River Flow Estimation Using Artificial Intelligence and Fuzzy Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
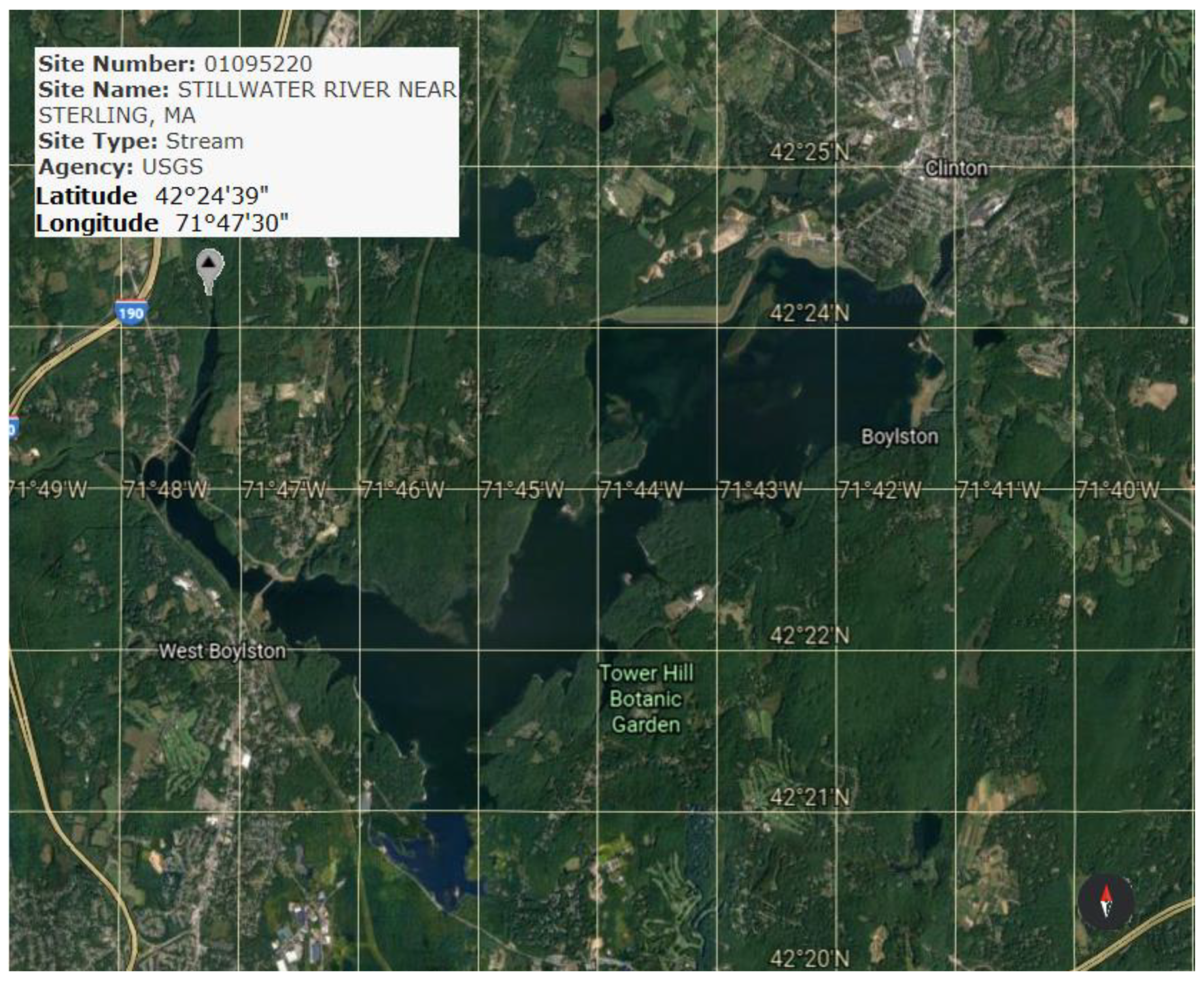
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Multiple Linear Regression (MLR)
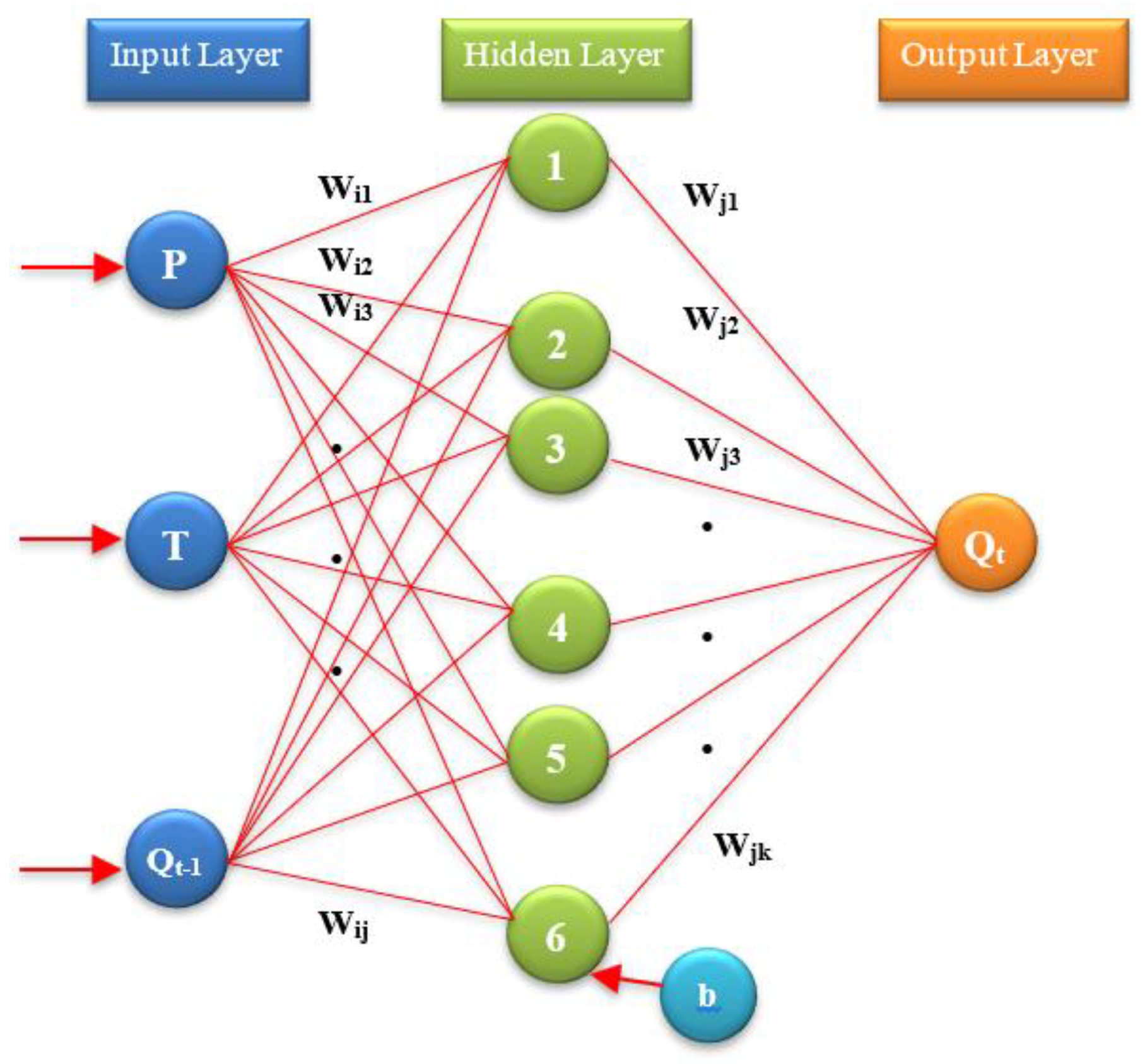
2.2.2. Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Model
2.2.3. M5 Decision Tree Model (M5T)
2.2.4. Mamdani Fuzzy Logic (M-FL) Model
2.2.5. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) Model
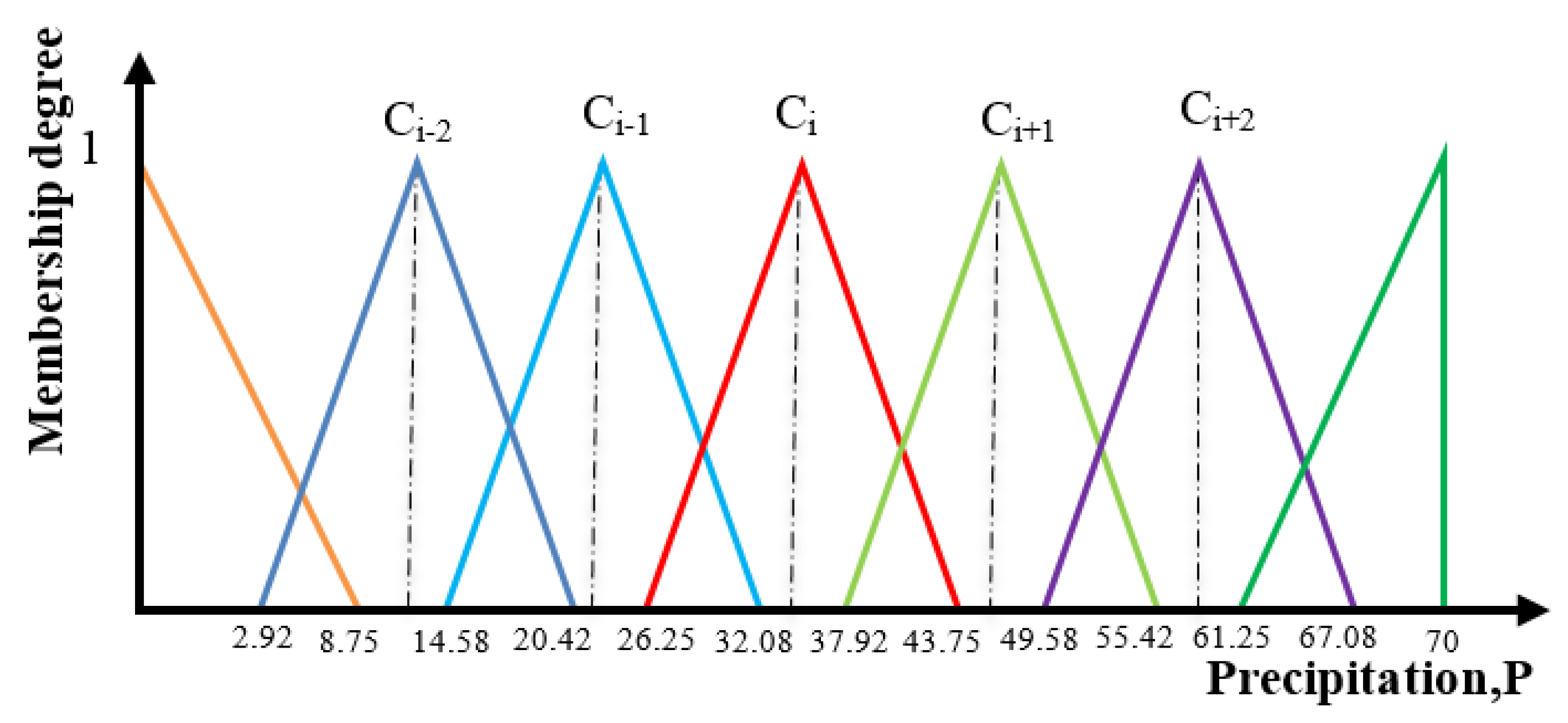
2.2.6. Simple Membership Functions and Fuzzy Rules Generation Technique (SMRGT)
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- The SMRGT model shows the best statistical performance compared to the other models. (MSE: 0.535 m6/s2, MAE: 0.318 m3/s and R: 0.927).
- The M-FL model exhibits a better performance (MSE: 0.595 m6/s2, MAE: 0.338 m3/s and R: 0.917) than the ANN, ANFIS, M5T and MLR models.
- The MLR and ANFIS models have nearly the same results. For MLR, MSE: 0.618 m6/s2, MAE: 0.347 m3/s and R: 0.902. For the ANFIS model, MSE: 0.611 m6/s2, MAE: 0.345 m3/s and R: 0.903.
- The ANN method gives better results than the MLR, ANFIS and M5T methods (MSE: 0.601 m6/s2, MAE: 0.349 m3/s and R: 0.907).
- The M5T method shows the lowest performance among all models (MSE: 0.747 m6/s2, MAE: 0.370 m3/s and R: 0.878).
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsu, K.L.; Gupta, H.V.; Sorooshian, S. Artificial neural network modeling of the rainfall-runoff process. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 2517–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, D.A.K.; Jayawardena, A.W. Runoff forecasting using RBF networks with OLS algorithm. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1998, 3, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokar, A.S.; Johnson, P.A. Rainfall-runoff modeling using artificial neural networks. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1999, 4, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, J.; Sahu, R.K.; Agarwal, A.; Pali, A.K.; Sinha, B.L. Rainfall-Runoff Modelling using Multi Layer Perceptron Technique—A Case Study of the upper Kharun Catchment in Chhattisgarh. J. Agric. Eng. 2013, 50, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, B.; Jayawardena, A.W.; Fernando, T.M.K.G. River flow forecasting: Use of phase-space reconstruction and artificial neural networks approaches. J. Hydrol. 2002, 265, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Das, A.; Srivastava, D.K. Application of ANN for reservoir inflow prediction and operation. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1999, 125, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuwanshi, N.S.; Singh, R.; Reddy, L.S. Runoff and Sediment yield modeling using artificial neural networks: Upper Siwane River, India. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2006, 11, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil Kumar, A.R.; Ojha, C.S.P.; Goyal, M.K.; Singh, R.D.; Swamee, P.K. Modeling of suspended sediment concentration at Kasol in India using ANN, fuzzy logic, and decision tree algorithms. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2012, 17, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nayak, P.C.; Sudheer, K.P.; Ramasastri, K.S. Fuzzy computing based rainfall–runoff model for real time flood forecasting. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamdani, E.H.; Assilian, S. An experiment in linguistic synthesis with a fuzzy logic controller. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 1999, 51, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, C.C.; Moyya, S.D. Runoff modelling using different membership functions in adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2014, 4, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.C.; Chang, F.J.; Tsai, Y.H. Fuzzy exemplar-based inference system for flood forecasting. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskey, S.; Guinot, V.; Price, R.K. Treatment of precipitation uncertainty in rainfall-runoff modelling: A fuzzy set approach. Adv. Water Resour. 2004, 27, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayfur, G.; Moramarco, T.; Singh, V.P. Predicting and forecasting flow discharge at sites receiving significant lateral inflow. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 1848–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilmant, A.; Vanclooster, M.; Duckstein, L.; Persoons, E. Comparison of fuzzy and nonfuzzy optimal reservoir operating policies. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2002, 128, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocabaş, F.; Ünal, B.; Ünal, S.; Fedakar, H.I.; Gemici, E. Fuzzy genetic approach for modeling of the critical submergence of an intake. Neural Comput. Appl. 2013, 23, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozel, H.U.; Gemici, B.T.; Ozel, H.B.; Gemici, E. Determination of Water Quality and Estimation of Monthly Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) Using by Different Artificial Neural Networks Models. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2017, 26, 5465–5476. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.S.; Rosen, M.R.; Reeves, R.R. Dynamic fuzzy modeling of storm water infiltration in urban fractured aquifers. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2002, 7, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahiri, A.; Azamathulla, H.M. Comparison between linear genetic programming and M5 tree models to predict flow discharge in compound channels. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 24, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattari, M.T.; Pal, M.; Apaydin, H.; Ozturk, F. M5 model tree application in daily river flow forecasting in Sohu Stream, Turkey. Water Resour. 2013, 40, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Pal, M.; Singh, V.P. Estimation of mean annual flood in Indian catchments using backpropagation neural network and M5 model tree. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 2007–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O.; Khosravinia, P.; Nikpour, M.R.; Sanikhani, H. Hydrodynamics of river-channel confluence: Toward modeling separation zone using GEP, MARS, M5 Tree and DENFIS techniques. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2019, 33, 1089–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abadi, A.M. Modeling of stage–discharge relationship for Gharraf River, southern Iraq using backpropagation artificial neural networks, M5 decision trees, and Takagi–Sugeno inference system technique: A comparative study. Appl. Water Sci. 2016, 6, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaghaghi, S.; Bonakdari, H.; Gholami, A.; Kisi, O.; Binns, A.; Gharabaghi, B. Predicting the geometry of regime rivers using M5 model tree, multivariate adaptive regression splines and least square support vector regression methods. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2019, 17, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, M.; Baltaci, A. Prediction of suspended sediment in river using fuzzy logic and multilinear regression approaches. Neural Comput. Appl. 2013, 23, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, M.; Üneş, F.; Saydemir, S. Suspended sediment estimation using an artificial intelligence approach. In Sediment Matters; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Üneş, F.; Demirci, M.; Kişi, Ö. Prediction of millers ferry dam reservoir level in USA using artificial neural network. Period. Polytech. Civ. Eng. 2015, 59, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üneş, F.; Demirci, M.; Ispir, E.; Kaya, Y.Z.; Mamak, M.; Tasar, B. Estimation of Groundwater Level Using Artificial Neural Networks: A Case Study of Hatay-Turkey. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference “Environmental Engineering”, Vilnius Gediminas Technical University, Vilnius, Lithuania, 27–28 April 2017; Volume 10, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Demirci, M.; Unes, F.; Kaya, Y.Z.; Tasar, B.; Varcin, H. Modeling of Dam Reservoir Volume Using Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Method. In Proceedings of the Air and Water Components of the Environment Conference, Sovata, Romania, 15–17 March 2018; pp. 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- USGS.gov | Science for a Changing World [WWW Document]. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 20 May 2019).
- Mamdani, E.H. Advances in the linguistic synthesis of fuzzy controllers. Int. J. Man-Machine Stud. 1976, 8, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, T.; Sugeno, M. Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. 1985, 1, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamdani, E.H. Application of fuzzy algorithms for control of simple dynamic plant. Proc. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1974, 121, 1585–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. A Study of Membership Functions on Mamdani-Type Fuzzy Inference System for Industrial Decision-Making. Master’s Thesis, Lehigh University, Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Math Works. Fuzzy Logic Toolbox, User’s Guide R2014a; The Mathworks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rodić, D.; Sekulić, M.; Gostimirović, M.; Pucovsky, V.; Kramar, D. Fuzzy logic and sub-clustering approaches to predict main cutting force in high-pressure jet assisted turning. J. Intell. Manuf. 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugeno, M.; Kank, G.T. Structure identification of fuzzy model. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1988, 28, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaş, E.; Aydın, M.C.; Toprak, Z.F. Açık kanal akımlarında su yüzü profilinin bulanık SMRGT yöntemiyle modellenmesi. Dicle Üniv. Mühendis. Fakültesi Mühendis. Derg. 2018, 9, 975–981. [Google Scholar]
- Toprak, Z.F. Flow discharge modeling in open canals using a new fuzzy modeling technique (SMRGT). Clean Soil Air Water 2009, 37, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprak, S.; ATAY, A.; Toprak, Z.F. SMRGT yöntemi ile bulanıklaştırılmış veriler için bulanık doğrusal regresyon. Erciyes Üniv. Fen Bilimleri Enst. Fen Bilimleri Derg. 2015, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Toprak, A.; Aykaç, Z.; Toprak, Z.F. Bulanık SMRGT yönteminin pratik uygulamaları. Dicle Üniv. Mühendis. Fak. Mühendis. Derg. 2017, 1, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Willmott, C.J.; Matsuura, K. Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Clim. Res. 2005, 30, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.; Hao, Z.; Xifeng, H.; Jingchun, L. Research on water temperature prediction based on improved support vector regression. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






















| Models | MSE (m3/s)2 | MAE (m3/s) | R |
|---|---|---|---|
| MLR | 0.618 | 0.347 | 0.902 |
| ANN | 0.601 | 0.349 | 0.907 |
| M5T | 0.747 | 0.370 | 0.878 |
| ANFIS | 0.611 | 0.345 | 0.903 |
| M-FL | 0.595 | 0.338 | 0.917 |
| SMRGT-FL | 0.535 | 0.318 | 0.927 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Üneş, F.; Demirci, M.; Zelenakova, M.; Çalışıcı, M.; Taşar, B.; Vranay, F.; Kaya, Y.Z. River Flow Estimation Using Artificial Intelligence and Fuzzy Techniques. Water 2020, 12, 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092427
Üneş F, Demirci M, Zelenakova M, Çalışıcı M, Taşar B, Vranay F, Kaya YZ. River Flow Estimation Using Artificial Intelligence and Fuzzy Techniques. Water. 2020; 12(9):2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092427
Chicago/Turabian StyleÜneş, Fatih, Mustafa Demirci, Martina Zelenakova, Mustafa Çalışıcı, Bestami Taşar, František Vranay, and Yunus Ziya Kaya. 2020. "River Flow Estimation Using Artificial Intelligence and Fuzzy Techniques" Water 12, no. 9: 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092427
APA StyleÜneş, F., Demirci, M., Zelenakova, M., Çalışıcı, M., Taşar, B., Vranay, F., & Kaya, Y. Z. (2020). River Flow Estimation Using Artificial Intelligence and Fuzzy Techniques. Water, 12(9), 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092427






