Contamination Status of Salmonella spp., Shigella spp. and Campylobacter spp. in Surface and Groundwater of the Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Sampling
2.3. Isolation and Identification of Pathogenic Bacteria
2.4. Serotype Identification-Serological Identification Method
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. GIS Thematic Mapping
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO; UNICEF. Global Drinking Water Coverage and Trends, 1990–2012. In Progress on Drinking Water and Sanitation, 2014 Update; Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 12, pp. 1–78. ISBN 978-92-4-150724-0. Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/112727/1/9789241507240_eng.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 25 July 2014).
- Pimentel, D.; Berger, B.; Filiberto, D.; Newton, M.; Wolfe, B.; Karabinakis, E.; Clark, S.; Poon, E.; Abbett, E.; Nandaopal, S. Water Resources, Agriculture, and the Environment; Report 04-1; New York State College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations World Water Assessment Programme. The United Nations World Water Development Report; Programme Office for Global Water Assessment, Division of Water Sciences, UNESCO: Perugia, Italy, 2019; pp. 1–11.
- Jayakody, P.; Raschid-Sally, L.; Abayawardana, S.A.K.; Najim, M. Urban growth and wastewater agriculture: A study from Sri Lanka. In Proceedings of the Population, 32nd WEDC International Conference, Colombo, Sri Lanka, 13–17 November 2006; pp. 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Manchanayaka, P.; Maddumabandara, C.M. Water Resources of Sri Lanka, National Science Foundation. Natural Resources Series; Colombo, Sri Lanka, 1999; Volume 4, p. 118. Available online: http://dl.nsf.ac.lk/handle/1/5406 (accessed on 7 June 2016).
- Mahagamage, M.; Chinthaka, S.; Manage, P.M. Multivariate analysis of physico-chemical and microbial parameters of surface water in Kelani river basin. Int. J. Multidiscip. Stud. 2014, 1, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES). Sustainable Groundwater management in Asian cities, Freshwater Resources Management Project; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies: Kanagawa, Japan, 2007; Volume 3, pp. 1–157.
- Mahagamage, M.G.Y.L.; Manage, P.M. Water Quality Index (CCME-WQI) Based Assessment Study of Water Quality in Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka. In Proceedings of the 1st Environment and Natural Resources International Conference (ENRIC 2014), Bangkok, Thailand, 6–7 November 2014; Mahidol University: Salaya, Thailand, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Mahagamage, M.G.Y.L.; Manage, P.M. Mapping spatial distribution of water quality parameters of groundwater in the Kelani river basin using GIS. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Environmental Science and Development (ICESD), Singapore, 20 December 2015; pp. 10–14. Available online: http://dr.lib.sjp.ac.lk/handle/123456789/6040 (accessed on 7 June 2016).
- Lagerblad, L. Wastewater Treatment Wetlands-Case Study in Colombo, Sri Lanka; Uppsala University: Uppsala, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Danish Hydraulic Institute. Kelani Ganga Basin Detailed Basin Assessment, Working Document C. Earthtrends 2003. Water Resources and Freshwater Ecosystems Country Profile Sri Lanka. 1999. Available online: http://earthtrends.wri.org/text/water-resources/country-profile-167.html (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- WHO. Campylobacter, WHO Media Centre; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs255/en/ (accessed on 7 August 2016).
- Abraham, W.-R. Megacities as Sources for Pathogenic Bacteria in Rivers and Their Fate Downstream. Int. J. Microbiol. 2010, 2011, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, R.M.; Linscott, A.J. Laboratory Diagnosis of Bacterial Gastroenteritis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Water-Related Diseases, Campylobacteriosis, Water Sanitation Health; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/campy/fs255/en/ (accessed on 12 August 2016).
- Crump, J.A.; Luby, S.P.; Mintz, E.D. The global burden of typhoid fever. Bull. World Health Organ. 2004, 82, 346–353. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, I.F.; Havt, A.; Lima, A. Update on molecular epidemiology of Shigella infection. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 31, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, P.; Faruque, A.S.; Naheed, A.; Sack, D.A. Decrease in shigellosis-related deaths without Shigella spp.-specific interventions. Asia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1718–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyogi, S.K. Shigellosis. J. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- The Community Summary Report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in the European Union in 2008. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1496. [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health Public Health Services. Collection, Storage, and Transport of Samples for Investigation. In Manual for the Sri Lanka Public Health Inspector; State Printing Corporation: Padukka, Sri Lanka, 2010; Chapter 8; pp. 275–284. ISBN 978-955-0505-00-5. [Google Scholar]
- Health Protection Agency. Detection of Salmonella Species. National Standard Method W 7. 2006. Available online: http://www.hpa-standardmethods.org.uk/pdf_sops.asp (accessed on 28 May 2014).
- Health Protection Agency. Detection of Shigella Species in Water. National Standard Method W 8. 2007. Available online: http://www.hpa-standardmethods.org.uk/pdf_sops.asp (accessed on 28 May 2014).
- Sri Lanka Collage of Microbiologists. Laboratory Manual in Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Sri Lanka College of Microbiologists: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2011; ISBN 978-8891-03-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe, E.; Jones, D.; Pearson, A. Latex agglutination for the detection of Campylobacter species in water. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1991, 12, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, J.P.S. Water Microbiology. Bacterial Pathogens and Water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3657–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahagamage, M.G.Y.L.; Pathmalal, M. Socio-Economic Background of the Head and Transitional Regions of the Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka. Asian J. Microbiol. Biotech. Env. Sci. 2018, 20, 744–756. [Google Scholar]
- Grisey, E.; Belle, E.; Dat, J.; Mudry, J.; Aleya, L. Survival of pathogenic and indicator organisms in groundwater and landfill leachate through coupling bacterial enumeration with tracer tests. Desalination 2010, 261, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahagamage, M.; Manage, P.S.; Manage, P.M. Water quality and microbial contamination status of groundwater in Jaffna Peninsula, Sri Lanka. J. Water Land Dev. 2019, 40, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahagamage, M.; Manage, P.M. Water quality and microbial contamination status of Madawachchiya, Padaviya and Kebithigollewa areas in Anuradhapura District, Sri Lanka. J. Water Land Dev. 2019, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozlica, J.; Claudet, A.L.A.L.; Solomon, D.; Dunn, J.R.J.R.; Carpenter, L.R.L.R. Waterborne Outbreak of Salmonella. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 1431–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levantesi, C.; Bonadonna, L.; Briancesco, R.; Grohmann, E.; Toze, S.; Tandoi, V. Salmonella in surface and drinking water: Occurrence and water-mediated transmission. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Kass, P.H.; Soupir, M.L.; Biswas, S.; Singh, V.P. Contamination of water resources by pathogenic bacteria. AMB Express 2014, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahagamage, M.G.Y.L.; Pathirage, S.; Pathmalal, M.M. Occurrence of pathogenic bacteria and water quality of the surface water in the Kelani river basin, Sri Lanka. In Proceedings of the 22th Annual Scientific Sessions of the Sri Lanka Association for Fisheries and Aquatic Resources, Colombo, Sri Lanka, 20 May 2016; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Hynds, P.D.; Thomas, M.K.; Pintar, K.D.M. Contamination of Groundwater Systems in the US and Canada by Enteric Pathogens, 1990–2013: A Review and Pooled-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majtán, V.; Majtan, T.; Majtan, J.; Szabóová, M.; Majtánová, L. Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky: Antimicrobial resistance and molecular analysis of clinical isolates from the Slovak Republic. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 59, 358–362. [Google Scholar]
- Barua, H.; Biswas, P.K.; Olsen, K.E.P.; Christensen, J.P. Prevalence and Characterization of Motile Salmonella in Commercial Layer Poultry Farms in Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fashae, K.; Hendriksen, R.S. Diversity and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from pig farms in Ibadan, Nigeria. Folia Microbiol. 2013, 59, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afema, J.A.; Byarugaba, D.K.; Shah, D.; Atukwase, E.; Nambi, M.; Sischo, W.M. Potential Sources and Transmission of Salmonella and Antimicrobial Resistance in Kampala, Uganda. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatawara, D. Garbage Disposal at Holy Mountain, a Challenge, Sunday Observer. 8 April 2012. Available online: http://archives.sundayobserver.lk/2012/04/08/fea11.asp (accessed on 7 August 2016).
- Le Hello, S.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Doublet, B.; Fisher, I.; Nielsen, E.M.; Whichard, J.M.; Bouchrif, B.; Fashae, K.; Granier, S.A.; Silva, N.J.-D.; et al. International Spread of an Epidemic Population of Salmonella enterica Serotype Kentucky ST198 Resistant to Ciprofloxacin. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thong, K.L.; Goh, Y.L.; Radu, S.; Noorzaleha, S.; Yasin, R.; Koh, Y.T.; Lim, V.K.E.; Rusul, G.; Puthucheary, S.D. Genetic Diversity of Clinical and Environmental Strains of Salmonella enterica Serotype Weltevreden Isolated in Malaysia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 2498–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aarestrup, F.M.; Lertworapreecha, M.; Evans, M.C.; Bangtrakulnonth, A.; Chalermchaikit, T.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Wegener, H.C. Antimicrobial susceptibility and occurrence of resistance genes among Salmonella enterica serovar Weltevreden from different countries. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, E.; Khan, A.A.; Cheng, C.-M.; Summage-West, C.; Cerniglia, C.E. Prevalence and characterization of Salmonella enterica serovar Weltevreden from imported seafood. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, S.V.; Dissanayake, S.A.M.S.; Iddamalgoda, I.A.V.P. Evaluation of Water Pollution Risk of Muskelioya—Kehelgamuoya Watershed by Watershed Unit Approach, Evaluation_of_Water_Pollution, Environmental Studies and Services Division; National Building Research Organization: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2010; pp. 1–7. Available online: https://www.nbro.gov.lk/images/content_image/publications/symposia/2010/evaluation_of_water_pollution.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2016).
- Ezekwe, I.C.; Chima, G.N.; Ikogori, G. An investigation of selected microbial pollutants in groundwater sources in Yenegoa Town, Bayelsa, Nigeria. Estudos de Biolgia. 2013, 35, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Salmonella Surveillance: Annual Summary, 2006; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2008.
- Zansky, S.; Wallace, B.; Schoonmaker-Bopp, D.; Smith, P.; Ramsey, F.; Painter, J.; Gupta, A.; Kalluri, P.; Noviello, S. From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreak of multi-drug resistant Salmonella Newport--United States, January–April 2002. JAMA 2002, 288, 545–548. [Google Scholar]
- McClelland, M.; Sanderson, K.E.; Spieth, J.; Clifton, S.W.; Latreille, P.; Courtney, L.; Porwollik, S.; Ali, J.; Dante, M.; Du, F.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium LT2. Nature 2001, 413, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rop, R.K. Impact of Anthropogenic Activities on Bacteriological Water Quality of Nyangores River, Mara Basin-Kenya. Ph.D. Thesis, Egerton University, Njoro, Kenya, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Søborg, D.A.; Hendriksen, N.B.; Kilian, M.; Kroer, N. Widespread Occurrence of Bacterial Human Virulence Determinants in Soil and Freshwater Environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5488–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polo, F.; Figueras, M.J.; Inza, I.; Sala, J.; Fleisher, J.M.; Guarro, J. Relationship between presence of Salmonella and indicators of faecal pollution in aquatic habitats. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 160, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baudart, J.; LeMarchand, K.; Brisabois, A.; LeBaron, P. Diversity of Salmonella Strains Isolated from the Aquatic Environment as Determined by Serotyping and Amplification of the Ribosomal DNA Spacer Regions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Popoff, M.Y.; Bockemühl, J.; Gheesling, L.L. Supplement 2002 (no. 46) to the Kauffmann–White scheme. Res. Microbiol. 2004, 155, 568–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroöter, M.; Roggentin, P.; Hofmann, J.; Speicher, A.; Laufs, R.; Mack, D. Pet Snakes as a Reservoir for Salmonella enterica subsp. diarizonae (Serogroup IIIb): A Prospective Study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 613–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gulasekharam, J.; Velaudapillai, T.; Nadarajah, K.N. Salmonella angoda: A new Salmonella. Indian J. Med Res. 1959, 47, 484–486. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner, C.P.; Mosbach, K.; Bibit, V.C.; Watson, C.H. Coconut and Salmonella Infection. Appl. Microbiol. 1967, 15, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abrahams, C.A.; Agbodaze, D.; Nakano, T.; Afari, E.A.; Longmatey, H.E.K. Prevalence and antibiogram of Salmonella in domestic animals in rural Ghana. J. Environ. Health 2000, 45, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Waithaka, P. Predisposing Factors, Isolation, Sensitivity to Antibiotics and Control Methods of Salmonellosis in Nakuru North Sub-County, Kenya. Ph.D. Thesis, Kenyatta University, Nairobi, Kenya, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L.; Mak, J.K.; White, P.A.; McIver, C.J.; Taylor, P. Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Strains Expressing Emerging Antibiotic Resistance Determinants. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 324–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoszowski, A.; Zając, M.; Lalak, A.; Przemyk, P.; Wasyl, D. Fifteen years of successful spread of Salmonella enterica serovar Mbandaka clone ST413 in Poland and its public health consequences. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2016, 23, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolman, C.E.; Ranta, L.E. A new Salmonella type; Salmonella vancouver. Can. J. Public Health 1950, 41, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Aissa, R.; Al-Gallas, N. Molecular typing ofSalmonella entericaserovars Enteritidis, Corvallis, Anatum and Typhimurium from food and human stool samples in Tunisia, 2001–2004. Epidemiol. Infect. 2007, 136, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Kopecko, D.J. Salmonella Typhi and Paratyphi. In Molecular Medical Microbiology; Sussman, M., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 1365–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Stratton, J.; Stefaniw, L.; Grimsrud, K.; Werker, D.H.; Ellis, A.; Ashton, E.; Chui, L.; Blewett, E.; Ahmed, R.; Clark, C.; et al. Outbreak of Salmonella paratyphi B var java due to contaminated alfalfa sprouts in Alberta, British Columbia and Saskatchewan. Can. Commun. Dis. Rep. 2001, 27, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miko, A.; Guerra, B.; Schroeter, A.; Dorn, C.; Helmuth, R. Molecular Characterization of Multiresistant d-Tartrate-Positive Salmonella enterica Serovar Paratyphi B Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 3184–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mammina, C.; Cannova, L.; Massa, S.; Goffredo, E.; Nastasi, A. Drug resistances in Salmonella isolates from animal foods, Italy 1998–2000. Epidemiol. Infect. 2002, 139, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, Y.; Yasin, R.; Puthucheary, S.; Koh, Y.; Lim, V.; Taib, Z.; Thong, K.L. DNA fingerprinting of human isolates of Salmonella enterica serotype Paratyphi B in Malaysia. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levings, R.S.; Lightfoot, D.; Hall, R.M.; Djordjevic, S.P. Aquariums as Reservoirs for Multidrug-resistant Salmonella Paratyphi B. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, E.; Rodriguez, J.L.; Herrera-León, S.; García, I.; De Castro, V.; Muniozguren, N. Salmonella Paratyphi B var Java infections associated with exposure to turtles in Bizkaia, Spain, September 2010 to October 2011. Eurosurveillance 2012, 17, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bridges, R.F.; Scott, W.M. A new organism causing paratyphoid fever in India. J. R. Army Med. Corps 1931, 56, 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Cleary, P.; Browning, L.; Coia, J.; Cowden, J.; Fox, A.; Kearney, J.; Lane, C.; Mather, H.; Quigley, C.; Syed, Q.; et al. A foodborne outbreak of Salmonella Bareilly in the United Kingdom, 2010. Eurosurveillance 2010, 15, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mermin, J.; Hutwagner, L.; Vugia, D.; Shallow, S.; Daily, P.; Bender, J.; Koehler, J.; Marcus, R.; Angulo, F.J. Reptiles, Amphibians, and Human Salmonella Infection: A Population-Based, Case-Control Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, M.; Luo, Y.; Monday, S.R.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Ottesen, A.R.; Muruvanda, T.; Senturk, I.F. Tracing origins of the Salmonella Bareilly strain causing a food-borne outbreak in the United States. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WHO. The WHO Recommended Classification of Pesticides by Hazard and Guidelines to Classification; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. Available online: http://www.who.int/ipcs/publications/pesticides_hazard_2009.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2016).
- Allard, M.W.; Muruvanda, T.; Strain, E.; Timme, R.E.; Luo, Y.; Wang, C.; Keys, C.E.; Payne, J.; Cooper, T.; Luong, K.; et al. Fully Assembled Genome Sequence for Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Serovar Javiana CFSAN001992. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e00293-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hendriksen, R.S.; Le Hello, S.; Bortolaia, V.; Pulsrikarn, C.; Nielsen, E.M.; Pornruangmong, S.; Chaichana, P.; Svendsen, C.A.; Weill, F.-X.; Aarestrup, F.M. Characterization of Isolates of Salmonella enterica Serovar Stanley, a Serovar Endemic to Asia and Associated with Travel. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 50, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hendriksen, R.S.; Bangtrakulnonth, A.; Pulsrikarn, C.; Pornruangwong, S.; Noppornphan, G.; Emborg, H.-D.; Aarestrup, F.M. Risk Factors and Epidemiology of the Ten Most CommonSalmonellaSerovars from Patients in Thailand: 2002–2007. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, J.A. Animal Disease Information and Prevention Materials Developed by the Center for Food Security and Public Health; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 2007; Volume 653, p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Premarathne, J.M.K.J.K.; Satharasinghe, D.A.; Huat, J.T.Y.; Basri, D.F.; Rukayadi, Y.; Nakaguchi, Y.; Nishibuchi, M.; Radu, S. Impact of humanCampylobacterinfections in Southeast Asia: The contribution of the poultry sector. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 57, 3971–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte-Ruiz, M.; Florez-Cuadrado, D.; Wassenaar, T.M.; Porrero, M.C.; Domínguez, L. Method Comparison for Enhanced Recovery, Isolation and Qualitative Detection of C. jejuni and C. coli from Wastewater Effluent Samples. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 2749–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Medema, G.J.; Shaw, S.; Waite, M.; Snozzi, M.; Morreau, A.; Grabow, W. Catchment characterization and source water quality. In Assessing Microbial Safety of Drinking Water; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; Volume 4, pp. 111–158. [Google Scholar]

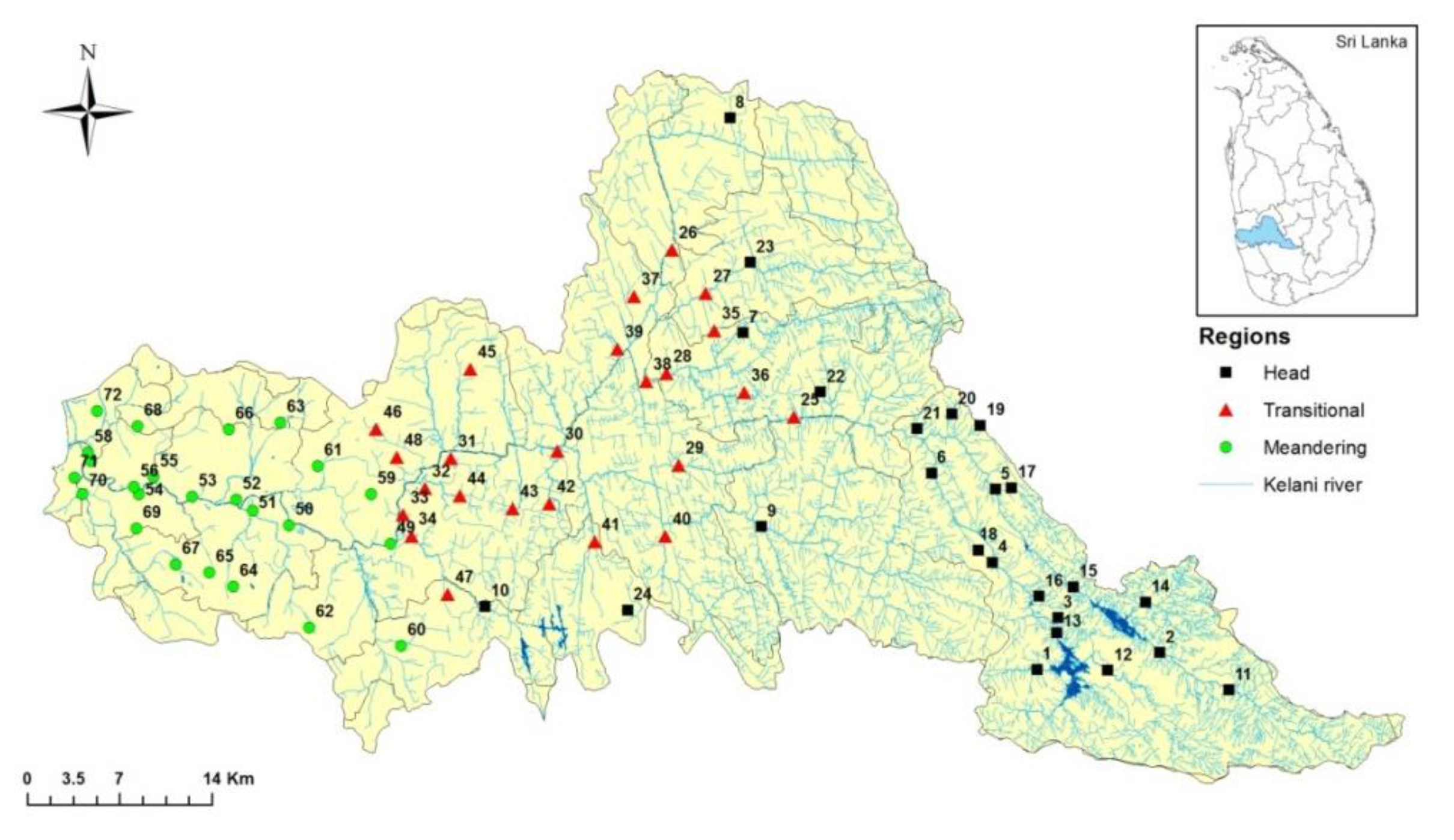


| No | Head Region | No | Transitional Region | No | Meandering Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kelani river (Nallathanniya) | 16 | Kelani river (Yatiyanthota) | 31 | Pusseli Oya |
| 2 | Sami male canal | 17 | We oya (Amanawala) | 32 | Kelani river (Ranala) |
| 3 | Kehelgamu oya (Norwood) | 18 | Ritigaha oya (Warawala) | 33 | Pahala bomariya ela |
| 4 | Dic oya | 19 | Gurugoda oya | 34 | Raggahawaththa oya |
| 5 | Maskeliya tank | 20 | Kahanawita canal (Dehiovita) | 35 | Kelani river (Kohila waththa) |
| 6 | Castlereigh tank | 21 | Seethawaka oya (Thalduwa) | 36 | Sebastian canal (Kelanithissa) |
| 7 | Norton tank | 22 | Eswaththa oya | 37 | Dutch canal |
| 8 | Kandura (Koththellena) | 23 | Pugoda oya (Pugoda) | 38 | Hamilton canal |
| 9 | Kelani river (Nagampitiya) | 24 | Wak oya (Kaluaggala) | 39 | Kelani river (Mattakkuliya) |
| 10 | Keselgamu oya (Tientsin) | 25 | Kelani river (Thaligama) | 40 | Raggahawaththa oya (Meegawaththa) |
| 11 | Mohini ella | 26 | Athalawa ela | 41 | Thalangama lake |
| 12 | Bokarabevila tributary | 27 | Getaheththa tributary | 42 | Diyawanna oya |
| 13 | Vidulipura tributary | 28 | Amthirigala tributary | 43 | Mahara |
| 14 | Alagal Oya (Gonagamuwa) | 29 | Pugada river (Mandawala) | 44 | Kittampahuwa ela (Wellampitiya) |
| 15 | Ritigaha oya (Bulathkohupitiya) | 30 | Pusseli Oya (Wewelpanawa) | 45 | Kalu oya |
| No | Head Region | No | Transitional Region | No | Meandering Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wana male | 25 | Thaligama | 49 | Pollaththawela |
| 2 | Norwood | 26 | Kotiyakumbura | 50 | Ranala |
| 3 | Lakham | 27 | Warawala | 51 | Pahalabomariya |
| 4 | Koththellena | 28 | Kabulumulla | 52 | Biyagama |
| 5 | Kalaweldeniya | 29 | Kahanavita | 53 | Bollagala |
| 6 | Bokarabevila | 30 | Kudagama | 54 | Kohilawaththa |
| 7 | Malalpola | 31 | Kananpella | 55 | Kelaniya |
| 8 | Pitagaldeniya | 32 | Akarawita | 56 | Pilapitiya |
| 9 | Deraniyagala | 33 | Kahatapitiya | 57 | Paliyagoda |
| 10 | Waga | 34 | Kaluaggala | 58 | Aliwaththa |
| 11 | Tientsin | 35 | Kelaniwaththa | 59 | Palugama |
| 12 | Samimale | 36 | Levent | 60 | Moragahahena |
| 13 | Maskeliya | 37 | Siyabalawa | 61 | Dekatana |
| 14 | Dicoya | 38 | Karawanaella | 62 | Godagama |
| 15 | Castlereigh | 39 | Nawagammane | 63 | Udupila |
| 16 | Norton junction | 40 | Batangala | 64 | Hokandara |
| 17 | Athis | 41 | Getaheththa | 65 | Arangala |
| 18 | Koththellena 2 | 42 | Puwakpitiya | 66 | Mawaramandiya |
| 19 | Ginigathhena | 43 | Hingurala | 67 | Thalangama |
| 20 | Badupola | 44 | Kosgama | 68 | Ederamulla |
| 21 | Kalugala | 45 | Viharakumbura | 69 | IDH |
| 22 | Gonagamuwa | 46 | Delgoda | 70 | Nawagampura |
| 23 | Bulathkohupitiya | 47 | Pinnawala | 71 | Mahawaththa |
| 24 | Thoranakada | 48 | Lunugama | 72 | Bangalawaththa |
| Location | Dry Season | Wet Season |
|---|---|---|
| Maskeliya Ground | Salmonella enterica subsp.diarizonae str. 61 1v1,5,7 | |
| Koththellena 2 | Salmonella enterica subsp.diarizonae str. 61 1v1,5,7 | |
| Ginigathhena | Campylobacter spp. | |
| Badupola | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium | |
| Bulathkohupitiya | Salmonella enterica serovar Weltevreden | |
| Kabulumulla | Salmonella enterica serovar Corvallis | |
| Kahanavita | Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky | |
| Kananpella | Salmonella enterica serovar Vancouver | |
| Levent | Salmonella enterica serovar Angoda | |
| Karawanaella | Salmonella enterica subsp indica str 6,14,25:a:enx/Salmonella enterica subsp. diarizonae Ser.61 | |
| Hingurala | Salmonella enterica serovar Poona | Salmonella enterica serovar Newport |
| Vihara kumbura | Salmonella enterica serovar Waycross | |
| Kiridiwela-Delgoda | Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky | |
| Biyagama | Salmonella enterica serovar Weltevreden | |
| Kelaniya | Campylobacter spp. | |
| Moragahahena | Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky | |
| Arangala | Salmonella enterica serovar Mbandaka | |
| Nawagampura | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium | |
| Bangalawaththa | Salmonella enterica subsp indica str 6,14,25:a:enx |
| Location | Dry Season | Wet Season |
|---|---|---|
| Nallathanniya | Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky | |
| Kandura (Koththellena) | Salmonella enterica subsp. diarizonae Ser.61 | Salmonella enterica subsp. diarizonae str. 61 z52z53 |
| Tinsil river | Salmonella enterica serovar Javiana | |
| Bokarabevila river | Salmonella enterica subsp enterica ser 9, [12]:-:1,5 | |
| Vidulipura | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium | |
| Gonagamuwa river | Salmonella enterica serovar Weltevreden | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium |
| Bulathkohupitiya river | Campylobacter spp. | |
| Ruwanwella | Salmonella enterica serovar Bareilly | |
| Thalduwa | Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky | |
| Aswaththa | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium | Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky |
| Poogoda | Campylobacter spp. | |
| Kaluaggala | Salmonella enterica serovar Javiana | |
| Thaligama river | Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi B Variety Java | |
| Getaheththa river | Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky | |
| Amthirigala | Salmonella enterica serovar Bredeney | |
| Pugada river | Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi B Variety Java | Salmonella enterica serovar Durban |
| Wewelpanawa | Salmonella enterica serovar Angola | |
| Pussella oya | Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi B Variety Java | |
| Ranala river | Salmonella enterica serovar Mount Pleasant | |
| Raggahawaththa ela | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium | |
| Kelanithissa | Salmonella enterica serovar Stanley | Salmonella enterica serovar Agona |
| Dutch canal | Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis | |
| Hemilton canal | Campylobacter spp. | Campylobacter spp. |
| Meegawaththa- Delgoda | Salmonella enterica serovar Newport | Salmonella enterica serovar Weltevreden/ Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi B Variety Java |
| Thalangama lake | Salmonella enterica serovar Manchester | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium |
| Diyawanna oya | Salmonella enterica serovar Litchfield | |
| Mahara | Salmonella enterica subsp enterica ser 4, [5], 12:b Salmonella enterica subsp enterica ser 9, [12]:-:1,5 | |
| Wellampitiya | Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky | |
| Muthuraja ela | Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky | Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky/Campylobacter spp. |
| TC | E. coli | Pseudomonas spp. | Salmonella spp. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | 0.390 | |||
| 0.000 | ||||
| Pseudomonas spp. | −0.374 | −0.460 | ||
| 0.000 | 0.000 | |||
| Salmonella spp. | 0.146 | 0.340 | −0.111 | |
| 0.025 | 0.000 | 0.091 | ||
| Cam1ylobacter spp. | 0.063 | 0.075 | −0.016 | 0.082 |
| 0.336 | 0.256 | 0.810 | 0.209 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahagamage, M.G.Y.L.; Pathirage, M.V.S.C.; Manage, P.M. Contamination Status of Salmonella spp., Shigella spp. and Campylobacter spp. in Surface and Groundwater of the Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka. Water 2020, 12, 2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082187
Mahagamage MGYL, Pathirage MVSC, Manage PM. Contamination Status of Salmonella spp., Shigella spp. and Campylobacter spp. in Surface and Groundwater of the Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka. Water. 2020; 12(8):2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082187
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahagamage, M.G.Y.L., M.V.S.C. Pathirage, and Pathmalal M. Manage. 2020. "Contamination Status of Salmonella spp., Shigella spp. and Campylobacter spp. in Surface and Groundwater of the Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka" Water 12, no. 8: 2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082187
APA StyleMahagamage, M. G. Y. L., Pathirage, M. V. S. C., & Manage, P. M. (2020). Contamination Status of Salmonella spp., Shigella spp. and Campylobacter spp. in Surface and Groundwater of the Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka. Water, 12(8), 2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082187





