Hydrochemical and Isotopic Characterization of the Impact of Water Diversion on Water in Drainage Channels, Groundwater, and Lake Ulansuhai in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling and Measurements
3.1.1. Sampling and Conservation
3.1.2. Measurements and Analysis
3.2. Study Method
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Hydrochemical Characteristic
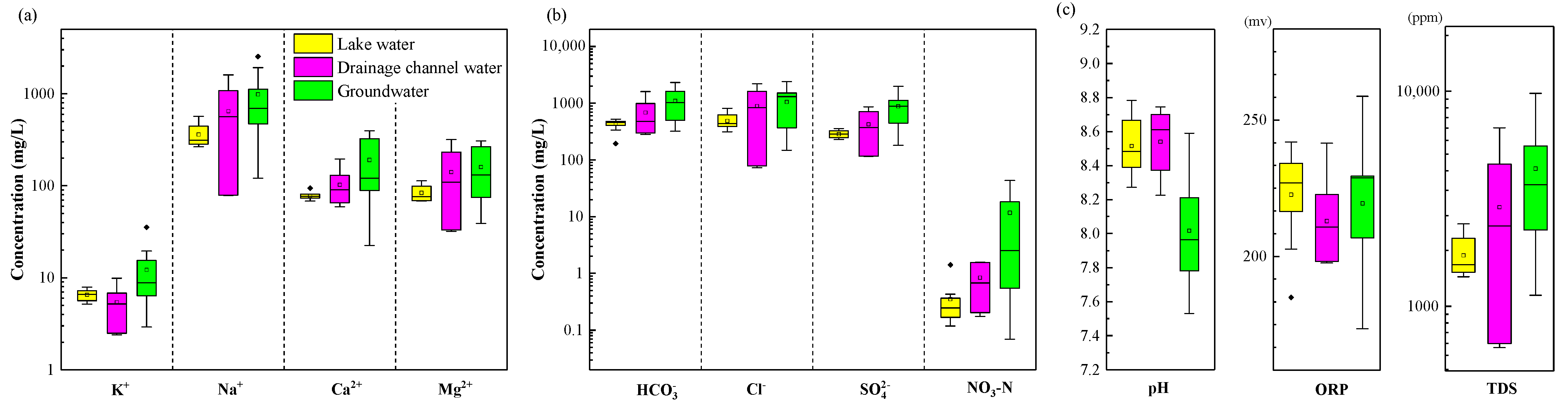
4.1.1. General Characteristics in 2021
4.1.2. Spatial Distributions in 2021
4.1.3. Temporal Evolution
4.2. Characterization of the Hydrochemical Types
4.2.1. General Characteristics in 2021
4.2.2. Temporal Evolution
4.3. Stable Isotope Characterization
4.3.1. Water Exchange
4.3.2. Stable Isotope Ratios for Water Exchange
4.4. The Regional Water Cycle
4.4.1. The Hydrological Cycle
4.4.2. The Hydrochemical Cycle
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, S.; Shen, S.; Zhou, A.; Lyu, H. Assessment and management of lake eutrophication: A case study in lake Erhai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Fang, J.; Ma, S.; Cai, Q.; Xiong, X.; Tian, D.; Zhao, X.; Fang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; et al. Changes in China’s lakes: Climate and human impacts. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Xing, W. Functional traits of submerged macrophytes in eutrophic shallow lakes affect their ecological functions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.; Null, S.; DeRose, R.; Wilcock, P.; Wurtsbaugh, W.; Null, S.; DeRose, R.; Hahnenberger, M.; Howe, F.; Moore, J. Decline of the world’s saline lakes. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 816–821. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wei, S.; Liang, H.; Zheng, W.; Li, X.; Hu, C.; Currell, M.; Zhou, F.; Min, L. Nitrogen stock and leaching rates in a thick vadose zone below areas of long-term nitrogen fertilizer application in the North China Plain: A future groundwater quality threat. J. Hydrol. 2019, 576, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Hough, R.; Yates, K.; Osprey, M.; Kerr, C.; Cooper, P.; Coull, M.; Zhang, Z. Effects of season and sediment-water exchange processes on the partitioning of pesticides in the catchment environment: Implications for pesticides monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yao, J.; Lai, X.; Li, X.; Wu, G.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; et al. Lake hydrology in China: Advances and prospects. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 1360–1379, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, L.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Feng, P. A non-stationary standardized streamflow index for hydrological drought using climate and human-induced indices as covariates. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Pang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, T.; Kaisam, J. Influence of water diversion on spatial and temporal distribution of flow field and total phosphorus (TP) concentration field in Taihu Lake. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 20, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dittmar, T.; Kothawala, D.; Tranvik, L.; Kellerman, A.; Kothawala, D.; Tranvik, L. Chemodiversity of dissolved organic matter in lakes driven by climate and hydrology. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3804. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Teng, Y.; Wang, G.; Du, Q.; Wang, J.; Yang, G. Water supply safety of riverbank filtration wells under the impact of surface water-groundwater interaction: Evidence from long-term field pumping tests. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 135141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Xia, X.; Yang, G.; Lu, H.; Ma, G.; Wang, G.; Teng, Y.; Yuan, W.; Shrestha, S. Trend, seasonality and relationships of aquatic environmental quality indicators and implications: An experience from Songhua River, NE China. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 145, 105706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydarizad, M.; Minaei, M.; Ichiyanagi, K.; Sori, R. The effects of local and regional parameters on the δ18O and δ2H values of precipitation and surface water resources in the Middle East. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Ye, X.; Du, X. Coupled effects of bacteria and suspended solids on clogging during managed aquifer recharge. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhai, Y.; Lei, Y.; Li, J.; Teng, Y.; Lu, H.; Xia, X.; Yue, W.; Yang, J. Spatiotemporal evolution of groundwater nitrate nitrogen levels and potential human health risks in the Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Zheng, F.; Zhao, X.; Xia, X.; Teng, Y. Identification of hydrochemical genesis and screening of typical groundwater pollutants impacting human health: A case study in Northeast China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1202–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhai, Y.; Xia, X.; Yin, Z.; Du, Q.; Zuo, R.; Wang, J.; Teng, Y.; Xu, M. Simulation of trinitrogen migration and transformation in the unsaturated zone at a desert contaminant site (NW China) using HYDRUS-2D. Water 2018, 10, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wannous, M.; Jahnke, C.; Troeger, U.; Falk, M.; Bauer, F. Hydrochemistry and environmental isotopes (18O, 2H, 3H, 3He/4He) of groundwater and floodwater in the great area of Hurghada, eastern desert of Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Guo, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Hydrogeochemical zonation and its implication for arsenic mobilization in deep groundwaters near alluvial fans in the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia. J. Hydrol. 2014, 518, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dudley, B.; Montgomery, K.; Hodgetts, W. Characterizing spatial and temporal variation in 18O and 2H content of New Zealand river water for better understanding of hydrologic processes. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 5474–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, M.; Leistert, H.; Gimbel, K.; Weiler, M. Illuminating hydrological processes at the soil-vegetation-atmosphere interface with water stable isotopes. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 674–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Yamanaka, T. Tracing groundwater recharge sources in a mountain-plain transitional area using stable isotopes and hydrochemistry. J. Hydrol. 2012, 464, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, W.; Han, D.; Song, X.; Liu, S. Environmental isotopes (δ18O, δ2H, 222Rn) and hydrochemical evidence for understanding rainfall-surface water-groundwater transformations in a polluted karst area. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yamanaka, T.; Zhou, X.; Tian, F.; Ma, W. Combined use of tracer approach and numerical simulation to estimate groundwater recharge in an alluvial aquifer system: A case study of Nasunogahara area, central Japan. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 833–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Lu, X.; Yu, R.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Geng, Y. Eutrophication decreased CO2 but increased CH4 emissions from lake: A case study of a shallow lake Ulansuhai. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; Yan, J.; Miao, Q.; Li, Z.; Akae, T. A study on water and salt transport, and balance analysis in sand dune–wasteland–lake systems of Hetao Oases, upper reaches of the Yellow River Basin. Water 2020, 12, 3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, R.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Xue, H.; Hao, Y.; Wang, L. Temporal and spatial variation trends in water quality based on the WPI index in the shallow lake of an arid area: A case study of Lake Ulansuhai, China. Water 2019, 11, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, R.; Zhao, J.; Shi, W.; Song, S.; Wang, C. Comprehensive assessment of water quality and pollution source apportionment in Wuliangsuhai Lake, Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Pei, G.; Zhao, S.; Shi, X.; Zhang, H.; Sun, B.; Song, S.; Sun, C.; Ma, H. Seasonal varieties and influential factors of heavy metals in sediments of Wuliangsuhai Lake. Water Sci. Technol.-Water Supply 2020, 20, 3779–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, R.; Hao, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Bu, X. A new method for mapping aquatic vegetation especially underwater vegetation in lake Ulansuhai using GF-1 satellite data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, M.; Dong, S.; Zhang, W.; Hou, Q.; Zhao, Z. Hydrochemical characteristics and genesis of groundwater in Wuliangsuhai lake area. Earth Environ. 2021, 49, 472–479, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Ryan, M.; Sun, B.; Li, C. The influence of irrigation and Wuliangsuhai Lake on groundwater quality in eastern Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, L.; Jillian, W.G. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too many sources. Oecologia 2003, 136, 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Dong, W.; An, Y.; Lu, W. A Bayesian-based integrated approach for identifying groundwater contamination sources. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Li, C.; Shi, X.; Shi, Y.; Fu, X. Seasonal changing characteristics of the major ions in the Lake Wuliangsuhai. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2013, 27, 137–142, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Du, D.; He, J.; Lv, C.; Bai, S.; Xie, Z.; Hou, D.; Wang, J. Water quality chemistry of several main anions in the Lake Ulansuhai and the Lake Daihai water environment. In Proceedings of the Agricultural Environment and Ecological Security—The Fifth National Symposium on Agricultural Environmental Science, Nanjing, China, 19–22 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Dong, S.; Gao, D.; Ma, M.; Chen, Y. Hydrogeochemical evolution and water and salt migration in the Wuliangsuhai Watershed. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 44, 108–114, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Zeng, H.; Ma, L. Analysis on water resources and their changes of main lakes in Inner Mongolia. Arid Zone Res. 2015, 32, 7–14, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Yang, F.; Shi, X.; Sun, B.; Zhao, S.; Cen, R.; Fan, C. Impact of seasonal ice cover on nutrient distribution in Ulansuhai Lake. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2016, 35, 1–8, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Liu, X.; Li, H. Spatial variations of δD and δ18O in lake water of western China and their controlling factors. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 1199–1211, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Song, X.; Sun, X.; Yuan, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Isotopic composition of precipitation over arid northwestern China and its implications for the water vapor origin. J. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Lan, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Chi, B.; Sauter, M. Water level response in wells to dynamic shaking in confined unconsolidated sediments: A laboratory study. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ji, B. Isotopic study on water supply relationship in Ulansuhai and its surrounding areas. Water Resour. Prot. 2013, 29, 12–18, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, F.; Wei, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X. The variations of stable isotopes (δD and δ18O) in the precipitation in Baotou area. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2013, 27, 157–162, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Guo, M.; Cao, X.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Yue, W. Hydrochemical and Isotopic Characterization of the Impact of Water Diversion on Water in Drainage Channels, Groundwater, and Lake Ulansuhai in China. Water 2021, 13, 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213033
Han Y, Zhai Y, Guo M, Cao X, Lu H, Li J, Wang S, Yue W. Hydrochemical and Isotopic Characterization of the Impact of Water Diversion on Water in Drainage Channels, Groundwater, and Lake Ulansuhai in China. Water. 2021; 13(21):3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213033
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yifan, Yuanzheng Zhai, Mengshen Guo, Xinyi Cao, Hong Lu, Jie Li, Shengrui Wang, and Weifeng Yue. 2021. "Hydrochemical and Isotopic Characterization of the Impact of Water Diversion on Water in Drainage Channels, Groundwater, and Lake Ulansuhai in China" Water 13, no. 21: 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213033
APA StyleHan, Y., Zhai, Y., Guo, M., Cao, X., Lu, H., Li, J., Wang, S., & Yue, W. (2021). Hydrochemical and Isotopic Characterization of the Impact of Water Diversion on Water in Drainage Channels, Groundwater, and Lake Ulansuhai in China. Water, 13(21), 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213033









