Abstract
Plant canopy morphology plays an important role in water balance, peculiarly in semiarid environments. Through a field experiment, the impact of plant morphology of two native plant species, Artemisia sacrorum Ledeb (ASL) and Spiraea pubescens Turcz (SPT), on partitioning rainwater was revealed. The results indicated that a fragmented leaf shape and apparently high stem density of ASL reduced the throughfall and its intensity effectively but facilitated soil moisture replenishment. Although SPT has a greater canopy cover and canopy depth than ASL does, larger throughfall, a smaller throughfall threshold, and stronger throughfall intensity were observed in the SPT site. Moreover, the SPT site has a higher soil steady infiltration rate, but produced more surface runoff and caused lower soil moisture content. This study highlights the importance of plant morphological traits, peculiarly leaf morphology, in partitioning rainwater in this semiarid region. We argue that plant morphological traits should be considered when selecting plant species for revegetation and assessing water balance.
1. Introduction
Revegetation increases evapotranspiration and decreases runoff in both wet and arid regions [1,2,3]. The ecohydrological function of plants is an important concern in vegetation restoration in arid and semiarid settings. In these regions, proper revegetation requires that plant species that consume less water be adopted [4,5,6]. It is fundamental to understand how the interception storage capacities differ among plant species [7]. Plants regulate rainfall efficiently by modifying rainfall intensity and raindrop size and reducing precipitation that reach the ground surface [8,9], altering infiltration, regulating runoff generation, and reducing soil erosion and sediment delivery. Morphological traits are the main contributors to the ecohydrological behavior of plants [10,11,12] and thus may facilitate ecological processes such as the nutrient input through leaves [13]. In addition, exploring the role plant morphology traits play is of particular importance in interpreting the variation of interception storage capacities among ecosystems [7]. Firstly, plant morphology traits affect the capacity of the canopy to intercept rainfall [11,14,15,16]. For example, small, light, soft, and noncircular leaves, densely situated on small branches, have more effective water adhesion capacity [11]. Large water drops are more likely to form on leaves with a larger area and a more unified shape [17]. In contrast, plants with small and fragmented leaves may crack the raindrops into smaller droplets and prevent the formation of large droplets for throughfall, thus increasing evaporation and leading to a smaller throughfall intensity and amount. Stem density is also an important plant morphology parameter that affects the plant’s ecohydrological function. A high stem density increases rainfall interception in the form of evaporation by increasing the effective plant surface area, reducing surface flow velocity, and promoting soil water infiltration [18]. For these reasons, morphological traits should be an important concern in selecting plant species for revegetation [6] and in evaluating ecohydrological consequences. However, canopy interception is one of the most underrated and underestimated processes in a rainfall–runoff analysis [4].
In the current study, the effects of plant morphology traits on ecohydrological functions were evaluated based on a comparison experiment in the Loess Plateau of China, where a vast revegetation project has been launched [19,20]. Two widely distributed native species in the Loess Plateau, the Spiraea pubescens Turcz (SPT) and Artemisia sacrorum Ledeb (ASL), were selected for the experiment. Based on the in situ investigation, the morphological traits of the two species were compared. The rainfall regulation of the two species was comparatively analyzed. Moreover, the runoff production and soil moisture dynamics of two abutting sites covered by these two plant species were observed and comparatively analyzed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Description
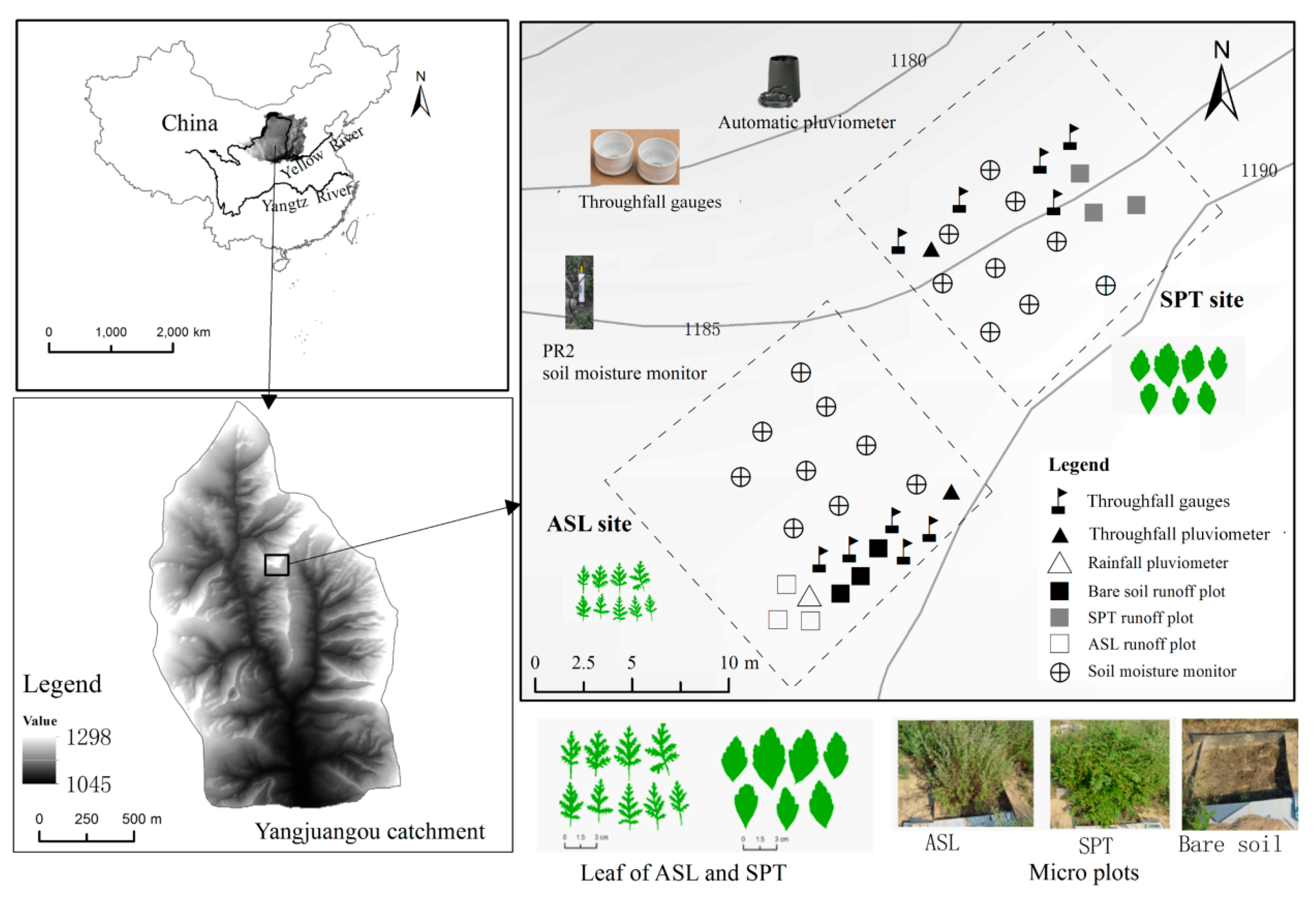
The study site is located in the Yangjuangou catchment (36°42′ N, 109°31′ E) in the hilly and gully region of the Loess Plateau in China (Figure 1). This region has a highly fragmented landscape. The slope gradient of this loess-covered catchment ranges from 10° to 30° [21]. It has a semiarid climate, with a mean annual precipitation of 535 mm [22], of which over 80% distributes between June and September, with a large interannual variation. Calcic Cambisol, characterized by uniform texture and a weak structure, covers most of the catchment [21]. Stipa bungeana and Artemisia scoparia are the dominant native herbivorous species. SPT, ASL, Prunus armeniaca, and Hippophae rhamnoides are the dominant native shrub species. Mosaic vegetation patches with various revegetation ages and rough topography are the typical landscape pattern in this catchment [22]. In this study, two 20 by 20 m rectangle sites on a northwest hillslope were selected for the experimental setup. The two sites were covered by SPT and ASL, respectively, and both at the same slope position. Within each site, three 60 by 60 cm micro plots were constructed for surface runoff gauge.
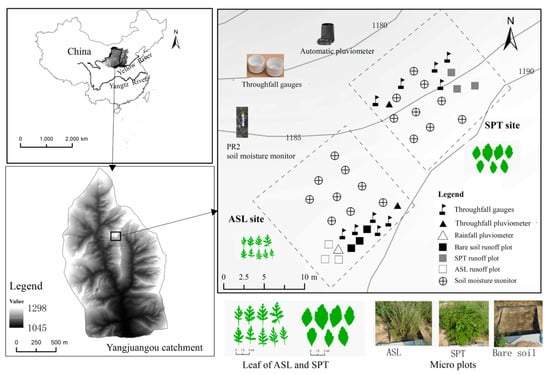
Figure 1.
Location of experimental sites and instruments.
2.2. Plant Morphology Quantification
Plant morphological traits were investigated based on random sampling. Morphological traits, including canopy cover area, basal area, canopy depth, plant height, canopy bottom height, leaf area, shape index (SPI) [23] of leaf, and stem density, were measured. The canopy cover area is defined as the total area of the vertical projection of the outermost canopy perimeter. Correspondingly, the basal area is the horizontal area covered by the plant basal. Canopy depth equates the height difference between the canopy top and the canopy bottom. An approximate circle or rectangle was used to fit the shape of the projection of plant canopy on the ground, and then an approximate area was computed. The plant height and canopy depth were measured by a steel ruler. For leaf area measurement and calculation of SPI, 123 leaves of each species were sampled randomly. All the leaves were scanned after being spread out on checked paper with printed square grids of 1 mm2. The pictures were digitized by using ArcMap (ESRI, Redland, CA, USA), and the area and SPI of each leaf were calculated. Stem density was measured in situ by counting the stems of each sampled plant. Twenty plants of ASL and SPT, respectively, with similar canopy cover and size, were selected for canopy morphological trait measurements. In total, eight traits, including plant height, canopy cover area, canopy bottom height, canopy depth, basal area, leaf area, leaf shape index, and stem density, were used in the analysis. For each micro plot with runoff gauging, the basal cover, canopy cover, and plant height were measured, following the photograph method [22].
2.3. Soil Properties Investigation
Twenty-seven soil samples were collected at each experimental site for soil properties analysis. Soil total nitrogen (TN), total carbon (TC), total sulfur (TS), organic carbon (SOC), pH, and electrical conductivity (EC) in two experimental sites were measured. TN, TC, and TS were tested through the dry combustion method [24] with an elemental analyzer (PE2400II Perkin-Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA). SOC was determined by using the dichromate oxidation method, where external heat was applied [25]. pH and EC were tested following Pansu and Gautheyrou [24]. Steady infiltration rate for the two sites was tested in situ with five replicates by using a double-ring infiltrometer.
2.4. Hydrological Response Measurement
Two methods were used to monitor the throughfall. Method 1 observed the throughfall depth of each rainfall event by placing a cylinder bucket gauge with a diameter of 20 cm and a height of 10 cm under the canopy. For each species, five plants were selected. The throughfall depth of the five gauges was averaged for each site. The observation was conducted from 11 May to 25 August 2009. For Method 2, tipping bucket pluviometers with an accuracy of 0.2 mm were set up under the plant canopy to record the throughfall dynamics for each rainfall event. Two plants with similar coverage and canopy depth within the SPT site and the ASL site were chosen for placing pluviometers. The monitoring by using this method started on 11 May and ended on 8 July 2009. Method 1 is simple and low cost and was applied to determine the difference in the throughfall depth between the two plant species. Method 2 was used to detect the effect of plant morphology on the rainfall threshold, start and end time of the throughfall, and the regulation of rainfall intensity. During the entire experimental period, one tipping bucket rain gauge was placed on the adjacent open bare area on the same hillslope to provide the rainfall reference for this experiment. Before the measurement, the clocks of the three pluviometers were synchronized.
Based on the monitoring, indicators including the rainfall threshold, depth, intensity, the start time lag (STL), and end time lag (ETL) of the throughfall, and runoff coefficient were determined. The rainfall threshold was defined as the minimum rainfall depth needed for the throughfall occurrence. STL indicates the delay of the start time of throughfall relative to the start time of outside rainfall. It was calculated as the difference between the start of rainfall outside and the commencement of throughfall under the canopy. Similarly, ETL is computed as the difference between the end time of rainfall outside and the terminal time of the throughfall. Based on the observation following Method 2, rainfall threshold, mean rainfall intensity, STL, and ETL of the two species were calculated. The runoff coefficient is defined as the ratio of rainfall transferred into surface runoff.
Soil volumetric moisture content (VWC) is defined as the fraction of the total volume of soil that is occupied by water, and was measured by a profile probe (PR2, Delta-T Devices Ltd., Cambridgeshire, UK) at depths of 0–10, 10–20, 20–30 and 30–40 cm from 20 May to 26 August 2009. The VWC measurements were calibrated against gravimetric measurements. Nine monitoring locations of soil moisture were set up in each site. At each depth of each site, the mean VWC of the site was calculated. The regular measurements were made at intervals of four days. Additional VWC measurements were conducted when there was a forecast of rainfall, whether or not it actually rained.
At each of the two instrumented sites (Figure 1), three 60 by 60 cm plots covered by single plant species were constructed to measure the runoff volume by using a graduated cylinder for each rainfall event.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Properties and Plant Morphology
As shown in Table 1, higher TN, TC, and EC were observed at the SPT site. The SOC and pH were higher in the ASL site. The soil at the two sites have similar TS. On the average, the steady infiltration rate at the SPT site was 3.11 mm min−1, and it was 2.28 mm min−1 at the ASL site.

Table 1.
Soil properties of the experimental sites.
Morphologically, SPT is significantly different from ASL. As shown in Table 2, the height of SPT is greater than that of ASL. In addition, the mean canopy cover area, canopy depth, leaf area, and mean canopy bottom height of SPT were greater than those of ASL. However, ASL has a larger basal area than SPT does. The leaf SPI indicates that the leaves of ASL are more irregular and fragmented, and the leaves of SPT are more cohesive. The canopy shape of ASL is almost cylindrical, whereas the shape of SPT is more like an upside-down cone. Moreover, the stem density of ASL was higher than that of SPT.

Table 2.
Plant morphological traits of ASL and SPT.
For throughfall-gauged plants, canopy cover and canopy depth were greater at the SPT site than at the ASL site (Table 3). For runoff-gauged micro plots, a higher canopy cover and larger plant height were observed at the SPT site than those at the ASL site. However, the ratio of basal area to the plot area of SPT was significantly smaller than that of ASL (Table 4).

Table 3.
Plant cover of throughfall-gauged plants.

Table 4.
Plant traits in plots for runoff monitoring.
3.2. Thresholds of Throughfall Occurrence
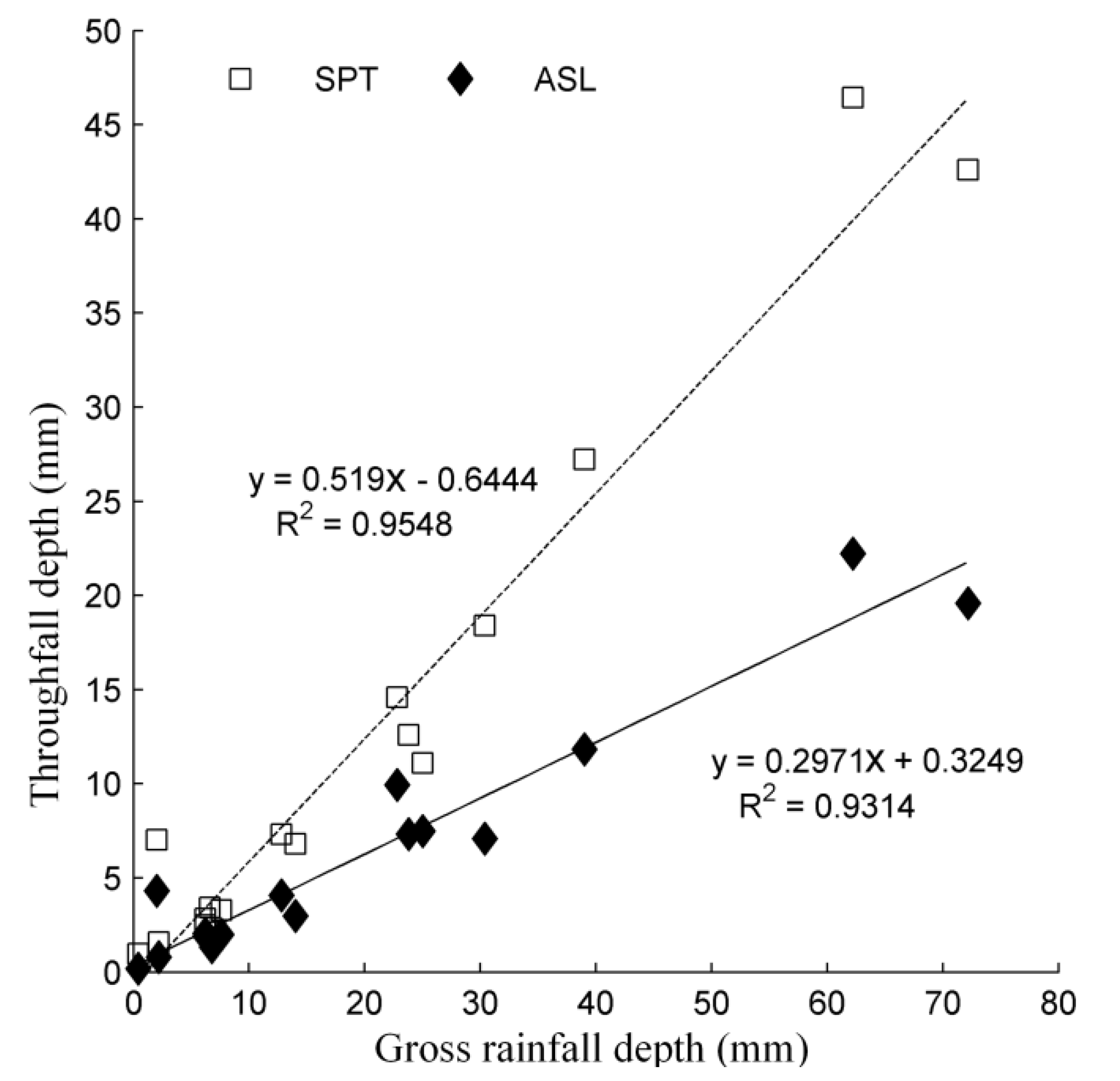
During the entire observation period, seventeen rainfall events with throughfall occurrence were recorded. The throughfall depth of both species is linearly related to the rainfall depth (Figure 2), but with a slope of 0.6519 and 0.2971 for SPT and ASL, respectively. The canopy covers of the five gauged SPT plants was greater than that of ASL plants. A similar canopy depth was observed for both SPT and ASL (Table 2 and Table 3). Usually, with higher canopy cover and larger canopy depth, there should be a smaller throughfall depth because of greater canopy interception [26,27]. However, the average throughfall depth of ASL was significantly less than that of SPT (p = 0.002).
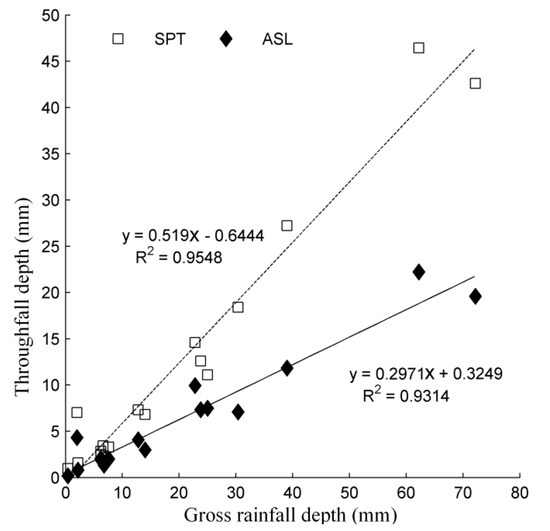
Figure 2.
Linear regression between throughfall depth and rainfall depth.
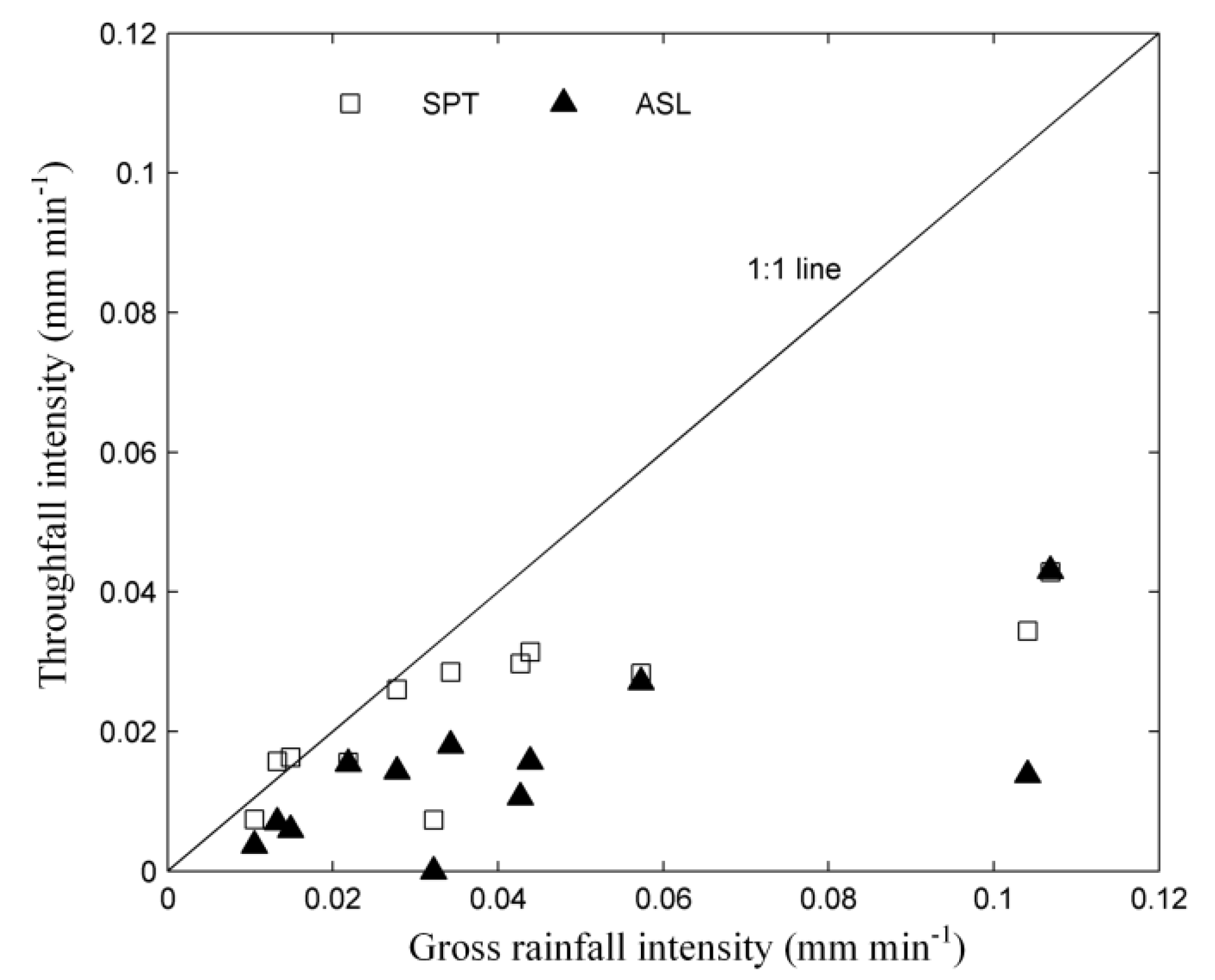
Plant canopy serves as a buffer to the kinetic energy of rainfall and alters the rainfall intensity that reaches the soil surface. The mean throughfall intensity (MTI) indicated that both ASL and SPT effectively reduced rainfall intensity, especially during heavy rainfall events (Figure 3). However, as shown in Figure 3, ASL reduced rainfall intensity more effectively than SPT did.
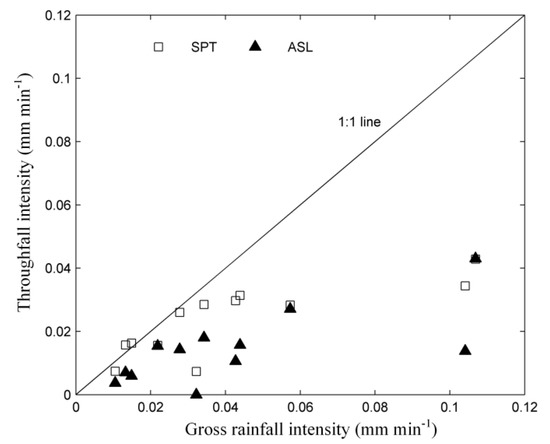
Figure 3.
Rainfall intensity reduction of the plant canopy.
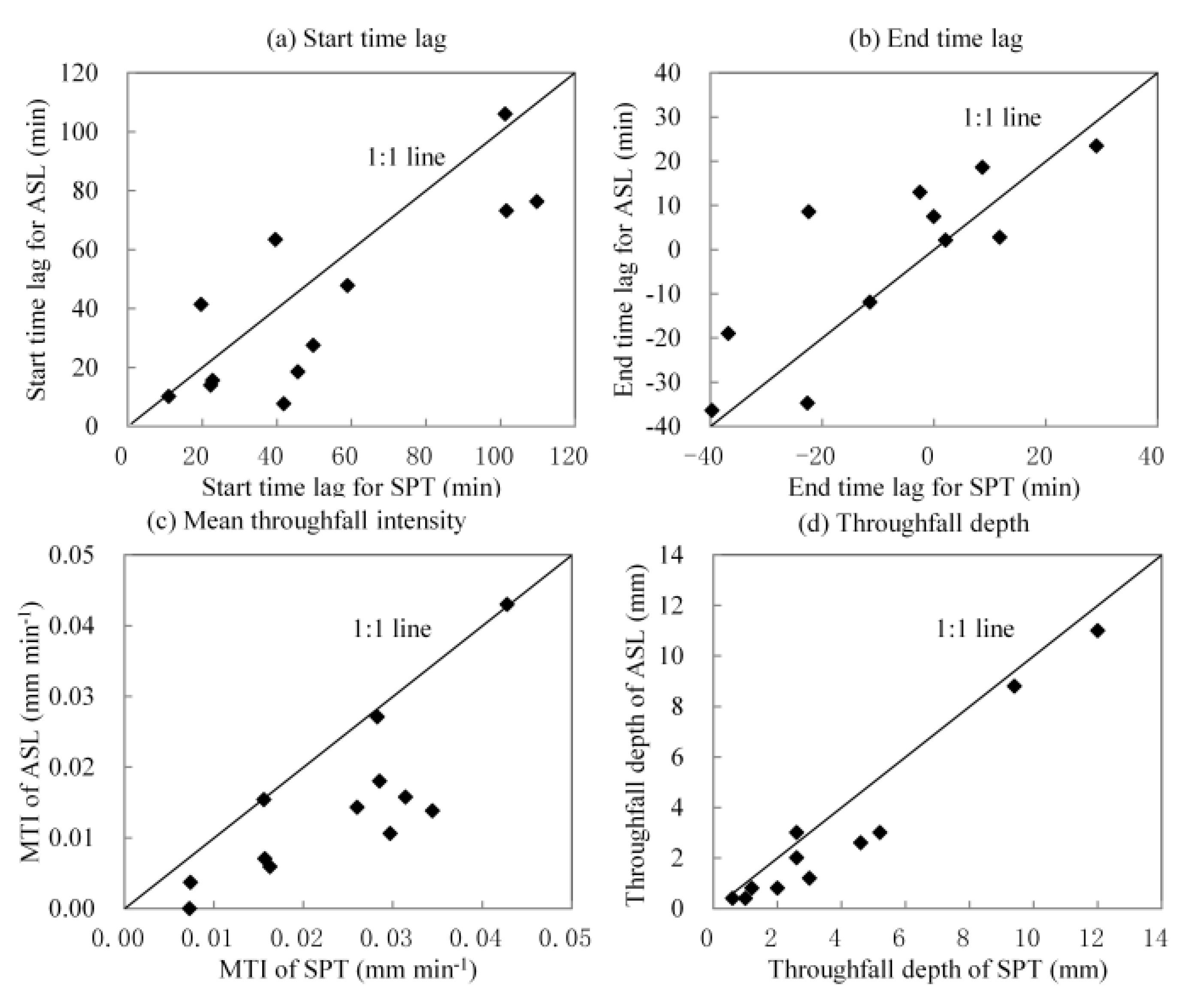
Twelve rainfall events with throughfall occurrence were recorded following Method 2 (measured by automatic pluviometers). The STL and ETL of throughfall were calculated for ASL and SPT. ASL has longer STL but shorter ETL than SPT (Figure 4). In addition, the throughfall depth of SPT was larger than that of ASL. This result implies that for most rainfall events, the throughfall started earlier and ended later at the SPT site than at the ASL site, and ASL mitigated rainfall intensity and intercepted precipitation more effectively than SPT.
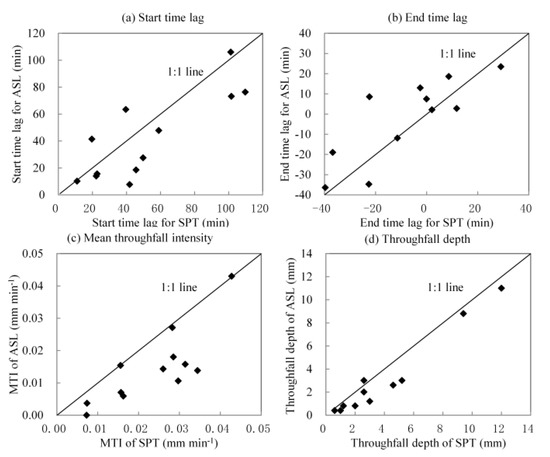
Figure 4.
Comparison of depth, mean intensity, start time lag (STL), and end time lag (ETL) of throughfall between the two sites.
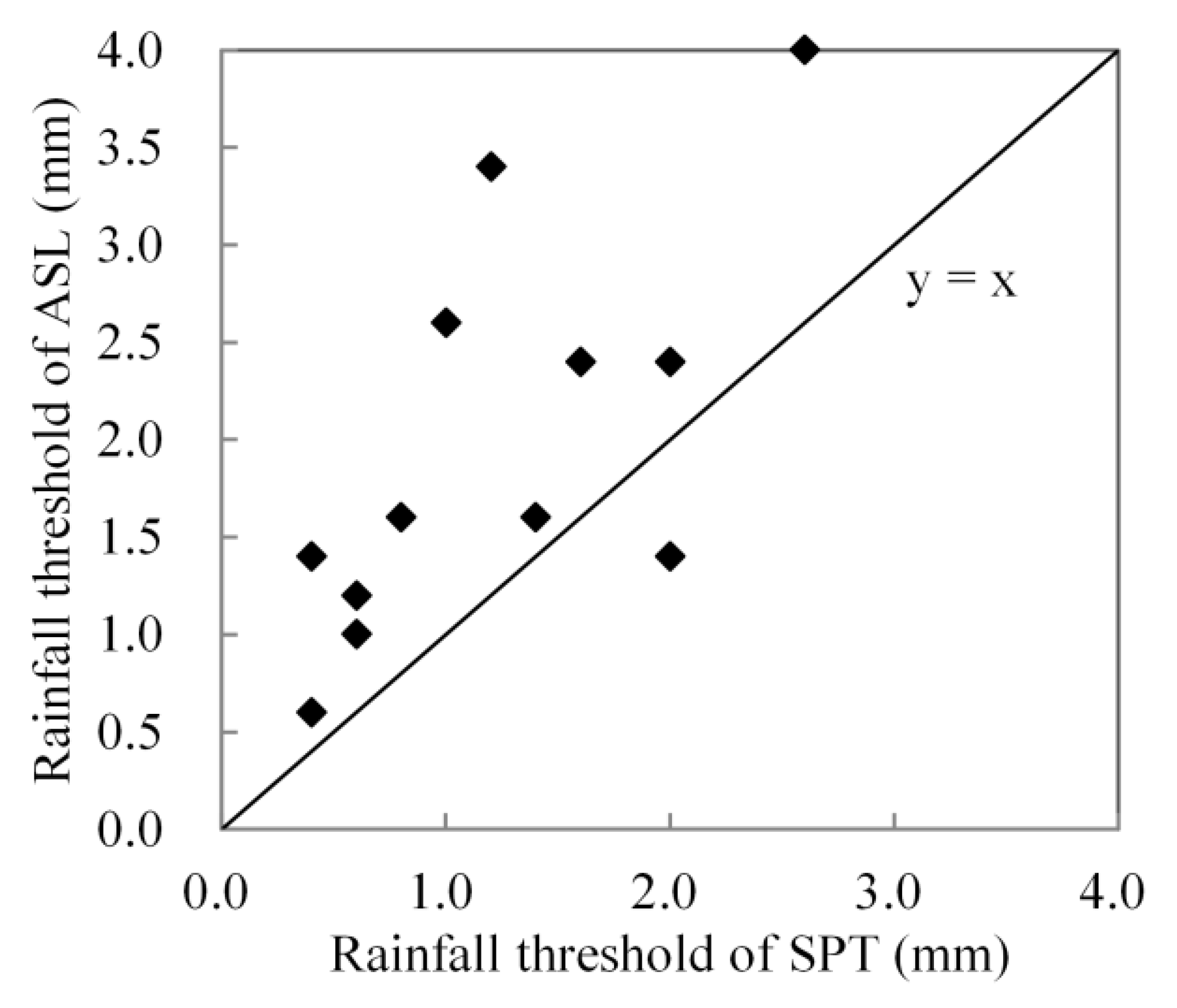
The threshold for throughfall (TRT) of each rainfall event is calculated using the rainfall records of the pluviometers. The TRT of ASL was significantly greater (p = 0.0024) than that of SPT (Figure 5).
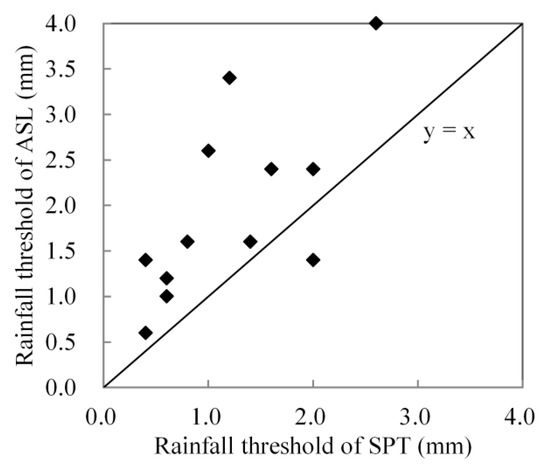
Figure 5.
Difference of rainfall thresholds of throughfall between SPT and ASL.
3.3. Rainfall Thresholds for Runoff Generation
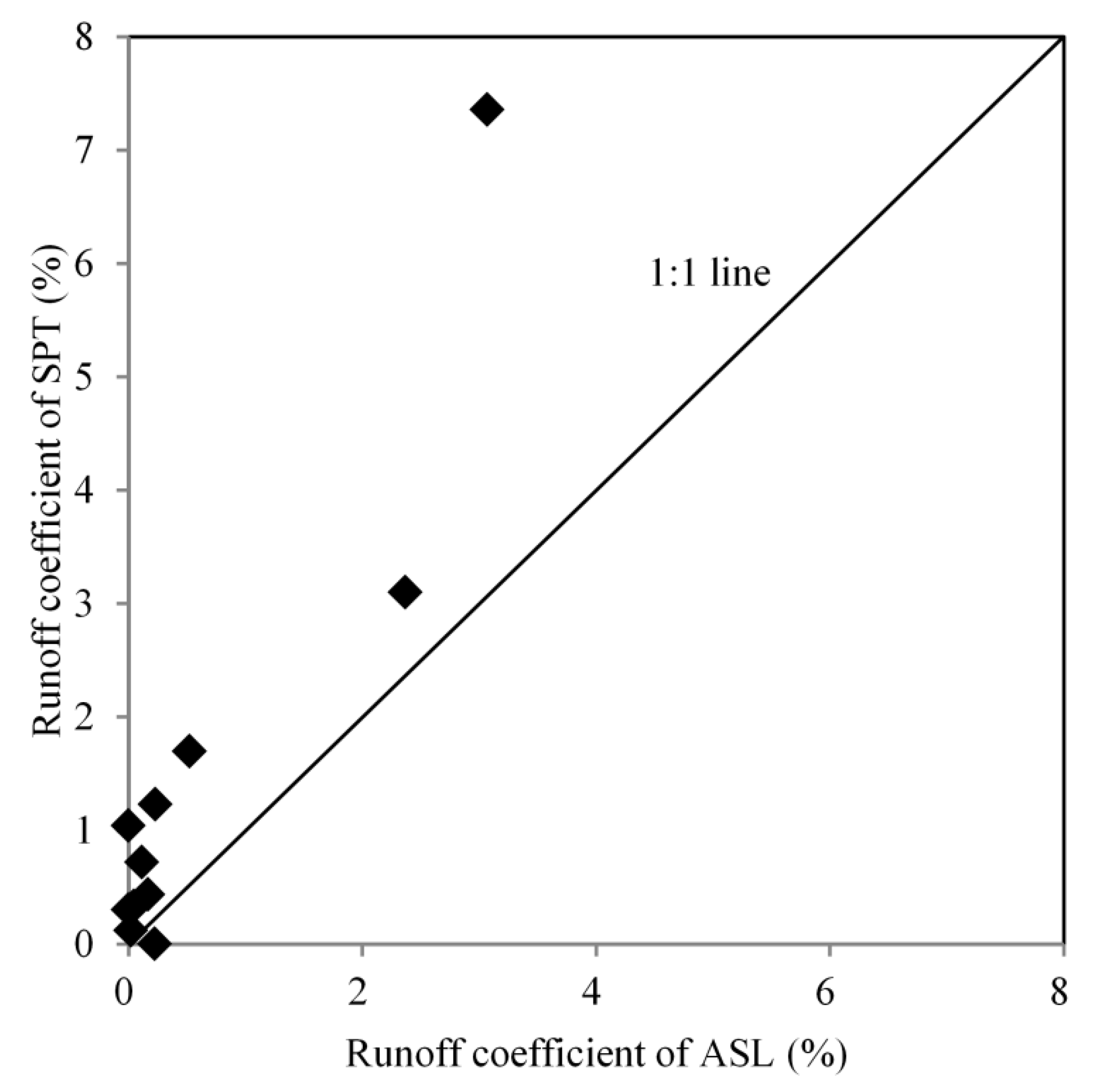
Runoff generation on the hillslopes in the study area mainly follows an excess infiltration mode [28]. Therefore, the alternation of rainfall intensity by the plant impacts the runoff generation dramatically. During the monitoring period from June 2008 to September 2009, eleven runoff events were observed. The runoff coefficient in SPT plots was significantly larger than in ASL plots (Figure 6).
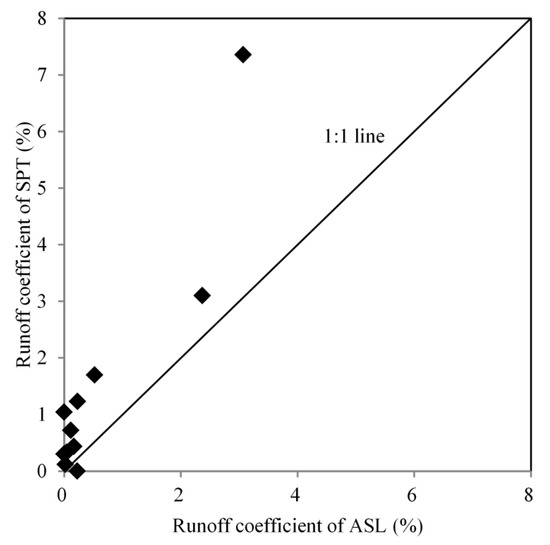
Figure 6.
Difference of runoff coefficients between the SPT site and the ASL site.
3.4. Response of Soil Moisture Dynamics
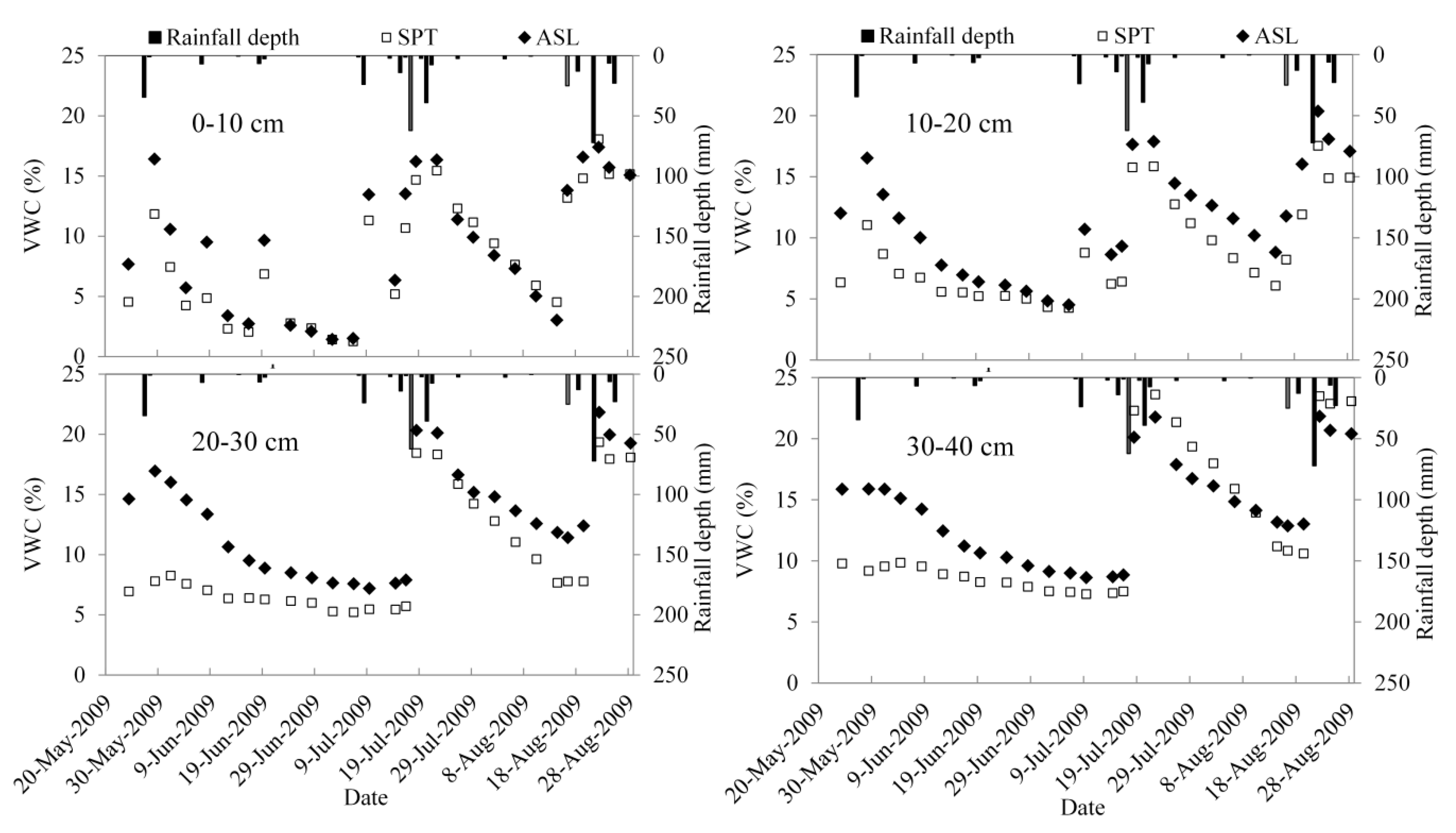
The difference in soil volumetric moisture content (VWC) between the two sites varied among soil depths (Figure 7). VWC under the two species was very similar at a soil depth of 0–10 cm. However, at depths of 10–20 and 20–30 cm, VWC was significantly higher at the ASL site than at SPT site before the rainy season (from June to September). When soil moisture is very low, the VWC at the ASL sites was greater than at the SPT site at the depths of 20–30 and 30–40 cm. In these two soil layers, the VWC difference between the two sites decreased as soil moisture increased. As illustrated by Figure 7, except for the soil layer of 0–10 cm, the heavy rainfall events tended to diminish the VWC gap between the two sites. After the rainfall events, VWC declined faster at depths of 10–20, 20–30, and 30–40 cm at the SPT site than at the ASL site.
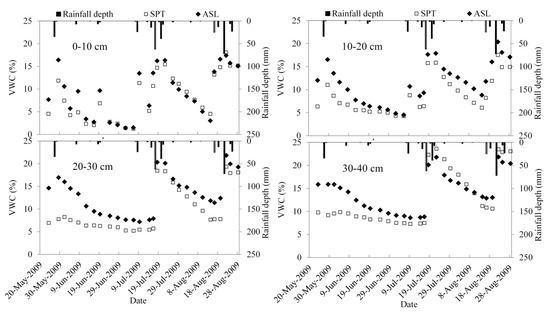
Figure 7.
Evolution of mean soil moisture at the two sites.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Plant Morphology on Ecohydrological Behavior
The two morphologically contrasting plant species, ASL and SPT, in this study led to different hydrological behaviors, which coincide with the literature [29,30]. Specifically, the amount, intensity, and duration of throughfall were clearly different between the two sites covered by the two species, respectively. ASL produced a larger TRT (Figure 5), smaller throughfall depth (Figure 4), and lower throughfall intensity (Figure 3) than SPT. Though both the canopy coverage and depth of SPT were apparently greater than ASL (Table 2), it was revealed that ASL intercepted precipitation and reduced rainfall intensity more effectively (Figure 4) than SPT. It can be inferred that the more fragmented leaf and higher stem density (Table 2) are the dominant contributors to the smaller throughfall depth. Compared with a more compact leaf, a fragmented leaf enhances water adhesion capacity [11], which promotes surface evaporation due to a large wet surface area [15], by preventing the formation of large droplets [29] and generating smaller droplets by splashing. Smaller droplets evaporate quickly and reduces throughfall [31].
By regulating rainfall characteristics, plant morphology traits dramatically affects Hortonian runoff generation and soil moisture dynamics at the two sites. Although a higher steady infiltration rate was observed at the SPT site, a greater runoff generation was observed (Figure 6). This result can be attributed to the greater throughfall intensity, larger throughfall depth, and smaller basal cover (Table 3), which impeded surface water flow and altered infiltration. Except at the soil surface layer (0–10 cm), the VWC at the SPT site was lower than at the ASL site before rainfall season (Figure 7). This can be attributed to the greater transpiration of SPT than ASL. The heavy rainfall events tended to diminish the VWC gap between the two sites. The smaller throughfall intensity facilitates water infiltration. The higher stem density and basal cover also promoted the opportunity for water infiltration by slowing runoff velocity [32] and providing more preferential pores [33]. As illustrated in Figure 7, large rainfall events produced a sufficiently large throughfall volume to reduce the VWC gap between the SPT site and the ASL site. In summary, the morphological traits of ASL eventually resulted in smaller runoffs and higher soil moisture than those of SPT.
4.2. Implication for Regional Revegetation and the Ecohydrological Assessment
The results of this study highlight the importance of plant morphology traits in ecohydrological behaviors in arid and semiarid regions, where the effect of plants on water balance should be evaluated carefully when restoring vegetation cover. Plant species of naturally restored ecosystems are usually adaptable to local ecohydrological settings. However, some exotic species, for example, Robinia pseudoacacia L., which consumes more soil water than provided by the available precipitation, were used for revegetation in the Loess Plateau [34]. A dried soil layer was recorded across the Loess Plateau [35,36], especially under the artificial exotic plant species [1,5]. Although climatic setting is the primary factor of soil drying, the water imbalance caused by plants, especially those that are artificially planted and have strong water consumption capacity, is another important contributor [37,38]. Overconsumption of soil water may lead to more severe soil water shortages, ecosystem degradation, and decreased water supply to the local communities. For these reasons, preventing soil drying and improving soil moisture conditions are key issues in ecosystem restoration on the Loess Plateau [39]. As illustrated by this study, suitable plant morphology traits can increase water infiltration into the soil and replenish soil moisture. Therefore, plant morphological traits should be a concern in revegetation in semiarid regions. The plants with morphology traits similar to ASL are more suitable for revegetation in this region in terms of the rainfall–runoff relationship and soil moisture regulation, even though ASL evaporates more rainwater and reduces net rainfall compared to SPT.
This study also highlights the importance of plant morphology traits for local and regional water balance assessment. Evaluating the impact of revegetation on water balance is a hot topic in the Loess Plateau region [1,3,40,41], where a massive revegetation program called the Green-for-Grain Project was launched [19,20]. Field experiments at plot/hillslope and watershed scales indicate that the revegetation has reduced runoff generation significantly [1,22,42] and was responsible for soil aridity [43]. Many studies have attributed the reduction in runoff or water yield to the water loss caused by enhanced water evapotranspiration after revegetation [3,43,44]. However, the mechanism of plants’ ecohydrological regulation needs to be understood in detail. Since plant morphological traits are critical in regulating the rainfall–runoff relationship and relationship between rainfall and soil moisture, it should be seriously incorporated in water balance assessments.
5. Conclusions
The plant morphological traits differ among plant species and contribute to the heterogeneity of ecohydrological functions. In this study, the effects of plant morphological traits of SPT and ASL on hydrological functions, including throughfall, soil moisture and runoff, were comparatively analyzed based on the field experiment. The results showed that the leaf shape, leaf area, stem density, and basal cover contributed to the significant difference in ecohydrological effects between the two plant species. ASL was more effective in rainfall interception and regulation because of its fragmented leaves, high stem density, and basal cover. However, with more compact leaves, relatively lower stem density and basal cover, SPT produced larger throughfall and less canopy interception than ASL did. SPT generated more runoff due to more intensive throughfall and low basal cover, and led to lower soil moisture, except for the large rainfall events that caused deep infiltration. These results imply that the morphological traits of plants should be taken into account when assessing the ecohydrological consequences of revegetation in semiarid regions.
Author Contributions
Y.L. designed the research, collected the field data and wrote the manuscript; L.Z. processed the data. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 41671186, and the International Partnership Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, grant number 121311KYSB20170004.
Acknowledgments
We thank the people in Yangjuangou village in Yan’an for their kind help in experiment set up and conduct. We give our thanks to the four reviewers for their efforts to improve the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Huang, M.B.; Zhang, L.; Gallichand, J. Runoff responses to afforestation in a watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 2599–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, K.A.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. Effects of afforestation on water yield: A global synthesis with implications for policy. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, X. Potential water yield reduction due to forestation across China. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savenije, H.H.G. The importance of interception and why we should delete the term evapotranspiration from our vocabulary. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 1507–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.M.; Jia, Z.K.; Han, Q.F. Dry soil layer forming and soil moisture restoration of alfalfa grassland in the semi-humid region of the Loess Plateau. J. Nat. Resour. 2008, 23, 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.-L.; Ma, K.-M.; Fu, B.-J.; Liu, W.; Song, C.-J. Soil and water erosion under different plant species in a semiarid river valley, SW China: The effects of plant morphology. Ecol Res. 2009, 24, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.T.; Aubrey, D.P.; Bader, M.Y.; Coenders-Gerrits, M.; Friesen, J.; Gutmann, E.D.; Guillemette, F.; Jiménez-Rodríguez, C.; Keim, R.F.; Klamerus-Iwan, A.; et al. Key Questions on the Evaporation and Transport of Intercepted Precipitation. In Precipitation Partitioning by Vegetation: A Global Synthesis; Van Stan, I.I.J.T., Gutmann, E., Friesen, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassette, C.; Bussière, F. Partitioning of splash and storage during raindrop impacts on banana leaves. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlier, J.B.; Moussa, R.; Cattan, P.; Cabidoche, Y.M.; Voltz, M. Modelling runoff at the plot scale taking into account rainfall partitioning by vegetation: Application to stemflow of banana (Musa spp.) plant. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 2151–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, I.; Forner, A.; Cuesta, B.; Valladares, F. Species-specific water use by forest tree species: From the tree to the stand. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 114, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-H.; Duan, C.-Q. How do plant morphological characteristics, species composition and richness regulate eco-hydrological function? J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2010, 52, 1086–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, C.D. The relationship between leaf water repellency and leaf traits in three distinct biogeographical regions. Plant Ecol. 2011, 212, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, V.; Eichert, T. Uptake of Hydrophilic Solutes Through Plant Leaves: Current State of Knowledge and Perspectives of Foliar Fertilization. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2009, 28, 36–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, C.D. Effects of leaf hydrophobicity and water droplet retention on canopy storage capacity. Ecohydrology 2013, 6, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamerus-Iwan, A.; Witek, W. Variability in the wettability and water storage capacity of Common Oak Leaves (Quercus robur L.). Water 2018, 10, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamerus-Iwan, A.; Błońska, E. Canopy storage capacity and wettability of leaves and needles: The effect of water temperature changes. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasson, R.P.D.M.; Krajewski, W.F. Characterization of the drop-size distribution and velocity–diameter relation of the throughfall under the maize canopy. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C. Vegetative-based technologies for erosion control. In Eco- and Ground Bio-Engineering: The Use of Vegetation to Improve Slope Stability, Proceedings of the First International Conference on Eco-Engineering, Thessaloniki, Greece, 13–17 September 2004; Stokes, A., Spanos, I., Norris, J.E., Cammeraat, E., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 103, pp. 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.X.; Chen, L.; Yu, X.X. Impact of China’s Grain for Green Project on the landscape of vulnerable arid and semi-arid agricultural regions: A case study in northern Shaanxi Province. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, W.; Miao, C. Hydrogeomorphic Ecosystem Responses to Natural and Anthropogenic Changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 45, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Poesen, J.; Yang, J.C.; Fu, B.; Zhang, J.H. Evaluating gully erosion using Cs-137 and Pb-210/Cs-137 ratio in a reservoir catchment. Soil Tillage Res. 2003, 69, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, B.; Lü, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, G. Hydrological responses and soil erosion potential of abandoned cropland in the Loess Plateau, China. Geomorphology 2012, 138, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaert, J.; Myneni, R.B.; Knyazikhin, Y. A mathematical comment on the formulae for the aggregation index and the shape index. Landsc. Ecol. 2002, 17, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansu, M.; Gautheyrou, J. Handbook of Soil Analysis: Mineralogical, Organic and Inorganic Methods; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; p. 993. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, B.; Lü, Y.; Chen, L. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil organic carbon sequestration at multiple scales in semi-arid Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2011, 85, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunjό, G.; Pardini, G.; Gispert, M. The role of land use-land cover on runoff generation and sediment yield at a microplot scale, in a small Mediterranean catchment. J. Arid Env. 2004, 57, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochet, E.; Poesen, J.; Rubio, J.L. Runoff and soil loss under individual plants of a semi-arid Mediterranean shrubland: Influence of plant morphology and rainfall intensity. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 2006, 31, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Z.; Zhang, L.; Song, X.Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Liu, X.Z.; Liang, Y.L.; Zheng, S.Q. Runoff and sediment loss responses to rainfall and land use in two agricultural catchments on the Loess Plateau of China. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanko, K.; Hotta, N.; Suzuki, M. Evaluating the influence of canopy species and meteorological factors on throughfall drop size distribution. J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geißler, C.; Nadrowski, K.; Kühn, P.; Baruffol, M.; Bruelheide, H.; Schmid, B.; Scholten, T. Kinetic energy of throughfall in subtropical forests of SE China—effects of tree canopy structure, functional traits, and biodiversity. PLoS ONE 2012, 8, e49618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, S. A proposal for a new forest canopy interception mechanism: Splash droplet evaporation. J. Hydrol. 2006, 319, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaan, W.P.; Sikking, A.F.S.; Hoogmoed, W.B. Vegetation barrier and tillage effects on runoff and sediment in an alley crop system on a Luvisol in Burkina Faso. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 83, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Cases, A.; Boix-Fayos, C.; Imeson, A.C. Runoff generation, sediment movement and soil water behaviour on calcareous (limestone) slopes of some Mediterranean environments in southeast Spain. Geomorphology 2003, 50, 269–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Liang, Z.; Zou, H. Water consumption properties of adaptable nursery stocks on Loess plateau. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 1994, 5, 210–213. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Shao, M.A.; Liu, Z.P. Large-scale spatial variability of dried soil layers and related factors across the entire Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma 2010, 159, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shao, M.a.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Z. Impacts of land use and plant characteristics on dried soil layers in different climatic regions on the Loess Plateau of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shao, M.A.; Wang, Q.J.; Jia, Z.K. Comparison of Soil Desiccations in Natural and Acacia Forests in the Ziwuling Mountain of the Loess Plateau. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2005, 27, 333–337. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, T.T.; Fu, B.J.; Liu, G.H.; Wang, Z. Hydrologic feasibility of artificial forestation in the semi-arid Loess Plateau of China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2519–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Huang, M.; Gallichand, J.; Shao, M. Optimization of plant coverage in relation to water balance in the Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma 2012, 173–174, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.M.; Zhang, L.; McVicar, T.R.; Chille, B.S.; Gau, P. Analysis of the impact of conservation measures on stream flow regime in catchments of the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 2124–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.Y.; Fu, B.J.; Lü, Y.H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J. Coupling the modified SCS-CN and RUSLE models to simulate hydrological effects of restoring vegetation in the Loess Plateau of China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 2347–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Yu, P.T.; Xiong, W.; Shen, Z.X.; Guo, M.C.; Shi, Z.J.; Du, A.; Wang, L.M. Water-yield reduction after afforestation and related processes in the semiarid Liupan Mountains, Northwest China. J. Am. Water Resour. 2008, 44, 1086–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, R.; Liu, Y.; Takayama, N.; Zhang, X.; Kamichika, M.; Matsuoka, N. Heat and water balances of the bare soil surface and the potential distribution of vegetation in the Loess Plateau, China. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 63, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, S.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.; Lü, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).