Multivariate and Spatial Analysis of Physicochemical Parameters in an Irrigation District, Chihuahua, Mexico
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Sampling
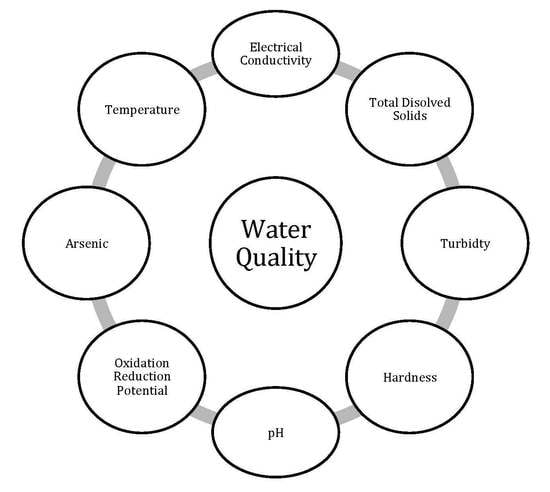
2.3. Physicochemical Parameters (PhP) Analysis
2.4. Multivariate Statistical Methods
2.5. Spatial Variability of the Physicochemical Parameters (PhP)
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Physicochemical Parameters (PhP)
3.2. Multivariate Analysis
3.3. Principal Components Analysis (PCA)
3.4. Cluster Analysis (CA)
3.5. Spatial Variability of Physicochemical Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kengnal, P.; Megeri, M.N.; Giriyappanavar, B.S.; Patil, R.R. Multivariate Analysis for the Water Quality Assessment in Rural and Urban Vicinity of Krishna River (India). Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2015, 12, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, S.; Davraz, A. Evaluation of the groundwater quality with WQI (Water Quality Index) and multivariate analysis: A case study of the Tefenni Plain (Burdur/Turkey). Environ. Earth. Sci. 2015, 73, 1725–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, A.; Malik, R.N.; Husain, S.Z. Spatio-temporal variations in water quality of Nullah Aik-tributary of the River Chenab, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 140, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, B.L.; Lawrence, A.R.; Chilton, P.J.C.; Adams, B.; Calow, R.C.; Klinck, B.A. Groundwater and its susceptibility to degradation: A global assessment of the problem and options for management; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2003; Volume 3, p. 118. ISBN 92-807-2297-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.K.; Agrawal, M.; Marshall, F. Heavy metal contamination of soil and vegetables in suburban areas of Varanasi, India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2007, 66, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Cao, Q.; Zheng, Y.M.; Huang, Y.Z.; Zhu, Y.G. Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, I.; Dhage, S.; Kumar, R. Study of variations in water quality of Mumbai coast through multivariate analysis techniques. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 38, 170–177. [Google Scholar]
- AlSuhaimi, A.O.; AlMohaimidi, K.M.; Momani, K.A. Preliminary assessment for physicochemical quality parameters of groundwater in Oqdus Area, Saudi Arabia. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahman, K.D.; Kazi, T.G.; Afridi, H.I.; Naseem, S.; Arain, S.S.; Ullah, N. Evaluation of high levels of fluoride, arsenic species and other physicochemical parameters in underground water of two sub districts of Tharparkar, Pakistan: A multivariate study. Water. Res. 2013, 47, 1005–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, P.N.; Sawant, D.V.; Deshmukh, R.N. Physico-chemical parameters for testing of water-A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 3, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangthong, S.; Shrestha, S. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: Case study of the Nampong River and Songkhram River, Thailand. Environ. Model. Assess. 2015, 187, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.; Qiu, Z. Understanding the relationship of land uses and water quality in Twenty First Century: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 173, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helena, B.; Pardo, R.; Vega, M.; Barrado, E.; Fernández, J.M.; Fernández, L. Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga river, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Res. 2000, 34, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Sinha, S. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti river (India) using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 538, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Bai, Y.; Tian, Z.; Li, J.; Shao, X.; Mustavish, L.F.; Li, B.L. Assessment of surface water quality via multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Songhua River Harbin region, China. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2013, 7, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Mohan, D.; Sinha, S. Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)—A case study. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3980–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.-F.; Shi, X.-Z.; Huang, B.; Dong-Sheng, Y.U.; Wang, H.-J.; Sun, W.-X.; Öboern, I.; Blombäck, K. Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils of an Industry-Based Peri-Urban Area in Wuxi, China. Pedosphere 2007, 17, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogna, D.; Michez, A.; Jacobs, S.; Dufrêne, M.; Vincke, C.; Dendoncker, N. Linking forest cover to water quality: A multivariate analysis of large monitoring datasets. Water 2017, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyacioglu, H. Surface water quality assessment using factor analysis. Water SA 2006, 32, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.; Rakib, M.A.; Dampare, S.B.; Ganyaglo, S.; Suzuki, S. Surface water quality assessment in the central part of Bangladesh using multivariate analysis. KSCE. J. Civ. Eng. 2011, 15, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batayneh, A.; Zumlot, T. Multivariate statistical approach to geochemical methods in water quality factor identification; application to the shallow aquifer system of the Yarmouk basin of North Jordan. Res. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 4, 756–768. [Google Scholar]
- Oketola, A.A.; Adekolurejo, S.M.; Osibanjo, O. Water quality assessment of River Ogun using multivariate statistical techniques. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 4, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, J.; Andrade, E.; López-Suárez, A.; Ledesma, R.; Cahill, T.A.; Wakabayashi, P.H. A receptor model for atmospheric aerosols from a southwestern site in Mexico City. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 3471–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, B.B. Multivariate Data Analysis: An Introduction; Prentice Hall: Irwin, Homewood, IL, USA, 1983; pp. 154–196. ISBN 978-0256028485. [Google Scholar]
- Wunderlin, D.A.; Diaz, M.P.; Ame, M.V.; Pesce, S.F.; Hued, A.C.; Bistoni, M.A. Pattern recognition techniques for the evolution of spatial and temporal variations in water quality. A case study: Suquia river basin (Cordoba-Argentina). Water Res. 2001, 35, 2881–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loska, K.; Wiechuła, D. Application of principal component analysis for the estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the Rybnik Reservoir. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, M.; Pardo, R.; Barrado, E.; Deban, L. Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3581–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bassam, A.M. Evaluation of ground water quality in Al-Qassim area, Saudi Arabia, using cluster and factor analyses. Kuwait J. Sci. Eng. 2006, 33, 101–121. [Google Scholar]
- Kazi, T.G.; Arain, M.B.; Jamali, M.K.; Jalbani, N.; Afridi, H.I.; Sarfraz, R.A.; Baig, J.A.; Shah, A.Q. Assessment of water quality of polluted lake using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, W.C. Modelación y Simulación Para el Drenaje de Tierras, en la Planicie Aluvial del Estado de Tabasco, México. Ph.D. Thesis, Autonomous University of Nuevo León, Marin, Nuevo León, Mexico, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Medellín-Vázquez, J.J. Análisis de la Vegetación en un Gradiente Altitudinal Mediante Técnicas Multivariadas, en el Campo Santa María, Lampazos de Naranjo, Nuevo León y Candela Coahuila. Master Thesis, Autonomous University of Nuevo León, Linares, Nuevo León, México, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Villatoro, M.; Henríquez, C.; Sancho, F. Comparación de los interpoladores IDW y Kriging en la variación espacial de pH, Ca, CICE y P del suelo. Agron. Costarric. 2008, 32, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Bhunia, G.S.; Shit, P.K.; Maiti, R. Comparison of GIS-based interpolation methods for spatial distribution of soil organic carbon (SOC). J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, T.B.; Lei, M.; Yang, J.; Guo, Q.J.; Song, B.; Zhou, X.Y. Spatial distribution of soil heavy metal pollution estimated by different interpolation methods: Accuracy and uncertainty analysis. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Mahmood, Q.; Peng, D.; Fu, W.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, D. The spatial distribution pattern of heavy metals and risk assessment of moso bamboo forest soil around lead–zinc mine in Southeastern China. Soil Till. Res. 2015, 153, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete Álvarez, M. Modelos Geoestadísticos del Precio de la Vivienda: Aproximación al Conocimiento Intraurbano de la Ciudad de Madrid. Ph.D. Thesis, Autonomous University of Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Huang, G.H.; Lin, Q.G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Y.R. Comparison of interpolation methods for estimating spatial distribution of precipitation in Ontario, Canada. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 3745–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez López, D.; Treviño Garza, E.J.; Reyes Gómez, V.M.; Muñoz Robles, C.A.; Aguirre Calderón, O.A.; Jiménez Pérez, J. Uso de modelos de regresión para interpolar espacialmente la precipitación media mensual en la cuenca del río Conchos. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agríc. 2014, 5, 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Skeppström, K.; Olofsson, B. A prediction method for radon in groundwater using GIS and multivariate statistics. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 666–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroju, S. Evaluation of five GIS-based interpolation techniques for estimating the radon concentration for unmeasured zip codes in the state of Ohio. Master Thesis, University of Toledo, Toledo, OH, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, K.; Ver Hoef, J.M.; Krivoruchko, K.; Lucas, N. Using ArcGIS Geostatistical Analyst; Redlands ESRI: Redlands, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Behera, S.K.; Shukla, A.K. Spatial distribution of surface soil acidity, electrical conductivity, soil organic carbon content and exchangeable potassium, calcium and magnesium in some cropped acid soils of India. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, J.; McBratney, A.B. A review of the contamination of soil with lead II. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of soil lead. Environ. Int. 2001, 27, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlins, B.G.; Lark, R.M.; Webster, R.; O’Donnell, K.E. The use of soil survey data to determine the magnitude and extent of historic metal deposition related to atmospheric smelter emissions across Humberside, UK. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 143, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, S.; Scheifler, R.; Benslama, M.; Crini, N.; Lucot, E.; Brahmia, Z.; Benyacoub, S.; Giraudoux, P. Spatial distribution of heavy metal concentrations in urban, suburban and agricultural soils in a Mediterranean city of Algeria. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2294–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, A.M.; Christensen, S.; Simmelsgaard, S.E. Spatial correlation between weed species densities and soil properties. Weed Res. 2002, 42, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaoyang, W.E.I.; Cheng, W.A.N.G.; Linsheng, Y.A.N.G. Characterizing spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in the soils from mining-smelting activities in Shuikoushan, Hunan Province, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Wei, C.Y. Multivariate and spatial analysis of heavy metal sources and variations in a large old antimony mine, China. J. Soil Sediments 2013, 13, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Gaucin, D.; Mejía Sáenz, E.; Palacios Vélez, E.; Rendón Pimentel, L.; Exebio García, A. Modelo de optimización de recursos para un distrito de riego. Terra Latinoamericana 2009, 27, 219–226. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre-Grijalva, E. Estudio de Factibilidad Técnica y Económica de 3 Métodos de Tecnificación del Riego en el Modulo 07 del Distrito 005. Master Thesis, Instituto Tecnológico de la Construcción, Chihuahua, Mexico, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega-Gaucin, D. Reglas de operación para el sistema de presas del Distrito de Riego 005 Delicias, Chihuahua, México. Ing. Agric. Biosist. 2012, 4, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SSA (Secretaría de Salud) 1993. NOM-014-SSA1. Procedimientos Sanitarios para el Muestreo de Agua para Uso y Consumo Humano en Sistemas de Abastecimiento de Agua Públicos y Privados. Available online: http://www.salud.gob.mx/unidades/cdi/nom/014ssa13.html (accessed on 15 May 2017).
- SCFI (Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial) 2001. NMX-AA-051-SCFI. Análisis de Agua Medición de Metales por Absorción Atómica en Aguas Naturales, Potables, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas—Método de Prueba. Available online: http://www.economia-nmx.gob.mx/normas/nmx/2010/nmx-aa-051-scfi-2016.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2017).
- Jothivenkatachalam, K.; Nithya, A.; Chandra, M.S. Correlation analysis of drinking water quality in and around Perur block of Coimbatore District, Tamil Nadu, India. Rasayan J. Chem. 2010, 3, 649–654. [Google Scholar]
- SAS (Statistical Analysis Software) Institute. SAS Software; Version 9.1.3; SAS Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Simeonov, V.; Stratis, J.A.; Samara, C.; Zachariadis, G.; Voutsa, D.; Anthemidis, A. Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4119–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T. Principal Component Analysis, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Charlottesville, VA, USA, 2002; pp. 150–166. ISBN 978-0-387-22440-4. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, M. Multivariate methods. In Analytical Chemistry; Kellner, R., Mermet, J.M., Otto, M., Widmer, H.M., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1998; p. 916. ISBN 3-527-28881-3. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, S.; Kazama, F. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji River Basin, Japan. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, J.E., Jr. An enhanced cluster analysis program with bootstrap significance testing for ecological community analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2003, 18, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.H., Jr. Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, B.K.; Davis, J.M.; Bloomfield, P. An automated classification scheme designed to better elucidate the dependence of ozone on meteorology. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 1182–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, H.T. Applied Multivariate Analysis, 1st ed.; Springer: Board, NY, USA, 2002; p. 532. ISBN 0-387-95347-7. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, H.; Turan, N.A. Estimation of spatial distribution of heavy metals in groundwater using interpolation methods and multivariate statistical techniques; its suitability for drinking and irrigation purposes in the Middle Black Sea Region of Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishaku, J.M.; Ankidawa, B.A.; Pwalas, A.J.D. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques, in Dashen Area, North Eastern Nigeria. Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.A. Sistemas y Análisis de la Información Geográfica. Manual de Autoaprendizaje con ArcGIS, 2nd ed.; Ra-Ma: Madrid, Spain, 2008; p. 908. ISBN 978-84-7897-838-0. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- CONAGUA (Comisión Nacional del Agua) 2017. Ley Federal de Derechos Disposiciones Aplicables en Materia de Aguas Nacionales. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/105138/Ley_Federal_de_Derechos.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2017).
- Gebreyohannes, F.; Gebrekidan, A.; Hedera, A.; Estifanos, S. Investigations of physico-chemical parameters and its pollution implications of Elala River, Mekelle, Tigray, Ethiopia. Momona Ethiop. J. Sci. 2015, 7, 240–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, C.; Thyne, G.D.; McCray, J.E.; Turner, K.A. Evaluation of graphical and multivariate statistical methods for classification of water chemistry data. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, A.; Xu, Y.; Ma, R.; Wei, W.; Liu, M. Heavy Metals in Surface Soils in the Upper Reaches of the Heihe River, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Feng, L. Multivariate and geostatistical analyzes of metals in urban soil of Weinan industrial areas, Northwest of China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 47, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Martos, F.; Jiménez-Espinosa, R.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Mapping groundwater quality variables using PCA and geostatistics: A case study of Bajo Andarax, Southeastern Spain. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2001, 46, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-W.; Lin, K.-H.; Kuo, Y.-M. Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Sci. Total. Environ. 2003, 313, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapagain, S.K.; Pandey, V.P.; Shrestha, S.; Nakamura, T.; Kazama, F. Assessment of deep groundwater quality in Kathmandu Valley using multivariate statistical techniques. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 210, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhiri, L.; Boudoukha, A.; Mouni, L. A multivariate statistical analysis of groundwater chemistry data. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2011, 5, 537–544. [Google Scholar]
- Yidana, S.M.; Banoeng-Yakubo, B.; Akabzaa, T.M. Analysis of groundwater quality using multivariate and spatial analyses in the Keta basin, Ghana. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2010, 58, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonte, M.; van Breukelen, B.M.; Stuyfzand, P.J. Temperature-induced impacts on groundwater quality and arsenic mobility in anoxic aquifer sediments used for both drinking water and shallow geothermal energy production. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5088–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, A.; Wang, J.; Qin, X.; Wang, K.; Han, P.; Zhang, S. Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and origin of heavy metals in the agricultural soils in Shunyi, Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 425, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mueller, U.A.; Grunsky, E.C. Multivariate spatial analysis of lake sediment geochemical data; Melville Peninsula, Nunavut, Canada. Appl. Geochem. 2016, 75, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, J.A.; Faz, A.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Zornoza, R.; Carmona, D.M.; Kabas, S. Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to evaluate heavy metals behavior in mine sites for future reclamation. J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 109, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kolsi, S.H.; Bouri, S.; Hachicha, W.; Dhia, H.B. Implementation and evaluation of multivariate analysis for groundwater hydrochemistry assessment in arid environments: A case study of Hajeb Elyoun–Jelma, Central Tunisia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas Alves, S.M.; de Queiroz, D.M.; de Alcântara, G.R.; dos Reis, E.F. Spatial Variability of Physical and Chemical Attributes of Soil Using Techniques of Principal Component Analysis. Biosci. J. 2014, 30, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, H.; Olson, J.R.; Bian, L.; Rogerson, P.A. Analysis of heavy metal sources in soil using kriging interpolation on principal components. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4999–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

 ), bold numbers denote the module number.
), bold numbers denote the module number.
 ), bold numbers denote the module number.
), bold numbers denote the module number.

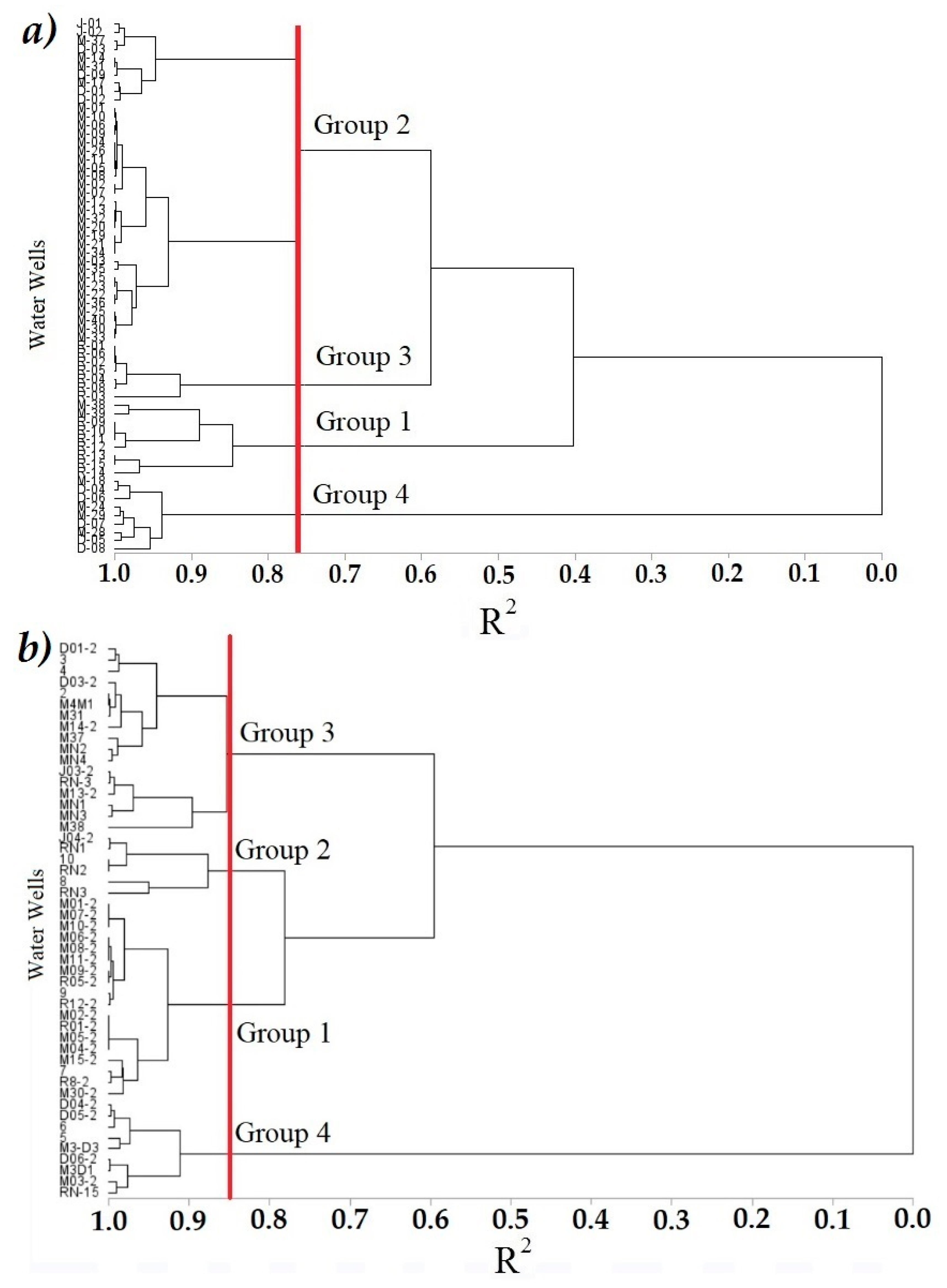
 ), Group 4 (▲), bold numbers denote the module number.
), Group 4 (▲), bold numbers denote the module number.
 ), Group 4 (▲), bold numbers denote the module number.
), Group 4 (▲), bold numbers denote the module number.



| Parameter | Unit | Analytical Method |
|---|---|---|
| As | mg/L | AAS Perkin Elmer Aanalist 700, coupled HG FIAS 100 |
| Temp | °C | Potentiometer Hanna portable (in situ) |
| EC | µS/cm | Electrical conductivity meter CYBERSCAN |
| ORP | mV | Potentiometer Hanna portable (in situ) |
| Hardness | mg/L | Titration net NET (indicator) |
| pH | dimensionless | Potentiometer Hanna portable (in situ) |
| TDS | mg/L | Electrical conductivity meter CYBERSCAN |
| Turb | NTU | Electrical conductivity meter CYBERSCAN |
| Parameter | Concentration Range S1 | Concentration Range S2 | MPL | Normative | Above MPL S1 (%) | Above MPL S2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As (mg/L) | ND–0.338 | ND–0.576 | 0.100 | [67] | 9 | 13 |
| Temp (°C) | 22.1–30.1 | 22.8–27.5 | - | Without regulation | - | - |
| EC (μS/cm) | 13.8–1981.6 | 553.6–2600 | - | Without regulation | - | - |
| ORP (mV) | 85.6–267.7 | 98.1–306.3 | - | Without regulation | - | - |
| Hardness (mg/L) | 13.3–814 | 0–611 | 500 | [52] | 9 | 5 |
| pH | 7.5–9.6 | 7.3–9.0 | 6.0–9.0 | [67] | 1.5 | 0 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 0–990 | 0–932.3 | 500 | [67] | 35 | 39 |
| Turb (NTU) | 0–1000 | 0.2–519 | 10 | [67] | 29 | 12 |
| As | EC | TDS | Turb | Hardness | pH | ORP | Temp | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 1.00 | |||||||
| EC | 0.07 | 1.00 | ||||||
| TDS | −0.17 | 0.625 ** | 1.00 | |||||
| Turb | 0.42 | −0.01 | −0.452 ** | 1.00 | ||||
| Hardness | −0.477 ** | 0.493 ** | 0.586 ** | −0.23 | 1.00 | |||
| pH | 0.441 * | 0.08 | −0.04 | 0.17 | −0.348 * | 1.00 | ||
| ORP | −0.092 * | −0.44 | −0.17 | −0.18 | −0.09 | −0.398 * | 1.00 | |
| Temp | 0.389 * | 0.327 * | 0.23 | 0.13 | −0.17 | 0.827 ** | −0.462 * | 1.00 |
| As | EC | TDS | Turb | Hardness | pH | ORP | Temp | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 1 | |||||||
| EC | −0.02 | 1 | ||||||
| TDS | 0.08 | 0.89 ** | 1 | |||||
| Turb | −0.14 | −0.2 | −0.55 ** | 1 | ||||
| Hardness | −0.46 * | 0.54 ** | 0.45 * | −0.15 | 1 | |||
| pH | 0.77 ** | −0.14 | −0.03 | −0.07 | −0.60 ** | 1 | ||
| ORP | 0.03 | −0.33 * | −0.41 * | 0.32 * | −0.13 | −0.04 | 1 | |
| Temp | −0.25 | −0.19 | −0.06 | −0.21 | 0.04 | −0.29 * | −0.04 | 1 |
| PhP | S1 | S2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | |
| As | 0.441 | −0.11 | 0.108 | 0.661 | −0.22 | 0.56 | 0.00 | 0.24 |
| EC | 0.066 | 0.533 | 0.312 | 0.261 | 0.49 | 0.21 | 0.31 | 0.07 |
| TDS | −0.13 | 0.544 | −0.19 | 0.318 | 0.50 | 0.32 | 0.03 | 0.17 |
| Turb | 0.305 | −0.19 | 0.727 | 0.011 | −0.28 | −0.27 | 0.53 | −0.31 |
| Hardness | −0.33 | 0.424 | 0.263 | −0.03 | 0.47 | −0.23 | 0.20 | 0.16 |
| pH | 0.518 | 0.1 | −0.34 | −0.16 | −0.28 | 0.55 | −0.02 | −0.03 |
| ORP | −0.29 | −0.33 | −0.26 | 0.604 | −0.29 | −0.22 | 0.26 | 0.87 |
| Temp | 0.48 | 0.271 | −0.27 | −0.04 | 0.06 | −0.26 | −0.72 | 0.17 |
| Eigenvalue | 2.708 | 2.473 | 1.031 | 0.757 | 2.8 | 2.15 | 1.24 | 0.75 |
| Variability | 0.338 | 0.309 | 0.128 | 0.094 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 0.09 |
| Cumulative | 0.338 | 0.647 | 0.776 | 0.871 | 0.35 | 0.62 | 0.77 | 0.86 |
| G | S1 | S2 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | EC | TDS | Turb | Hardness | pH | ORP | Temp | As | EC | TDS | Turb | Hardness | pH | ORP | Temp | |
| 1 | 0.098 | 1117.65 | 93.84 | 687.63 | 144.34 | 8.21 | 150.29 | 25.25 | 0.017 | 686.111 | 344.552 | 8.182 | 196.074 | 7.701 | 231.456 | 24.796 |
| 2 | 0.035 | 832.62 | 415.06 | 3.89 | 208.06 | 7.98 | 208.57 | 24.42 | 0.005 | 768.717 | 78.938 | 382.933 | 164.533 | 7.665 | 270.156 | 23.856 |
| 3 | 0.014 | 15.25 | 185.71 | 295.56 | 207.03 | 7.53 | 230.08 | 22.59 | 0.106 | 1102.486 | 563.371 | 5.753 | 157.647 | 8.024 | 210.418 | 24.170 |
| 4 | 0.008 | 1773.36 | 883.91 | 38.01 | 497.41 | 7.77 | 138.66 | 25.07 | 0.005 | 1779.137 | 885.278 | 5.228 | 384.678 | 7.525 | 195.219 | 24.203 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prieto-Amparán, J.A.; Rocha-Gutiérrez, B.A.; Ballinas-Casarrubias, M.D.L.; Valles-Aragón, M.C.; Peralta-Pérez, M.D.R.; Pinedo-Alvarez, A. Multivariate and Spatial Analysis of Physicochemical Parameters in an Irrigation District, Chihuahua, Mexico. Water 2018, 10, 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081037
Prieto-Amparán JA, Rocha-Gutiérrez BA, Ballinas-Casarrubias MDL, Valles-Aragón MC, Peralta-Pérez MDR, Pinedo-Alvarez A. Multivariate and Spatial Analysis of Physicochemical Parameters in an Irrigation District, Chihuahua, Mexico. Water. 2018; 10(8):1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081037
Chicago/Turabian StylePrieto-Amparán, Jesús Alejandro, Beatriz Adriana Rocha-Gutiérrez, María De Lourdes Ballinas-Casarrubias, María Cecilia Valles-Aragón, María Del Rosario Peralta-Pérez, and Alfredo Pinedo-Alvarez. 2018. "Multivariate and Spatial Analysis of Physicochemical Parameters in an Irrigation District, Chihuahua, Mexico" Water 10, no. 8: 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081037
APA StylePrieto-Amparán, J. A., Rocha-Gutiérrez, B. A., Ballinas-Casarrubias, M. D. L., Valles-Aragón, M. C., Peralta-Pérez, M. D. R., & Pinedo-Alvarez, A. (2018). Multivariate and Spatial Analysis of Physicochemical Parameters in an Irrigation District, Chihuahua, Mexico. Water, 10(8), 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081037