Effects of Irrigation Discharge on Salinity of a Large Freshwater Lake: A Case Study in Chagan Lake, Northeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
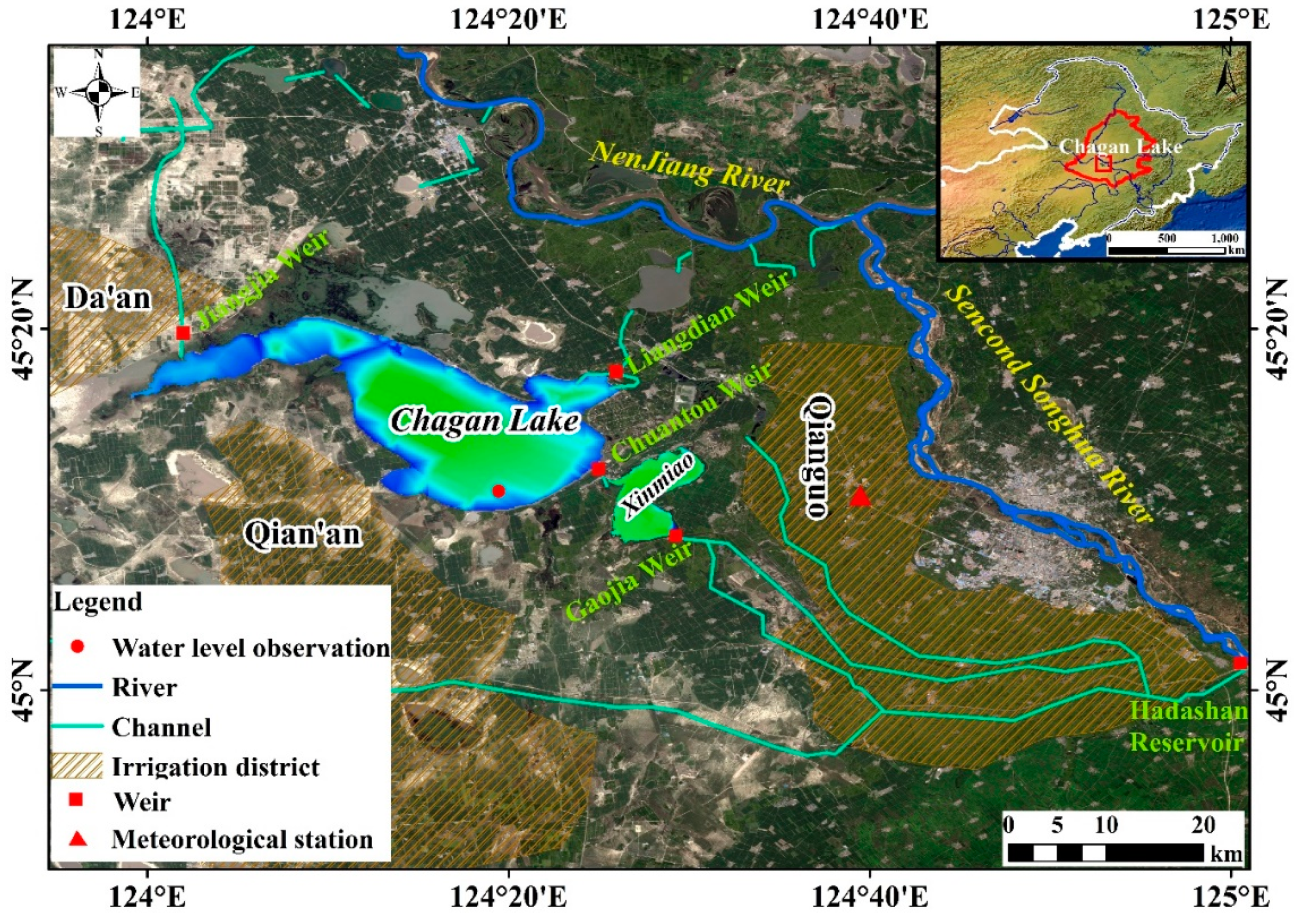
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Model Inputs
2.2.1. Sample Collections
2.2.2. Model Inputs
2.3. Model Setup, Calibration and Simulation
2.3.1. Modeling Setup
2.3.2. Boundary and Discharge
2.3.3. Calibration and Validation
2.4. Irrigation Districts Development Scenarios
3. Results
3.1. Long-Term Variation and Spatial-Temporal Distribution of Salinity in the Lake
3.2. Salt Accumulation in the Lake
3.3. Time to Reach Salinity Threshold for Freshwater Fish Farming
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial-Temporal Changes of Lake Water Salinity
4.2. The Effect of Salinization on Lake Ecosystem Health
4.3. Strategy for Sustainable Lake Water Management to Control Salinization
5. Conclusions
Data Availability Statement
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, W.D. Salinity as a determinant of the structure of biological communities in salt lakes. Hydrobiologia 1998, 381, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, W.D. Salinisation: A major threat to water resources in the arid and semi-arid regions of the world. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 1999, 4, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zandt, P.A.; Tobler, M.A.; Mouton, E.; Hasenstein, K.H.; Mopper, S. Positive and negative consequences of salinity stress for the growth and reproduction of the clonal plant, Iris hexagona. J. Ecol. 2003, 91, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefford, B.J.; Nugegoda, D. No evidence for a critical salinity threshold for growth and reproduction in the freshwater snail Physa acuta. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 134, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Peng, W.; Dong, F.; Chen, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, R. Hydroclimatic influence on the salinity and water volume of a plateau lake in southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yihdego, Y.; Webb, J. Modeling of seasonal and long-term trends in lake salinity in southwestern Victoria, Australia. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 112, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ashry, M.T.; Van Schilfgaarde, J.; Schiffman, S. Salinity pollution from irrigated agriculture. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1985, 40, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A. Salinization of agricultural lands due to poor drainage: A viewpoint. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Managing the salinization and drainage problems of irrigated areas through remote sensing and GIS techniques. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Alternative management options for irrigation-induced salinization and waterlogging under different climatic conditions. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, B.; Gächter, R. Increasing chloride concentrations in Lake Constance: Characterization of sources and estimation of loads. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 74, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Duan, S.; Doody, T.R.; Haq, S.; Smith, R.M.; Johnson, T.A.N.; Wood, K.L. Human-accelerated weathering increases salinization, major ions, and alkalinization in fresh water across land use. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 83, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Likens, G.E.; Pace, M.L.; Utz, R.M.; Haq, S.; Gorman, J.; Grese, M. Freshwater salinization syndrome on a continental scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E574–E583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swinton, M.W.; Eichler, L.W.; Boylen, C.W. Road salt application differentially threatens water resources in Lake George, New York. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2015, 31, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugan, H.A.; Bartlett, S.L.; Burke, S.M.; Doubek, J.P.; Krivak-Tetley, F.E.; Skaff, N.K.; Roberts, D.C. Salting our freshwater lakes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4453–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Connor, J.D.; Schwabe, K.; King, D.; Knapp, K. Irrigated agriculture and climate change: The influence of water supply variability and salinity on adaptation. Ecol. Econ. 2012, 77, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, W.D. Anthropogenic salinisation of inland waters. In Saline Lakes; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2001; pp. 329–337. [Google Scholar]
- Umali, D.L. Irrigation-Induced Salinity: A Growing Problem for Development and the Environment; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Aragüés, R.; Urdanoz, V.; Çetin, M.; Kirda, C.; Daghari, H.; Ltifi, W.; Lahlou, M.; Douaik, A. Soil salinity related to physical soil characteristics and irrigation management in four Mediterranean irrigation districts. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, Y.; Shang, S.; Rahman, K.U.; Xia, Y.; Ren, D. A semi-distributed drainage model for monthly drainage water and salinity simulation in a large irrigation district in arid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 230, 105962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hollanders, P.H.J.; Wang, S.; Fang, S. Effect of field groundwater table control on water and salinity balance and crop yield in the Qingtongxia Irrigation District, China. Irrig. Drain. 2004, 53, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Bosch, A.; Rigol-Sanchez, J.P.; Vallejos, A.; Andreu, J.M.; Ceron, J.C.; Molina-Sanchez, L.; Sola, F. Impacts of agricultural irrigation on groundwater salinity. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Impact of anthropogenic activities on the enrichment of fluoride and salinity in groundwater in the Yuncheng Basin constrained by Cl/Br ratio, δ18O, δ2H, δ13C and δ7Li isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.J.; Chen, X.L.; Wen, X.Y.; Fu, C.H.E.N.; Zhang, H.L.; Chu, Q.Q.; Dikgwatlhe, S.B. Applying a salinity response function and zoning saline land for three field crops: A case study in the Hetao Irrigation District, Inner Mongolia, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritzema, H.P. Drain for Gain: Managing salinity in irrigated lands—A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- James, K.R.; Hart, B.T. Effect of salinity on four freshwater macrophytes. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1993, 44, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbanbaev, R.E.; Matsapaeva, I.V.; Konstantinova, L.G. The role of collecting drainage systems in the formation of Chemical Composition of Lake water in the Amu Darya Lower Reaches. Water Res. 2002, 29, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.Y.; Tang, X.M.; Gao, G.; Chen, D.; Shao, K.Q.; Cai, X.L.; Zhang, L. Effects of salinity and nutrients on sedimentary bacterial communities in oligosaline Lake Bosten, northwestern China. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 69, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, B.D.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A. The effects of salinity on plankton and benthic communities in the Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA: A microcosm experiment. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginatullina, E.; Atwell, L.; Saito, L. Resilience and resistance of zooplankton communities to drought-induced salinity in freshwater and saline lakes of Central Asia. J. Arid Environ. 2017, 144, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Luo, W.; Xie, J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, S.; Liu, W. Salinity dynamics of wetland ditches receiving drainage from irrigated agricultural land in arid and semi-arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 100, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficker, H.; Luger, M.; Pamminger-Lahnsteiner, B.; Achleitner, D.; Jagsch, A.; Gassner, H. Diluting a salty soup: Impact of long-lasting salt pollution on a deep Alpine lake (Traunsee, Austria) and the downside of recent recovery from salinization. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 81, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Groffman, P.M.; Likens, G.E.; Belt, K.T.; Stack, W.P.; Kelly, V.R.; Fisher, G.T. Increased salinization of fresh water in the northeastern United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13517–13520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chapra, S.C.; Dove, A.; Warren, G.J. Long-term trends of Great Lakes major ion chemistry. J. Great Lakes Res. 2012, 38, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogora, M.; Mosello, R.; Kamburska, L.; Salmaso, N.; Cerasino, L.; Leoni, B.; Buzzi, F. Recent trends in chloride and sodium concentrations in the deep subalpine lakes (Northern Italy). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 19013–19026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, W.D.; Sherwood, J.E. Definition and measurement of salinity in salt lakes. Int. J. Salt Lake Res. 1994, 3, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magazinovic, R.S.; Nicholson, B.C.; Mulcahy, D.E.; Davey, D.E. Bromide levels in natural waters: Its relationship to levels of both chloride and total dissolved solids and the implications for water treatment. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoades, J.D.; Lesch, S.M.; LeMert, R.D.; Alves, W.J. Assessing irrigation/drainage/salinity management using spatially referenced salinity measurements. Agric. Water Manag. 1997, 35, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.N.; Sheng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Kang, H.Q.; Liu, Y. Desalination of saline farmland discharge water through wetland plants. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 156, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Chowdary, V.M.; Mal, B.C.; Billib, M. Runoff and sediment yield modeling from a small agricultural watershed in India using the WEPP model. J. Hydrol. 2008, 348, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Wan, Y. Time series modeling and prediction of salinity in the Caloosahatchee River Estuary. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 5804–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, S.; Shamsai, A.; Saghafian, B. Reduced-Order Salinity Modeling of the Urmia Lake Using MIKE3 and Proper Orthogonal Decomposition Models. Water Res. 2018, 45, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, A.; James, D.E.; Hannoun, I.A. Effects of lake water level fluctuation due to drought and extreme winter precipitation on mixing and water quality of an alpine lake, Case Study: Lake Arrowhead, California. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danesh-Yazdi, M.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B. Lake Urmia crisis and restoration plan: Planning without appropriate data and model is gambling. J. Hydrol. 2019, 576, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, C.T.; Narayan, K.A. Modeling density-dependent flow and solute transport at the Lake Tutchewop saline disposal complex, Victoria. J. Hydrol. 1998, 206, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Dou, M.; Chen, X.; Zhou, K. Physically-based model for studying the salinization of Bosten Lake in China. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 432–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menshutkin, V.V.; Rukhovets, L.A.; Filatov, N.N. Ecosystem modeling of freshwater lakes (review): 2. Models of freshwater lake’s ecosystem. Water Res. 2014, 41, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, N.J.; Couture, R.M.; Norton, S.A.; Birkel, S.D.; Amirbahman, A. Modeling response of water quality parameters to land-use and climate change in a temperate, mesotrophic lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauw, A.N.; Los, H.F.; Bokhorst, M.; Erftemeijer, P.L. GEM: A generic ecological model for estuaries and coastal waters. Hydrobiologia 2009, 618, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huckelbridge, K.H.; Stacey, M.T.; Glenn, E.P.; Dracup, J.A. An integrated model for evaluating hydrology, hydrodynamics, salinity and vegetation cover in a coastal desert wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Wu, W.; Chen, Y. Assessment of the salinization processes in the largest inland freshwater lake of China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bao, A.; Chen, X.; Zhong, R.A. Model Study of the Discharges Effects of Kaidu River on the Salinity Structure of Bosten Lake. Water 2019, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Adawy, A.; Negm, A.M.; Elzeir, M.A.; Saavedra, O.C.; El-Shinnawy, I.A.; Nadaoka, K. Modeling the hydrodynamics and salinity of el-Burullus Lake (Nile Delta, northern Egypt). J. Clean Energy Technol. 2013, 1, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.; Podger, G.; Cooke, R. IQQM—A hydrologic modelling tool for water resource and salinity management. Environ. Softw. 1996, 11, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, A.; Adamowski, J.; Halbe, J.; Prasher, S. Using causal loop diagrams for the initialization of stakeholder engagement in soil salinity management in agricultural watersheds in developing countries: A case study in the Rechna Doab watershed, Pakistan. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 152, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, U.T. Saline Lake Ecosystems of the World; Springer Science & Business Media: Berklin, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, W.D. Chinese and Mongolian saline lakes: A limnological overview. Hydrobiologia 1991, 210, 39–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hipsey, M.R.; Zhang, G.X.; Busch, B.; Li, H.Y. Simulation of multiple water source ecological replenishment for Chagan Lake based on coupled hydrodynamics and water quality models. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 17, 1774–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Wu, X. Present situation and tendency of saline-alkali soil in west Jilin Province. J. Geogr. Sci. 2001, 11, 321. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, L.; Shuwen, Z.; Jiuchun, Y.; Liping, C.; Haijuan, Y.; Kun, B. Effects of land use change on ecosystem services value in West Jilin since the reform and opening of China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 31, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Sun, G.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.Q. Multiple approaches to surface water quality and eutrophication assessment provide insight for inland lakes experiencing irrigation district development. Water 2019, 11, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.B. Assessment of water quality of best water management practices in lake adjacent to the high-latitude agricultural areas, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 3338–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.R.; Zhang, G.X.; Wei, X.H. The evolutional characteristics of water environment of Chagan Lake wetland. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2014, 34, 762–768. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, G.X.; Huang, Z.G. Hydrological regimes of Chagan Lake in western. Jilin Prov. Wetl. Sci. 2014, 12, 43–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Wei, X.D.; Dong, J.W. Analysis on Water Quality Changes in Chagan Lake. China Resour. Compr. Util. 2015, 33, 56–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.Z. Water quality status analysis and eutrophication evaluation of Chagan lake reservoir. Agric. Technol. 2018, 38, 59–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yelland, M.; Taylor, P.K. Wind stress measurements from the open ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1996, 26, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedzadeh, A.; Panahi, A.; Maroufpoor, E.; Singh, V.P. Development of an analytical method for estimating Manning’s coefficient of roughness for border irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2019, 37, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.E. Atmosphere-Ocean Dynamics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Hydraulics, D. Delft3D-FLOW User Manual; Deltares: Delft, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dunsbergen, D.W. Particle Models for Transport in Three-Dimensional Shallow Water Flow. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University, Delft, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Nabi, M.; De Vriend, H.J.; Mosselman, E.; Sloff, C.J.; Shimizu, Y. Detailed simulation of morphodynamics: 1. Hydrodynamics model. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W12523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.X.; Zhang, L.; Fan, W.; Feng, X.Q.; Dong, L.Q. Wetland Eco-Hydrology and Water Resources Management; Science press: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Azab, A.M. Integrating GIS, Remote Sensing and Mathematical Modelling for Surface Water Quality Management in Irrigated Watersheds; IHE Delft Institute for Water Education: Delft, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ASCE Task Committee on Definition of Criteria for Evaluation of Watershed Models of the Watershed Management Committee, Irrigation and Drainage Division. Criteria for evaluation of watershed models. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1993, 119, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and water quality models: Performance measures and evaluation criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, J.; Bi, X.; Xu, Z.; He, Y.; Gin, K.Y.H. Developing an integrated 3D-hydrodynamics and emerging contaminant model for assessing water quality in a Yangtze Estuary Reservoir. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Chacón, A.; Dahm, C.N.; Hostetler, S.W.; Lind, O.T.; Starkweather, P.L.; Wurtsbaugh, W.W. Sensitivity of aquatic ecosystems to climatic and anthropogenic changes: The Basin and Range, American Southwest and Mexico. Hydrol. Process. 1997, 11, 1023–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, F.; Inbar, N.; Siebert, C.; Rosenthal, E.; Guttman, J.; Möller, P. Transient simulations of large-scale hydrogeological processes causing temperature and salinity anomalies in the Tiberias Basin. J. Hydrol. 2015, 520, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Miller, C.; Null, S.E.; DeRose, R.J.; Wilcock, P.; Hahnenberger, M.; Moore, J. Decline of the world’s saline lakes. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallenberg, M.; Hall, C.J.; Burns, C.W. Consequences of climate-induced salinity increases on zooplankton abundance and diversity in coastal lakes. Marome Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 251, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timms, B.V. A study of the salt lakes and salt springs of Eyre Peninsula, South Australia. Hydrobiologia 2009, 626, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Song, K.; Zhang, B.; Liu, D.; Guo, Z. Assessment for salinized wasteland expansion and land—Use change using GIS and remote sensing in the west region of Northeast China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 131, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, E.P.; Brown, J.J.; Blumwald, E. Salt tolerance and crop potential of halophytes. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1999, 18, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, I.T. The hydrodynamics and salinity regime of a coastal lagoon–The Coorong, Australia–Seasonal to multi-decadal timescales. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 90, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Yi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H. Effects of ecological flow release patterns on water quality and ecological restoration of a large shallow lake. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, B.T.; Bailey, P.; Edwards, R.; Hortle, K.; James, K.; McMahon, A.; Swadling, K. Effects of salinity on river, stream and wetland ecosystems in Victoria, Australia. Water Res. 1990, 24, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Dong, H.; Yu, B.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Ji, S.; Zhang, C.L. Microbial response to salinity change in Lake Chaka, a hypersaline lake on Tibetan plateau. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2603–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, E.S.; Yu, R.Q.; Barkay, T.; Hamilton, T.L.; Baxter, B.; Naftz, D.L.; Marvin-DiPasquale, M. Effect of salinity on mercury methylating benthic microbes and their activities in Great Salt Lake, Utah. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schröder, M.; Sondermann, M.; Sures, B.; Hering, D. Effects of salinity gradients on benthic invertebrate and diatom communities in a German lowland river. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollheim, W.M.; Lovvorn, J.R. Effects of macrophyte growth forms on invertebrate communities in saline lakes of the Wyoming High Plains. Hydrobiologia 1996, 323, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintz, W.D.; Relyea, R.A. A salty landscape of fear: Responses of fish and zooplankton to freshwater salinization and predatory stress. Oecologia 2017, 185, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, C.; Curtis, A. Regional scale adaptive management: Lessons from the North East Salinity Strategy (NESS). Australasian. J. Environ. Manag. 2003, 10, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raats, P.A. Salinity management in the coastal region of the Netherlands: A historical perspective. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 157, 12–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemma, B. Ecological changes in two Ethiopian lakes caused by contrasting human intervention. Limnologica 2003, 33, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahi, K.A.; Halihan, T. Salinity evolution of the Tigris River. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2018, 18, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal, A. Seeking sustainability: Israel’s evolving water management strategy. Science 2006, 313, 1081–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Kaluarachchi, J.J. A risk-based hydro-economic analysis for land and water management in water deficit and salinity affected farming regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 166, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sserwadda, M.; Kagambe, E.; Van Stappen, G. The brine shrimp Artemia survives in diluted water of Lake Bunyampaka, an inland saline lake in Uganda. Water 2018, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mor, Z.; Assouline, S.; Tanny, J.; Lensky, I.M.; Lensky, N.G. Effect of water surface salinity on evaporation: The case of a diluted buoyant plume over the Dead Sea. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 1460–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Meng, D.; Zhou, H.; Qin, Y. Management of water quality targets based on river-lake water quality response relationships for lake basins–A case study of Dianchi Lake. Environ. Res. 2020, 11, 109479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micklin, P.P. Desiccation of the Aral Sea: A water management disaster in the Soviet Union. Science 1988, 241, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]









| Parameters | Mean | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Wind (m/s) | 2.19a | 0–26.6 |
| Water Depth (m) | 2.50b | 0.5–4.5 |
| Water temperature (°C) | 15.48a | 3.5–30.20 |
| Air temperature (°C) | 3.93a | −28.2–33.9 |
| Salinity (psu) | 0.49b | 0.31–0.78 |
| pH | 8.75b | 8.20–9.13 |
| Electrical conductivity (μs/cm) | 0.94b | 0.49–1.07 |
| Precipitation (mm/h) | 0.08a | 0–28.4 |
| Evaporation (mm/h) | 0.12a | 0–14.7 |
| Relative humidity (%) | 70.38a | 7–99 |
| Solar radiation (w m2) | 263.00a | 0–400.04 |
| Parameters | Value | Use Category | Unit | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gravity | 9.81 | Constants | m s−2 | Lab value |
| Water density | 1000 | Constants | kg/m3 | |
| Air density | 1.0 | Constants | kg/m3 | |
| Wind drag coefficients at wind speed, range of 0–6 m/s | 0.00063 | Wind stress | - | [67] |
| Wind drag coefficients at wind speed, range of 6–26 m/s | 0.00723 | Wind stress | - | [67] |
| Wind drag coefficients at wind speed above 26 m/s | 0.00723 | Wind stress | - | [67] |
| Bed roughness for Manning Roughness formulation | 0.022 | Roughness | - | [68] |
| Background eddy viscosity | 2.0 | Viscosity | m2/s | Dependent on grid size |
| Background eddy diffusivity | 2.0 | Viscosity | m2/s | Dependent on grid size |
| Secchi depth | 0.5 | Heat flux model | m | Field survey |
| Dalton number for evaporative heat flux | 0.0013 | Heat flux model | - | [69] |
| Stanton number for heat convection | 0.0013 | Heat flux model | - | [69] |
| Inflow Water (108 m3) | Outflow Water (108 m3) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boundaries | P | CT | JJ | Gin | E | LD | Gout |
| Water quantity | 1.18 | 1.60 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 2.81 | 1.54 | 0.24 |
| Sources | a | b | b | c | a | b | c |
| Sampling Stations | Salinity (psu) | Temperature (°C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSE | PBIAS | NSE | PBIAS | |
| Calibration (six observations for each station) | ||||
| S1 | 0.62 | 5.88 | 0.75 | 1.65 |
| S2 | 0.51 | 4.30 | 0.94 | 1.65 |
| S3 | 0.68 | 10.54 | 0.94 | 3.88 |
| S4 | 0.41 | 7.15 | 0.99 | 0.68 |
| S5 | 0.69 | 9.98 | 0.94 | 2.97 |
| S6 | 0.38 | 5.01 | 0.74 | 2.47 |
| Validation (six observations for each station) | ||||
| A1 | 0.81 | 2.76 | 0.99 | –0.56 |
| A2 | 0.77 | –0.54 | 0.99 | –0.76 |
| A3 | 0.76 | 1.71 | 0.99 | –0.67 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.J.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Sun, G.; Chen, Y.; Ma, H. Effects of Irrigation Discharge on Salinity of a Large Freshwater Lake: A Case Study in Chagan Lake, Northeast China. Water 2020, 12, 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082112
Liu X, Zhang G, Zhang J, Xu YJ, Wu Y, Wu Y, Sun G, Chen Y, Ma H. Effects of Irrigation Discharge on Salinity of a Large Freshwater Lake: A Case Study in Chagan Lake, Northeast China. Water. 2020; 12(8):2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082112
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xuemei, Guangxin Zhang, Jingjie Zhang, Y. Jun Xu, Yao Wu, Yanfeng Wu, Guangzhi Sun, Yueqing Chen, and Hongbo Ma. 2020. "Effects of Irrigation Discharge on Salinity of a Large Freshwater Lake: A Case Study in Chagan Lake, Northeast China" Water 12, no. 8: 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082112
APA StyleLiu, X., Zhang, G., Zhang, J., Xu, Y. J., Wu, Y., Wu, Y., Sun, G., Chen, Y., & Ma, H. (2020). Effects of Irrigation Discharge on Salinity of a Large Freshwater Lake: A Case Study in Chagan Lake, Northeast China. Water, 12(8), 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082112











