Identifying Groundwater and River Water Interconnections Using Hydrochemistry, Stable Isotopes, and Statistical Methods in Hanumante River, Kathmandu Valley, Central Nepal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
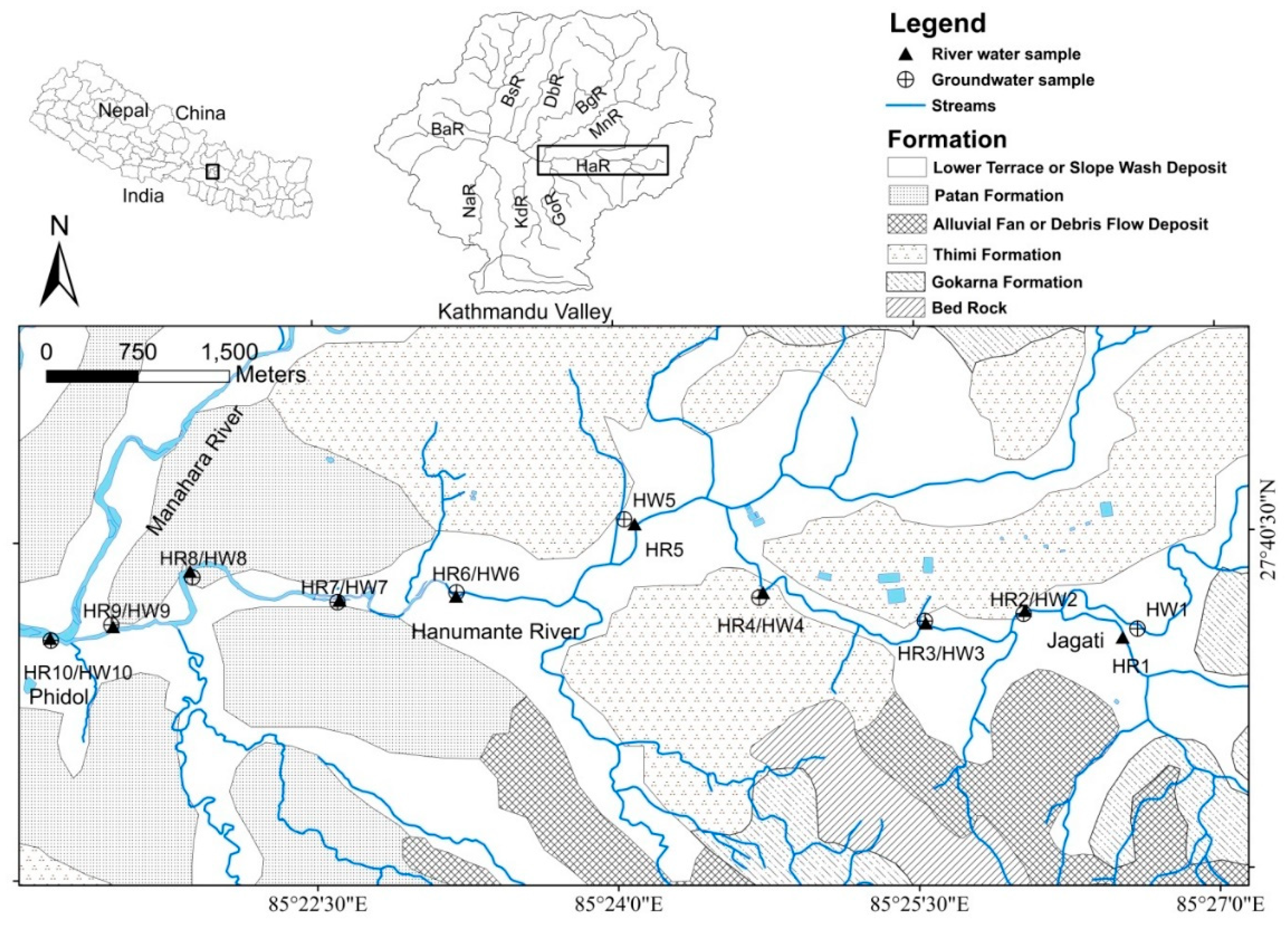
2.1. Study Area
2.2. FieldMeasurement and Water Sampling
2.3. Chemical and Isotopic Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. InSitu Parameters
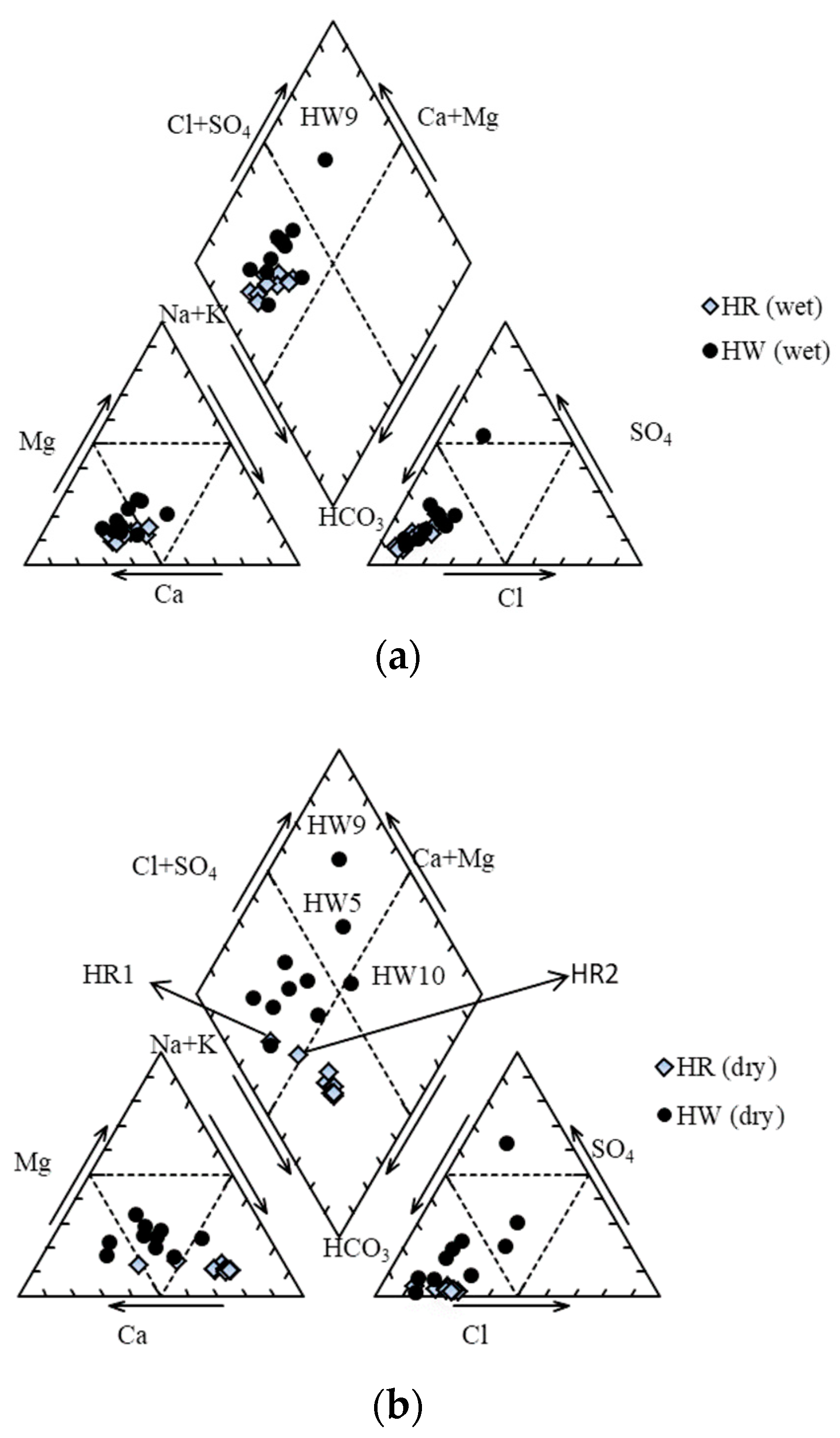
3.2. Hydro-Chemical Parameters
3.3. Isotopic Composition
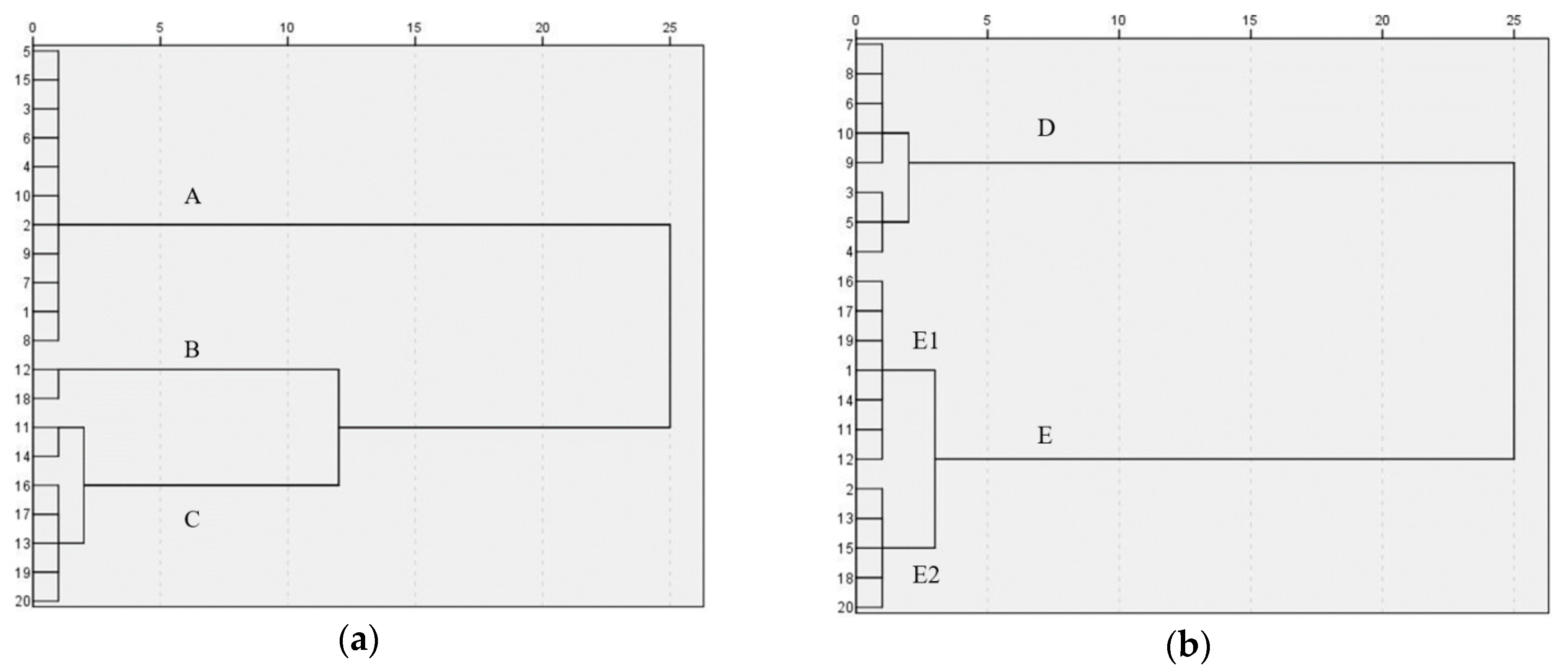
3.4. Clustering of River Water and Groundwater
3.5. Identifying Areas of River Water and Groundwater Interconnection
3.6. River Water Contribution to Groundwater
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woessner, W.W. Stream and fluvial plain grondwater interaction: Rescaling hydroeologic thought. Ground Water 2000, 38, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophocleous, M. Interaction between groundwater and surface water: The state of the science. Hydrol. J. 2002, 10, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derx, J.; Blaschke, A.P.; Bloschl, G. Three-dimensional flow patterns at the river-aquifer interface—A case study at the Danube. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yamanaka, T. Tracing groundwater recharge sources in a mountain-plain transitional area using stable isotopes and hydrochemistry. J. Hydrol. 2012, 464–465, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winter, T.C.; Harvey, J.W.; Franke, O.L.; Alley, W.M. Ground Water and Surface Water: A Single Resource; DIANE Publishing Inc.: Darby, PA, USA, 1998; Volume 79. [Google Scholar]
- Ezugwu, C.N.; Apeh, S. Groundwater and surface water as one resource: Connectivity and interaction. J. Mech. Civil Eng. 2017, 14, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, X.; Xia, J.; Yu, J.; Tang, C. A study of interaction between surface water and groundwater using environmental isotope in Huaisha River basin. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2006, 49, 1299–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.K.; Ajeena, A.R. Assessment of interconnection between surface water and groundwater in Sawa lake area, Southern Iraq, using stable isotope technique. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Han, S. Assessment by Multivariate Analysis of groundwater – surface water interactions in the coal-mining exploring district, China. Earth Sci. Res. J. 2016, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Kim, Y. Determining the seasonality of groundwater recharge using water isotopes: A case study from the upper North Han River basin, Korea. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menció, A.; Mas-Pla, J. Assessment by multivariate analysis of groundwater-surface water interactions in urbanized mediterranean streams. J. Hydrol. 2008, 352, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, C.; Han, Z.; Cao, Y. Hydrochemical characteristic and interaction process of surface and groundwater in mid-lower reach of Hanjiang River, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tang, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.L. The Interaction between surface water and groundwater and its effect on water quality in the Second Songhua River Basin, Northeast China. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 125, 1495–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunke, M.; Gonser, T. The ecological significance of exchange processes between rivers and groundwater. Freshwater Biol. 1997, 37, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brindha, K.; Neena Vaman, K.V.; Srinivasan, K.; Sathis Babu, M.; Elango, L. Identification of surface water-groundwater interaction by hydrogeochemical indicators and assessing its suitability for drinking and irrigational purposes in Chennai, Southern India. Appl. Water Sci. 2014, 4, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, S.; Kong, X.; Zheng, W.; Feng, W.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, R.; Song, X.; Sprenger, M. Interaction of surface water and groundwater influenced by groundwater over-extraction, waste water discharge and water transfer in Xiong’an New area, China. Water 2019, 11, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gautam, R.; Shrestha, J.K.; Shrestha, G.K.C. Assessment of river water intrusion at the periphery of Bagmati River in Kathmandu Valley. Nepal J. Sci. Technol. 2013, 14, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malla, R.; Shrestha, S.; Chapagain, S.K.; Shakya, M.; Nakamura, T. Physico-chemical and oxygen-hydrogen isotopic assessment of Bagmati and Bishnumati rivers and the shallow groundwater along the river corridors in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2015, 7, 1435–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajracharya, R.; Nakamura, T.; Shakya, B.M.; Nishida, K.; Shrestha, S.D.; Tamrakar, N.K. Identification of river water and groundwater interaction at central part of the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal using stable isotope tracers. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Tech. Res. 2018, 3, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moog, O.; Sharma, S. Biological rapid assessment of water quality in the Bagmati River and its tributaries, Kathmandu. In Proceedings of the Ecohydrology Conference on High Mountain Areas, Kathmandu, Nepal, 24–28 March 1996; pp. 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Devkota, D.C.; Watanabe, K. Impact of solid waste on water quality of Bishnumati River and surrounding areas in Kathmandu, Nepal. J. Nepal Geol. Soc. 2005, 31, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajracharya, R.; Tamrakar, N.K. Environmental status of Manahara River, Kathmandu, Nepal. Bull. Dep. Geol. 2007, 10, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajracharya, R.; Tamrakar, N.K.; Shrestha, M.; Bohara, B. Status of shallow wells along major rivers of the Kathmandu Valley, Central Nepal. J. Nepal Geol. Soc. 2018, 56, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S. Water pollution and health. Kath. Uni. Med. J. 2006, 4, 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Kalbus, E.; Reinstorf, F.; Schirmer, M. Measuring methods for groundwater—Surface water interactions: A review. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 10, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terwey, J.L. Isotopes in groundwater hydrology. Chall. Afr. Hydrol. Water Resour. 1984, 144, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, B.G.; Coplen, T.B.; Bullen, T.D.; Hal Davis, J. Use of chemical and isotopic tracers to characterize the interactions between ground water and surface water in mantled karst. Ground Water 1997, 35, 1014–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, R.J.; Strand, M.; Walker, J.F. Measuring groundwater-surface water interaction and its effect on wetland stream benthic productivity, Trout Lake Watershed, Northern Wisconsin, USA. J. Hydrol. 2006, 320, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brenot, A.; Petelet-Giraud, E.; Gourcy, L. Insight from surface water-groundwater interactions in an alluvial aquifer: Contributions of δ2H and δ18O of water, δ34SSO4 and δ18OSO4 of sulfates, 87Sr/86Sr Ratio. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 13, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, A.M.; Krishnamurthy, R.V.; Kehew, A.E.; Crossey, L.J.; Karlstrom, K.K. Factors affecting the stable isotopes ratios in groundwater impacted by intense agricultural practices: A case study from the Nile Valley of Egypt. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleckenstein, J.H.; Krause, S.; Hannah, D.M.; Boano, F. Groundwater-surface water interactions: New methods and models to improve understanding of processes and dynamics. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerhoff, S.B.; Maxwell, R.M.; Revil, A.; Martin, J.B.; Karaoulis, M.; Graham, W.D. Characterization of groundwater and surface water mixing in a semiconfined karst aquifer using time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 2566–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLachlan, P.J.; Chambers, J.E.; Uhlemann, S.S.; Binley, A. Geophysical characterisation of the groundwater–surface water interface. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 109, 302–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakakibara, K.; Tsujimura, M.; Song, X.; Zhang, J. Interaction between surface water and groundwater revealed by multi-tracer and statistical approaches in the Baiyangdian Lake watershed, North China Plain. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2016, 10, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epting, J.; Huggenberger, P.; Radny, D.; Hammes, F.; Hollender, J.; Page, R.M.; Weber, S.; Banninger, D.; Auckenthaler, A. Spatiotemporal scales of river-groundwater interaction—The role of local interaction processes and regional groundwater regimes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1224–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Zhang, B.; Long, D. Characterizing interactions between surface water and groundwater in the Jialu River Basin using major ion chemistry and stable isotopes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 4265–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guggenmos, M.R.; Daughney, C.J.; Jackson, B.M.; Morgenstern, U. Regional-scale identification of groundwater-surface water interaction using hydrochemistry and multivariate statistical methods, Wairarapa Valley, New Zealand. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 3383–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sada, R. Trajectory of urban river degradation:Initiatives for conservation and restoration (a case study of Hamunante River in Bhaktapur, Nepal). South Asisn Water Stud. 2014, 4, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, P. Climate Change Impact on River Dynamics of the Bagmati Basin, Kathmandu Nepal; Report Submitted to National Adaptation Program of Action to Climate Change Project; Government of Nepal: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2010; Volume 36.
- Pathak, D.R.; Yatabe, R.; Bhandary, N.P. Indentification of major affecting spatial and temporal variation of water quality in Kathmandu Basin, Nepal, using multivariate statistical analysis. Int. J. Water 2015, 9, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, B.R.; Ishidaira, H.; Pandey, V.P.; Shakya, N.M. Impact assessment of Gorkha earthquake 2015 on portable water supply in Kathmandu Valley: Preliminary analysis. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. 2016, 72, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, M.; Igarashi, Y. Neogene to quaternary lacustrine sediment in the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. J. Nepal Geol. Soc. 1984, 4, 37–100. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, T.; Gajurel, A.P.; Tabata, H.; Ooi, N.; Takagawa, T.; Kitagawa, H.; Upreti, B.N. Revised lithostratigraphy of fluvial-lacustrine sediments comprising northern Kathmandu basin in central Nepal. J. Nepal Geol. Soc. 2008, 37, 25–44. [Google Scholar]
- Dhittal, M.R. Geology of Nepal Himalayas: Regional Perspective of the Classic Collided Orogeen; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotway, C.A.; Helsel, D.R.; Hirsch, R.M. Statistical methods in water resources. Technometics 1994, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, R.R.; Zhang, F.; Rehman, F.U.; Wang, G.; Ye, M.; Zeng, C.; Tang, H. Spatiotemporal variations of hydrogeochemistry and its controlling factors in the Gandaki River Basin, Central Himalaya Nepal. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishara, A.J.; Hittner, J.B. Testing the significance of a correlation with nonnormal data: Comparision of Pearson, Spearman, transformation, and resampling approaches. Psychol. Methods 2012, 17, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, M.; Ramanathan, A.; Keshari, A.K. Understanding the extent of interactions between groundwater and surface water through major ion chemistry and multivariate statistical techniques. Hydrol. Process 2009, 23, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiyu, S.A.; Badmus, B.S.; Olurin, O.T.; Ojekunle, Z.O. Evaluation of seasonal variation of water quality using multivariate statistical analysis and irrigation parameter indices in Ajakanga area, Ibadan, Nigeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ward, J.H. Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Kumar, S.R. Quality assessment of groundwater for drinking and irrigation use in semi-urban area of Tripura, India. Ecol. Environ. Cons. 2015, 21, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khatib, M.; Al-Najar, H. Hydro-geochemical characteristics of groundwater beneath the Gaza Strip. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2011, 3, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhat, S.A.; Meraj, G.; Yaseen, S.; Pandit, A.K. Statistical assessment of water quality parameters for pollution source identification in Sukhnag Stream: An inflow stream of Lake Wular (Ramsar iite), Kashmir Himalaya. J. Ecosyst. 2014, 2014, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Alfy, M.; Merkel, B. Assessment of human impact on quaternary aquifers of Rafah Area, NE Sinai, Egypt. Int. J. Econ. Environ. Geol. 2004, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, M.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, W.; Huang, H. Analyzing the significant environmental factors on the spatial and temporal distribution of water quality utilizing multivariate statistical techniques: A case study in the Balihe Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 29418–29432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.J.S. Hydrogeochemical and multivariate statistical appraisal of pollution sources in the groundwater of the lower Bhavani River basin in Tamil Nadu. Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shakya, B.M.; Nakamura, T.; Shrestha, S.D.; Nishida, K. Identifying the deep groundwater recharge processes in an intermountain basin using the hydrogeochemical and water isotope characteristics. Hydrol. Res. 2019, 50, 1216–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shakya, B.M.; Nakamura, T.; Kamei, T.; Shrestha, S.D.; Nishida, K. Seasonal groundwater quality status and nitrogen contamination in the shallow aquifer system of the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Water 2019, 11, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gajurel, A.P.; France-Lanord, C.; Huyghe, P.; Guilmette, C.; Gurung, D. C and O isotope compositions of modern fresh-water mollusc shells and river waters from the Himalaya and Ganga Plain. Chem. Geol. 2006, 233, 156–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giri, U. Evaluation of Stable Isotope Ratios within Meteoric, Surface, and Groundwater within the Kathmandu Valley. Master’s Thesis, Georgia State University, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018. Available online: http://scholarwork.gsu.edu/geoscience_theses/116 (accessed on 10 November 2019).
- Matheswaran, K.; Khadka, A.; Dhaubanjar, S. Delineation of spring recharge zones using environmental isotopes to support climate-resilient interventions in two mountainous catchments in far-western Nepal. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 2181–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Han, G.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q. Spatial and seasonal variation of O and H isotopes in the Jiulong River, Southeast China. Water 2018, 10, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lachniet, M.S.; Patterson, W.P. Oxygen isotope values of precipitation and surface waters in northern Central America ( Belize and Guatemala ) are dominated by temperature and amount effects. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 284, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R. The relatioship between the isotopic composition of precipitation, surface runoff and groundwater for semiarid and arid zones. Appl. Tracesrs Arid Zone Hydrol. 1995, 232, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, R.; Tian, L.; Weng, Y.B.; Liu, Z.F.; Zhao, Z.P. The altitude effect of δ18O in precipitation and river water in the Southern Himalayas. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, S.; Kazama, F. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji River Basin, Japan. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, S. Assessment of community vulnerability to flood in Hanumante River, Bhaktapur, Nepal: Finding the causes and mitigation approaches. Int. J. Lsld. Environ. 2013, 1, 77–78. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatta, B.P.; Pandey, R.K. Bhaktapur urban flood related disaster risk and strategy after 2018. J. APF Command Staff Coll. 2020, 3, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Nishida, K.; Kazama, F. Influence of a dual monsoon system and two sources of groundwater recharge on Kofu Basin alluvial fans, Japan. Hydrol. Res. 2017, 48, 1071–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sampling ID | N | E | River Bank | Distance from River (m) | Well Depth (m) | Water Level Depth (m) | EC (μs/cm) | pH | DO (mg/L) | Water Temp (°C) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet | Dry | Difference WLD | Wet | Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | Dry | ||||||
| HW1 | 27.66936 | 85.44028 | Right | 100 | 3.3 | 1 | 2.82 | 1.82 | 839 | 797 | 7.03 | 6.40 | 2.05 | 0.44 | 22.3 | 20.5 |
| HW2 | 27.6696 | 85.43617 | Left | 10 | 15.7 | 1 | 1.97 | 0.97 | 934 | 820 | 8.05 | 7.35 | 1.54 | 0.51 | 20.7 | 18.9 |
| HW3 | 27.66915 | 85.42796 | Right | 15 | 8.2 | 0.9 | 4.1 | 3.2 | 784 | 1323 | 7.22 | 6.79 | 1.14 | 0.52 | 23.6 | 19.0 |
| HW4 | 27.67104 | 85.41425 | Left | 60 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 1.74 | 1.14 | 681 | 576 | 7.16 | 6.40 | 2.38 | 2.27 | 22.0 | 13.4 |
| HW5 | 27.67638 | 85.40083 | Right | 80 | 5 | 1 | 3.38 | 2.38 | 290 | 637 | 7.75 | 6.09 | 3.16 | 1.27 | 24.1 | 17.5 |
| HW6 | 27.67166 | 85.38907 | Right | 20 | 2.8 | 1.7 | 2.35 | 0.65 | 520 | 611 | 7.06 | 6.13 | 2.56 | 1.25 | 22.8 | 17.5 |
| HW7 | 27.67103 | 85.37917 | Left | 30 | 7 | 4.3 | 5.8 | 1.5 | 591 | 856 | 7.52 | 6.48 | 2.45 | 1.97 | 22.7 | 17.6 |
| HW8 | 27.673 | 85.36717 | Left | 35 | 5 | 3.6 | 4.5 | 0.9 | 889 | 1192 | 7.25 | 6.39 | 4.10 | 1.82 | 22.6 | 20.4 |
| HW9 | 27.67027 | 85.3619 | Right | 20 | 2.8 | 0.8 | 4.4 | 3.6 | 769 | 964 | 6.73 | 6.28 | 3.00 | 2.08 | 21.0 | 18.3 |
| HW10 | 27.66843 | 85.35531 | Left | 10 | 2.4 | 0.1 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 623 | 1168 | 7.61 | 6.70 | 3.29 | 1.65 | 22.8 | 16.2 |
| HR1 | 27.66722 | 85.44194 | 164.2 | 604 | 8.00 | 7.45 | 6.48 | 5.54 | 22.3 | 14.9 | ||||||
| HR2 | 27.66916 | 85.43388 | 171.6 | 1340 | 8.06 | 6.84 | 6.30 | 1.67 | 22.4 | 16.5 | ||||||
| HR3 | 27.66833 | 85.42555 | 186.6 | 2010 | 7.22 | 7.02 | 5.50 | 0.51 | 23.0 | 16.6 | ||||||
| HR4 | 27.67083 | 85.41222 | 226 | 1780 | 7.78 | 6.88 | 4.43 | 0.67 | 23.0 | 14.0 | ||||||
| HR5 | 27.67583 | 85.40166 | 224 | 2060 | 7.85 | 6.75 | 4.59 | 0.55 | 23.9 | 15.6 | ||||||
| HR6 | 27.67083 | 85.38666 | 227 | 1924 | 7.81 | 7.00 | 4.26 | 0.24 | 24.3 | 17.2 | ||||||
| HR7 | 27.67055 | 85.37694 | 240 | 1998 | 7.96 | 7.00 | 3.99 | 0.32 | 23.5 | 16.7 | ||||||
| HR8 | 27.67277 | 85.36472 | 237 | 1955 | 7.80 | 6.99 | 4.03 | 0.15 | 23.5 | 17.1 | ||||||
| HR9 | 27.66861 | 85.35805 | 247 | 1960 | 6.70 | 7.00 | 4.05 | 0.07 | 23.0 | 17.9 | ||||||
| HR10 | 27.66805 | 85.35305 | 239 | 1985 | 7.96 | 6.98 | 4.25 | 0.44 | 23.4 | 16.4 | ||||||
| (a) River Water | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | DO | EC | pH | Na+ | NH4+-N | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | Cl− | NO3-N | PO4-P | SO42− | HCO3− |
| DO | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| EC | −0.86 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| pH | 0.64 ** | −0.72 | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| Na+ | −0.77 | 0.76 ** | −0.54 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| NH4+-N | −0.83 | 0.87 ** | −0.61 | 0.87 ** | 1.00 | ||||||||
| K+ | −0.72 | 0.80 ** | −0.49 | 0.92 ** | 0.92 ** | 1.00 | |||||||
| Mg2+ | −0.78 | 0.81 ** | −0.54 | 0.98 ** | 0.90 ** | 0.95 ** | 1.00 | ||||||
| Ca2+ | −0.73 | 0.74 ** | −0.49 | 0.94 ** | 0.82 ** | 0.87 ** | 0.92 ** | 1.00 | |||||
| Cl− | −0.77 | 0.79 ** | −0.57 | 0.98 ** | 0.91 ** | 0.95 ** | 0.98 ** | 0.92 ** | 1.00 | ||||
| NO3-N | 0.14 | −0.30 | 0.30 | 0.15 | −0.09 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 1.00 | |||
| PO4-P | −0.61 | 0.93 ** | −0.37 | 0.67 * | 0.89 ** | 0.88 ** | 0.69 * | 0.40 | 0.66 * | 0.70 * | 1.00 | ||
| SO42− | −0.70 | 0.77 ** | −0.50 | 0.92 ** | 0.89 ** | 0.98 ** | 0.94 ** | 0.88 ** | 0.93 ** | 0.12 | 0.75 ** | 1.00 | |
| HCO3− | −0.85 | 0.86 ** | −0.62 | 0.92 ** | 0.92 ** | 0.90 ** | 0.95 ** | 0.90 ** | 0.94 ** | −0.05 | 0.68 * | 0.89 ** | 1.00 |
| (b) Groundwater | |||||||||||||
| Parameters | DO | EC | pH | Na+ | NH4+-N | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | Cl− | NO3-N | PO4-P | SO42− | HCO3− |
| DO | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| EC | −0.39 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| pH | 0.36 | −0.18 | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| Na+ | −0.26 | 0.66 ** | −0.53 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| NH4+-N | −0.72 | 0.74 ** | −0.26 | 0.38 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| K+ | −0.38 | 0.75 ** | −0.03 | 0.42 | 0.63 ** | 1.00 | |||||||
| Mg2+ | 0.00 | 0.69 ** | −0.46 | 0.78 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.40 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Ca2+ | 0.10 | 0.51 * | −0.07 | 0.55* | 0.22 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 1.00 | |||||
| Cl− | −0.32 | 0.71 ** | −0.54 | 0.94 ** | 0.44 | 0.47 * | 0.81 ** | 0.49 * | 1.00 | ||||
| NO3-N | 0.30 | −0.10 | −0.28 | 0.11 | −0.45 | 0.07 | −0.10 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 1.00 | |||
| PO4-P | −0.19 | 0.74 * | 0.69 | 0.14 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.00 | −0.54 | 1.00 | ||
| SO42− | 0.25 | 0.12 | −0.36 | 0.54 * | −0.21 | −0.12 | 0.24 | 0.45 * | 0.47 * | 0.19 | −0.48 | 1.00 | |
| HCO3− | −0.33 | 0.48 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.45 * | 0.48 * | 0.49 * | 0.36 | 0.27 | −0.21 | 0.55 | −0.33 | 1.00 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bajracharya, R.; Nakamura, T.; Ghimire, S.; Man Shakya, B.; Kazi Tamrakar, N. Identifying Groundwater and River Water Interconnections Using Hydrochemistry, Stable Isotopes, and Statistical Methods in Hanumante River, Kathmandu Valley, Central Nepal. Water 2020, 12, 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061524
Bajracharya R, Nakamura T, Ghimire S, Man Shakya B, Kazi Tamrakar N. Identifying Groundwater and River Water Interconnections Using Hydrochemistry, Stable Isotopes, and Statistical Methods in Hanumante River, Kathmandu Valley, Central Nepal. Water. 2020; 12(6):1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061524
Chicago/Turabian StyleBajracharya, Ramita, Takashi Nakamura, Subesh Ghimire, Bijay Man Shakya, and Naresh Kazi Tamrakar. 2020. "Identifying Groundwater and River Water Interconnections Using Hydrochemistry, Stable Isotopes, and Statistical Methods in Hanumante River, Kathmandu Valley, Central Nepal" Water 12, no. 6: 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061524
APA StyleBajracharya, R., Nakamura, T., Ghimire, S., Man Shakya, B., & Kazi Tamrakar, N. (2020). Identifying Groundwater and River Water Interconnections Using Hydrochemistry, Stable Isotopes, and Statistical Methods in Hanumante River, Kathmandu Valley, Central Nepal. Water, 12(6), 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061524




