Temporal and Spatial Flow Variations over a Movable Scour Hole Downstream of a Grade-Control Structure with a PIV System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Set-Up and Procedure
2.1. Experimental Design and Flume
2.2. PIV Measuring System
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Verification of the PIV Measuring System
3.2. Two-Dimensional Velocity Distribution
3.3. Turbulence Intensities
3.4. Reynolds Shear Stress
4. Conclusions
- A PIV system with a high-resolution digital camera, halogen lamps, and ABS seeding particles was adopted and employed to successfully measure the temporal and spatial variations in the flow over the movable scour hole.
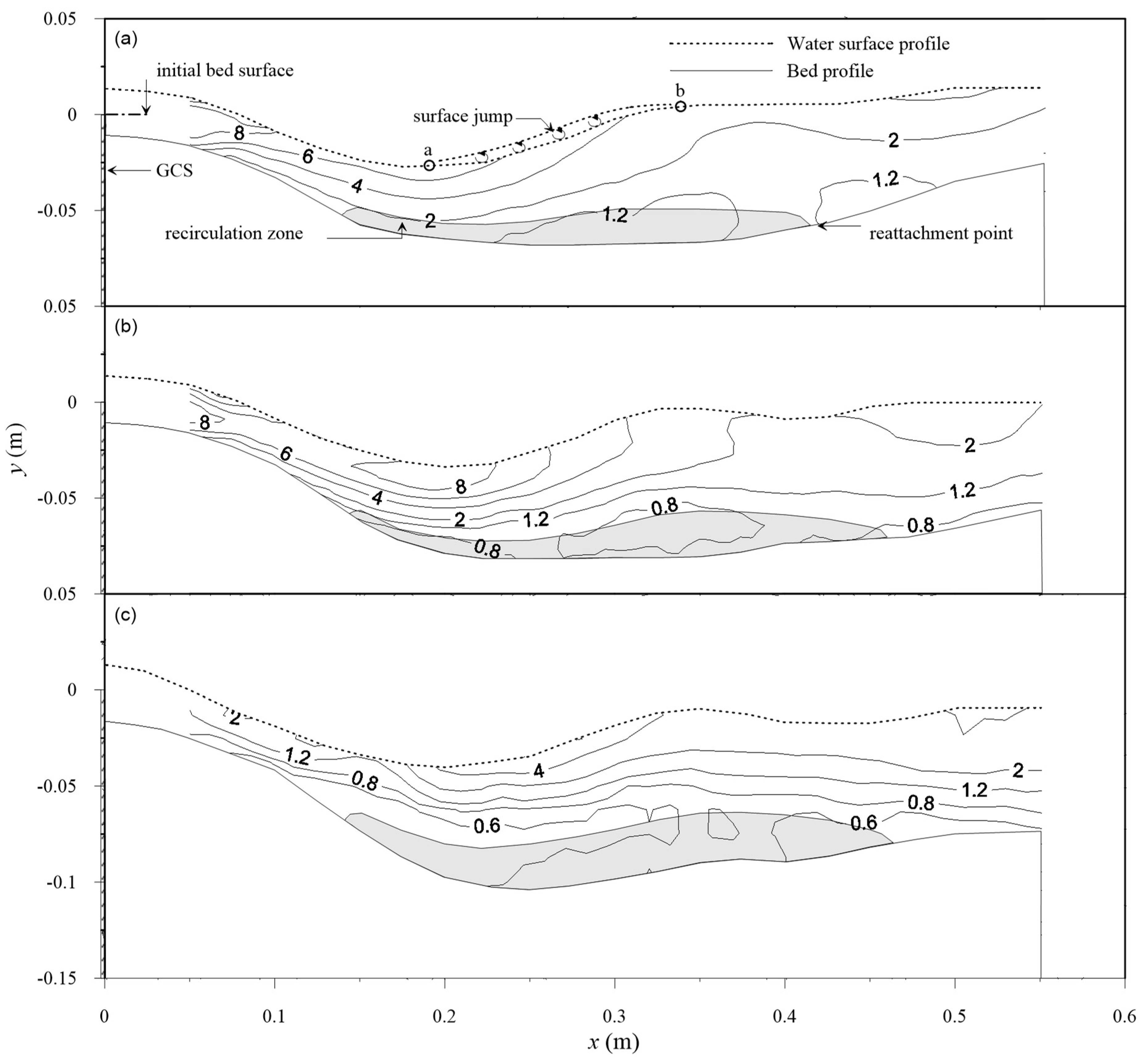
- According to the measured vectorial mean velocity profiles (Figure 4), the flow field in the scour hole can be classified into three regions—jet and diffusion, transition, and acceleration regions. Additionally, a recirculation zone was noted near the channel bottom. The reattachment point of the recirculation zone usually moves slowly downstream with time.
- In general, the dimensionless longitudinal turbulence intensity is higher than the dimensionless vertical turbulence intensity, indicating the turbulent flow is anisotropic in the jet and diffusion region. In this study, the distributions of and were similar because there were two local maxima occurring at the entrance and the surface jump. In general, and values decreased with time as the scour hole gradually approached equilibrium.
- By assuming that the longitudinal mean velocity () and vertical mean velocity () are independently and normally distributed, a theoretical Reynolds stress () distribution can be derived (Equation (5)). The measured Reynolds stress can be fitted with the theoretical equation reasonably well (Figure 10).
- This study demonstrated the significance of the instantaneous shear stress, especially at the early stage of the scouring process, which also quantified Shen and Lu’s [28] findings. Furthermore, the experimental results show that the exceeding probability increased with the unit flow discharge and bed slope, and decreased gradually with time.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, J.Y.; Hong, J.H.; Chang, K.P.; Lu, T.F. Evolution of scouring process downstream of grade-control structures under steady and unsteady flows. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 2699–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoklitsch, A. Kolkbildung unter uberfallstrahlen. Wasserwirtschaft 1932, 24, 341–343. [Google Scholar]
- Bormann, N.E.; Julien, P.Y. Scour downstream of grade-control structures. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1991, 117, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmans, G.J.C.M.; Verheij, H.J. Scour Manual; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gaudio, R.; Marion, A.; Bovolin, V. Morphological effects of bed sills in degrading rivers. J. Hydraul. Res. 2000, 38, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudio, R.; Marion, A. Time evolution of scouring downstream of bed sills. J. Hydraul. Res. 2003, 41, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, M.A.; Marion, A.; Comiti, F.; Gaudio, R. Local scouring in low and high gradient streams at bed sills. J. Hydraul. Res. 2002, 40, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, M.A.; Marion, A.; Comiti, F. Local scouring at grade-control structures in alluvial mountain rivers. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenzi, M.A.; Marion, A.; Comiti, F. Interference processes on scouring at bed sills. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 2003, 28, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, A.; Lenzi, M.A.; Comiti, F. Effect of sill spacing and sediment size grading on scouring at grade-control structures. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 2004, 29, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, A.; Tregnaghi, M.; Tait, S. Sediment supply and local scouring at bed sills in high-gradient streams. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagliara, S. Influence of sediment gradation on scour downstream of block ramps. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2007, 133, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregnaghi, M.; Marion, A.; Coleman, S. Scouring at bed sills as a response to flash floods. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2009, 135, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregnaghi, M.; Marion, A.; Coleman, S.; Tait, S. Effect of flood recession on scouring at bed sills. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2010, 136, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Rajaratnam, N. Submerged flow regimes of rectangular sharp-crested weirs. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1996, 122, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.W.; Melville, B.W.; Friedrich, H. Live-bed scour at submerged weirs. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2015, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.W.; Melville, B.; Friedrich, H. Local scour at submerged weirs in sand-bed channels. J. Hydraul. Res. 2016, 54, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.W.; Melville, B.W.; Friedrich, H. Flow patterns and turbulence structures in a scour hole downstream of a submerged weir. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 140, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudio, R.; Tafarojnoruz, A.; Calomino, F. Combined flow-altering countermeasures against bridge pier scour. J. Hydraul. Res. 2012, 50, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, D.; Tafarojnoruz, A.; Gaudio, R.; Cardoso, A.H. Effects of pile cap thickness on the maximum scour depth at a complex pier. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2013, 139, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D.M. Flow resistance in gravel-bed rivers: Progress in research. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 136, 301–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathurst, J.C.; Li, R.M.; Simons, D.B. Resistance equation for large-scale roughness. J. Hydraul. Div. 1981, 107, 1593–1613. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, D.S.L. Macroscale surface roughness and frictional resistance in overland flow. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 1997, 22, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezu, I.; Rodi, W. Open-channel flow measurements with a laser doppler anemometer. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1986, 112, 335–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Chang, F.H.; Lu, T.F. Characteristics of shallow rain-impacted flow over smooth bed. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1998, 124, 1242–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodaro, G.; Tafarojnoruz, A.; Stefanucci, F.; Adduce, C.; Calomino, F.; Gaudio, R.; Sciortino, G. An experimental and numerical study on the spatial and temporal evolution of a scour hole downstream of a rigid bed. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Fluvial Hydraulics, River Flow, Lausanne, Switzerland, 3–5 September 2014; pp. 1415–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Dodaro, G.; Tafarojnoruz, A.; Sciortino, G.; Adduce, C.; Calomino, F.; Gaudio, R. Modified Einstein sediment transport method to simulate the local scour evolution downstream of a rigid bed. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.W.; Lu, J.Y. Development and prediction of bed armoring. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1983, 109, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y. Statistical notes for clinical researchers: Assessing normal distribution (2) using skewness and kurtosis. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2013, 38, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Lu, T.F.; Hong, J.H. Experimental study of extreme shear stress for shallow flow under simulated rainfall. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 1660–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiew, Y.-M.; Parker, G. Incipient sediment motion on non-horizontal slopes. J. Hydraul. Res. 1994, 32, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Run | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (m2/s) | (m/s) | (m/s) | (m) | (m) | (m) | |||||
| M-1 | 0.01 | 0.017 | 0.0167 | 0.98 | 0.0397 | 2.41 | 15,757 | 35 | 0.049 | 0.18 | 0.56 |
| M-2 | 0.01 | 0.025 | 0.0283 | 1.13 | 0.0476 | 2.29 | 26,045 | 24 | 0.066 | 0.25 | 0.98 |
| S-1 | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.0167 | 1.04 | 0.0473 | 2.63 | 17,327 | 38 | 0.082 | 0.19 | 0.70 |
| S-2 | 0.015 | 0.023 | 0.0283 | 1.23 | 0.0561 | 2.59 | 26,206 | 26 | 0.118 | 0.23 | 1.03 |
| Run | Time | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-1 | 15 min | 0.065 | 0.05 | 0.97 | 1.70 | 0.018 | 0.02 | 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.00 |
| 1 h | 0.016 | 0.03 | 0.37 | 0.85 | 0.008 | 0.02 | −0.06 | 0.17 | −0.07 | |
| 5 h | −0.009 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.45 | 0.006 | 0.02 | −0.07 | 0.50 | −0.07 | |
| M-2 | 15 min | 0.057 | 0.06 | 1.18 | 1.68 | 0.001 | 0.02 | −0.15 | 0.66 | −0.20 |
| 1 h | 0.070 | 0.05 | 0.65 | 1.13 | 0.013 | 0.03 | −0.01 | 1.81 | −0.05 | |
| 5 h | −0.048 | 0.04 | 0.63 | 2.03 | 0.000 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 0.03 | |
| S-1 | 15 min | 0.017 | 0.06 | 0.52 | 1.45 | 0.009 | 0.03 | −0.91 | 2.36 | −0.40 |
| 1 h | −0.101 | 0.03 | −0.42 | 0.25 | 0.000 | 0.02 | −0.01 | 0.29 | −0.06 | |
| 5 h | −0.075 | 0.03 | −0.56 | 0.72 | −0.001 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.22 | −0.12 | |
| S-2 | 15 min | −0.054 | 0.08 | −0.06 | −0.17 | 0.034 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.66 | −0.16 |
| 1 h | −0.037 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.20 | 0.015 | 0.03 | −0.13 | 0.52 | −0.12 | |
| 5 h | −0.090 | 0.04 | −0.26 | 1.43 | −0.006 | 0.02 | −0.35 | 1.22 | 0.02 |
| Run | Time | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-1 | 15 min | −0.001 | 1.19 | 0.133 |
| 1 h | 0.042 | 0.56 | 0.012 | |
| 5 h | 0.035 | 0.53 | 0.008 | |
| M-2 | 15 min | 0.333 | 1.93 | 0.136 |
| 1 h | 0.061 | 1.58 | 0.112 | |
| 5 h | −0.013 | 0.70 | 0.025 | |
| S-1 | 15 min | 0.973 | 3.56 | 0.276 |
| 1 h | 0.041 | 0.71 | 0.027 | |
| 5 h | 0.066 | 0.50 | 0.016 | |
| S-2 | 15 min | 0.553 | 3.77 | 0.354 |
| 1 h | 0.168 | 1.41 | 0.135 | |
| 5 h | −0.013 | 0.83 | 0.039 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, S.-Y.; Lu, J.-Y.; Shih, D.-S. Temporal and Spatial Flow Variations over a Movable Scour Hole Downstream of a Grade-Control Structure with a PIV System. Water 2018, 10, 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081002
Lu S-Y, Lu J-Y, Shih D-S. Temporal and Spatial Flow Variations over a Movable Scour Hole Downstream of a Grade-Control Structure with a PIV System. Water. 2018; 10(8):1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081002
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Shi-Yan, Jau-Yau Lu, and Dong-Sin Shih. 2018. "Temporal and Spatial Flow Variations over a Movable Scour Hole Downstream of a Grade-Control Structure with a PIV System" Water 10, no. 8: 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081002
APA StyleLu, S.-Y., Lu, J.-Y., & Shih, D.-S. (2018). Temporal and Spatial Flow Variations over a Movable Scour Hole Downstream of a Grade-Control Structure with a PIV System. Water, 10(8), 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081002






