Water, Soil, and Plants Interactions in a Threatened Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Water and Soil—Valuable Natural Resources
2.1. Water in the Environment
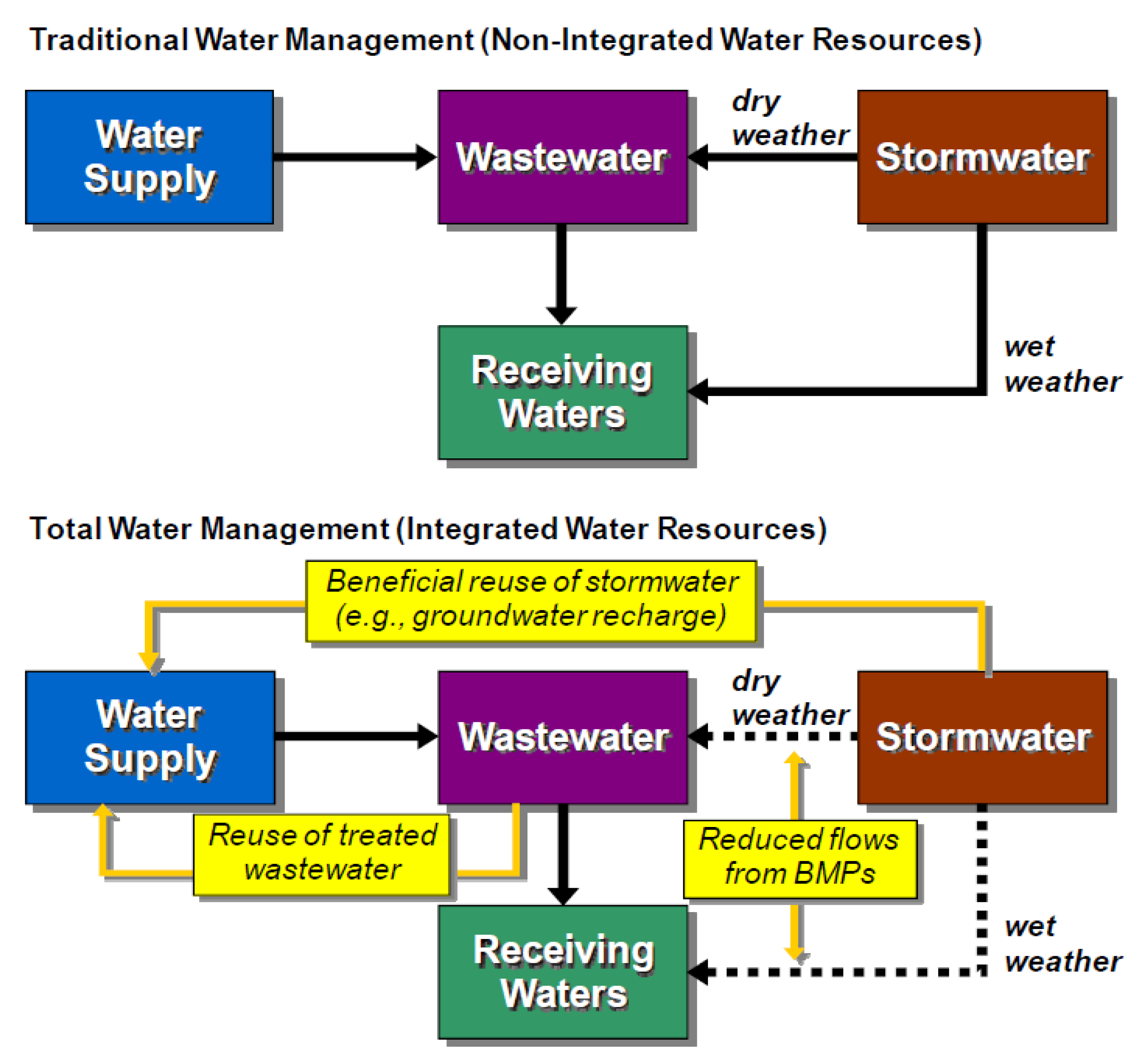
2.1.1. The Need for Water Resource Management
2.1.2. Water in Soil
2.1.3. Water Pollution
2.2. Soil
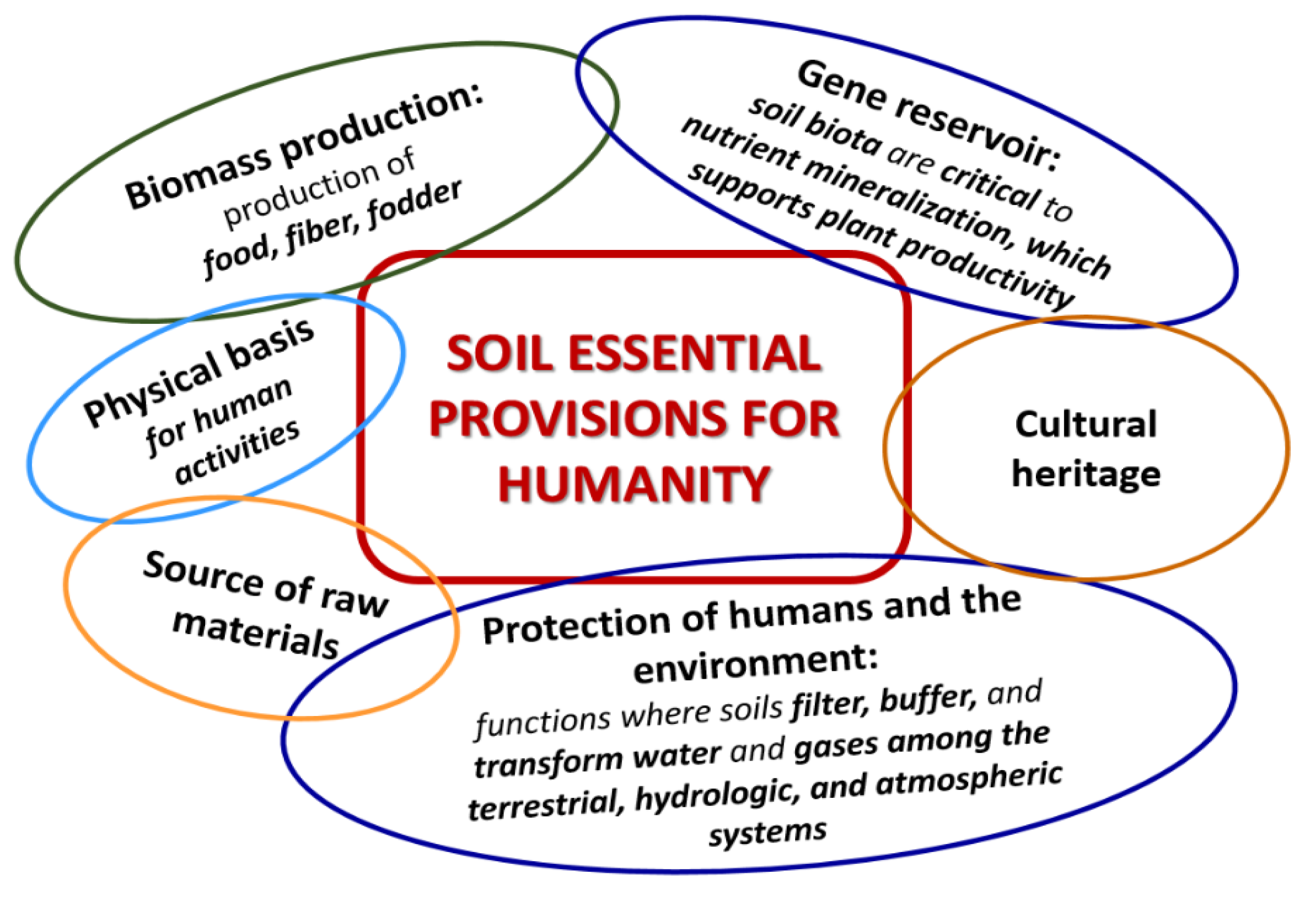
2.2.1. Soil Resource
2.2.2. Soil Pollution
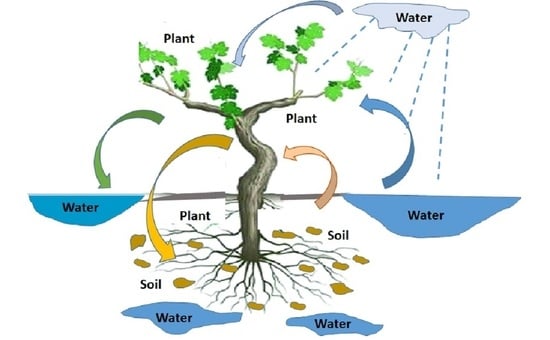
2.3. Soil and Water Interactions
2.3.1. Mechanisms of Interactions
2.3.2. Soil Management for Water Use Efficiency
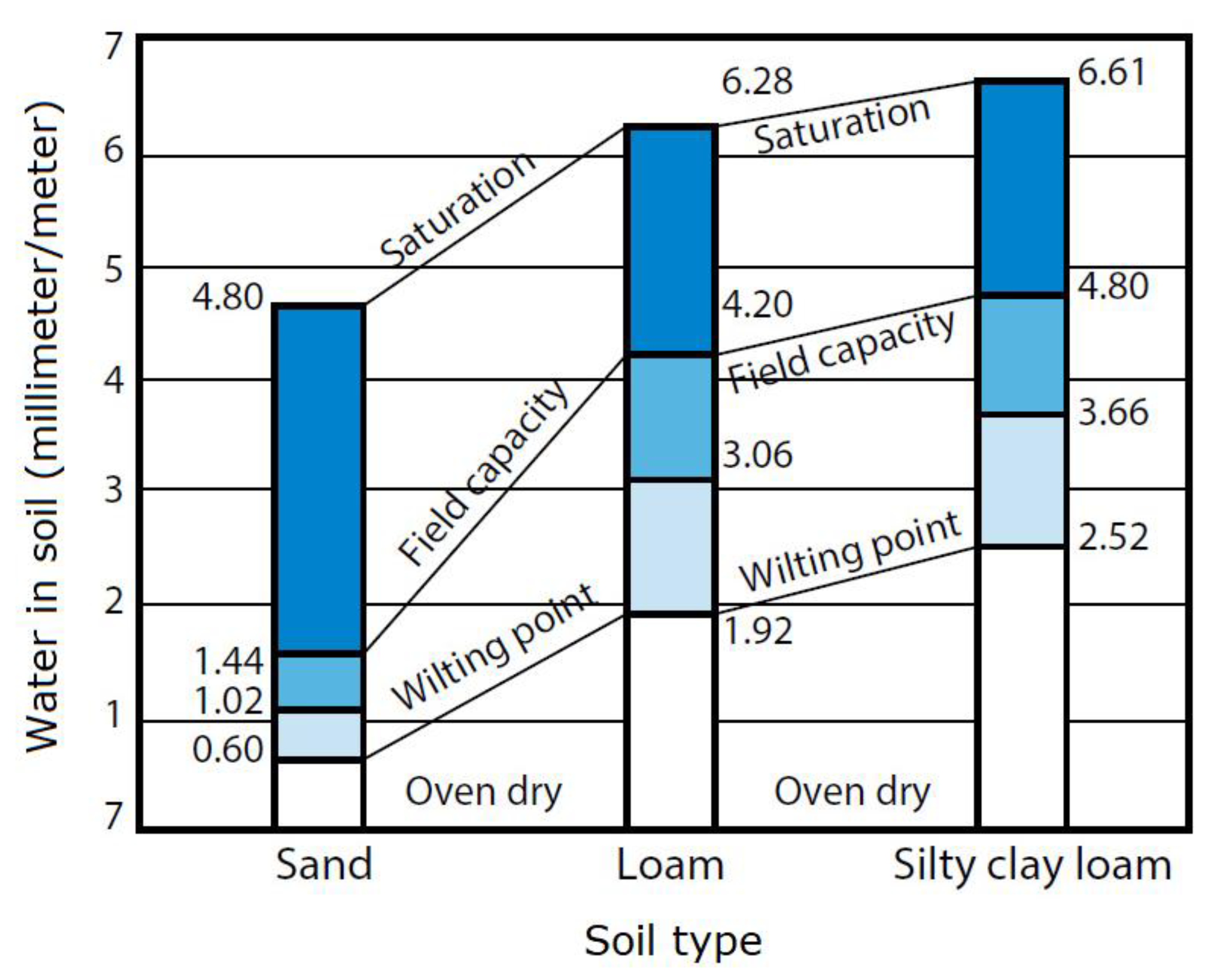
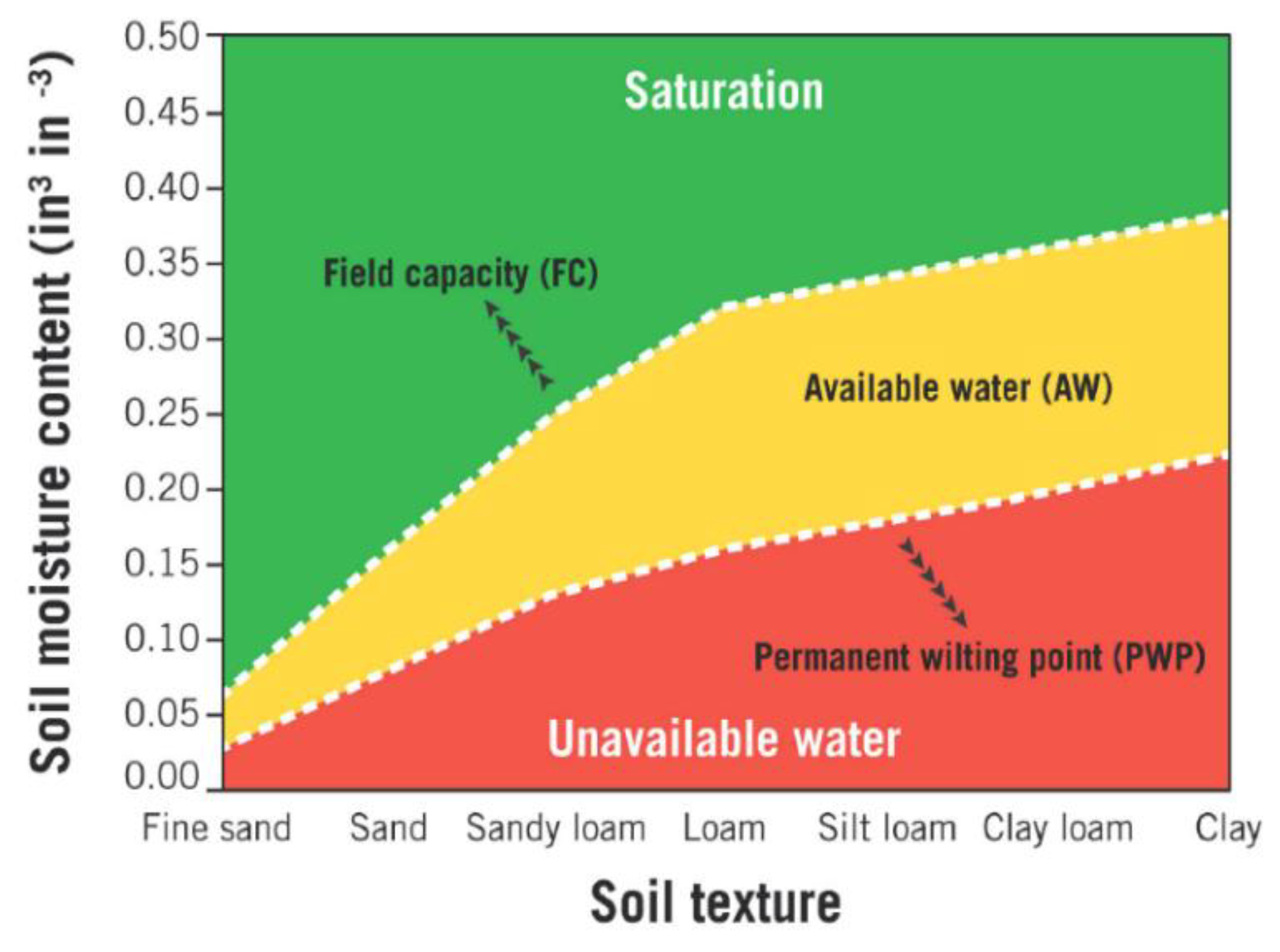
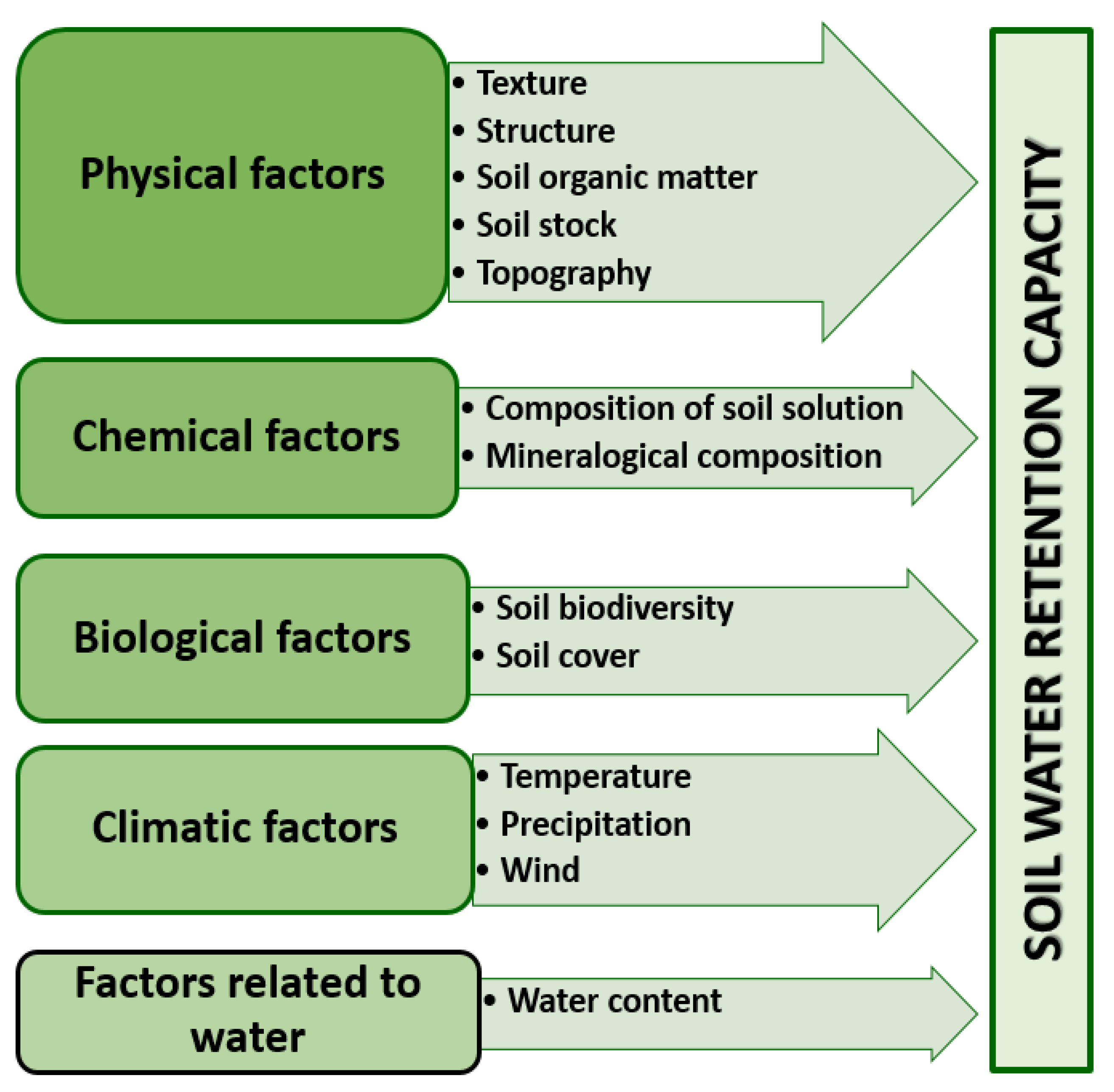
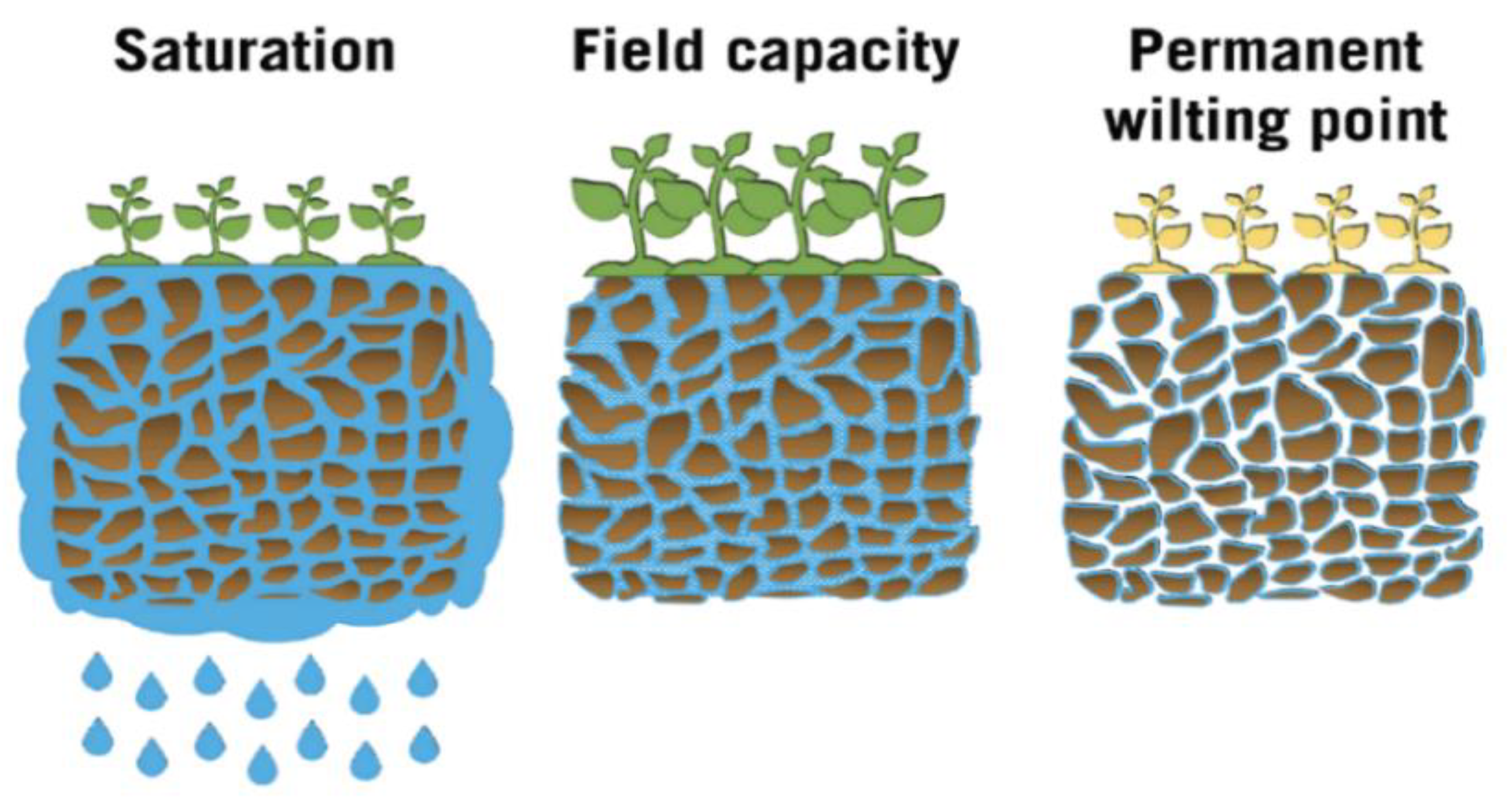
2.3.3. Soil Moisture
- -
- Plant-available volumetric soil moisture (W), the depth of a column of water contained in a given depth of soil;
- -
- Total volumetric soil moisture (WT), the volumetric percentage of water in a given soil depth;
- -
- Porosity (P), the fraction of soil consisting of pores filled with water or air;
- -
- Total water holding capacity (W0), the fraction of soil consisting of pores completely filled with water.
3. Plants Interactions with Soil and Water
3.1. Soil–Plants Interactions
3.2. Effects of Soil Pollution on Plants and Flora
3.3. Plant Growth and Water Use
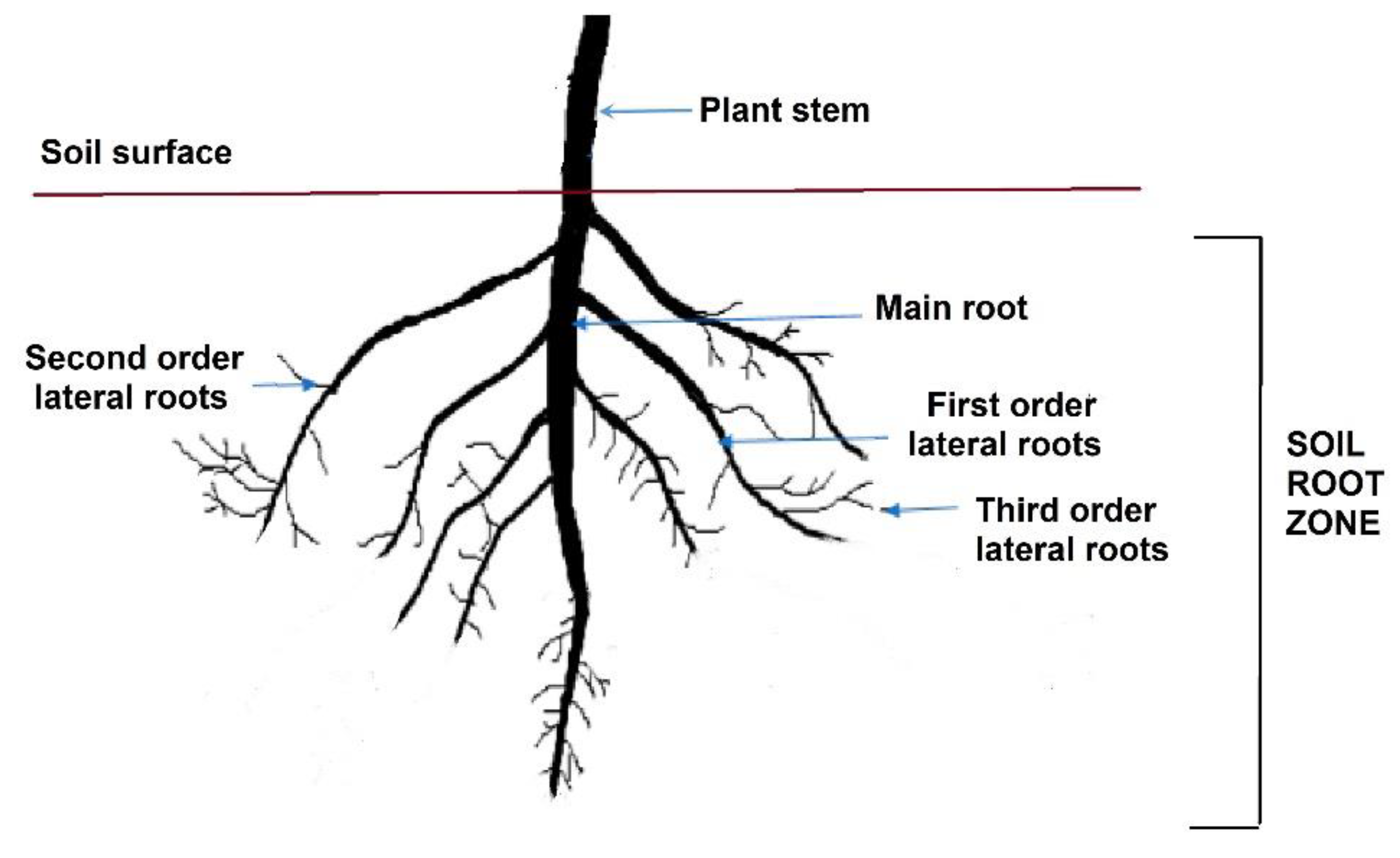
3.4. Soil–Plant–Water Relationship
4. Concluding Remarks and Perspectives
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tylianakis, J.; Didham, R.; Bascompte, J.; Wardle, D. Global change and species interactions in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNEP. Responsible Resource Management for a Sustainable World: Findings from the International Resource Panel; United Nations Environment Programme: Paris, France, 2012; Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/10580/RRMSW_Report_EN.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Panagos, P.; Imeson, A.; Meusburger, K.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Alewell, C. Soil conservation in Europe: Wish or reality? Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- COM 231. Communication from the Commission to the Council, the European Parliament, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions; Thematic Strategy for Soil Protection, Commission of the European Communities: Brussels, Belgium, 2006; Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:52006DC0231&from=EN (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Science for Environment Policy. Soil and water: A larger-scale perspective. In Thematic Issue 52. Issue produced for the European Commission DG Environment by the Science Communication Unit; UWE: Bristol, UK, 2015; pp. 3–6. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/integration/research/newsalert/pdf/soil_and_water_larger_scale_perspective_52si_en.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- World Bank. Water Resources Management; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/waterresourcesmanagement (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- EEA. Water Resources Across Europe—Confronting Water Scarcity and Drought; EEA Report No 2/2009; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2009; Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/water-resources-across-europe (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 414/2007 of 13 March 2007 concerning the technical guidelines for the planning, implementation and operational use of river information services (RIS) referred to in Article 5 of Directive 2005/44/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on harmonised river information services (RIS) on inland waterways in the Community. Off. J. Eur. Union 2014, L105, 1–34.
- Molden, D. Water for Food, Water for Life: A Comprehensive Assessment of Water Management in Agriculture; Earthscan: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bisselink, B.; Bernhard, J.; Gelati, E.; Adamovic, M.; Guenther, S.; Mentaschi, L.; de Roo, A. Impact of a changing climate, land use, and water usage on Europe’s water resources. In A Model Simulation Study; Joint Research Centre (JRC). European Commission: Luxembourg, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtergaele, F.; Biancalani, R.; Biancalani, R.; Nachtergaele, F.; Petri, M.; Bunning, S. Land Degradation Assessment in Drylands Methodology and Results; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2013; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i6362e.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Gourbesville, P. Challenges for integrated water resources management. Phys. Chem. Earth 2008, 33, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Water Commission. A Water Secure World: Vision for Water, Life and the Environment; World Water Council: Marseille, France, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Loucks, D.P.; van Beek, E. Water Resource Systems Planning and Management: An Introduction to Methods, Models, and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- EC Directive 60. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2000, L327, 1–72. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/resource.html?uri=cellar:5c835afb-2ec6-4577-bdf8-756d3d694eeb.0004.02/DOC_1&format=PDF (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Shani, U.; Ben-Gal, A.; Tripler, E.; Dudley, L.M. Plant response to the soil environment: An analytical model integrating yield, water, soil type, and salinity. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W08418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, T.P.; Rodrigo, D.; Cannan, A. Total water management: The new paradigm for urban water resources planning. In World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2010: Challenges of Change; Palmer, R.N., Ed.; American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Reston, VI, USA, 2010; pp. 3251–3260. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, J. Soil and Water Relationships; Noble Research Institute: Ardmore, OK, USA, 2001; Available online: https://www.noble.org/news/publications/ag-news-and-views/2001/september/soil-and-water-relationships/ (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Rogers, D.A.; Aguilar, J.; Kisekka, I.; Barnes, P.L.; Lamm, F.R. Soil, water, and plant relationships. Irrig. Manag. Ser. 2014, L904, 1–8. Available online: https://bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/L904.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- O’Geen, A.T. Soil water dynamics. Nat. Educ. Knowl. 2013, 4, 9. Available online: https://www.nature.com/scitable/knowledge/library/soil-water-dynamics-103089121/ (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Voroney, P. Soils for horse pasture management. In Horse Pasture Management; Sharpe, P., Ed.; Elsevier-Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.L.B.R.; Coolong, T.; Diaz-Perez, J.C. Principles of irrigation and scheduling for vegetable crops in Georgia. UGA Coop. Ext. Bull. 2019, 1511, 2–12. Available online: https://secure.caes.uga.edu/extension/publications/files/pdf/B%201511_1.PDF (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Hoekstra, A.Y. Green-blue water accounting in a soil water balance. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 129, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fankelman, M.; Rockström, J. The new blue and green water paradigm: Breaking new ground for water resources planning and management. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2006, 132, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissen, V.; Mol, H.; Klump, E.; Umlauf, G.; Nadal, M.; van der Ploeg, M.; van de Zee, S.E.A.T.M.; Ritsema, C.J. Emerging pollutants in the environment: A challenge for water resource management. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhav, S.; Ahamad, A.; Singh, A.K.; Kushawaha, J.; Chauhan, J.S.; Sharma, S.; Singh, P. Water pollutants: Sources and impact on the environment and human health. In Sensors in Water Pollutants Monitoring: Role of Material; Pooja, D., Kumar, P., Singh, P., Patil, S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2020; pp. 43–62. [Google Scholar]
- Pepper, I.L.; Gerba, C.P.; Brusseau, M.L. Environmental and Pollution Science; Elsevier: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanakis, A.I.; Becker, J.A. A review of emerging contaminants in water: Classification, sources, and potential risks. In Impact of Water Pollution on Human Health and Environmental Sustainability; McKeown, A.E., Bugyi, G., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 55–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Wen, Y.; Marshall, M.R.; Zhao, J.; Gui, H.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Jones, D.L.; Zang, H. Microplastics as an emerging threat to plant and soil health in agroecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kwak, J.I.; An, Y.J. Effects of bisphenol A in soil on growth, photosynthesis activity, and genistein levels in crop plants (Vigna radiata). Chemosphere 2018, 209, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pop, C.-E.; Draga, S.; Măciucă, R.; Niță, R.; Crăciun, N.; Wolff, R. Bisphenol A effects in aqueous environment on Lemna minor. Processes 2021, 9, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Water for People, Water for Life: The United Nations World Water Development Report: A Joint Report by the Twenty-Three UN Agencies Concerned with Freshwater. In World Water Assessment Programme (UNESCO WWAP); UNESCO: Paris, France, 2003; Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000129726.page=1 (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Water. Sanitation and Hygiene Annual Report 2008. In UNICEF WASH Section Programmes; UNICEF: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Available online: https://reliefweb.int/sites/reliefweb.int/files/resources/74B17C2332E35029C12575D200343A36-UNICEF_May2009.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Vié, J.C.; Hilton-Taylor, C.; Stuart, S.N. (Eds.) Wildlife in a Changing World—An Analysis of the 2008 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2009; Available online: https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/RL-2009-001.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Morosini, C.; Poste, E.; Mostachetti, M.; Torretta, V. Pharmaceuticals in water cycle: A review on risk assessment and wastewater and sludge treatment. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2020, 19, 1339–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorlini, S.; Collivignarelli, M.C.; Carnevale Miino, M. Technologies for the control of emerging contaminants in drinking water treatment plants. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2019, 18, 203–2216. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilescu, M.; Demnerová, K.; Aamand, J.; Agathos, S.; Fava, F. Emerging pollutants in the environment: Present and future challenges in biomonitoring, ecological risks and bioremediation. New Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilachi, I.C.; Asiminicesei, D.M.; Fertu, D.I.; Gavrilescu, M. Occurrence and fate of emerging pollutants in water environment and options for their removal. Water 2021, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, W.E.H. Functions of soil for society and the environment. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2005, 4, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford , C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, C.P.J.; Branfireun, B.A.; Kolka, R.K. Spatial characteristics of net methylmercury production hot spots in peatlands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavernia, B.G.; Nelson, M.D.; Seilheimer, T.S.; Gormanson, D.D.; Perry, C.H.; Caldwell, P.V.; Sun, G. Conservation and maintenance of soil and water resources. In Future Forests of the Northern United States; Shifley, S.R., Moser, W.K., Eds.; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Northern Research Station, One Gifford Pinchot Drive Madison: Madison, WI, USA, 2016; pp. 145–175. Available online: https://www.fs.fed.us/nrs/pubs/gtr/gtr_nrs151-chapters/gtr-nrs-151-chapter-6.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Amin, M.N.; Hossain, M.S.; de Bruyn, L.L.; Wilson, B. A systematic review of soil carbon management in Australia and the need for a social-ecological systems framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 719, 135182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brevik, E.C. Soils and human health: An overview. In Soils and Human Health; Brevik, E.C., Burgess, L.C., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 29–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Maah, M.J.; Yusoff, I. Soil contamination, risk assessment and remediation. In Environmental Risk Assessment of Soil Contamination; Hernandez-Soriano, M.C., Ed.; Intech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2014; pp. 3–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cachada, A.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Duarte, A.C. Soil and pollution: An introduction to the main issues. In Soil Pollution from Monitoring to Remediation; Duarte, A.C., Cachada, A., Rocha-Santos, T., Eds.; Elsevier-Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Snow, D.D.; Cassada, D.A.; Larsen, M.L.; Mware, N.A.; Li, X.; D’Alessio, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sallach, J.B. Detection, occurrence and fate of emerging contaminants in agricultural environments. Water Environ. Res. 2017, 89, 897–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gavrilescu, M. Fate of pesticides in the environment and its bioremediation. Eng. Life Sci. 2005, 5, 497–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, B.; Taak, P. Biotechnological Strategies for Effective Remediation of Polluted Soils; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yaron, B.; Calvet, R.; Prost, R. Soil Pollution: Processes and Dynamics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Durães, N.; Novo, L.A.B.; Candeias, C.; Ferreira da Silva, E. Distribution, transport and fate of pollutants. In Soil Pollution from Monitoring to Remediation; Duarte, A.C., Cachada, A., Rocha-Santos, T., Eds.; Elsevier-Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 29–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Khorshidi, M. Mechanisms for soil-water retention and hysteresis at high suction range. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 2015, 141, 04015032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frydman, S.; Baker, R. Theoretical soil-water characteristic curves based on adsorption, cavitation, and a double porosity model. Int. J. Geomech. 2009, 9, 50–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Niu, J.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, Z.; Zhu, W. Interaction between plant roots and soil water flow in response to preferential flow paths in northern China. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2016, 28, 648–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study on Soil and Water in a Changing Environment; Final Report. European Commission (DG ENV). Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2014. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/soil/pdf/Soil%20and%20Water.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Hatfield, J.L. Soil Management for Increasing Water Use Efficiency in Field Crops under Changing Climates; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2011. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Dold, C. Water-use efficiency: Advances and challenges in a changing climate. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basso, B.; Ritchie, J.T. Evapotranspiration in high-yielding maize and under increased vapor pressure deficit in the US Midwest. Agric. Environ. Lett. 2018, 3, 170039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Vinocur, B.; Altman, A. Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: Towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 2003, 218, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, P.W.; Stewart, B.A. Soil management for efficient water use: An overview. In Limitations to Efficient Water Use in Crop Production; Taylor, H.M., Jordan, W.R., Sinclair, T.R., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1983; pp. 419–459. [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Sauer, T.J.; Prueger, J.H. Managing soils to achieve greater water use efficiency: A review. Agron. J. 2001, 93, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Molden, D.; Cook, S. Water use efficiency in agriculture: Measurement, current situation and trends. In Managing Water and Fertilizer for Sustainable Agricultural Intensification; Drechsel, P., Heffer, P., Magen, H., Mikkelsen, R., Wichelns, D., Eds.; International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA), International Water Management Institute (IWMI), International Plant Nutrition Institute (IPNI), and International Potash Institute (IPI): Paris, France, 2015; pp. 39–64. [Google Scholar]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowsky, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating soil moisture–climate interactions in a changing climate: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobriya, P.; Qureshi, A.; Badola, R.; Hussain, S.A. A review of the methods available for estimating soil moisture and its implications for water resource management. J. Hydrol. 2012, 458–459, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robock, A.; Vinnikov, K.Y.; Srinivasan, G.; Entin, J.K.; HoIIinger, S.E.; Speranskaya, N.A.; Liu, S.; Namkhai, A. The global soil moisture data bank. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 1281–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Camici, S.; Tarpanelli, A. Soil moisture for hydrological applications: Open questions and new opportunities. Water 2017, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.M.; Firestone, M.K. Mechanisms for soil moisture effects on activity of nitrifying bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nord, E.A.; Lynch, J.P. Plant phenology: A critical controller of soil resource acquisition. J. Bot. 2009, 60, 1927–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pissolito, C.; Garibotti, I.A.; Varela, S.A.; Arana, V.; Gonzalez-Polo, M.; Marchelli, P.; Bruzzone, O. Water-mediated changes in plant–plant and biological soil crust–plant interactions in a temperate forest ecosystem. Web. Ecol. 2019, 19, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glick, B.R. Plant growth-promoting bacteria: Mechanisms and applications. Scientifica 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramakrishna, W.; Yadava, R.; Li, K. Plant growth promoting bacteria in agriculture: Two sides of a coin. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 124, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobariu, D.L.; Tudorache Fertu, D.I.; Diaconu, M.; Pavel, L.V.; Hlihor, R.M.; Dragoi, E.N.; Curteanu, S.; Lenz, M.; Corvini, P.X.F.; Gavrilescu, M. Rhizobacteria and plant symbiosis in heavy metal uptake and its implications for soil bioremediation. New Biotechnol. 2015, 39, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconu, M.; Pavel, L.V.; Hlihor, R.M.; Rosca, M.; Fertu, D.I.; Lenz, M.; Corvini, P.X.; Gavrilescu, M. Characterization of heavy metal toxicity in some plants and microorganisms—A preliminary approach for environmental bioremediation. New Biotechnol. 2020, 56, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, G.; Song, Z.; Wang, J.; Guo, L. Interactions of soil bacteria and fungi with plants during long-term grazing exclusion in semiarid grasslands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.C.; Jansa, J. Mycorrhizas: At the interface of biological, soil, and earth sciences. In Mycorrhizal Mediation of Soil: Fertility, Structure, and Carbon Storage; Johnson, N.C., Gehring, C., Jansa, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibuike, G.U.; Obiora, S.C. Heavy metal polluted soils: Effect on plants and bioremediation methods. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2014, 2014, 752708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gavrilescu, M. Biosorption in environmental remediation. In Bioremediation Technology—Theory & Application; Fulekar, M.H., Ed.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2010; pp. 35–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlihor, R.M.; Apostol, L.C.; Smaranda, C.; Pavel, V.L.; Caliman, F.A.; Robu, B.M.; Gavrilescu, M. Bioavailability processes for contaminants in soils and their use in risk assessment. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2009, 8, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Y.W.; Chang, H.Q.; Li, Z.J.; Xue, J.M. Uptake and translocation of organic pollutants in plants: A review. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inui, H.; Wakai, T.; Gion, K.; Kim, Y.S.; Eun, H. Differential uptake for dioxin-like compounds by Zucchini subspecies. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1602–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kvesitadze, G.; Khatisashvili, G.; Sadunishvili, T.; Kvesitadze, E. Plants for remediation: Uptake, translocation and transformation of organic pollutants. In Plants, Pollutants and Remediation; Öztürk, M., Ashraf, M., Aksoy, A., Ahmad, M.S.A., Hakeem, K.R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 241–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Qin, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, L.; Zhang, Z. Interactions between soil water content and fertilizer on growth characteristics and biomass yield of Chinese white poplar (Populus tomentosa Carr.) seedlings. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2011, 57, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, M.G.; Pimentel, C. Daily balance of leaf sugars and amino acids as indicators of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) metabolic response and drought intensity. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2009, 15, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cassiani, G.; Boaga, J.; Vanella, D.; Perri, M.T.; Consoli, S. Monitoring and modelling of soil–plant interactions: The joint use of ERT, sap flow and eddy covariance data to characterize the volume of an orange tree root zone. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2213–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Dawes, W.R.; Walker, G.R. Response of mean annual evapotranspiration to vegetation changes at catchment scale. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Paco, T.A.; Sousa, V.; Silva, C.M. Hydrological performance of green roofs in Mediterranean climates: A Review and evaluation of patterns. Water 2021, 13, 2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schar, C.; Luthi, D.; Beyerle, U.; Heise, E. The soil–precipitation feedback: A process study with a regional climate model. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 722–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, W.; Fu, J. Vegetation response to precipitation anomalies under different climatic and biogeographical conditions in China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ning, T.; Li, Z.; Feng, Q.; Liu, W.; Li, Z. Comparison of the effectiveness of four Budyko-based methods in attributing long-term changes in actual evapotranspiration. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Fu, B.J.; Zhang, L. Advances in hydrological modelling with the Budyko framework: A review. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2016, 40, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yu, B.; Huang, Y.; Wang, G. The complementary relationship and generation of the Budyko functions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acosta-Motos, J.R.; Ortuño, M.F.; Bernal-Vicente, A.; Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Sanchez-Blanco, M.J.; Hernandez, J.A. Plant responses to salt stress: Adaptive mechanisms. Agronomy 2017, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, X.; Mu, X.; Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Brestic, M. Global plant-responding mechanisms to salt stress: Physiological and molecular levels and implications in biotechnology. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2015, 35, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, B.; Walker, G.; Katupitiya, A.; Doolan, J. Salinity management in the Murray–Darling Basin, Australia. Water 2020, 12, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fu, B.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z. Soil moisture–plant interactions: An ecohydrological review. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H. Fundamentals of Irrigation and on-Farm Water Management; Springer Science-Business Media: Berlin-Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, V.; Ondrašek, G.; Filipović, L. Modelling water dynamics, transport processes and biogeochemical reactions in soil vadose zone. In Groundwater—Contaminant and Resource Management; Javaid, M.S., Ed.; Intech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 133–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schellenberger Costa, D.; Classen, A.; Ferger, S.; Helbig-Bonitz, M.; Peters, M.; Böhning-Gaese, K.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Kleyer, M. Relationships between abiotic environment, plant functional traits, and animal body size at Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.; Roy, M.M. Climatic responses, environmental indices and interrelationships between qualitative and quantitative traits in clusterbean Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (L) Taub. under arid conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 85, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanan, E.J.; Ross, M.S. Across-scale patterning of plant-soil-water interactions surrounding tree islands in Southern Everglades landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2010, 25, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kroll, S.A.; Ringler, N.H.; De las Heras, J.; Gomez-Alday, J.J.; Moratalla, A.; Briggs, R.D. Analysis of anthropogenic pressures in the Segura Watershed (SE Spain), with a focus on inter-basin transfer. Ecohydrology 2013, 6, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, J.T. Soil water balance and plant water stress. In Understanding Options for Agricultural Production. Systems Approaches for Sustainable Agricultural Development; Tsuji, G.Y., Hoogenboom, G., Thornton, P.K., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 7, pp. 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connellan, G. Water Use Efficiency for Irrigated Turf and Landscape; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, D.; Garrido, A.; Mínguez, M.I.; Ruiz-Ramos, M. Impact of climate change on maize’s water needs, yields and profitability under various water prices in Spain. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 9, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Man, Z. Natural vegetation distribution and climate ecology prediction based on geographic information system. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2020, 19, 1623–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Threats to Water | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|
| Waste (sewage, industrial, agricultural etc.) discharged in water | 2 million tons of waste in water/day | [32] |
| Wastewater produced by humanity | 1500 km3/year (six times more than water from all rivers) | [32] |
| People living without adequate sanitation, which causes water contamination | 2.5 billion people without sanitation | [33] |
| Species of freshwater fish at risk of extinction | 50% of native freshwater fish under threats | [34] |
| Category of Pollutants | Examples | Effects | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biological/infectious agents | Pathogenic bacteria, pathogenic yeasts, pathogenic protozoa, parasitic worms, enteroviruses, coliform organisms, saprophytic bacteria, fungi, algae, crustaceans, etc. |
| Human and animal waste, domestic sewage |
| Oxygen-demanding waste/biodegradable organic compounds | Organic waste (animal waste, plant debris) able to be biodegraded by aerobic microorganisms |
| Sewage, feedlots, paper mills, food processing |
| Organic chemicals/slowly or non-biodegradable organic compounds (refractory) | Pesticides, personal care products, drugs, organic solvents, oil with its refining and processing products, tannins and lignins, cellulose and phenols |
| Industrial effluents, household cleansers, runoff from farms and yards |
| Inorganic chemicals | Water soluble acids, compounds of toxic metals (arsenic, cadmium, chromium, copper, lead, mercury, silver, zinc, etc.), salts (primarily chloride and sulfate, nitrites and nitrates), fluorides |
| Industrial effluents, surface runoff, household cleansers, pesticides |
| Nutrients | Water soluble compounds containing nitrogen, phosphorous (as NO-3, PO43, NH-4) (macronutrients) |
| Sewage, organic waste (manure, biosolids), fertilizers |
| Radioactive materials | Radioactive isotopes of iodine, radon, uranium, cesium, and thorium |
| Power plants (nuclear- and coal-based)Mining and processing of radioactive oresProduction of nuclear weapons |
| Sediments | Soil, silt, and other solid matters |
| Erosion, runoff |
| Thermal pollution | Excessive heat |
| Cooling water in power plants, industrial plants |
| Part of Plant | Water Potential (bar) |
|---|---|
| Soil | −0.5 |
| Roots | −0.4 |
| Stem | −7 |
| Leaf | −10 |
| Atmosphere | −500 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gavrilescu, M. Water, Soil, and Plants Interactions in a Threatened Environment. Water 2021, 13, 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192746
Gavrilescu M. Water, Soil, and Plants Interactions in a Threatened Environment. Water. 2021; 13(19):2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192746
Chicago/Turabian StyleGavrilescu, Maria. 2021. "Water, Soil, and Plants Interactions in a Threatened Environment" Water 13, no. 19: 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192746
APA StyleGavrilescu, M. (2021). Water, Soil, and Plants Interactions in a Threatened Environment. Water, 13(19), 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192746