Towards Monitoring of Nutrient Pollution in Coastal Lake Using Remote Sensing and Regression Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
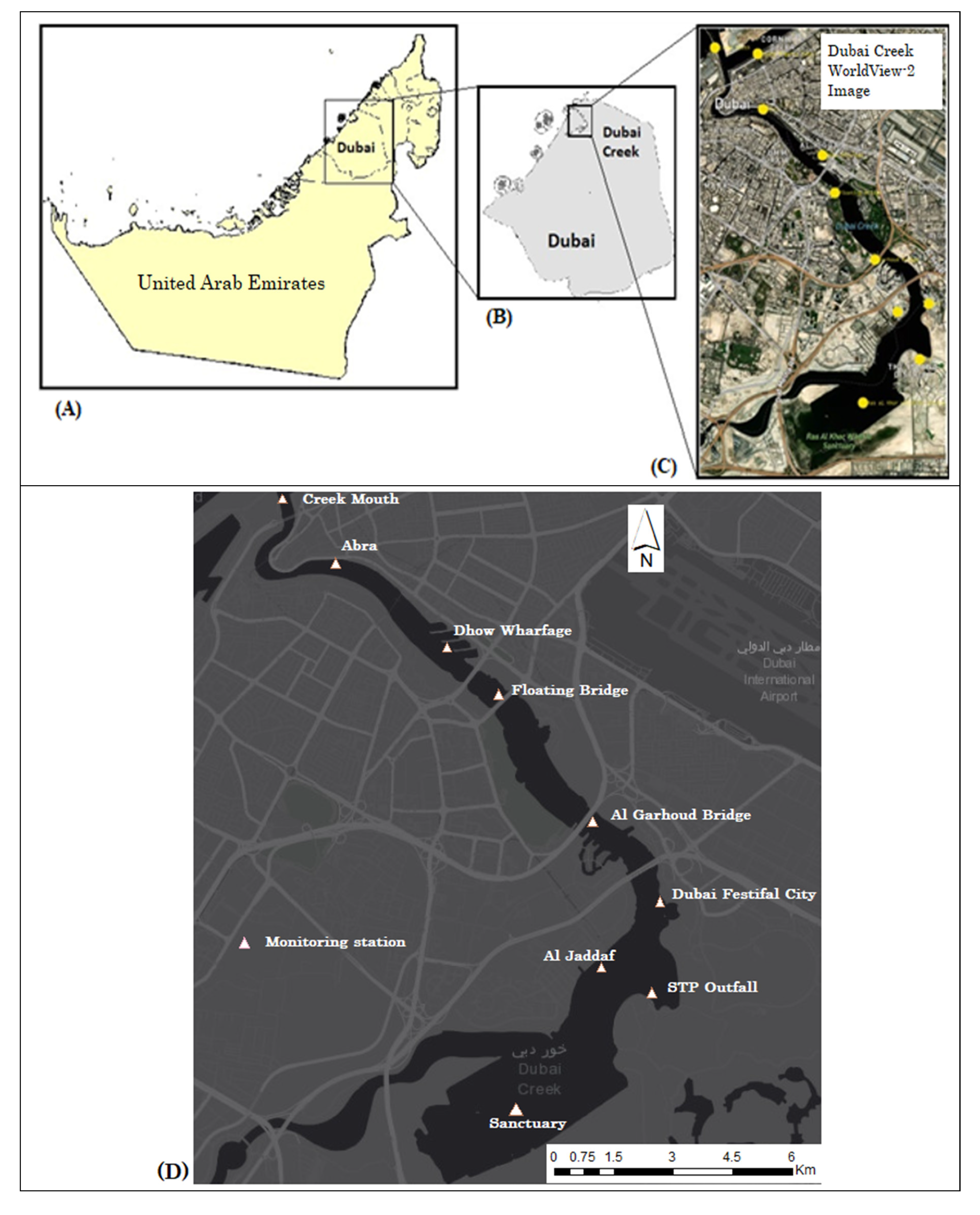
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Data Preparation
2.2.2. In-Situ Data
2.2.3. Landsat ETM+ Images
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Preprocessing of WorldView-2 Image and In Situ Data
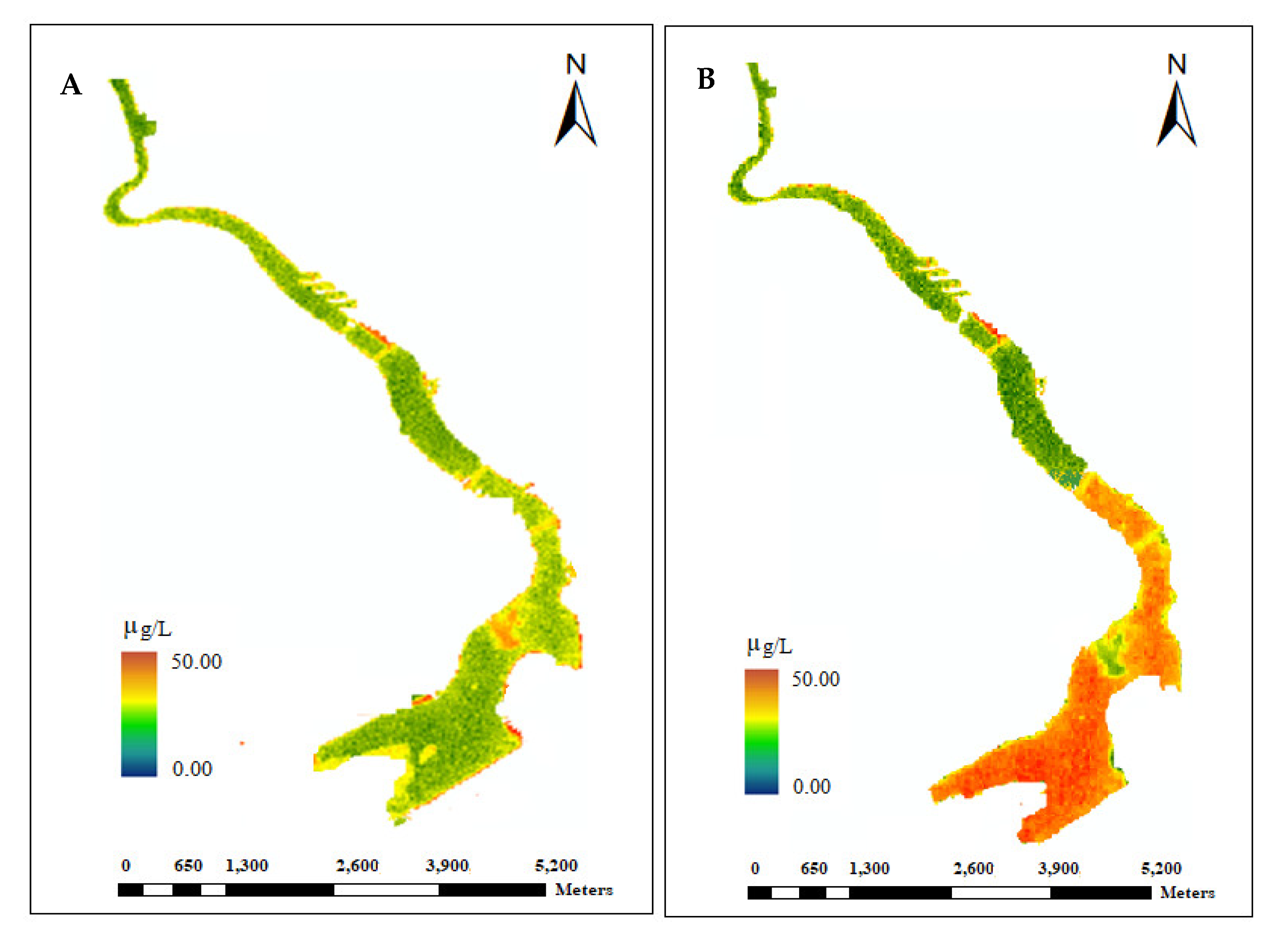
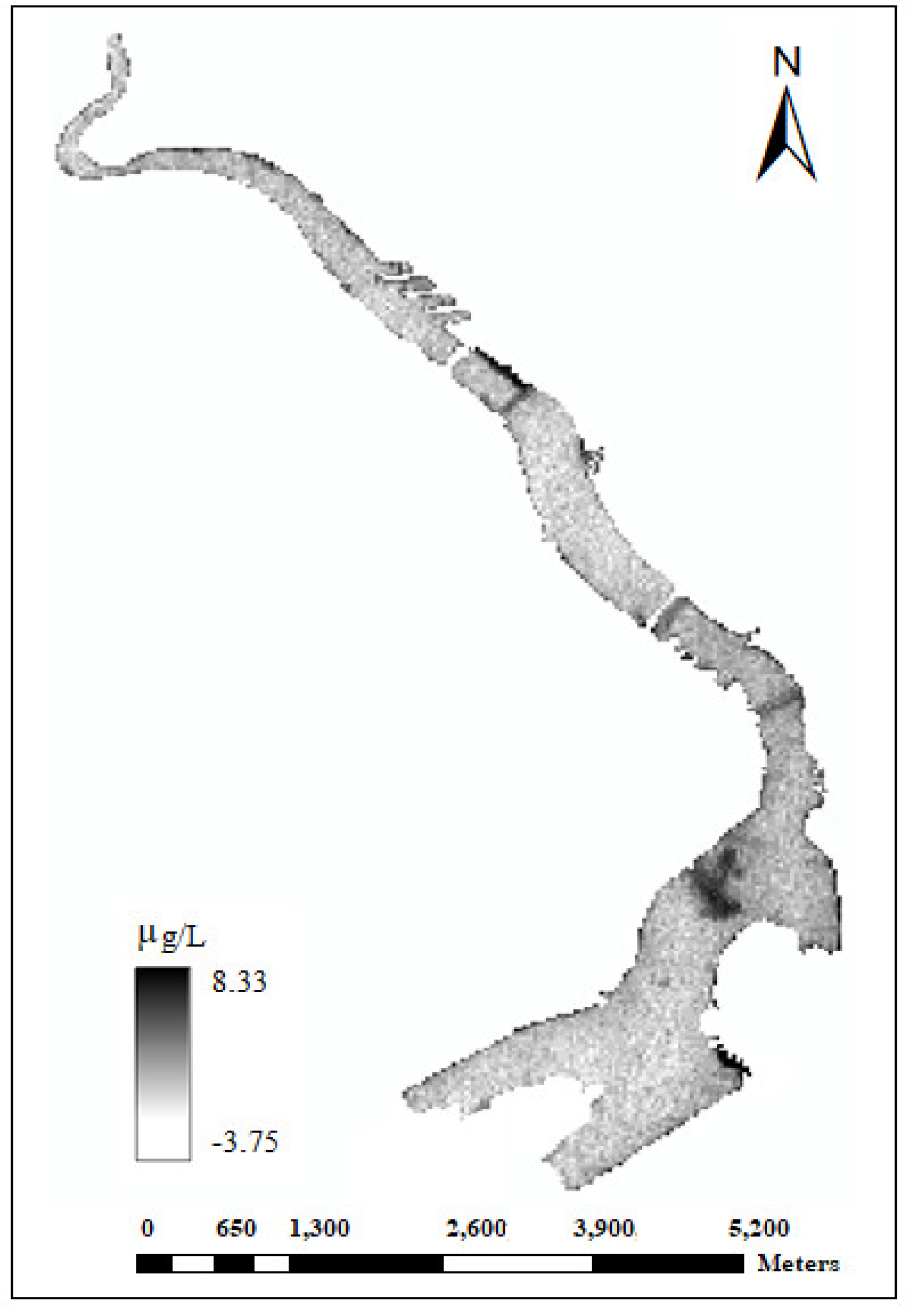
2.3.2. Model Based on Chlorophyll-a Spectral Value from WorldView-2 Image
2.3.3. Preprocessing of Landsat ETM+ Images
2.3.4. Modelling the Field Chlorophyll-a against Nutrients
3. Results and Discussion
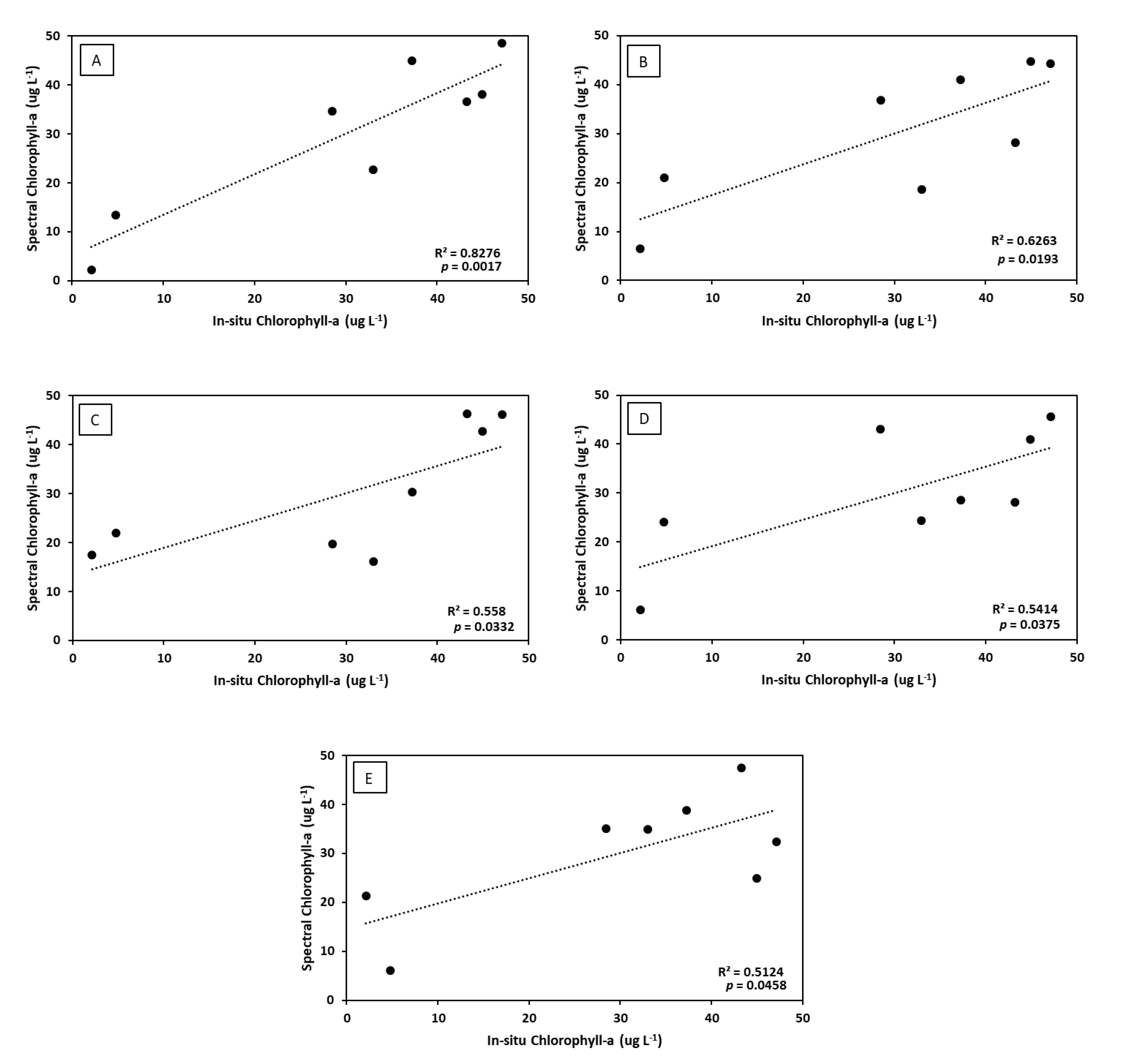
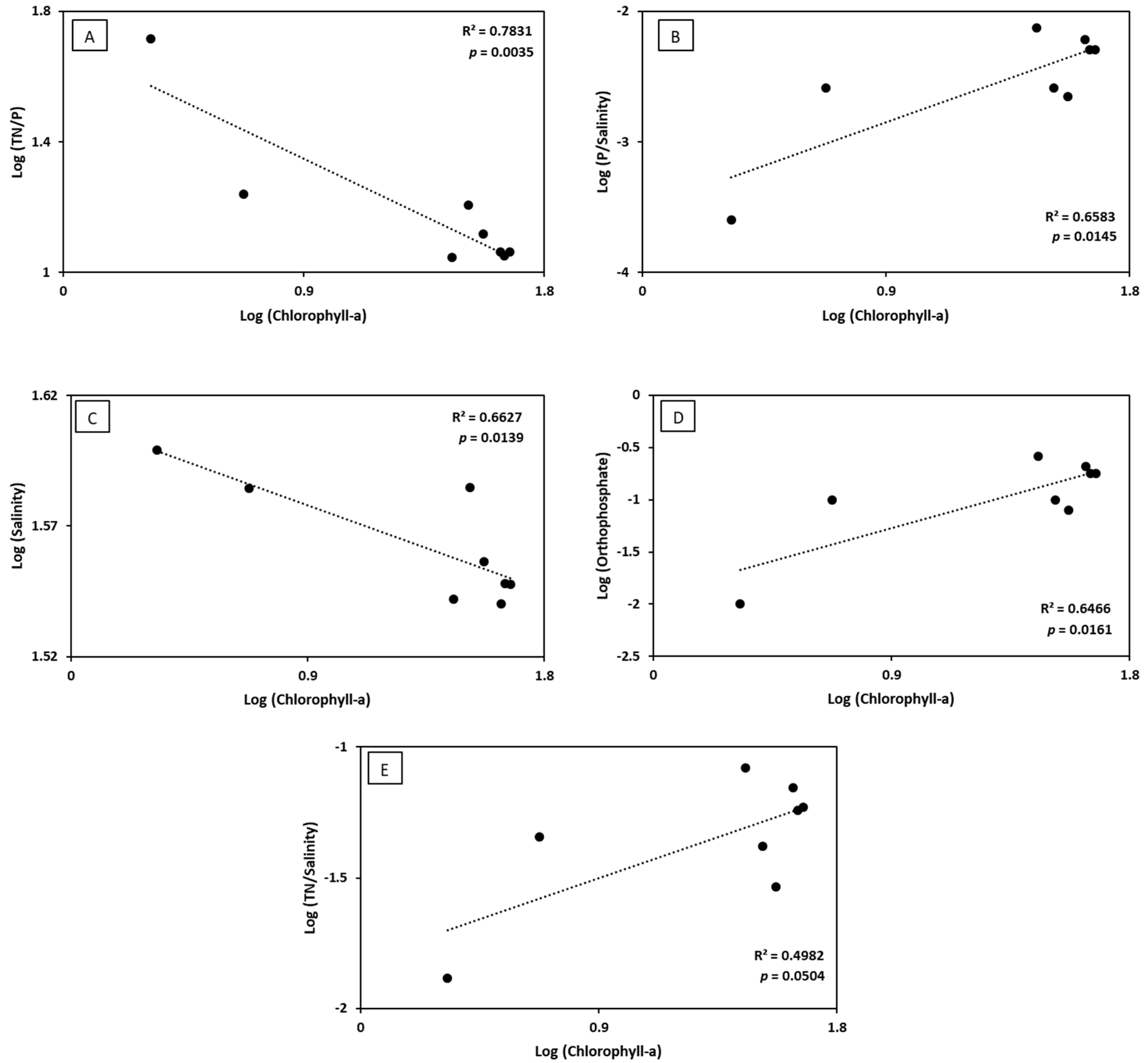
3.1. Relationship between In-Situ Chlorophyll-a and the Eutrophication Indicators
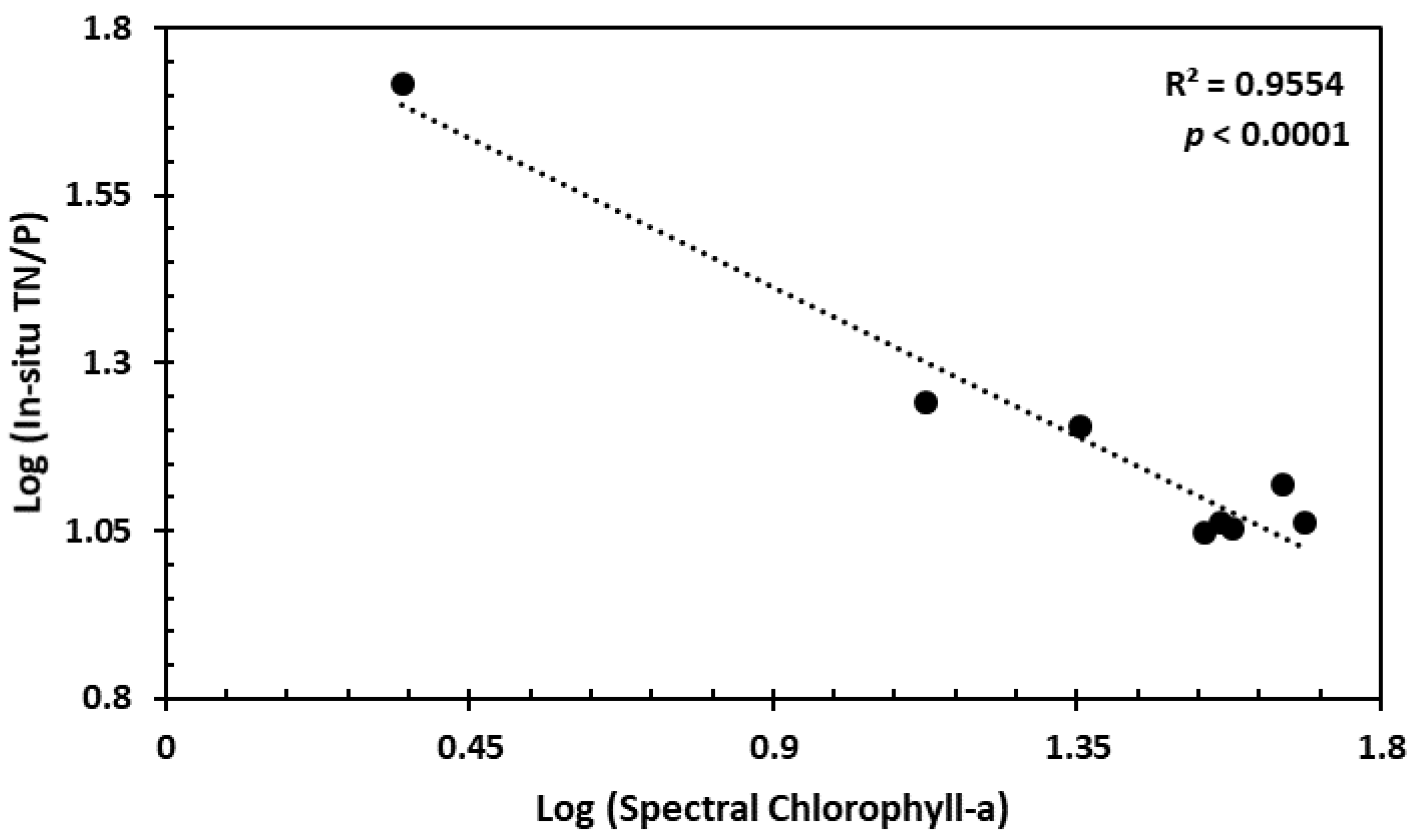
3.2. Relationship between Spectral Chlorophyll-a and the Eutrophication Indicators
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Napiorkowska-Krzebietke, A.; Kalinowska, K.; Bogacka-Kapusta, E.; Stawecki, K.; Traczuk, P. Cyanobacterial Blooms and Zooplankton Structure in Lake Ecosystem under Limited Human Impact. Water 2020, 12, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, H.; Cai, S.; He, Q. Quantile Analysis of Long-Term Trends of Near-Surface Chlorophyll-a in the Pearl River Plume. Water 2020, 12, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, M.S.A.; Lin, J.; Hsieh, L.C.; Zafirah, Y.; Andhikaputra, G.; Wang, Y. Influencing Factors Analysis of Taiwan Eutrophicated Reservoirs. Water 2020, 12, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, T.D.; Kumarasamy, M. Application of Multivariate Statistical Analysis in the Development of a Surrogate Water Quality Index (WQI) for South African Watersheds. Water 2020, 12, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.C.D.; Paco, T.; Branquinho, C.; Silva, J.M.D. Using Chlorophyll a Fluorescence Imaging to Select Desiccation-Tolerant Native Moss species for Water-Sustainable Green Roofs. Water 2020, 12, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, D.; Neves, R.; Branco, M.A.; Prazeres, A.; Rodriques, S.; Concalves, M.C.; Ramos, T.B. Assessing Water and Nutrient Long-Term Dynamics and Loads in the Enxoe Temporary River Basin (Southeast Portugal). Water 2019, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmalik, K. Role of statistical remote sensing for Inland water quality parameters prediction. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2018, 21, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Seto, K.; Stokes, E.; Deng, C.; Pickett, S.; Taubenbock, H. Understanding an urbanizing planet: Strategic directions for remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 228, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tian, L.; Song, Q.; Sun, Z.; Yu, H.; Xing, Q. Temporal Variation of Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in Highly Dynamic Waters from Unattended Sensors and Remote Sensing Observations. Sensors 2018, 18, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blix, K.; Palffy, K.; Toth, V.R.; Eltoft, T. Remote Sensing of Water Quality Parameters over Lake Balaton by Using Sentinel-3 OLCI. Water 2018, 10, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, R.C.; Martinez, J.M.; Marques, D.D.M.; Cirilo, J.A.; Fragoso, C.R. Assessment of Chlorophyll-a Remote Sensing Algorithms in Productive Tropical Estuarine-Lagoon System. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, B.; Salama, M.S.; Wernand, M.R.; Verhoef, W. MOD2SEA: A coupled Atmosphere-Hydro-Optical Model for the Retrieval of Chlorphyll-a from Remote Sensing Observations in Complex Turbid Water. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittings, J.; Raitsos, D.; Racault, M.; Brewin, R.; Pradhan, Y.; Sathyendranath, S.; Platt, T. Seasonal phytoplankton blooms in the Gulf of Aden revealed by remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 189, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richlen, M.; Morton, S.; Jamali, E.; Rajan, A.; Anderson, D. The catastrophic 2008–2009 red tide in the Arabian gulf region, with observations on the identification and phylogeny of the fish-killing dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeau-Patissier, D.; Gowe, J.; Dekker, A.; Phinn, S.; Brando, V. A review of ocean color remote sensing methods and statistical techniques for the detection, mapping and analysis of phytoplankton blooms in coastal and open oceans. Prog. Oceanogr. 2014, 123, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, M. A current review of empirical procedures of remote sensing in inland and near-coastal transitional waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 6855–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T. Quantitative detection of chlorophyll in cyanobacterial blooms by satellite remote sensing. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 2179–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma, M.M.; Bonansea, M.; Ledesma, C.R.; Rodriquez, C.; Carreno, J.; Pinotti, L. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration using Landsat 8 in the Cassaffousth reservoir. Water Supply 2019, 19, 2021–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Weathers, K.C.; Norouzi, H.; Steele, B. Assessing the effectiveness of Landsat 8 Chlorophyll a retrieval algorithms for regional freshwater monitoring. Ecol. Appl. 2018, 28, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buditama, G.; Damayanti, A.; Pin, T.G. Identifying Distribution of Chlorophyll-a Concentration Using Landsat 8 OLI on Marine Waters Area of Cirebon. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 98, 012040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wu, X.; Bing, Q.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, J. Study on Retrieval of chlorophyll-a Concentration Based on Landsat OLI Imagery in the Haihe River, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podder, S.; Chacko, N.; Swain, D. Estimation of Chlorophyll-a in Northern Coastal Bay of Bengal Using Landsat-8 OLI and Sentinel-2 MSI Sensors. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, C.; Valerio, A.D.M.; Ward, N.; Loken, L.; Sawakuchi, H.O.; Kampel, M.; Richey, J.; Stadler, P.; Crawford, J.; Striegl, R.; et al. Performance of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 surface reflectance products for river remote sensing retrievals of chlorophyll-a and turbidity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.; Alcantara, E.; Rodriques, T.; Rotta, L.; Bernardo, N.; Imai, N. Remote sensing of the chlorophyll-a based on OLI/Landsat-8 and MSI/Sentinel-2A (Barra Bonita reservoir, Brazil). An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2018, 90, 1987–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebbs, E.; Remedios, J.; Harper, D. Remote sensing of chlorophyll-a as a measure of cyanobacterial biomass in Lake Bogoria, a hypertrophic, saline–alkaline, flamingo lake, using Landsat ETM+. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 135, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbick, N.; Hu, F.; Zhang, J.; Qi, J.; Becker, B. Mapping Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in West Lake, China using Landsat 7 ETM+. J. Great Lakes Res. 2008, 34, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezonik, P.; Menken, K.D.; Bauer, M. Landsat-based remote sensing of lake water quality characteristics, including chlorophyll and colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM). Lake Reserv. Manag. 2005, 21, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ghedira, H. Monitoring red tide with satellite imagery and numerical models: A case study in the Arabian Gulf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 97, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Mortula, M.; Atabay, S. Study of water quality in Dubai Creek using DubaiSat-1 multispectral imagery. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2013, 398, 200–210. [Google Scholar]
- Isenstein, E.; Park, M. Assessment of nutrient distributions in Lake Champlain using satellite remote sensing. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1831–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, K.; Wang, Y.; Oki, T.; Yamashiki, Y.; Takara, K.; Miura, S.; Imai, A.; Komatsu, K.; Kawasaki, N. Analysis of stream water quality and estimation of nutrient load with the aid of Quick Bird remote sensing imagery. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2012, 57, 850–860. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, T.; Mortula, M.; Atabay, S. Monitoring and assessment of water quality of a coastal lake using high resolution imagery and GIS. Pollut. Res. 2017, 36, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, H.; Atabay, S.; Mortula, M.M.; Ali, T. Investigation of Water Quality Parameters for Coastal Lagoon. Pollut. Res. 2017, 37, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, T.; Mortula, M.; Atabay, S. GIS-based study on the Susceptibility of Dubai Creek (UAE) to Eutrophication. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 2275–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; 874p. [Google Scholar]
- Upkide, T.; Comp, C. Radiometric Use of WorldView-2 Imagery. 2010. Available online: https://dg-cms-uploads-production.s3.amazonaws.com/uploads/document/file/104/Radiometric_Use_of_WorldView-2_Imagery.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- Chavez, P. Image-based atmospheric correction: Revisited and improved. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1996, 62, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Brivio, P.; Giardino, C.; Zilioli, E. Determination of chlorophyll concentration changes in Lake Garda using an image-based radiative transfer code for Landsat TM images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspers, H. Eutrophication of waters. Monitoring, assessment and control. Organ. Econ. Coop. Dev. 1982, 69, 200. [Google Scholar]
- Dial, G.; Bowen, H.; Gerlach, F.; Grodecki, J.; Oleszczuk, R. The Benefits of the 8 Spectral Bands of WorldView-2. 2010. Available online: http://www.army.mil/article/70358/Nano_technology_marches_ on/ (accessed on 4 March 2020).
- Ali, T.; Mortula, M.; Atabay, S.; Navadeh, E. A GIS-based spatiotemporal study of the variability of water quality in the Dubai Creek, UAE. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 2015, 51, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hakanson, L.; Eklund, J. Relationships between chlorophyll, salinity, phosphorus, and nitrogen in lakes and marine areas. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 26, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Band: Center Wavelength (Width) | Description |
|---|---|
| Coastal Blue (CB): 427 nm (400–450 nm) | Absorbed by chlorophyll in healthy plants, it therefore aids in vegetation analysis |
| Near Infrared 1 (NIR1): 831 nm (770–895 nm) | Useful in separating water from vegetation |
| Near Infrared 2 (NIR2): 908 nm (860–1040 nm) | Aids in vegetation analysis and biomass studies |
| Blue (B): 478 nm (450–510 nm) | It gets absorbed by chlorophyll in plants |
| Green (G): 546 nm (510–580 nm) | Characterized by high reflectance in healthy plants |
| Yellow (Y): 608 nm (585–625 nm) | Detects the degree of yellow color of vegetation |
| Red edge (RED): 724 nm (705–745 nm) | Targeted at the high reflectivity portion of vegetation response |
| Red (R): 659 nm (630–690 nm) | Highly absorbed by healthy plants |
| WorldView-2 Band Combinations | R2 | RMSE | Confidence Interval (CI) (95%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Coastal blue + Near infrared 1)/Near infrared 2 | (CB + NIR1)/NIR2 | 0.83 | 6.839 | 0.0551 |
| (Blue + Near infrared 1)/Near infrared 2 | (B + NIR1)/NIR2 | 0.63 | 10.07 | 0.0668 |
| (Green + Near infrared 1)/Near infrared 2 | (G + NIR1)/NIR2 | 0.56 | 10.95 | 0.0717 |
| (Yellow + Near infrared 1)/Near infrared 2 | (Y + NIR1)/NIR2 | 0.54 | 11.15 | 0.0772 |
| (Red edge + Near infrared 2)/Near infrared 1 | (RED + NIR2)/NIR1 | 0.53 | 11.29 | 0.0765 |
| (Blue + Near infrared 1)/Red edge | (B + NIR1)/RED | 0.51 | 11.50 | 0.0980 |
| (Yellow + Red)/Red edge | (Y + R)/RED | 0.46 | 12.07 | 0.0018 |
| Near infrared 1/Near infrared 2 | NIR1/NIR2 | 0.43 | 12.40 | 0.0491 |
| Red edge/Near infrared 1 | RED/NIR1 | 0.41 | 12.63 | 0.0560 |
| Yellow/Red edge | Y/RED | 0.32 | 13.71 | 0.0514 |
| Sampling Station | In-Situ Chlorophyll-a (µg/L) | Spectral Chlorophyll-a (µg/L) | % Residual |
|---|---|---|---|
| Creek Mouth | 2.130 | 2.24 | 5.16 |
| Abra | 32.98 | 22.61 | 31.44 |
| Dhow Wharfage | 4.750 | 13.4 | 182.10 |
| Floating Bridge | 28.48 | 34.65 | 21.66 |
| Dubai Festival City (DFC) | 43.25 | 36.6 | 15.38 |
| Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) | 44.93 | 38.01 | 15.4 |
| Al Jaddaf | 47.13 | 48.48 | 2.86 |
| Ras Al Khor Wildlife Sanctuary | 37.25 | 44.98 | 20.75 |
| Sampling Station | Q2, 2010 (µg/L) | Q2, 2011 (µg/L) | Q2, 2012 (µg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Creek Mouth | 0.1 | 8.1 | 4.6 |
| Hyatt Regency Dubai | 10.8 | 11.2 | 15.6 |
| Abra | 6.4 | 29.8 | 5.9 |
| Dhow Wharfage | 9.2 | 32.8 | 4.6 |
| Floating Bridge | 7.7 | 22.4 | 57.5 |
| Average | 6.84 | 20.86 | 17.64 |
| Sampling Station | In-Situ Chl-a (µg/L) | LOG (TN/P) (Modelled) | TN/P (Modelled) | LOG (TN/P) (In-Situ) | TN/P (In-Situ) | % Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Creek Mouth | 2.13 | 1.57 | 37.22 | 1.72 | 52 | 28.42 |
| Abra | 32.98 | 1.11 | 12.86 | 1.21 | 16.1 | 20.15 |
| Dhow Wharfage | 4.75 | 1.44 | 27.27 | 1.24 | 17.4 | 56.71 |
| Floating Bridge | 28.48 | 1.13 | 13.61 | 1.05 | 11.15 | 22.02 |
| Dubai Festival City (DFC) | 43.25 | 1.06 | 11.57 | 1.06 | 11.57 | 0.01 |
| Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) | 44.93 | 1.06 | 11.40 | 1.05 | 11.28 | 1.11 |
| Al Jaddaf | 47.13 | 1.05 | 11.19 | 1.06 | 11.56 | 3.13 |
| Ras Al Khor Wildlife Sanctuary | 37.25 | 1.09 | 12.26 | 1.12 | 13.13 | 6.57 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mortula, M.; Ali, T.; Bachir, A.; Elaksher, A.; Abouleish, M. Towards Monitoring of Nutrient Pollution in Coastal Lake Using Remote Sensing and Regression Analysis. Water 2020, 12, 1954. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071954
Mortula M, Ali T, Bachir A, Elaksher A, Abouleish M. Towards Monitoring of Nutrient Pollution in Coastal Lake Using Remote Sensing and Regression Analysis. Water. 2020; 12(7):1954. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071954
Chicago/Turabian StyleMortula, Maruf, Tarig Ali, Abdallah Bachir, Ahmed Elaksher, and Mohamed Abouleish. 2020. "Towards Monitoring of Nutrient Pollution in Coastal Lake Using Remote Sensing and Regression Analysis" Water 12, no. 7: 1954. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071954
APA StyleMortula, M., Ali, T., Bachir, A., Elaksher, A., & Abouleish, M. (2020). Towards Monitoring of Nutrient Pollution in Coastal Lake Using Remote Sensing and Regression Analysis. Water, 12(7), 1954. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071954








