The Effects of Land Use and Climate Change on the Water Yield of a Watershed in Colombia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
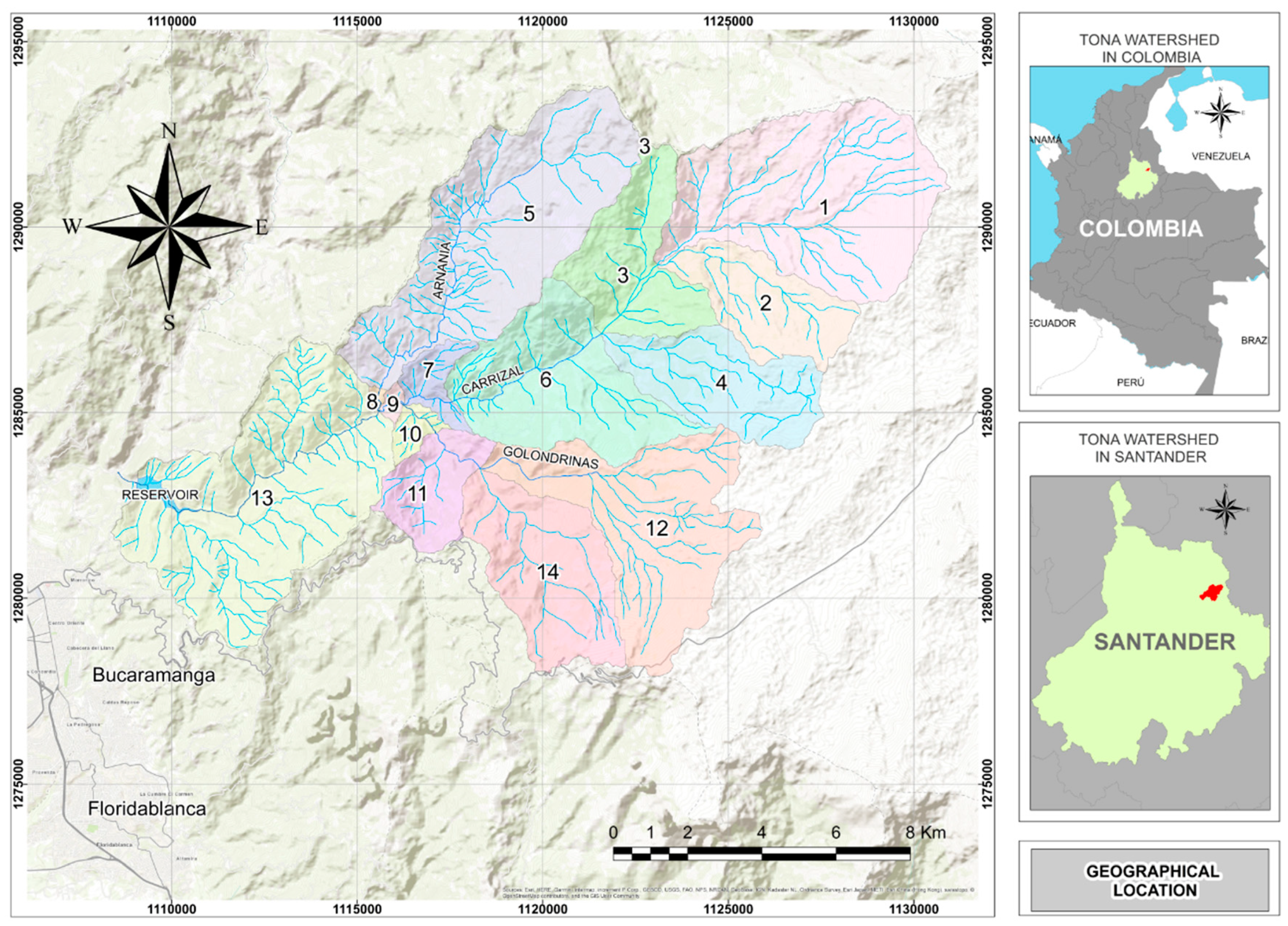
2.1. Study Site
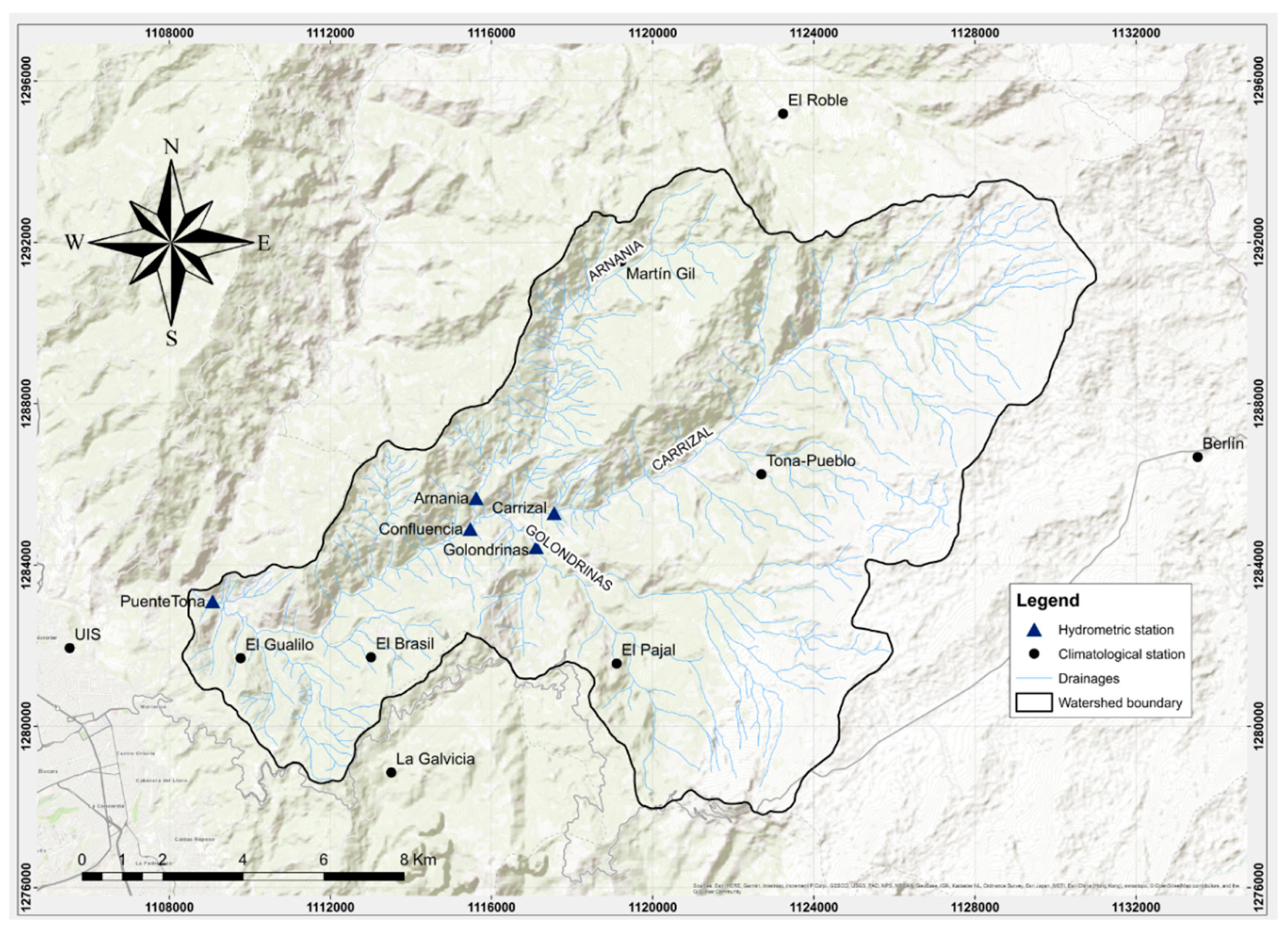
2.2. Data for the SWAT Model of the Tona Watershed
2.3. SWAT Model Setup for the Tona Watershed
2.4. Model Calibration and Validation
2.5. Future Scenarios
3. Results
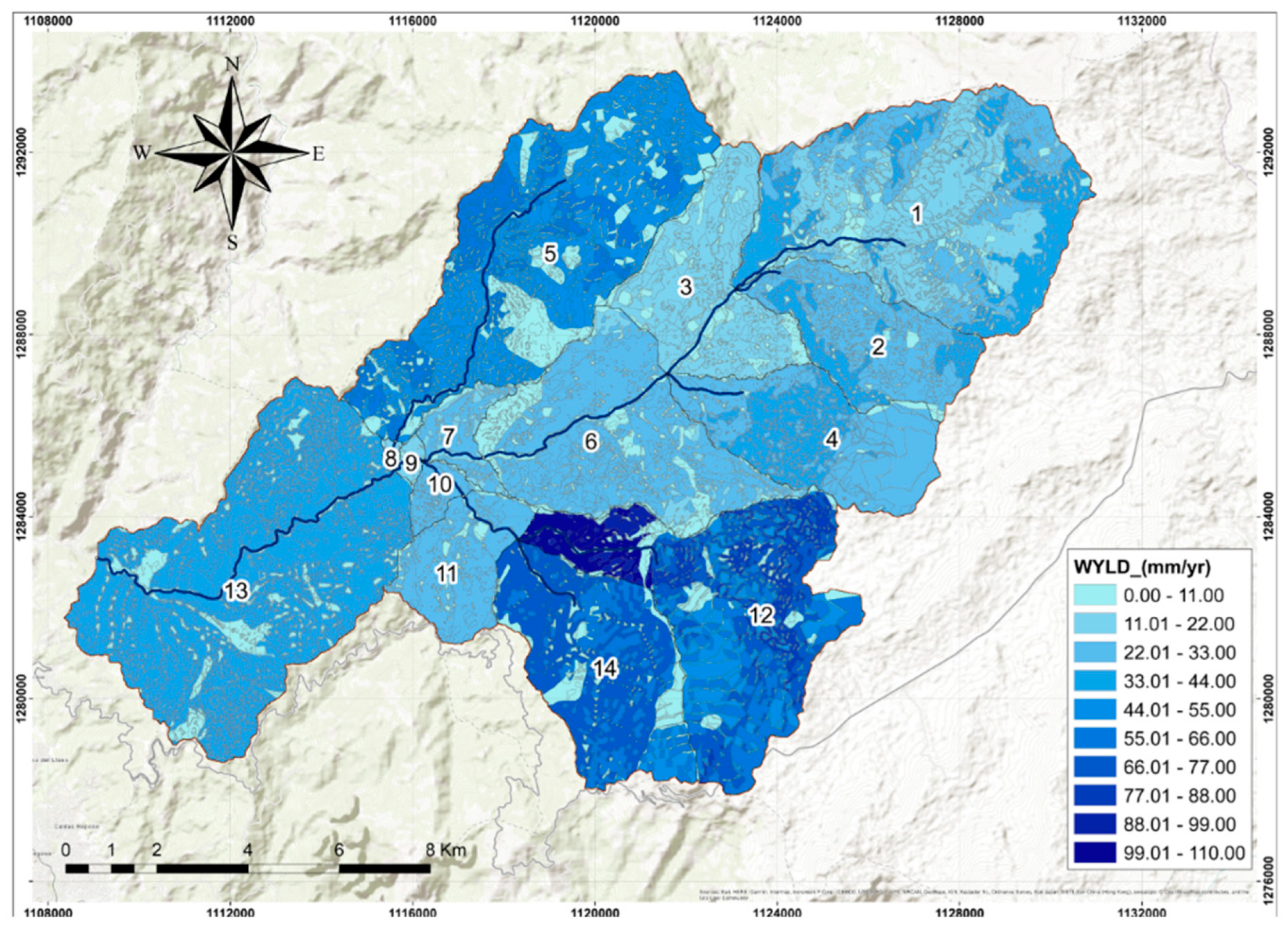
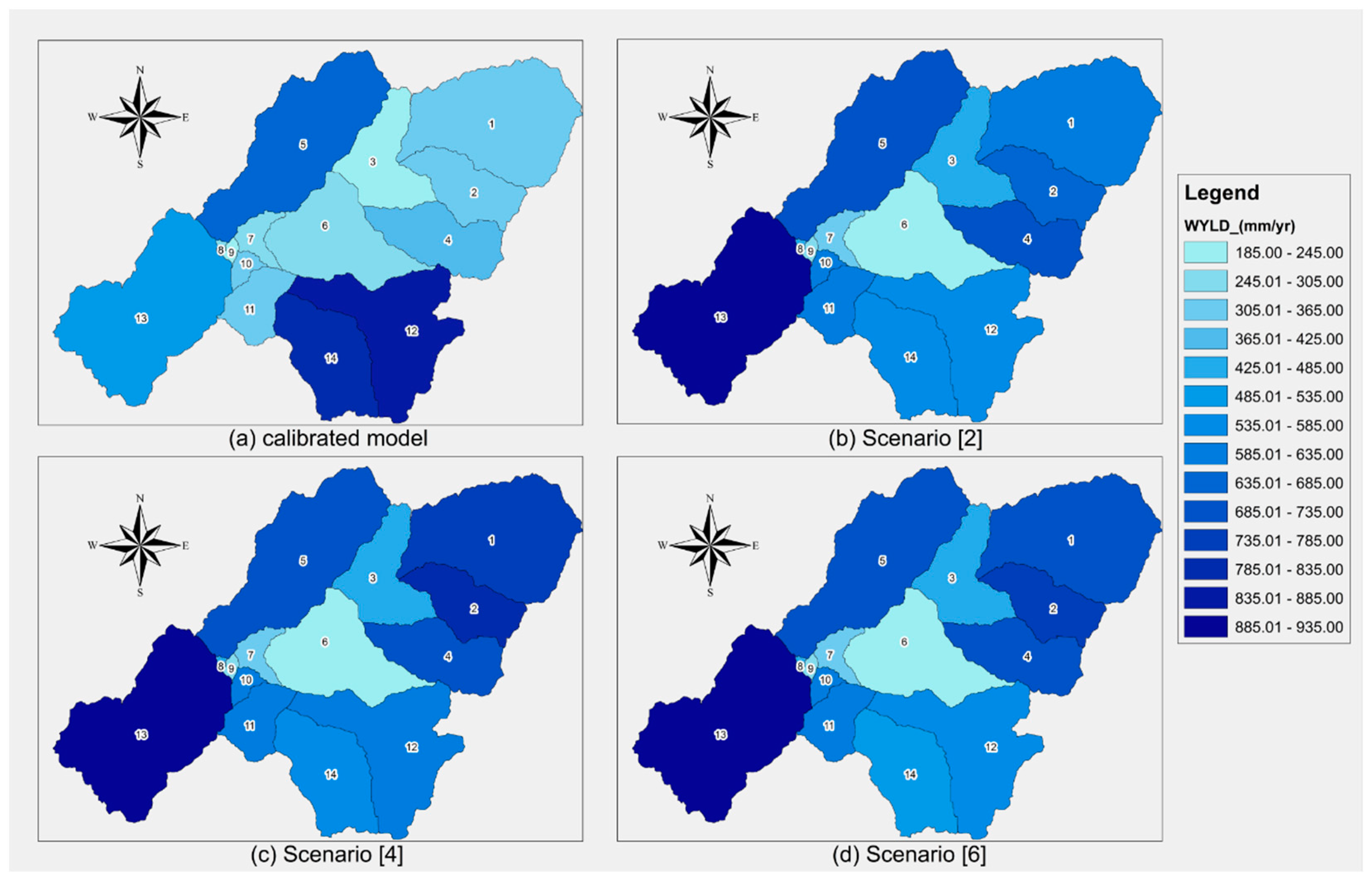
3.1. Water Yield for the Calibrated Model
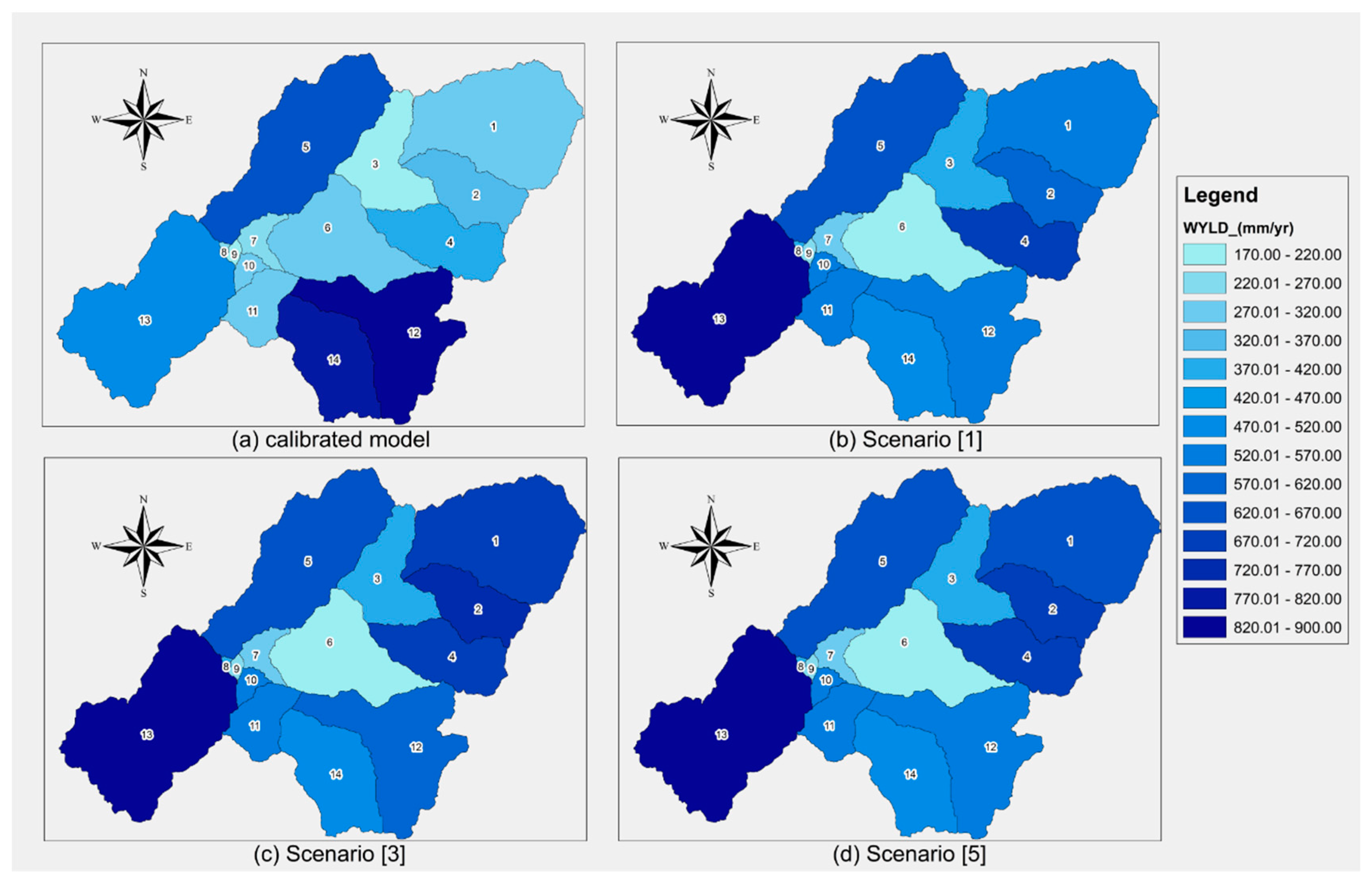
3.2. Water Yield for Future Scenarios
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Chapter 20 Watershed Yield. In National Engineering Handbook; Part 630; Volume Hydrology; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Lüke, A.; Hack, J. Comparing the Applicability of Commonly Used Hydrological Ecosystem Services Models for Integrated Decision-Support. Sustainability 2018, 10, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallis, H. Natural Capital: Theory and Practice of Mapping Ecosystem Services; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-0-19-958899-2. [Google Scholar]
- Guzha, A.C.; Rufino, M.C.; Okoth, S.; Jacobs, S.; Nóbrega, R.L.B. Impacts of land use and land cover change on surface runoff, discharge and low flows: Evidence from East Africa. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 15, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, N.; Harper, R.; Li, Q.; Liu, K.; Wei, X.; Ning, D.; Hou, Y.; Liu, S. A global review on hydrological responses to forest change across multiple spatial scales: Importance of scale, climate, forest type and hydrological regime. J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.C.P.; Macedo, M.N.; Costa, M.H.; Coe, M.T.; Neill, C. Effects of land cover change on evapotranspiration and streamflow of small catchments in the Upper Xingu River Basin, Central Brazil. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 4, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.; Futter, M.N.; Bishop, K. On the forest cover–water yield debate: From demand- to supply-side thinking. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 806–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, A.; Vanacker, V.; Balthazar, V.; Mora, D.; Govers, G. Complex land cover change, water and sediment yield in a degraded Andean environment. J. Hydrol. 2012, 472–473, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, C.; Lara, A.; McPhee, J.; Urrutia, R. Revealing the impact of forest exotic plantations on water yield in large scale watersheds in South-Central Chile. J. Hydrol. 2009, 374, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.E.; Jha, M.K.; Zhang, Y.-K.; Gassman, P.W.; Wolter, C.F. Impact of land use and land cover change on the water balance of a large agricultural watershed: Historical effects and future directions. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.E.; Zhang, L.; McMahon, T.A.; Western, A.W.; Vertessy, R.A. A review of paired catchment studies for determining changes in water yield resulting from alterations in vegetation. J. Hydrol. 2005, 310, 28–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, R.A.; Alfieri, L.; Bradshaw, C.; Caesar, J.; Feyen, L.; Friedlingstein, P.; Gohar, L.; Koutroulis, A.; Lewis, K.; Morfopoulos, C.; et al. Changes in climate extremes, fresh water availability and vulnerability to food insecurity projected at 1.5 °C and 2 °C global warming with a higher-resolution global climate model. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2018, 376, 20160452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysanova, V.; Hattermann, F.F. Intercomparison of climate change impacts in 12 large river basins: Overview of methods and summary of results. Clim. Chang. 2017, 141, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, G.; Wang, X.; Han, J.; Fan, Y. Impacts of future climate change on river discharge based on hydrological inference: A case study of the Grand River Watershed in Ontario, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548–549, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorribas, M.V.; Paiva, R.C.D.; Melack, J.M.; Bravo, J.M.; Jones, C.; Carvalho, L.; Beighley, E.; Forsberg, B.; Costa, M.H. Projections of climate change effects on discharge and inundation in the Amazon basin. Clim. Chang. 2016, 136, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.M.; Mendoza, K.; Daggupati, P.; Srinivasan, R.; Rosenberg, N.J.; Deb, D. High-Resolution Simulations of Decadal Climate Variability Impacts on Water Yield in the Missouri River Basin with the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT). J. Hydrometeor. 2015, 17, 2455–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Werners, S.E.; Ludwig, F.; Huang, H.Q. Hydrological response to climate change: The Pearl River, China under different RCP scenarios. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 4, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.; Deryng, D.; Müller, C.; Frieler, K.; Konzmann, M.; Gerten, D.; Glotter, M.; Flörke, M.; Wada, Y.; Best, N.; et al. Constraints and potentials of future irrigation water availability on agricultural production under climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3239–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, H.; Lawrence, D.; Lang, M.; Martinkova, M.; Kjeldsen, T.R. Review of trend analysis and climate change projections of extreme precipitation and floods in Europe. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 3634–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schewe, J.; Heinke, J.; Gerten, D.; Haddeland, I.; Arnell, N.W.; Clark, D.B.; Dankers, R.; Eisner, S.; Fekete, B.M.; Colón-González, F.J.; et al. Multimodel assessment of water scarcity under climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3245–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.; Chiew, F.; Fu, B. Understanding the impacts of climate and landuse change on water yield. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 33, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, P.V.; Miniat, C.F.; Elliott, K.J.; Swank, W.T.; Brantley, S.T.; Laseter, S.H. Declining water yield from forested mountain watersheds in response to climate change and forest mesophication. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 2997–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creed, I.F.; Spargo, A.T.; Jones, J.A.; Buttle, J.M.; Adams, M.B.; Beall, F.D.; Booth, E.G.; Campbell, J.L.; Clow, D.; Elder, K.; et al. Changing forest water yields in response to climate warming: Results from long-term experimental watershed sites across North America. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 3191–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Tian, H.; Friedrichs, M.A.M.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Yang, J. Hydrological Responses to Climate and Land-Use Changes along the North American East Coast: A 110-Year Historical Reconstruction. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 51, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; McNulty, S.G.; Myers, J.A.M.; Cohen, E.C. Impacts of Multiple Stresses on Water Demand and Supply Across the Southeastern United States1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2008, 44, 1441–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wei, X.; Chen, X.; Zhou, P.; Liu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, G.; Scott, D.F.; Zhou, S.; Han, L.; et al. Global pattern for the effect of climate and land cover on water yield. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roa-García, M.C.; Brown, S.; Schreier, H.; Lavkulich, L.M. The role of land use and soils in regulating water flow in small headwater catchments of the Andes. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohl, E.; Barros, A.; Brunsell, N.; Chappell, N.A.; Coe, M.; Giambelluca, T.; Goldsmith, S.; Harmon, R.; Hendrickx, J.M.H.; Juvik, J.; et al. The hydrology of the humid tropics. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtinho, F.; Tague, C.; de Bievre, B.; Eakin, H.; Lopez-Carr, D. Water Scarcity in the Andes: A Comparison of Local Perceptions and Observed Climate, Land Use and Socioeconomic Changes. Hum. Ecol. 2013, 41, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merwade, V.; Baffaut, C.; Bieger, K.; Boithias, L.; Rathjens, H. Featured Series Introduction: SWAT Applications for Emerging Hydrologic and Water Quality Challenges. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 53, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Griensven, A.; Ndomba, P.; Yalew, S.; Kilonzo, F. Critical review of SWAT applications in the upper Nile basin countries. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3371–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysanova, V.; Arnold, J.G. Advances in ecohydrological modelling with SWAT—A review. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassman, P.W.; Reyes, M.R.; Green, C.H.; Arnold, J.G. The soil and water assessment tool: Historical development, applications, and future research directions. Trans. Asabe 2007, 50, 1211–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshmidevi, T.V.; Nagesh Kumar, D.; Mehrotra, R.; Sharma, A. Estimation of the climate change impact on a catchment water balance using an ensemble of GCMs. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yeo, I.-Y.; Sadeghi, A.M.; McCarty, G.W.; Hively, W.D.; Lang, M.W.; Sharifi, A. Comparative analyses of hydrological responses of two adjacent watersheds to climate variability and change using the SWAT model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 689–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Brown, D.G.; Steiner, A.L. Sensitivity to climate change of land use and management patterns optimized for efficient mitigation of nutrient pollution. Clim. Chang. 2018, 147, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Rajib, M.A.; Ahiablame, L. Spatial and Temporal Evaluation of Hydrological Response to Climate and Land Use Change in Three South Dakota Watersheds. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 53, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Bressiani, D.; Gassman, P.W.; Fernandes, J.G.; Garbossa, L.H.P.; Srinivasan, R.; Bonumá, N.B.; Mendiondo, E.M. Review of Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) applications in Brazil: Challenges and prospects. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2015, 8, 9–35. [Google Scholar]
- Tapasco, J.; Quintero, M.; Uribe, N.; Valencia, J.; Calderón, S.; Romero, G.; Ordóñez, D.A.; Álvarez, A.; Sanchez-Aragon, L.; Ludeña, C.E. Impactos Económicos del Cambio Climático en Colombia: Recurso Hídrico; Banco Interamericano de Desarrollo/Inter-American Development Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Castañeda Morales, Y. Modelación del Efecto del Cambio de Uso del Suelo en la Cuenca del Rio Coello, Bajo Escenario de Cambio Climático, A Través De La Aplicación Del Modelo Hidrológico SWAT (Soil And Water Assessment Tool); Universidad Distrital: Bogotá, Colombia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyos, N.; Correa-Metrio, A.; Jepsen, S.M.; Wemple, B.; Valencia, S.; Marsik, M.; Doria, R.; Escobar, J.; Restrepo, J.C.; Velez, M.I. Modeling Streamflow Response to Persistent Drought in a Coastal Tropical Mountainous Watershed, Sierra Nevada De Santa Marta, Colombia. Water 2019, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GRADEX Plan de Ordenamiento Ambiental Territorial Microcuenca río Tona; Corporación de Defensa de la Meseta de Bucaramanga: Bucaramanga, Colombia, 2012.
- Tobler, W. Measuring spatial resolution. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Geographic Information Systems, Beijing, China, 2–6 June 1987; Volume 48. [Google Scholar]
- Batjes, N.H. Harmonized soil profile data for applications at global and continental scales: Updates to the WISE database. Soil. Use Manag. 2009, 25, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPAW Download Page. Available online: https://hrsl.ba.ars.usda.gov/SPAW/SPAWDownload.html (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Valencia Gómez, J. Estimated Calibration Parameters in SWAT Model for Andean Watersheds. In Proceedings of the 2013 International SWAT Conference, Toulouse, France, 15–19 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Uribe Rivera, N.; Valencia Gómez, J. Impacto del Uso de la Tierra en la Generación de Caudales y Sedimentos: Caso Cuenca del Río Tunjuelo—Cundinamarca—Observatorio Ambiental de Bogotá; International Center for Tropical Agriculture: Santiago de Cali, Colombia, 2010; p. 67. [Google Scholar]
- Valencia Gómez, J.; Nuevos Usos del Suelo en SWAT—Solicitud de Orientación. Personal communication, 2017.
- Instituto de Hidrología, Meteorología y Estudios Ambientales Solicitud de Información—IDEAM. Available online: http://www.ideam.gov.co/solicitud-de-informacion (accessed on 11 December 2018).
- CDMB Applied Research Committee for Environmental Management of the CDMB—CIAGA. Available online: http://www.cdmb.gov.co/web/sitios-de-interes-ambiental/ciaga (accessed on 11 December 2018).
- Acueducto Metropolitano de Bucaramanga S.A. E.S.P. Conócenos. Available online: http://www.amb.com.co:8081/wp_contenido/ (accessed on 11 December 2018).
- Palomino-Lémus, R.; Córdoba-Machado, S.; Gámiz-Fortis, S.R.; Castro-Díez, Y.; Estéban-Parra, M.J. Statistical downscaling of summer precipitation in Colombia. In Proceedings of the Cambio Climático y Cambio Global, Almería, España, 28–30 October 2014; p. 10. Available online: http://aeclim.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/Cambio-Climatico-y-Cambio-Global.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2019).
- Bonilla-Ovallos, C.A.; Mesa Sánchez, O.J. Validación de la precipitación estimada por modelos climáticos acoplados del proyecto de intercomparación CMIP5 en Colombia. Rev. Acad. Colomb. Cienc. ExactasFísicas Y Nat. 2017, 41, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Estupiñán, D.F.; Rodríguez Buitrago, A.D. Aplicabilidad de datos Climatológicos Escalados Para la Modelación Hidrológica de la Cuenca del río Tona en Santander; Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana: Floridablanca, Santander, Colombia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration Advancing Research and Applications with NASA Climate Model Data. Available online: https://cds.nccs.nasa.gov/nex-gddp/ (accessed on 8 August 2018).
- Sandra, R. Villamizar SWAT Modeling for the Tona Watershed. Available online: https://figshare.com/projects/SWAT_modeling_for_the_Tona_Watershed/37520 (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- ArcSWAT. Available online: https://swat.tamu.edu/software/arcswat/ (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Atlas Interactivo—Climatológico—IDEAM. Available online: http://atlas.ideam.gov.co/visorAtlasClimatologico.html (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Numerical Terradynamic Simulation Group. Available online: http://www.ntsg.umt.edu/project/project/modis/mod16.php (accessed on 15 December 2018).
- Arnold, J.G.; Allen, P.M.; Muttiah, R.; Bernhardt, G. Automated Base Flow Separation and Recession Analysis Techniques. Groundwater 1995, 33, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SWAT-CUP. Available online: https://swat.tamu.edu/software/swat-cup/ (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- DMoriasi, N.; Arnold, J.G.; van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center, N.C.P. NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center. Available online: http://origin.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/analysis_monitoring/ensostuff/ONI_v5.php (accessed on 11 August 2018).
- Siqueira, V.A.; Paiva, R.C.D.; Fleischmann, A.S.; Fan, F.M.; Ruhoff, A.L.; Pontes, P.R.M.; Paris, A.; Calmant, S.; Collischonn, W. Toward continental hydrologic–hydrodynamic modeling in South America. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 4815–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalew, S.G.; Pilz, T.; Schweitzer, C.; Liersch, S.; van der Kwast, J.; van Griensven, A.; Mul, M.L.; Dickens, C.; van der Zaag, P. Coupling land-use change and hydrologic models for quantification of catchment ecosystem services. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 109, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, C.; Aggett, G. Land-use forecasting and hydrologic model integration for improved land-use decision support. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 84, 494–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| POAT LULC | Assigned Swat Code 1 | Definition | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Constructions | Urban land | URBN | Residential |
| Agricultural land | Transitory crops | BANA | Bananas |
| Permanent crops | COFF | Coffee | |
| Natural pastures | PAST | Pasture | |
| Cultivated pastures | SPAS | Summer pasture | |
| Crops and pastures | RYEG | Patterns of permanent crops and pastures | |
| Shrub and crops | SWRN | Patterns of permanent crops, pastures and natural areas | |
| Agroforestry land | Wooded pastures | RNGB | Range-brush |
| Permanent and/or semi-permanent crops with shade | ORCD | Orchard | |
| Forest | Secondary Forest | FRST | Forest-Mixed |
| Brush | MESQ | Honey mesquite—Shrub and/or herbaceous vegetation associations | |
| Planted forest | PINE | Pine | |
| Special forms of vegetation | Páramo vegetation | FESP | Páramo and subpáramo vegetation |
| Grassy brush | MESQ | Honey mesquite—Shrub and/or herbaceous vegetation associations | |
| Barren land | Rocky outcrop | BARR | Barren land |
| Item | Format | File Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital elevation model | ESRI GRID | dem | Digital elevation model of the watershed |
| Land cover/land use | ESRI GRID | lulc | Map of land use and land cover (LULC) of the watershed |
| Land use look up table | dBase | lulct | Table associating the watershed’s LULC with SWAT’s LULC database |
| Soils | ESRI GRID | soil | Map of soils for the watershed |
| Soil look up table | dBase | soilt | Table associating the watershed’s soil types with SWAT’s soils database |
| Precipitation gauge location table | ASCII | pcptona | Table with the geographic coordinates of the precipitation stations |
| Daily precipitation data table | ASCII | pbrasil, pgalvic, pberlin, ptonapu, puiside | Tables containing the daily time series of precipitation for each of the stations |
| Temperature gauge location table | ASCII | tmptona | Table with the geographic coordinates of the temperature stations |
| Daily temperature data table | ASCII | pberlin, puiside | Tables containing the daily time series of precipitation for each of the stations |
| Gauging station points location table | dBase | strflowtona | Table with the projected and geographic coordinates of the gauging stations |
| Masking file | ESRI GRID | amask | Map with the definition of the watershed’s boundary—helps on automatic watershed delineation |
| Burn-in file | Shape | BurnIn | Map containing the watershed’s drainages—helps on automatic delineation of drainages |
| Characteristic | Calibration | Validation |
|---|---|---|
| Simulation period | 1987–1997 (11 years) | 1998–2002 (5 years) |
| Warm-up years (NYSKIP) | 1987–1989 (3 years) | 1998 (1 year) |
| Effective period | 1990–1997 (8 years) | 1999–2002 (4 years) |
| Interval of model output | Monthly | Monthly |
| Column | Scenario C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current LULC | LULC Changes | Subwatersheds | Current LULC | LULC Changes | Subwatersheds |
| BANA | COFF | 13 | BANA | FRST | 13 |
| PAST | MESQ | 1,2,3,6,13,14 | PAST | FRST | 1,2,3,5,6,13,14 |
| PAST | PINE | 5 | RNGB | FRST | 1,5,12,13 |
| RNGB | MESQ | 1,5,12,13 | RYEG | FRST | 2,3,5,6,11,12,13,14 |
| RYEG | COFF | 13 | RYEG | MESQ | 7 |
| RYEG | MESQ | 2,3,5,6,7 | RYEG | RNGB | 8 |
| RYEG | RNGB | 8,9,10,11,12,14 | SPAS | FRST | 1,12,14 |
| SPAS | MESQ | 1,12,14 | SWRN | FRST | 3,4,6 |
| ORCD | MESQ | 6 | ORCD | FRST | 6 |
| SWRN | MESQ | 3,4,6 | |||
| Scenarios | Time Windows for Model Runs | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario | LULC + Climate | Characteristic | Time Period |
| {1} | Scenario A + RCP 4.5 | Simulation period | 2006–2050 (45 years) |
| {2} | Scenario A + RCP 8.5 | Warm-up years | 2006–2009 (4 years) |
| {3} | Scenario B + RCP 4.5 | Effective period | 2010–2050 (41 years) |
| {4} | Scenario B + RCP 8.5 | Interval of model output | Monthly |
| {5} | Scenario C + RCP 4.5 | ||
| {6} | Scenario C + RCP 8.5 | ||
| Climate Scenario | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCP 4.5 (P = 1334.80 mm) | RCP 8.5 (P = 1400 mm) | |||
| LULC Scenario | WYLD (mm year−1) | Actual ET (mm year−1) | WYLD (mm year−1) | Actual ET (mm year−1) |
| A | {1} 588.3 | {1} 653.2 | {2} 627.6 | {2} 665.1 |
| B | {3} 622.1 (5.9%) | {3} 687.3 (5.2%) | {4} 662.6 (5.6%) | {4} 700.1 (5.3%) |
| C | {5} 605.2 (2.9%) | {5} 684.2 (4.8%) | {6} 646.0 (2.9%) | {6} 697.4 (4.9%) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villamizar, S.R.; Pineda, S.M.; Carrillo, G.A. The Effects of Land Use and Climate Change on the Water Yield of a Watershed in Colombia. Water 2019, 11, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020285
Villamizar SR, Pineda SM, Carrillo GA. The Effects of Land Use and Climate Change on the Water Yield of a Watershed in Colombia. Water. 2019; 11(2):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020285
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillamizar, Sandra R., Sergio M. Pineda, and Gustavo A. Carrillo. 2019. "The Effects of Land Use and Climate Change on the Water Yield of a Watershed in Colombia" Water 11, no. 2: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020285
APA StyleVillamizar, S. R., Pineda, S. M., & Carrillo, G. A. (2019). The Effects of Land Use and Climate Change on the Water Yield of a Watershed in Colombia. Water, 11(2), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020285




