Spatial Changes in Invertebrate Structures as a Factor of Strong Human Activity in the Bed and Catchment Area of a Small Urban Stream
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
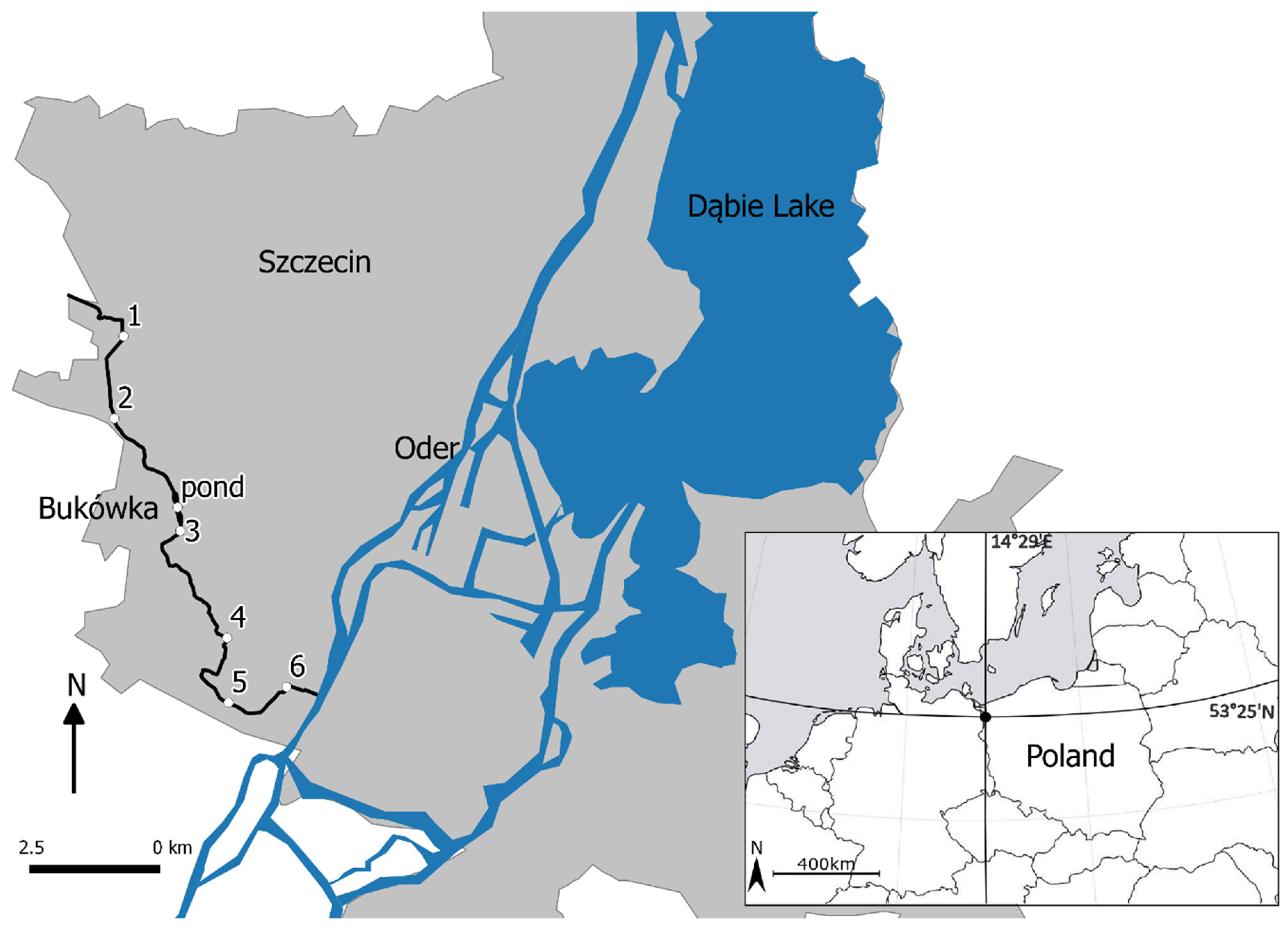
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Methods
2.2.1. Environmental Factors
2.2.2. Zooplankton
2.2.3. Macrozoobenthos—Macroinvertebrates
2.2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
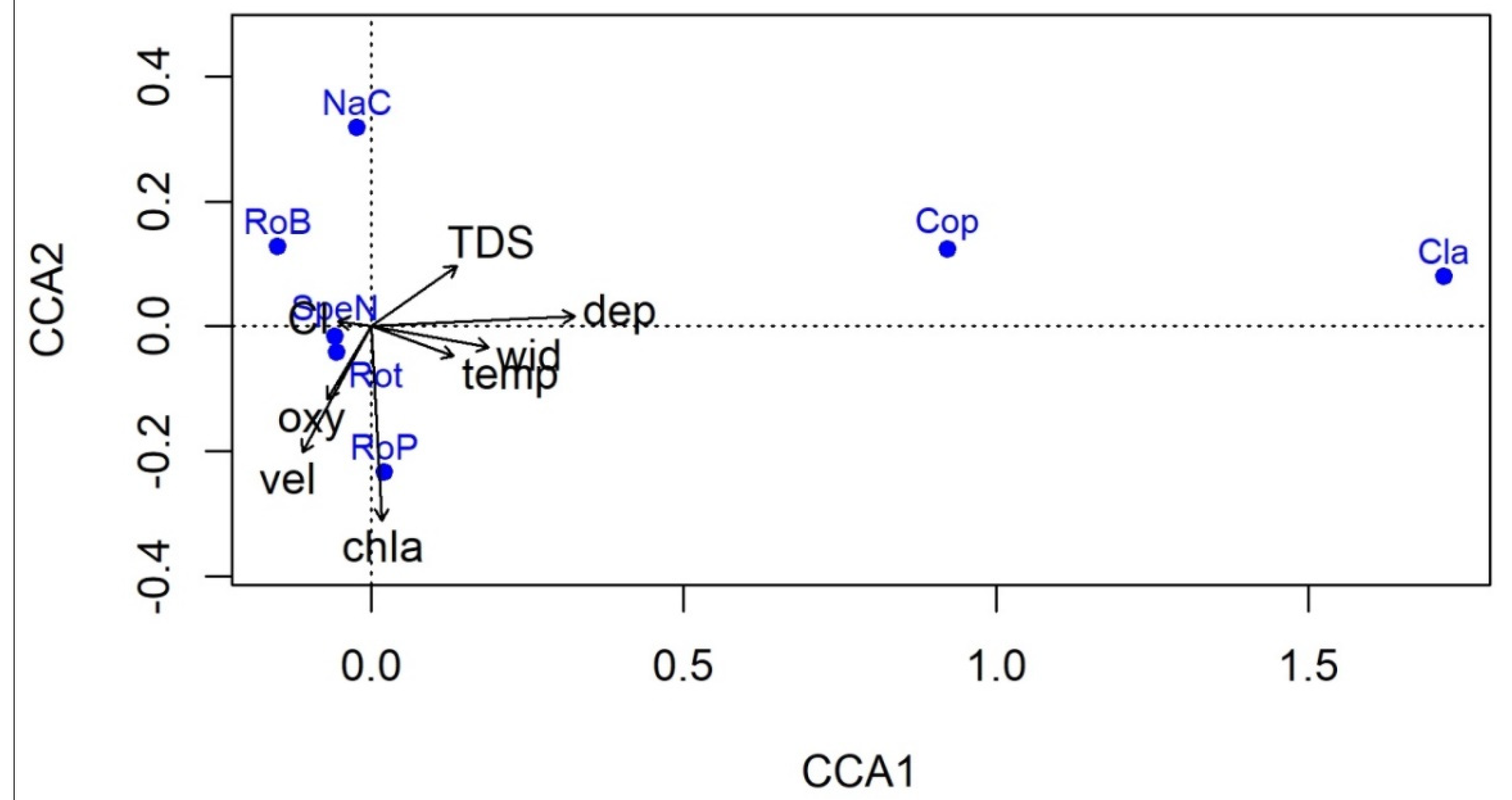
3.1. Zooplankton
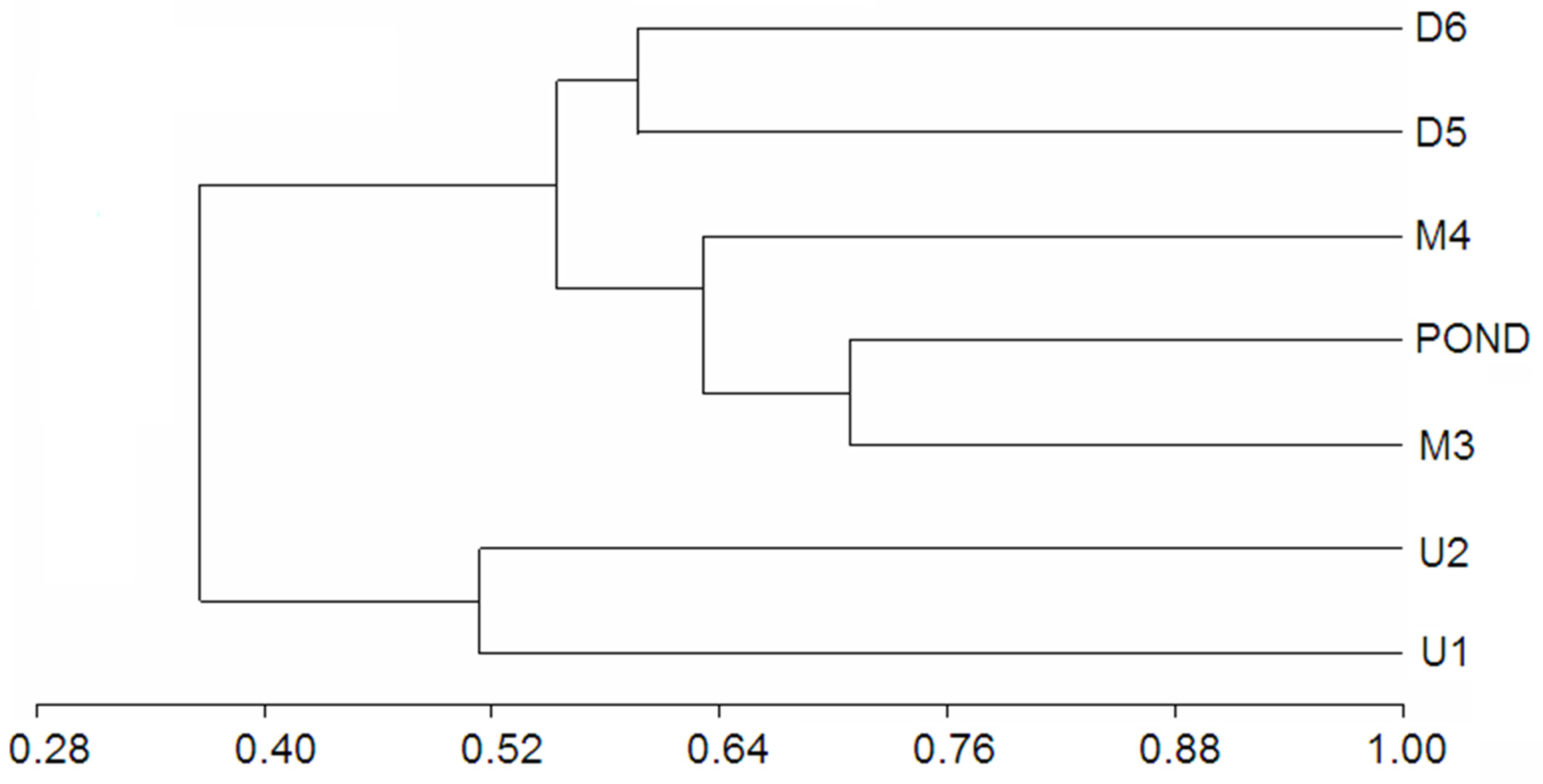
3.2. Macrozoobenthos—Macroinvertebrates
4. Discussion
4.1. Zooplankton
4.2. Macroinvertebrates
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zalewski, M.; Wagner, I. Ecohydrology—The use of water and ecosystem processes for healthy urban environments. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2005, 5, 263. [Google Scholar]
- Krepski, T.; Czerniawski, R. Shaping of macroinvertebrate structures in a small fishless lowland stream exposed to anthropopressure, including the environmental conditions. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2018, 419, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohl, E. The significance of small streams. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 11, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.R.; Taylor, C.M. Influence of fish predation on assemblage structure of macroinvertebrates in an intermittent stream. T. Am. Fish. Soc. 2003, 132, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhmer, J.; Zenker, A.; Ackermann, B.; Kappus, B. Macrozoobenthos communities and biocoenotic assessment of ecological status in relation to degree of human impact in small streams in southwest Germany. J. Aquat. Ecosyst. Stress Recov. 2001, 8, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H.; Doi, H.; Imai, H.; Gunji, F.; Nakano, S.I. Longitudinal changes in zooplankton distribution below a reservoir outfall with reference to river planktivory. Limnology 2008, 9, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerniawski, R.; Kowalska-Góralska, M. Spatial changes in zooplankton communities in a strong human-mediated river ecosystem. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagała, J.; Krepski, T.; Czerniawski, R.; Pilecka-Rapacz, M. Prey availability and selective feeding of sea trout (Salmo trutta L.; 1758) fry stocked in small forest streams. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2015, 31, 375–380. [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist, M.J.; Zhu, W. Aquatic insect diversity in streams across a rural–urban land-use discontinuum. Hydrobiologia 2019, 837, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerniawski, R.; Sługocki, Ł. A comparison of the effect of beaver and human-made impoundments on stream zooplankton. Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, R.D.M.G.; Facure, K.G.; Pavanin, L.A.; Jacobucci, G.B. Influence of environmental factors on benthic macroinvertebrate communities of urban streams in Vereda habitats, Central Brazil. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2011, 23, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerniawski, R. Zooplankton community changes between forest and meadow sections in small headwater streams, NW Poland. Biologia 2013, 68, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Lu, D.; Cai, D.; Wang, B. Influences of dispersal and local environmental factors on stream macroinvertebrate communities in Qinjiang River, Guangxi, China. Aquat. Biol. 2014, 20, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerniawski, R.; Domagała, J. Small dams profoundly alter the spatial and temporal composition of zooplankton communities in running waters. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2014, 99, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakouei, K.; Kiesel, J.; Kail, J.; Pusch, M.; Jähnig, S.C. Quantitative hydrological preferences of benthic stream invertebrates in Germany. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 79, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Radwan, S. Freshwater Fauna of Poland; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Łódzkiego: Łódź, Polska, 2004; pp. 1–447. [Google Scholar]
- Rybak, J.I.; Błędzki, L.A. Planktonic Crustaceans of Freshwaters; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Warszawskiego: Warszawa, Poland, 2010; pp. 1–366. [Google Scholar]
- Kownacki, A.; Soszka, H. Guidelines for Assessing the State of the River on the Basis of Macroinvertebrates and for Collecting a Sample of Macroinvertebrates in Lakes; Instytut Ochrony Środowiska, Zakład Ochrony Przyrody PAN: Warszawa–Kraków, Poland, 2004; pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Akopian, M.; Garnier, J.; Pourriot, R. A large reservoir as a source of zooplankton for the river: Structure of the populations and influence of fish predation. J. Plankton Res. 1999, 21, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourriot, R.; Rougier, C.; Miquelis, A. Origin and development of river zooplankton: Example of the Marne. Hydrobiologia 1997, 345, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpowicz, M. Influence of eutrophic lowland reservoir on crustacean zooplankton assemblages in river valley oxbow lakes. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 2055–2061. [Google Scholar]
- Gołdyn, R.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K. Interactions between phytoplankton and zooplankton in the hypertrophic Swarzędzkie lake in western Poland. J. Plankton Res. 2008, 30, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Lair, N. A review of regulation mechanisms of metazoan plankton in riverine ecosystems: Aquatic habitat versus biota. Riv. Res. Appl. 2006, 22, 567–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejsmont-Karabin, J.; Kuczyńska-Kippen, N. Urban Rotifers: Structure and Densities of Rotifer Communities in Water Bodies of the Poznań Agglomeration Area (Western Poland). In Rotifer IX; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Czerniawski, R.; Krepski, T. Zooplankton size as a factor determining the food selectivity of roach (Rutilus rutilus) in water basins outlets. Water 2019, 11, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, J.D.; Thorp, J.H. Impacts of fish predation on an Ohio River zooplankton community. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havel, J.E.; Shurin, J.B. Mechanisms, effects, and scales of dispersal in freshwater zooplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, W.B. Microcrustacea in flowing water: Experimental analysis of washout times and a field test. Freshw. Biol. 1992, 28, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczyńska-Kippen, N.M.; Nagengast, B. The influence of the spatial structure of hydromacrophytes and differentiating habitat on the structure of rotifer and cladoceran communities. Hydrobiologia 2006, 559, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerniawski, R.; Sługocki, Ł. Analysis of zooplankton assemblages in man-made ditches in relation to current velocity. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2017, 46, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudduth, E.B.; Meyer, J.L. Effects of bioengineered streambank stabilization on bank habitat and macroinvertebrates in urban streams. Environ. Manag. 2006, 38, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygoruk, M.; Frąk, M.; Chmielewski, A. Agricultural rivers at risk: Dredging results in a loss of macroinvertebrates. Preliminary observations from the Narew Catchment, Poland. Water 2015, 7, 4511–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, D.A.; Robertson, A.I. Relationships between riverine fish and woody debris: Implications for lowland rivers. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1999, 50, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acreman, M.; Arthington, A.H.; Colloff, M.J.; Couch, C.; Crossman, N.D.; Dyer, F.; Overton, I.; Pollino, C.A.; Stewardson, M.J.; Young, W. Environmental flows for natural, hybrid, and novel riverine ecosystems in a changing world. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 12, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couceiro, S.R.M.; Hamada, N.; Luz, S.L.B.; Forsberg, B.R.; Pimentel, T.P. Deforestation and sewage effects on aquatic macroinvertebrates in urban streams in Manaus, Amazonas, Brazil. Hydrobiologia 2007, 575, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołdyn, R.; Szpakowska, B.; Świerk, D.; Domek, P.; Buxakowski, J.; Dondajewska, R.; Barałkiewicz, D.; Sajnóg, A. Influence of stormwater runoff on macroinvertebrates in a small urban river and a reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.; Hu, X.; He, Q.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, H.; Hu, Z.; Mazumder, A. Impacts of rapid urbanization on the water quality and macroinvertebrate communities of streams: A case study in Liangjiang New Area, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1601–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfritzson, M.P.; Batucan, L.S.; De Jesus, I.B.B.; Triño, E.M.C.; Ishida, Y.U.T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ko, C.-Y.; Iwata, T.; Borja, A.S.; Briones, J.C.A.; et al. Nutrient loadings and deforestation decrease benthic macroinvertebrate diversity in an urbanised tropical stream system. Limnologica 2020, 80, 125744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medupin, C. Spatial and temporal variation of benthic macroinvertebrate communities along an urban river in Greater Manchester, UK. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, J.; Niedzielska, K. Analiza biologiczna jakości wody rzeki Rudna graniczącej z zbiornikiem osadów poflotacyjnych “Żelazny Most”. The biological water quality assessment of the Rudna River situated near the post-flotation tailing pond “Żelazny Most” on the basis of communities of benthic invertebrates. Inżynieria Ekologiczna 2012, 29, 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Korycińska, M.; Królak, E. The use of various biotic indices for evaluation of water quality in the lowland rivers of Poland (exemplified by the Liwiec river). Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15, 419–428. [Google Scholar]
- Karr, J.R. Defining and assessing ecological integrity: Beyond water quality. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1993, 12, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, J.; Mueller, M.; Pander, J.; Geist, J. Effectiveness of catchment erosion protection measures and scale-dependent response of stream biota. Hydrobiologia 2019, 830, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Site | Temp | Dissolved Oxygen | Ph | Cond | Chlorophyll A | Chloride | Total Dissolved Solids | Width | Depth | Current Velocity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (°C) | (mg L−1) | (µS cm−1) | (mg L−1) | (mg L−1) | (mg L−1) | (m) | (m) | (m s−1) | ||
| U1 | 14.0 ± 7.3 | 7.1 ± 2.8 | 8.5 ± 0.5 | 866 ± 118 | 3.4 ± 1.7 | 2141 ± 3860 | 0.5216 ± 0.1174 | 0.88 ± 0.48 | 0.10 ± 0.05 | 0.030 ± 0.020 |
| U2 | 13.8 ± 7.2 | 5.8 ± 3.0 | 8.5 ± 0.3 | 792 ± 161 | 5.3 ± 3.2 | 2150 ± 4128 | 0.4932 ± 0.1147 | 0.74 ± 0.41 | 0.12 ± 0.07 | 0.053 ± 0.037 |
| POND | 17.4 ± 7.6 | 8.9 ± 3.5 | 8.8 ± 0.4 | 536 ± 306 | 193.0 ± 108.9 | 1769 ± 2933 | 0.4217 ± 0.1285 | - | - | - |
| M3 | 16.7 ± 6.1 | 7.1 ± 3.2 | 8.6 ± 0.4 | 608 ± 312 | 222.9 ± 122.6 | 1530 ± 2328 | 0.4277 ± 0.1339 | 0.94 ± 0.41 | 0.10 ± 0.04 | 0.285 ± 0.145 |
| M4 | 15.0 ± 6.1 | 8.3 ± 2.0 | 8.6 ± 0.3 | 727 ± 160 | 81.1 ± 42.8 | 1980 ± 3359 | 0.4623 ± 0.1033 | 1.63 ± 0.47 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.392 ± 0.166 |
| D5 | 14.2 ± 6.0 | 7.1 ± 1.9 | 8.5 ± 0.3 | 1026 ± 231 | 39.1 ± 17.8 | 1669 ± 2224 | 0.6504 ± 0.1373 | 3.08 ± 0.30 | 0.18 ± 0.05 | 0.265 ± 0.058 |
| D6 | 15.4 ± 7.4 | 7.9 ± 3.2 | 8.5 ± 0.4 | 903 ± 246 | 42.6 ± 25.5 | 1951 ± 3034 | 0.6392 ± 0.0636 | 4.19 ± 1.04 | 0.73 ± 0.19 | 0.038 ± 0.033 |
| Site | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | U1 | U2 | POND | M3 | M4 | D5 | D6 |
| Rotifera | |||||||
| Anuraeopsis fissa | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Asplanchna sieboldi | + | + | + | ||||
| Bdelloidea | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Brachionus angularis | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Brachionus calyciflorus | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Brachionus quadridentatus | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Brachionus sp. | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Brachionus rubens | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Brachionus urceolaris | + | ||||||
| Cephalodella gibba | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Cephalodella sp. | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Cephalodella ventripes | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Collotheca mutabilis | + | ||||||
| Colurella adriatica | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Colurella sp. | + | + | + | + | |||
| Colurella colurus | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Colurella uncinata | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Conochilus unicornis | + | + | + | + | |||
| Euchlanis dilatata | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Filinia brachiata | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Filinia longiseta | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Filinia sp. | + | ||||||
| Filinia terminalis | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Keratella cochlearis cochlearis | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Keratella cochlearis hispida | + | ||||||
| Keratella cochlearis tecta | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Keratella quadrata | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Keratella testudo | - | + | + | ||||
| Keratella testudo gossei | + | ||||||
| Keratella ticinensis | + | + | + | ||||
| Keratella valga | + | + | |||||
| Lecane bulla | + | + | |||||
| Lecane closterocerca | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Lecane flexilis | + | + | |||||
| Lecane hamata | + | + | + | ||||
| Lecane luna | + | ||||||
| Lecane sp. | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Lepadella acuminata | + | + | + | ||||
| Lepadella ovalis | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Lepadella sp. | + | + | |||||
| Monommata longiseta | + | ||||||
| Mytilina mucronata | + | ||||||
| Notholca acuminata | + | + | + | ||||
| Notholca squamula | + | + | |||||
| Polyarthra dolichoptera | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Polyarthra remata | + | + | |||||
| Polyarthra sp. | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Polyarthra vulgaris | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Proales sp. | - | + | |||||
| Rotifera not identified | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Synchaeta pectinata | + | + | |||||
| Synchaeta sp. | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Taphrocampa sp. | + | ||||||
| Trichocerca capucina | + | ||||||
| Trichocerca dixon-nutalli | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Trichocerca elongata | + | + | + | ||||
| Trichocerca pusilla | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Trichocerca rousseleti | + | ||||||
| Trichocerca sp. | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Trichocerca stylata | + | ||||||
| Trichocerca weberi | + | + | |||||
| Cladocera | |||||||
| Acroperus harpae | + | ||||||
| Bosmina longirostris | + | + | + | ||||
| Ceriodaphnia sp. | + | ||||||
| Chydorus sphaericus | + | + | |||||
| Diaphanosoma brachyurum | + | + | |||||
| Moina micrura | + | ||||||
| Pleuroxus aduncus | + | ||||||
| Polyphemus pediculus | + | ||||||
| Scaphaloberis mucronata | + | + | + | ||||
| Cladocera juv | + | ||||||
| Copepoda | |||||||
| Eucyclops macruroides | + | + | + | ||||
| Eucyclops macrurus | + | ||||||
| Eurytemora velox | + | + | |||||
| Macrocyclops albidus | + | ||||||
| Thermocyclops oithonoides | + | ||||||
| Nauplii Cyclopoida | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Copepodid Calanoida | + | + | |||||
| Copepodid Cyclopoida | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Site | U1 | U2 | M3 | M4 | D5 | D6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U2 | 76.5 | X | ||||
| M3 | 58.8 | 52.6 | X | |||
| M4 | 50.0 | 44.4 | 64 | X | ||
| D5 | 64.3 | 56.3 | 47 | 73 | X | |
| D6 | 44.4 | 47.4 | 32 | 47 | 50 | X |
| POND | 44.4 | 47.4 | 32 | 47 | 61.5 | 60 |
| Site/Month | BMWP-PL | Margalef Index | ASPT | Shannon-Weaver | TBI | GOLD (%) | % Diptera |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1/April | 35 | 3.33 | 3.89 | 0.990 | 3 | 91 | 42 |
| U1/October | 45 | 4.01 | 3.75 | 0.990 | 4 | 90 | 49 |
| U2/April | 37 | 4.16 | 3.36 | 1.648 | 4 | 85 | 35 |
| U2/October | 47 | 5.86 | 2.94 | 0.796 | 6 | 94 | 74 |
| M3/April | 46 | 3.84 | 3.54 | 0.964 | 6 | 94 | 36 |
| M3/October | 31 | 3.40 | 3.44 | 1.684 | 5 | 36 | 10 |
| M4/April | 26 | 3.35 | 3.25 | 1.160 | 4 | 93 | 17 |
| M4/October | 25 | 3.09 | 3.57 | 1.476 | 5 | 53 | 40 |
| D5/April | 17 | 2.49 | 3.40 | 0.399 | 3 | 100 | 11 |
| D5/October | 31 | 3.45 | 3.44 | 1.236 | 4 | 43 | 23 |
| D6/April | 16 | 3.49 | 3.20 | 0.907 | 3 | 59 | 6 |
| D6/October | 43 | 5.78 | 4.30 | 0.989 | 7 | 79 | 73 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czerniawski, R.; Sługocki, Ł.; Krepski, T.; Wilczak, A.; Pietrzak, K. Spatial Changes in Invertebrate Structures as a Factor of Strong Human Activity in the Bed and Catchment Area of a Small Urban Stream. Water 2020, 12, 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030913
Czerniawski R, Sługocki Ł, Krepski T, Wilczak A, Pietrzak K. Spatial Changes in Invertebrate Structures as a Factor of Strong Human Activity in the Bed and Catchment Area of a Small Urban Stream. Water. 2020; 12(3):913. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030913
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzerniawski, Robert, Łukasz Sługocki, Tomasz Krepski, Anna Wilczak, and Katarzyna Pietrzak. 2020. "Spatial Changes in Invertebrate Structures as a Factor of Strong Human Activity in the Bed and Catchment Area of a Small Urban Stream" Water 12, no. 3: 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030913
APA StyleCzerniawski, R., Sługocki, Ł., Krepski, T., Wilczak, A., & Pietrzak, K. (2020). Spatial Changes in Invertebrate Structures as a Factor of Strong Human Activity in the Bed and Catchment Area of a Small Urban Stream. Water, 12(3), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030913





