Contamination Profiles of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Groundwater in the Alluvial–Pluvial Plain of Hutuo River, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
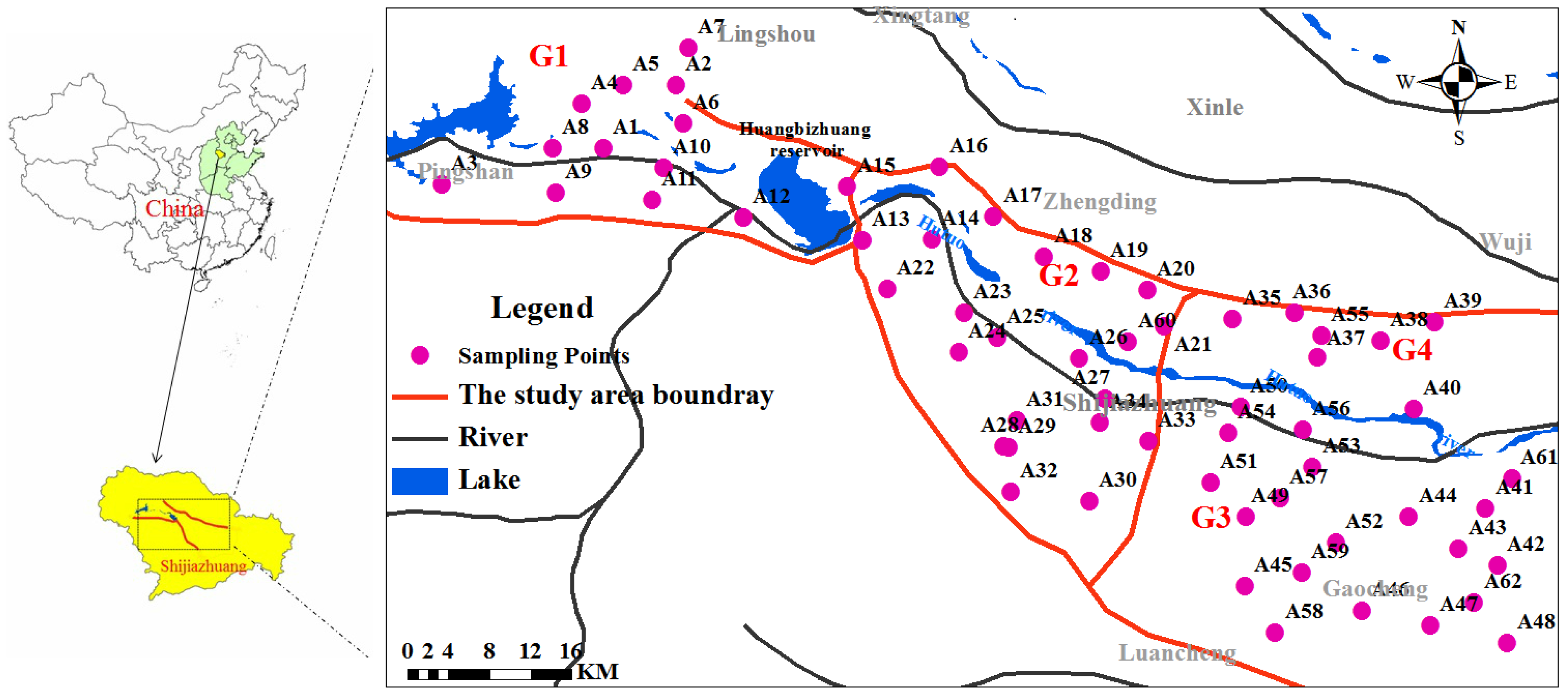
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Chemicals and Reagents
2.4. Extraction and Analysis
2.5. Quality Assurance and Control
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Properties of Groundwater
3.2. Occurrence of PFAS in Groundwater
3.3. Effects of Groundwater Hydrological Conditions on PFAS Distribution
3.4. Compositional Profiles of PFAS and Source Identification
4. Conclusions
- (1)
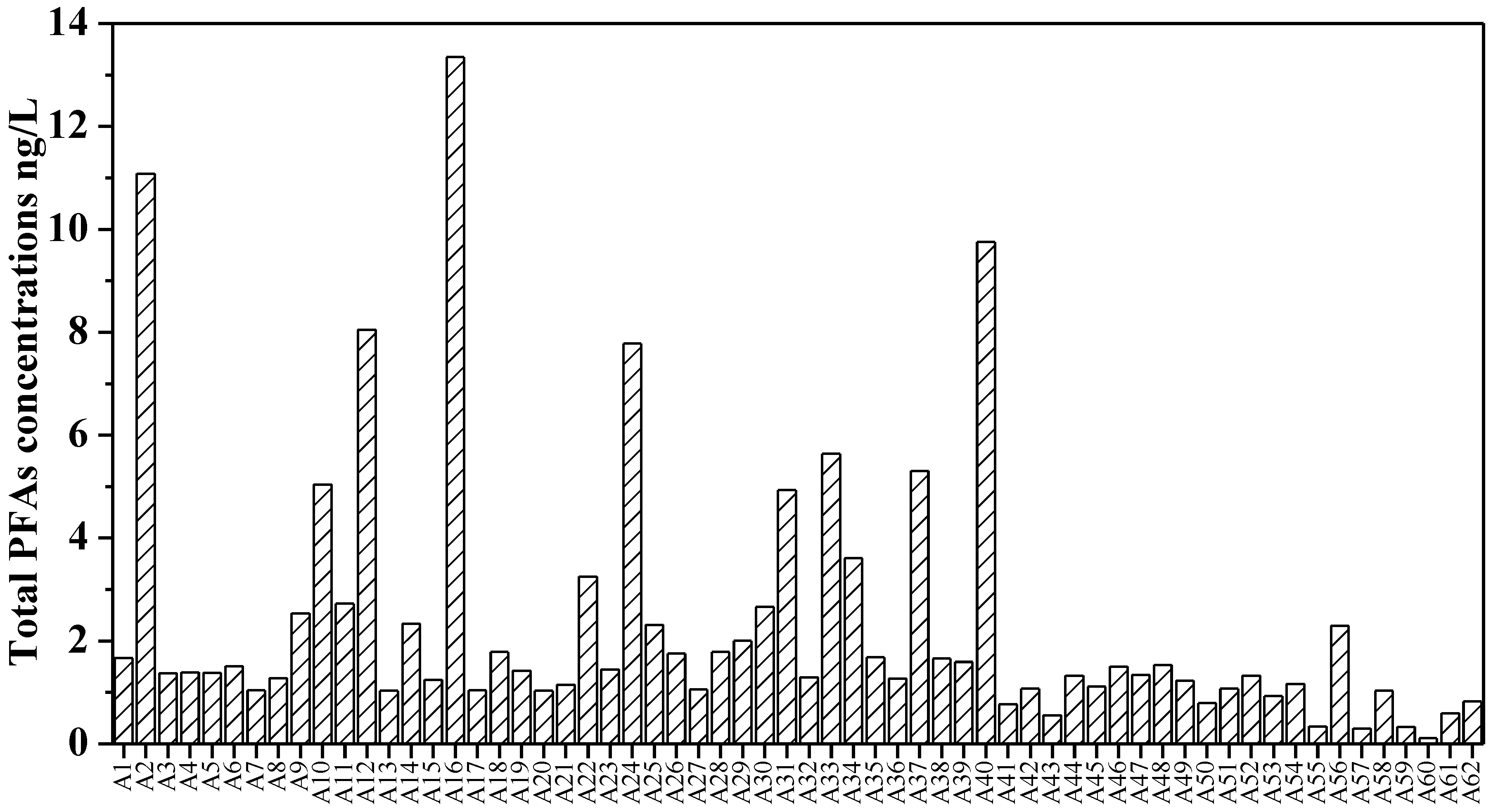
- The ∑PFAS ranged from 0.56 to 13.34 ng/L, and the PFOA and PFHxA were dominant PFAS contaminants with high detection frequencies of 98.39% and 95.16%, respectively. Generally, the concentrations of PFAS in groundwater in NCP are not very high compared to previous reports in other areas in China [48]. Compared to other regions worldwide, the PFAS contamination levels in this study were in the range of slightly to moderately impacted [31,45].
- (2)
- The distribution of PFAS in the study area was affected by the hydrogeological conditions. The average concentrations of PFAS were the highest in the Fissure and pore water unit in the valley in Gangnan Reservoir and Huangbizhuang Reservoir (G1), followed by Pore water unit in the top APPHR (G2), Shallow pore water unit in the middle APPHR (G3), and Deep pore water unit in the middle APPHR (G4).
- (3)
- Principal component analysis suggested that the short-chained PFAS (C4–C7) had the same pollution sources as the long-chained PFAS (C8–C10), and removing long-chain PFAS from water during the infiltration process is adsorbed by soil and rock. Spearman correlation analysis further indicated that the precursors’ biodegradation might have an important contribution to the presence of PFOA and PFNA.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Higgins, C.P.; Field, J.A.; Criddle, C.S.; Luthy, R.G. Quantitative determination of perfluorochemicals in sediments and domestic sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3946. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joyce Dinglasan-Panlilio, M.; Prakash, S.S.; Baker, J.E. Perfluorinated compounds in the surface waters of Puget Sound, Washington and Clayoquot and Barkley Sounds, British Columbia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 78, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemine, S.; Matsumura, C.; Yamamoto, K.; Suzuki, M.; Tsurukawa, M.; Imaishi, H.; Nakano, T.; Kondo, A. Discharge of perfluorinated compounds from rivers and their influence on the coastal seas of Hyogo prefecture, Japan. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beskoski, V.P.; Takemine, S.; Nakano, T.; Slavkovic Beskoski, L.; Gojgic-Cvijovic, G.; Ilic, M.; Miletic, S.; Vrvic, M.M. Perfluorinated compounds in sediment samples from the wastewater canal of Pancevo (Serbia) industrial area. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhu, L.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Distribution and desorption of perfluorinated compounds in fractionated sediments. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, L.L.; Snyder, B.D.; Olsen, A.R.; Kincaid, T.M.; Wathen, J.B.; McCarty, H.B. Perfluorinated compounds in fish from U.S. urban rivers and the Great Lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, C.; D’Hollander, W.; Roosens, L.; Covaci, A.; Smolders, R.; Van Den Heuvel, R.; Govarts, E.; Van Campenhout, K.; Reynders, H.; Bervoets, L. First assessment of population exposure to perfluorinated compounds in Flanders, Belgium. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, J.L. Health risks of dietary exposure to perfluorinated compounds. Environ. Int. 2012, 40, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerregaard-Olesen, C.; Bach, C.C.; Long, M.; Ghisari, M.; Bossi, R.; Bech, B.H.; Nohr, E.A.; Henriksen, T.B.; Olsen, J.; Bonefeld-Jorgensen, E.C. Time trends of perfluorinated alkyl acids in serum from Danish pregnant women 2008–2013. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.M.; Bennett, D.H.; Calafat, A.M.; Kato, K.; Strynar, M.; Andersen, E.; Moran, R.E.; Tancredi, D.J.; Tulve, N.S.; Hertz-Picciotto, I. Serum concentrations of perfluorinated compounds (PFC) among selected populations of children and adults in California. Environ. Res. 2015, 136, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Kang, Q.; Peng, H.; Ding, M.; Zhao, F.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, M.; Tao, S.; et al. Relationship between perfluorooctanoate and perfluorooctane sulfonate blood concentrations in the general population and routine drinking water exposure. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Perfluoroalkyls—Draft for Public Comment; States Environmental Protection Agency: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Drinking Water Health Advisory for Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA); United States Environmental Protection Agency: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2016; EPA 822-R-16-005.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Drinking Water Health Advisory for Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS); United States Environmental Protection Agency: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2016; EPA 822-R-16-002.
- Grandjean, P.; Clapp, R. Changing interpretation of human health risks from perfluorinated compounds. Public Heal. Rep. 2014, 129, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Toxicology Program. Bioassay of o-anisidine hydrochloride for possible carcinogenicity. Natl. Cancer Inst. Carcinog. Tech. Rep. 1978, 89, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Boone, J.S.; Vigo, C.; Boone, T.; Byrne, C.; Ferrario, J.; Benson, R.; Donohue, J.; Simmons, J.E.; Kolpin, D.W.; Furlong, E.T. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in source and treated drinking waters of the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingelido, A.M.; Abballe, A.; Gemma, S.; Dellatte, E.; Iacovella, N.; Angelis, G.D.; Zampaglioni, F.; Marra, V.; Miniero, R.; Valentini, S. Biomonitoring of perfluorinated compounds in adults exposed to contaminated drinking water in the Veneto Region, Italy. Environ. Int. 2018, 110, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boiteux, V.; Dauchy, X.; Bach, C.; Colin, A.; Hemard, J.; Sagres, V.; Rosin, C.; Munoz, J.F. Concentrations and patterns of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in a river and three drinking water treatment plants near and far from a major production source. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboré, H.A.; Vo, D.S.; Munoz, G.; Méité, L.; Desrosiers, M.; Liu, J.; Sory, T.K.; Sauvé, S. Worldwide drinking water occurrence and levels of newly-identified perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimeddulam, D.; Wu, K.Y. River water contaminated with perfluorinated compounds potentially posing the greatest risk to young children. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalsager, L.; Christensen, N.; Husby, S.; Kyhl, H.; Nielsen, F.; Høst, A.; Grandjean, P.; Jensen, T.K. Association between prenatal exposure to perfluorinated compounds and symptoms of infections at age 1–4 years among 359 children in the Odense Child Cohort. Environ. Int. 2016, 96, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supreeyasunthorn, P.; Boontanon, S.K.; Boontanon, N. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) contamination from textiles. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2016, 51, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.; Auounsson, G.A.; Benford, D. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS), perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and their salts. Scientific opinion of the panel on contaminants in the food chain. EFSA J. 2008, 6, 1–131. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO | Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Post, G.B.; Louis, J.B.; Cooper, K.R.; Boros-Russo, B.J.; Lippincott, R.L. Occurrence and potential significance of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) detected in New Jersey public drinking water systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Edition of the Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Fact Sheet PFOA & PFOS Drinking Water Health Advisories; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; EPA 800-F-16-003.
- Schaider, L.A.; Rudel, R.A.; Ackerman, J.M.; Dunagan, S.C.; Brody, J.G. Pharmaceuticals, perfluorosurfactants, and other organic wastewater compounds in public drinking water wells in a shallow sand and gravel aquifer. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, M.; Bergmann, S.; Dieter, H.H. Occurrence of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in drinking water of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany and new approach to assess drinking water contamination by shorter-chained C4–C7 PFCs. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2010, 213, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jiao, X.C.; Gai, N.; Li, X.J.; Wang, X.C.; Lu, G.H.; Piao, H.T.; Rao, Z.; Yang, Y.L. Perfluorinated compounds in soil, surface water, and groundwater from rural areas in eastern China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 211, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, B.; Hu, H.; Zhang, T.; Yamazaki, E.; Taniyasu, S.; Yamashita, N.; Sun, H. Distribution and primary source analysis of per-and poly-fluoroalkyl substances with different chain lengths in surface and groundwater in two cities, North China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 108, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.; Guo, H.; Zhan, Y. Groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and processes along flow paths in the North China Plain. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 70–71, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Wang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Ma, T.; Zhang, D.; Zhan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, Y.; Wang, S. Iodine in groundwater of the North China Plain: Spatial patterns and hydrogeochemical processes of enrichment. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 135, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, Y.; Chen, H.; Qian, Y.; Dun, Y. Investigation of quality and pollution characteristics of groundwater in the Hutuo River Alluvial Plain, North China Plain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.E.; Chen, J.; Qian, Y. Assessment of deep groundwater over-exploitation in the North China Plain. Geosci. Front. 2011, 2, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, H.T.; Jiao, J.J.; Liu, K.; Guo, H.; Yang, S. Geochemical signature of pore water from core samples and its implications on the origin of saline pore water in Cangzhou, North China Plain. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 157, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C. NO and N2O emissions from agricultural fields in the North China Plain: Origination and mitigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551–552, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakhem, B.A.; Hafez, R. Hydrochemical, isotopic and statistical characteristics of groundwater nitrate pollution in Damascus Oasis (Syria). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 2781–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Geng, M.; Bao, Z. Pollution levels and risk assessment of BHT and TEP in groundwater in alluvial-pluvial fan of Hutuo River, Shijiazhuang City. Resea Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 49–54, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Khim, J.S.; Chen, C.; Naile, J.E.; Lu, Y.; Kannan, K.; Park, J.; Luo, W.; Jiao, W.; Hu, W.; et al. Perfluorinated compounds in surface waters from Northern China: Comparison to level of industrialization. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, M.K.; Taniyasu, S.; Yamashita, N.; Giesy, J.P.; Zheng, J.; Fang, Z.; Im, S.H.; Lam, P.K.S. Perfluorinated compounds in coastal waters of Hong Kong, South China, and Korea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4056–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Jiao, X.C.; Gai, N.; Li, X.J.; Wang, X.C.; Lu, G.H.; Piao, H.T.; Rao, Z.; Yang, Y.L. Perfluorinated compounds in soil, surface water, and groundwater from rural areas in eastern China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 211, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierke, L.; Möller, A.; Klitzke, S. Transport of perfluoroalkyl acids in a water-saturated sediment column investigated under near-natural conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 186, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, G.; Labadie, P.; Botta, F.; Lestremau, F.; Lopez, B.; Geneste, E.; Pardon, P.; Dévier, M.H.; Budzinski, H. Occurrence survey and spatial distribution of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl surfactants in groundwater, surface water, and sediments from tropical environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michio, M.; Hiroyuki, S.; Hideshige, T. Evaluation of wastewater and street runoff as sources of perfluorinated surfactants (PFSs). Chemosphere 2009, 74, 487–493. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.; Simcik, M.F.; Halbach, T.R.; Gulliver, J.S. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in soils and groundwater of a U.S. metropolitan area: Migration and implications for human exposure. Water Res. 2015, 72, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Song, L.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Ma, H.; Cai, M.; Codling, G.; Ebinghaus, R.; et al. Occurrence and trends in concentrations of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in surface waters of eastern China. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Wu, M.; Tang, L.; Li, J.; Qian, Z.; Han, T.; Xu, G. Perfluorinated compounds in surface waters of Shanghai, China: Source analysis and risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 149, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



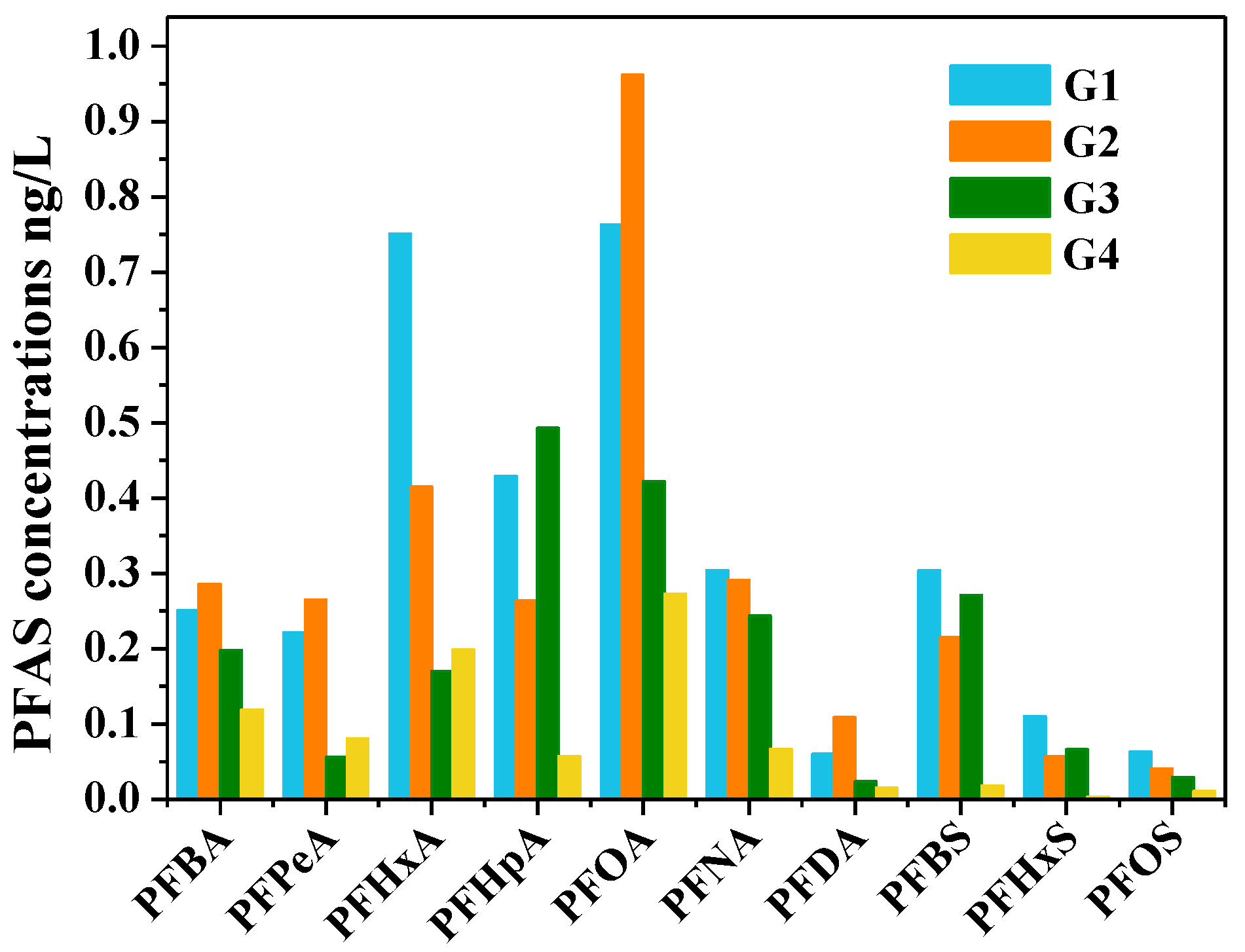
| PFBA | PFPeA | PFHxA | PFHpA | PFOA | PFNA | PFDA | PFBS | PFHxS | PFOS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFBA | 1 | |||||||||
| PFPeA | 0.028 | 1 | ||||||||
| PFHxA | 0.145 | 0.603 ** | 1 | |||||||
| PFHpA | −0.051 | 0.291 * | 0.414 ** | 1 | ||||||
| PFOA | 0.106 | 0.475 ** | 0.525 ** | 0.354 * | 1 | |||||
| PFNA | 0.267 * | 0.162 | 0.491 ** | 0.382 ** | 0.512 ** | 1 | ||||
| PFDA | −0.023 | 0.215 | 0.510 ** | 0.275 * | 0.189 | 0.669 ** | 1 | |||
| PFBS | 0.051 | 0.024 | 0.100 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.070 | 0.126 | 1 | ||
| PFHxS | 0.204 | 0.178 | 0.371 | 0.223 | 0.161 | 0.362 | 0.130 | 0.418 | 1 | |
| PFOS | −0.021 | 0.163 | 0.441 | 0.523 | 0.095 | 0.613 | 0.818 | 0.075 | 0.382 | 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Qiao, X.; Hao, S.; Lu, J.; Duan, X.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Zheng, B. Contamination Profiles of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Groundwater in the Alluvial–Pluvial Plain of Hutuo River, China. Water 2019, 11, 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112316
Liu Y, Li X, Wang X, Qiao X, Hao S, Lu J, Duan X, Dionysiou DD, Zheng B. Contamination Profiles of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Groundwater in the Alluvial–Pluvial Plain of Hutuo River, China. Water. 2019; 11(11):2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112316
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yan, Xue Li, Xing Wang, Xiaocui Qiao, Shuran Hao, Jingrang Lu, Xiaodi Duan, Dionysios D. Dionysiou, and Binghui Zheng. 2019. "Contamination Profiles of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Groundwater in the Alluvial–Pluvial Plain of Hutuo River, China" Water 11, no. 11: 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112316
APA StyleLiu, Y., Li, X., Wang, X., Qiao, X., Hao, S., Lu, J., Duan, X., Dionysiou, D. D., & Zheng, B. (2019). Contamination Profiles of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Groundwater in the Alluvial–Pluvial Plain of Hutuo River, China. Water, 11(11), 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112316






_Dionysiou.jpg)

