Modeling of Fertilizer Transport for Various Fertigation Scenarios under Drip Irrigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. System Description
Soil Parameters
2.2. Solute Parameters
2.3. Batch Experiments
2.4. Initial Conditions
2.5. Boundary Conditions
2.6. Fertilizer Application
2.7. Root Parameters
2.8. Simulation Scenarios
3. Results and Discussion
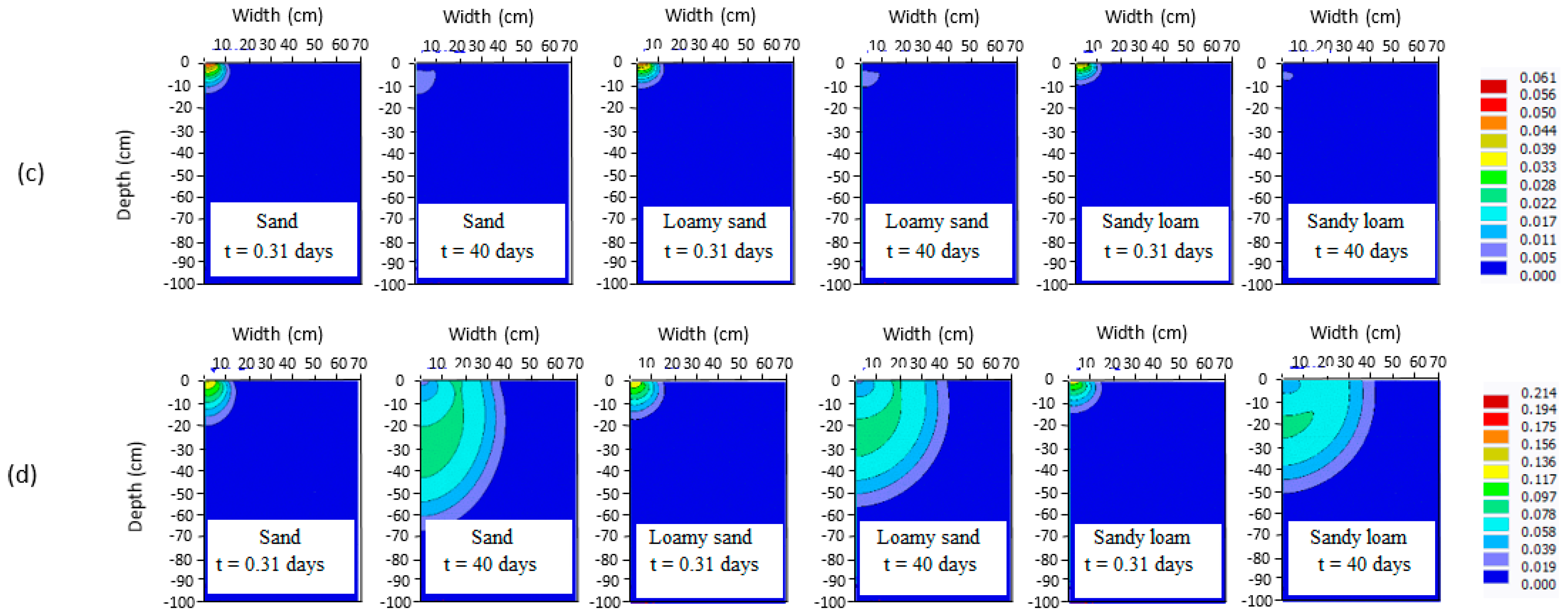
3.1. Distribution of Fertilizers
3.2. Effect of Soil Type
3.3. Effect of Irrigation System
3.4. Fertilizer Leaching
3.5. Root Fertilizer Uptake
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magen, H. Fertigation: An overview of some practical aspects. Fert. News 1995, 40, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kafkafi, U.; Tarchitzky, J. A Tool for Efficient Fertilizer and Water Management; International Fertilizer Association/International Potash institute: Paris/Horgen, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Fertilizer Use by Crop in Egypt; Land and Plant Nutrition Management Service, Land and Water Development Division: Roma, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, M.H. Chemical fertilizers and irrigation system in Egypt. In Proceedings of the FAO Regional Workshop on Guidelines for Efficient Fertilizers Use through Irrigation, Cairo, Egypt, 14–16 December 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, B.R.; Simunek, J.; Hopmans, J.W. Evaluation of urea–ammonium–nitrate fertigation with drip irrigation using numerical modeling. Agric. Water. Manag. 2006, 86, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Delgado, A.M.; Shukla, M.K. Transport of nitrate and chloride in variably saturated porous media. J. Irrig. Drain Eng. 2014, 140, 04014006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corley, R.H.V.; Tinker, P.B.H. The Oil Palm (World Agriculture Series), 4th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2003; p. 592. ISBN 978-0-632-05212-7. [Google Scholar]
- Griffioen, J. Potassium adsorption ratios as an indicator for the fate of agricultural potassium in groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2001, 254, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigen, A.; Ravina, I.; Shalhevet, J. Effect of Irrigation with Treated Sewage Effluent on Soil, Plant and Environment. In Irrigation with Treated Sewage Effluent; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth, T. Nitrogen in the soil-plant system nitrogen balances. Cer. Res. Commun. 2006, 34, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Josipovic, M.; Kovačević, V.; Šostarić, J.; Plavšić, H.; Liovic, J. Influences of irrigation and fertilization on soybean properties and nitrogen leaching. Cer. Res. Commun. 2006, 34, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemcic, J.; Mesić, M.; Bašić, F.; Kisić, I.; Zgorelec, Z. Nitrate concentration in drinking water from wells at three different locations in Northwest Croatia. Cer. Res. Commun. 2007, 35, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, B.; Schwankl, L.; Granttan, S.; Prichard, T. Drip Irrigation for Row Crops; Water Management Handbook Series (Publication 93-05); University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Simunek, J.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Šejna, M. Recent Developments and Applications of the HYDRUS Computer Software Packages. Vadose Zone J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, C.M.; Bristow, K.L.; Charlesworth, P.B.; Cook, F.J.; Thorburn, P.J. Analysis of soil wetting and solute transport in subsurface trickle irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2003, 22, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardenas, A.I.; Hopman, J.W.; Hanson, B.R.; Simunek, J. Two-dimensional modeling of nitrate leaching for various fertigation scenarios under micro-irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 74, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajdary, K.; Singh, D.K.; Singh, A.K.; Khanna, M. Modeling of nitrogen leaching from experimental onion field under drip fertigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 89, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crevoisier, D.; Popova, Z.; Mailhol, J.C.; Ruelle, P. Assessment and simulation of water and nitrogen transfer under furrow irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siyal, A.A.; Bristow, K.L.; Simunek, J. Minimizing nitrogen leaching from furrow irrigation through novel fertilizer placement and soil surface management strategies. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 115, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.B.; Simunek, J.; Goncalves, M.C.; Martins, J.C.; Prazeres, A.; Pereira, L.S. Two-dimensional modeling of water and nitrogen fate from sweet sorghum irrigated with fresh and blended saline waters. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 111, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyal, A.A.; Siyal, A.G. Strategies to reduce nitrate leaching under furrow irrigation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2013, 4, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, W.; Jiusheng, L.; Yanfeng, L. Simulation of nitrate leaching under varying drip system uniformities and precipitation patterns during the growing season of maize in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 142, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Raij, I.; Simunek, J.; Ben-Gal, A.; Lazarovitch, N. Water flow and multicomponent solute transport in drip irrigated lysimeters: Experiments and modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 6557–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, A.A.; Navabian, M.; Varaki, M.E.; Pirmoradian, N. Evaluation of HYDRUS-2D model to simulate the loss of nitrate in subsurface controlled drainage in a physical model scale of paddy fields. Padd. Water Environ. 2017, 15, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekofteh, H.; Afyuni, M.; Hajabbasi, M.A. Modeling of nitrate leaching from a potato field using HYDRUS-2D. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2013, 44, 2917–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, S.; El Agroudy, N.; Shafiq, F.A.; Abdel Fatah, H.Y. The Effects of the environmental pollution in Egypt. Intern. J. Environ. 2015, 4, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hillel, D. Environmental Soil Physics; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Abou Lila, T.S.; Berndtsson, R.; Persson, M.; Somaida, M.; El_Kiki, M.; Hamed, Y.; Mirdan, A. Numerical evaluation of subsurface trickle irrigation with brackish water. Irrig Sci. 2013, 31, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.P. Movement of contaminants in groundwater: Groundwater transport-advection and dispersion. In Groundwater Contamination. Studies in Geophysics; National Academy: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; pp. 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Cote, C.M.; Bristow, K.L.; Ford, E.J.; Verburg, K.; Keating, B. Measurement of Water and Solute Movement in Large Undisturbed Soil Cores: Analysis of Macknade and Bundaderg Data; Technical Report 07/2001; CSIRO Land and Water: Canberra, Australia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lotse, E.G.; Jabro, J.D.; Simmons, K.E.; Baker, D.E. Simulation of nitrogen dynamics and leaching from arable soils. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1992, 10, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, P.E.; Karlberg, L. Coupled Heat and Mass Transfer Model for Soil–Plant–Atmosphere Systems; Royal Institute of Technology, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering: Stockholm, Sweden, 2001; p. 321. [Google Scholar]
- Flury, M.; Fluhler, H. Tracer characteristics of Brilliant Blue FCF. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1995, 59, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, T.; Berndtsson, R.; Persson, M.; Somaida, M.; El-Kiki, M.; Hamed, Y.; Mirdan, A.; Zhou, Q. Influence of geometric design of alternate partial root-zone subsurface drip irrigation (APRSDI) with brackish water on soil moisture and salinity distribution. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 103, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuvelink, E. Growth, development and yield of a tomato crop: periodic destructive measurements in a greenhouse. Hort. Sci. 1995, 61, 77–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrugt, J.A.; van Wijk, M.T.; Hopmans, J.W.; Simunek, J. Comparison of one, two, and three-dimensional root water uptake functions for transient water flow modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 2457–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddes, R.A.; Kowalik, P.J.; Zaradny, H. Simulation of Field Water Use and Crop Yield; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]





| Soil Type | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) | Bulk Density (gm/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | 92.0 | 3.6 | 4.4 | 1.66 |
| Loamy sand | 79.7 | 12.3 | 8.0 | 1.73 |
| Sandy loam | 65.2 | 30.8 | 4.0 | 1.78 |
| Soil Type | θr (m3 m−3) | θs (m3 m−3) | α | n | Ks (cm day−1) | l |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | 0.024 | 0.447 | 0.124 | 1.87 | 878.20 | 0.5 |
| Loamy sand | 0.074 | 0.453 | 0.045 | 1.72 | 288.50 | 0.5 |
| Sandy loam | 0.038 | 0.486 | 0.025 | 1.72 | 194.06 | 0.5 |
| Soil Type | pH | Calcium Carbonate (%) | Na (meq/L) | Mg (meq/L) | Ca (meq/L) | Fe (ppm) | Cu (ppm) | Zn (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | 8.5 | 0.7 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 6.9 | 0.86 | 1.9 |
| Loamy sand | 8.0 | 2.1 | 2.7 | 11.1 | 8.2 | 5.5 | 0.24 | 3.0 |
| Sandy loam | 7.9 | 0.8 | 40.1 | 12.4 | 11.1 | 12.8 | 0.74 | 2.8 |
| Soil Type | Sand | Loamy Sand | Sandy Loam |
|---|---|---|---|
| Potassium | 2.50 | 3.26 | 3.99 |
| Phosphorus | 3.62 | 4.31 | 4.41 |
| Ammonium | 2.20 | 2.50 | 2.86 |
| Nitrate | 0.65 | 0.72 | 0.89 |
| Soil Type | Fertigation Strategy | DI | SDI with Emitter Depth of 10 cm | SDI with Emitter Depth of 20 cm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | P | N | K | P | N | K | P | N | ||
| Sand | C | 24.4 | 26.4 | 32.7 | 32.7 | 36.2 | 34.0 | 49.98 | 52.61 | 43.30 |
| E | 23.7 | 25.8 | 31.9 | 32.6 | 36.2 | 34.2 | 50.05 | 52.73 | 43.34 | |
| M | 24.6 | 26.6 | 33.0 | 33.6 | 37.0 | 35.0 | 51.23 | 53.49 | 44.41 | |
| B | 24.9 | 26.8 | 33.1 | 31.9 | 35.3 | 32.9 | 49.3 | 51.6 | 42.2 | |
| Loamy sand | C | 13.8 | 15.1 | 27.7 | 22.1 | 25.1 | 28.7 | 40.2 | 42.8 | 36.3 |
| E | 13.3 | 14.6 | 27.2 | 22.2 | 25.4 | 28.9 | 40.1 | 43.2 | 36.5 | |
| M | 13.8 | 15.1 | 27.8 | 22.5 | 25.6 | 29.1 | 40.7 | 43.1 | 36.7 | |
| B | 14.2 | 15.5 | 28.2 | 21.9 | 24.5 | 27.7 | 39.9 | 42.2 | 35.7 | |
| Sandy loam | C | 7.7 | 10.1 | 24.4 | 15.9 | 20.1 | 26.3 | 35.7 | 39.0 | 35.4 |
| E | 7.4 | 9.8 | 23.9 | 16.0 | 20.4 | 26.7 | 35.6 | 39.3 | 35.5 | |
| M | 7.7 | 10.2 | 24.4 | 16.1 | 20.3 | 26.6 | 35.9 | 39.1 | 35.5 | |
| B | 8.0 | 10.5 | 24.9 | 15.6 | 19.7 | 25.6 | 35.9 | 38.9 | 35.1 | |
| Soil Type | Fertigation Strategy | DI | SDI with Emitter Depth of 10 cm | SDI with Emitter Depth of 20 cm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | P | N | K | P | N | K | P | N | ||
| Sand | C | 15.4 | 15.3 | 35.5 | 15.5 | 15.4 | 36.2 | 14.5 | 14.4 | 34.3 |
| E | 15.5 | 15.4 | 35.8 | 15.6 | 15.7 | 36.4 | 14.6 | 14.4 | 34.5 | |
| M | 15.4 | 15.3 | 35.5 | 15.5 | 15.3 | 36.0 | 14.4 | 14.3 | 34.0 | |
| B | 15.4 | 15.3 | 35.2 | 15.4 | 15.3 | 36.2 | 14.5 | 14.3 | 34.5 | |
| Loamy sand | C | 12.0 | 12.7 | 31.9 | 12.3 | 13.0 | 33.1 | 11.8 | 12.4 | 32.2 |
| E | 12.0 | 12.7 | 32.1 | 12.3 | 13.1 | 33.3 | 11.8 | 12.4 | 32.2 | |
| M | 12.0 | 12.7 | 32.0 | 12.3 | 13.0 | 33.0 | 11.7 | 12.4 | 32.2 | |
| B | 12.0 | 12.7 | 31.7 | 12.3 | 13.0 | 32.9 | 11.7 | 12.4 | 32.0 | |
| Sandy loam | C | 9.0 | 11.0 | 26.3 | 9.4 | 11.4 | 27.4 | 9.0 | 11.0 | 26.8 |
| E | 9.1 | 11.1 | 26.5 | 9.4 | 11.5 | 27.6 | 9.1 | 11.0 | 26.8 | |
| M | 9.0 | 11.0 | 26.3 | 9.4 | 11.4 | 27.3 | 9.0 | 11.0 | 26.7 | |
| B | 9.0 | 11.0 | 26.2 | 9.3 | 11.4 | 27.2 | 9.0 | 11.0 | 26.7 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elasbah, R.; Selim, T.; Mirdan, A.; Berndtsson, R. Modeling of Fertilizer Transport for Various Fertigation Scenarios under Drip Irrigation. Water 2019, 11, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050893
Elasbah R, Selim T, Mirdan A, Berndtsson R. Modeling of Fertilizer Transport for Various Fertigation Scenarios under Drip Irrigation. Water. 2019; 11(5):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050893
Chicago/Turabian StyleElasbah, Romysaa, Tarek Selim, Ahmed Mirdan, and Ronny Berndtsson. 2019. "Modeling of Fertilizer Transport for Various Fertigation Scenarios under Drip Irrigation" Water 11, no. 5: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050893
APA StyleElasbah, R., Selim, T., Mirdan, A., & Berndtsson, R. (2019). Modeling of Fertilizer Transport for Various Fertigation Scenarios under Drip Irrigation. Water, 11(5), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050893






