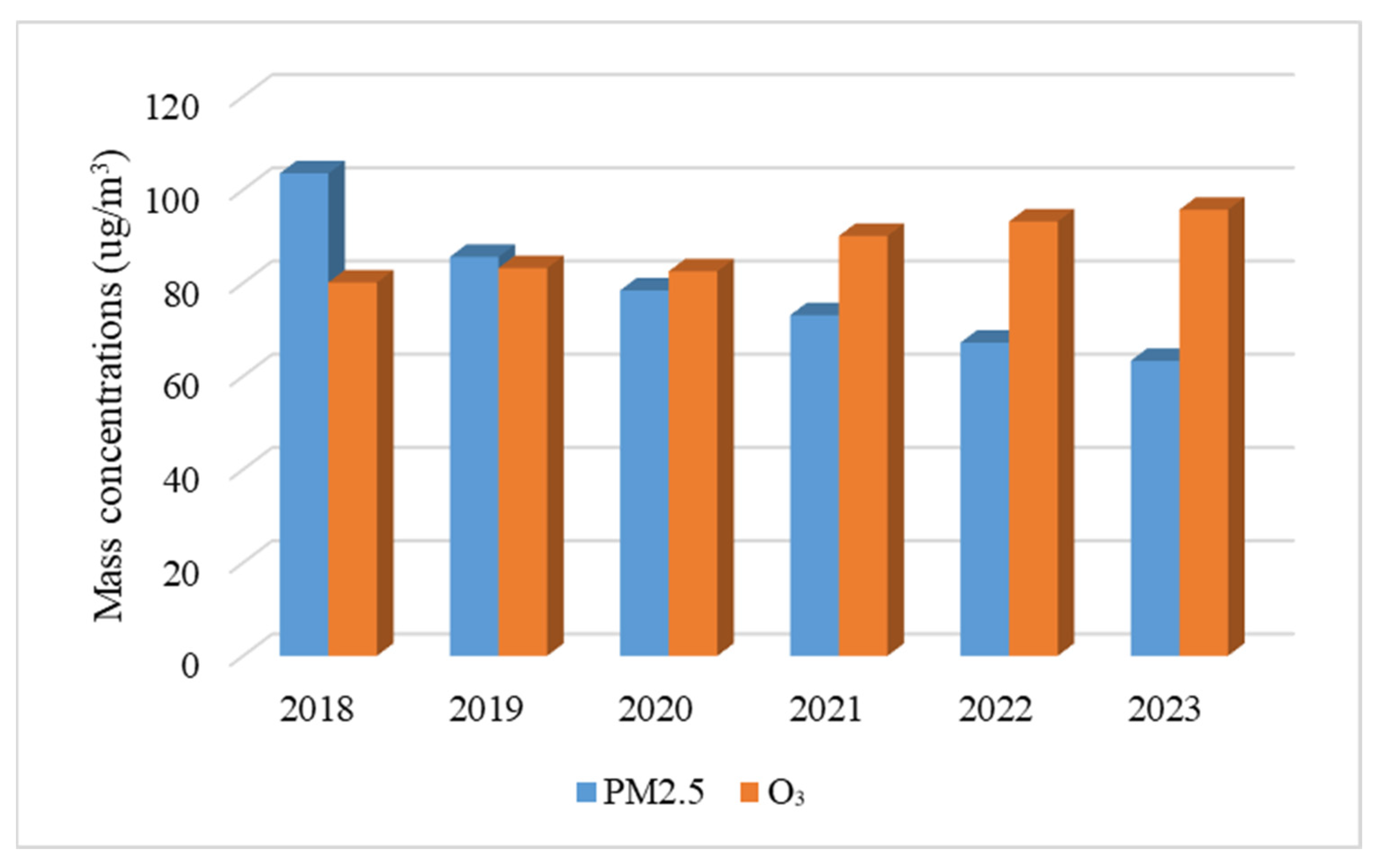
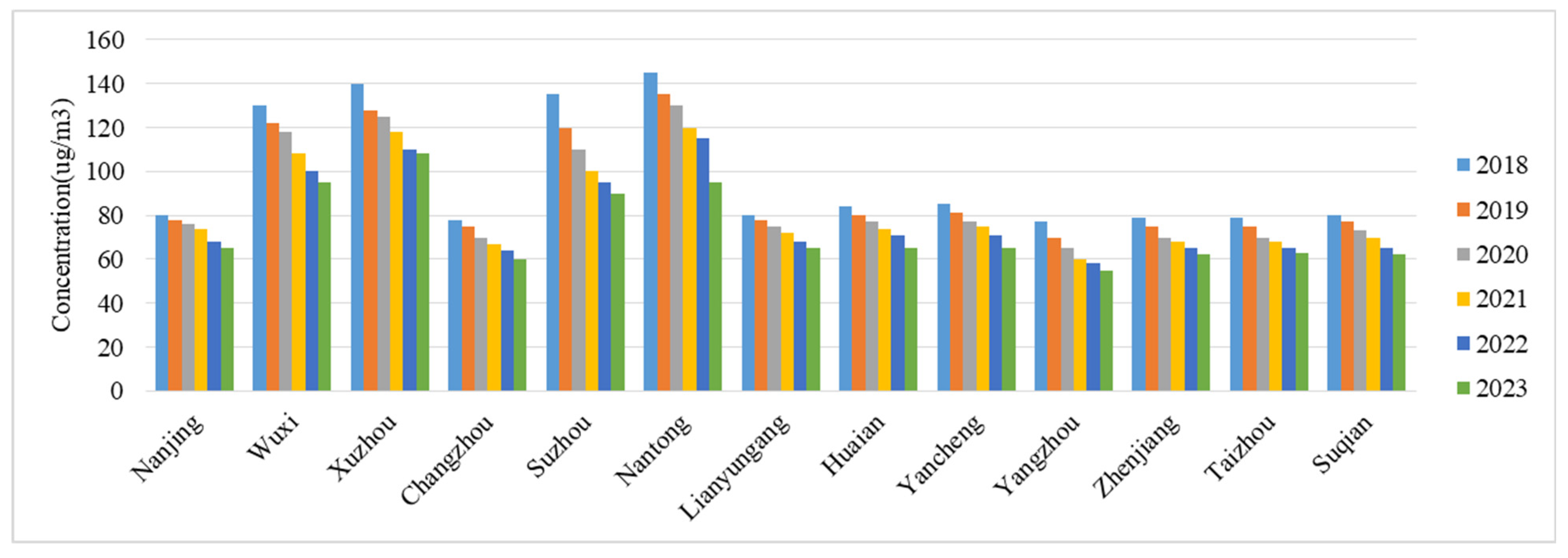
3.1. Characteristics of Changes in Atmospheric Pollutant Concentrations in Jiangsu Province from 2018 to 2023
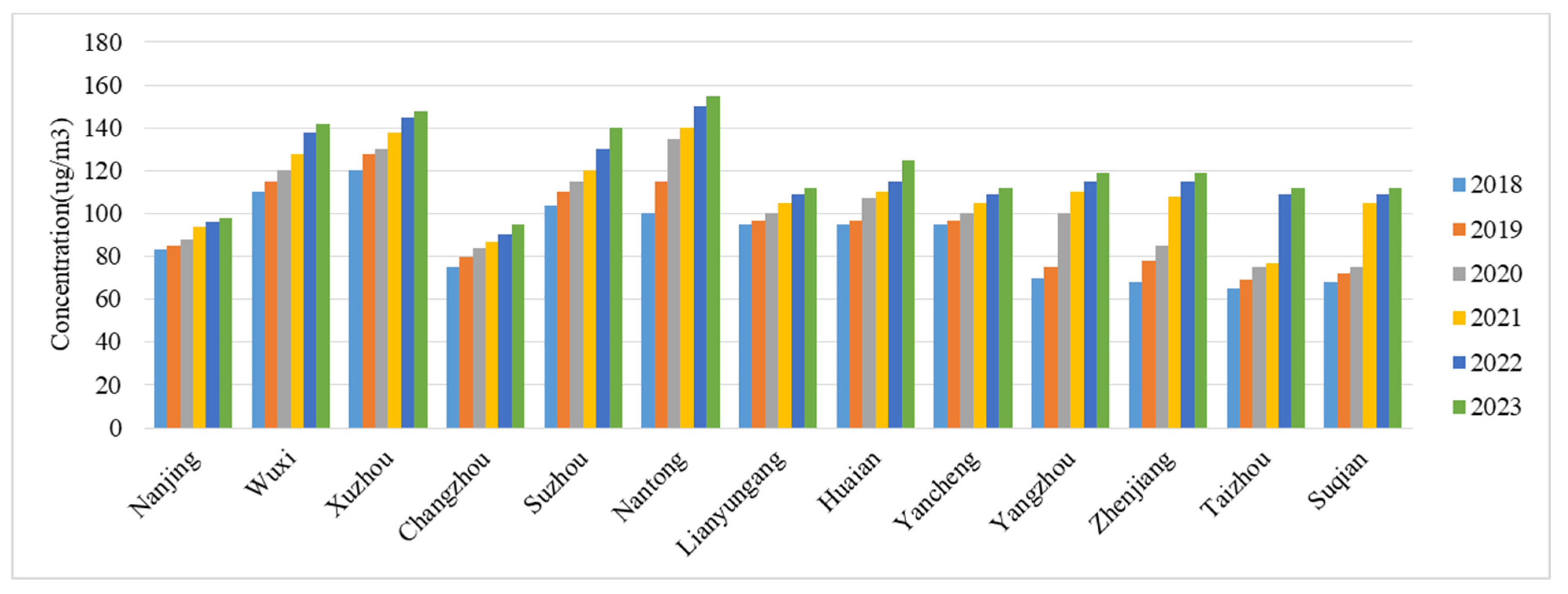
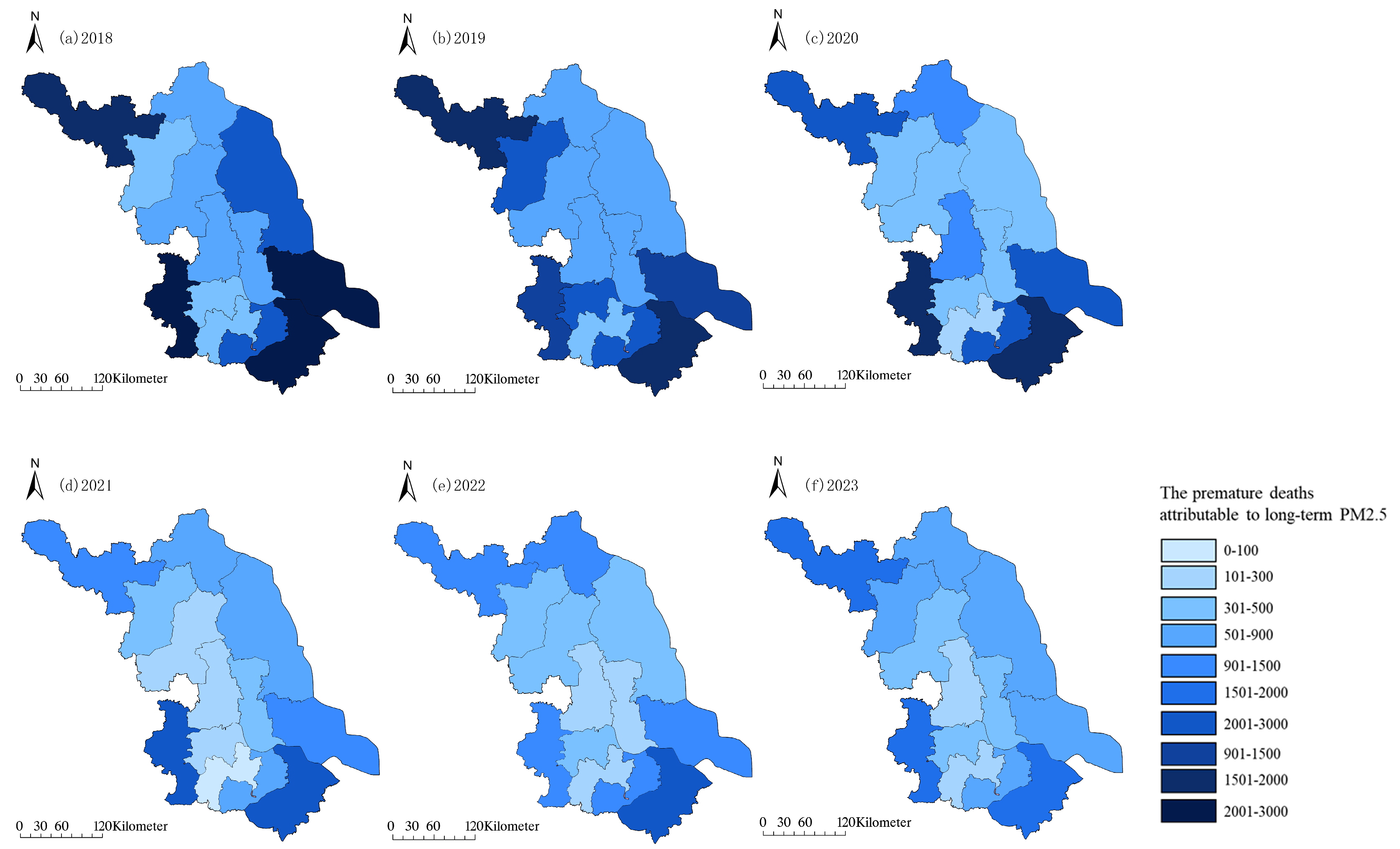
3.2. Spatial Variation Characteristics of PM2.5 and O3 Pollution in Different Years
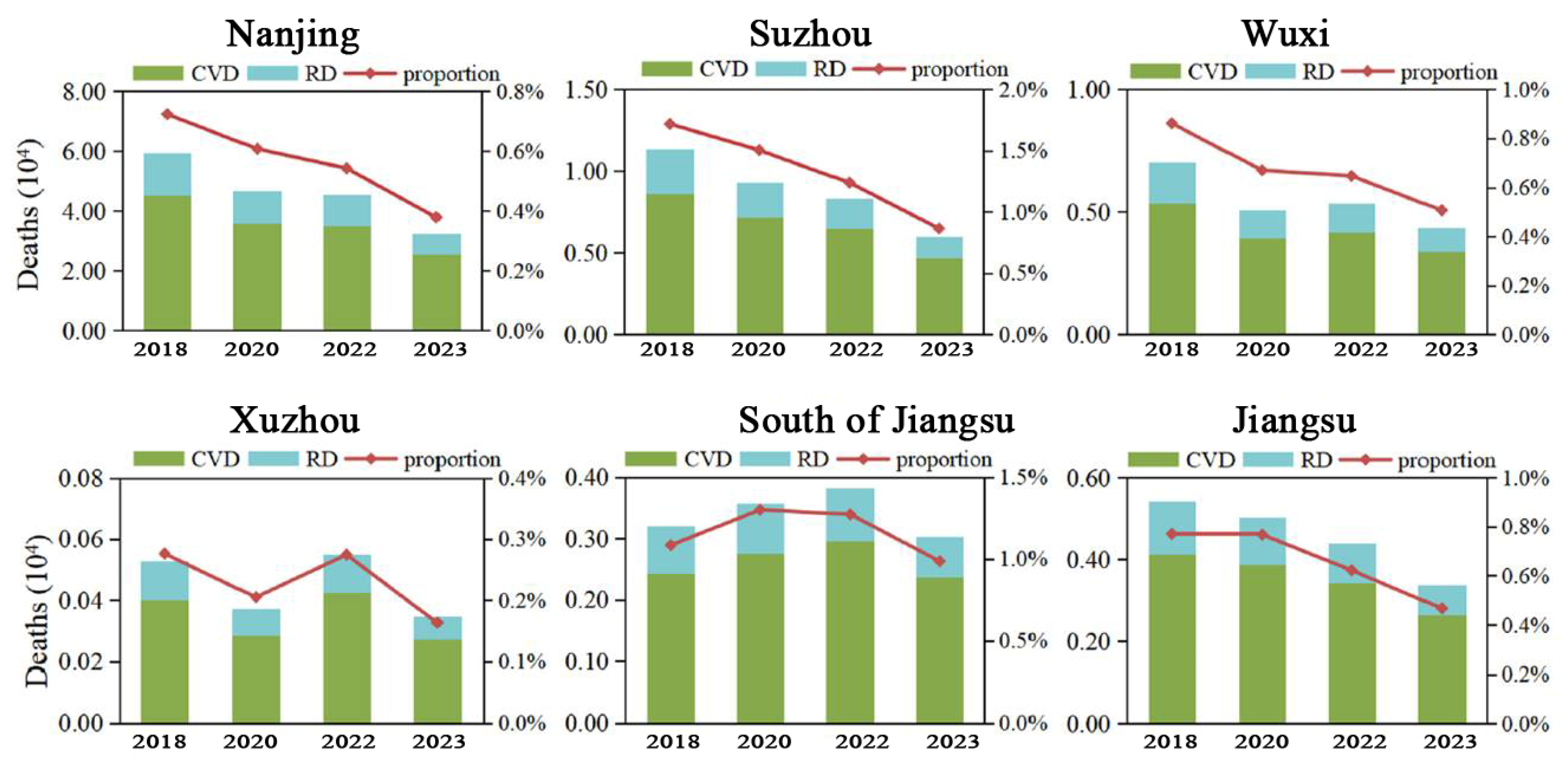
3.3. The Number of Premature Deaths Caused by Short-Term Exposure to PM2.5 Has Significantly Decreased
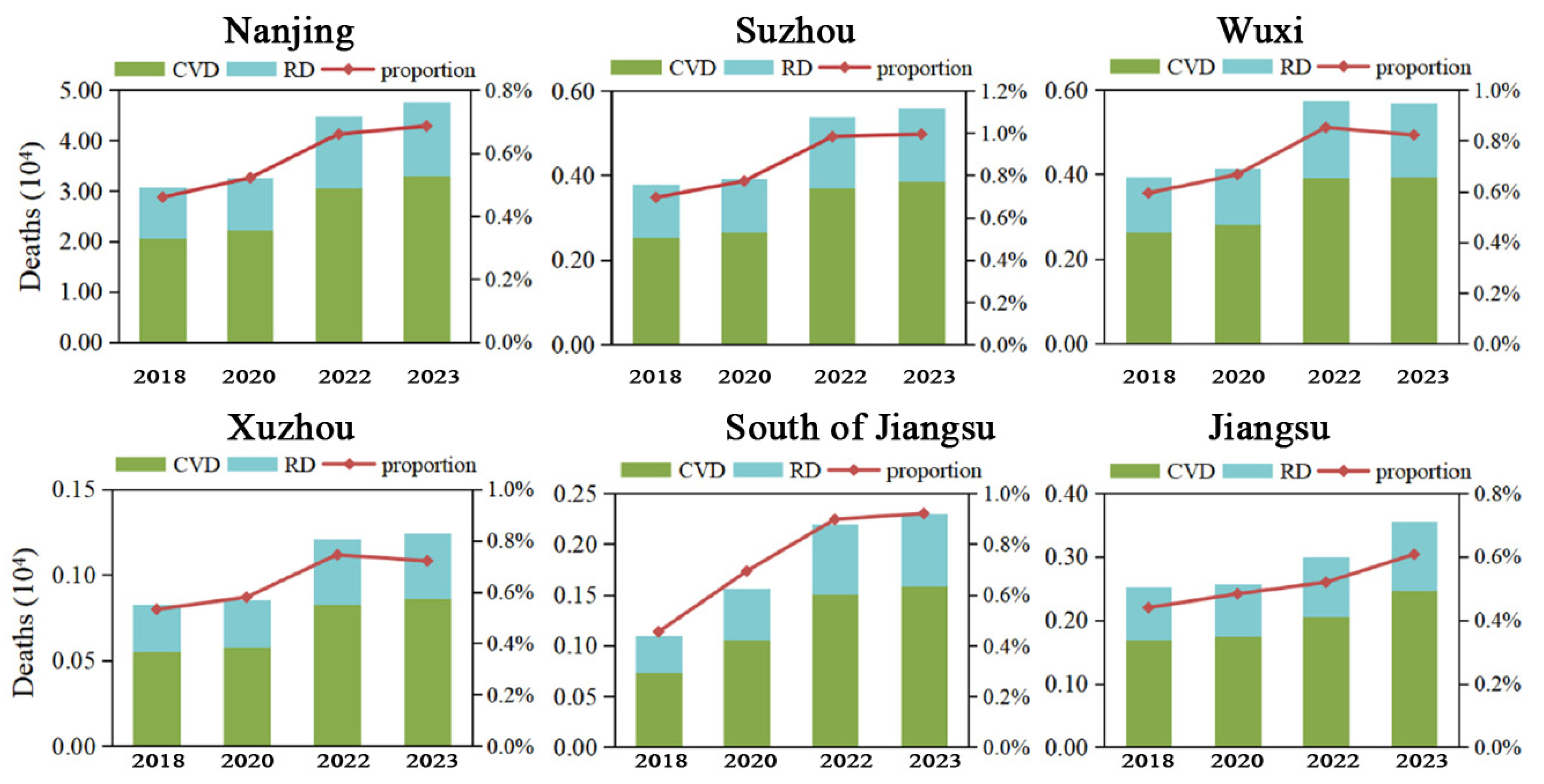
3.4. City Level and Population Structure Play an Important Role in the Health Effects of Air Pollution
4. Discussion
4.1. Total Number of Premature Deaths Under Long-Term Exposure to PM2.5 Has Decreased by Approximately 87%
4.2. Total Number of Premature Deaths Under Long-Term Exposure to O3 Has Increased by Approximately 216%
4.3. Short-Term Exposure to High Concentrations of Pollutants Has a Significant Impact on the Health of Individuals with Underlying Diseases
4.4. Long-Term Exposure Values of Pollutants Can Better Reflect the Overall Health Burden of Populations Experiencing Long-Term Exposure
5. Conclusions
5.1. Key Findings
5.2. Implications
5.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chee, F.P.; Ooi, C.G.; Wong, Y.J.; Sentian, J.; Dayou, J.; Latif, M.T. Modelling climatic variable impacts on ground-level ozone in Malaysia using backward trajectory and generative additive models. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 22, 6021–6048. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki, A.; Komazawa, S.; Ogata, S. Dissolved concentration and lifetime of ozone ultrafine bubbles. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2025, 58, 045207. [Google Scholar]
- Carlos, N.; Jacinto, R.L.; Santos, M.S. Potential of drying carrot using ozone pre-treatment: Mass transfer modeling and techno-functional properties. Food Bioprod. Process. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. Part C 2024, 146, 1772–1783. [Google Scholar]
- Dececco, A.C.; Conrad, A.R.; Floyd, A.M.; Jasper, A.W.; Hansen, N.; Dagaut, P. Tracking the reaction networks of acetaldehyde oxide and glyoxal oxide criegee intermediates in the ozone-assisted oxidation reaction of croton aldehyde. PCCP 2024, 26, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Isaacman-Vanwertz, G.; Frazier, G.; Willison, J.; Faiola, C. Missing measurements of sesquiterpene ozonolysis rates and composition limit understanding of atmospheric reactivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. ES&T 2024, 3, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Fabrication of mno2 coating on aluminum honeycomb for fast catalytic decomposition of ozone at room temperature. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 177, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Belz, D.C.; Woo, H.; Putcha, N.; Paulin, L.M.; Koehler, K.; Fawzy, A. Ambient ozone effects on respiratory outcomes among smokers modified by neighborhood poverty: An analysis of spiromics air. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 38, 829. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.T.; Yang, Y.C.; Zeng, S.S.; Arowo, M.; Zhang, X.Q.; Zheng, B.D. Treatment of organic wastewater by ozone in a continuous rotating solid foam stirrer tank. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2022, 174, 108866. [Google Scholar]
- Dedoussi, I.C.; Eastham, S.D.; Monier, E.; Barrett, S.R.H. Premature mortality related to United States cross-state air pollution. Nature 2020, 578, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.Z.; De Marco, A.; Anav, A.; Gualtieri, M.; Sicard, P.; Tian, H.Q.; Fornasier, F.; Tao, F.L.; Guo, A.H.; Paoletti, E. Economic losses due to O3 impacts on human health, forest productivity and crop yield across China. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Du, N.; Wang, L.; Deng, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L. Impacts of meteorological and precursor emission factors on pm2.5 and o3 from 2019 to 2022: Insights from multiple perspectives. Atmos. Res. 2025, 315, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wong, T.W.; Law, C.K.; Dong, G.H.; Ho, K.F.; Yang, Y.; Yim, S.H.L. Impacts of sectoral emissions in China and the implications: Air quality, public health, crop production, and economic costs. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 084–096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Pan, X.C.; Guo, X.B.; Li, G.X. Health impact of China’s Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan: An analysis of national air quality monitoring and mortality data. Lancet Planet Health 2018, 2, e313–e323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, N.; Wang, X.; Zheng, B.; Henze, D.K. Changing responses of pm2.5 and ozone to source emissions in the Yangtze river delta using the adjoint model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Sun, L.; Huang, L.; Xie, Y.; Yang, S.; Sun, L. Inequality of exposure to pm2.5 and ozone among age groups and cities in Japan in 2030 and 2050. Microelectron. J. 2024, 55, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Bates, K.H. Anthropogenic drivers of 2013-2017 trends in summer surface O3 in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Gao, W.; Song, T.; Sun, Y. Exploring the regional pollution characteristics and meteorological formation mechanism of PM2.5 in North China during 2013–2017. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Li, X.L.; Teng, Y.; Fu, H.C.; Chen, L.; Mao, J.; Zhang, H.; Gao, S.; Sun, Y.L.; Ma, Z.X.; et al. Estimation of health and economic benefits based on O3 exposure level with high spatial-temporal resolution by fusing satellite and station observations. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, G.; He, X.J.; Ma, X.L.; Li, S.; Sabel, C.E.; Wang, H.K. Impacts of on premature mortality and crop yield loss across China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 194, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Xue, B.R.; Lv, Z.F.; Meng, Z.H.; Yang, X.F.; Xue, T.; Yu, Q.; He, K.B. Ground-level O3 pollution and its health impacts in China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 173, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Hong, J.Y.; Zhang, L.; Cooper, O.R.; Schultz, M.G.; Xu, X.B.; Wang, T.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.H. Severe surface O3 pollution in China: A global perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chao, K.; Zhu, Z.; Yue, J.; Qie, X.; Wang, M. A study on a health impact assessment and healthcare cost calculation of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei residents under pm 2.5 and o 3 pollution. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, L.; Wang, T.; Li, M.; Xie, M.; Liu, J. Optimizing emission control strategies for mitigating pm2.5 and o3 pollution: A case study in the Yangtze river delta region of eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 319, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, K.J. Substantial changes in PM2.5 pollution and corresponding premature deaths across China during 2015-2019: A model prospective. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, K.J.; Ye, W.F.; Arora, M.; Shiva Nagendra, S.M. PM2.5-related health and economic loss assessment for 338 Chinese cities. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 392–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, K.J.; Ye, W.F.; Arora, M.; Nagendra, S.M.S. O3 pollution in Chinese cities: Assessment of seasonal variation, health effects and economic burden. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malley, C.S.; Henze, D.K.; Kuylenstierna, J.C.I.; Vallack, H.W.; Davila, Y.; Anenberg, S.C.; Turner, M.C.; Ashmore, M.R. Updated global estimates of respiratory mortality in adults ≥30 years of age attributable to long-term O3 exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 087021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A.; Cohen, A.J.; Burnett, R.T. Cardiovascular disease and fine particulate matter: Lessons and limitations of an integrated exposure-response approach. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1645–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloster, M.E. Air pollution and stroke: What nurses need to know. Stroke 2024, 55, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltzer, K.M.; Shindell, D.T.; Malley, C.S. Measurement-based assessment of health burdens from long-term O3 exposure in the United States, Europe, and China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 104018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazorla, M.; Giles, D.M.; Herrera, E.; Suárez, L.; Estevan, R.; Andrade, M. Latitudinal and temporal distribution of aerosols and precipitable water vapor in the tropical andes from aeronet, sounding, and merra-2 data. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.B.; He, J.J.; Wu, L.; Jin, T.S.; Chen, X.; Li, R.P.; Ren, P.P.; Zhang, L.; Mao, H.J. Health burden attributable to ambient PM2.5 in China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.M.; Huang, M.J.; Zhong, L.J.; Chen, D.H.; Wang, X.M. Trends of outdoor air pollution and the impact on premature mortality in the Pearl River Delta region of southern China during 2006–2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, T.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Geng, G.N.; Zheng, Y.X.; Tong, D.; Liu, Z.; Guan, D.B.; Bo, Y.; Zhu, T.; et al. Rapid improvement of PM2.5 pollution and associated health benefits in China during 2013-2017. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.H.; Wu, G.H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.Y. Estimating health burden and economic loss attributable to short-term exposure to multiple air pollutants in China. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 109184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, S.L.H.; Wang, M.Y.; Gu, Y.F.; Yang, Y.J.; Dong, G.H.; Li, Q.X. Effect of urbanization on O3 and resultant health effects in the Pearl River Delta region of China. J. Geophys. Res.—Atmos. 2019, 124, 11568–11579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikamoto, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hipps, L.W.; Simon, R.B. Interannual variability and trends of summertime pm2.5-based air quality in the intermountain west. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.X.; Jacob, D.J.; Wang, X.; Shen, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Gui, K.; Zhao, T.L.; Liao, H. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) trends in China, 2013–2018: Separating contributions from anthropogenic emissions and meteorology. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11031–11041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.N.; Ma, F.; Qin, C.B.; Li, Y.F. Spatiotemporal trends in PM2.5 levels from 2013 to 2017 and regional demarcations for joint prevention and control of atmospheric pollution in China. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



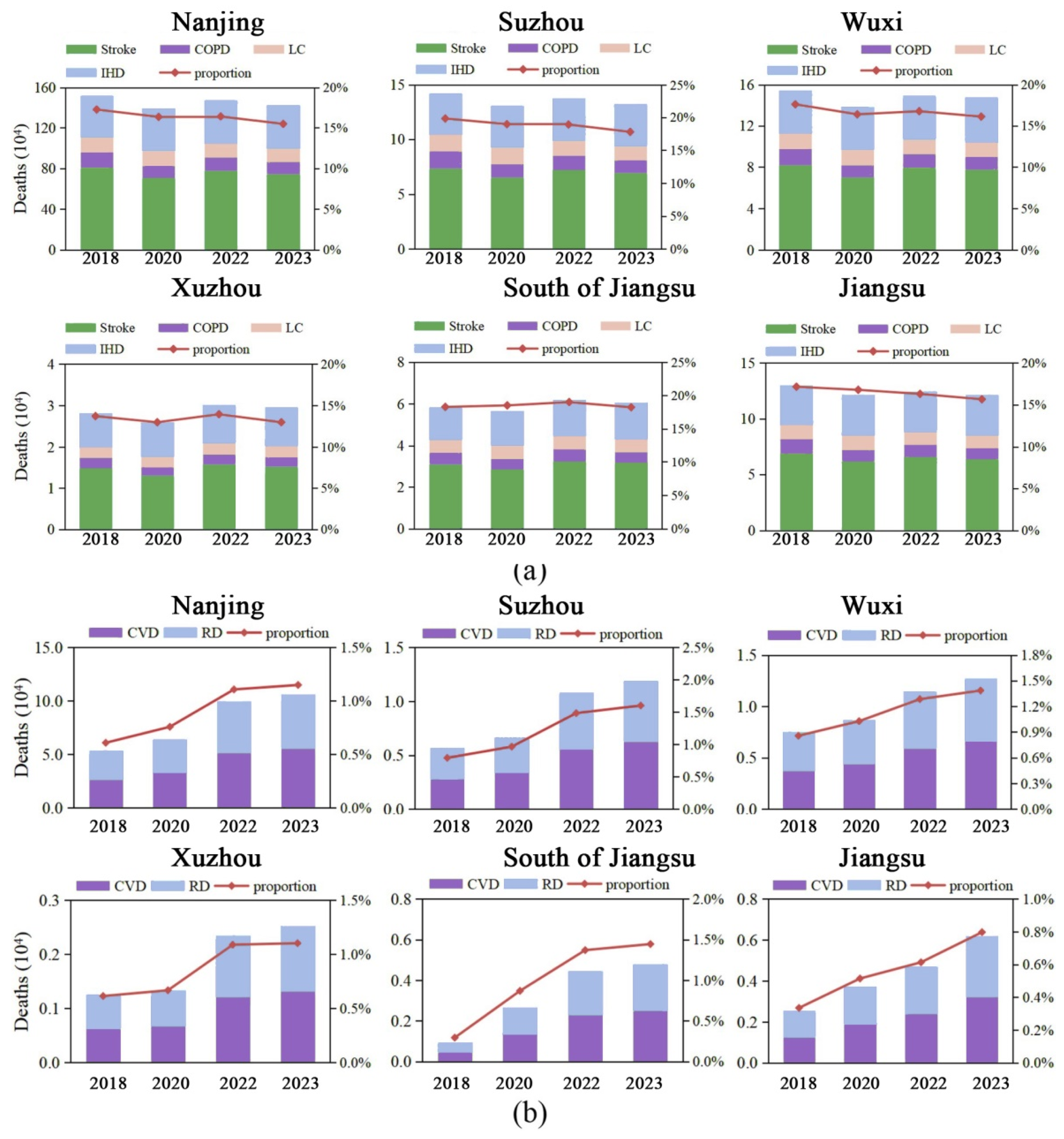

| All Cause | CVD | RD | IHD | Stroke | COPD | LC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 638.39 | 288.76 | 76.92 | 99.72 | 139.32 | 59.18 | 42.95 |
| 2019 | 640.12 | 297.53 | 77.18 | 108.43 | 135.82 | 57.23 | 44.32 |
| 2020 | 642.26 | 281.37 | 78.54 | 112.72 | 140.23 | 60.32 | 46.08 |
| 2021 | 616.18 | 275.89 | 69.31 | 114.74 | 126.72 | 49.33 | 48.33 |
| 2022 | 648.39 | 294.23 | 73.88 | 118.66 | 142.08 | 55.67 | 47.18 |
| 2023 | 662.52 | 308.18 | 72.45 | 126.68 | 144.56 | 54.86 | 48.31 |
| Variable (Unit) | Description | Mean/Day | Variance | Minimum Value | Maximum Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AQI (value) | Daily air quality index | 67.12 | 27.78 | 19.32 | 123.31 |
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) | Mass concentrations of particulate matter with aerodynamic equivalent diameter less than or equal to 2.5 μm | 72.28 | 22.87 | 21.14 | 117.91 |
| PM10 (μg/m3) | Mass concentrations of particulate matter with aerodynamic equivalent diameter less than or equal to 10 μm | 81.15 | 21.31 | 31.29 | 109.34 |
| CO (mg/m3) | Mass concentrations of carbon monoxide | 3.98 | 0.18 | 2.72 | 4.98 |
| NO2 (μg/m3) | Mass concentrations of nitrogen dioxide | 36.15 | 9.18 | 28.81 | 49.12 |
| O3 (μg/m3) | Mass concentrations of O3 | 72.28 | 26.72 | 39.56 | 91.32 |
| SO2 (mg/m3) | Mass concentrations of sulfur dioxide | 83.38 | 18.72 | 65.34 | 178.33 |
| Dependent Variable | Explanatory Variable | Secondary Indicator | Variable Interpretation (Unit) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Health effects | Air Pollution | Concentration of air pollution (PM2.5 and O3) | Annual average emissions of core indicators (μg/m3) |
| Duration of air pollution (PM2.5 and O3) | Duration of high concentration of pollution per year (days) | ||
| Coverage of air pollution (PM2.5 and O3) | Proportion of high-pollution areas in total administrative area (%) | ||
| City Level | Total economic development | Regional Gross Domestic Product (1 billion) | |
| Local average income | Per-capita income level of each city (yuan) | ||
| Medical service capability | Number of high-level hospitals in each city (number) | ||
| Population Structure | Age structure | Proportion of elderly people aged 60 and above (%) | |
| Chronic patients | Proportion of people with chronic diseases (%) | ||
| Family formation | Proportion of individuals living alone (%) |
| Factor | Corbach’s Alpha Value | Standardized Corbach’s Alpha Value |
|---|---|---|
| Air pollution concentration | 0.882 | 0.901 |
| Duration of air pollution | 0.875 | 0.823 |
| Coverage of air pollution | 0.792 | 0.822 |
| Total economic development | 0.723 | 0.746 |
| Local average income | 0.703 | 0.753 |
| Medical service capability | 0.689 | 0.781 |
| Age structure | 0.752 | 0.821 |
| Chronic patients | 0.736 | 0.796 |
| Family formation | 0.813 | 0.827 |
| Z-Score | p-Value | Confidence Level (%) |
|---|---|---|
| <−1.55 or >1.55 | <0.1 | 90 |
| <−1.86 or >1.86 | <0.05 | 95 |
| <−2.68 or >2.68 | <0.01 | 99 |
| Exposure Type | Contaminants | Method | Health Risks | RR | β | C0(μg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short-term | O3 | Equation (7) | Total | 1.0031 (95%CI)—10 μg/m3 | 0.0024 (95%CI) | 70 (WHO) |
| CVD | 1.0008 (95%CI)—10 μg/m3 | 0.0027 (95%CI) | ||||
| RD | 1.0022 (95%CI)—10 μg/m3 | 0.0051 (95%CI) | ||||
| PM2.5 | Total | 1.0052 (95%CI)—10 μg/m3 | 0.0014 (95%CI) | 35 (secondary standard) | ||
| CVD | 1.0038 (95%CI)—10 μg/m3 | 0.0064 (95%CI) | ||||
| RD | 1.0024 (95%CI)—10 μg/m3 | 0.0058 (95%CI) | ||||
| Long-term | O3 | Equation (8) | CVD | 1.0139 (95%CI)—10 ppb | 0.0062 (95%CI) | 70 (WHO) |
| RD | 1.0096 (95%CI)—10 ppb | 0.0071 (95%CI) | ||||
| PM2.5 | IHD | 0.842 (95%CI)—10 μg/m3 | 0.0058 (95%CI) | 6.92 | ||
| Stroke | 1.031 (95%CI)—10 μg/m3 | 0.0051 (95%CI) | 8.12 | |||
| COPD | 19.32 (95%CI)—10 μg/m3 | 0.0048 (95%CI) | 7.33 | |||
| LC | 135.2 (95%CI)—10 μg/m3 | 0.0039 (95%CI) | 7.19 |
| First Level Indicator | Explanatory Variables | Random Effects Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Z-Statistic | p-Value | ||
| Air Pollution | Concentration of air pollution | 2.477 | 3.341 | 0.001 *** |
| Duration of air pollution | 2.381 | 2.765 | 0.001 *** | |
| Coverage of air pollution | 1.423 | 2.922 | 0.001 *** | |
| City Level | Total economic development | 0.016 | 0.941 | 0.049 ** |
| Local average income | 0.477 | 0.298 | 0.14 | |
| Medical service capability | 2.453 | 0.331 | 0.044 ** | |
| Population Structure | Age structure | −0.361 | 4.801 | 0.073 * |
| Chronic patients | 0.781 | 0.912 | 0.021 ** | |
| Family formation | 0.023 | 6.201 | 0.032 ** | |
| Constant | 7.064 | 2.136 | / | |
| R2 | Inter-group | 0.357 | ||
| Within group | 0.912 | |||
| Total R2 | 0.906 | |||
| F-statistic | 22.31 | |||
| Hausman test p-value | 0.031 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Ju, Q.; Chen, S.; Xu, C.; Cao, Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Regional Air Pollution Exposure and Health Effects Assessment in Jiangsu Province, China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040446
Yang J, Ju Q, Chen S, Xu C, Cao Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Regional Air Pollution Exposure and Health Effects Assessment in Jiangsu Province, China. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(4):446. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040446
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jin, Qiuyu Ju, Shifan Chen, Chen Xu, and Yang Cao. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Evolution of Regional Air Pollution Exposure and Health Effects Assessment in Jiangsu Province, China" Atmosphere 16, no. 4: 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040446
APA StyleYang, J., Ju, Q., Chen, S., Xu, C., & Cao, Y. (2025). Spatiotemporal Evolution of Regional Air Pollution Exposure and Health Effects Assessment in Jiangsu Province, China. Atmosphere, 16(4), 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040446





