Abstract
Green roofs (GRs) are a feasible solution for mitigating increased runoff volumes in urban areas. Though many studies have focused their analysis on the quantity and quality of GR runoff, with respect to the relevance of specific site conditions in GR performance, the information gathered for the tropical Andes is not sufficient. This study assessed the hydrological performance and runoff water quality of 12 green roof modular systems located at the Universidad de los Andes campus (Bogotá, Colombia). Based on 223 rainfall events spanning a 3-year period, average rainfall retention was 85% (coefficient of variation = 29%). t-tests, the Welch Test, multiple linear regressions, and correlation analysis were performed in order to assess the potential effect of air temperature, substrate type, vegetation cover, relative humidity, antecedent dry weather period (ADWP), rainfall duration, and rainfall maximum intensity. In some cases, GR design variables (i.e., substrate type and vegetation cover) were found to be significant for describing rainfall retention efficiencies and, depending on the GR type, some hydrological variables were also correlated with rainfall retention. Rainfall and GR runoff from 12 rainfall events were also monitored for total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN), nitrates, nitrites, ammonia, total phosphorus (TP), phosphates, pH, total dissolved solids (TDS), total suspended solids (TSS), color, turbidity, biological oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total coliforms, metals (i.e., zinc, copper, nickel, lead, selenium, aluminum, barium, boron, calcium, strontium, iron, lithium, magnesium, manganese, potassium, sodium), and polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). The results obtained confirmed that GR systems have the ability to neutralize pH, but are a source of the rest of the aforementioned parameters, excluding PAHs (with concentrations below detection limits), ammonia, TSS, selenium and lithium, where differences with control cases (rainfall and plastic panel runoff) were not statistically significant. Substrate type, event size, and rainfall regime are relevant variables for explaining runoff water quality.
1. Introduction
With the passage of time and the continuous development of society, migration from rural to urban areas has increased at an accelerated pace [1,2]. This has meant that in the last 60 years urbanization rates have increased significantly [3] and for the first time in history more than half of the world’s population lives in urban areas [1]. An environmental problem created by the urbanization process is the increase of impervious areas in urban watersheds, which leads to significant reductions in infiltration rates, thus causing more frequent flash floods and failures of the sewer systems [2].
Urban growth therefore demands more sustainable urban drainage systems. There is a need to return to pre-development hydrologic conditions by attenuating runoff flows generated by impervious areas, as well as improving the runoff water quality [4]. One of the most popular technologies within the framework of sustainable urban drainage systems are green roofs (GRs) [5]. GRs involve the installation of a natural vegetated cover on a building’s roofs [6] in order to reduce the impervious area and therefore the runoff that flows into the sewer system or directly into receiving streams. Although the aim of GRs is to change runoff generation patterns, it has been shown that they also alter the rainfall water quality [7].
A GR modifies the patterns of urban runoff generation by attenuating and delaying peak flows and reducing runoff volumes [2]. The effect of GRs on the amount of runoff is a widely studied phenomenon, and all related studies suggest that GRs have significant percentages of water retention [2]. Although there is a general consensus on the positive effect of GRs regarding water retention, varying results are reported in the literature. On one hand, Dietz [8] reported average retention values for different climatic conditions ranging between 60% and 70%, with an average value of 63%. On the other, Carpenter and Kaluvakolanu [9] found an average retention range of 20% to 100%, while more recent studies have estimated retention rates ranging between 40% and 82% [1,10,11,12]. The variation in the retention rates found in previous studies is explained by the fact that this phenomenon relies on the configuration of the GR (e.g., type of substrate and its depth, vegetation cover, slope, and filter system) and the specific climatological conditions of the study area (e.g., rainfall depth and evapotranspiration), as well as the characteristics of rainfall events, such as maximum intensity, duration, and dry antecedent period [2,13,14]. Furthermore, the variability in the results can also be associated with the length of the monitoring period [15].
Reaffirming the relevance of specific conditions, Brunetti et al. [16] and Chenot et al. [17] analyzed the hydrological performance of GRs and its configuration under Mediterranean climates. They concluded, in accordance with Stovin et al. [18], that the hydrological response to single precipitation events might be mainly influenced by initial soil moisture, which is mainly affected by substrate depth and composition. However, these results may apply only for their particular GR design and climatological conditions, highlighting the importance of identifying a particular substrate design for every context [19].
GRs are promoted for their potential to provide high runoff retention efficiencies; however, the effect that a GR may have on the runoff water quality is still not fully understood [20] due to inconclusive and even contradictory findings in the research [1,3,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. The high variability concerning GR runoff water quality is mainly a result of its high dependence on the substrate, vegetation cover, and hydrological variables of each specific site [2]. Because of the relevance of GRs as a strategy for sustainable water management in urban centers [32], it is important to better understand the role of GR configuration and local hydrological variables in runoff quantity and quality. This is even more relevant in tropical climates like Colombia’s as there is not much research on GR performance that considers the GR configurations typical of these regions and local hydrological conditions [33]. This research aims to improve understanding of the retention capacity and changes in GR runoff water quality in a subtropical highland climate with two rainy seasons per year, through an instrumented experimental setup located at the Universidad de los Andes campus in Bogotá (Colombia).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
This research was carried out at the main campus of the Universidad de los Andes (4°35′56″ N 74°04′51″ W) in Bogotá (Colombia), which is located at an altitude of 2640 m.a.s.l. There is a main road near the experimental site and no industrial activity in the neighboring area. The main surrounding land uses are official, commercial, and residential. The experimental setup was located on the rooftop of the Physics Department building. Bogotá has a subtropical highland climate, with a mean annual temperature of 14.5 °C, varying monthly between 12 and 15 °C [34]. The mean annual rainfall depth ranges between 600 and 1200 mm, and the rainfall regime is bimodal, with two rainy seasons (April–May and October–November) and two dry periods (January–February and July–August) [34].
2.2. Experimental Setup
The experimental setup consisted of different modular GRs implemented over a three-year period in order to address different research objectives (See Figure 1). According to the depth of the substrate layer, GRs can be categorized as intensive or extensive. In general, the substrate depth for intensive GR is over 15 cm, while the substrate depth for an extensive GR tends to be shallower. However, we used a depth of 6 cm for all monitored GR configurations (thus all configurations in our study correspond to the extensive group in terms of depth) along with substrates that are commercial and commonly used in either intensive or extensive GRs. The general vertical composition of the monitored GR modules (0.7 m × 0.7 m each) is as follows (from surface to bottom): (1) vegetation layer; (2) substrate layer or growing medium; (3) filter layer (nonwoven geotex Sika 1800 or recycled textile felt); and (4) drainage layer (Sika T-20 Garden). These layers were confined within the walls and bottom of the module (by means of plastic or cold rolled steel sheet) acting as a waterproofing membrane as if it were the decking of a conventional roof. Throughout the monitoring period all modules were leveled horizontally with a drainage slope of less than 1%.
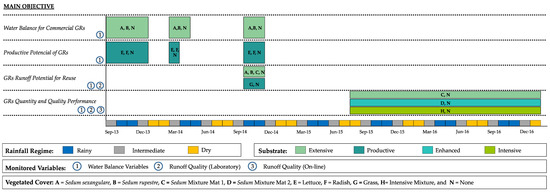
Figure 1.
Experimental setup description. The Extensive Substrate has saturated hydraulic conductivity of 1.8 × 10−7 m/s and apparent density of 421 kg/m3. The Enhanced Substrate has the following distribution on a dry basis: organic matter = 27.40%, total phosphorus = 3.47%, total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN) = 0.14%, and total suspended solids (TSS) = 63.20%. The Intensive Substrate has the following distribution on a dry basis: organic matter = 15.90%, total phosphorus = 3.22%, TKN = 0.14%, TSS = 76.30%. GR: green roof.
Different plant species were evaluated: homogeneous configurations of Sedum sexangulare, Sedum rupestre, Raphanus sativus (radish), Lactuca sativa (lettuce), and grass; a heterogeneous mixture of Dietes iridioides (water lily), Bergenia cordifolia (bergenia), and Lavanda dentate (lavender) (named the Intensive Mixture), and two different types of heterogeneous Sedum mixtures (Sedum Mixture Mat 1: sexangulare, chatre, album, acre, and kamtschaticum and Sedum Mixture Mat 2: blue, acre, fino, sexangulare, chatre, and oregano) (see Figure 2). The plant selection was based on the local environmental authority’s GR guide, which especially recommends crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) and C3 plants due to their tolerance to drought and shallow root system. Sedum species were selected because they are currently the most widely used type of vegetation cover for GRs in Colombia, given their ability to grow without the need for irrigation beyond that which is provided by the rainfall regime. We also tested productive vegetation on GRs due to local interest in promoting their potential for urban agriculture [35].

Figure 2.
(A) Homogeneous configuration of Sedum sexangulare; (B) Homogeneous configuration of Sedum rupestre; (C) Heterogeneous Sedum mixtures (Sedum Mixture Mat 1: sexangulare, chatre, album, acre, and kamtschaticum; (D) Heterogeneous Sedum mixtures (Sedum Mixture Mat 2: blue, acre, fino, sexangulare, chatre and oregano); (E) Homogeneous configuration of Lactuca sativa (lettuce); (F) Homogeneous configuration of Raphanus sativus (radish); (G) Homogeneous configuration of grass; and (H) Heterogeneous mixture of Dietes iridioides (water lily), Bergenia cordifolia (bergenia) and Lavanda dentate (lavender) (Intensive Mixture).
In the experimental setup, four different types of substrates were tested: the Extensive Substrate (standard extensive substrate, that uses the most common commercially available substrate for extensive GRs), the Enhanced Substrate (extensive substrate enhanced for runoff volume reduction: several organic and inorganic substrates were tested, revealing that a mixture of black soil (40%), rice husk (20%), coarse pumice (18%), zeolite (14%), and granular activated carbon (8%) provided the higher reductions), the Intensive Substrate (that uses the most common commercially available substrate for intensive GRs), and the Productive Substrate (fertilized black soil mixed with rice husk for vegetables). A summary of the characteristics of the GR modules that were used in this study is shown in Figure 1.
It is important to mention that weeds were removed manually every week in each of the GRs. Additional irrigation was only used for GR configurations that use the Productive Substrate (approximately 4 mm/m2 for radish and 5 mm/m2 for lettuce every 2 days). No additional irrigation was provided for GR configurations that use extensive or intensive substrates. In order to compare the water quality performance of GRs with raw rainfall and runoff from conventional roof surfaces (control cases), a rainfall harvesting tank and a plastic roofing panel were installed on the same rooftop.
2.3. Monitoring System, Sampling and Laboratory Characterization
GR runoff quantity was monitored using tipping bucket rain gauges with a sampling rate of one minute and 0.1-mm resolution (DAVIS model rain collector II). Rainfall was measured with a sampling rate of one second and 0.2-mm resolution, using an ISCO tipping bucket rain gauge. In order to capture the experimental on-site hydrologic conditions, temperature and humidity were measured using a sampling rate of 1 min, by means of a DAVIS weather station model VANTAGE Pro 2. The schematic representation of the assembly of different GR modules during one of the monitoring periods is shown in Figure 3.
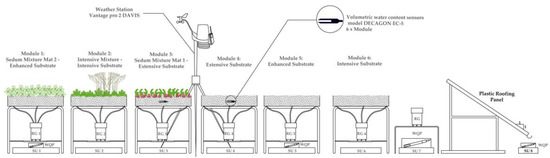
Figure 3.
Experimental setup in the monitoring period from August 2015 to January 2017. RG: Rain gauge, WQP: water quality probe, SU: storage unit (used for measuring volume weighted concentrations).
Water samples were taken from the storage units for each GR, as well as from the reference plastic roofing panel and rainfall collected after a rain event (Figure 3). Water quality parameters were determined in the laboratory, following the methods outlined in Eaton [36]. Additionally, pH, conductivity and temperature were also monitored using a YSI multiparameter probe model 600R and Global Water probes, models WQ-201 and W-cond.
2.4. Definition of Rainfall Categories
Taking into account that for a better understanding of GR performance it is necessary to evaluate both “significant” and “routine” rainfall events to avoid misleading results that bias conclusions [37]; we categorized rainfall events and regimes when conducting our analyses.
2.4.1. By Similarity
A cluster analysis was performed using the collected rainfall database in order to establish groups of rainfall events with similar characteristics. This categorization was carried out according to values of variables such as antecedent dry weather period (ADWP), maximum 1-min intensity, duration, and depth, defining which events can be treated as small, intermediate, or large. This categorization was made in order to understand whether the event size would have an effect on GR runoff retention and quality.
2.4.2. By Rainfall Regime
As mentioned, rainfall conditions in Bogotá follow a bimodal pattern, seeing annually two rainy and two dry seasons of two months each [34]. Based on this pattern, each rainfall event was classified either as occurring during a rainy, dry or intermediate period. These three periods of four months each were defined in order to evaluate their retention on GR modules. The months corresponding to the rainy period are April, May, October, and November. Dry period months include January, February, July, and August. The rest of the months (March, June, September, and December) correspond to the intermediate period.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
To identify differences between the runoff retention efficiency of different substrates and vegetation types ANOVA, Welch’s test, post hoc tests (i.e., Bonferroni and Games and Howell), t-tests, and boxplots were performed. To complement the previous analyses, multiple linear regressions were used to identify statistically significant rainfall variables correlating with the runoff retention process. For a subset of the monitoring database, k-means cluster analysis was performed to establish groups of events with similar characteristics (ADWP, maximum 1-min intensity, rainfall depth and duration), establishing three analysis groups as mentioned before: small, intermediate, and large events. Welch’s tests were carried out to quantify the effect of the rainfall regime and event characteristics on the runoff quantity and quality. Five different analyses on water quality data were conducted according to the following descriptive variables: (1) runoff source (rainfall, conventional roof with plastic roofing panels and GRs); (2) substrate type; (3) vegetation type; (4) event characteristics; and (5) rainfall regime.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Quantity
The two variables measured in order to estimate the runoff retention efficiency were rainfall and runoff depths, with the difference between the two representing the retention depth. For this estimation, 223 rainfall events distributed between October 2013 and January 2017 were analyzed. Figure 4 summarizes the rainfall characteristics during the monitoring periods.
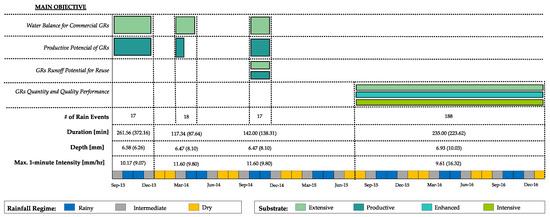
Figure 4.
Rainfall events characteristics for the different monitoring periods.
3.1.1. Effect of Substrate on Water Retention Efficiency
An overall average retention efficiency of 85% with a coefficient of variation (CV) of 29% was obtained when considering all monitoring periods. Due to the known effect of the type of substrate in the retention process [2,38,39,40,41], each type of substrate was individually analyzed and evidenced average retention values of 69% for modules using the Extensive Substrate (CV = 52% and n = 72), 85% for modules using the Enhanced Substrate (CV = 29% and n = 727), 63% for modules using the Productive Substrate (CV = 54% and n = 54), and 92% for modules using the Intensive Substrate (CV = 18% and n = 339) (see Figure 5).
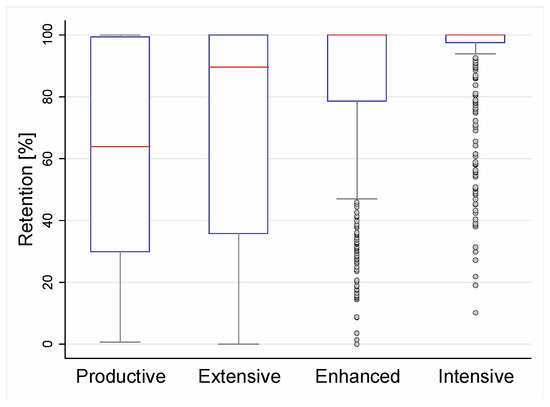
Figure 5.
Effect of substrate on water retention efficiency.
The Intensive Substrate had the best performance, with statistically significant differences from the Extensive Substrate (p-value = 0.000), Enhanced Substrate (p-value = 0.000), and Productive Substrate (p-value = 0.000). The Enhanced Substrate had higher retention efficiency than Extensive Substrate with statistically significant differences (p-value = 0.003). The Productive Substrate showed the lowest average retention efficiency, with statistically significant differences compared to the Enhanced Substrate (p-value = 0.000) but not to the Extensive Substrate (p-value = 0.789).
3.1.2. Effect of Vegetation on Water Retention Efficiency
In order to establish the effect of vegetation on retention of storm water runoff, an analysis comparing vegetated and non-vegetated modules was performed (regardless of the type of substrate). Figure 6 presents the box and whisker diagram for the vegetated and non-vegetated modules for all types of GR substrates that were monitored in this study. It is possible to identify similarities between the retention efficiencies for vegetated (85.65%) and non-vegetated (84.76%) modules. The results of the t-test indicate no statistically significant differences between the two groups (p-value = 0.548), obtaining similar results as in some previous studies [38,42,43], which have stated that vegetation does not have a clear effect on water retention efficiency for GRs. The previous result contrasts with that of Chenot et al. [17] who concluded that vegetated coverage does have an influence on water retention even though substrate composition and depth have a greater effect. This disagreement may be the result of not considering the hydrological conditions. Therefore, more detailed analyses on the impact of such conditions are presented.
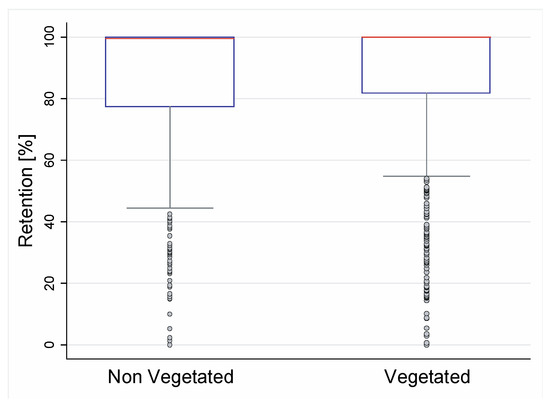
Figure 6.
Effect of vegetation on water retention efficiency.
Having found that the type of substrate is an important variable for determining the runoff retention efficiency, an additional analysis was carried out in which different groups were categorized based on the type of substrate, and differences between non-vegetated and vegetated modules were analyzed within each group. The modules with the Extensive Substrate showed statistically significant difference, with a significance of 10%, but not with a significance of 5% (p-value = 0.084). Of the vegetated modules, Sedum rupestre vegetation performed best, with an average retention of 84.81%, while the Sedum sexangulare module and the non-vegetated module averaged 65.52% and 60.17% respectively. The modules with the Enhanced Substrate showed statistically significant differences (p-value = 0.001) and the Games and Howell post hoc test showed differences between the grass and Sedum Mixture Mat 1 vegetated modules (p-value = 0.024), with an average retention capacity of 54.73% and 85.34% respectively. The grass and Sedum Mixture Mat 2 vegetated modules (p-value = 0.007) had an average retention of 54.73% and 91.05% respectively. The Sedum Mixture Mat 2 module exhibited a significantly higher retention than the non-vegetated Enhanced Substrate module, confirming findings from Beecham and Razzaghmanesh [1], Teemusk and Mander [25], and Morgan et al. [39], where it was indicated that vegetation was a relevant variable in the increase of retention rates. Productive and intensive substrates showed no statistically significant differences between vegetated and non-vegetated modules. Our results do not coincide with some recent research in tropical climates in which non-vegetated GRs were observed to be more efficient than vegetated GRs [44].
3.1.3. Effect of Hydrological Variables on Water Retention Efficiency
Multiple linear regressions were carried out to identify statistically significant rainfall variables correlating with the runoff retention process. The independent variables included in the multiple linear regressions were air temperature, air humidity, ADWP, rainfall at maximum intensity, and rainfall duration. In order to avoid problems of multicollinearity and to identify the correlations between the independent variables as well as each independent variable with the dependent variable, a correlation matrix was performed. The observed correlation between independent variables was lower than 0.728 in all cases, and correlation with retention efficiency depended highly on the specific independent variable.
Due to the relevance of the type of substrate in the process of rainfall retention, the decision was made to carry out a general regression analysis on all the data, as well as independent regression models for each type of substrate, with significances of 1%, 5%, and 10% (Table 1 shows regressions coefficients for each of the regressions). When all data was analyzed together using a multiple linear regression model, all variables were significant at 1% significance. The coefficient of determination (R2) was 0.229 with a total of 1114 observations.

Table 1.
Multiple linear regressions for runoff retention rate filtering data by type of substrate. ADWP: antecedent dry weather period.
The global model showed the relevance of the variables selected, since all were significant at 1% significance. When classifying by type of substrate, air humidity was not significant for the Productive Substrate and the Extensive Substrate. Similar results were obtained for air temperature as it was not significant for the Extensive Substrate and was only significant for the Productive Substrate at a 10% significance level. For all substrates, the rainfall characteristics (ADWP, maximum intensity and duration) were significant at both at 5% and 1% in accordance with the findings of Garofalo et al. [19] for Mediterranean conditions. The R2 values for the Extensive Substrate and Enhanced Substrate were 0.353 with 72 observations and 0.229, with a total of 675 observations, respectively. The Productive Substrate yielded a R2 of 0.514 with 54 observations and for the Intensive Substrate, the coefficient of determination resulted at 0.373 with a total of 313 observations.
3.1.4. Effect of Event Characteristics and Rainfall Regime on Water Retention Efficiency
Using the hydrological variables database (ADWP, rainfall maximum 1-min intensity, rainfall duration and rainfall depth), a k-means cluster analysis was performed to categorize event groups according to their characteristics. Figure 7 shows the range of values of the groups for each variable. Although statistical differences were found for all variables, rainfall depth and maximum 1-min intensity were the most important variables to take into account when establishing the categories. According to the previous categorization, three event groups were defined (small, intermediate, and large events). The Welch’s test showed that significant differences exist between the mean retention of these groups (p-value = 0.000), supporting the findings of Teemusk and Mander [25], Carpenter et al. [45], and Fassman-Beck et al. [15] that confirm a difference in retention due to event size. GRs show the highest retention for small events (96.1%) followed by intermediate events (78.9%) and the lowest retention corresponding to large events (62.6%).
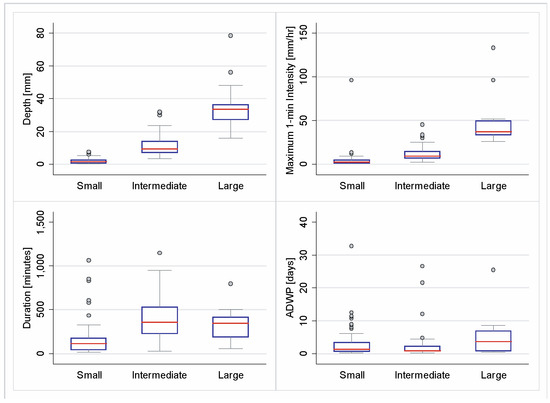
Figure 7.
Characteristics of hydrological variables for each event size group.
Taking into account the type of substrate, the GRs with the Intensive Substrate showed statistically higher retentions than those with the Enhanced Substrate, corresponding to small and intermediate events at 1% significance. Vegetation cover was also analyzed, and results showed that GRs with vegetated coverage have higher retentions for small events (p-value = 0.077). No significant differences were found for neither intermediate nor large events.
Mean retention of GRs was calculated for each rainfall regime. Welch’s test showed that retention in the rainy period (85.3%) is statistically lower than those in the intermediate (90.8%) and dry period (91.8%). This behavior matches the findings of Sims et al. [12] where drier climate conditions were associated with higher average retention efficiencies.
Analyzing the relevance of the substrate and coverage in different conditions, the Intensive Substrate showed a higher retention performance than the Enhanced Substrate for dry and intermediate periods at 5% significance and for the rainy period at 10% significance. Vegetated GRs yielded a significantly higher retention than non-vegetated GRs for dry and intermediate periods. No statistically significant differences were found for the rainy period. According to results obtained by Viola et al. [13] and Fassman-Beck et al. [15], climate regime appears to be a relevant determinant for the retention performance of GRs.
3.2. Water Quality Results
For the runoff water quality analysis, 12 rain events were characterized over a period of 14 months. The characteristics of these events are summarized in Table 2. A group that comprises all GRs monitored in this study (GR group) was compared with a control group (i.e., rainfall and plastic roofing panel runoff, grouped as similar concentrations were measured in both cases). Mean concentrations were calculated as a simple average for each group.

Table 2.
Characteristics of rainfall events for water quality analysis.
3.2.1. Effect of Green Roofs on Water Quality
For pH and conductivity (Table 3) the GR group and the control case showed statistically significant differences, in both cases obtaining higher averages for the GR group. Similar results were obtained for organic matter (Figure 8), phosphorus, and coliforms, with concentrations for GRs that were significantly higher than the control cases’ concentrations (Table 3). These are similar to results presented in previous studies, indicating GRs as a source of organic matter [7,46], phosphorus [22,24,25,47,48], pathogens [48], and total dissolved solids [1,30], as well as the pH neutralization effect from GRs [1,22,25,26,31,49,50,51,52].

Table 3.
Descriptive statistics and t-test results for the effect of green roofs on water quality parameters.
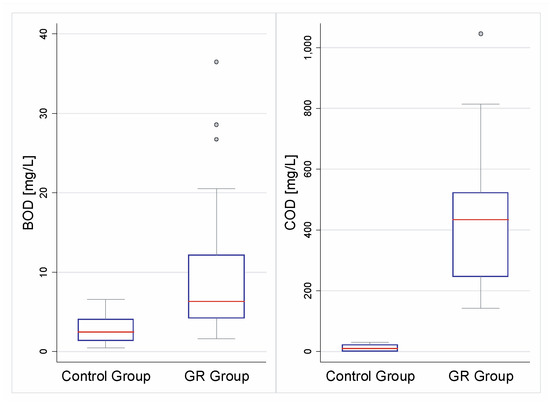
Figure 8.
Effect of green roofs on organic matter parameters. BOD: biological oxygen demand; COD: chemical oxygen demand.
GRs had significantly higher concentrations for total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN), nitrates, and nitrites than the control cases, confirming the findings of Aitkenhead-Peterson et al. [46], Greogoire and Clausen [53], Moran et al. [54], and Whittinghill et al. [55]. This was in contrast to concentrations of ammonia, where the average GRs concentrations were below those found in the control cases and where no statistically significant difference (Table 3) was found. These results are similar to those presented by Berndtsson et al. [21] and Buffam et al. [22]. This phenomenon might be due to the transformation and utilization of nitrogen compounds during the biological and chemical processes of GR vegetation. When looking at the physical parameters (Table 3), color was significantly higher for GR samples, indicating color contributed by vegetated structures and confirming Li and Babcock’s [7] findings, that can be explained by the organic content of the GR substrates [49]. The t-test for turbidity only showed differences with a significance of 5%, indicating a higher presence of TDS due to GR contributions. In the case of total suspended solids (TSS), the t-test showed no statistically significant difference, confirming the high performance of the filter layers used in the GR modules. Finally, although there were higher averages for metals from the GRs in all cases (Table 3), the t-tests showed statistical similarity for selenium and lithium, indicating that GRs do not markedly contribute to these parameters. For the rest of the metals (zinc, copper, nickel, lead, aluminum, barium, boron, calcium, strontium, iron, magnesium, manganese, potassium, and sodium) statistically significant contributions were found in GRs, confirming the findings of Berndtsson et al. [21], Buffam et al. [22], and Vijayaraghavan and Joshi [26]; the presence of these metals in GR leachate can be associated with the composition of the substrate.
3.2.2. Effect of Substrate on Water Quality
Our results showed that the effect of substrate on runoff water quality is highly dependent on the type of substrate, which makes selecting the most appropriate substrate for a GR challenging. Mean biological oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) values obtained for the Enhanced Substrate were 10.18 mg/L and 441.01 mg/L respectively, while the analysis for the Intensive Substrate yielded mean values of 7.94 mg/L and 391.37 mg/L for the aforementioned parameters. t-tests showed no difference in significance for BOD and COD parameters between substrates (p-values > 0.340). Results for total coliforms showed no significant differences between Intensive and Enhanced Substrates, with p-values above 0.264 for the t-tests performed, and mean values of 1.9 × 105 Most Probable Number (MPN) for the Enhanced Substrate and 1.1 × 105 MPN for the Intensive Substrate. Different results were obtained for phosphorus, with significantly lower concentrations for the Intensive Substrate (p-values < 0.002) confirming the findings of Harper el al. [3] and Kok et al. [56] that associate nutrient loadings with substrate media type.
TKN and nitrates evidenced significantly higher concentrations for the Enhanced Substrate (mean values of 13.75 mg/L and 11.78 mg/L respectively) compared with concentrations for the Intensive Substrate (mean values of 10.07 mg/L and 6.35 mg/L), with p-values of 0.038 for TKN and 0.018 for nitrate t-tests, obtaining consistent results with those presented in Harper et al. [3]. For the other nitrogen parameters (nitrites and ammonia), mean values for the Enhanced Substrate were 0.139 mg/L for nitrites and 0.46 mg/L for ammonia, while the results for the Intensive Substrate were 0.05 mg/L and 0.54 mg/L for nitrites and ammonia; however, there is not enough statistical evidence to assert differences between groups (p-values > 0.05), which is why it is not possible to confirm a marked effect of the substrate for these cases.
A similar behavior was observed for the physical parameters, in which the Intensive Substrate runoff had significantly less color (p-value: 0.002 with mean values of 42.17 Platinum-Cobalt Scale (PCS) for the Enhanced Substrate and 26.74 for the Intensive Substrate) and turbidity (p-value: 0.073 with mean values of 26.643 Nefelometric Turbidity Unit (NTU) for the Enhanced Substrate and 10.834 NTU for the Intensive Substrate), but not for total suspended solids, the parameter in which the performance of the Enhanced Substrate (mean value of 25.68 mg/L) was better than the Intensive Substrate (mean value of 36.70 mg/L). However, no statistically significant differences were found.
Results for metals were highly variable depending on the specific metal under consideration. For zinc, nickel, aluminum, barium, calcium, strontium, lithium, magnesium, and sodium, concentrations in the Intensive Substrate runoff were higher than concentrations in that of the Enhanced Substrate; however, t-tests only evidenced statistically significant differences for zinc, barium, calcium, strontium, and magnesium (p-values < 0.05); therefore, it cannot be said that the type of substrate strongly effects these parameters. Meanwhile, for copper, lead, selenium, iron, manganese and potassium, the Enhanced Substrate had higher concentrations; t-tests only evidenced significant differences for copper and lead.
The same analysis was carried out for pollutant loads, and results evidence that the Intensive substrate had higher loads of most physicochemical parameters and all metals. However, differences were only significant for total phosphorus where the Enhanced Substrate had a higher load (p-value: 0.030). For zinc, calcium, strontium, magnesium and sodium, the Intensive Substrate showed significantly higher loads.
3.2.3. Effect of Vegetation on Water Quality
Results for organic matter, phosphorus and total coliform were consistent over all parameters. For organic matter parameters, vegetated modules presented mean concentration values of 9.15 mg/L and 464.08 mg/L for BOD and COD, respectively. The mean concentration of total phosphorus was 4.16 mg/L and 5.40mg/L for phosphates in the vegetated modules. Total coliform MPN in vegetated modules was 1.8 × 105. In all cases, vegetated roofs yielded higher concentrations than those without any plant coverage. However, no statistical differences were found. The analysis of the effect of vegetation for pH and conductivity, where vegetated modules presented values of 8.24 and 1231.20 μs/cm respectively, did not identify significant differences in any of the vegetation types compared with the values for the non-vegetated modules, yielding a mean pH of 8.17 and a mean conductivity of 930.40 μs/cm. These results demonstrate that it is not possible to state that the presence of vegetation modifies the way in which GRs affect these parameters of water quality.
For nitrogen parameters (TKN, nitrates, nitrites, and ammonia), although non-vegetated modules present higher concentrations, no statistical differences were observed in any case. According to these results, it is not possible to state that vegetation has a buffering effect on the levels of nitrogen. For turbidity and TSS, non-vegetated modules presented lower values (17.88 NTU and 20.91 mg/L) than vegetated modules (19.67 NTU and 42.41 mg/L). On the other hand, vegetated roofs (30.23 PCS) appeared to buffer the presence of color. The analysis for the physical parameters did not show evidence of the effect of vegetation.
For metals, there was also no clear effect of the presence of vegetation in most of the parameters characterized. For copper, lead, selenium, aluminum, barium, boron, calcium, strontium, iron, magnesium, manganese, potassium and sodium, no effect was perceived. Only for zinc (p-value = 0.000) and nickel (p-value = 0.05) were there statistically significant contributions from vegetated modules.
Pollutant loads were also considered in order to evaluate the effect of the vegetation on runoff quality. Results showed that non-vegetated roofs produced higher loads than roofs with vegetated coverage for all physicochemical parameters excluding Total Phosphorus and for all metals except for zinc and lithium. Statistical tests evidenced that there are no significant differences; however, the consistent presence of higher pollutant loads in runoff from non-vegetated roofs confirm findings by Beecham and Razzaghmanesh [1] and Wang et al. [52] that mention enhanced pollutant removal for vegetated roofs.
3.2.4. Effect of Event Characteristics and Rainfall Regime on Water Quality
Analysis was carried out to find correlations between the water quality parameters of concentrations and loads, and the rainfall characteristics (ADWP, rainfall depth, rainfall maximum intensity and rainfall duration). Pollutant loads evidenced consistent and higher correlations with the rainfall depth and maximum intensity than with concentration values. However, when analyzing the effect of the event characteristics using pollutant loads, the t-test did not show evidence of these effects, only large rainfall events presented higher TP loads than intermediate events, at a 10% significance (0.099). For all the other measured parameters large events yielded higher loads, but no statistical evidence was found. On the other hand, concentrations analysis showed higher concentrations of COD (p-value: 0.013) and nitrates (p-value: 0.086) for intermediate events. Zinc, lead, calcium, strontium, magnesium, potassium and sodium concentrations are statistically higher for intermediate events than for large events. These results coincide with Teemusk and Mander’s [19] conclusions asserting that low magnitude events can lead to higher concentrations in the water quality.
For pollutant loads, the effect of the rainfall regime was only appreciable for COD where the intermediate months yielded higher loads (p-value: 0.042). Carpenter et al. [45] determined that there are higher nutrient loads in the growing season (warm temperatures); however, in this study phosphorus loads were higher in the rainy period and nitrogen loads were higher in the intermediate. For the rest of the physicochemical parameters no effect was found. Regarding metals, there were higher loads in the intermediate period, with zinc, barium, calcium, strontium, magnesium, potassium and sodium being significant.
Buffam et al. [22] found a correlation between the air temperature and some parameter concentrations, resulting in higher concentrations in summer; however, in Bogotá’s climate this correlation does not apply for every parameter, taking into account that the changes in temperature are not as dramatic as changes in countries with seasons. Concentration analysis showed statistically significant differences for organic matter, TSS and total coliforms. Dry months presented higher concentrations of BOD (p-value = 0.039) and TSS (p-value = 0.017). The rainy period yielded higher values of COD (p-value = 0.003) and total coliforms (p-value = 0.047). Rainfall regime effect was also identified for nickel, boron, calcium, strontium, magnesium, manganese, potassium, and sodium (p-value < 0.05).
4. Conclusions
The water retention analysis identified the type of substrate as the most important variable when studying the performance of GRs in terms of water quantity, while the presence of vegetation was not evidenced to have an effect when conducting an analysis with all data. The second round of analysis, which consisted of grouping by affinity the modules with the same type of substrate, showed that vegetation is a relevant explanatory variable in the model, significantly increasing the retention efficiencies of the GRs. The rainfall event characteristics and the rainfall regime were found to be important for assessing rainfall retention. GRs perform differently depending on the event magnitude and the month of the year, with best results found in dry months and for small events.
Analysis looking for the effect of GRs on runoff water quality identified a significant increase in the presence of most of the parameters, except for ammonium, TSS, selenium, and lithium. On the other hand, the type of substrate was shown to be relevant in determining the presence of phosphorus, TKN, nitrates, color and turbidity, found in higher concentrations in runoff from modules with extensive substrate. Finally, analysis of the effects of different substrates on the presence of metals yielded highly variable results depending on the specific metal under consideration.
The evidence on the effects of vegetation was limited, because although the vegetated modules presented higher concentrations for most of the parameters, no statistically significant differences were found to support these findings. Similarly, for most of the metals analyzed, vegetated modules presented higher concentrations. However, these were only significantly higher for zinc and nickel. Rain event characteristics had an effect on COD, nitrates, zinc, lead, calcium, strontium, magnesium, potassium, and sodium, parameters for which intermediate events showed higher concentrations. The rainfall regime was relevant when looking at the concentrations of BOD, COD, TSS, total coliforms, nickel, boron, calcium, strontium, magnesium, manganese, potassium, and sodium.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.F., C.V.R., G.P., J.P.R., and M.D.-G.; Monitoring, P.F., C.V.R., and G.P.; Data Analysis, P.F., C.V.R., and G.P.; Supervision, J.P.R. and M.D.-G.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, P.F., C.V.R.; Writing—Review and Editing, P.F., C.V.R., J.P.R., and M.D.-G.
Funding
This research was funded by Departamento de Ingeniería Civil y Ambiental, Universidad de los Andes; Fondo de Apoyo para Profesores Asistentes, Universidad de los Andes and Departamento Administrativo de Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación (COLCIENCIAS).
Acknowledgments
We thank Groncol for providing the substrates and vegetated covers, Faindry J. Monroy for her support in the automatization process of the experimental setting, Oscar Vazquez for developing the productive roofs, Natalia Franco for her collaboration with some of the laboratory analyses, and four anonymous reviewers for providing constructive comments that helped us to improve this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Beecham, S.; Razzaghmanesh, M. Water quality and quantity investigation of green roofs in a dry climate. Water Res. 2015, 70, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czemiel Berndtsson, J. Review: Green roof performance towards management of runoff water quantity and quality: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, G.; Limmer, M.; Showalter, W.; Burken, J. Nine-month evaluation of runoff quality and quantity from an experiential green roof in Missouri, USA. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 78, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresno, D.C.; Rodríguez, J.; Rodríguez, J.; Ballester, F. Sistemas Urbanos De Drenaje Sostenible SUDS. Interciencia 2005, 30, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Mentens, J.; Raes, D.; Hermy, M. Green roofs as a tool for solving the rainwater runoff problem in the urbanized 21st century? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 77, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghmanesh, M.; Beecham, S.; Kazemi, F. Impact of green roofs on stormwater quality in a South Australian urban environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Babcock, R. Green roofs against pollution and climate change. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, M. Low impact development practices: A review of current research and recommendations for future directions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 186, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, D.; Kaluvakolanu, P. Effect of roof surface type on storm-Water runoff from full-Scale roofs in a temperate climate. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2011, 137, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghmanesh, M.; Beecham, S. The hydrological behaviour of extensive and intensive green roofs in a dry climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volder, A.; Dvorak, B. Event size, substrate water content and vegetation affect storm water retention efficiency of an un-irrigated extensive green roof system in Central Texas. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2014, 10, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla, A.; Gnecco, I.; Lanza, L. Hydrologic Restoration in the Urban Environment Using Green Roofs. Water 2010, 2, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, A.; Robinson, C.; Smart, C.; Voogt, J.; Hay, G.; Lundholm, J.; O’Carroll, D. Retention performance of green roofs in three different climate regions. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, F.; Hellies, M.; Deidda, R. Retention performance of green roofs in representative climates worldwide. J. Hydrol. 2017, 553, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassman-Beck, E.; Voyde, E.; Simcock, R.; Hong, Y. 4 living roofs in 3 locations: Does configuration affect runoff mitigation? J. Hydrol. 2013, 490, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, G.; Simunek, J.; Piro, P. A comprehensive analysis of the variably saturated hydraulic behavior of a green roof in Mediterranean climate. Vadose Zone J. 2016, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenot, J.; Gaget, E.; Moinardeau, C.; Jaunatre, R.; Buisson, E.; Dutoit, T. Substrate Composition and Depth Affect Soil Moisture Behavior and Plant-Soil Relationship on Mediterranean Extensive Green Roofs. Water 2017, 9, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovin, V.; Vesuviano, G.; Kasmin, H. The hydrological performance of a green roof test bed under UK climatic conditions. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, G.; Palermo, S.; Principato, F.; Theodosiou, T.; Piro, P. The Influence of Hydrologic Parameters on the Hydraulic Efficiency of an Extensive Green Roof in Mediterranean Area. Water 2016, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K. Green roofs: A critical review on the role of components, benefits, limitations and trends. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 740–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndtsson, J.C.; Bengtsson, L.; Jinno, K. Runoff water quality from intensive and extensive vegetated roofs. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffam, I.; Mitchell, M.E.; Durtsche, R.D. Environmental drivers of seasonal variation in green roof runoff water quality. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yuan, J.-G.; Yang, J.-Z.; Chen, A.-K.; Yang, Z.-Y. Effect of substrate depth on initial growth and drought tolerance of Sedum lineare in extensive green roof system. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 74, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, M.; Mirande, C.; Saad, M.; Gromaire, C. The Potential Incidence of Green Roofs on Urban Runoff Quality. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Urban Drainage, Sarawak, Malaysia, 7–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Teemusk, A.; Mander, Ü. Rainwater runoff quantity and quality performance from a greenroof: The effects of short-term events. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 30, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Joshi, U.M. Can green roof act as a sink for contaminants? A methodological study to evaluate runoff quality from green roofs. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 194, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Joshi, U.M. Research Paper: Application of seaweed as substrate additive in green roofs: Enhancement of water retention and sorption capacity. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 143, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Raja, F.D. Pilot-scale evaluation of green roofs with Sargassum biomass as an additive to improve runoff quality. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 75, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Miao, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, B.; Liu, J. Research Paper: The capacity of greening roof to reduce stormwater runoff and pollution. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Hou, P.; Wan, W.; Li, R.; Ren, Y.; Ouyang, Z. Quality and seasonal variation of rainwater harvested from concrete, asphalt, ceramic tile and green roofs in Chongqing, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 132, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, X. The influence of dual-substrate-layer extensive green roofs on rainwater runoff quantity and quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versini, P.A.; Ramier, D.; Berthier, E.; de Gouvello, B. Assessment of the hydrological impacts of green roof: From building scale to basin scale. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo Escobar, N.; Torres, A. Hydric Attenuation and Hydrological Benefits for Implementing Productive Green Roof in Soacha, Colombia. Ing. Univ. 2014, 18, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, G.; Rosero, M.; Cadena, M.; Montealegre, J.; Sanabria, F. Estudio de la Caracterización Climática de Bogotá y Cuenca Alta del Río Tunjuelo. In Instituto de Hidrología, Meteorología y Estudios Ambientales IDEAM—Fondo de Prevención y Atención de Emergencias FOPAE; Instituto de Hidrología: Bogotá, Colombia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Secretaría Distrital de Ambiente de Bogotá. Guía de Techos Verdes en Bogotá; Secretaría Distrital de Ambiente de Bogotá: Bogotá, Colombia, 2011. Available online: http://www.ambientebogota.gov.co/c/document_library/get_file?uuid=f807042d-064e-4a7a-adf1-75e1e4b7aaaa&groupId=10157 (accessed on 28 June 2018).
- Eaton, A.D. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Stovin, V.; Vesuviano, G.; De-Ville, S. Defining green roof detention performance. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnett, N.; Nagase, A.; Hallam, A. The dynamics of planted and colonising species on a green roof over six growing seasons 2001–2006: Influence of substrate depth. Urban Ecosyst. 2008, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.; Celik, S.; Retzlaff, W. Green roof storm-water runoff quantity and quality. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getter, K.; Rowe, D.; Andresen, J. Quantifying the effect of slope on extensive green roof stormwater retention. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 31, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, M.; Kim, R.; Rafiq, M. Green roof benefits, opportunities and challenges—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 90, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanwoert, N.D.; Rowe, D.B.; Andersen, J.A.; Rugh, C.L.; Fernandez, R.T.; Xia, L. Green roof stormwater retention: Effects of roof surface, slope, and media depth. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soulis, K.; Ntoulas, N.; Nektarios, P.; Kargas, G. Runoff reduction from extensive green roofs having different substrate depth and plant cover. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiola, C.; Mary, W.; Pimentel da Silva, L. Hydrological performance of modular-tray green roof systems for increasing the resilience of mega-cities to climate change. J. Hydrol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, C.M.G.; Todorov, D.; Driscoll, C.T.; Montesdeoca, M. Water quantity and quality response of a green roof to storm events: Experimental and monitoring observations. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorov, D.; Driscoll, C.; Todorova, S.; Montesdeoca, M. Water quality function of an extensive vegetated roof. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitkenhead-Peterson, J.; Dvorak, B.; Volder, A.; Stanley, N. Chemistry of growth medium and leachate from green roof systems in south-central texas. Urban Ecosyst. 2011, 14, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, M.; Gromaire, M.-C.; Saad, M.; De Gouvello, B. Effect of substrate depth and rain-event history on the pollutant abatement of green roofs. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 183, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, S.S.G.; Mahmud, H.B.; Ashraf, M.A. Performance of green roofs with respect to water quality and reduction of energy consumption in tropics: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-F. Review: Performance evaluation and development strategies for green roofs in Taiwan: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, C.B.; Klenzendorf, J.B.; Afshar, B.R.; Simmons, M.T.; Barrett, M.E.; Kinney, K.A.; Kirisits, M.J. The effect of roofing material on the quality of harvested rainwater. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2049–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Qin, J.; Hu, Y. Are green roofs a source or sink of runoff pollutants? Ecol. Eng. 2017, 107, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoire, B.G.; Clausen, J.C. Effect of a modular extensive green roof on stormwater runoff and water quality. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, A.; Hunt, B.; Jennings, G. A North Carolina field study to evaluate green roof runoff quantity, runoff quality, and plant growth. In World Water & Environmental Resources Congress; North Carolina State University: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Whittinghill, L.; Rowe, D.; Andresen, J.; Cregg, B. Comparison of stormwater runoff from sedum, native prairie, and vegetable producing green roofs. Urban Ecosyst. 2015, 18, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, K.H.; Mohd Sidek, L.; Chow, M.F.; Zainal Abidin, M.R.; Basri, H.; Hayder, G. Evaluation of green roof performances for urban stormwater quantity and quality controls. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2016, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).