Pilot Performance of Chemical Demulsifier on the Demulsification of Produced Water from Polymer/Surfactant Flooding in the Xinjiang Oilfield
Abstract
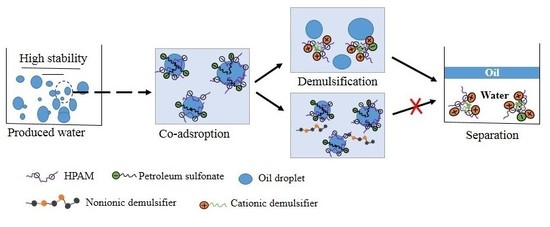
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Characteristics of Produced Water
2.2. Materials
2.3. Solution Preparation
2.4. Demulsification Tests
2.5. Field Pilot Study
2.6. Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Demulsification Performance of Different Demulsifiers
3.2. The Performance of the Pilot Treatment Plant
3.3. Interfacial Tension and Dilational Rheology Analysis of the Simulated Demulsification Processes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alvarado, V.; Manrique, E. Enhanced oil recovery: An update review. Energies 2010, 3, 1529–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique, E.; Thomas, C.; Ravikiran, R.; Izadi, M.; Lantz, M.; Romero, J.; Alvarado, V. EOR: Current status and opportunities. In Proceedings of the SPE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Tulsa, OK, USA, 24–28 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fakhru’l-Razi, A.; Pendashteh, A.; Abdullah, L.C.; Biak, D.R.A.; Madaeni, S.S.; Abidin, Z.Z. Review of technologies for oil and gas produced water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 530–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Maamari, R.S.; Sueyoshi, M.; Tasaki, M.; Kojima, K.; Okamura, K. Polymer-Flood Produced-Water-Treatment Trials. Oil Gas Facil. 2014, 3, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, B.; Lu, L.; Yue, Q.; Wang, Q.; Jia, Y. Treatment of produced water from polymer flooding in oil production by the combined method of hydrolysis acidification-dynamic membrane bioreactor–coagulation process. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2010, 74, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Bai, R.; Chen, J.P.; Yu, G.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, F. Effects of alkaline/surfactant/polymer on stability of oil droplets in produced water from ASP flooding. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 211, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebali, G.; Kaytash, A.; Etemadi, N. Efficient breaking of water/oil emulsions by a newly isolated de-emulsifying bacterium, Ochrobactrum anthropi strain RIPI5-1. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 98, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutyala, S.; Fairbridge, C.; Paré, J.R.J.; Bélanger, J.M.R.; Ng, S.; Hawkins, R. Microwave applications to oil sands and petroleum: A review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.W.; Zhang, G.L.; Shen, C.; Sun, G.S.; Wang, R.X.; Yin, L.J.; Meng, Q. Application of rhamnolipid as a novel biodemulsifier for destabilizing waste crude oil. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perles, C.E.; Volpe, P.L.O.; Bombard, A.J.F. Study of the Cation and Salinity Effect on Electrocoalescence of Water/Crude Oil Emulsions. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 6914–6924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Sadeghi, N.; Houston, C. Chemical Interactions and Demulsifier Characteristics for Enhanced Oil Recovery Applications. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 2742–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, Y.H.; Rudolph, V.; Ho, K.C.; Lo, C.C.M.; Wu, K.C. Evaluation of different demulsifiers for Marpol oil waste recovery. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 17, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirasaki, G.J.; Miller, C.A.; Raney, O.G.; Poindexter, M.K.; Nguyen, D.T.; Hera, J. Separation of Produced Emulsions from Surfactant Enhanced Oil Recovery Processes. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Ma, Y.; Fang, S.; Shi, P.; Zhang, J.; Jing, B. Treatment of wastewater produced from polymer flooding using polyoxyalkylated polyethyleneimine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 133, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoggins, M.W.; Miller, J.W. Determination of Water-Soluble Polymers Containing Primary Amide Groups Using the Starch-Triiodide Method. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 1979, 19, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q. Study on emulsification stability of wastewater produced by polymer flooding. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2013, 110, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-G.; Peng, Y.-R.; Xie, F.; Jiang, W.-Y.; Zou, H.; Qiu, H.-D.; Chen, J.-H. Determination of anionic surfactant in surface water by resonance light-scattering technology. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2010, 90, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celia, C.; Trapasso, E.; Cosco, D.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M. Turbiscan Lab (R) Expert analysis of the stability of ethosomes (R) and ultradeformable liposomes containing a bilayer fluidizing agent. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 72, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengual, O.; Meunier, G.; Cayré, I.; Puech, K.; Snabre, P. TURBISCAN MA 2000: Multiple light scattering measurement for concentrated emulsion and suspension instability analysis. Talanta 1999, 50, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff-Pérez, M.; Torcello-Gómez, A.; Gálvez-Ruíz, M.J.; Martín-Rodríguez, A. Stability of emulsions for parenteral feeding: Preparation and characterization of o/w nanoemulsions with natural oils and Pluronic f68 as surfactant. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-W.; Zhang, L.; Cao, X.-L.; Li, Z.-Q.; Zhang, L.; Luo, L.; Zhao, S. Surface dilational rheological and lamella properties of branched alkyl benzene sulfonate solutions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 412, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-L.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Q.-T.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, S.; Yu, J.-Y. Interfacial Dilational Properties of Tri-Substituted Alkyl Benzene Sulfonates. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2010, 26, 631–637. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.-P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Luo, L.; Zhao, S.; Yu, J.-Y. Dynamic interfacial dilational properties of hydroxy-substituted alkyl benzenesulfonates. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 5640–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.-C.; Gong, Q.-T.; Zhang, L.; Luo, L.; Zhao, S.; Yu, J.-Y. Interfacial dilational properties of tri-substituted alkyl benzene sulfonates at air/water and decane/water interfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 327, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Yu, G.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Ting, Y.P. Destabilization of oil droplets in produced water from ASP flooding. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 252, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, E.J.; Carpenter, A.P.; Olson, C.M.; Ciszewski, R.K.; Richmond, G.L. Metal Ion Induced Adsorption and Ordering of Charged Macromolecules at the Aqueous/Hydrophobic Liquid Interface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 15260–15273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, E.J.; Richmond, G.L. Molecular Insights in the Structure and Layered Assembly of Polyelectrolytes at the Oil/Water Interface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 28331–28343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaman, D.K.; Robertson, E.J.; Richmond, G.L. Ordered polyelectrolyte assembly at the oil-water interface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3226–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, H.-B. Dilational viscoelasticity of anionic polyelectrolyte/surfactant adsorption films at the water-octane interface. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, E.; Llamas, S.; Maestro, A.; Fernandez-Pena, L.; Akanno, A.; Miller, R.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, R.G. Polymer-surfactant systems in bulk and at fluid interfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 233, 38–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristen, N.; Vullings, A.; Laschewsky, A.; Miller, R.; von Klitzing, R. Foam Films from Oppositely Charged Polyelectolyte/Surfactant Mixtures: Effect of Polyelectrolyte and Surfactant Hydrophobicity on Film Stability. Langmuir 2010, 26, 9321–9327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noskov, B.A. Dilational surface rheology of polymer and polymer/surfactant solutions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauser, H.; Von, K.R.; Campbell, R.A. Surface Adsorption of Oppositely Charged C14TAB-PAMPS Mixtures at the Air/Water Interface and the Impact on Foam Film Stability. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.5 | Salinity | 8305.6 mg/L |
| Oil content | 128.3~7364.4 mg/L | Mg2+ | 36.9 mg/L |
| HPAM | 177.1 mg/L | Ca2+ | 67.9 mg/L |
| Petroleum sulfonate | 35.1 mg/L | K+ + Na+ | 2602.7 mg/L |
| Suspended solids | 153.7~990.0 mg/L | Cl− | 1276.5 mg/L |
| Zeta potential | −32.5 mV | SO42− | 2847.0 mg/L |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, D.; Li, F.; Gao, Y.; Yang, M. Pilot Performance of Chemical Demulsifier on the Demulsification of Produced Water from Polymer/Surfactant Flooding in the Xinjiang Oilfield. Water 2018, 10, 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121874
Chen D, Li F, Gao Y, Yang M. Pilot Performance of Chemical Demulsifier on the Demulsification of Produced Water from Polymer/Surfactant Flooding in the Xinjiang Oilfield. Water. 2018; 10(12):1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121874
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Dong, Feng Li, Yingxin Gao, and Min Yang. 2018. "Pilot Performance of Chemical Demulsifier on the Demulsification of Produced Water from Polymer/Surfactant Flooding in the Xinjiang Oilfield" Water 10, no. 12: 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121874
APA StyleChen, D., Li, F., Gao, Y., & Yang, M. (2018). Pilot Performance of Chemical Demulsifier on the Demulsification of Produced Water from Polymer/Surfactant Flooding in the Xinjiang Oilfield. Water, 10(12), 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121874