Dynamics of the Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum in the Taiwan Strait and Its Linkages to Surrounding Populations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Treatment
2.2. PCR Amplifications and Sequencing
2.3. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Extraction of DNA
2.5. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
2.6. Growth Experiment
2.7. Analysis of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Identification of A. pacificum
3.2. Assessment of the DNA Extraction Procedure
3.3. Assessment of the qPCR Assay
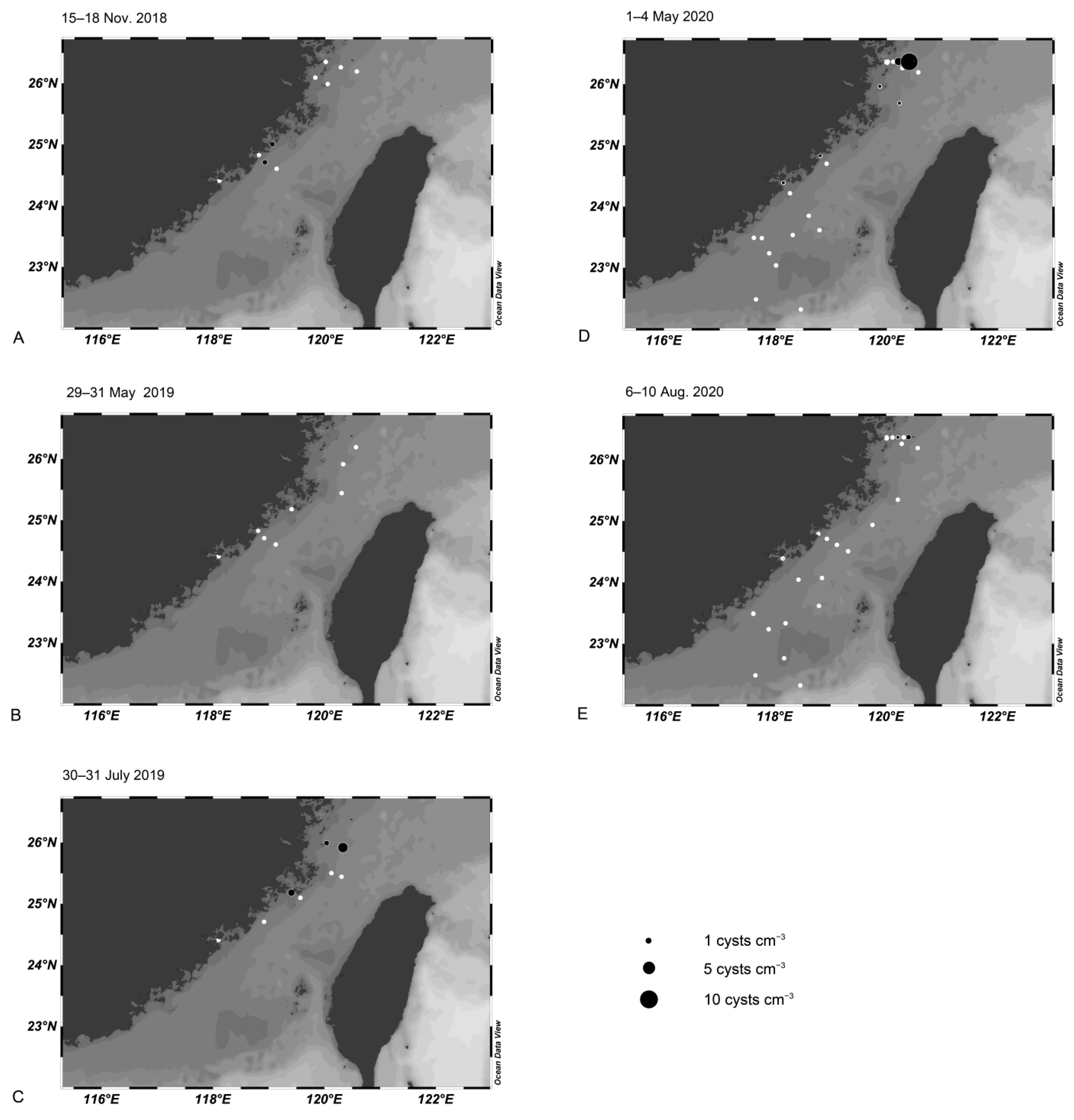
3.4. Cyst Dynamics in the Taiwan Strait
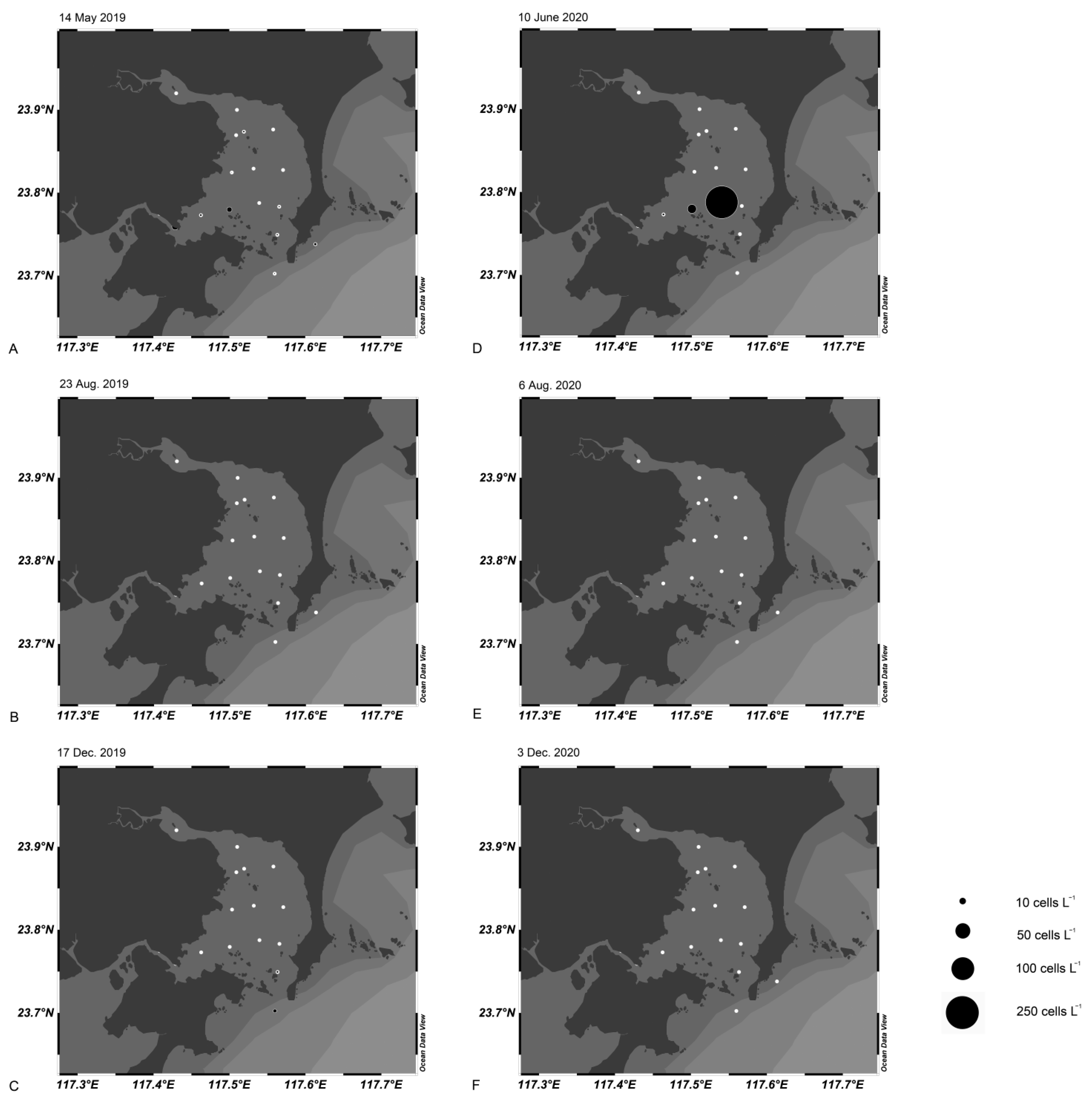
3.5. Cell Dynamics in the Taiwan Strait Using qPCR
3.6. Cell Dynamics in Dongshan Bay and Xiamen Bay Using qPCR
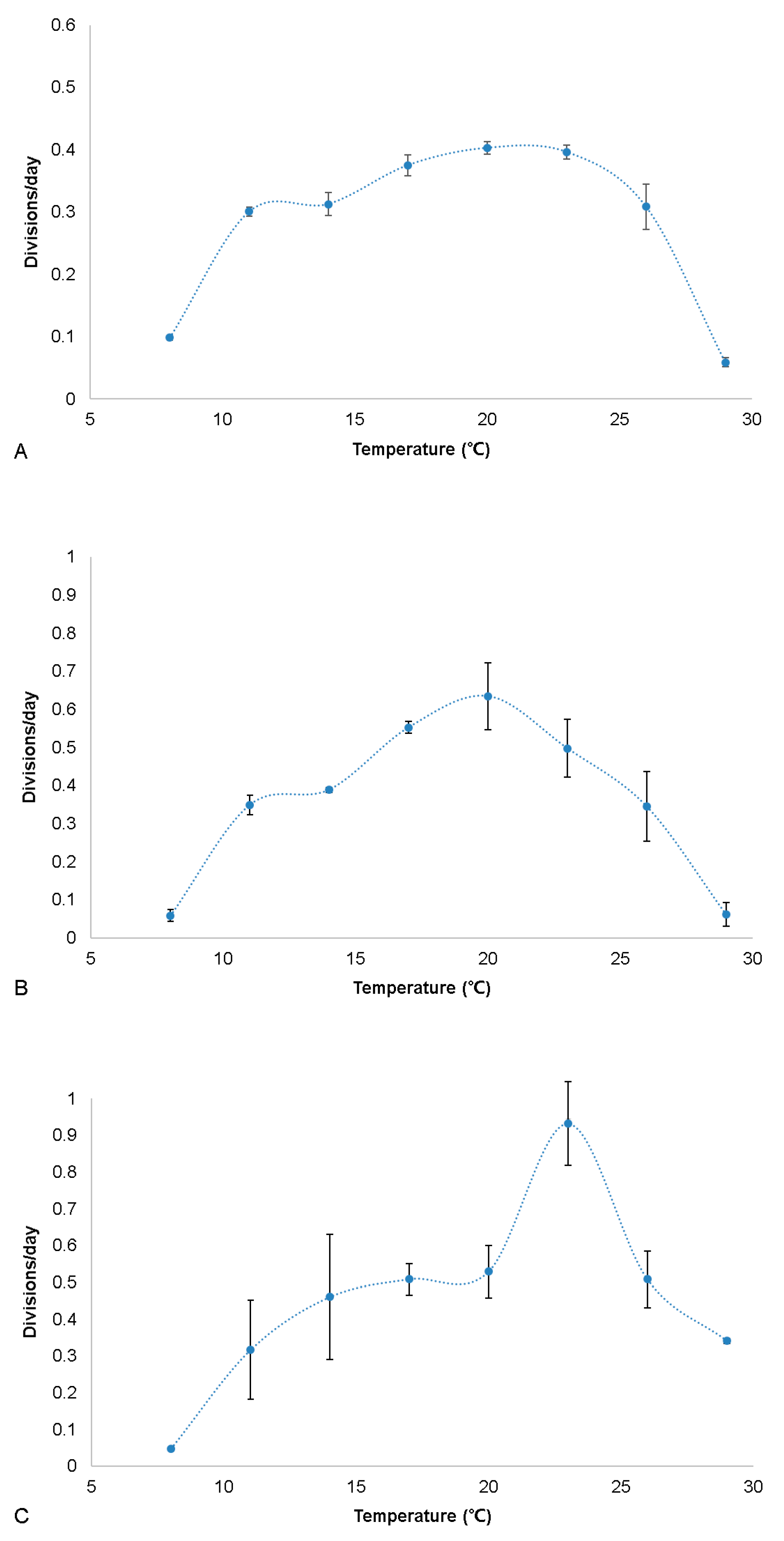
3.7. Growth Experiments
3.8. Toxin Profiles
3.9. Environmental Parameters in the Taiwan Strait in May 2019 and 2020
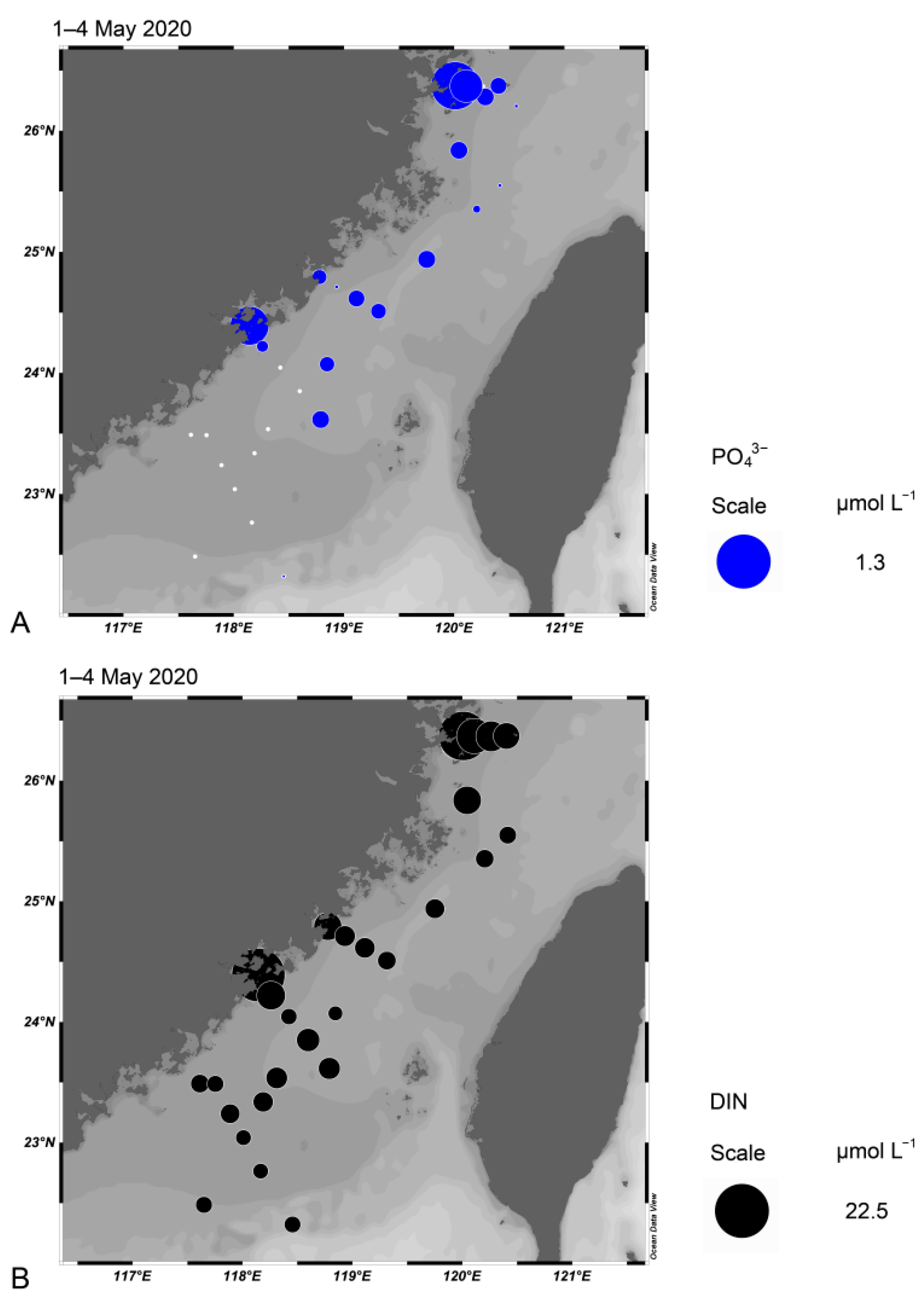
3.10. Nutrient Concentrations in the Taiwan Strait in May 2020
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of A. pacificum Cells in the Taiwan Strait and Surrounding Waters
4.2. Possible Origins of A. pacificum Blooms in the Taiwan Strait
4.3. Identifying Populations Based on Physiological Differentiation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, S.A.; Ruvindy, R.; Kohli, G.S.; Anderson, D.M.; Brosnahan, M.L. Evaluation of sxtA and rDNA qPCR assays through monitoring of an inshore bloom of Alexandrium catenella Group 1. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, U.; Litaker, R.W.; Montresor, M.; Murray, S.A.; Brosnahan, M.; Anderson, D.M. Formal Revision of the Alexandrium tamarense Species Complex (Dinophyceae) Taxonomy: The Introduction of Five Species with Emphasis on Molecular-based (rDNA) Classification. Protist 2014, 165, 779–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hallegraeff, G.M.; Bolch, C.J.S.; Condie, S.; Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Murray, S.A.; Quinlan, R.; Ruvindy, R.; Turnbull, A.; Ugalde, S.; Wilson, K. Unprecedented Alexandrium blooms in a previously low biotoxin risk area of Tasmania, Australia. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Florianopolis, Brasil, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Natsuike, M.; Yokoyama, K.; Nishitani, G.; Yamada, Y.; Yoshinaga, I.; Ishikawa, A. Germination fluctuation of toxic Alexandrium fundyense and A. pacificum cysts and the relationship with bloom occurrences in Kesennuma Bay, Japan. Harmful Algae 2017, 62, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.H.; Li, Z.; Kim, E.S.; Park, J.-W.; Lim, W.A. Which species, Alexandrium catenella (Group I) or A. pacificum (Group IV), is really responsible for past paralytic shellfish poisoning outbreaks in Jinhae-Masan Bay, Korea? Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Zeng, N.; Liu, T.; Yang, W.; Müller, A.; Krock, B. Morphology, toxicity, and phylogeny of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) species along the coast of China. Harmful Algae 2013, 27, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yu, R.-C.; Chen, J.-H.; Zhang, Q.-C.; Kong, F.-Z.; Zhou, M.-J. Distribution of Alexandrium fundyense and A. pacificum (Dinophyceae) in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 96, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovesi, B.; Laabir, M.; Masseret, E.; Collos, Y.; Vaquer, A.; Grzebyk, D. Dormancy and germination features in resting cysts of Alexandrium tamarense species complex (Dinophyceae) can facilitate bloom formation in a shallow lagoon (Thau, southern France). J. Plankton Res. 2009, 31, 1209–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laabir, M.; Collos, Y.; Masseret, E.; Grzebyk, D.; Abadie, E.; Savar, V.; Sibat, M.; Amzil, Z. Influence of Environmental Factors on the Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Content and Profile of Alexandrium catenella (Dinophyceae) Isolated from the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1583–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hallegraeff, G. Transport of toxic dinoflagellates via ships’ ballast water:bioeconomic risk assessment and efficacy of possible ballast water management strategies. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 168, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, D.M. Physiology and bloom dynamics of toxic Alexandrium species, with emphasis on life cycle transitions. Nato Asi Ser. G Ecol. Sci. 1998, 41, 29–48. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.M.; Keafer, B.A.; Kleindinst, J.L.; McGillicuddy, D.; Martin, J.L.; Norton, K.; Pilskaln, C.H.; Smith, J.L.; Sherwood, C.R.; Butman, B. Alexandrium fundyense cysts in the Gulf of Maine: Long-term time series of abundance and distribution, and linkages to past and future blooms. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2014, 103, 6–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, H.; Lan, D.; Fang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Cai, F. Distribution and germination of Alexandrium sp. cysts in coastal areas of Southeast China Sea. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 14, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H.F.; Fang, Q.; Li, R.X.; Lan, D.Z.; Zhu, M.Y. Preliminary study on dinoflagellate cysts in changjiang river estuary. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2004, 35, 413–423. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Geng, H.-X.; Yu, R.-C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.-Y.; Wang, J.-X.; Zhang, Q.-C.; Kong, F.-Z.; Zhou, M.-J. Distribution of Alexandrium pacificum cysts in the area adjacent to the Changjiang River estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Matsuoka, K.; Qi, Y.; Chen, J.; Lü, S. Dinoflagellate cyst records in recent sediments from Daya Bay, South China Sea. Phycol. Res. 2004, 52, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovesi, B.; Mouillot, D.; Laugier, T.; Fiandrino, A.; Laabir, M.; Vaquer, A.; Grzebyk, D. Influences of sedimentation and hydrodynamics on the spatial distribution of Alexandrium catenella/tamarense resting cysts in a shellfish farming lagoon impacted by toxic blooms. Harmful Algae 2013, 25, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertouna-Bellakhal, M.; Dhib, A.; Fathalli, A.; Bellakhal, M.; Chomérat, N.; Masseret, E.; Laabir, M.; Turki, S.; Aleya, L. Alexandrium pacificum Litaker sp. nov (Group IV): Resting cyst distribution and toxin profile of vegetative cells in Bizerte Lagoon (Tunisia, Southern Mediterranean Sea). Harmful Algae 2015, 48, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, T.-J.; Wu, F.; Zhang, F. Seasonal dynamics of Alexandrium tamarense and occurrence of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in bivalves in Nanji Islands, East China Sea. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 65, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.D.; Xu, N.; Lu, S.H.; Wang, Z.H. Dynamics of Alexandrium population and environmental factors in Daya Bay, the South China Sea. Ecol. Sci. 2006, 25, 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zou, J.; Lu, S.; Zhang, L. Identifying the Source Organisms Producing Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in a Subtropical Bay in the South China Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3124–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laabir, M.; Jauzein, C.; Genovesi, B.; Masseret, E.; Grzebyk, D.; Cecchi, P.; Vaquer, A.; Perrin, Y.; Collos, Y. Influence of temperature, salinity and irradiance on the growth and cell yield of the harmful red tide dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella colonizing Mediterranean waters. J. Plankton Res. 2011, 33, 1550–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-J.; Park, J.-A.; Kwon, H.-K.; Yang, H.-S.; Lim, W.-A. Ecophysiological Studies on the Population Dynamics of Two Toxic Dinoflagellates Alexandrium tamarense and Alexandrium catenella Isolated from the Southern Coast of Korea—I. Effects of Temperature and Salinity on the Growth. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Environ. Energy 2012, 15, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Kulis, D.M.; Qi, Y.-Z.; Zheng, L.; Lu, S.; Lin, Y.-T. Paralytic shellfish poisoning in Southern China. Toxicon 1996, 34, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Z.; Jiang, T.J.; Hsieh, D.P. Toxin composition variations in cultures of Alexandrium species isolated from the coastal waters of southern China. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Z.; Zhang, S.G.; Gu, H.F.; Chan, L.L.; Hong, H.S. Paralytic shellfish toxin profiles and toxin variability of the genus Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) isolated from the Southeast China Sea. Toxicon 2006, 48, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, A.; Ajani, P.A.; Ruvindy, R.; Farrell, H.; Zammit, A.; Brett, S.; Hill, D.; Sarowar, C.; Hoppenrath, M.; Murray, S.A. First Detection of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins from Alexandrium pacificum above the Regulatory Limit in Blue Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) in New South Wales, Australia. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-J.; Kim, C.-H.; Sako, Y. Paralytic shellfish poisoning toxin analysis of the genus Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) occurring in Korean coastal waters. Fish. Sci. 2005, 71, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Lee, H.; Anderson, D.M.; Kim, B. Paralytic shellfish toxin production by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum (Chinhae Bay, Korea) in axenic, nutrient-limited chemostat cultures and nutrient-enriched batch cultures. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hadjadji, I.; Laabir, M.; Frihi, H.; Collos, Y.; Shao, Z.J.; Berrebi, P.; Abadie, E.; Amzil, Z.; Chomérat, N.; Rolland, J.L.; et al. Unsuspected intraspecific variability in the toxin production, growth and morphology of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum R.W. Litaker (Group IV) blooming in a South Western Mediterranean marine ecosystem, Annaba Bay (Algeria). Toxicon 2020, 180, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D.; Sullivan, J.J.; Boyer, G.L.; Taylor, F.; Andersen, R.J. Variation in paralytic shellfish toxin composition within the Protogonyaulax tamarensis/catenella species complex; red tide dinoflagellates. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1987, 15, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Yu, R.C.; Lu, D.D.; Lü, S.H.; Zhu, D.D.; Zhang, C.S.; Yan, T.; Zhang, Q.C.; Zhou, M.J. Recurrent toxic blooms of Alexandrium spp. in the East China Sea-potential role of Taiwan Warm Current in bloom Initiation. J. Ecol. Toxicol. 2018, 2, 115. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.Y. Assessment of quality of mariculture shellfish in the middle east of Fujian coast. J. Fish. Res. 2020, 42, 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Bolch, C.J.S. The use of sodium polytungstate for the separation and concentration of living dinoflagellate cysts from marine sediments. Phycologia 1997, 36, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, R.R.L.; Ryther, J.H. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms: I Cyclotella nana hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (cleve) Gran. Can. J. Microbiol. 1962, 8, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Gu, H.; Krock, B.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y. Toxic dinoflagellate blooms of Gymnodinium catenatum and their cysts in Taiwan Strait and their relationship to global populations. Harmful Algae 2020, 97, 101868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, T. BioEdit: A User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D. jModelTest: Phylogenetic Model Averaging. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML-VI-HPC: Maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2688–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boc, A.; Diallo, A.B.; Makarenkov, V. T-REX: A web server for inferring, validating and visualizing phylogenetic trees and networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W573–W579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hariganeya, N.; Tanimoto, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Nishimura, T.; Tawong, W.; Sakanari, H.; Yoshimatsu, T.; Sato, S.; Preston, C.M.; Adachi, M. Quantitative PCR Method for Enumeration of Cells of Cryptic Species of the Toxic Marine Dinoflagellate Ostreopsis spp. in Coastal Waters of Japan. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kon, N.F.; Teng, S.T.; Hii, K.S.; Yek, L.H.; Mujahid, A.; Lim, H.C.; Lim, P.T.; Leaw, C.P. Spatial distribution of toxic Alexandrium tamiyavanichii (Dinophyceae) in the southeastern South China Sea-Sulu Sea: A molecular-based assessment using real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) assay. Harmful Algae 2015, 50, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Ye, R.-M.; Zheng, J.W.; Luo, Z.H.; Gu, H.F.; Yang, W.D.; Li, H.Y.; Liu, J.S. Molecular phylogeny and PSP toxin profile of the Alexandrium tamarense species complex along the coast of China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 89, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, R.R.L. Division rates. In Handbook of Phycological Methods: Culture Methods and Growth Measurements; Stein, J.R., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1973; pp. 289–311. [Google Scholar]
- Schlitzer, R. Ocean Data View. Available online: http://odvawide (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Song, X.K.; Ma, J.X.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, L.J.; Ma, Y.Q.; Ren, L.H.; Tang, X.C. Evolution and formation of Alexandrium tamarense red tide in the sea area of the Nanhuangcheng Island. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2009, 30, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhao, D.; Syvitski, J.P.; Saito, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, M. Anthropogenic impacts on the decreasing sediment loads of nine major rivers in China, 1954–2015. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 739, 139653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, D.W.; Pettigrew, N.R.; Thomas, A.C. Offshore blooms of the red tide dinoflagellate, Alexandrium sp., in the Gulf of Maine. Cont. Shelf Res. 2001, 21, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, R.C.; Loder, T.C.; Keafer, B.A. Nutrient conditions during Alexandrium fundyense blooms in the western Gulf of Maine, USA. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2005, 52, 2450–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M. Bloom dynamics of toxic Alexandrium species in the northeastern U.S. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Kawamura, H.; Li, C.; Hong, H.; Jiang, Y. Review on current and seawater volume transport through the Taiwan Strait. J. Oceanogr. 2010, 66, 591–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anglès, S.; Garcés, E.; Reñé, A.; Sampedro, N. Life-cycle alternations in Alexandrium minutum natural populations from the NW Mediterranean Sea. Harmful Algae 2012, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.O.; Choi, J.; Baek, S.H.; Lee, M.; Oh, H.-M. Tracking Alexandrium catenella from seed-bed to bloom on the southern coast of Korea. Harmful Algae 2020, 99, 101922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, M.; Garcés, E.; Masò, M.; Camp, J. Is the distribution of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella expanding along the NW Mediterranean coast? Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 222, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, E.L.; Kulis, D.M.; Gentien, P.; Anderson, D.M. Paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in France linked to a human-introduced strain of Alexandrium catenella from the western Pacific: Evidence from DNA and toxin analysis. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genovesi, B.; Berrebi, P.; Nagai, S.; Reynaud, N.; Wang, J.; Masseret, E. Geographic structure evidenced in the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum Litaker (A. catenella—Group IV (Whedon & Kofoid) Balech) along Japanese and Chinese coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 98, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Yu, R.C.; Geng, H.X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.C.; Kong, F.Z.; Chen, Z.F.; Zhao, J.Y.; Zhou, M.J. Resting cysts of Alexandrium catenella and A. pacificum (Dinophyceae) in the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China: Abundance, distribution and implications for toxic algal blooms. Harmful Algae 2020, 93, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellmann, R.; Mihali, T.K.; Jeon, Y.J.; Pickford, R.; Pomati, F.; Neilan, B.A. Biosynthetic Intermediate Analysis and Functional Homology Reveal a Saxitoxin Gene Cluster in Cyanobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 4044–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Guo, R.; Lim, W.A.; Allen, A.E.; Ki, J.S. Comparative transcriptomics of toxin synthesis genes between the non-toxin producing dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides and toxigenic Alexandrium pacificum. Harmful Algae 2020, 93, 101777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Sako, Y.; Uchida, A.; Kakutani, T.; Arakawa, O.; Noguchi, T.; Ishida, Y. Purification and characterization of sulfotransferase specific to O-22 of 11-hydroxy saxitoxin from the toxic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum (dinophyceae). Fish. Sci. 2002, 68, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Alpermann, T.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Collos, Y.; Masseret, E.; Montresor, M. The globally distributed genus Alexandrium: Multifaceted roles in marine ecosystems and impacts on human health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 10–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.W.; Wang, H.S.; Han, G.D.; Ke, C.H.; Zhan, X.; Nakano, T.; Williams, G.A. The Impact of Yangtze River Discharge, Ocean Currents and Historical Events on the Biogeographic Pattern of Cellana toreuma along the China Coast. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacKenzie, L.; de Salas, M.; Adamson, J.; Beuzenberg, V. The dinoflagellate genus Alexandrium (Halim) in New Zealand coastal waters: Comparative morphology, toxicity and molecular genetics. Harmful Algae 2004, 3, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




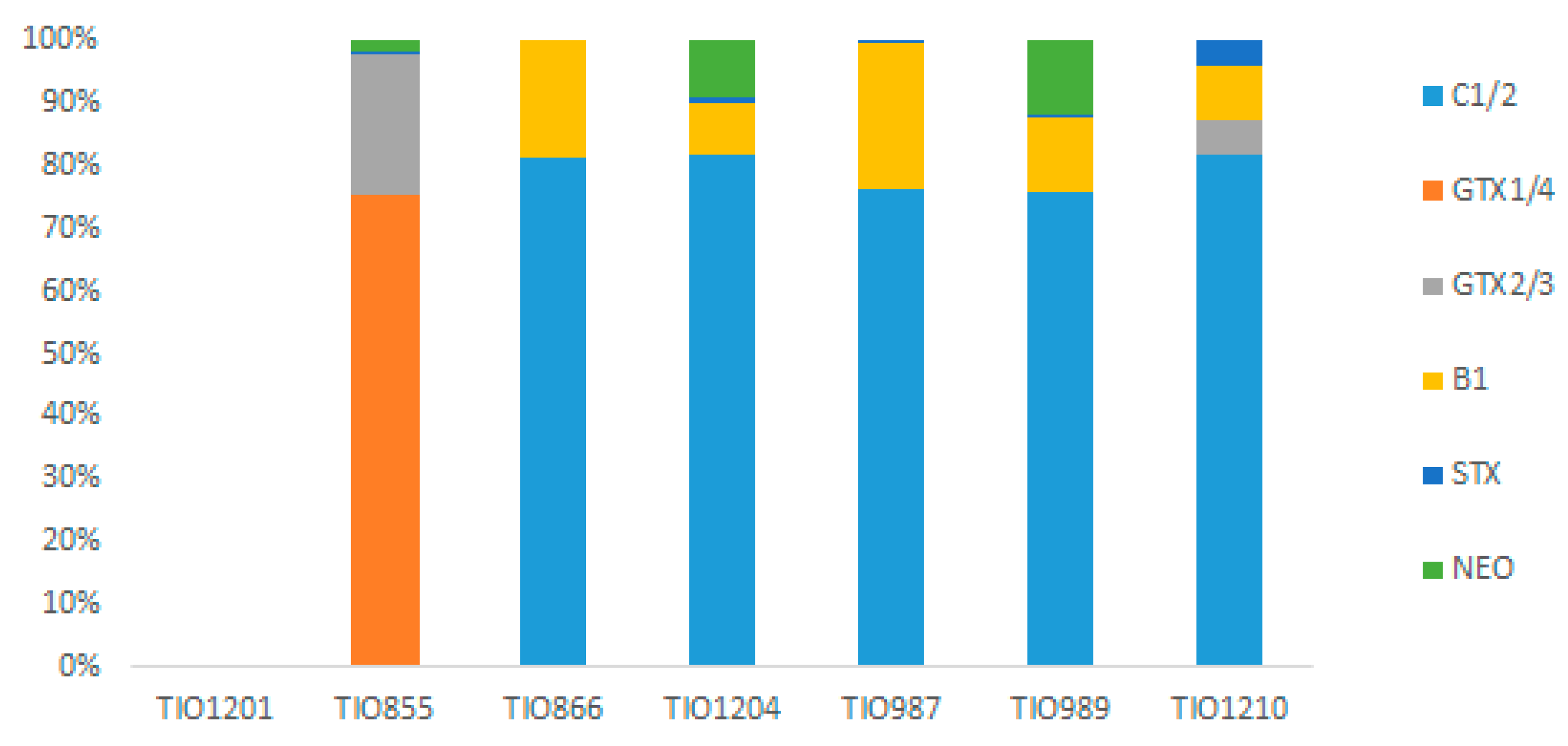

| Strains | Location | Latitude | Longitude | Collection Time | Origin | Toxin | Growth Experiment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIO855 | Yantai, Yellow Sea | 37°29.28′ N | 121°37.24′ E | 3 September 2016 | Cell | Present | Yes |
| TIO1201 | Qingdao, Yellow Sea | 36°0.15′ N | 120°21.27′ E | 29 September 2017 | Cyst | None | No |
| TIO1204 | Taiwan Strait | 25°57.90′ N | 119°52.10′ E | 16 November 2018 | Cyst | Present | No |
| TIO1205 | Taiwan Strait | 25°57.90′ N | 119°52.10′ E | 16 November 2018 | Cyst | NA | No |
| TIO1208 | Taiwan Strait | 25°57.90′ N | 119°52.10′ E | 16 November 2018 | Cyst | NA | No |
| TIO987 | Pingtan, Taiwan Strait | 25°38.04′ N | 119°48.97′ E | 16 April 2020 | Cell | Present | No |
| TIO989 | Pingtan, Taiwan Strait | 25°38.04′ N | 119°48.97′ E | 16 April 2020 | Cell | Present | No |
| ATDH46 | East China Sea | 27°35.24′ N | 122°7.65′ E | 6 August 2009 | Cyst | NA | Yes |
| TIO866 | Beihai, South China Sea | 21°0.64′ N | 109°6.05′ E | 11 April 2017 | Cyst | Present | Yes |
| TIO1210 | New Zealand | 41°16.04′ S | 174°12.14′ E | 8 February 2018 | Cyst | Present | No |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Zheng, J.; Krock, B.; Ding, G.; MacKenzie, L.; Smith, K.F.; Gu, H. Dynamics of the Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum in the Taiwan Strait and Its Linkages to Surrounding Populations. Water 2021, 13, 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192681
Liu M, Zheng J, Krock B, Ding G, MacKenzie L, Smith KF, Gu H. Dynamics of the Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum in the Taiwan Strait and Its Linkages to Surrounding Populations. Water. 2021; 13(19):2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192681
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Minlu, Jing Zheng, Bernd Krock, Guangmao Ding, Lincoln MacKenzie, Kirsty F. Smith, and Haifeng Gu. 2021. "Dynamics of the Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum in the Taiwan Strait and Its Linkages to Surrounding Populations" Water 13, no. 19: 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192681
APA StyleLiu, M., Zheng, J., Krock, B., Ding, G., MacKenzie, L., Smith, K. F., & Gu, H. (2021). Dynamics of the Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum in the Taiwan Strait and Its Linkages to Surrounding Populations. Water, 13(19), 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192681







