Small Reservoirs, Landscape Changes and Water Quality in Sub-Saharan West Africa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- What have been the dominant LULC changes occurring around SRs in Burkina Faso between 2002 and 2014?
- What are the possible linkages between LULC and demographic situations, and the water quality assessed in 2014 within a set of selected SRs?
- What have been the impacts of LULC changes observed between 2002 and 2014 on the water quality of a sub-series of these SRs studied twice, in 2004/5 and in 2014?
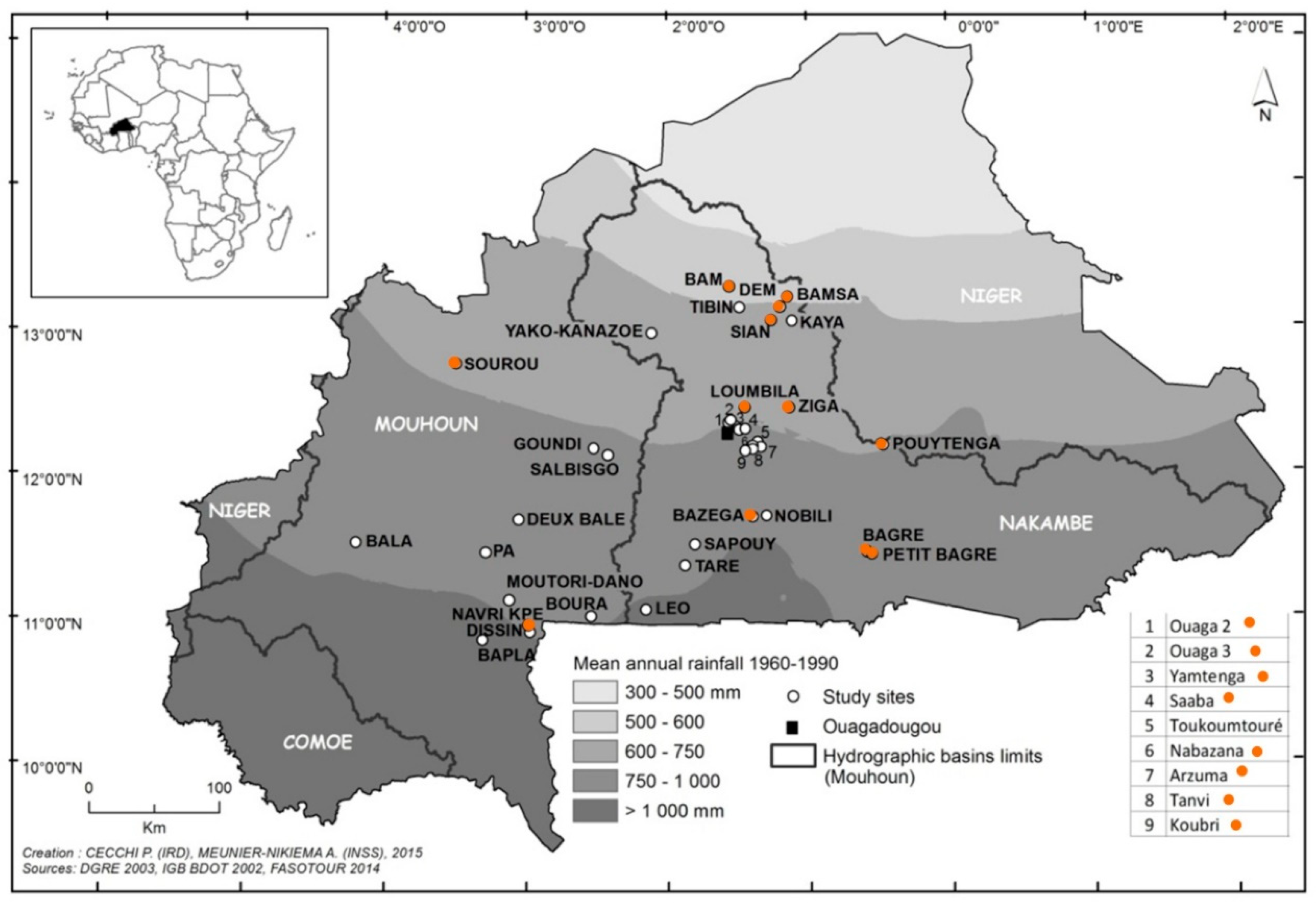
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. LULC Changes (2002–2014) at Multiple Scales
3.2. Indicators of Anthropogenic Pressures
- Contribution of the cropland class to LULC calculated in buffer areas of 5-km radius around reservoirs, associated with local anthropogenic pressures. This is possible because synoptic information is available at this scale: (i) such a buffer area corresponds to a 78.5 km2 area; (ii) remote sensing information is based on Landsat ETM+/OLI-based description of land use at the national scale in using 30 m × 30 m pixels; (iii) there is thus enough information for defining classes and then calculating cropland contribution.
- Population densities calculated at the watershed scale, associated with global anthropogenic pressures. This is possible because (i) this corresponds to the least disaggregated data level that is not an administrative division; and (ii) these data are not correlated to the data quantifying the cropland class contribution to LULC at local scales.
3.3. Synchronic Analysis
3.3.1. Water Quality Characteristics
3.3.2. Impact of Anthropogenic Factors on Water Quality
3.4. Diachronic Perspective
4. Discussion
4.1. LULC Changes
4.2. SPM Concentration Measurements
4.3. Synchronic Analysis
4.4. Diachronic Perspective
4.5. Defining Scales of Interest
5. Conclusions
Recommendations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saruchera, D.; Lautze, J. Small Reservoirs in Africa: A Review and Synthesis to Strengthen Future Investment; IWMI Working Paper 189; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2019; 40p. [Google Scholar]
- Cecchi, P.; Meunier-Nikiema, A.; Moiroux, N.; Sanou, B. Towards an atlas of lakes and reservoirs in Burkina Faso. In Small Reservoirs Toolkit; Andreini, M., Schuetz, T., Harrington, L., Eds.; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2009; 23p. [Google Scholar]
- Douxchamps, S.; Ayantunde, A.; Barron, J. Taking stock of forty years of agricultural water management interventions in smallholder systems of Burkina Faso. Water Resour. Rural Dev. 2014, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boelee, E.; Cecchi, P. Health Impacts of Small Reservoirs in Burkina Faso; IWMI Working Paper 136; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2009; 50p. [Google Scholar]
- Boelee, E.; Yohannes, M.; Poda, J.-N.; McCartney, M.; Cecchi, P.; Kibret, S.; Hagos, F.; Laamrani, H. Options for water storage and rainwater harvesting to improve health and resilience against climate change in Africa. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2012, 13, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Saez, J.; Mari, L.; Bertuzzo, E.; Casagrandi, R.; Sokolow, S.H.; De Leo, G.A.; Mande, T.; Ceperley, N.C.; Froehlich, J.-M.; Sou, M.; et al. A theoretical analysis of the geography of schistosomiasis in burkina faso highlights the roles of human mobility and water resources development in disease transmission. PLOS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venot, J.P.; Cecchi, P. Valeurs d’usage ou performances techniques: Comment apprécier le rôle des petits barrages en Afrique subsaharienne ? Cah. Agric. 2011, 20, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Venot, J.-P.; De Fraiture, C.; Acheampong, E.N. Revisiting Dominant Notions: A Review of Costs, Performance and Institutions of Small Reservoirs in Sub-Saharan Africa; IWMI Research Report 144; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2012; 39p. [Google Scholar]
- Schmengler, A.C.; Vlek, P.L.G. Assessment of accumulation rates in small reservoirs by core analysis, 137Cs measurements and bathymetric mapping in Burkina Faso. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2015, 40, 1951–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sally, H.; Lévite, H.; Cour, J. Local water management of small reservoirs: Lessons from two case studies in Burkina Faso. Water Altern. 2011, 4, 365–382. [Google Scholar]
- De Fraiture, C.; Kouali, G.N.; Sally, H.; Kabre, P. Pirates or pioneers? Unplanned irrigation around small reservoirs in Burkina Faso. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 131, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedraogo, I.; Tigabu, M.; Savadogo, P.; Compaoré, H.; Oden, P.C.; Ouadba, J.M. Land cover change and its relation with population dynamics in Burkina Faso, West Africa. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.F.; Wang, G.; You, L.; Yu, M. Potential impact of climate and socioeconomic changes on future agricultural land use in West Africa. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2016, 7, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pare, S.; Söderberg, U.; Sandewall, M.; Ouadba, J.M. Land use analysis from spatial and field data capture in southern Burkina Faso, West Africa. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 127, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoungrana, B.J.-B.; Conrad, C.; Amekudzi, L.K.; Thiel, M.; Da, E.D.; Forkuor, G.; Löw, F. Multi-temporal landsat images and ancillary data for land use/cover change (LULCC) detection in the southwest of burkina faso, West Africa. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12076–12102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yira, Y.; Diekkrueger, B.; Steup, G.; Bossa, A. Modeling land use change impacts on water resources in a tropical West African catchment (Dano, Burkina Faso). J. Hydrol. 2016, 537, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, E.; Grippa, M.; Kergoat, L.; Pinet, S.; Gal, L.; Cochonneau, G.; Martinez, J.-M. Monitoring water turbidity and surface suspended sediment concentration of the Bagre Reservoir (Burkina Faso) using MODIS and field reflectance data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 52, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Hipt, F.O.; Diekkrueger, B.; Steup, G.; Yira, Y.; Hoffmann, T.; Rode, M.; Näschen, K. Modeling the effect of land use and climate change on water resources and soil erosion in a tropical West African catch-ment (Dano, Burkina Faso) using SHETRAN. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larbi, I.; Forkuor, G.; Hountondji, F.C.; Agyare, W.A.; Mama, D. Predictive land use change under business-as-usual and afforestation scenarios in the vea catchment, West Africa. Int. J. Adv. Remote Sens. GIS 2019, 8, 3011–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Coe, M.; Ramankutty, N.; De Jong, R. Modeling the hydrological impact of land-use change in West Africa. J. Hydrol. 2007, 337, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awotwi, A.; Yeboah, F.; Kumi, M. Assessing the impact of land cover changes on water balance components of White Volta Basin in West Africa. Water Environ. J. 2014, 29, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.I.; Leavitt, P.R.; Quinlan, R.; Dixit, A.S.; Smol, J.P. Effects of agriculture, urbanization, and climate on water quality in the northern Great Plains. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sponseller, R.A.; Benfield, E.F.; Valett, H.M. Relationships between land use, spatial scale and stream macroinvertebrate communities. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 1409–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, L.B.; Vanni, M.J.; Renwick, W.H. Phytoplankton primary production and photosynthetic parameters in reservoirs along a gradient of watershed land use. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Catherine, A.; Mouillot, D.; Maloufi, S.; Troussellier, M.; Bernard, C. Projecting the impact of regional land-use change and water management policies on lake water quality: An application to periurban lakes and reservoirs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.; Qiu, Z. Understanding the relationship of land uses and water quality in Twenty First Century: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 173, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steinmann, P.; Keiser, J.; Bos, R.; Tanner, M.; Utzinger, J. Schistosomiasis and water resources development: Systematic review, meta-analysis, and estimates of people at risk. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, S.I.; Lillie, R.A.; Will-Wolf, S. Land use, water chemistry, aquatic vegetation, and zooplankton community structure of shallow lakes. Ecol. Appl. 2005, 15, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declerck, S.A.J.; De Bie, T.; Ercken, D.; Hampel, H.; Schrijvers, S.; Van Wichelen, J.; Gillard, V.; Mandiki, S.N.M.; Losson, B.J.; Bauwens, D.; et al. Ecological characteristics of small farmland ponds: Associations with land use practices at multiple spatial scales. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 131, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, M.A.; Johnson, S.A.; Cook, A.J.; Packer, T.V.; Taylor, B.M.; Townsley, E.R. Correlations between watershed and reservoir characteristics, and algal blooms in subtropical reservoirs. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4105–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weijters, M.J.; Janse, J.; Alkemade, R.; Verhoeven, J.T.A. Quantifying the effect of catchment land use and water nutrient concentrations on freshwater river and stream biodiversity. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2009, 19, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.J.; Cabral, J.A.; Bastos, R.; Cortes, R.; Vicente, J.R.; Eitelberg, D.A.; Yu, H.; Honrado, J.P.; Santos, M.A. A stochastic dynamic model to assess land use change scenarios on the ecological status of fluvial water bodies under the Water Framework Directive. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melcher, A.H.; Ouedraogo, R.; Schmutz, S. Spatial and seasonal fish community patterns in impacted and protected semi-arid rivers of Burkina Faso. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 48, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouédraogo, O.; Chételat, J.; Amyot, M. Bioaccumulation and trophic transfer of mercury and selenium in African sub-tropical fluvial reservoirs food webs (Burkina Faso). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C. Land use/land cover water quality nexus: Quantifying anthropogenic influences on surface water quality. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novikmec, M.; Hamerlík, L.; Kočický, D.; Hrivnák, R.; Kochjarová, J.; Oťaheľová, H.; Paľove-Balang, P.; Svitok, M. Ponds and their catchments: Size relationships and influence of land use across multiple spatial scales. Hydrobiologia 2015, 774, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adwubi, A.; Amegashie, B.K.; Agyare, W.A.; Tamene, L.; Odai, S.N.; Quansah, C.; Vlek, P. Assessing sediment inputs to small reservoirs in Upper East Region, Ghana. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2009, 14, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, B. Water pollution by agriculture. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 363, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.H.; Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication science: Where do we go from here? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.; Perkin, J.S.; Gerken, J.E. Human impact on freshwater ecosystem services: A global perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9061–9068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doody, D.G.; Withers, P.J.; Dils, R.M.; McDowell, R.W.; Smith, V.; McElarney, Y.R.; Dunbar, M.; Daly, D. Optimizing land use for the delivery of catchment ecosystem services. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 14, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallya, G.; Hantush, M.; Govindaraju, R.S. Composite measures of watershed health from a water quality perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 214, 104–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, C.; Agus, F.; Alamban, R.; Boosaner, A.; Bricquet, J.; Chaplot, V.; De Guzman, T.; De Rouw, A.; Janeau, J.-L.; Orange, D.; et al. Runoff and sediment losses from 27 upland catchments in Southeast Asia: Impact of rapid land use changes and conservation practices. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 128, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilotta, G.; Brazier, R. Understanding the influence of suspended solids on water quality and aquatic biota. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2849–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomazzo, M.; Bertolo, A.; Brodeur, P.; Massicotte, P.; Goyette, J.-O.; Magnan, P. Linking fisheries to land use: How anthropogenic inputs from the watershed shape fish habitat quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 135377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S. Particulate Matter and Aquatic Contaminants; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; 224p. [Google Scholar]
- Rochelle-Newall, E.; Ribolzi, O.; Viguier, M.; Thammahacksa, C.; Silvera, N.; Latsachack, K.; Dinh, R.P.; Naporn, P.; Sy, H.T.; Soulileuth, B.; et al. Effect of land use and hydrological processes on Escherichia coli concentrations in streams of tropical, humid headwater catchments. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaboré, S.; Cecchi, P.; Mosser, T.; Toubiana, M.; Traoré, O.; Ouattara, A.S.; Traoré, A.S.; Barro, N.; Colwell, R.R.; Monfort, P.; et al. Occurrence of Vibrio cholerae in water reservoirs of Burkina Faso. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, F.; Hubbart, J. Quantifying Escherichia coli and Suspended Particulate Matter concentrations in a mixed-Land USE Appalachian watershed. Water 2020, 12, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schubert, B.; Heininger, P.; Keller, M.; Claus, E.; Ricking, M. Monitoring of contaminants in suspended particulate matter as an alternative to sediments. Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 36, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, S.; Rasmussen, J.J.; Süß, A.; Kalettka, T.; Golla, B.; Horney, P.; Stähler, M.; Hommel, B.; Schäfer, R.B. Specifics and challenges of assessing exposure and effects of pesticides in small water bodies. Hydrobiologia 2016, 793, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamene, L.; Park, S.J.; Dikau, R.; Vlek, P.L.G. Reservoir siltation in the semi-arid highlands of northern Ethiopia: Sediment yield–catchment area relationship and a semi-quantitative approach for predicting sediment yield. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2006, 31, 1364–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Burkina Faso: Overview. 2017. Available online: http://www.worldbank.org/en/country/burkinafaso/overview (accessed on 31 July 2018).
- Evans, A.E.V.; Giordano, M.; Clayton, T. Investing in Agricultural Water Management to Benefit Smallholder Farmers in Burkina Faso. AgWater Solutions Project Country Synthesis Report; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2012; Volume 149, 30p. [Google Scholar]
- Fowe, T.; Karambiri, H.; Paturel, J.-E.; Poussin, J.-C.; Cecchi, P. Water balance of small reservoirs in the Volta basin: A case study of Boura reservoir in Burkina Faso. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 152, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Giesen, N.; Liebe, J.; Junge, G. Adapting to climate change in the Volta Basin, West Africa. Curr. Sci. 2010, 98, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Obuobie, E.; Barry, B. Burkina Faso. In Groundwater Availability and Use in Sub-Saharan Africa; A Review of Fifteen Countries; Pavelic, P., Mark Giordano, M., Keraita, B., Ramesh, V., Rao, T., Eds.; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2012; pp. 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, N.; Haque, O.; Leigh, L.; Aaron, D.; Helder, D.; Markham, B. Radiometric cross calibration of Landsat 8 operational land imager (OLI) and Landsat 7 enhanced thematic mapper plus (ETM+). Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12619–12638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forkuor, G.; Conrad, C.; Thiel, M.; Zoungrana, B.J.-B.; Tondoh, J.E. Multiscale remote sensing to map the spatial distribution and extent of cropland in the sudanian savanna of West Africa. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linard, C.; Gilbert, M.; Snow, R.W.; Noor, A.M.; Tatem, A.J. Population distribution, settlement patterns and accessibility across Africa in 2010. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inglada, J.; Arias, M.; Tardy, B.; Hagolle, O.; Valero, S.; Morin, D.; Dedieu, G.; Sepulcre, G.; Bontemps, S.; Defourny, P.; et al. Assessment of an operational system for crop type map production using high temporal and spatial resolution satellite optical imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12356–12379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forkuor, G.; Hounkpatin, K.O.L.; Welp, G.; Thiel, M. High resolution mapping of soil properties using remote sensing variables in South-Western Burkina Faso: A comparison of machine learning and multiple linear regression models. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by random forest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2017. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 31 August 2017).
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principles and Practices, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; 200p. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, L.C. Is land being degraded? A multi-scale investigation of landscape change in southwestern Burkina Faso. Land Degrad. Dev. 1999, 10, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reij, C.; Tappan, G.; Belemvire, A. Changing land management practices and vegetation on the Central Plateau of Burkina Faso (1968–2002). J. Arid Environ. 2005, 63, 642–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stéphenne, N.; Lambin, E. A dynamic simulation model of land-use changes in Sudano-sahelian countries of Africa (SALU). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 85, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahe, G.; Paturel, J.-E.; Servat, E.; Conway, D.; Dezetter, A. The impact of land use change on soil water holding capacity and river flow modelling in the Nakambe River, Burkina-Faso. J. Hydrol. 2005, 300, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braimoh, A.K. Random and systematic land-cover transitions in northern Ghana. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 113, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aduah, M.S.; Aabeyir, R. Land cover dynamics in WA municipality, upper west region of Ghana. Res. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 4, 658–664. [Google Scholar]
- Kleemann, J.; Baysal, G.; Bulley, H.N.; Fürst, C. Assessing driving forces of land use and land cover change by a mixed-method approach in north-eastern Ghana, West Africa. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 196, 411–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, S.; Boyle, P.; Lambin, E.F. Modelling inter-provincial migration in Burkina Faso, West Africa: The role of socio-demographic and environmental factors. Appl. Geogr. 2003, 23, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braimoh, A.K. Seasonal migration and land-use change in Ghana. Land Degrad. Dev. 2004, 15, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Geest, K.; Vrieling, A.; Dietz, T. Migration and environment in Ghana: A cross-district analysis of human mobility and vegetation dynamics. Environ. Urban. 2010, 22, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilgo, A.; Masse, D.; Sall, S.; Serpantié, G.; Chotte, J.-L.; Hien, V. Chemical and microbial properties of semiarid tropical soils of short-term fallows in Burkina Faso, West Africa. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2007, 43, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, T. Soil degradation, land scarcity and food security: Reviewing a complex challenge. Sustainability 2016, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laube, W.; Schraven, B.; Awo, M. Smallholder adaptation to climate change: Dynamics and limits in Northern Ghana. Clim. Chang. 2011, 111, 753–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taniwaki, R.H.; Piggott, J.J.; Ferraz, S.F.; Matthaei, C.D. Climate change and multiple stressors in small tropical streams. Hydrobiologia 2016, 793, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessah, E.; Raji, A.O.; Taiwo, O.J.; Agodzo, S.K.; Ololade, O.O.; Strapasson, A. Hydrological responses to climate and land use changes: The paradox of regional and local climate effect in the Pra River Basin of Ghana. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 27, 100654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfi, R.; Bouvy, M.L.; Cecchi, P.; Pagnao, M.; Thomas, S. Factors limiting phytoplankton productivity in 49 shallow reservoirs of North Côte d’Ivoire (West Africa). Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2001, 4, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiga, A.H.; Konaté, Y.; Denyigba, K.; Karambiri, H.; Wethe, J. Risques d’eutrophisation et de comblement des retenues d’eau au Burkina Faso. In Proceedings of the Fifth FRIEND World Conference, Havana, Cuba, November 2006; IAHS Publication: Wallingford, UK, 2006; Volume 308, pp. 606–611. Available online: https://iahs.info/uploads/dms/13728.109-606-611-53-308-Maiga-et-al.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Orange, D.; Arfi, R.; Picouet, C.; Hetcheber, H. Comportement du carbone organique dans les eaux du fleuve Niger lors de leur traversée du delta intérieur du Niger (au Mali). Bull. Réseau Eros. 2004, 22, 432–445. [Google Scholar]
- Meybeck, M.; Laroche, L.; Dürr, H.; Syvitski, J. Global variability of daily total suspended solids and their fluxes in rivers. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2003, 39, 65–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Cecchi, P.; Corbin, D.; Lemoalle, J. The different primary producers in a small African tropical reservoir during a drought: Temporal changes and interactions. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 45, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmaeus, J.M.; Håkanson, L. A dynamic model to predict suspended particulate matter in lakes. Ecol. Model. 2003, 167, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, M.V.K.; Gnoumou, F. Agroclimatology of West Africa: Burkina Faso; Information Bulletin 23; International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT): Hyderabad, India, 1987; Available online: http://oar.icrisat.org/864/1/RA_00104.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2020).
- Beadle, L.C. The Inland Waters of Tropical Africa. An Introduction to Tropical Limnology; Longman: London, UK, 1974; 365p. [Google Scholar]
- Talling, J.F.; Lemoalle, J. Ecological Dynamics of Tropical Inland Waters; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998; 441p. [Google Scholar]
- Dokulil, M.T. Environmental control of phytoplankton productivity in turbulent turbid systems. Hydrobiologia 1994, 289, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyhenmeyer, G.; Meili, M.; Pierson, D. A simple method to quantify sources of settling particles in lakes: Resuspension versus new sedimentation of material from planktonic production. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1995, 46, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, T. The effect of resuspension on algal production in a shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 1991, 213, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, J. A conceptual framework for predicting the occurrence of sediment focusing and sediment redistribution in small lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1985, 30, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloesch, J. Mechanisms, measurement and importance of sediment resuspension in lakes. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1995, 46, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Gao, Y.; Annandale, G.W.; Morris, G.L.; Jiang, E.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Carling, P.A.; Fu, K.; Guo, Q.; et al. Sustainable sediment management in reservoirs and regulated rivers: Experiences from five continents. Earth’s Future 2014, 2, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliva, L.; Williams, D.D. Buffer zone versus whole catchment approaches to studying land use impact on river water quality. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3462–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, B.; Chang, H. Effects of land cover, topography, and built structure on seasonal water quality at multiple spatial scales. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, A.; Trolle, D.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.; Bjerring, R.; Olesen, J.E.; Jeppesen, E. Watershed land use effects on lake water quality in Denmark. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhaojiang, H.; Liu, Q.; Hou, Z.; Liao, J.; Fu, L.; Peng, Q. Influences of the land use pattern on water quality in low-order streams of the Dongjiang River basin, China: A multi-scale analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Bian, J.; Wang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Wan, H. Evaluating and Predicting the Effects of Land Use Changes on Water Quality Using SWAT and CA–Markov Models. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 4923–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, K.L.; Sullivan, C.; Weil, R.; Sanchez, P. The State of Soil Degradation in Sub-Saharan Africa: Baselines, Trajectories, and Solutions. Sustainability 2015, 7, 6523–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, P.S.; Murillo, J.F.M. Editorial overview: Sustainable soil management and land restoration. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Heal. 2018, 5, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeloudar, F.T.; Sepanlou, M.G.; Emadi, S.M. Impact of land use change on soil erodibility. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2018, 4, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, A.; Walling, D.; Sichingabula, H.; Leeks, G. Suspended sediment source fingerprinting in a small tropical catchment and some management implications. Appl. Geogr. 2001, 21, 387–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellner, E.; Hubbart, J. Improving understanding of mixed-land-use watershed suspended sediment regimes: Mechanistic progress through high-frequency sampling. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellner, E.; Hubbart, J.A. Flow class analyses of suspended sediment concentration and particle size in a mixed-land-use watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J. Spatial Variations in the Relationships between Land Use and Water Quality across an Urbanization Gradient in the Watersheds of Northern Georgia, USA. Environ. Manag. 2011, 51, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Assessing the impacts of land use on downstream water quality using a hydrologically sensitive area concept. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 213, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gu, S.; Liu, W.; Han, H.; Zhang, Q. Water quality in relation to land use and land cover in the upper Han River Basin, China. Catena 2008, 75, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalí, J.; Gimenez, R.; Diez, J.; Álvarez-Mozos, J.; Lersundi, J.D.V.D.; Goñi, M.; Campo-Bescós, M.A.; Chahor, Y.; Gastesi, R.; López, J.J. Sediment production and water quality of watersheds with contrasting land use in Navarre (Spain). Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosbie, B.; Chow-Fraser, P. Percentage land use in the watershed determines the water and sediment quality of 22 marshes in the Great Lakes basin. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1999, 56, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutal, H.; Reis, M. Determining the effects of land use on soil erodibility in the Mediterranean highland regions of Turkey: A case study of the Korsulu stream watershed. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, O.; Niyogi, D.K.; Townsend, C.R. Scale-dependence of land use effects on water quality of streams in agricultural catchments. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 130, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Ma, K.; Yang, L.; He, K. Testing a Dynamic Complex Hypothesis in the Analysis of Land Use Impact on Lake Water Quality. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 24, 1313–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brogna, D.; Dufrêne, M.; Michez, A.; Latli, A.; Jacobs, S.; Vincke, C.; Dendoncker, N. Forest cover correlates with good biological water quality. Insights from a regional study (Wallonia, Belgium). J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 211, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uriarte, M.; Yackulic, C.B.; Lim, Y.; Arce-Nazario, J.A. Influence of land use on water quality in a tropical landscape: A multi-scale analysis. Landsc. Ecol. 2011, 26, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tao, F. Spatial pattern of surface water quality in China and its driving factors—Implication for the environment sustainability. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 25, 1789–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gove, N.E.; Edwards, R.T.; Conquest, L.L. Effects of scale on land use and water quality relationships: A longitudinal basin-wide perspective. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 1721–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Q.; Pontius, R.G.; Klemas, V.; Hong, H. Detecting the Dynamic Linkage between Landscape Characteristics and Water Quality in a Subtropical Coastal Watershed, Southeast China. Environ. Manag. 2011, 51, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hunter, P.D.; Tyler, A.N.; Willby, N.J. The influence of hydrological and land use indicators on macrophyte richness in lakes—A comparison of catchment and landscape buffers across multiple scales. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, G. Influence of land use and land cover patterns on seasonal water quality at multi-spatial scales. Catena 2017, 151, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, R.L.G.; Caliman, A.; Cabral, C.R.; Araújo, F.D.C.; Guérin, J.; Dantas, F.D.C.C.; Quesado, L.B.; Venticinque, E.M.; Guariento, R.D.; Amado, A.M.; et al. Precipitation, landscape properties and land use interactively affect water quality of tropical freshwaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossio, D.; Geheb, K.; Critchley, W. Managing water by managing land: Addressing land degradation to improve water productivity and rural livelihoods. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zougmore, R.; Jalloh, A.; Tioro, A. Climate-smart soil water and nutrient management options in semiarid West Africa: A review of evidence and analysis of stone bunds and zaï techniques. Agric. Food Secur. 2014, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinare, H.; Gordon, L.J.; Kautsky, E.E. Assessment of ecosystem services and benefits in village landscapes—A case study from Burkina Faso. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 21, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benton, T.G.; Vickery, J.A.; Wilson, J.D. Farmland biodiversity: Is habitat heterogeneity the key? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.J.J.A.; Booij, C.; Tscharntke, T. Sustainable pest regulation in agricultural landscapes: A review on landscape composition, biodiversity and natural pest control. Proc. R. Soc. B 2006, 273, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landis, D.A. Designing agricultural landscapes for biodiversity-based ecosystem services. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2017, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Mello, K.; Randhir, T.O.; Valente, R.A.; Vettorazzi, C.A. Riparian restoration for protecting water quality in tropical agricultural watersheds. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 108, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mander, Ü.; Tournebize, J.; Sauvage, S.; Sánchez-Pérez, J. Wetlands and buffer zones in watershed management. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 103, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Fernandes, M.R.; Aguiar, F.C.; Branco, M.R.; Ferreira, M. Effects of riverine landscape changes on pollination services: A case study on the River Minho, Portugal. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joniak, T.; Kuczyńska-Kippen, N.; Gąbka, M. Effect of agricultural landscape characteristics on the hydrobiota structure in small water bodies. Hydrobiologia 2016, 793, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanzanova, D.; Whitney, C.; Shepherd, K.; Luedeling, E. Improving development efficiency through decision analysis: Reservoir protection in Burkina Faso. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 115, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Mao, J.; Zhu, D.; Lin, C. Impacts of Land Use and Land Cover on Water Quality at Multiple Buffer-Zone Scales in a Lakeside City. Water 2019, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biggs, J.; Von Fumetti, S.; Kelly-Quinn, M. The importance of small waterbodies for biodiversity and ecosystem services: Implications for policy makers. Hydrobiologia 2016, 793, 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleiss, A.J.; Franca, M.; Juez, C.; De Cesare, G. Reservoir sedimentation. J. Hydraul. Res. 2016, 54, 595–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Site | Latitude | Longitude | Depth | dS | pH | C25 | Chl a | SPM | PIM | Capacity | Cropland | Surface | Pop. Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | (cm) | (i.u.) | (µS·L−1) | (µg·L−1) | (mg·L−1) | (%) | (Mm3) | (%) | (km2) | (Inh·km−2) | |||
| Arzuma | 12°13′07.6″ | 01°17′46.0″ | 150 | 48.0 | 7.8 | 105.3 | 27.1 | 20.7 | 47 | 1.4 | 69.4 | 885 | 141.6 |
| Bagré | 11°29′25.7″ | 00°32′56.9″ | 1190 | 16.0 | 7.5 | 86.6 | 2.6 | 44.7 | 82.5 | 1700.0 | 37.1 | 35,308 | 158.3 |
| Bala | 11°33′37.9″ | 04°09′24.8″ | 160 | 137.0 | 6.6 | 129.6 | 5.3 | 5.0 | 62.9 | 1.5 | 8.7 | 37.3 | 13.7 |
| Bam | 13°19′57.4″ | 01°30′48.8″ | 160 | 19.5 | 7.6 | 101.1 | 10.5 | 38.1 | 81.1 | 31.0 | 21.8 | 2608 | 71.7 |
| Bamsa | 13°15′36.2″ | 01°06′02.8″ | 220 | 23.8 | 7.9 | 115.4 | 12.0 | 46.7 | 74.5 | n.d. | 55.7 | 189 | 52.2 |
| Bapla-Diébougou | 10°52′56.0″ | 03°15′46.7″ | 300 | 90.5 | 8.5 | 257.0 | 23.8 | 9.4 | 28.9 | n.d. | 24.1 | 423 | 40.6 |
| Bazega | 11°44′06.2″ | 01°21′12.0″ | 230 | 36.5 | 7.4 | 94.9 | 44.1 | 25.3 | 41 | 11.2 | 37.1 | 246 | 78 |
| Boura | 11°02′49.3″ | 02°29′52.1″ | 330 | 56.5 | 8.1 | 75.0 | 15.9 | 11.9 | 51.2 | 4.2 | 40.6 | 156 | 16.7 |
| Dem | 13°11′27.8″ | 01°09′12.1″ | 120 | 38.1 | 7.8 | 141.4 | 25.8 | 20.4 | 68.6 | 4.0 | 30.1 | 577 | 65.1 |
| Deux Balé | 11°43′04.9″ | 03°00′37.5″ | n.d. | 26.0 | 7.7 | 132.7 | 42.8 | 26.8 | 42.9 | 6.0 | 17.7 | 1000 | 45.7 |
| Dissin | 10°56′21.7″ | 02°55′36.4″ | 60 | 9.0 | 7.5 | 73.8 | n.m. | 237.9 | 85 | 0.1 | 24.1 | 0.6 | 9282.2 |
| Goundi | 12°12′48.4″ | 02°28′37.1″ | 100 | 11.0 | 8.6 | 106.4 | 17.9 | 53.2 | 77.2 | n.d. | 42.6 | 9.8 | 47.9 |
| Kaya | 13°05′33.4″ | 01°04′07.5″ | n.d. | 11.0 | 8.5 | 230.3 | 25.4 | 391.0 | 84.3 | 1.1 | 25.9 | 9.1 | 368.1 |
| Koubri | 12°11′34.0″ | 01°24′16.2″ | 205 | 1.5 | 5.7 | n.d. | n.m. | 1240.0 | 87 | 9.7 | 55.9 | 449 | 211.8 |
| Leo | 11°05′34.0″ | 02°06′35.4″ | 60 | 7.5 | 6.3 | 114.0 | n.m. | 485.0 | 87.6 | 0.1 | 47.3 | 9.3 | 2308.2 |
| Loumbila | 12°29′34.0″ | 01°24′25.8″ | 330 | 64.7 | 7.6 | n.d. | n.d. | 11.9 | 56.3 | 42.2 | 29.4 | 2079 | 87.1 |
| Moutori-Dano | 11°09′29.7″ | 03°04′32.3″ | 60 | 17.5 | 8.3 | 170.7 | 64.6 | 63.5 | 65.5 | n.d. | 10.3 | 7.8 | 67.3 |
| Nabazana | 12°12′13.4″ | 01°21′07.8″ | 100 | 20.0 | 7.7 | 97.6 | 24.7 | 51.7 | 71 | 4.0 | 60.1 | 679 | 167.2 |
| Navri Kpè | 10°59′05.3″ | 02°56′26.7″ | n.d. | 46.0 | 7.4 | 117.9 | 53.8 | 21.2 | 27.8 | 2.6 | 19.4 | 76.2 | 72 |
| Nobili | 11°44′27.6″ | 01°15′24.0″ | 60 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 97.0 | n.m. | 217.9 | 83.7 | 0.7 | 68.8 | 14 | 78.4 |
| Ouaga2 | 12°23′16.7″ | 01°31′22.4″ | 85 | 10.0 | 7.7 | 309.8 | 64.5 | 144.5 | 73.5 | 1.2 | 3.6 | 310 | 1892.6 |
| Ouaga3 | 12°23′24.9″ | 01°30′29.3″ | 140 | 28.5 | 8.6 | 92.5 | 65.5 | 53.6 | 72 | 1.5 | 2.9 | 369 | 3127.5 |
| Pa | 11°29′23.9″ | 03°14′33.6″ | 200 | 80.5 | 7.7 | 96.4 | 17.4 | 8.6 | 58.4 | n.d. | 69.7 | 246 | 45.9 |
| Petit Bagré | 11°28′25.4″ | 00°30′47.0″ | n.d. | 17.0 | 7.5 | 111.1 | 1.2 | 52.1 | 82.5 | 3.5 | 47.6 | 32.8 | 65.4 |
| Pouytenga | 12°13′41.5″ | 00°25′54.9″ | 60 | 2.5 | 7.4 | 480.9 | n.m. | 3153.3 | 87.5 | 0.6 | 76.1 | 13.4 | 421.4 |
| Saaba | 12°20′39.8″ | 01°24′12.2″ | 60 | n.d. | 7.9 | 369.9 | 66.3 | 333.0 | 84.4 | 5.4 | 47.4 | 141 | 2572.1 |
| Salbisgo | 12°09′53.6″ | 02°22′36.1″ | 100 | 10.0 | 7.7 | 362.8 | 15.8 | 481.3 | 87.5 | 3.6 | 43.4 | 188 | 135.7 |
| Sapouy | 11°32′38.6″ | 01°45′45.8″ | 160 | 7.0 | 6.3 | n.d. | n.m. | 313.2 | 83.9 | 0.7 | 74.4 | 34 | 46.9 |
| Sian | 13°05′46.1″ | 01°13′04.7″ | 100 | 14.7 | 7.8 | 163.3 | 14.3 | 64.7 | 83.5 | 2.0 | 18.7 | 760 | 71 |
| Sourou | 12°48′07.2″ | 03°26′55.9″ | 320 | 57.0 | 8.6 | 226.0 | 33.4 | 18.2 | 45.1 | 370.0 | 29.3 | 30,214 | 21.3 |
| Tanvi Nakemtenga | 12°13′35.7″ | 01°21′06.6″ | 170 | 29.0 | 7.6 | 105.3 | 15.8 | 53.1 | 69.1 | 0.6 | 57.5 | 25 | 54.4 |
| Taré | 11°23′55.7″ | 01°49′55.9″ | 60 | 20.0 | 6.9 | n.d. | 52.2 | 81.5 | 72.9 | n.d. | 58.3 | 4.5 | 40.9 |
| Tibin | 13°11′11.8″ | 01°26′36.0″ | n.d. | n.d. | 7.3 | 138.6 | 15.0 | 167.6 | 89 | 0.0 | 27.5 | 3052 | 72.5 |
| Toukoumtouré | 12°15′17.3″ | 01°19′02.6″ | 60 | 4.5 | 6.7 | 75.1 | n.m. | 580.0 | 85.3 | 0.4 | 61.8 | 12.1 | 58.4 |
| Yako-Kanazoé | 13°00′41.9″ | 02°03′55.1″ | 410 | 79.0 | 7.6 | 136.1 | 11.7 | 9.9 | 71.2 | 75.0 | 35 | 8127 | 105.6 |
| Yamtenga | 12°20′20.1″ | 01°26′51.0″ | 60 | 9.0 | 7.9 | 350.0 | n.m. | 319.0 | 86.2 | 0.6 | 15.1 | 12.2 | 5256.3 |
| Ziga | 12°29′24.4″ | 01°05′25.5″ | 290 | 35.0 | 7.4 | 112.3 | 9.0 | 23.0 | 77.6 | 200.0 | 18.2 | 20,689 | 97.8 |
| 5-km Buffer | Sparse vegetation | Dense vegetation | Water | Artificial areas |
| Cropland | −0.648 (<0.001) | −0.228 (0.151) | −0.142 (0.374) | −0.281(0.075) |
| Sparse vegetation | 0.131(0.413) | 0.223 (0.160) | 0.112 (0.486) | |
| Dense vegetation | −0.058 (0.717) | −0.594 (<0.001) | ||
| Water | −0.098 (0.541) | |||
| Watershed | Sparse vegetation | Dense vegetation | Water | Artificial areas |
| Cropland | −0.354 (0.023) | −0.164 (0.302) | 0.112 (0.484) | −0.259 (0.102) |
| Sparse vegetation | 0.152 (0.341) | 0.143 (0.370) | −0.160 (0.317) | |
| Dense vegetation | −0.476 (0.002) | −0.672 (<0.001) | ||
| Water | 0.192 (0.227) |
| Watershed | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population Density | Cropland | Sparse Vegetation | Dense Vegetation | Water | Artificial Areas | ||
| Watershed | Population Density | −0.070 | −0.324 | −0.465 | 0.071 | 0.601 | |
| 0.664 | 0.039 | 0.002 | 0.655 | <0.001 | |||
| 5-km Buffer area | Cropland | −0.015 | 0.667 | −0.340 | 0.009 | 0.051 | −0.259 |
| 0.927 | <0.001 | 0.030 | 0.956 | 0.751 | 0.101 | ||
| Sparse vegetation | −0.220 | −0.323 | 0.747 | 0.030 | 0.212 | −0.046 | |
| 0.165 | 0.040 | <0.001 | 0.853 | 0.182 | 0.775 | ||
| Dense vegetation | −0.447 | −0.135 | 0.065 | 0.742 | −0.528 | −0.469 | |
| 0.004 | 0.399 | 0.687 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | ||
| Water | −0.033 | 0.173 | 0.238 | −0.001 | 0.212 | 0.042 | |
| 0.836 | 0.277 | 0.134 | 0.995 | 0.182 | 0.793 | ||
| Artificial areas | 0.540 | −0.264 | −0.059 | −0.676 | 0.304 | 0.788 | |
| <0.001 | 0.095 | 0.714 | <0.001 | 0.053 | <0.001 | ||
| PIM (%) | Depth (cm) | dS (cm) | pH (i.u.) | C25 (µS·cm−1) | Chl a (µg·L−1) | Cropland (%) | Surface (km2) | Pop. Density (Inh·km−2) | Capacity (Mm3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPM | 0.846 | −0.723 | −0.950 | −0.245 | 0.216 | 0.245 | 0.238 | −0.524 | 0.534 | −0.569 |
| (mg·L−1) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.143 | 0.225 | 0.207 | 0.157 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| PIM | −0.555 | −0.864 | −0.325 | 0.160 | −0.354 | 0.219 | −0.303 | 0.523 | −0.513 | |
| (%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.050 | 0.370 | 0.064 | 0.191 | 0.068 | <0.001 | 0.003 | |
| Depth | 0.649 | 0.096 | −0.231 | −0.559 | −0.127 | 0.724 | −0.374 | 0.773 | ||
| (cm) | <0.001 | 0.598 | 0.234 | 0.006 | 0.485 | <0.001 | 0.035 | <0.001 | ||
| dS | 0.323 | −0.065 | −0.016 | −0.258 | 0.474 | −0.490 | 0.558 | |||
| (cm) | 0.058 | 0.725 | 0.936 | 0.134 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.002 | |||
| pH | 0.280 | 0.385 | −0.314 | 0.099 | −0.027 | 0.187 | ||||
| (i.u.) | 0.113 | 0.043 | 0.058 | 0.557 | 0.874 | 0.319 | ||||
| C25 | 0.261 | −0.238 | −0.003 | 0.109 | 0.009 | |||||
| (µS·cm−1) | 0.187 | 0.181 | 0.987 | 0.545 | 0.960 | |||||
| Chl a | −0.137 | −0.271 | 0.217 | −0.201 | ||||||
| (µg·L−1) | 0.482 | 0.161 | 0.264 | 0.376 | ||||||
| Cropland | −0.201 | −0.091 | −0.144 | |||||||
| (%) | 0.231 | 0.591 | 0.435 | |||||||
| Surface | −0.056 | 0.737 | ||||||||
| (km2) | 0.740 | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Pop. Density | −0.206 | |||||||||
| (Inh·km−2) | 0.264 |
| Δ (PIM) | Δ (Crop Areas) | Δ (Sparse Vegetation) | Δ (Dense Vegetation) | Δ (Water Bodies) | Δ (Artificial Areas) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δ (SPM) | 0.248 | −0.240 | −0.330 | −0.071 | −0.521 | 0.457 |
| 0.274 | 0.289 | 0.141 | 0.754 | 0.016 | 0.037 | |
| Δ (PIM) | 0.579 | −0.419 | −0.317 | −0.360 | 0.274 | |
| 0.006 | 0.058 | 0.159 | 0.107 | 0.225 | ||
| Δ (Crop areas) | −0.438 | −0.418 | −0.181 | 0.310 | ||
| 0.047 | 0.058 | 0.428 | 0.168 | |||
| Δ (Sparse vegetation) | 0.171 | 0.514 | −0.400 | |||
| 0.452 | 0.017 | 0.071 | ||||
| Δ (Dense vegetation) | 0.436 | −0.647 | ||||
| 0.047 | 0.002 | |||||
| Δ (Water bodies) | −0.610 | |||||
| 0.003 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cecchi, P.; Forkuor, G.; Cofie, O.; Lalanne, F.; Poussin, J.-C.; Jamin, J.-Y. Small Reservoirs, Landscape Changes and Water Quality in Sub-Saharan West Africa. Water 2020, 12, 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071967
Cecchi P, Forkuor G, Cofie O, Lalanne F, Poussin J-C, Jamin J-Y. Small Reservoirs, Landscape Changes and Water Quality in Sub-Saharan West Africa. Water. 2020; 12(7):1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071967
Chicago/Turabian StyleCecchi, Philippe, Gerald Forkuor, Olufunke Cofie, Franck Lalanne, Jean-Christophe Poussin, and Jean-Yves Jamin. 2020. "Small Reservoirs, Landscape Changes and Water Quality in Sub-Saharan West Africa" Water 12, no. 7: 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071967
APA StyleCecchi, P., Forkuor, G., Cofie, O., Lalanne, F., Poussin, J.-C., & Jamin, J.-Y. (2020). Small Reservoirs, Landscape Changes and Water Quality in Sub-Saharan West Africa. Water, 12(7), 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071967





