Abstract
Effective precipitation plays an important role in crop growth, and subsoiling may have an impact on the effective precipitation of farmland. The question how subsoiling influences effective precipitations has prompted this research. The major objective of this study was to quantify the effect of subsoiling on effective precipitation of farmland. The main soil type in the study area is loam. Six scenarios were set with three factors, namely, the thickness of the soil ploughing layer, porosity, and soil permeability. The hydrological process from 2000 to 2015 was simulated with a distributed hydrological model. The results showed that a 10-cm increase in the soil thickness of the plough layer had little effect on the effective precipitation. When soil porosity increased by 0.1, the effective precipitation increased by approximately 19%. When the soil permeability coefficient increased by 0.5 times, the farmland and watershed surface runoff decreased by 24% and 13%, respectively, and the effective precipitation increased by 1.7%. This study proves that subsoiling has a positive effect on the local effective precipitation and confirms previous hypotheses.
1. Introduction
Recently, the sustainable development of agriculture in the north of China has been threatened by water shortages, water pollution, and groundwater over-exploitation [1,2,3]. Moreover, intensive conventional tillage (i.e., moldboard plowing and rotary tillage) reduces the soil water-holding capacity, destroys the soil structural stability and biological activities, and reduces the nutrient supply and storage [4,5,6,7,8]. Subsoiling can break soil compaction [4,6] and change soil physical properties [3,9]. How subsoiling affects the water cycle process of farmland is an important topic among studies focused on improving the use of precipitation by crops.
Rainfall is very important in arid areas, and effective precipitation plays a significant role in crop growth. Soil plays an important role in the utilization of farmland precipitation. Effective precipitation refers specifically to the portion of rainfall used to meet crop evapotranspiration under dry farming conditions. It excludes surface runoff and percolation below the root zone of the crop and does not include the deep percolation of precipitation required to leach salt [10,11,12]. The effective precipitation mentioned in this paper refers to this type of precipitation, which is difficult to quantify. An inexact stochastic-fuzzy programing method was developed to determine effective precipitation for water resources allocation and land resources utilization management under multiple uncertainties [13]. The Budyko framework, which explores the relationship between crop evapotranspiration and regional total evapotranspiration in the regional water–energy balance was applied to access virtual water content of agricultural crops [14]. The effect of soil tillage and land cover on soil water infiltration was evaluated in areas under bare soil, soybeans (conventional tillage and no-tillage), and pasture [15]. Two statistical methods, random forest and multiple linear regression, were compared to evaluate the effects of various parameters, including subsoiling, on corn plant height, and seasonal mean water table depth [8]. Singh and Choudhary et al. investigated the direct and residual effect of subsoiling on the soil physical properties and productivity of a cotton–wheat cropping system by a field experiment [16]. However, the relationship between subsoiling and effective precipitation has been less studied. In addition, the change of a single physical property is difficult to control during the subsoiling process and the effective precipitation of the farmland is not easy to monitor. Changes in physical characteristics represent a direct manifestation of subsoiling, and farmland precipitation is a key condition for crop growth. Based on the above description, we formed a hypothesis that changes in soil physical properties (plough layer thickness, porosity, permeability, etc.) will affect the transport and storage of precipitation in farmland and the available water content for crops in the soil. Therefore, this paper quantitatively examines the effect of subsoiling on the effective precipitation through a hydrological model at the basin scale.
2. Materials and Methods
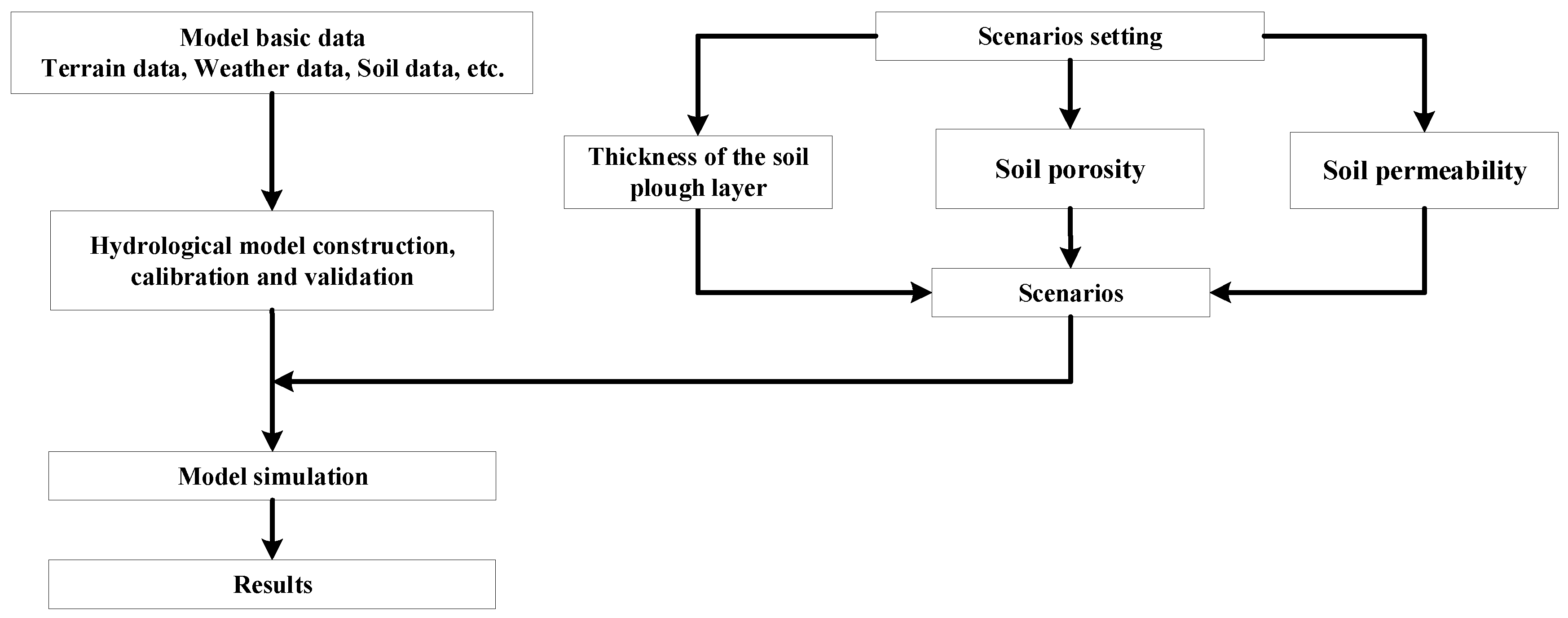
In this paper, the effect of subsoiling on effective precipitation was quantitatively analyzed by a hydrological model. The study comprises three parts: model construction and validation, scenario setting, and scenario simulation. The detailed process is shown in Figure 1.
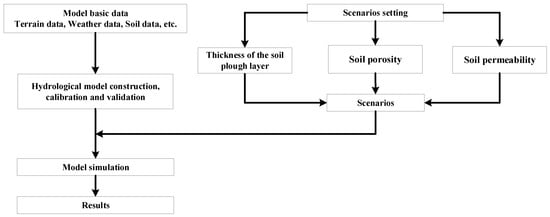
Figure 1.
Method route.
2.1. Research Area
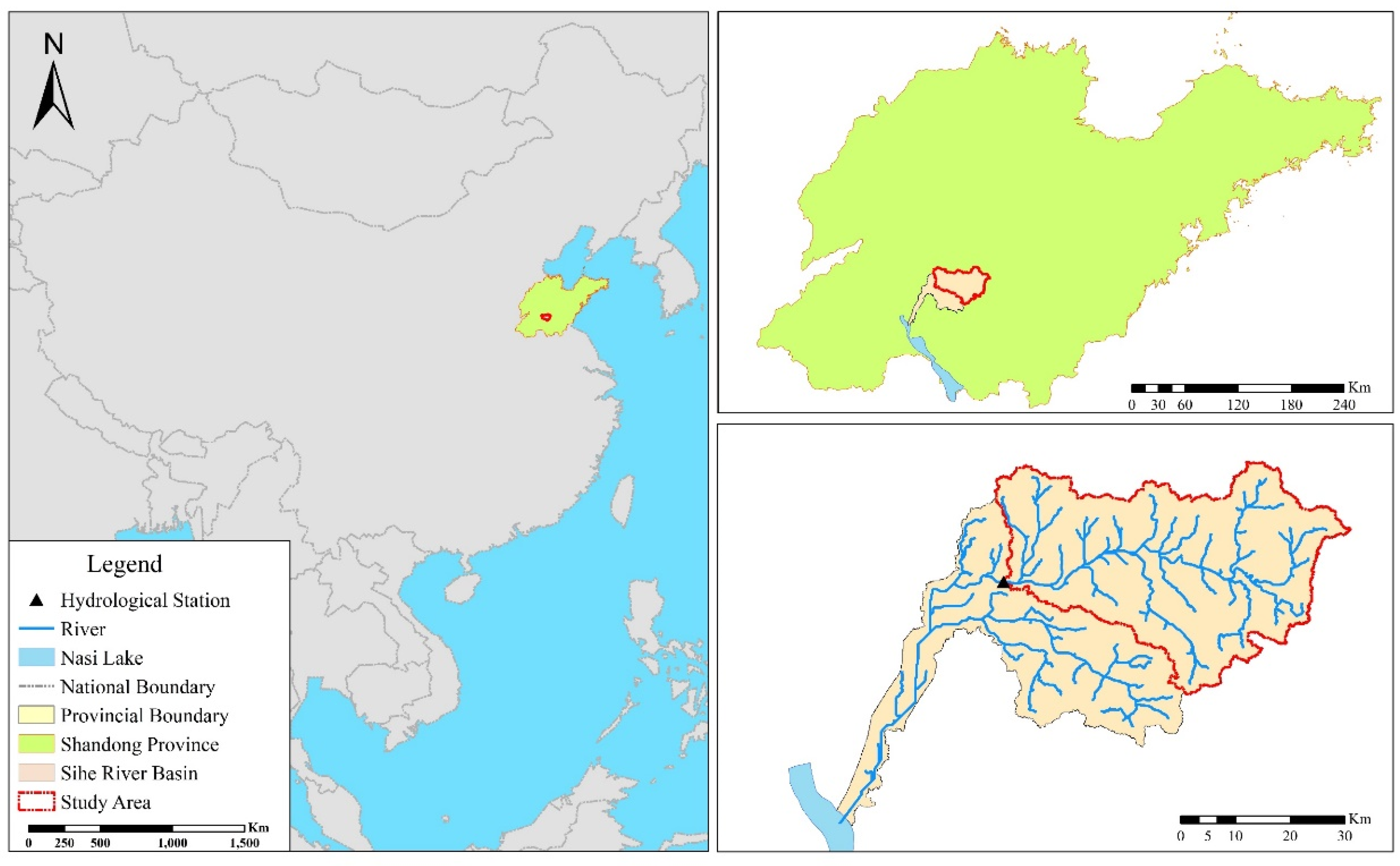
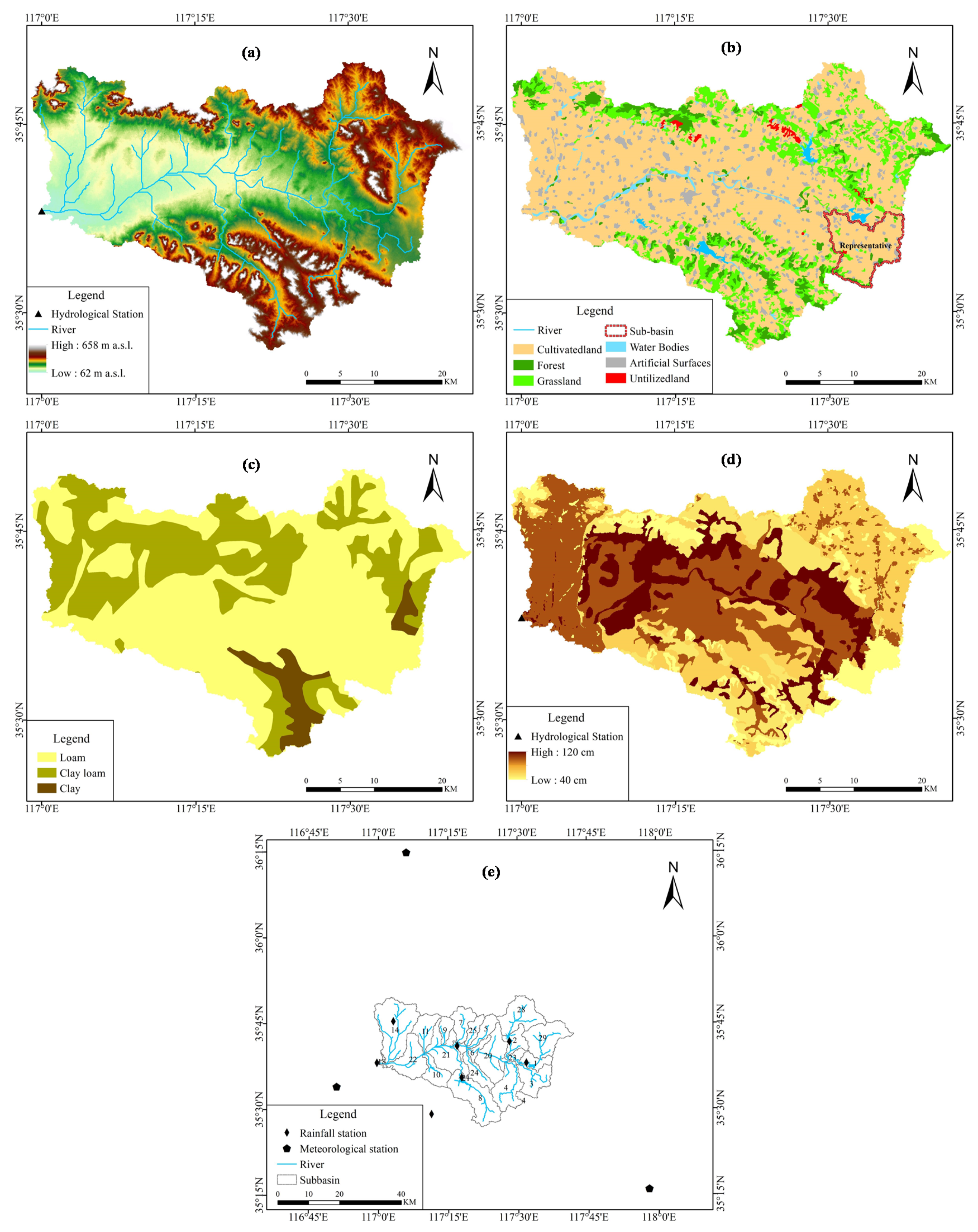
The Sihe River, which originates on the west side of the Taiping peak in Xintai City belongs to the Nansi Lake water system in the Huaihe River basin. It is the largest mountainous river that enters the Nansi Lake. The Sihe River basin has a monsoon climate in a mid-latitudes zone with four distinct seasons. The average annual precipitation in the basin for the period of 1968 to 2015 was 740 mm. Precipitation during the year is mainly concentrated from June to September, accounting for 75% of the whole year. The monthly average precipitation is about 55 mm, the maximum monthly precipitation is 484 mm, and the minimum monthly precipitation is 0 mm. The multi-year average temperature is 13.4 °C, and the monthly average maximum temperature is 26.7 °C, which mostly occurs in July. The monthly average minimum temperature is −2.1 °C, which occurs in January. The Sihe River basin is located in the transition area between the Taiyi low hills and the piedmont alluvial plain in southern Shandong Province. The topography of the basin varies greatly and has an average elevation of 137 m. The upper middle reaches are hilly mountains and the lower reaches are piedmont alluvial plains. In this study, the upper basin of the Shuyuan hydrological station was selected as the study area as shown in Figure 2. The area of the study site is 1554 km2, which is divided into 29 sub-basins. In the study area, a sub-basin with a large area of cultivated land was selected as a representative simulation area, and interactions between the sub-basins were not observed. The topography, land use, soil type, and soil thickness of the basin is shown in Figure 3a–d. The main soil type in the study area is loam, the soil porosity is 0.4, and the permeability coefficient is 2.5 × 10−5 m/s.
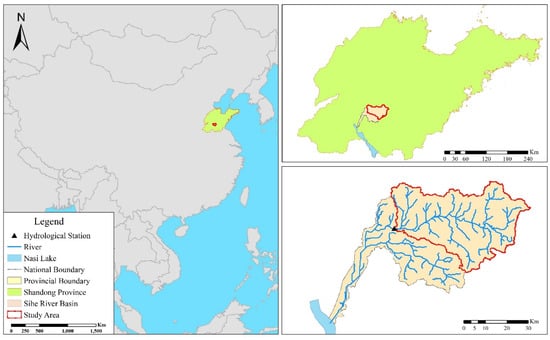
Figure 2.
Location of the study area.
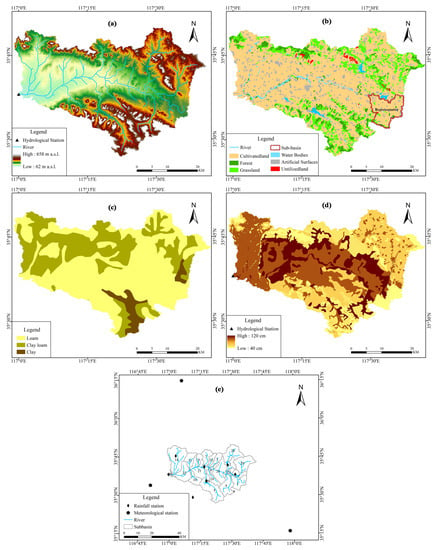
Figure 3.
Basic information of study area: (a) basin topography, (b) basin land use and studied sub-basin, (c) soil type of basin, (d) soil thickness of basin, (e) meteorological station and rainfall station.
2.2. Data Source
Daily data of three meteorological stations (Figure 3e) (including stations around the basin) were collected from 1968 to 2015, including wind speed, temperature, illumination time, and relative humidity data, from the National Meteorological Information Center.
Other data (Figure 3a–d) were sourced from the local agriculture department.
2.3. Model Construction and Calibration
2.3.1. Model Construction
The most prominent feature of a distributed watershed hydrological model is its combination with a DEM (digital elevation model) to control the temporal and spatial changes of the hydrological cycle based on physical processes with partial differential equations. Such an approach can describe processes and outputs in a distributed manner [17,18]. The physical processes of the hydrological cycle can simulate objective reality, and hydrological cycle processes can be simulated, which is the inevitable trend in the development of hydrological modeling [19].
The WEP (water and energy transfer processes model) is a distributed hydrological model developed by IWHR (China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research) based on a DEM. For hydrological processes, evapotranspiration is computed by the Penman–Monteith equation [20], infiltration excess during heavy rains is simulated by a generalized Green–Ampt model, and saturation excess during the remaining periods is obtained by performing a water balance analysis in the unsaturated soil layers [21]. A two-dimensional simulation of multilayered aquifers is performed for groundwater flow. Flow routing is conducted using the kinematic wave method in a one-dimensional scheme. For energy processes, shortwave radiation is based on observations or deduced from the sunshine duration, and longwave radiation is calculated according to the illumination time; latent and sensible heat fluxes are computed by the aerodynamic method and surface temperature is determined by the force–restore method [22].
2.3.2. Model Calibration and Validation
Abrupt Test and Selection of Calibration and Validation Period
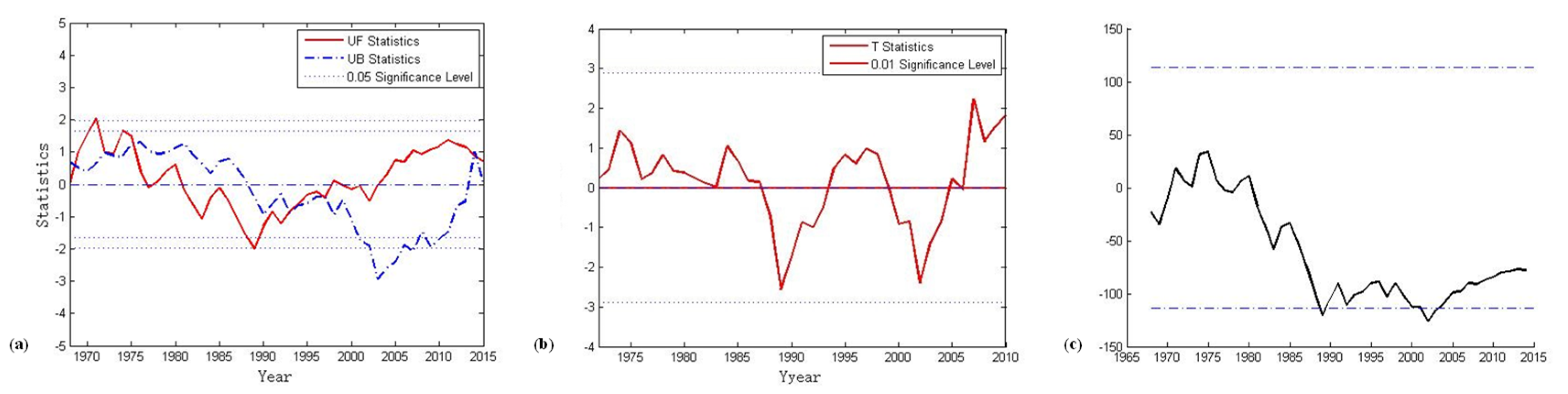
The annual rainfall was analyzed based on the Mann–Kendal method [23], sliding t-test [24], and Pettitt method [25], and the results are shown in Figure 4a–c. The results show that there are two main abrupt change points in the rainfall series, which are 1987 and 2003. Therefore, to ensure the representativeness of the model and the accuracy of the simulation, the sudden change point test results and the runoff data were combined, and the years 1968–1990 were selected as the calibration period and 1991–2015 as the validation period of the model.
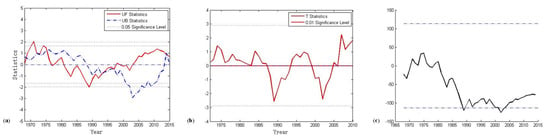
Figure 4.
Results of rainfall analysis through three methods: (a) Mann–Kendal test, (b) sliding t-test, and (c) Pettitt test.
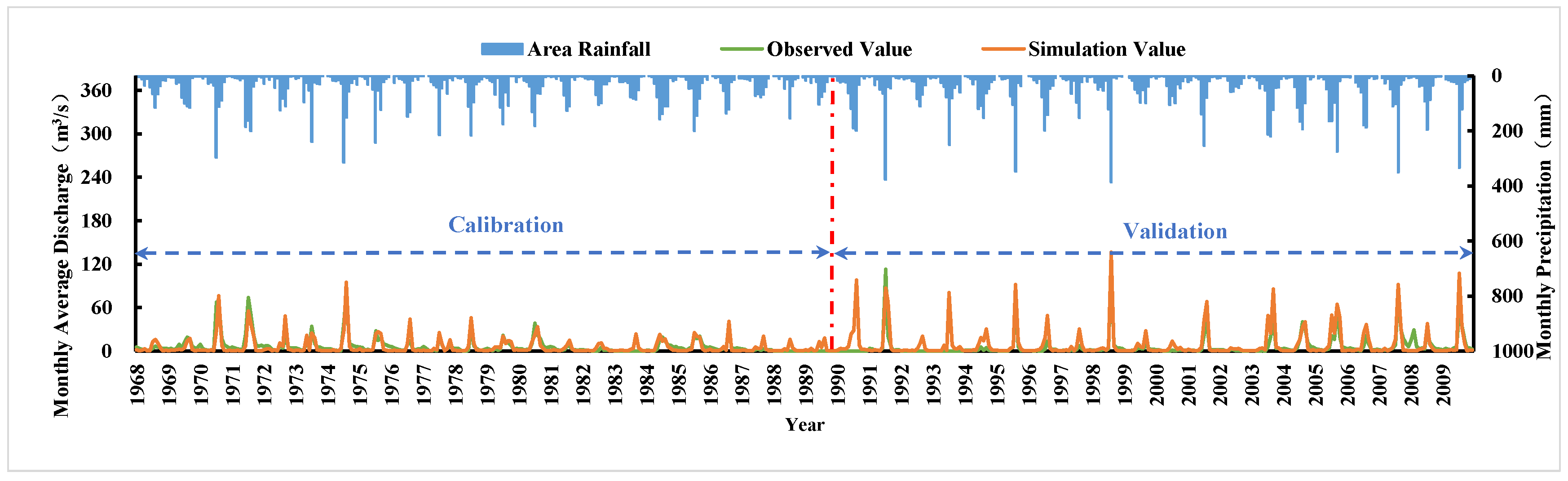
Model Calibration and Validation Results
Under the current rainfall, land use, and soil conditions, the relevant parameters of the model were debugged and the results of calibration and validation are shown in Figure 5. The average annual runoff error during the calibration period is −4.89%. The NSE (Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient) and correlation coefficient between the simulated monthly runoff and hydrological station data were 0.72 and 0.87, respectively. During the validation period, the average annual runoff error was 4.49%, and the NSE and correlation coefficient between the simulated annual runoff and hydrological station data were 0.81 and 0.91, respectively. The specific simulation results are shown in Table 1.
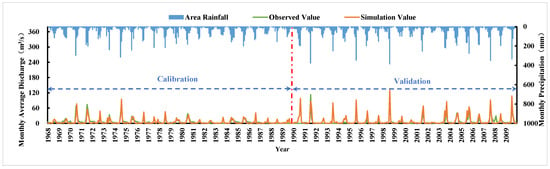
Figure 5.
Calibration and validation of model.

Table 1.
Simulation effect of surface monthly runoff at Shuyuan hydrological station.
2.4. Scenarios Setting and Basis
2.4.1. Theoretical Analysis
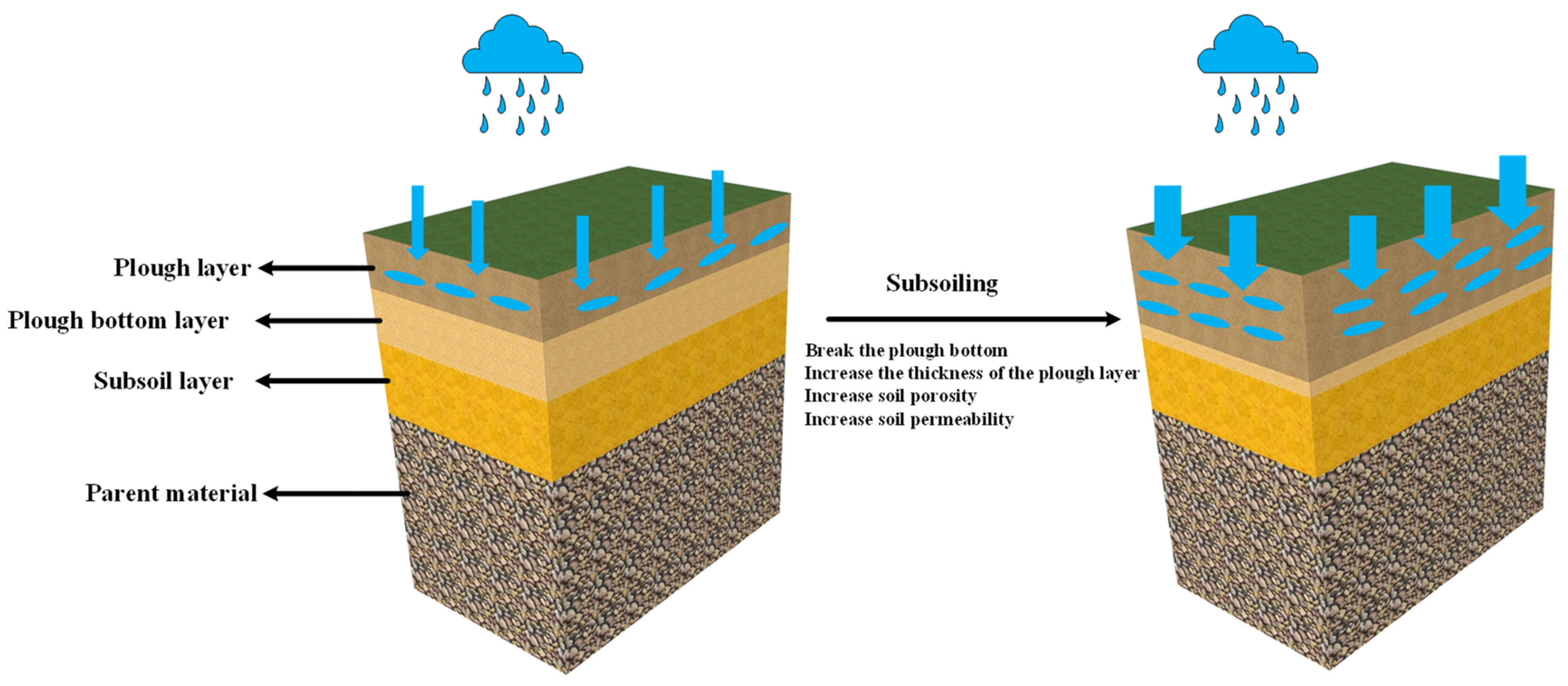
Subsoiling can break the bottom of the soil plough layer, increase the plough layer thickness (Figure 6), improve the soil structure, and improve the soil water-holding capacity [26]. From the perspective of the hydrological cycle, changes in the soil structure caused by subsoiling will affect the soil permeability and soil water-holding capacity. Changes in the soil water-holding capacity will affect the growth environment of crop roots, impacting the evapotranspiration of crops and soil, and further influence effective precipitation.
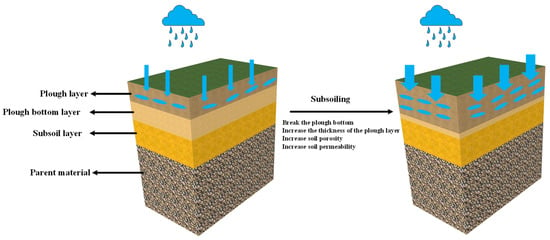
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram of the effect of subsoiling on the soil plough layer.
2.4.2. Scenario Setting
Scholars have conducted many experiments on different farming methods at the farm scale, mainly for the observation of soil properties, structure, and moisture. These methods are summarized based on the following three aspects.
Effect of Subsoiling on the Thickness of the Soil Plough Layer
The structure and thickness of the plough layer determine the survival environment of crops and the supply of nutrients and water [27]. Subsoiling can reduce the soil hardness, especially in the depth of 20–35 cm [28]. Compared with conventional rotary tillage and no-tillage, subsoiling (depth 30 cm) can reduce the soil hardness by 25.6% and 32.3%, respectively [29]. Increasing the tillage depth in the wheat and corn continuous cropping area in North China can reduce the soil bulk density and increase the precipitation infiltration and the soil water content [30].
Effect of Subsoiling on the Soil Porosity
Soil pores represent the channels for soil respiration, water movement, and nutrient transport; thus, they directly affect plant growth. The effect of subsoiling on the soil pore structure mainly increases soil porosity, increases soil permeability, reduces surface runoff, and weakens the potential threat of soil erosion. Moreover, deep soil water evaporation caused by capillary action not only improves the soil gas exchange conditions but also achieves the effect of water storage and preservation [31]. During the fallow period, subsoiling increases the soil water storage of the 0–300 cm soil layer [32]. Compared with traditional tillage (rotary tillage), subsoiling (depth 35 cm) can reduce the soil bulk density by 0.14 g/cm3 and increase the soil porosity by 10–20%. After subsoiling (depth 30 cm) of loam, the total soil porosity in the 10–20 cm and 20–30 cm layers reached 54.99% and 48.58%, respectively, while the 0–10 cm and 30–40 cm layers changed little [31]. Many experiments in China have showed that compared with the traditional rotary tillage 15 cm control, autumn subsoiling to 30 cm decreased the soil quality of the corn plough layer and increased the available water content of the main root and deep soil, which significantly improved the yield and water use efficiency [33].
Effect of Subsoiling on Soil Permeability
Soil permeability determines the redistribution of rainfall, which affects the surface runoff and soil moisture status [34,35]. The better the soil permeability, the smaller the soil surface runoff and the more obvious the effect of soil and water conservation [36]. Compared with shallow tillage, subsoiling can increase soil porosity, significantly increase the soil saturated hydraulic at a depth of 0–20 cm, and increase the soil water uptake [37].
Scenarios Setting
Based on previous field experiments, different factor scenarios (P1–P6) were set up (Table 2) to simulate and quantitatively evaluate the changes of effective precipitation. In these scenarios, P3 vs. P1 and P4 vs. P2 were used to simulate the effect of thickness of the soil plough layer on effective precipitation; P2 vs. P1 and P4 vs. P3 were used to simulate the effect of porosity on effective precipitation; P5 vs. P3 and P6 vs. P3 were used to simulate the effect of soil permeability on effective precipitation; P5 vs. Original and P6 vs. Original were used to simulate the effect of actual subsoiling tillage on effective precipitation.

Table 2.
Simulation scenario settings.
In the model, the soil layers were divided according to the thickness of the soil: when the soil thickness was greater than 1 m, 0.4 m was set as the plough layer depth, 0.6 m was set as the plough bottom, and the remainder was set as the subsoil layer; when the soil thickness was between 0.4 and 0.6 m, 0.4 m was set as the plough layer and the remainder was set as the plough bottom; and when the soil thickness was less than 0.4 m, the entire soil was set as the plough layer. The other two soil parameters involved in the model were porosity and soil permeability coefficient.
2.4.3. Simulation Results Display
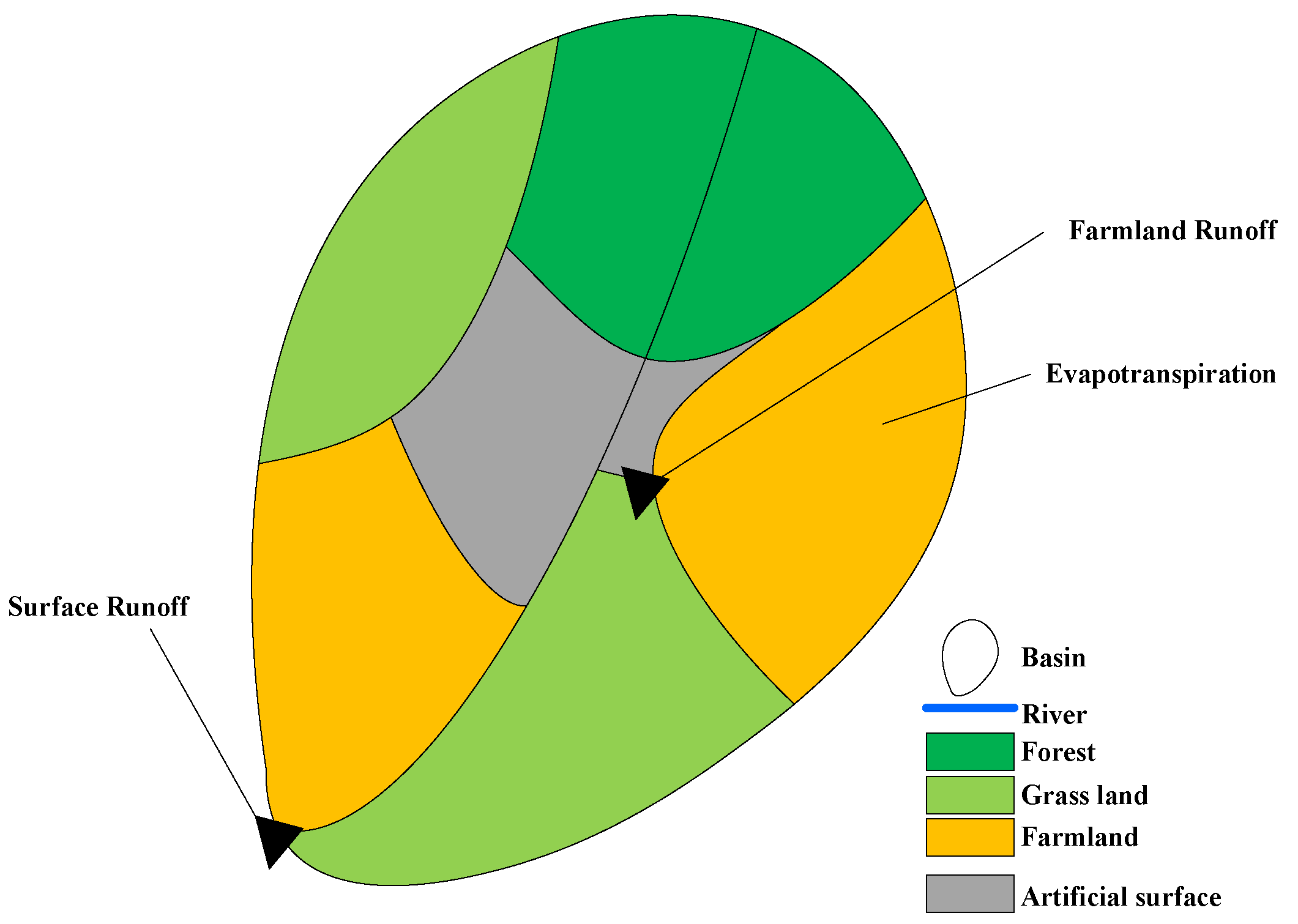
The scenarios (P1–P6) were simulated by the verified WEP model. The effect of subsoiling on effective precipitation was studied by comparing the difference of surface runoff, farmland runoff, and evapotranspiration (Figure 7) in different scenarios.
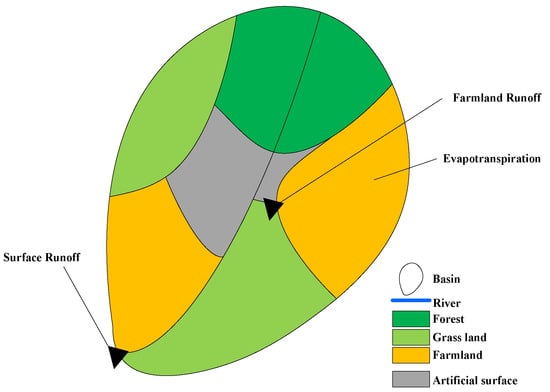
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of surface runoff, farmland runoff, and evapotranspiration.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Plough Layer Thickness on the Effectiveness of Local Precipitation
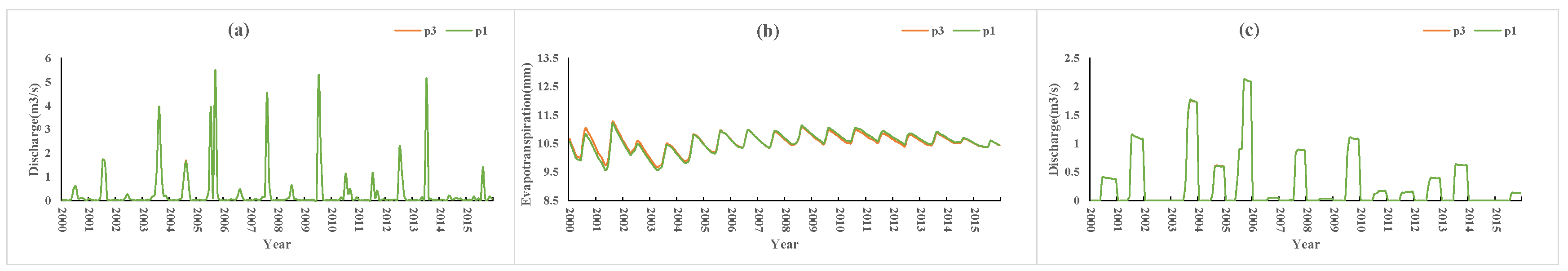
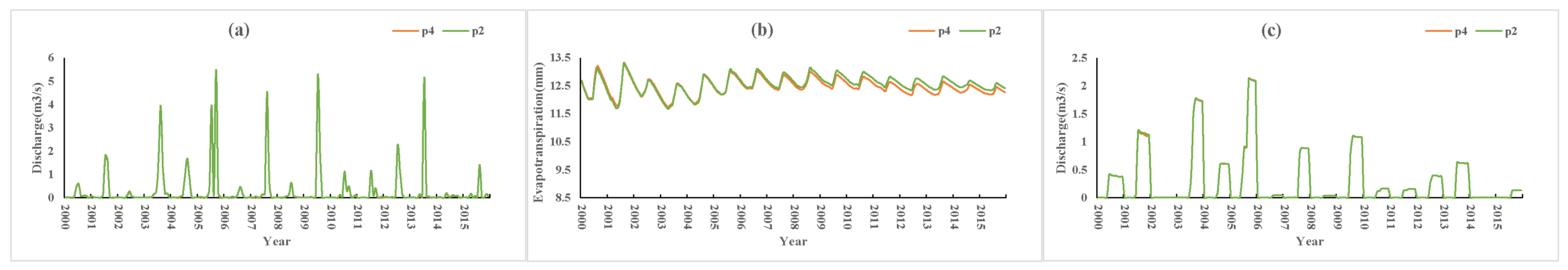
Figure 8 shows the simulation results under conditions P3 and P1 in which the thickness of the ploughing layer of P3 was 10 cm greater than that of P1. The results showed that under the condition of increasing soil thickness, evapotranspiration decreased slightly and the surface runoff and farmland runoff did not change. Figure 9 shows the simulation results under the P4 and P2 conditions in which the plough layer of P4 was 10 cm thicker than that of P2. The results showed that evapotranspiration decreased by 0.1 mm (approximately 0.6% of the P2 condition), and the surface runoff and farmland runoff did not change.
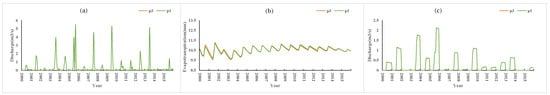
Figure 8.
P3 vs. P1 simulation results: (a) surface runoff, (b) evapotranspiration, (c) farmland runoff.
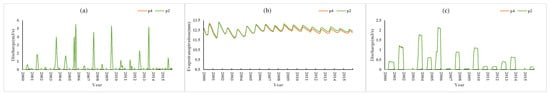
Figure 9.
P4 vs. P2 simulation results: (a) surface runoff, (b) evapotranspiration, (c) farmland runoff.
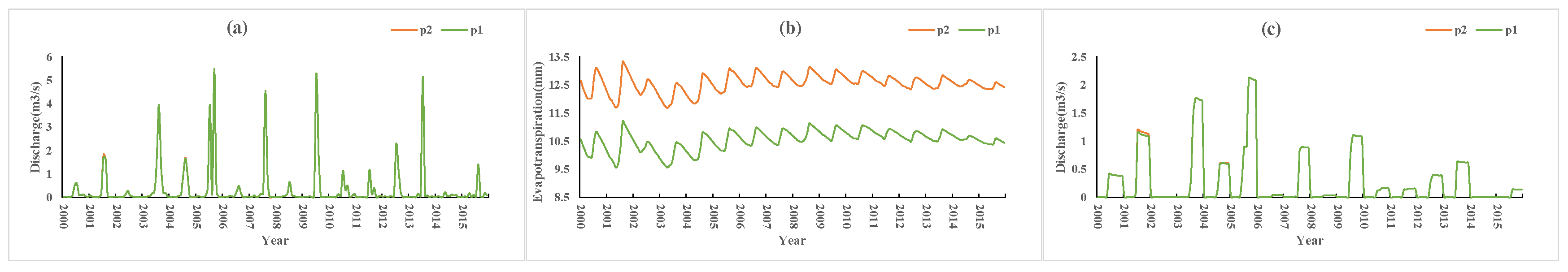
3.2. Effect of the Soil Porosity on the Effectiveness of Local Precipitation
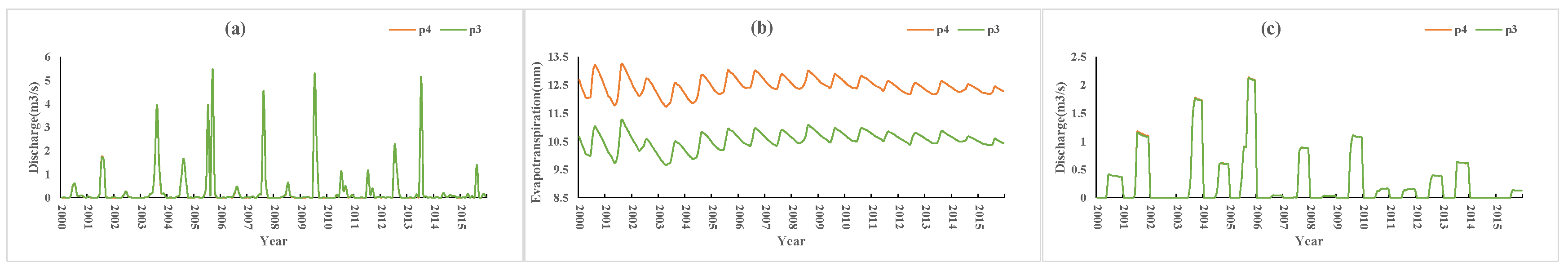
Figure 10 shows a comparison of the results of the P2 and P1 scenario simulations. Compared with P1, P2 increased the soil porosity by 0.1 while the other conditions remained the same. The results (P2 vs. P1) showed that evapotranspiration increased by 2 mm (approximately 19% of the P1 condition), and the surface and farmland runoff showed no obvious change. Compared with P3, the soil porosity of P4 increased by 0.1. The simulation results (P4 vs. P3) (Figure 11) showed that evapotranspiration increased by 1.9 mm (approximately 18% of the P3 condition) and surface runoff and farmland runoff did not change.
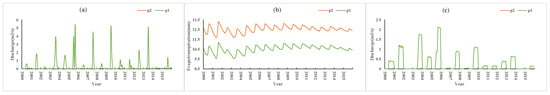
Figure 10.
P2 vs. P1 simulation results: (a) surface runoff (b) evapotranspiration (c) farmland runoff.
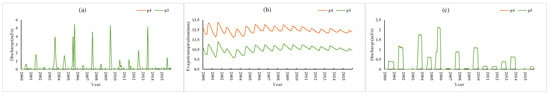
Figure 11.
P4 vs. P3 simulation results: (a) surface runoff, (b) evapotranspiration, (c) farmland runoff.
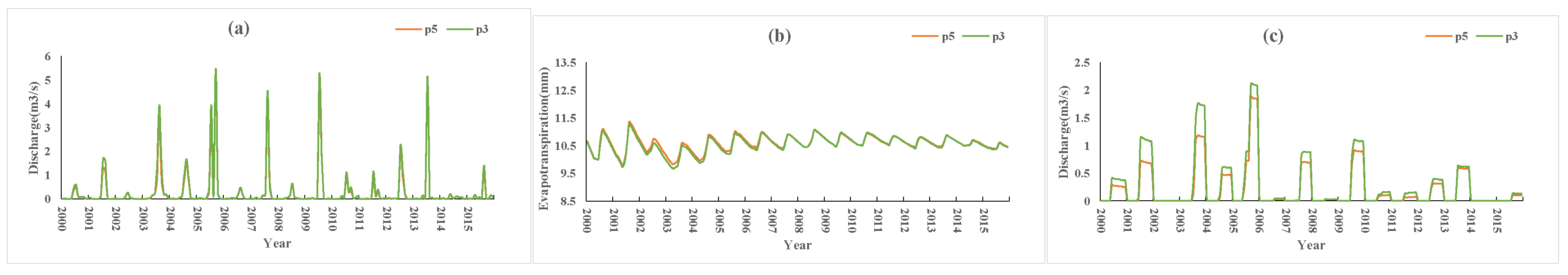
3.3. Effect of Soil Permeability on the Effectiveness of Local Precipitation
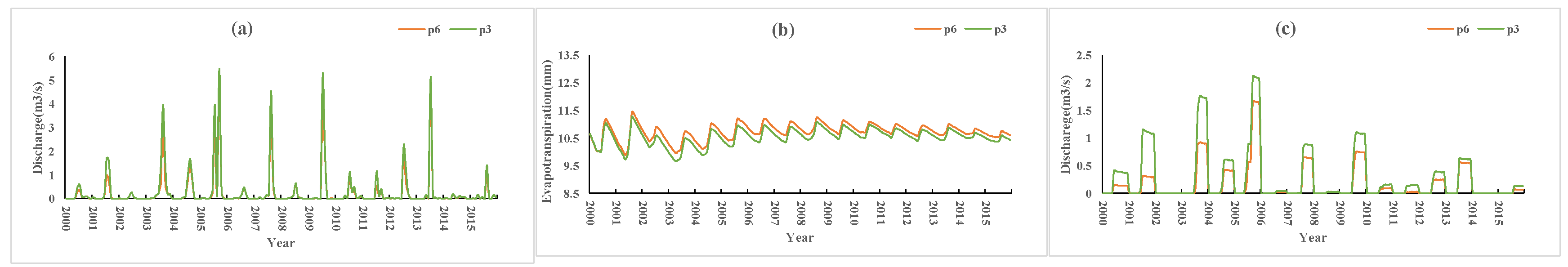
Figure 12 shows a comparison of the P5 and P3 scenario simulations. Compared with P3, the soil permeability coefficient of P5 was increased by 0.5 times, and other conditions were unchanged. The results (P5 vs. P3) showed that the average monthly farmland runoff decreased by 0.1 m3/s (approximately 24% of the P3 condition) during the flood season (June to September), and the monthly average surface runoff (flood season) decreased by 0.12 m3/s (approximately 13% of the P3 condition), and evapotranspiration did not change. Compared with P3, the soil permeability coefficient of P6 was doubled. The simulation results (P6 vs. P3) (Figure 13) showed that the monthly average farmland runoff decreased by 0.15 m3/s (approximately 21% of the P3 condition) during the flood season, the average monthly surface runoff decreased by 0.21 m3/s (approximately 41% of the P3 condition) during the flood season, and evapotranspiration increased by 0.19 mm (approximately 2% of the P3 condition).
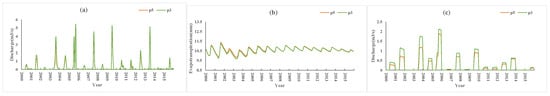
Figure 12.
P5 vs. P3 simulation results: (a) surface runoff, (b) evapotranspiration, (c) farmland runoff.
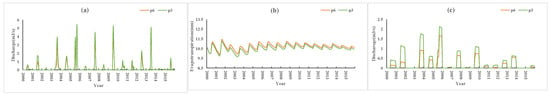
Figure 13.
P6 vs. P3 simulation results: (a) surface runoff, (b) evapotranspiration, (c) farmland runoff.
3.4. Effect of Actual Subsoiling Tillage on the Effectiveness of Local Precipitation
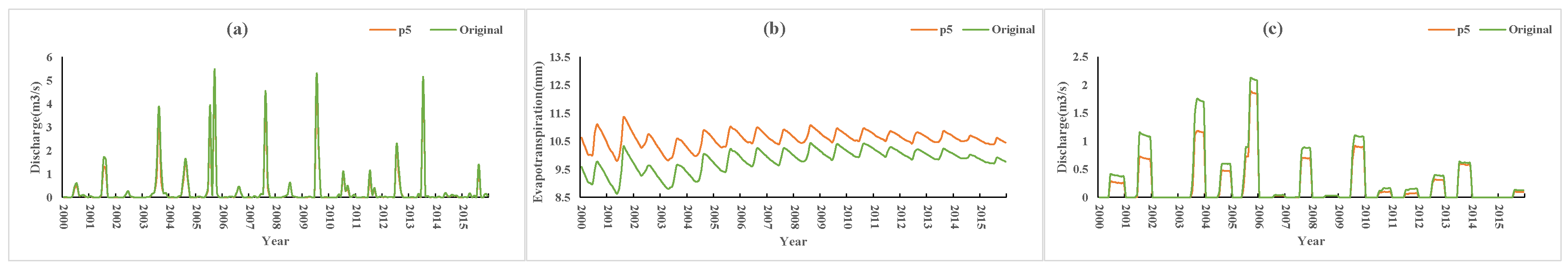
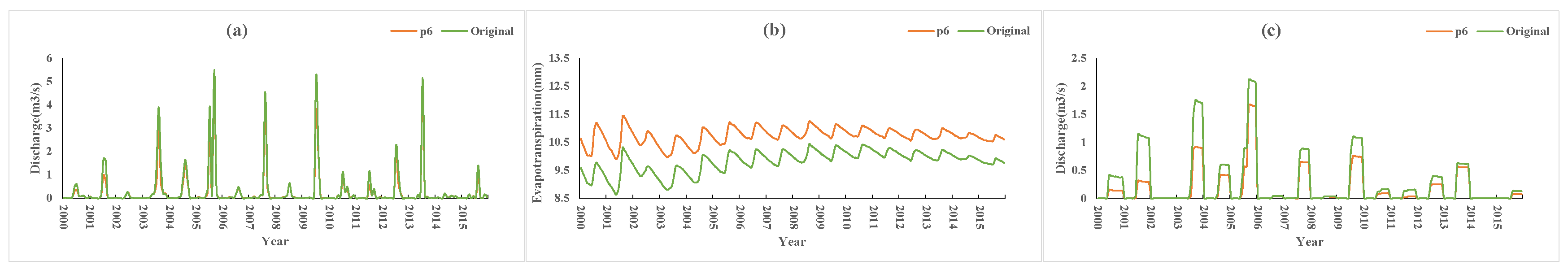
Figure 14 shows the simulation results of P5 and the original conditions. Compared with the original conditions, the thickness of the soil plough layer of P5 increased by 20 cm, the porosity increased by 0.1, and the soil permeability coefficient increased by 0.5 times. The results (P5 vs. Original) showed that the monthly average farmland runoff (flood season) and surface runoff decreased by 0.09 m3/s (approximately 24% of the original condition) and 0.11 m3/s (approximately 13% of the original condition), respectively, and evapotranspiration increased by 0.8 mm (approximately 8% of the original condition). Similarly, compared with the original condition, the thickness of the soil plough layer of P6 increased by 20 cm, the porosity increased by 0.1, and the soil permeability coefficient increased by 1.0 times. The simulation results (P6 vs. Original) (Figure 15) showed that the monthly average farmland runoff (flood season) and surface runoff were reduced by 0.15 m3/s (approximately 41% of the original condition) and 0.18 m3/s (approximately 21% of the original condition), respectively, and evapotranspiration was increased by 1 mm (approximately 9% of the original condition).
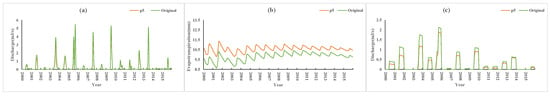
Figure 14.
P5 vs. Original simulation results: (a) surface runoff, (b) evapotranspiration, (c) farmland runoff.
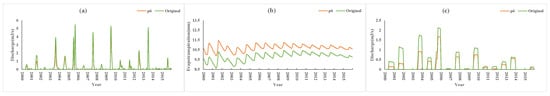
Figure 15.
P6 vs. Original simulation results: (a) surface runoff, (b) evapotranspiration, (c) farmland runoff.
4. Discussion
The farmland soil water cycle is divided into three independent process: soil water infiltration [38], soil water redistribution, and soil evaporation [39]. The transpiration of crops is related to the water absorption process of roots [40]. There are internal and external factors that affect the water absorption process of roots. Internal factors include leaf area, root density, etc.; external factors include soil factors and atmospheric factors. However, subsoiling can change the soil physical properties [41] and water-holding characteristics [42], which will have an impact on the soil water cycle and crop transpiration process.
4.1. Effect of the Plough Layer Thickness on Soil Water Cycle
Subsoiling broke the plough layer, and the upper part of the original plough bottom was turned into a new plough layer [43]. P1 vs. P3 and P2 vs. P4 represent comparison scenarios set for changes in soil thickness. In these two scenario comparisons, 10 cm of the plough bottom was converted to a new plough layer. However, the soil structure around the crop roots had not changed. Part of the soil water was stored in the new plough layer. Affected by the depth of the soil, the roots’ suction on the deep soil water had weakened [44]. Therefore, there was a slight decrease in crop transpiration. Similarly, soil evaporation was also affected by soil depth [45], it has also decreased. In summary, the increase in the thickness of the plough layer reduced the evapotranspiration, but the decrease was not obvious because the thickness of the new soil plough layer was still smaller than the limit depth of evaporation. Therefore, the increase in the plough layer thickness had only a small effect. The evapotranspiration reductions in the P2 and P4 scenarios were larger than those in the P1 and P3 scenarios because the soil porosity of the plough layer in the P2 and P4 scenarios was 0.1 greater than those of P1 and P3. Under the same precipitation conditions, the water storage of the plough layer (P2 and P4) was larger.
4.2. Effect of the Soil Porosity on Soil Water Cycle
Subsoiling can loosen the soil and increase the soil porosity [46]. P1 vs. P2 and P3 vs. P4 represent comparison scenarios set for changes in soil porosity. In these two comparative scenarios, the soil porosity of the plough layer increased by 0.1, and other conditions remained unchanged. When the thin-walled cells of the crop root reached saturation, the water potential was equal to zero and no longer absorbed water, but the cells around the vessel still metabolized and continuously secreted inorganic salts and simple organic matter into the vessel [47]. The water potential of the vessel solution decreased, while the water potential of nearby living cells was higher. Water continuously flowed into the vessel. Similarly, the moisture of the outer cells moved inwards, and finally the soil moisture entered the vessel along the root hairs and cortex and was further transported upwards back to the atmosphere. Increased soil porosity improved soil water storage space. Therefore, under the same precipitation conditions, the soil water content increased. The metabolism of the roots had been on-going, and thus more soil water entered the vessel through the crop roots and returned to the atmosphere. Therefore, the increase of soil porosity led to an increase in evapotranspiration [46] and improved the efficiency of local precipitation.
4.3. Effect of the Soil Permeability on Soil Water Cycle
Subsoiling not only loosens the soil but also increases the soil permeability [48]. P3 vs. P5 and P3 vs. P6 were comparison scenarios set for changes in soil permeability. The results showed that under the two comparison scenarios, the farmland runoff and the surface runoff showed obvious changes. The precipitation that reached the ground was divided into two parts, surface and underground [49]. As the soil permeability increased, the speed of movement of the soil water in the soil was accelerated [50]. Therefore, the more precipitation entered the ground, the less the surface runoff, which was the reason for the reduction of farmland runoff and surface runoff. The increase in soil water permeability only speeded up the process of transporting soil water to the underground, and the soil structure around the crop roots had not changed, so the transpiration would not change significantly. However, the simulation results showed that there was a slight increase in evapotranspiration. This may be due to the increase in the soil water flow rate, which increased the water potential around the roots, prompted the process of roots absorbing soil water, and increased crop transpiration, thereby increasing the evapotranspiration of farmland.
4.4. Effect of Subsoiling on Soil Water Cycle
In the actual subsoiling process, the soil plough layer thickness, porosity, and soil permeability change concurrently [51]. In the actual subsoiling process, the thickness of the plough layer, the porosity, and the permeability of the soil will increase [52]. The Original vs. P5 and Original vs. P6 comparison scenarios were set for actual subsoiling. The results showed that surface runoff and farmland runoff decreased and evapotranspiration increased. The increase in thickness, porosity, and permeability of soil plough layer had a huge impact on the soil water cycle process. The soil thickness and porosity mainly affected the redistribution of soil water, and the permeability mainly affected the infiltration process of precipitation. The increases of the three elements had changed the storage and transportation of water in the soil, and thus changed the soil environment around the crop roots, and promoted the transpiration of crops and the evaporation of soil. These results were consistent with those of Guan and Zhang et al. [53] and Ma and Yu et al. [54]. However, this change was not a linear combination of the abovementioned single change scenarios, which showed that the joint action of multi-elements was not the liner superposition of single elements.
5. Conclusions
In this study, three factors (thickness, porosity, and permeability) were considered and quantitatively simulated by a hydrological model. The comparison of scenario simulation results proved that changes in soil characteristics caused by subsoiling will influence the effective precipitation.
Among the three factors, the effect of soil porosity on effective precipitation was the largest. When soil porosity increased by 0.1, the effectiveness of precipitation increased by approximately 19%. The permeability had a small effect on precipitation efficiency, but significantly affected the farmland runoff. The plough layer thickness had little effect on the effective precipitation.
This article studies the effectiveness of local precipitation from the perspective of a hydrological model. However, the parameters characterizing the effect of subsoiling in the model were drawn from literature research. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out further field experiments in the study area to optimize model parameters and thus improve the model.
Author Contributions
Drafted the manuscript, J.W.; Designed the project and provided overall guidance, T.Q.; Provided the simulation method, X.L., K.W. and H.N.; Finalized the manuscript, J.W. and T.Q.; Collected the data, Z.L., F.L. and S.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (Grant No. 51725905; 51879275) and National Key Research and Development Project (Grant No. 2016YFA0601503; 2017YFA0605004).
Acknowledgments
The authors much appreciate the editors and the reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions, which are extremely helpful for improving the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, D.; Yu, Z.; White, P.J. The effect of supplemental irrigation after jointing on leaf senescence and grain filling in wheat. Field Crops Res. 2013, 151, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifmanesh, H.; Deng, A.; Nawaz, M.M.; Li, L.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, P.; Song, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C.; et al. Integrative impacts of rotational tillage on wheat yield and dry matter accumulation under corn-wheat cropping system. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 184, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Shi, Y.; Yu, Z. Subsoiling improves soil physical and microbial properties, and increases yield of winter wheat in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 187, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, M.A.; Anderson, W.K. Soil compaction in cropping systems: A review of the nature, causes and possible solutions. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 82, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissett, A.; Richardson, A.E.; Baker, G.; Kirkegaard, J.; Thrall, P.H. Bacterial community response to tillage and nutrient additions in a long-term wheat cropping experiment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.F.; Bourrié, G.; Trolard, F. Soil compaction impact and modelling. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wie, J.B.; Adam, J.C.; Ullman, J.L. Conservation tillage in dryland agriculture impacts watershed hydrology. J. Hydrol. 2013, 483, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djiemon, A.; Gasser, M.O.; Gallichand, J. Random forests to detect subsoiling and subsurface drainage effects on corn plant height and water table depth. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 192, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, G.F.; Tolon-Becerra, A.; Lastra-Bravo, X.; Tourn, M. Tillage and traffic effects (planters and tractors) on soil compaction and soybean (Glycine max L.) yields in Argentinean pampas. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 110, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboutalebi, M.; Torres-Rua, A.F.; Allen, N. Spatial and temporal analysis of precipitation and effective rainfall using gauge observations, satellite, and gridded climate data for agriculturalwater management in the upper Colorado River Basin. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Kim, J.; Jeong, S. Rainfall intensity-duration thresholds for landslide prediction in South Korea by considering the effects of antecedent rainfall. Landslides 2018, 15, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.Q.; Zhu, M.M.; Li, W.J. Effective precipitation and water requirements of crops in Hebei province over 60 years. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.L.; Xia, D.X.; Ji, L.; Huang, G.H. An inexact stochastic-fuzzy optimization model for agricultural water allocation and land resources utilization management under considering effective rainfall. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 92, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Yin, X.; Yang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Cai, Y. Assessing crop virtual water content under non-standard growing conditions using Budyko framework. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 131, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, W.S.; Panachuki, E.; de Oliveira, P.T.S.; da Silva Menezes, R.; Sobrinho, T.A.; de Carvalho, D.F. Effect of soil tillage and vegetal cover on soil water infiltration. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Choudhary, O.P.; Singh, H.P.; Singh, A.; Mishra, S.K. Sub-soiling improves productivity and economic returns of cotton-wheat cropping system. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 189, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P.; Woolhiser, D.A. Mathematical Modeling of Watershed Hydrology. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2002, 7, 270–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranch, H.; Simonovic, S. Computer Models of Watershed Hydrology. Director 1995, 14, 1995–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sivapalan, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Franks, S.W.; Gupta, V.K.; Karambiri, H.; Lakshmi, V.; Liang, X.; McDonnell, J.J.; Mendiondo, E.M.; O’Connell, P.E.; et al. IAHS Decade on Predictions in Ungauged Basins (PUB), 2003-2012: Shaping an exciting future for the hydrological sciences. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2003, 48, 857–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djaman, K.; O’Neill, M.; Diop, L.; Bodian, A.; Allen, S.; Koudahe, K.; Lombard, K. Evaluation of the Penman-Monteith and other 34 reference evapotranspiration equations under limited data in a semiarid dry climate. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 137, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Ni, G.; Kawahara, Y.; Suetsugi, T. Simulation of hydrological cycle in an urbanized watershed and effect evaluation of infiltration facilities with WEP model. J. Hydrosci. Hydraul. Eng. 2001, 19, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Ni, G.; Kawahara, Y.; Suetsugi, T. Development of WEP model and its application to an urban watershed. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 2175–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Tang, D.; Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Wagan, B. Precipitation trends over time using Mann-Kendall and spearman’s Rho tests in swat river basin, Pakistan. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longobardi, A.; Villani, P. Trend analysis of annual and seasonal rainfall time series in the Mediterranean area. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Zin, W.Z.; Jamaludin, S.; Deni, S.M.; Jemain, A.A. Recent changes in extreme rainfall events in Peninsular Malaysia: 1971–2005. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 99, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. Effects of Subsoiling on Soil Physical Properties and Research of Border Irrigation Technicalparameters; Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lampurlanés, J.; Cantero-Martínez, C. Soil bulk density and penetration resistance under different tillage and crop management systems and their relationship with barley root growth. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Song, B.; Wang, C.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, L.; Hao, X.; Liu, F. Soil amelioration by deep ploughing of different machineries and its effect on promoting crop growth and yield. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Han, C.; Zeng, S.; Wu, Q.; Liu, L. Effects of Different Tillage Managements on the Yield and Characters of Maize. J. Maize Sci. 2014, 22, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, K.; Ji, B.; Guo, H.; Xue, Z.; Li, C. Responses of soil properties, root growth and crop yield to tillage and crop residue management in a wheat-maize cropping system on the North China Plain. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 78, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. Study on Capacity of Moisture Conservation and the Response of Maize Growth in Dryland; Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Gao, Z.Q.; Ren, A.X.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, W.F.; Zhao, H.M.; Yang, Z.P.; He, L.H.; Zong, Y. Contribution of subsoiling in fallow period and nitrogen fertilizer to the soil-water balance and grain yield of dry-land wheat. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2015, 17, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wen, X.; Liao, Y. Coupling effects of plastic film mulching and urea types on water use efficiency and grain yield of maize in the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 157, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Klaghofer, E. Impacts of forest vegetation on runoff generation mechanisms: A review. J. Nat. Resour. 2001, 16, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Pan, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhan, W.; Yuan, J. Measurement of rainfal l-erosion impacted soil infiltration capabil ity of slope land with run-on-ponding water. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2006, 22, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, W.; Wen, Z. Soil infiltration capatiey and its influencing factors of different land use types in Karst slope. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Jabro, J.D.; Stevens, W.B.; Iversen, W.M.; Evans, R.G. Tillage depth effects on soil physical properties, sugarbeet yield, and sugarbeet quality. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 41, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharati, L.; Lee, K.H.; Isenhart, T.M.; Schultz, R.C. Soil-water infiltration under crops, pasture, and established riparian buffer in Midwestern USA. Agrofor. Syst. 2002, 56, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, R.C.; Baumhardt, R.L.; Evett, S.R. Tillage effects on soil water redistribution and bare soil evaporation throughout a season. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 110, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Leung, A.K.; Ng, C.W.W. Transpiration reduction and root distribution functions for a non-crop species Schefflera heptaphylla. Catena 2015, 135, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, M.; Wu, W.; Tanveer, S.K.; Wen, X.; Liao, Y. The effects of conservation tillage practices on the soil water-holding capacity of a non-irrigated apple orchard in the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 130, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Steinbach, H.S. A review of the effects of tillage systems on some soil physical properties, water content, nitrate availability and crops yield in the Argentine Pampas. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 104, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewry, J.J.; Lowe, J.A.H.; Paton, R.J. Effect of subsoiling on soil physical properties and pasture production on a Pallic soil in Southland, New Zealand. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2000, 43, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.K.; Garg, A.; Ng, C.W.W. Effects of plant roots on soil-water retention and induced suction in vegetated soil. Eng. Geol. 2015, 193, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Tang, C.S.; Xu, S.K.; Gong, X.P.; Shi, B.; Inyang, H.I. Effects of soil characteristics on moisture evaporation. Eng. Geol. 2018, 239, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Miao, F.; Wang, G. Dryland maize yield and water-use efficiency responses to mulching and tillage practices. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 1196–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertolas, J.; Alcobendas, R.; Alarcón, J.J.; Dodd, I.C. Long-distance abscisic acid signalling under different vertical soil moisture gradients depends on bulk root water potential and average soil water content in the root zone. Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikul, J.L.; Aase, J.K. Water Infiltration and Storage affected by Subsoiling and Subsequent Tillage. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Gu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Jiao, L.; Zhu, N. Stable isotope evidence for identifying the recharge mechanisms of precipitation, surface water, and groundwater in the Ebinur Lake basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, N.C.; Gulliver, J.S.; Nieber, J.L.; Kayhanian, M. Remediation to improve infiltration into compact soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 117, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.D.; Lindstrom, M.J.; Voorhees, W.B.; Moncrief, J.F.; Nelson, G.A. Effect of subsoiling and subsequent tillage on soil bulk density, soil moisture, and corn yield. Soil Tillage Res. 1996, 38, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lu, C.; Li, H.; He, J.; Sarker, K.K.; Rasaily, R.G.; Liang, Z.; Qiao, X.; Li, H.; Mchugh, A.D.J. The effects of no-tillage with subsoiling on soil properties and maize yield: 12-Year experiment on alkaline soils of Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 137, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Al-Kaisi, M.M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z. Tillage practices effect on root distribution and water use efficiency of winter wheat under rain-fed condition in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 146, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Gao, Z.; Luo, L.; Chu, P.; Guo, Z. Soil water use, grain yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat in a long-term study of tillage practices and supplemental irrigation on the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 150, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).