Remote Retrieval of Suspended Particulate Matter in Inland Waters: Image-Based or Physical Atmospheric Correction Models?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
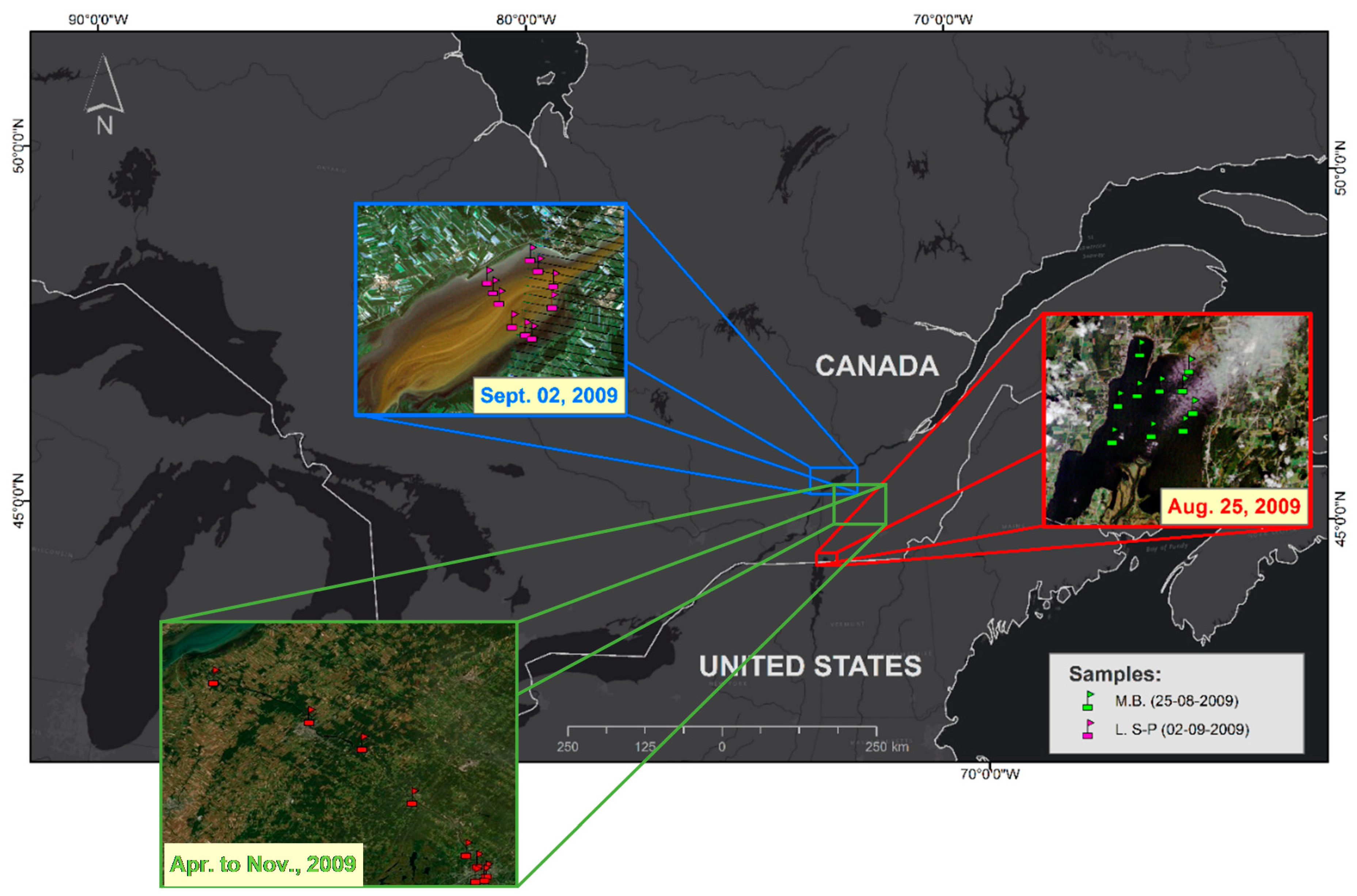
2.1. Calibration and Cross-Validation Database
2.2. Validation Test Database
2.3. Image Pre-Processing
2.3.1. Atmospheric Correction for Flat Terrain (ATCOR)
2.3.2. Fast Line-of-Sight Atmospheric Analysis of Spectral Hypercubes (FLAASH)
2.3.3. ACOLITE
2.3.4. Apparent Reflectance at the Top of Atmosphere (ToA)
2.3.5. Dark Object Subtraction (DOS)
2.3.6. Cosine of the Sun Zenith Angle (COST)
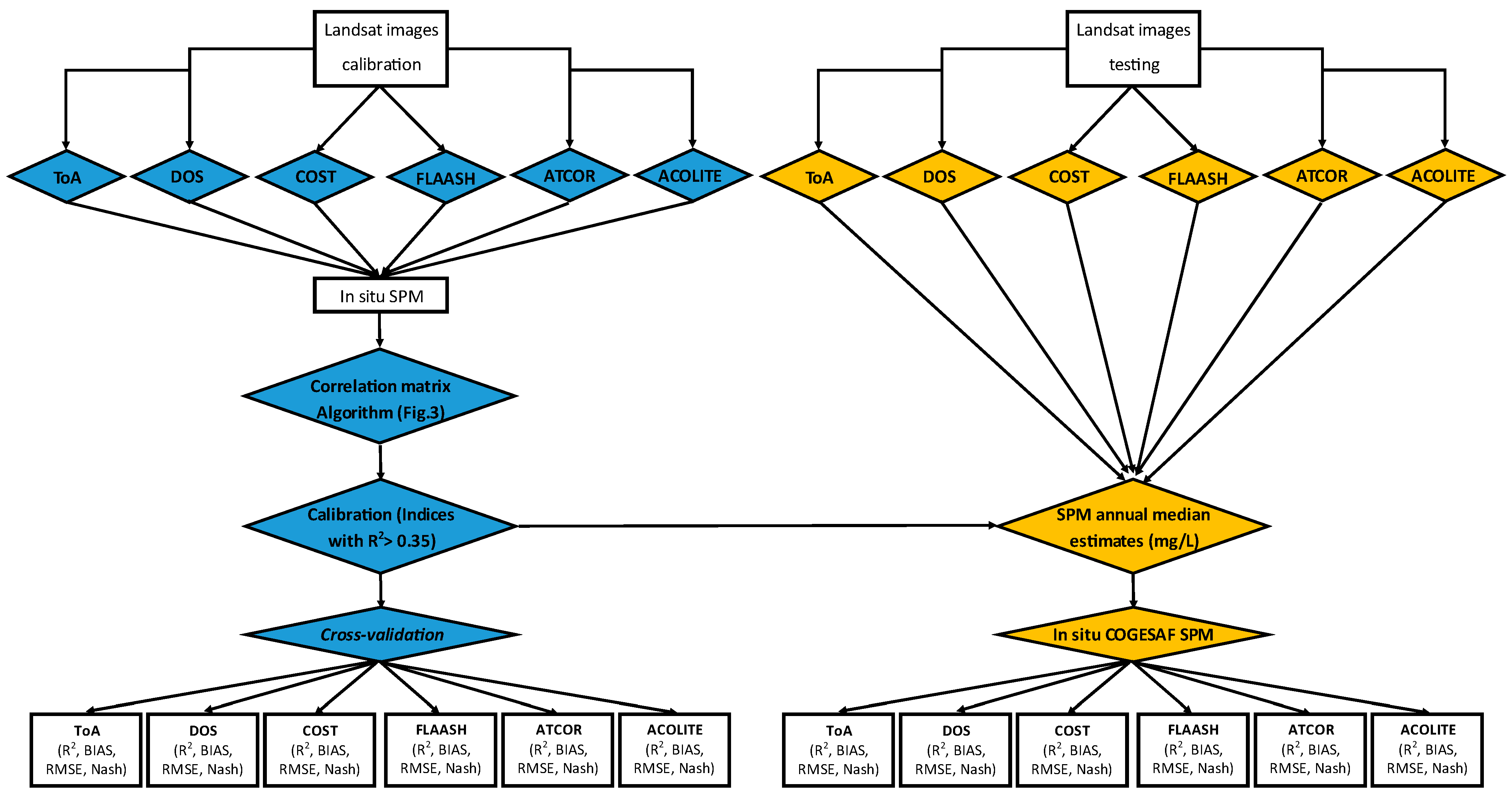
2.4. Methodological Approach and Evaluation Indices
3. Results
3.1. Spectral Analysis
3.2. Modeling of Suspended Particulate Matter
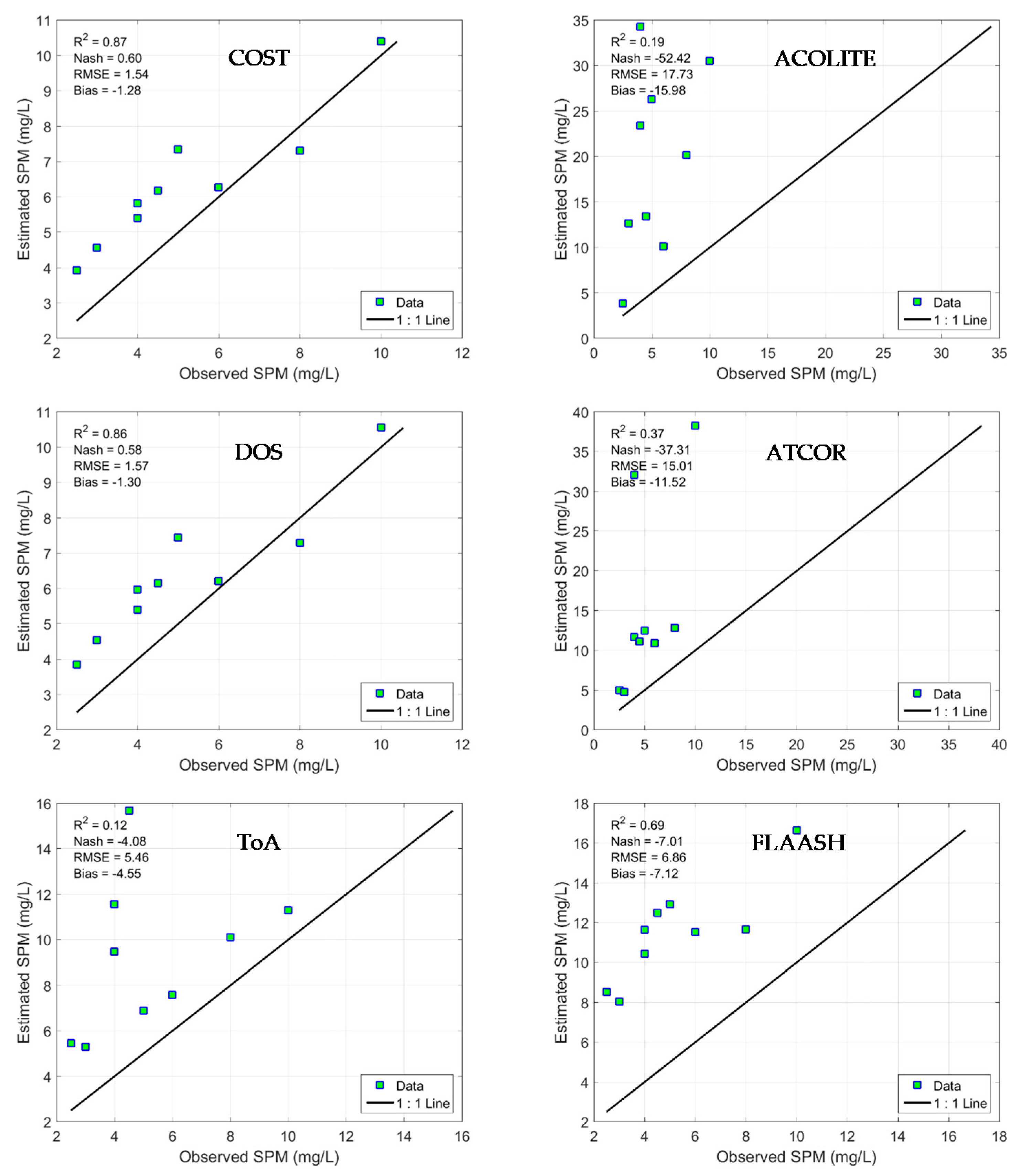
3.2.1. Calibration of the Models
3.2.2. Cross-Validation of the SPM Modeling
3.2.3. Evaluation of the SPM Modeling with the Blind Test Validation Data
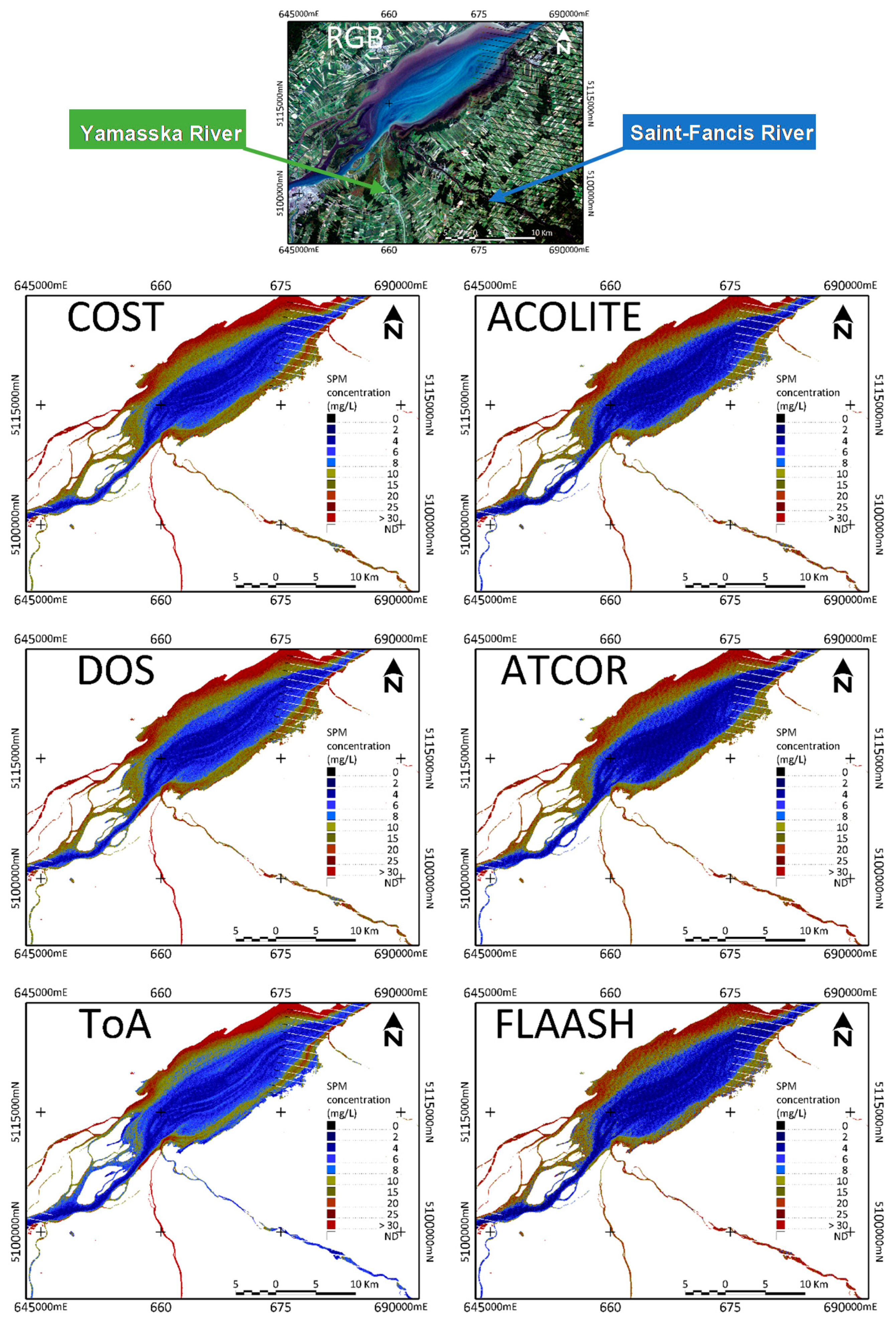
3.2.4. Spatial Distribution Assessment of the SPM
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Håkanson, L.; Eckhéll, J. Suspended particulate matter (SPM) in the Baltic Sea—New empirical data and models. Ecol. Model. 2005, 189, 130–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Duan, H.; Yu, S.; Shen, M.; Xue, K. Human-induced eutrophication dominates the bio-optical compositions of suspended particles in shallow lakes: Implications for remote sensing. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 667, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houma, F.B. Modélisation et Cartographie de la Pollution Marine et de La Bathymétrie à Partir de L’imagerie Satellitaire. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris-Est, Créteil, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Shi, T.; Hu, S.; Wu, G.; Zhou, Q. Application of Sentinel 2 MSI Images to Retrieve Suspended Particulate Matter Concentrations in Poyang Lake. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robert, E.; Kergoat, L.; Soumaguel, N.; Merlet, S.; Martinez, J.-M.; Diawara, M.; Grippa, M. Analysis of Suspended Particulate Matter and Its Drivers in Sahelian Ponds and Lakes by Remote Sensing (Landsat and MODIS): Gourma Region, Mali. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giani, A.; Bird, D.F.; Prairie, Y.; Lawrence, J.F. Empirical study of cyanobacterial toxicity along a trophic gradient of lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 2100–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.W. An Overview of Toxic Cyanobacteria Research in the United States: Toxic Cyanobacteria: Current Status of Research and Management; Australian Centre for Water Quality Research: Salisbury, Australia, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Chorus, I.; Bartram, J. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water. A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; E & FN Spon, for World Health Organization, Routledge: London, UK, 1999; p. 416. [Google Scholar]
- Svrcek, C.; Smith, D.W. Cyanobacteria toxins and the current state of knowledge on water treatment options: A review. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2004, 3, 155–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Quan, W.; Cui, T.; Song, Q. Estimation of total suspended matter concentration from MODIS data using a neural network model in the China eastern coastal zone. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 155, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxaran, D.; Froidefond, J.-M.; Lavender, S.; Castaing, P. Spectral signature of highly turbid waters: Application with SPOT data to quantify suspended particulate matter concentrations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topliss, B.; Almos, C.; Hill, P. Algorithms for remote sensing of high concentration, inorganic suspended sediment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1990, 11, 947–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Dong, Q.; Cui, T.; Xue, C.; Zhang, S. Suspended sediment monitoring and assessment for Yellow River estuary from Landsat TM and ETM+ imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 146, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.F.; Aiken, J.; Lavender, S.J. The atmospheric correction of water colour and the quantitative retrieval of suspended particulate matter in Case II waters: Application to MERIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1713–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick, K.G.; Ovidio, F.; Rijkeboer, M. Atmospheric correction of SeaWiFS imagery for turbid coastal and inland waters. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shang, P.; Shen, F. Atmospheric Correction of Satellite GF-1/WFV Imagery and Quantitative Estimation of Suspended Particulate Matter in the Yangtze Estuary. Sensors 2016, 16, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Li, D.; Wang, D.; Liu, W.; Yang, J. A Landsat-based model for retrieving total suspended solids concentration of estuaries and coasts in China. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 4347–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pahlevan, N.; Lee, Z.; Wei, J.; Schaaf, C.; Schott, J.R.; Berk, A. On-orbit radiometric characterization of OLI (Landsat-8) for applications in aquatic remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. A Comprehensive Review on Water Quality Parameters Estimation Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Sensors 2016, 16, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, D.; Schluchter, W.M. A Novel Algorithm for Predicting Phycocyanin Concentrations in Cyanobacteria: A Proximal Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Approach. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 758–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, H. Influence of atmospheric correction on the estimation of biophysical parameters of crop canopy using satellite remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1245–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, J. Evaluation of Atmospheric Aerosol Particle Size Distribution from Scattering Measurements in the Visible and Infrared. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1961, 51, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabins, F.F., Jr. Remote Sensing-Principles and Interpretation; WH Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, R.; Malila, W.; Nalepka, R. Importance of atmospheric scattering in remote sensing, or everything you’ve always wanted to know about atmospheric scattering but were afraid to ask. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 17–21 May 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, A.; Bélanger, S. Improved detection of turbid waters from ocean color sensors information. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavender, S.; Pinkerton, M.; Moore, G.; Aiken, J.; Blondeau-Patissier, D. Modification to the atmospheric correction of SeaWiFS ocean colour images over turbid waters. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Advantages of high quality SWIR bands for ocean colour processing: Examples from Landsat-8. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 161, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richter, R. Correction of atmospheric and topographic effects for high spatial resolution satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, R. Atmospheric correction of satellite data with haze removal including a haze/clear transition region. Comput. Geosci. 1996, 22, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.P.; Felde, G.W.; Hoke, M.L.; Ratkowski, A.J.; Cooley, T.W.; Chetwynd, J.J.H.; Gardner, J.A.; Adler-Golden, S.M.; Matthew, M.W.; Berk, A.; et al. MODTRAN4-based atmospheric correction algorithm: FLAASH (Fast Line-of-sight Atmospheric Analysis of Spectral Hypercubes). In Algorithms and Technologies for Multispectral, Hyperspectral, and Ultraspectral Imagery VIII; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kotchenova, S.Y.; Vermote, E.F.; Matarrese, R.; Klemm, J.F.J. Validation of a vector version of the 6S radiative transfer code for atmospheric correction of satellite data Part I: Path radiance. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 6762–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moran, M.; Jackson, R.D.; Slater, P.N.; Teillet, P.M. Evaluation of simplified procedures for retrieval of land surface reflectance factors from satellite sensor output. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 41, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, P.S., Jr. An Improved Dark-Object Subtraction Technique for Atmospheric Scattering Correction of Multispectral data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 24, 459–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, P.S. Image-based atmospheric corrections-revisited and improved. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1996, 62, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Laliberté, D. La Qualité de L’eau des Rivières Richelieu et Yamaska; Ministère de L’Environnement et de la Lutte contre les Changements Climatiques, Ed.; Gouvernement du Québec: Montréal, QC, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- OBVY. Diagnostic du Bassin Versant de la Rivière Yamaska; OBVY, Ed.; Regroupement des Organismes de Bassins Verssants du Québec: Québec, QC, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- COGESAF. Outil de Cartographie Dynamique du Conseil de Gouvernance de L’eau des Bassins Versants de la Rivière Saint-François. 2003–2018. Available online: http://cogesaf.sigmont.org/cogesaf/cogesaf.php (accessed on 28 January 2020).
- Caron, S.; Lucotte, M.; Teisserenc, R. Mercury transfer from watersheds to aquatic environments following the erosion of agrarian soils: A molecular biomarker approach. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 88, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nazeer, M.; Nichol, J.E.; Yung, Y.-K. Evaluation of atmospheric correction models and Landsat surface reflectance product in an urban coastal environment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6271–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahru, M.; Mitchell, B.G.; Diaz, A.; Miura, M. MODIS detects a devastating algal bloom in Paracas Bay, Peru. Eos 2004, 85, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toming, K.; Kutser, T.; Laas, A.; Sepp, M.; Paavel, B.; Nõges, T. First Experiences in Mapping Lake Water Quality Parameters with Sentinel-2 MSI Imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M. Retrieval of water-leaving radiance and aerosol optical thickness over the oceans with SeaWiFS: A preliminary algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Parameters | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M.B. Mean ± Std (min–max) | St-P. Mean ±Std (min–max) | M.B. Mean ± Std (min–max) | St-P. Mean ± Std (min–max) | M.B. Mean ± Std (min–max) | St-P. Mean ± Std (min–max) | |
| SPM (mg/L) | 3.94 ± 2.12 (2.10–9.30) | – | 4.77 ± 2.15 (1.60–12.30) | 10.75 ± 8.22 (2.80–40.20) | 13.12 ± 9.17 (7.80–51.20) | – |
| chl_a (µg/L) | 7.80 ± 6.68 (3.30–26.41) | – | 13.28 ± 8.51 (5.00–51.05) | 6.16 ± 10.43 (1.47–63.71) | 23.65 ± 7.88 (4.37–34.21) | – |
| DOC (mg C/L) | 4.72 ± 0.61 (4.38–6.61) | – | 4.77 ± 0.20 (4.40–5.12) | 4.69 ± 1.61 (2.46–7.43) | 6.91 ± 0.68 (5.40–8.53) | – |
| TOC (mg C/L) | – | – | 4.88 ± 0.19 (4.45–5.40) | 4.80 ± 1.68 (2.57–7.96) | 7.43 ± 0.65 (5.66–8.61) | – |
| TN (mg N/L) | – | – | – | – | 0.84 ± 0.18 (0.55–1.51) | – |
| TP (mn P/L) | – | – | 0.05 ± 0.01 (0.03–0.07) | 0.03 ± 0.03 (0.01–0.08) | 0.07 ± 0.01 (0.05–0.09) | – |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Alem, A.; Lhissou, R.; Chokmani, K.; Oubennaceur, K. Remote Retrieval of Suspended Particulate Matter in Inland Waters: Image-Based or Physical Atmospheric Correction Models? Water 2021, 13, 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162149
El Alem A, Lhissou R, Chokmani K, Oubennaceur K. Remote Retrieval of Suspended Particulate Matter in Inland Waters: Image-Based or Physical Atmospheric Correction Models? Water. 2021; 13(16):2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162149
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Alem, Anas, Rachid Lhissou, Karem Chokmani, and Khalid Oubennaceur. 2021. "Remote Retrieval of Suspended Particulate Matter in Inland Waters: Image-Based or Physical Atmospheric Correction Models?" Water 13, no. 16: 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162149
APA StyleEl Alem, A., Lhissou, R., Chokmani, K., & Oubennaceur, K. (2021). Remote Retrieval of Suspended Particulate Matter in Inland Waters: Image-Based or Physical Atmospheric Correction Models? Water, 13(16), 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162149








