Drought Analysis in the Yellow River Basin Based on a Short-Scalar Palmer Drought Severity Index
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
3. Methods
3.1. VIC Model Simulation
3.2. Modified scPDSI
3.2.1. Coupling VIC Model for Hydrologic Accounting
3.2.2. Time Scale Modification
3.3. Standardized Drought Indices
4. Results and Discussion
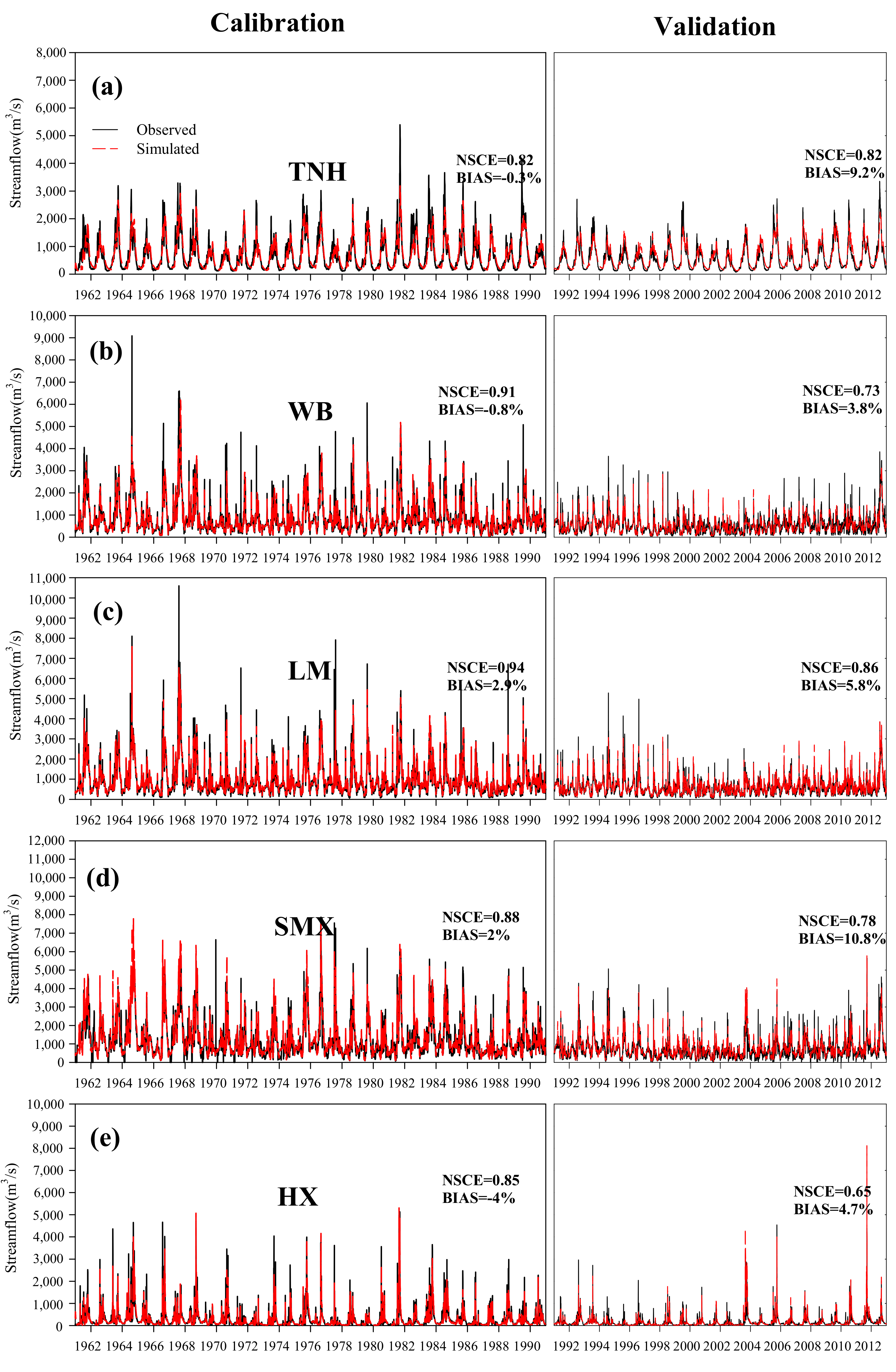
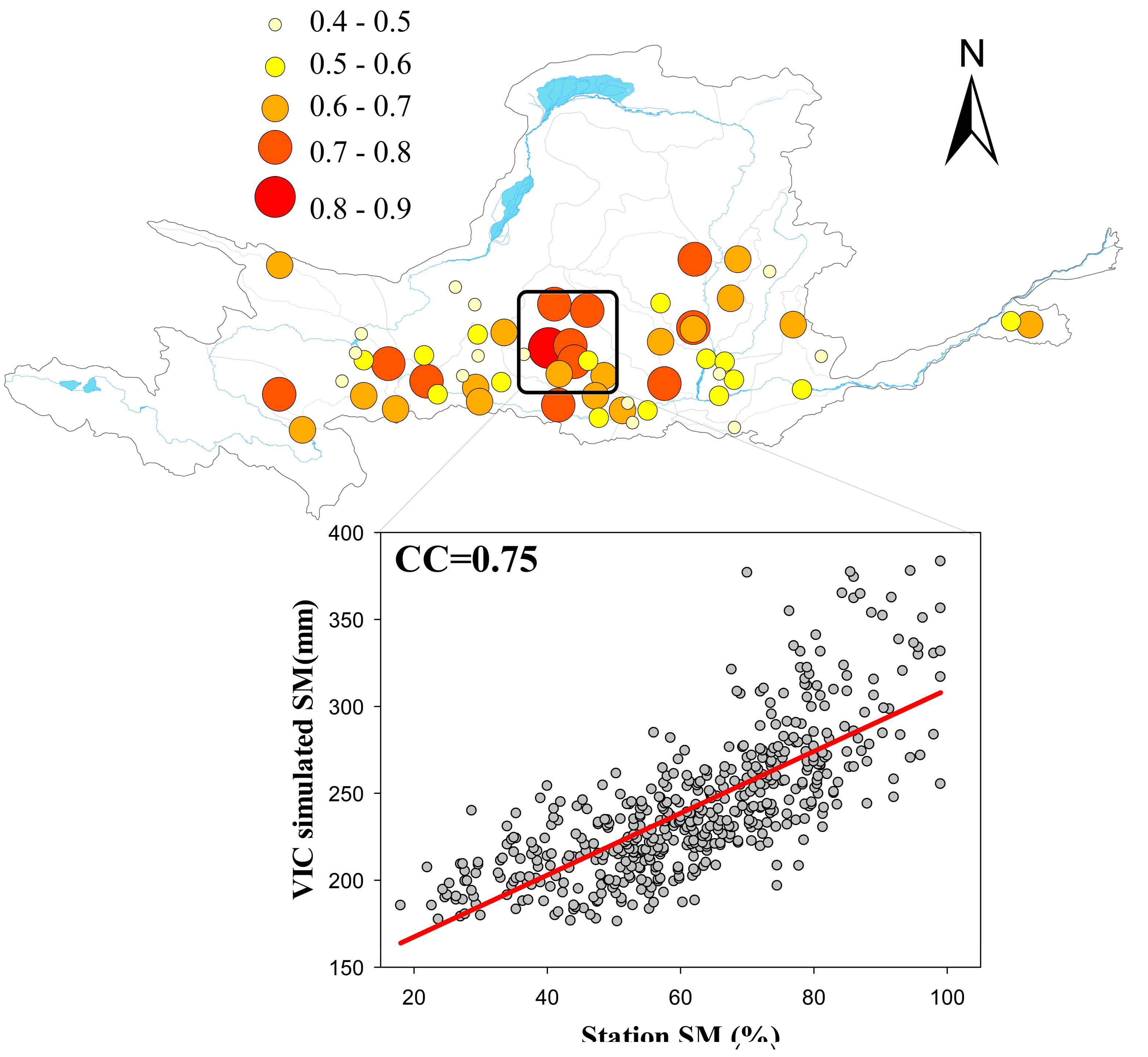
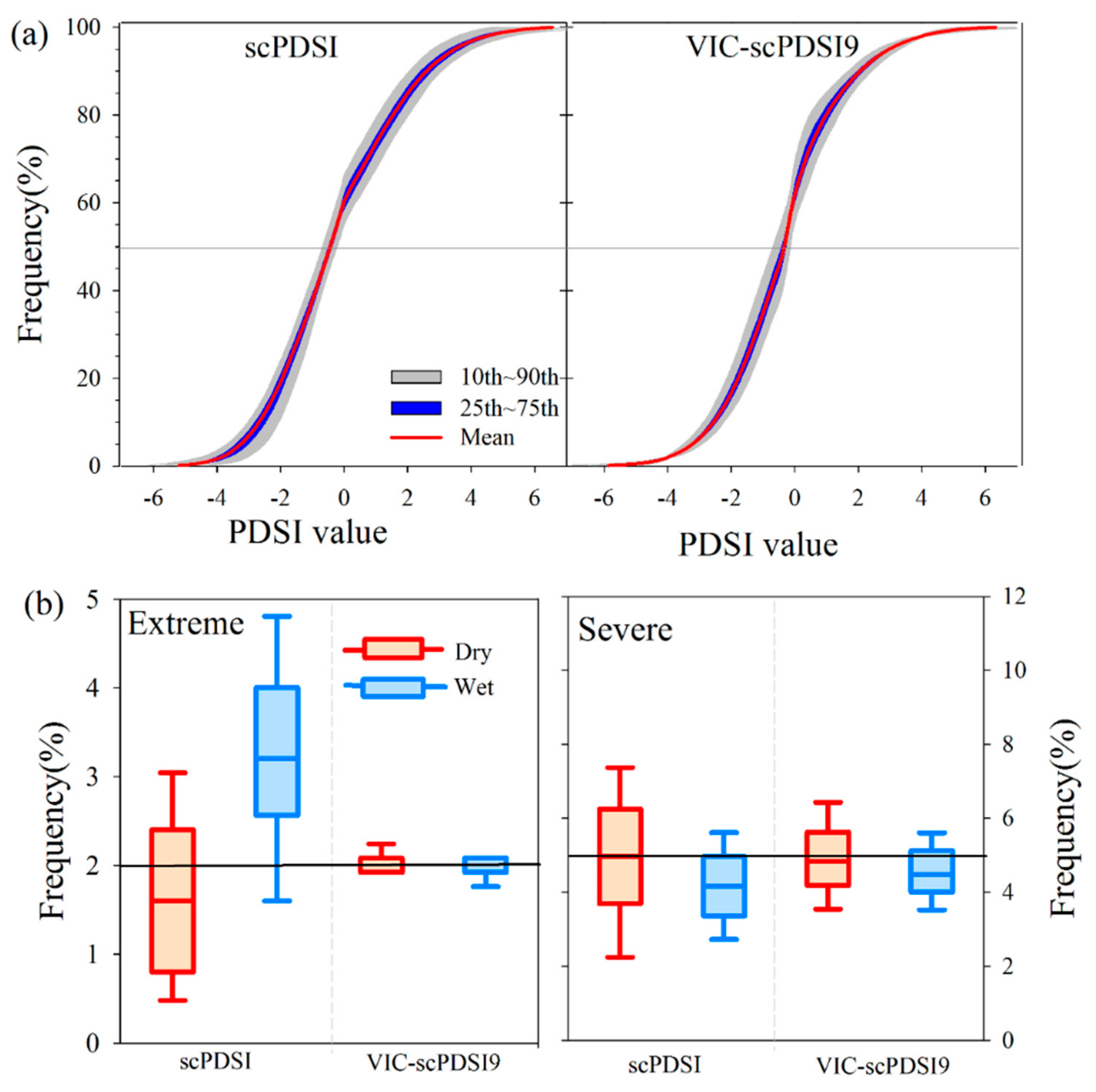
4.1. Model Performance
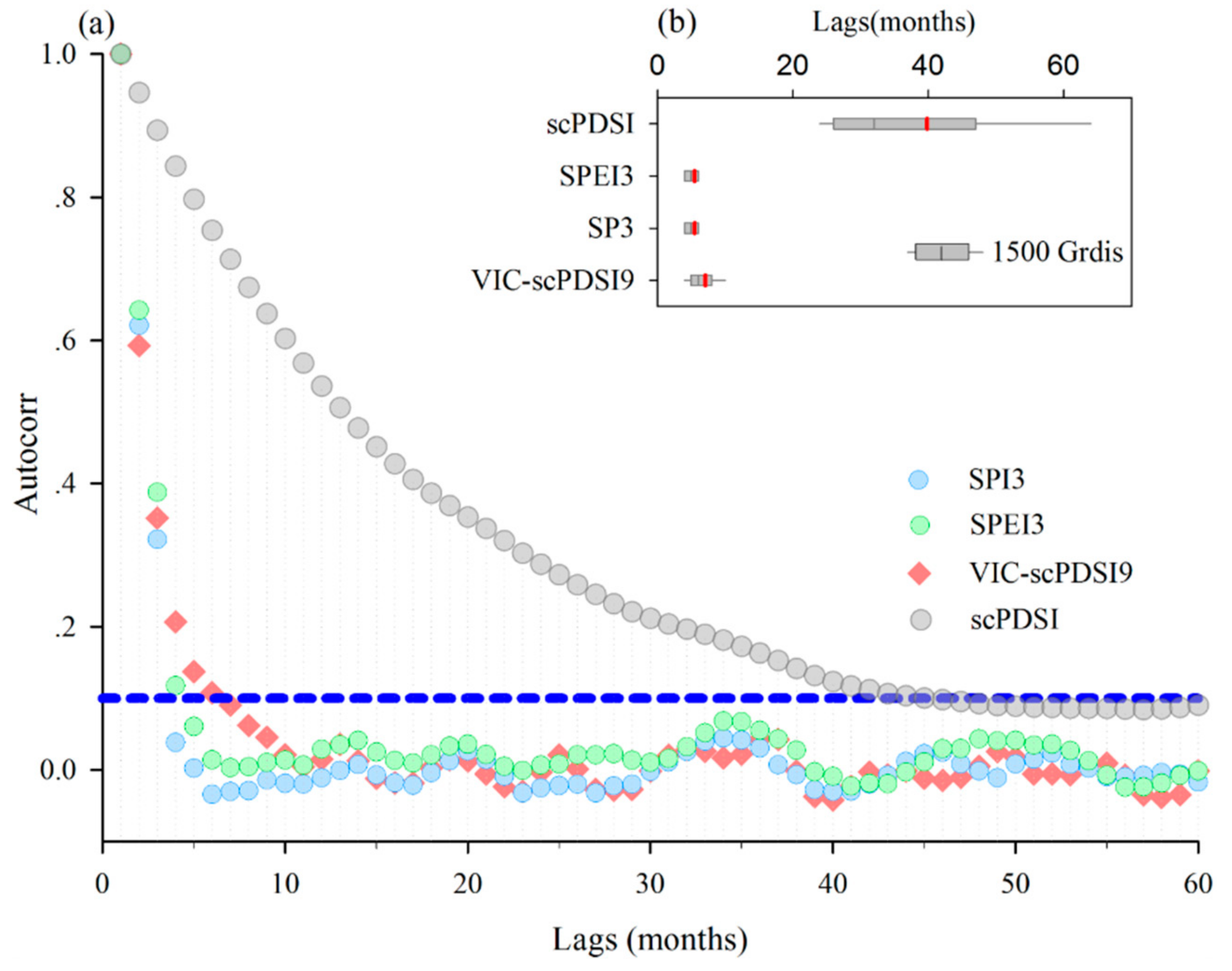
4.2. Time Scale and Frequency Analysis
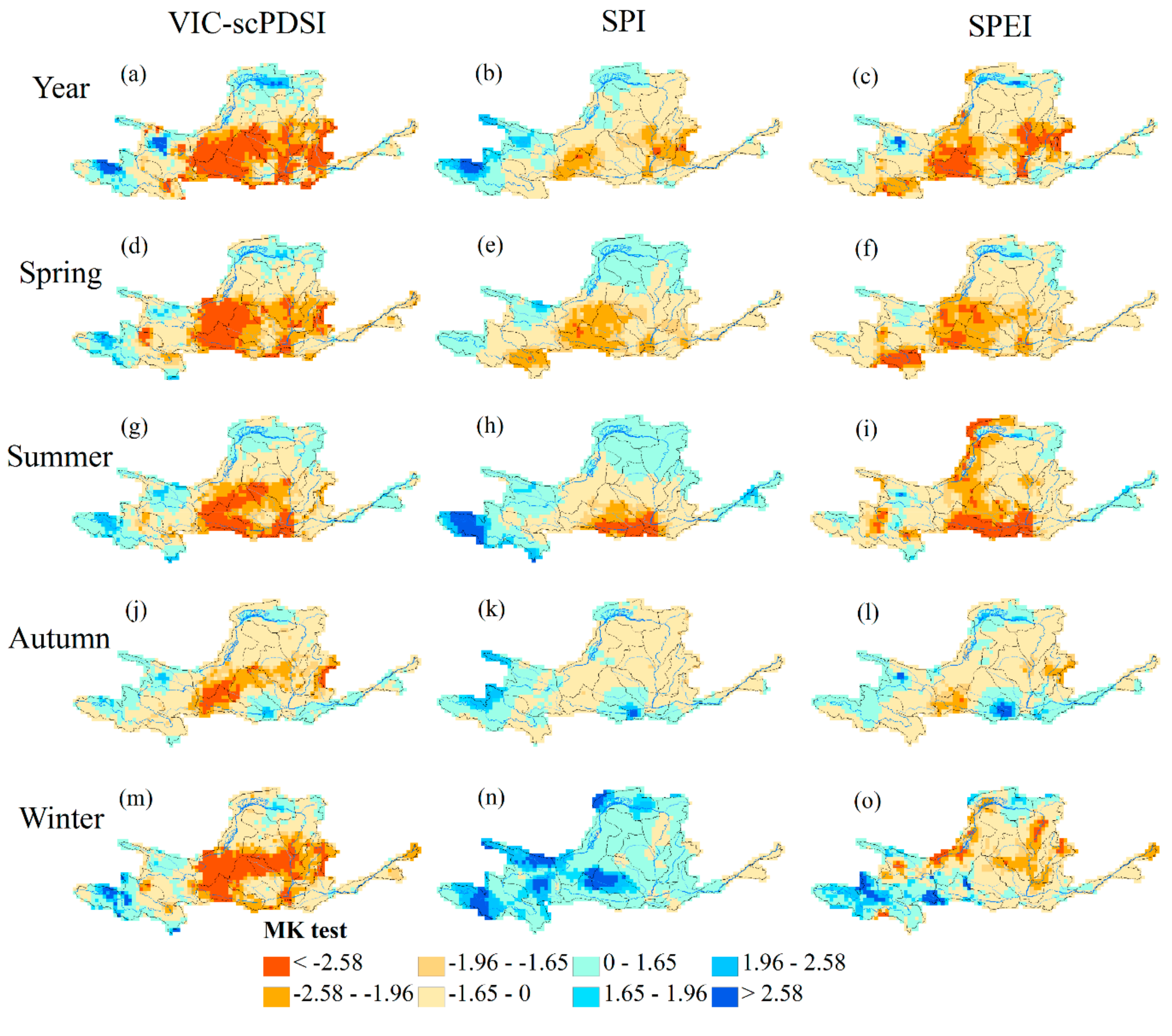
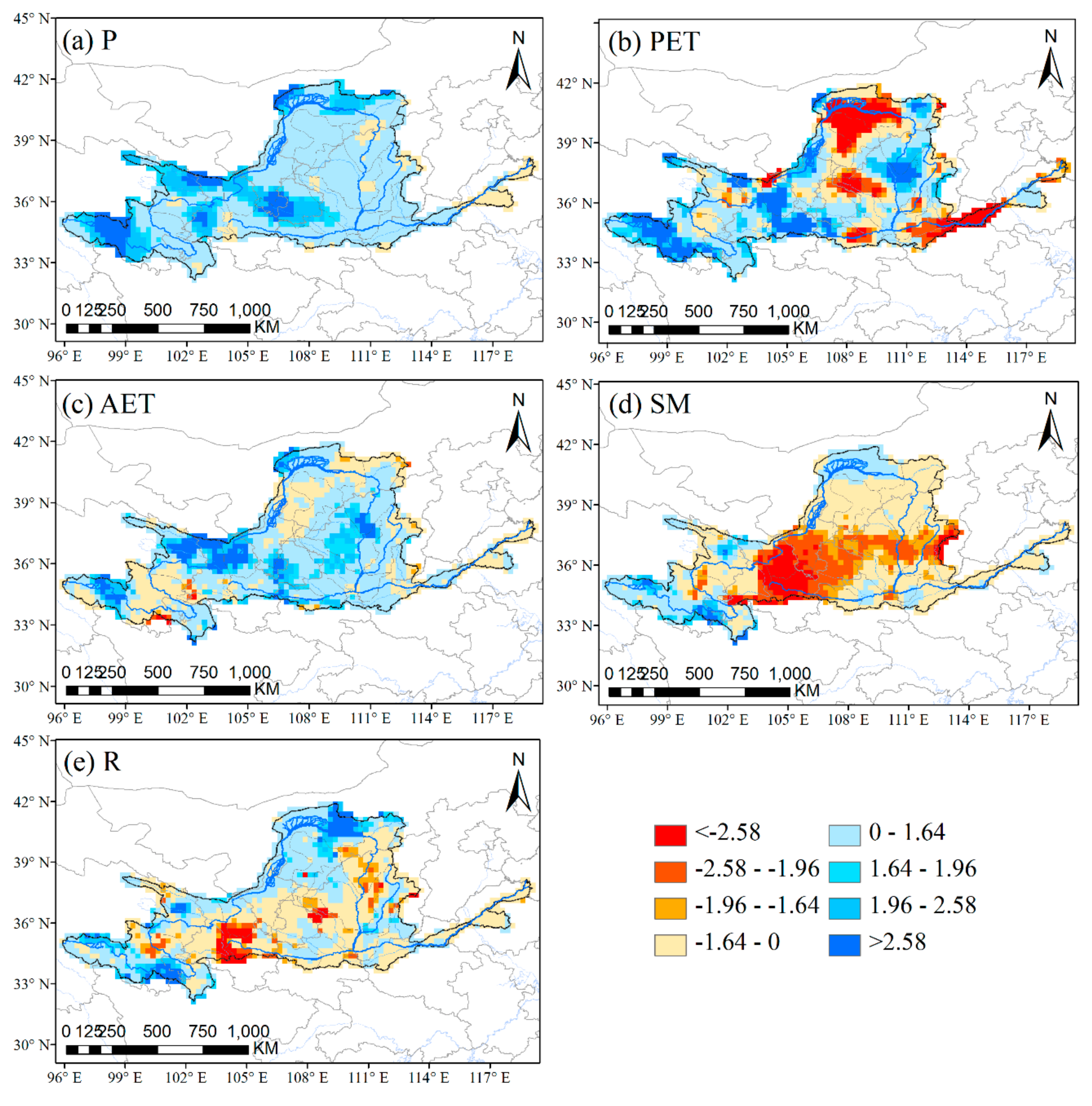
4.3. Drought Trend and Its Influencing Factors
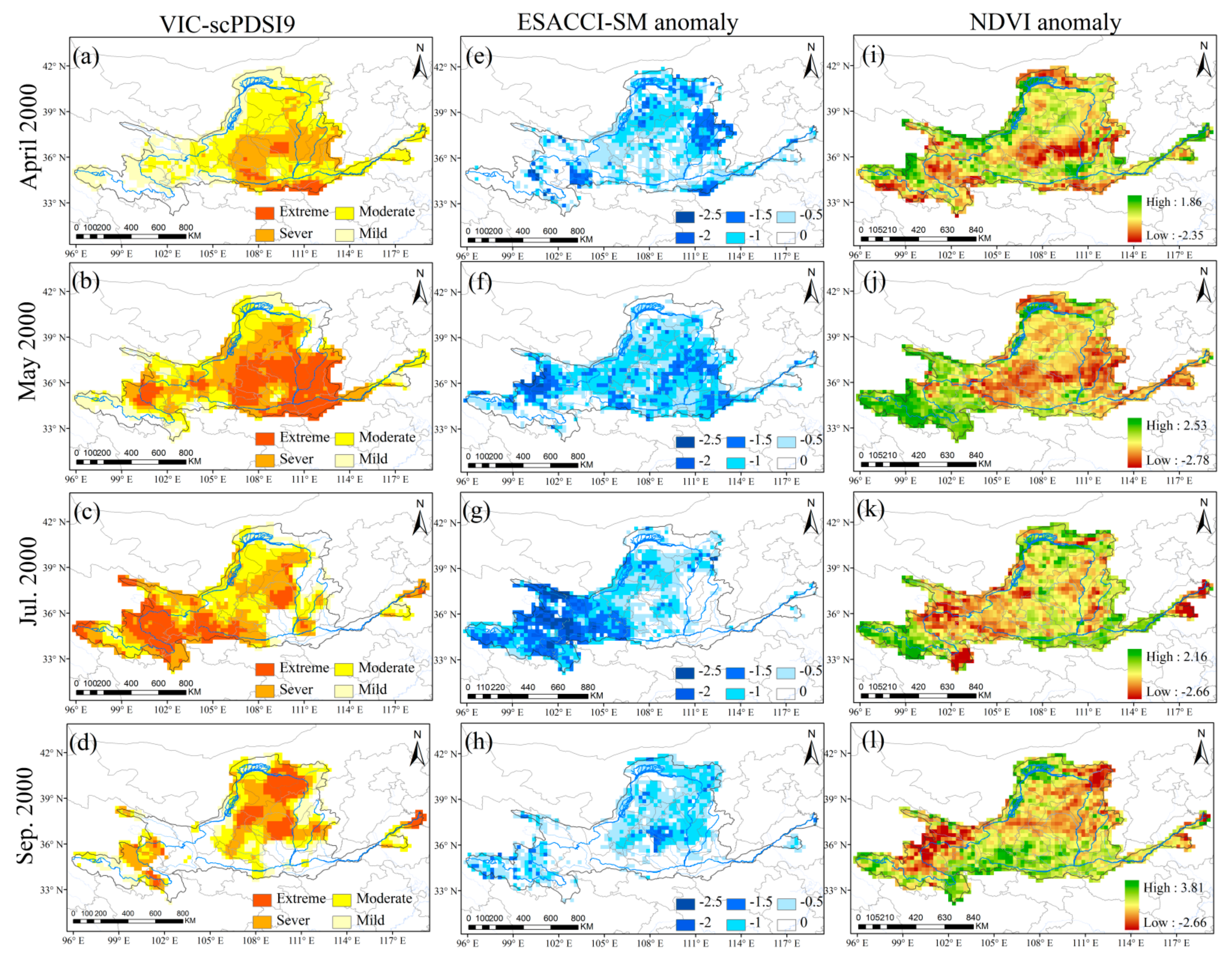
4.4. Performances in Drought Monitoring
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cook, B.I.; Smerdon, J.E.; Seager, R.; Coats, S. Global warming and 21st century drying. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 2607–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P. A review of drought concepts. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; van der Schrier, G.; Jones, P.D.; Barichivich, J.; Briffa, K.R.; Sheffield, J. Global warming and changes in drought. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Shen, S.H.; Wang, Q. Trend and Variability in Droughts in Northeast China Based on the Reconnaissance Drought Index. Water 2018, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.; Win, K.W.W.; Ren, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Assessment of GPM and TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Products in Streamflow Simulations in a Data-Sparse Mountainous Watershed in Myanmar. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, R.; Singh, V.P.; Song, C. Low Flow Regimes of the Tarim River Basin, China: Probabilistic Behavior, Causes and Implications. Water 2018, 10, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Begueria, S.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I. Comment on “Characteristics and trends in various forms of the Palmer Drought Severity Index (PDSI) during 1900–2008” by Aiguo Dai. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D19112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargar, A.; Sadiq, R.; Naser, B.; Khan, F.I. A review of drought indices. Environ. Rev. 2011, 19, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Singh, V.; Hao, F. Compound Extremes in Hydroclimatology: A Review. Water 2018, 10, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, W.J.; Maher, J.V. Rainfall deciles as drought indicators. In Bureau of Meteorology Bull. No. 48; Commonwealth of Australia: Melbourne, Australia, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, W.C. Meteorological Drought; Weather Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 1965; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Requirements; Irrigation and Drainage Paper; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Roma, Italy, 1998; p. 56. [Google Scholar]
- Guttman, N.B. Comparing the palmer drought index and the standardized precipitation index. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiris, G.; Pangalou, D.; Vangelis, H. Regional drought assessment based on the Reconnaissance Drought Index (RDI). Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Begueria, S.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I. A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbins, M.T.; Wood, A.; Mcevoy, D.J.; Justin, L.H.; Morton, C.; Anderson, M.; Hain, C. The evaporative demand drought index. Part I: Linking drought evolution to variations in evaporative demand. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1745–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyantash, J.A.; Dracup, J.A. An aggregate drought index: Assessing drought severity based on fluctuations in the hydrologic cycle and surface water storage. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W09304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.C.; Govindaraju, R.S. A copula-based joint deficit index for droughts. J. Hydrol. 2010, 380, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ren, L.; Yong, B.; Singh, V.P.; Yuan, F.; Jiang, S.; Yang, X. On the mechanisms of two composite methods for construction of multivariate drought indices. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 647, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Ren, L.; Yuan, F.; Jiang, S.; Ma, M. A new physically based self-calibrating Palmer drought severity index and its performance evaluation. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 4833–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajsekhar, D.; Singh, V.P.; Mishra, A.K. Multivariate drought index: An information theory based approach for integrated drought assessment. J. Hydrol. 2015, 526, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doeskin, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, S.; Wood, A.W. Use of a standardized runoff index for characterizing hydrologic drought. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L02405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Ren, L.; Yuan, F.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Kong, H.; Gong, L. A new standardized Palmer drought index for hydro-meteorological use. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 5645–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, W.; Singh, V.P.; Liu, Y. Combined use of meteorological drought indices at multi-time scales for improving hydrological drought detection. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ren, L.; Singh, V.P.; Yang, X.; Yuan, F. A multiscalar Palmer drought severity index. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 6850–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, N.; Goddard, S.; Hayes, M.J. A self-calibrating Palmer drought severity index. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 2335–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Singh, V.P.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, L.; Sun, W. Variation in ecological flow regimes and their response to dams in the upper yellow river basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Defries, R.S.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Sohlbert, R. Global land cover classification at 1 km spatial resolution using a classification tree approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 1331–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- China Meteorological Administration (CMA). Agrometeorological Observation Specification—Soil Volume; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 1993. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W.; Albergel, C.; Albrecht, F.; Balsamo, G.; Brocca, L.; Chung, D.; Ertl, M.; Forkel, M.; Gruber, A.; et al. ESA CCI Soil Moisture for improved Earth system understanding: State-of-the art and future directions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 203, 185–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Wood, E.F.; Burges, S.J. A simple hydrologically based model of land surface water and energy fluxes for GCMs. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 14415–14428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wood, E.F.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Surface soil moisture parameterization of the VIC-2L model: Evaluation and modification. Glob. Planet. Chang. 1996, 13, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuttleworth, W. Handbook of Hydrology; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 4.1–4.2. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, F.; Lu, C.; Chen, Y. Assessing Agricultural Drought in the Anthropocene: A Modified Palmer Drought Severity Index. Water 2017, 9, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank correlation methods. Br. J. Psychol. 1990, 25, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liang, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q. Response of soil moisture to hydro-meteorological variables under different precipitation gradients in the Yellow River basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 1867–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
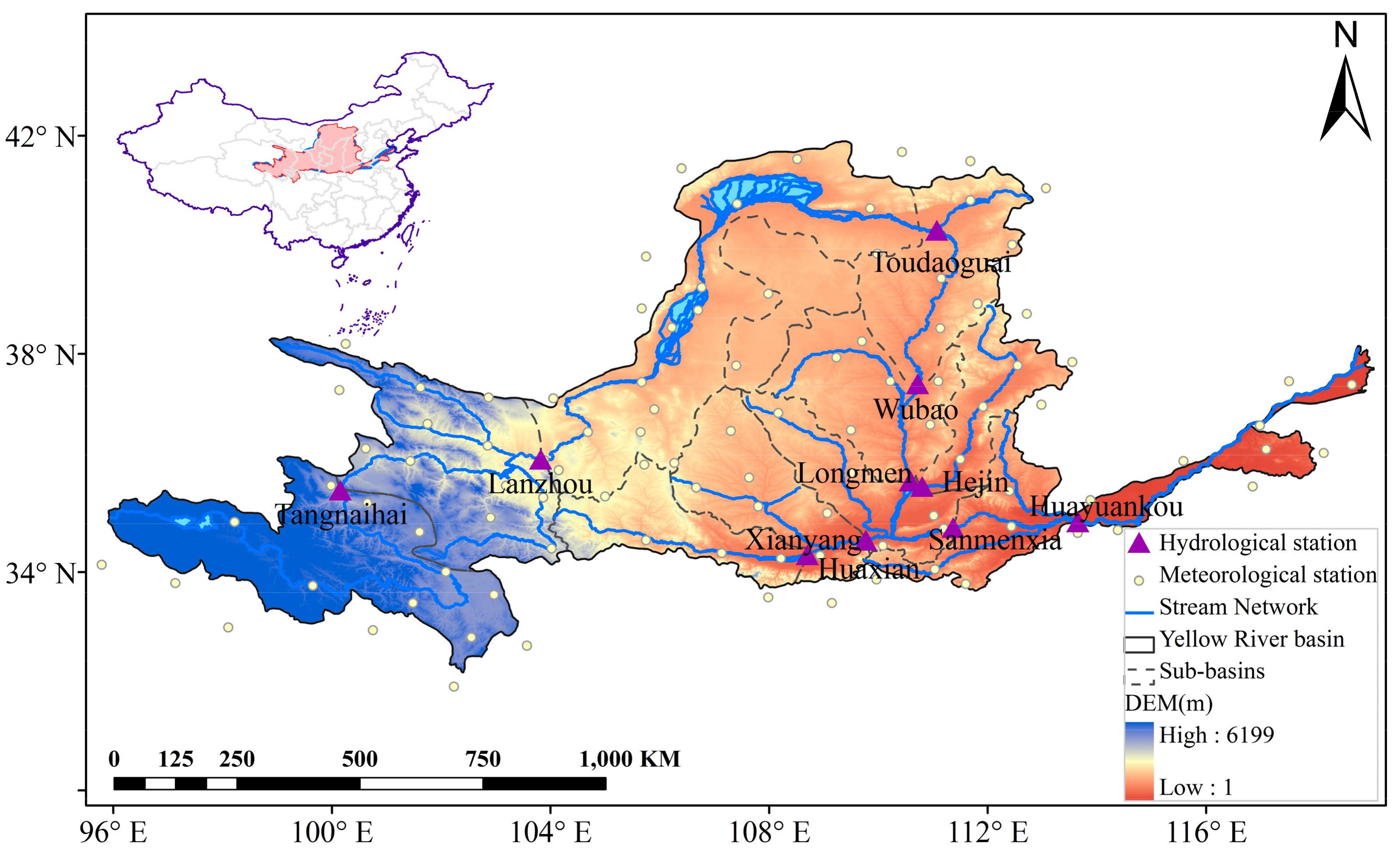




| Hydrological Station | Abbreviation | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) | Digital Elevation Model (m) | Drainage Area (104 km2) | Areal Average Precipitation (mm/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tangnaihai | TNH | 100°09′ | 35°30′ | 2960 | 12.2 | 520.8 |
| Lanzhou | LZ | 103°49′ | 36°04′ | 1774 | 10.07 | 480.7 |
| Toudaoguai | TDG | 111°04′ | 40°16′ | 1000 | 14.53 | 390.9 |
| Wubao | WB | 110°43′ | 37°27′ | 960 | 6.56 | 394.5 |
| Longmen | LM | 110°35′ | 35°40′ | 393 | 6.24 | 402.2 |
| Hejin | HJ | 110°48′ | 35°34′ | 553 | 12.21 | 485.7 |
| Xianyang | XY | 108°42′ | 34°19′ | 406 | 10.07 | 555.1 |
| Huaxian | HX | 109°46′ | 34°35′ | 481 | 14.53 | 544.3 |
| Sanmenxia | SMX | 111°22′ | 34°49′ | 614 | 4.75 | 398.2 |
| Huayuankou | HYK | 113°39′ | 34°55′ | 106 | 4.18 | 440.2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Ren, L.; Singh, V.P. Drought Analysis in the Yellow River Basin Based on a Short-Scalar Palmer Drought Severity Index. Water 2018, 10, 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111526
Zhu Y, Liu Y, Ma X, Ren L, Singh VP. Drought Analysis in the Yellow River Basin Based on a Short-Scalar Palmer Drought Severity Index. Water. 2018; 10(11):1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111526
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Ye, Yi Liu, Xieyao Ma, Liliang Ren, and Vijay P. Singh. 2018. "Drought Analysis in the Yellow River Basin Based on a Short-Scalar Palmer Drought Severity Index" Water 10, no. 11: 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111526
APA StyleZhu, Y., Liu, Y., Ma, X., Ren, L., & Singh, V. P. (2018). Drought Analysis in the Yellow River Basin Based on a Short-Scalar Palmer Drought Severity Index. Water, 10(11), 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111526





