Spatiotemporal Variations of Summer Precipitation and Their Correlations with the East Asian Summer Monsoon in the Poyang Lake Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Climate Indices
2.3.2. EOF Method
2.3.3. Wavelet Analysis
3. Results
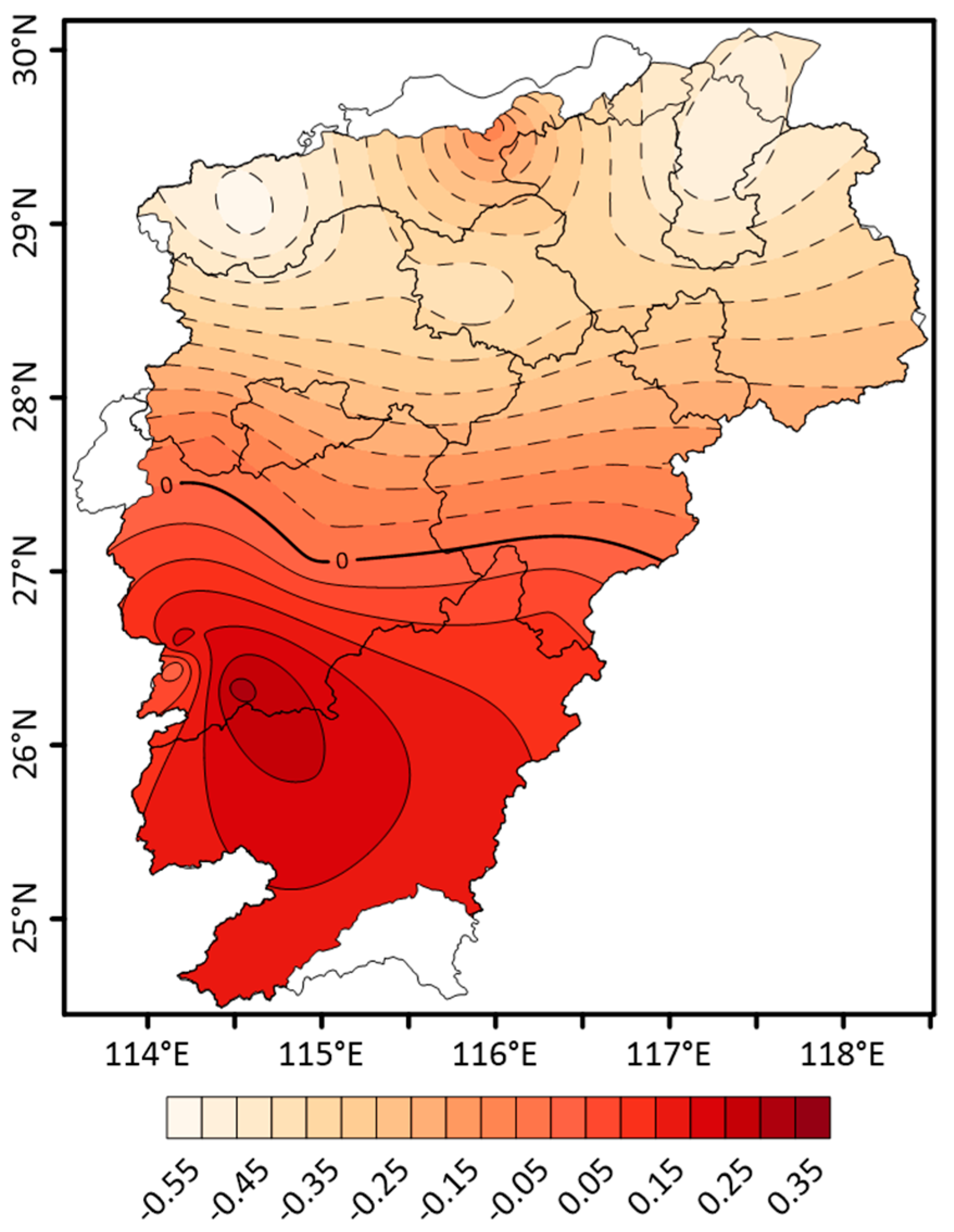
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Summer Precipitation
3.2. Temporal Variations of Summer Precipitation
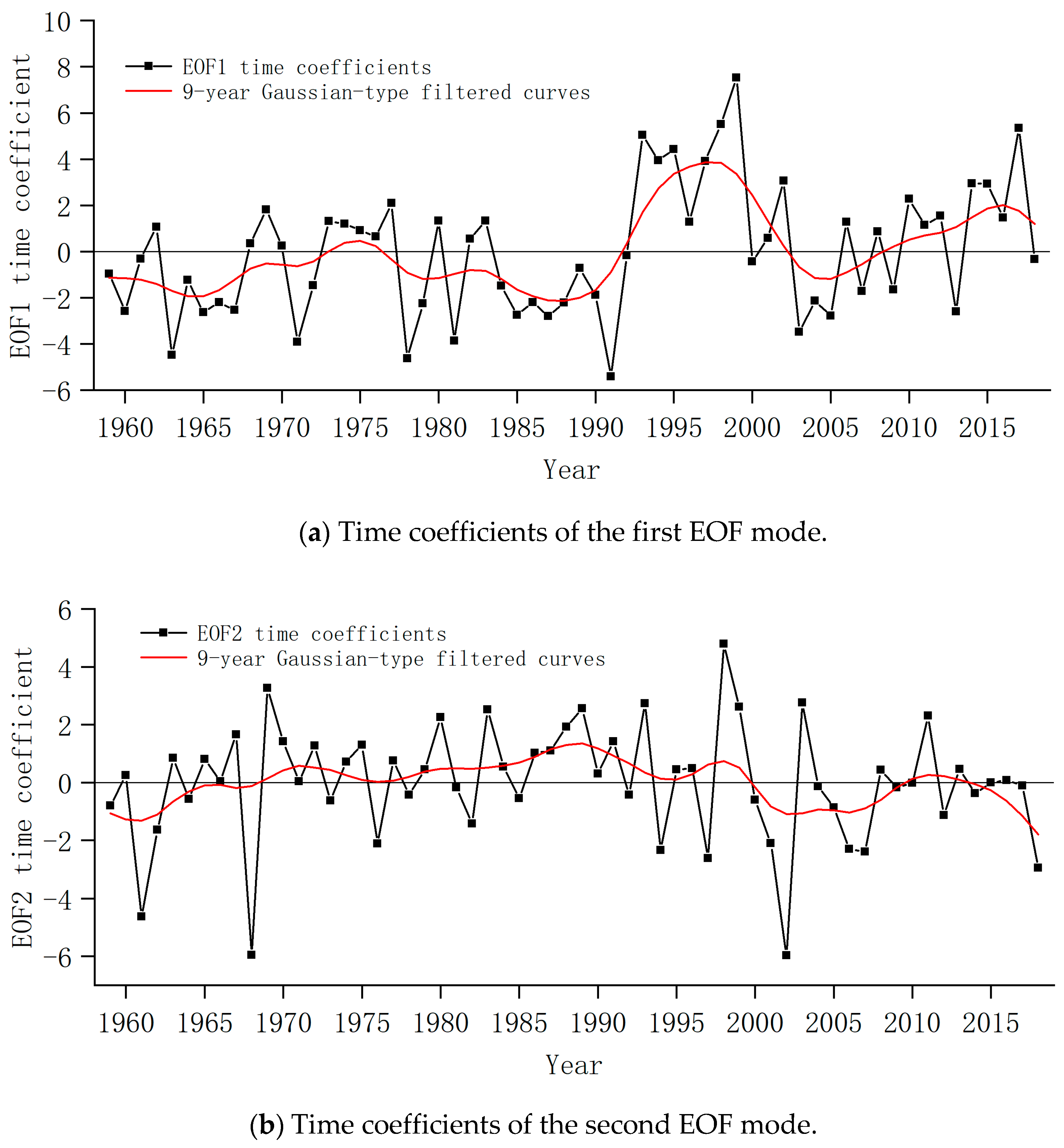
3.2.1. Inter-Annual and Inter-Decadal Variations of Summer Precipitation
3.2.2. Period Characteristics of Summer Precipitation
3.3. The Connection between Summer Precipitation and East Asian Summer Monsoon
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- There were two modes of summer precipitation in the PYLB: the mode that is consistent over the whole area and the mode of the opposite relationship between the south of PYLB and the north of PYLB. The first mode effectively reflects the spatial consistency of summer precipitation in the PYLB. The second mode effectively reflects the summer precipitation of the opposite relationship between the south of PYLB and the north of PYLB in the basin.
- (2)
- The summer precipitation in the PYLB had apparent trend changes and inter-decadal features. The basin received below normal precipitation from the 1960s to the mid-1990s. The summer precipitation has been increasing significantly since the mid-1990s. The summer precipitation in the north of the PYLB from the 1980s to the 1990s was relatively higher than that in the south of the PYLB, and the rest of the periods vice versa. The summer precipitation of the first two modes also had multi-time-scale periodic characteristics. The summer precipitation corresponding to the first mode had cycles of 2–3 years, 5 years, and 16 years. The summer precipitation corresponding to the second mode had cycles of 2–3 years and 4–6 years.
- (3)
- There was no significant correlation between EASMI and summer precipitation corresponding to the mode being consistent over the whole area. However, there was a significant negative correlation between EASMI and summer precipitation corresponding to the mode of the opposite relationship between the south of the PYLB and the north of the PYLB, and both of them had common variation characteristics of the quasi-2–3 years oscillation period.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg3/ (accessed on 16 September 2014).
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Singh, V.P.; Gu, X.; Kong, D.; Xiao, M. Impacts of ENSO and ENSO Modoki+A regimes on seasonal precipitation variations and possible underlying causes in the Huai River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, X.; Tian, L.; Gan, W. Assessment of inundation changes of Poyang Lake using MODIS observations between 2000 and 2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, A.M.; Tedeschi, R.G. ENSO and Extreme Rainfall Events in South America. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 1589–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.F.; Raible, C.C. Climate change—Water cycle shifts gear. Nature 2005, 434, 830–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.F.; Liu, Y.B. Evaluation of Satellite Precipitation Products with Rain Gauge Data at Different Scales: Implications for Hydrological Applications. Water Sui 2016, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.A.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.D.; Zhang, Z.X. Precipitation and hydrological variations and related associations with large-scale circulation in the Poyang Lake basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Ye, X.C. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Dry-Wet Abrupt Transition Based on Precipitation in Poyang Lake Basin, China. Water Sui 2015, 7, 1943–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, H.; Jiang, W.; Li, W. Changed relationships between the East Asian summer monsoon circulations and the summer rainfall in eastern China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2014, 28, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.W.; Zhou, T.J.; Zhu, Y.X.; Lin, Y.H. The strengthening East Asia summer monsoon since the early 1990s. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 1553–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Song, Y. Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon Part II: Possible causes. Int. J. Clim. 2009, 29, 1926–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ho, L. Rainy Season of the Asian–Pacific Summer Monsoon. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.; Zhang, X.; Wan, H.; Pan, X. Trends in Total Precipitation and Frequency of Daily Precipitation Extremes over China. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 1096–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Gong, T.L.; Li, J.Y. Decadal trend of climate in the Tibetan Plateau—regional temperature and precipitation. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 3056–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Cui, B. Spatial and temporal variability of annual precipitation during 1961–2006 in Yellow River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2008, 361, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, F.; Wu, C.; Qu, A.; Xia, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Y. Changes in Extreme Precipitation: A Case Study in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River in China. Water 2017, 9, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Hao, Z.; Yuan, F.; Chen, X.; Cao, Q. Spatiotemporal Variability of Extreme Summer Precipitation over the Yangtze River Basin and the Associations with Climate Patterns. Water 2017, 9, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Fan, Z. Choice of South Asian Summer Monsoon Indices. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, M.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P. Influences of ENSO, NAO, IOD and PDO on seasonal precipitation regimes in the Yangtze River basin, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 3556–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Xu, L.G.; Fan, H.X. Drought Characteristics and Its Response to the Global Climate Variability in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Water Sui 2019, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Hu, Q. Spatiotemporal Changes in Extreme Precipitation and Its Dependence on Topography over the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; You, Q.; Ye, L.; Chen, C. Spatio-temporal characteristics and possible mechanisms of rainy season precipitation in Poyang Lake Basin, China. Clim. Res. 2017, 72, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Wang, J.; Lv, S.; Bing, J. Spatial and temporal variability of seasonal precipitation in Poyang Lake basin and possible links with climate indices. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, M.; Singh, V.P.; Chen, Y.D. Max-stable based evaluation of impacts of climate indices on extreme precipitation processes across the Poyang Lake basin, China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 122, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Lu, J.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, D.; Xu, Q. Precipitation projections using a spatiotemporally distributed method: A case study in the Poyang Lake watershed based on the MRI-CGCM. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 1649–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Xiao, X.; Wang, X.; Dai, S.; Zhao, B. Long-Term Dynamic of Poyang Lake Surface Water: A Mapping Work Based on the Google Earth Engine Cloud Platform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, M.; Li, J.; Singh, V.P.; Wang, Z. Topography-based spatial patterns of precipitation extremes in the Poyang Lake basin, China: Changing properties and causes. J. Hydrol. 2014, 512, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Xu, C.Y. Distinguishing the relative impacts of climate change and human activities on variation of streamflow in the Poyang Lake catchment, China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 494, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Xu, L.; Tao, H.; Feng, W.; Cheng, J.; You, H. Accessing the Difference in the Climate Elasticity of Runoff across the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Water 2017, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wan, R.; Yang, G. Non-stationary water-level fluctuation in China’s Poyang Lake and its interactions with Yangtze River. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhu, M.; He, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Razafindrabe, B.H. Analysis of Water Balance in Poyang Lake Basin and Subsequent Response to Climate Change. J. Coast. Res. 2014, 68, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Kryjov, V.N.; Ahn, J.B. One-Month-Lead Predictability of Asian Summer Monsoon Indices Based on the Zonal Winds by the APCC Multimodel Ensemble. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 8945–8960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wei, H.; Jin, L.Y.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, S.Q.; Chen, F.H. A climatological northern boundary index for the East Asian summer monsoon and its interannual variability. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Guan, Z. A joint monsoon index for East Asian-Australian monsoons during boreal summer. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2017, 18, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, J.S.; Huang, W.; Wang, B. A potential vorticity-based index for the East Asian winter monsoon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 9382–9399. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.; Huang, G.; Wu, R.; Tao, W.; Gong, H.; Qu, X.; Hu, K. A New Upper-Level Circulation Index for the East Asian Summer Monsoon Variability. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 9977–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.; Hu, J.; Tao, Y. An index for the interface between the Indian summer monsoon and the East Asian summer monsoon. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, B.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Annamalai, H. A broad-scale circulation index for the interannual variability of the Indian summer monsoon. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 125, 611–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.M.; Yang, S. Seasonal Variation, Abrupt Transition, and Intraseasonal Variability Associated with the Asian Summer Monsoon in the GLA GCM. J. Clim. 1996, 9, 965–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.P.; Zheng, Q.C. A new monsoon index and the geographical distribution of the global monsoons. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 20, 299–302. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.P.; Zeng, Q.C. A unified monsoon index. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Section of planetary sciences: The predictability pf hydrodynamic flow. Trans. New York Acad. Sci. 2012, 25, 409–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, G.R.; Bell, T.L.; Cahalan, R.F.; Moeng, F.J. Sampling Errors in the Estimation of Empirical Orthogonal Functions. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1982, 110, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A Practical Guide to Wavelet Analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Yuan, H.Z.; Guan, Z.Y. Effects of enso on the relationship between iod and summer rainfall in china. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2009, 15, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, W.; Li, C. Influences of the Indian Ocean dipole on the Asian summer monsoon in the following year. Int. J. Clim. 2008, 28, 1849–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.K.; Ren, F.M. Changes in Regional Heavy Rainfall Events in China during 1961–2012. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Guo, E.; Zhao, C.; Cao, T. Spatial and temporal variations of precipitation concentration and their relationships with large-scale atmospheric circulations across Northeast China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 222, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Yan, M.; Ning, L. Decadal Variations of the East Asian Summer Monsoon Forced by the 11-Year Insolation Cycle. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 2735–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.Y.; Zhang, T. Oscillation characteristics of summer precipitation in the Huaihe River valley and relevant climate background. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T. Interannual and Interdecadal Variations of the East Asian Summer Monsoon and Tropical Pacific SSTs. Part I: Roles of the Subtropical Ridge. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 4310–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giorgetta, M.A.; Bengtsson, L.; Arpe, K. An investigation of QBO signals in the east Asian and Indian monsoon in GCM experiments. Clim. Dyn. 1999, 15, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.D.; Liu, C.L.; Lin, H. Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation maxima during 1960–2005 in the Yangtze River basin and possible association with large-scale circulation. J. Hydrol. 2008, 353, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y. Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in East China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon.Part I: Observed evidences. Int. J. Clim. 2008, 28, 1139–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, M.Z.; Singh, V.P.; Wang, Y.Q. Spatiotemporal variations of temperature and precipitation extremes in the Poyang Lake basin, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 124, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, R.; Liu, W.; Fu, G.; Liu, C.; Hu, L.; Wang, H. Linkages between ENSO/PDO signals and precipitation, streamflow in China during the last 100 years. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3651–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Eigenvectors | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variance contribution rates (%) | 42.1 | 22.4 | 6.6 | 5.1 | 3.6 | 3.3 | 2.9 | 2.6 | 2.4 | 1.6 |
| Cumulative variance contribution rates (%) | 42.1 | 64.5 | 71.1 | 76.2 | 79.8 | 83.1 | 86.0 | 88.6 | 91.0 | 92.6 |
| SMP (station) | EASMI | SMP (station) | EASMI |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMP (Xiushui) | −0.534 ** | SMP (Poyang) | −0.353 ** |
| SMP (Yichun) | −0.054 | SMP (Jingdezhen) | −0.495 ** |
| SMP (Ji’anxian) | −0.025 | SMP (Nanchang) | −0.39 ** |
| SMP (Xiaping) | 0.013 | SMP (Zhangshu) | −0.262 * |
| SMP (Jinggangshan) | 0.213 | SMP (Guixi) | −0.237 |
| SMP (Suichuan) | 0.32 * | SMP (Yushan) | −0.283 * |
| SMP (Ganxian) | 0.253 | SMP (Nancheng) | −0.092 |
| SMP (Jiujiang) | −0.268 * | SMP (Guangchang) | 0.093 |
| SMP (Lushan) | −0.051 | SMP (Xunxwu) | 0.148 |
| Niño 3.4-0 | Niño 3.4-1 | PDO-0 | PDO-1 | IOD-0 | IOD-1 | NAO-0 | NAO-1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | −0.043 | 0.043 | 0.081 | 0.182 | 0.248 | 0.222 | −0.037 | 0.040 |
| T2 | −0.110 | 0.242 | 0.049 | 0.152 | −0.190 | 0.115 | 0.147 | −0.049 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, H.; Xu, L.; Jiang, J.; Fan, H. Spatiotemporal Variations of Summer Precipitation and Their Correlations with the East Asian Summer Monsoon in the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Water 2019, 11, 1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081705
Zhu H, Xu L, Jiang J, Fan H. Spatiotemporal Variations of Summer Precipitation and Their Correlations with the East Asian Summer Monsoon in the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Water. 2019; 11(8):1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081705
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Hua, Ligang Xu, Jiahu Jiang, and Hongxiang Fan. 2019. "Spatiotemporal Variations of Summer Precipitation and Their Correlations with the East Asian Summer Monsoon in the Poyang Lake Basin, China" Water 11, no. 8: 1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081705
APA StyleZhu, H., Xu, L., Jiang, J., & Fan, H. (2019). Spatiotemporal Variations of Summer Precipitation and Their Correlations with the East Asian Summer Monsoon in the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Water, 11(8), 1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081705






