Combined Application of Ozone and Hydrogen Peroxide to Degrade Diesel Contaminants in Soil and Groundwater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
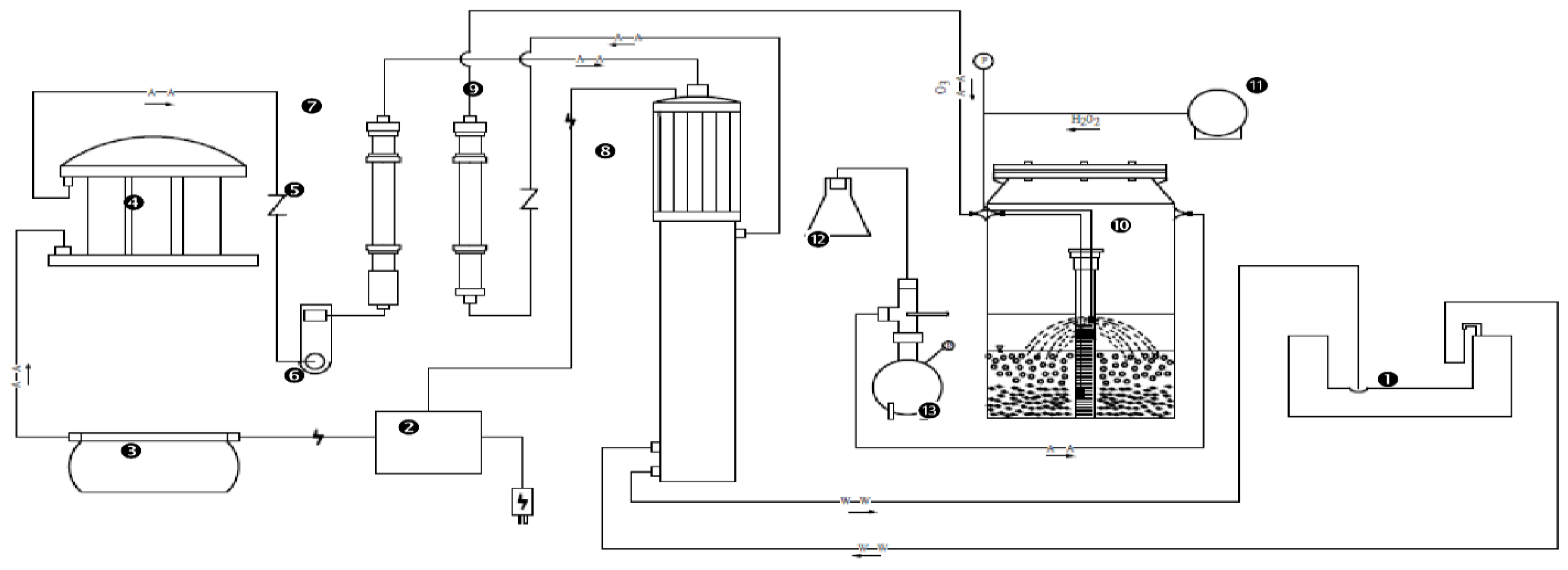
2.1. Experimental Procedure and Design
2.2. Operating Conditions of Ozone and Hydrogen Peroxide Reaction System
2.3. Sampling and Analysis
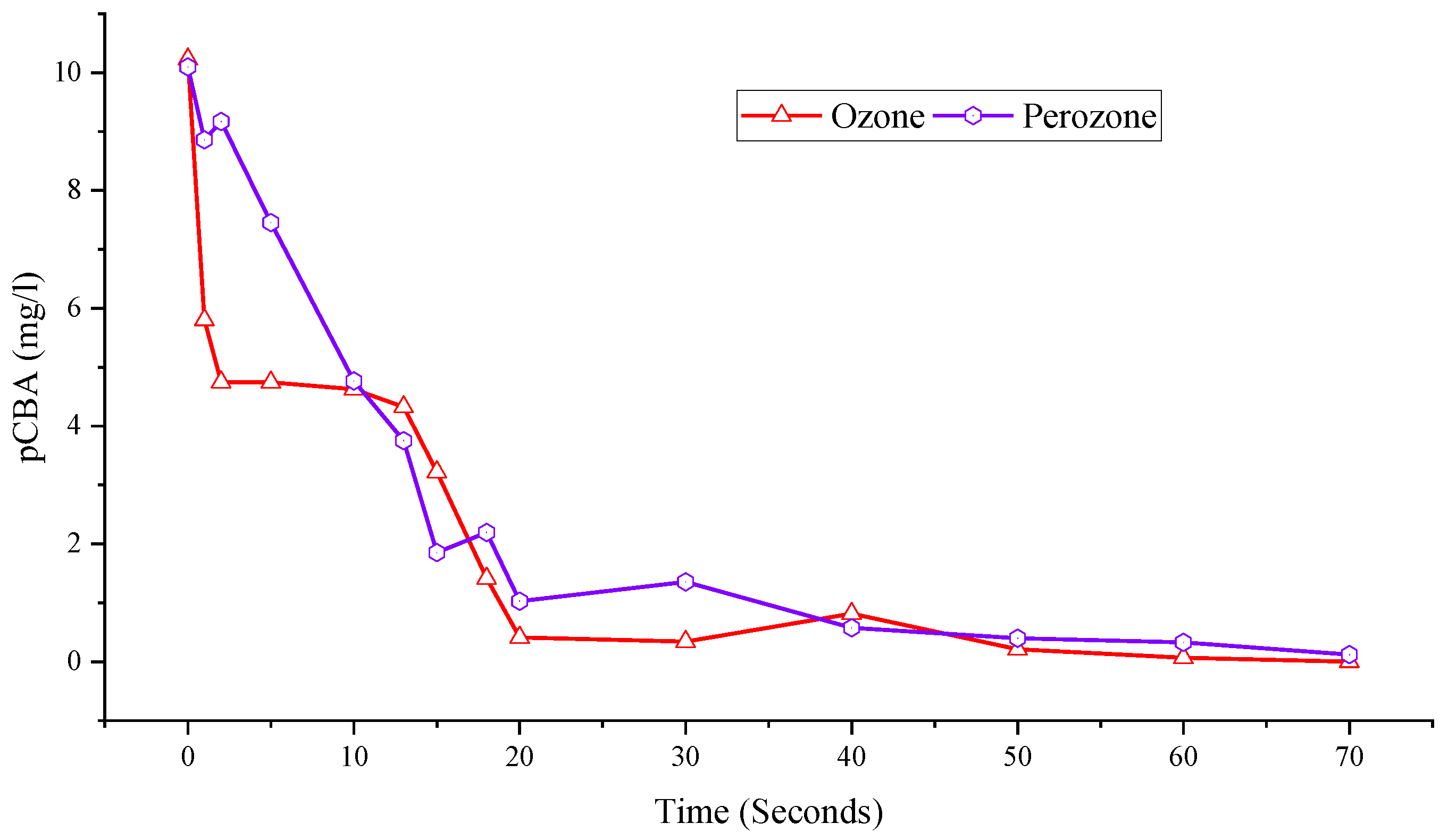
2.4. Hydroxyl Radical Conversion Rate
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Background Investigation
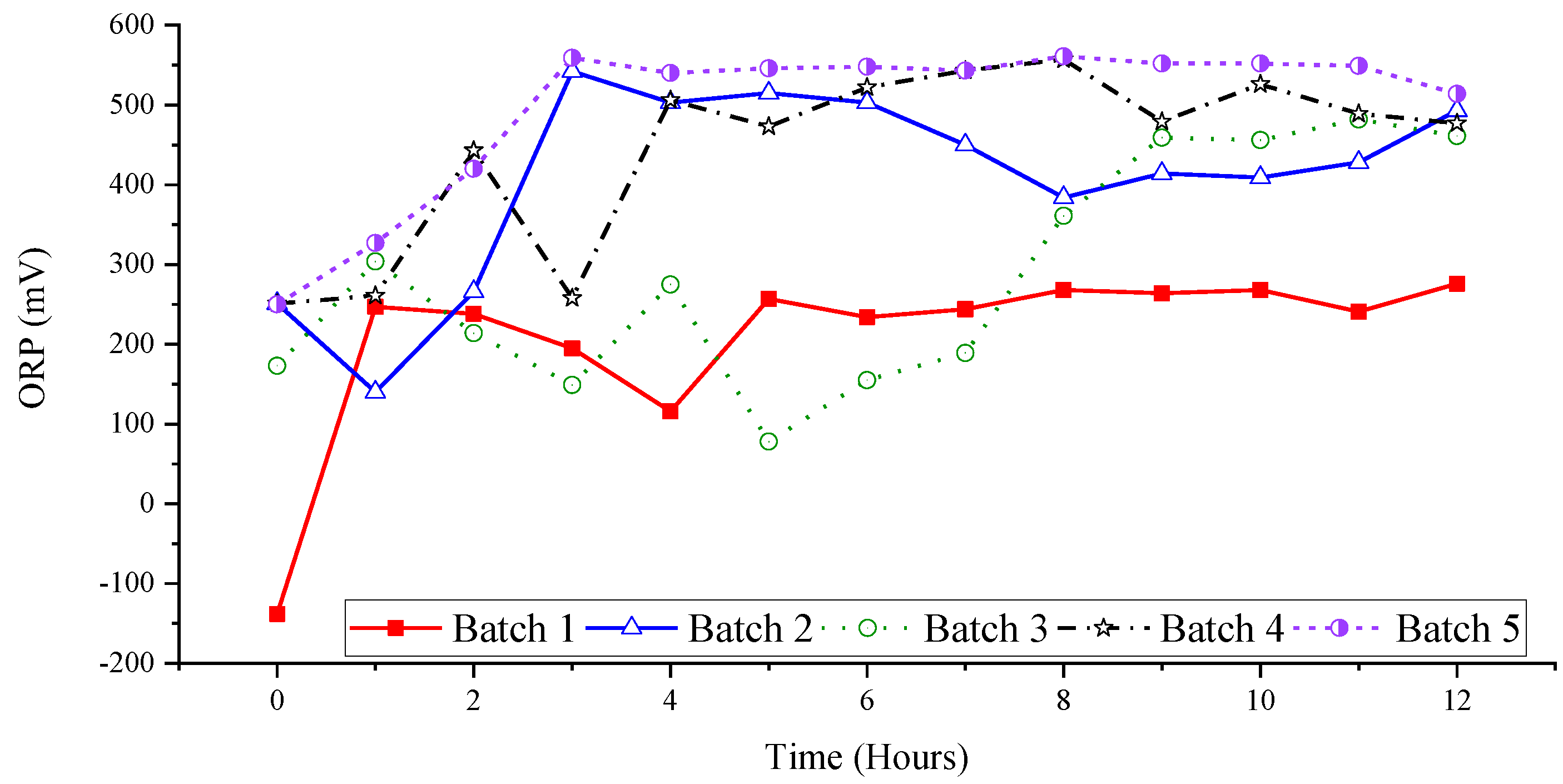
3.2. Effect of Ozone and Perozone on Oxidation-Reduction Potential of Groundwater
3.3. Effect of Ozone and Perozone on pH Value of Groundwater
3.4. Effect of Ozone and Perozone on Diesel Degradation of Groundwater
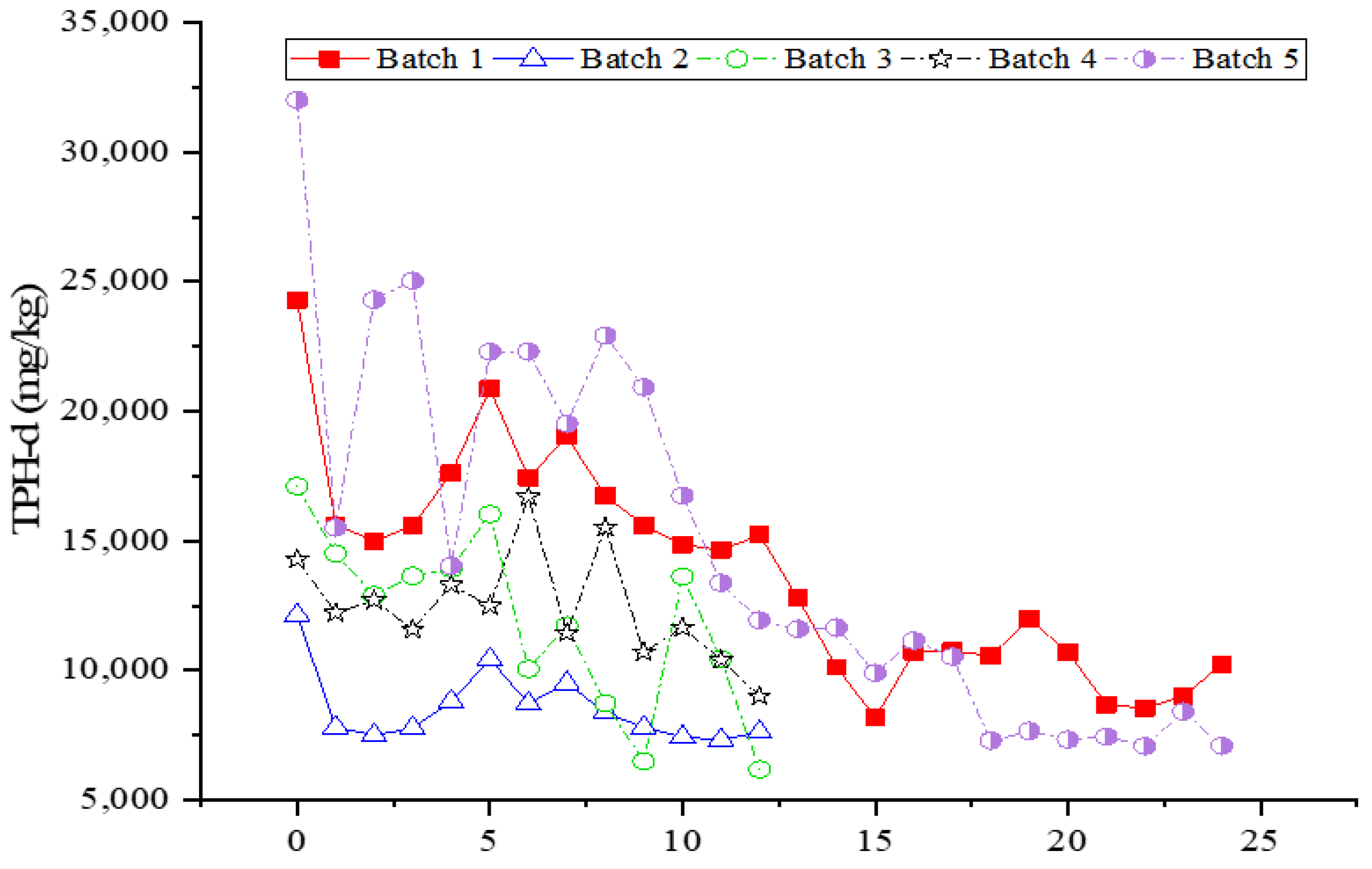
3.5. Effect of Ozone and Perozone in Diesel Contaminated Soil
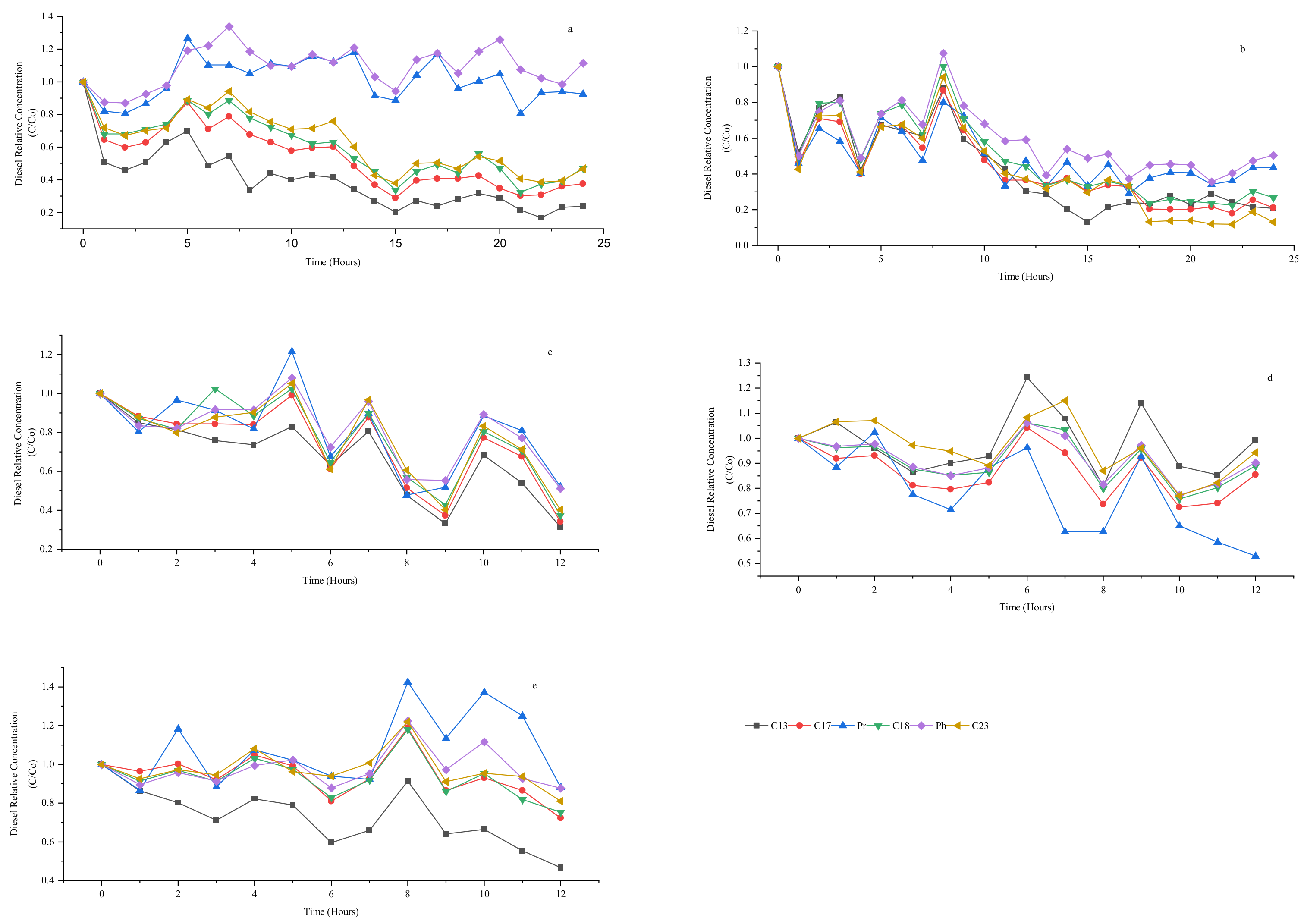
3.6. Effect of Ozone and Perozone in C13, C17, Pristane, C18, Phytane, and C23 Degradation
3.7. Hydroxyl Radical Conversion Rate (Rct)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolters, V. Biodiversity of soil animals and its function. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2001, 37, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Gudmundsson, L.; Hauser, M.; Qin, D.; Li, S.; Seneviratne, S.I. Soil moisture dominates dryness stress on ecosystem production globally. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Barberán, A.; Yang, Y.; Hu, S.; Guo, H. Nitrogen-induced acidification plays a vital role driving ecosystem functions: Insights from a 6-year nitrogen enrichment experiment in a Tibetan alpine meadow. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 153, 108107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Reich, P.B.; Trivedi, C.; Eldridge, D.J.; Abades, S.; Alfaro, F.D.; Bastida, F.; Berhe, A.A.; Cutler, N.A.; Gallardo, A.; et al. Multiple elements of soil biodiversity drive ecosystem functions across biomes. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brussaard, L.; de Ruiter, P.C.; Brown, G.G. Soil biodiversity for agricultural sustainability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 121, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baştabak, B.; Gödekmerdan, E.; Koçar, G. A holistic approach to soil contamination and sustainable phytoremediation with energy crops in the Aegean Region of Turkey. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wu, Y.; Liang, P.; Song, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Wu, W.; Liu, X.; Dong, C. Alkaline amendments improve the health of soils degraded by metal contamination and acidification: Crop performance and soil bacterial community responses. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittet, P.-A.; Josset, M.; Boilley, D.; Bernollin, A.; Rougier, G.; Froidevaux, P. Origin and age of an ongoing radioactive contamination of soils near La hague reprocessing plant based on 239+240Pu/238Pu and 241Am/241Pu current ratios and 90Sr and Ln(III) soil contents. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 129332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, A. In recognition of this special journal issue on real-world emissions on CARB’s leadership and central role in uncovering and resolving the environmental violations from Volkswagen’s use of illegal diesel defeat devices. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 1441–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziabari, S.-S.H.; Khezri, S.-M.; Kalantary, R.R. Ozonation optimization and modeling for treating diesel-contaminated water. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin Al Manmi, D.A.M.; Abdullah, T.O.; Al-Jaf, P.M.; Al-Ansari, N. Soil and Groundwater Pollution Assessment and Delineation of Intensity Risk Map in Sulaymaniyah City, NE of Iraq. Water 2019, 11, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cocârţă, D.; Stoian, M.; Karademir, A. Crude Oil Contaminated Sites: Evaluation by Using Risk Assessment Approach. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, B.; Lan, T.; Lu, D.; Liu, Z. Ecological and enzymatic responses to petroleum contamination. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakowska, J. Remediation of diesel-contaminated soil enhanced with firefighting foam application. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Song, S.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Meng, J.; Sweetman, A.J.; Jenkins, A.; Ferrier, R.C.; Li, H.; Luo, W.; et al. Impacts of soil and water pollution on food safety and health risks in China. Environ. Int. 2015, 77, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsitonaki, A.; Petri, B.; Crimi, M.; Mosbk, H.; Siegrist, R.L.; Bjerg, P.L. In situ chemical oxidation of contaminated soil and groundwater using persulfate: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 40, 55–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Du, J.; Bahar, M.M.; Wang, H.; Subashchandrabose, S.; Duan, L.; Yang, X.; Megharaj, M.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, W.; et al. Metagenomics analysis identifies nitrogen metabolic pathway in bioremediation of diesel contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahinejad, B.; Pasalari, H.; Jafari, A.J.; Esrafili, A.; Farzadkia, M. Bioremediation of diesel and gasoline-contaminated soil by co-vermicomposting amended with activated sludge: Diesel and gasoline degradation and kinetics. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Radian, A.; Long, M. Calcium superphosphate as an inorganic stabilizer for modified-Fenton treatment of diesel-contaminated soil with two different exogenous iron sources. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homem, V.; Santos, L. Degradation and removal methods of antibiotics from aqueous matrices—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 2304–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Giannakis, S.; Lu, X.; Chi, H.; Song, S.; Qi, J. Enhanced mineralization of atrazine by surface induced hydroxyl radicals over light-weight granular mixed-quartz sands with ozone. Water Res. 2019, 149, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, Z.-J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, L.; Cao, H.; Gong, J. Single-Atom Mn–N 4 Site-Catalyzed Peroxone Reaction for the Efficient Production of Hydroxyl Radicals in an Acidic Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 12005–12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Chen, D. Kinetics of ozone decomposition in aqueous solution with and without ultraviolet radiation. J. Chin. Inst. Chem. Eng. 1993, 24, 207. [Google Scholar]
- Rosal, R.; Rodríguez, A.; Perdigón-Melón, J.A.; Petre, A.; García-Calvo, E.; Gómez, M.J.; Agüera, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Degradation of caffeine and identification of the transformation products generated by ozonation. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Canonica, S.; von Gunten, U. Efficiency and energy requirements for the transformation of organic micropollutants by ozone, O3/H2O2 and UV/H2O2. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3811–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, D. Degradation of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid by O_3 and O_3/H_2O_2. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2005, 24, 690–693. [Google Scholar]
- Acero, J.L.; Gunten, U. Von Characterization of Oxidation processes: Ozonation and the AOP O3/H2O2. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2001, 93, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusic, H.; Koprivanac, N.; Srsan, L. Azo dye degradation using Fenton type processes assisted by UV irradiation: A kinetic study. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2006, 181, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-J.; Park, S.; Adil, S.; Lee, S.; Cho, K. Biogeochemical Alteration of an Aquifer Soil during In Situ Chemical Oxidation by Hydrogen Peroxide and Peroxymonosulfate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5301–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testolin, R.C.; Mater, L.; Sanches-Simões, E.; Dal Conti-Lampert, A.; Corrêa, A.X.R.; Groth, M.L.; Oliveira-Carneiro, M.; Radetski, C.M. Comparison of the mineralization and biodegradation efficiency of the Fenton reaction and Ozone in the treatment of crude petroleum-contaminated water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, L. AOPs-based remediation of petroleum hydrocarbons-contaminated soils: Efficiency, influencing factors and environmental impacts. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Iranmanesh, S.; Keir, I.; Achari, G. A Field Pilot Study on Treating Groundwater Contaminated with Sulfolane Using UV/H2O2. Water 2020, 12, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adil, S.; Maryam, B.; Kim, E.-J.; Dulova, N. Individual and simultaneous degradation of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim by ozone, ozone/hydrogen peroxide and ozone/persulfate processes: A comparative study. Environ. Res. 2020, 189, 109889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremasco, M.A.; Mochi, V.T. Reaction of dissolved ozone in hydrogen peroxide produced during ozonization of an alkaline medium in a bubble column. Acta Sci. Technol. 2013, 36, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farzaneh, H.; Loganathan, K.; Saththasivam, J.; McKay, G. Ozone and ozone/hydrogen peroxide treatment to remove gemfibrozil and ibuprofen from treated sewage effluent: Factors influencing bromate formation. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgin, M.; Borowska, E.; Helbing, J.; Hollender, J.; Kaiser, H.-P.; Kienle, C.; McArdell, C.S.; Simon, E.; von Gunten, U. Effect of operational and water quality parameters on conventional ozonation and the advanced oxidation process O3/H2O2: Kinetics of micropollutant abatement, transformation product and bromate formation in a surface water. Water Res. 2017, 122, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falciglia, P.P.; Urso, G.; Vagliasindi, F.G.A. Microwave heating remediation of soils contaminated with diesel fuel. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogelschatz, U.; Eliasson, B.; Hirth, M. Ozone Generation from Oxygen and Air: Discharge Physics and Reaction Mechanisms. Ozone Sci. Eng. 1988, 10, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, S.-H.; Jo, J.-H.; Jo, Y.-H.; Lee, H.-K.; Kong, S.-H. Application of a peroxymonosulfate/cobalt (PMS/Co(II)) system to treat diesel-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, H. Non-parametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1745, 13, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods, 4th ed.; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, R. Statistical Methods for Environmental Pollution Monitoring; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons Analysis in Soil by Using Gas Chromatography/Flame Ionization Detector (NIEA S703.62B). Available online: https://www.epa.gov.tw/niea/4BDDD939C0C096FE (accessed on 6 November 2021).
- Elovitz, M.S.; von Gunten, U. Hydroxyl Radical/Ozone Ratios during Ozonation Processes. I. The Rct Concept. Ozone Sci. Eng. 1999, 21, 239–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcantara-Garduño, M.E.; Okuda, T.; Tsai, T.-Y.; Nishijima, W.; Okada, M. Experimental and mathematical evaluation of trichloroethylene removal from saturated soil using acetic acid with saturated ozone. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 60, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.S.; Amy, G.L.; Murphy, B.D. Ozone enhanced removal of natural organic matter from drinking water sources. Water Res. 1997, 31, 3098–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.P.; Liang, Y.Y.; Chang, C.N.; Chao, A.C. Differentiating ozone direct and indirect reactions on decomposition of humic substances. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 2395–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, S.-H.; Kwon, C.-I.; Kim, M.-H. Ozone kinetics and diesel decomposition by ozonation in groundwater. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2003, 20, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Initial Diesel Concentration (mg/kg) | Experiment ID | H2O2 Concentration | H2O2:Soil Ratio (Weight Basis) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24,200 | Batch 1 | 0% | x |
| 24,223 | Batch 2 | 4% | 1:50 |
| 17,115 | Batch 3 | 7% | 1:50 |
| 14,286 | Batch 4 | 10% | 1:50 |
| 32,131 | Batch 5 | 7% | 1:100 |
| Items | Groundwater w/o Ozone Sparging (mg/L) | Groundwater after 1 h Ozone Sparging (mg/L) | Groundwater after 6 h Ozone Sparging (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 9.49 | 2.85 | 2.22 |
| Br− | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.05 |
| BrO3− | <0.0006 | <0.0006 | <0.0006 |
| NO3− | 0.80 | 380 | 1090 |
| PO43− | 0.50 | <0.013 | 0.60 |
| Cl− | 6.80 | 9.80 | 20.2 |
| F− | <0.013 | 0.50 | 1.00 |
| SO42− | 5.20 | 14.8 | 71.5 |
| NO2− | <0.011 | 1.00 | 1.90 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.-Y.; Pokhrel, P.; Wang, Y.-S.; Lin, S.-L.; Liu, M.-H. Combined Application of Ozone and Hydrogen Peroxide to Degrade Diesel Contaminants in Soil and Groundwater. Water 2021, 13, 3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233404
Chen W-Y, Pokhrel P, Wang Y-S, Lin S-L, Liu M-H. Combined Application of Ozone and Hydrogen Peroxide to Degrade Diesel Contaminants in Soil and Groundwater. Water. 2021; 13(23):3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233404
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wen-Yu, Prakash Pokhrel, Ying-Shun Wang, Sheng-Lung Lin, and Min-Hsin Liu. 2021. "Combined Application of Ozone and Hydrogen Peroxide to Degrade Diesel Contaminants in Soil and Groundwater" Water 13, no. 23: 3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233404
APA StyleChen, W.-Y., Pokhrel, P., Wang, Y.-S., Lin, S.-L., & Liu, M.-H. (2021). Combined Application of Ozone and Hydrogen Peroxide to Degrade Diesel Contaminants in Soil and Groundwater. Water, 13(23), 3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233404






