Experimental Study on Landslides in Terraced Fields in the Chinese Loessial Region under Extreme Rainfall
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Soil Properties
2.2. Test Device
2.3. Soil-Filling and Sensor Embedding
2.4. Test Method
3. Results and Discussion
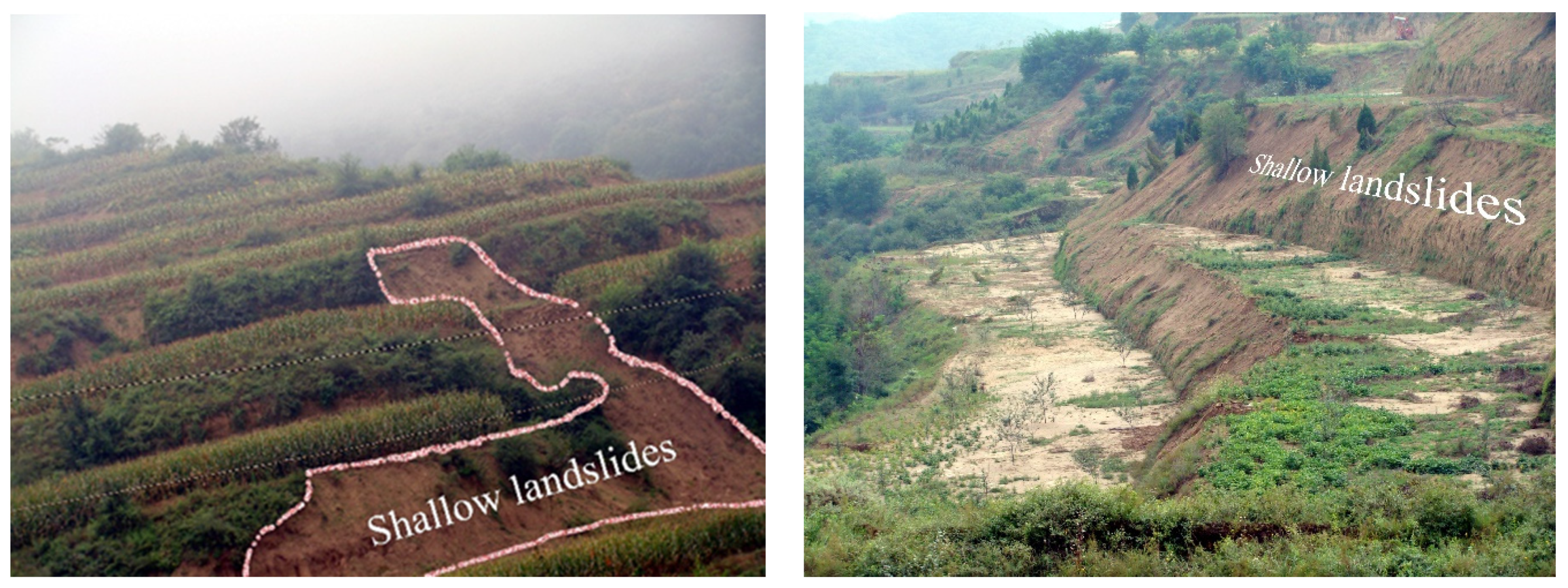
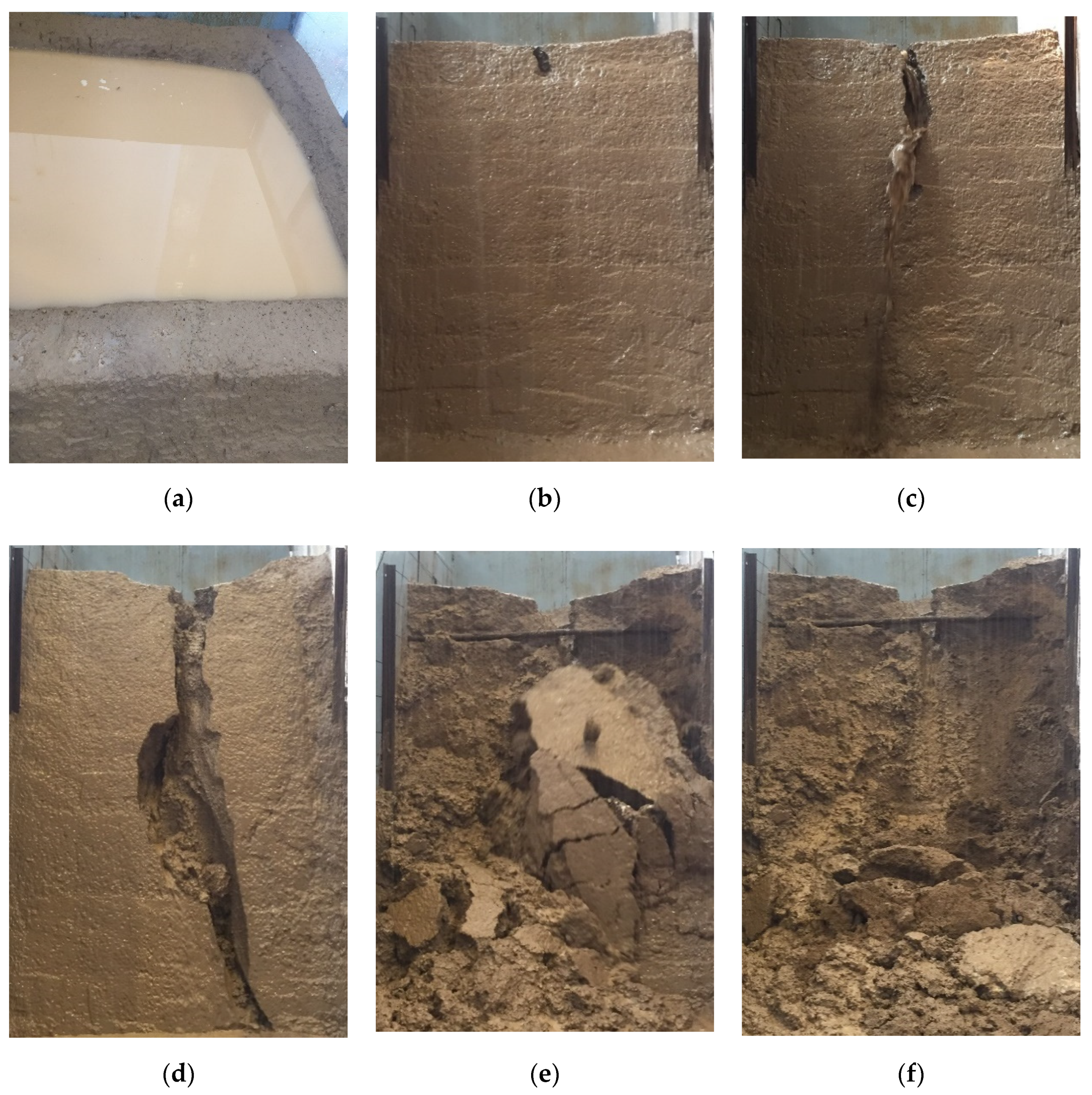
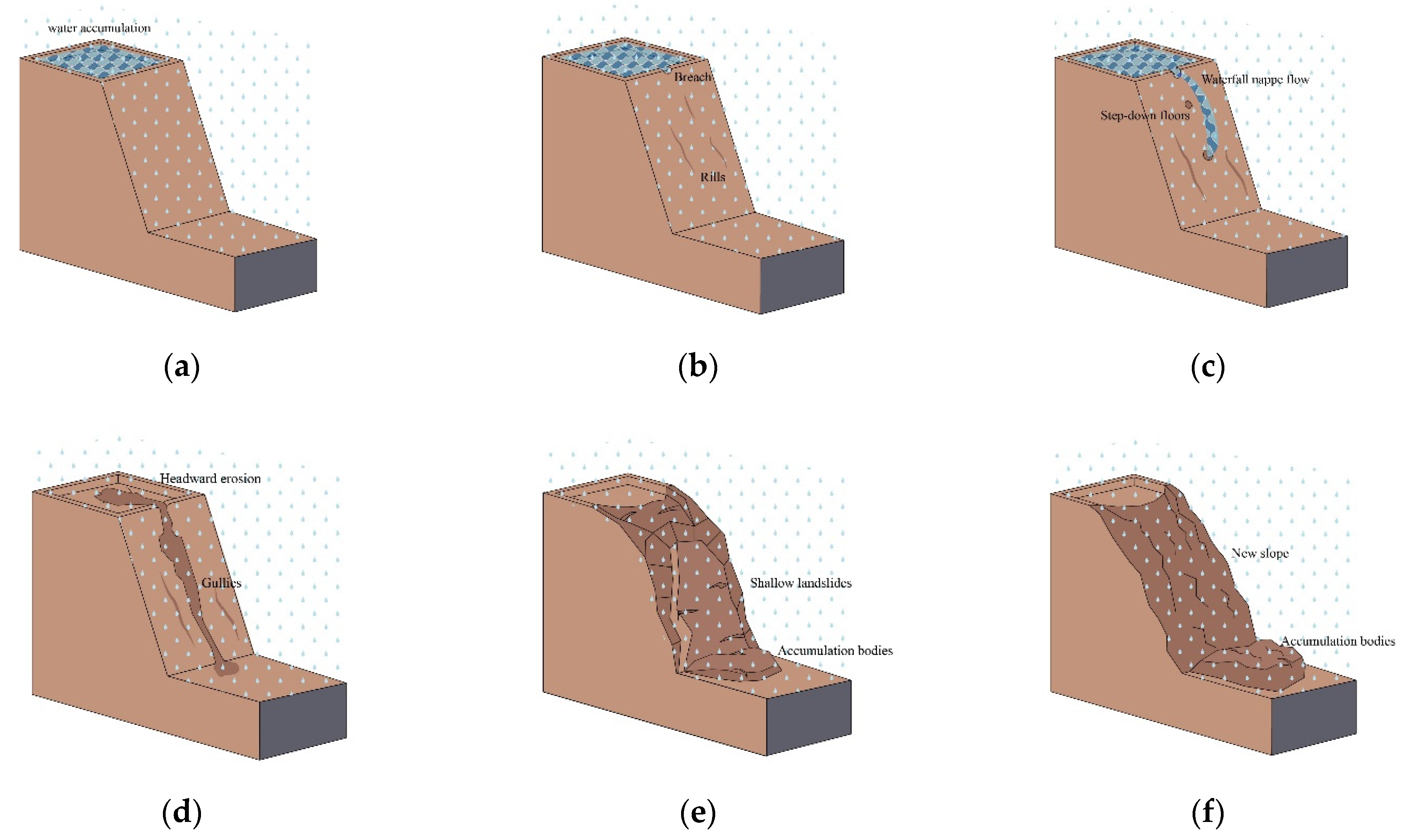
3.1. Mechanism and Process of Shallow Landslides of Terraces
3.1.1. Mechanism of Shallow Landslides of Terraces
3.1.2. Process and Mode of Shallow Landslides of the Terraces
3.2. The Factors of Deep Slip Surface of Terraces
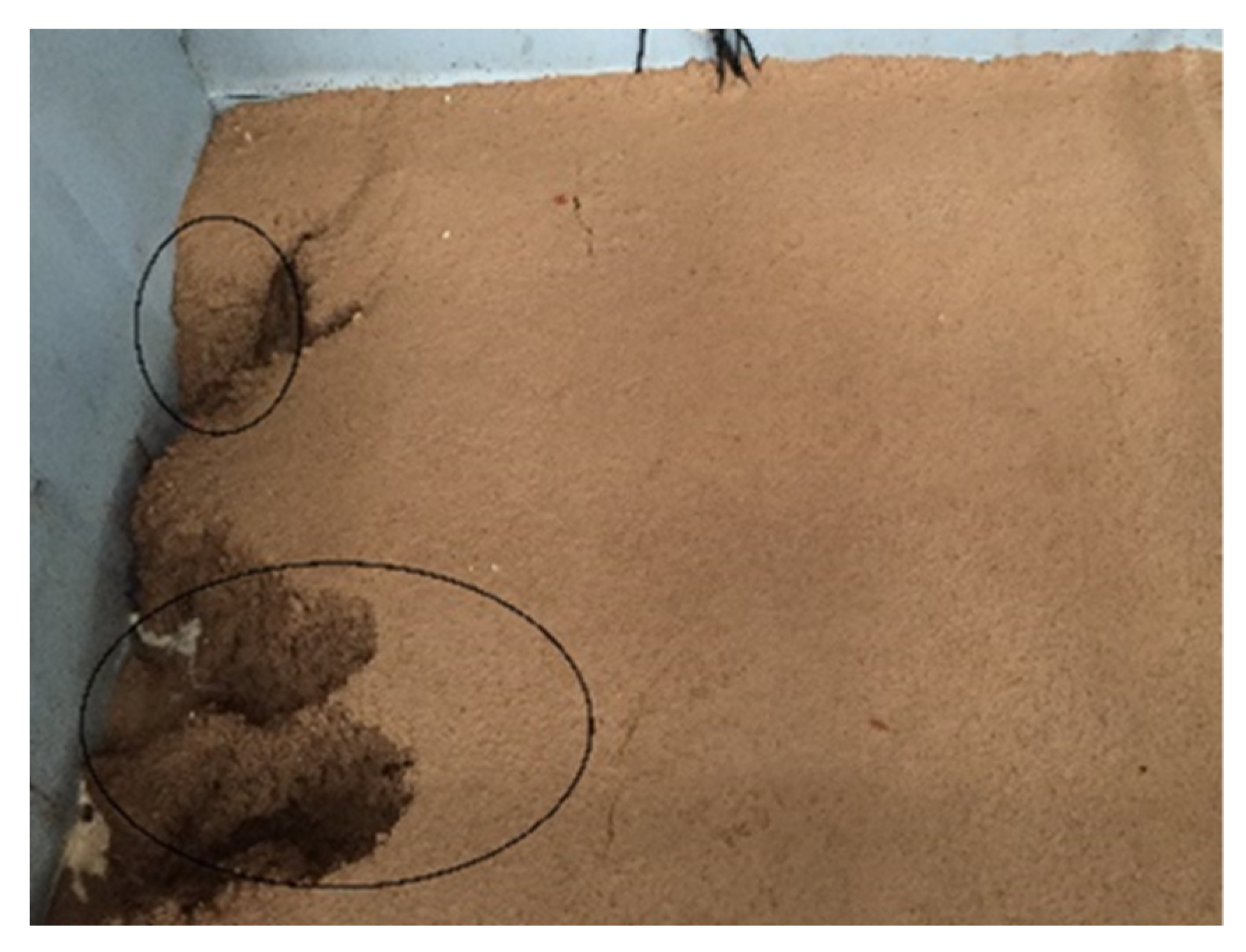
3.2.1. Rainfall Infiltration
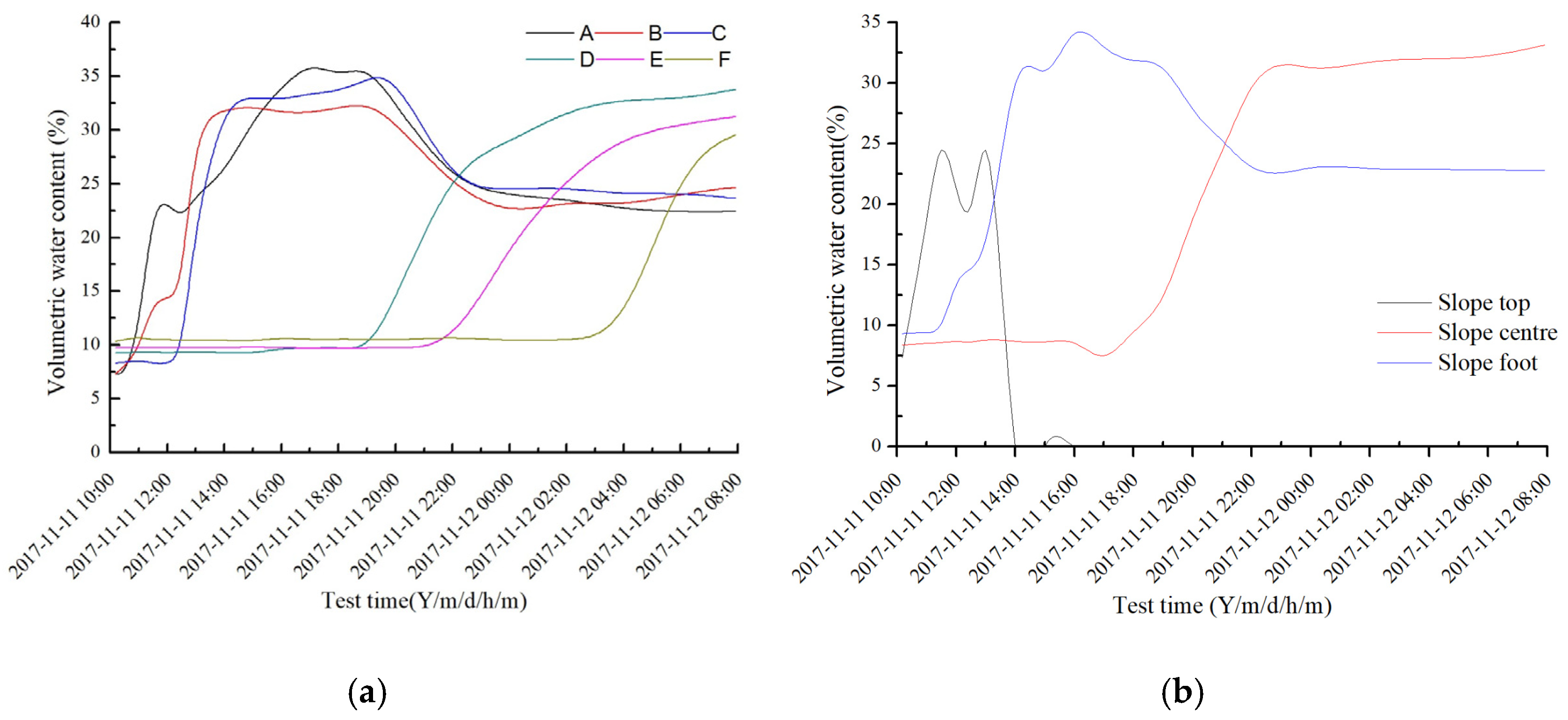
3.2.2. Water Content
3.2.3. Pore Water Pressure and Suction
3.3. Shape Characteristics and Mechanism of Deep Slip Surface
3.3.1. Shape Characteristics
3.3.2. Mechanical Mechanism
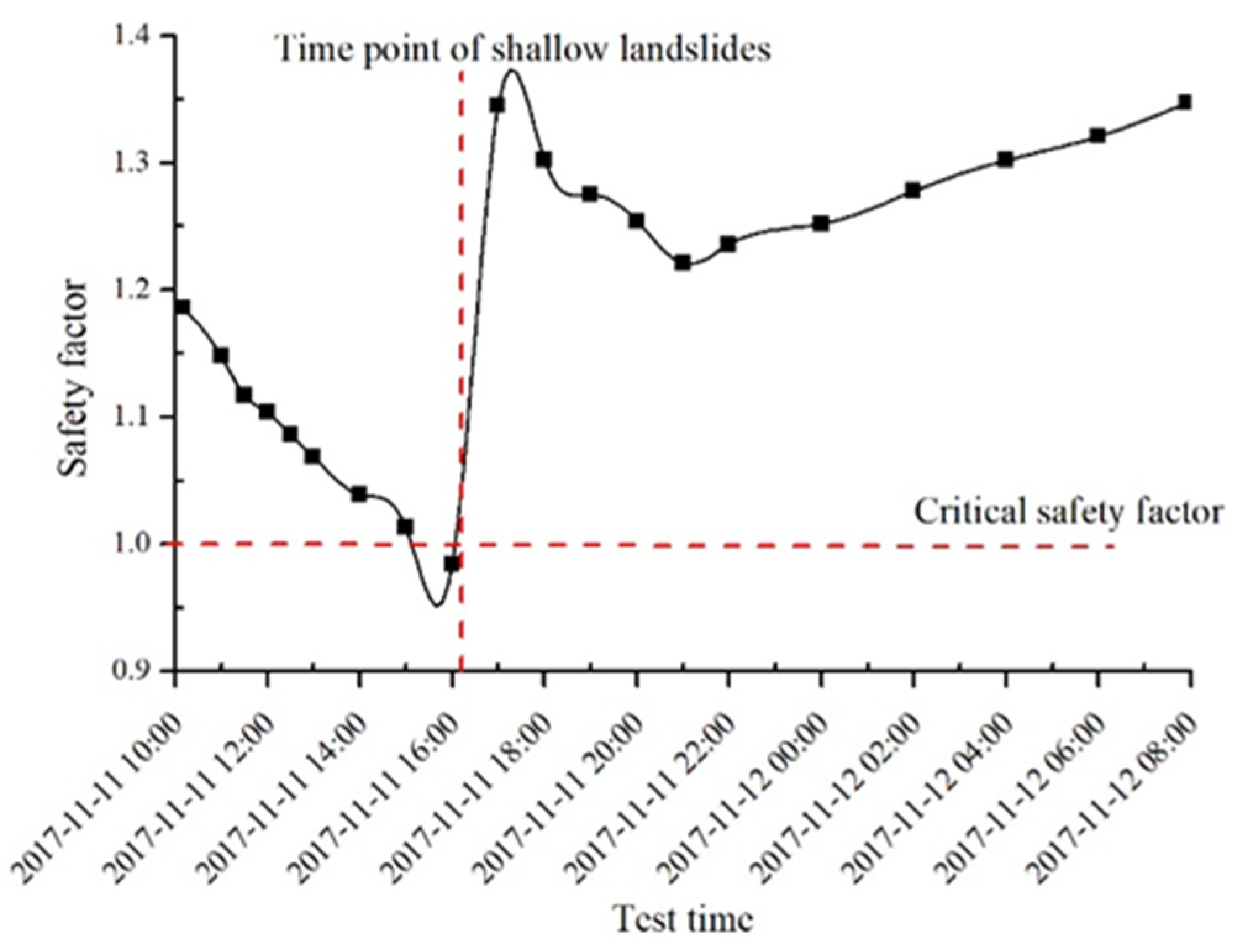
3.3.3. Variation in Characteristic Points Displacement with Accumulated Rainfall
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, W.; Chen, D.; Wang, L.; Daryanto, S.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Sun, G.; Feng, T. Global synthesis of the classifications, distributions, benefits and issues of terracing. Earth Sci. Rev. 2016, 159, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Lindstrom, M.J. Evaluating Soil Quality-Soil Redistribution Relationship on Terraces and Steep Hillslope. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Peng, J.; Wang, G.; Iqbal, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, X. Prediction of rainfall-induced shallow landslides in the Loess Plateau, Yan’an, China, using the TRIGRS model. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Bruijnzeel, L.A. Runoff and soil loss from bench terraces. 1. An event-based model of rainfall infiltration and surface runoff. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 55, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wang, Q.J.; Scott, B.J. Soil water depletion and recharge under different land cover in China’s Loess Plateau. Ecohydrology 2015, 9, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Bruijnzeel, L.A. Terrace erosion and sediment transport model: A new tool for soil conservation planning in bench-terraced steep lands. Software 2003, 18, 839–850. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Seeger, M.; Iserloh, T.; González, J.M.S.; Ruiz-Sinoga, J.D.; Ries, J.B. Rainfall-simulated quantification of initial soil erosion processes in sloping and poorly maintained terraced vineyards—Key issues for sustainable management systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.F.; Gao, P.; Mu, X.M. Response of soil erosion to rainfall intensity in terraced slope in the Loess Plateau. J. Sediment Res. 2017, 6, 46–51. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, W.; Guo, M.; Chen, Z.; Feng, L.; Zhao, M.; Xiao, H. The impact of flow discharge on the hydraulic characteristics of headcut erosion processes in the gully region of the Loess Plateau. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tony, L.T.; Zhan, G.W.; Jia, Y.M. An analytical solution for rainfall infiltration into an unsaturated infinite slope and its application to slope stability analysis. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2012, 37, 1737–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, J.Y.; Wang, W.Z. Quality and soil-water conservation effectiveness of level terrace on the Loess Plateau. Trans. CSAE 1999, 2, 59–63. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bandara, S.; Ferrari, A.; Laloui, L. Modelling landslides in unsaturated slopes sub-jected to rainfall infiltration using ma-terial point method. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2016, 40, 1358–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.-C.; Tan, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-H. The influence of water retention curve hysteresis on the stability of unsaturated soil slopes. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 3563–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.D.; Gu, T.F.; Zhang, M.S. Experimental study of loess disintegration charac-teristics. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2019, 44, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.; Oka, F.; Kimoto, S. Numerical analysis of a one-dimensional infiltration problem in unsaturated soil by a seepage-deformation coupled method. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2011, 35, 544–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.I.; Arosio, D.; Tresoldi, G.; Hojat, A.; Zanzi, L.; Papini, M.; Longoni, L. Investigation on the Role of Water for the Stability of Shallow Landslides—Insights from Experimental Tests. Water 2020, 12, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bui, D.T.; Pradhan, B.; Lofman, O.; Revhaug, I.; Dick, Ø.B. Regional prediction of landslide hazard using probability analysis of intense rainfall in the Hoa Binh province, Vietnam. Nat. Hazards 2012, 66, 707–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonstorch, H.; Zorita, E.; Cubasch, U. Downscaling of global cli-mate-change estimates to regional scales—An application to iberian rainfall in wintertime. J. Clim. 1993, 6, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.Z.; Yu, Y.Z.; Li, G.X. Influence of rainfall characteristics on soil slope failure. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2009, 1, 198–294. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Z.B.; Zhang, L.L.; Wang, J.H. Model tests on rainfall-induced colluvium land-slides: Effects of particle-size distribution. J. Geotech. Eng. 2015, 7, 1319–1327. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Q.; Sun, H.Y.; Sun, X.M. Influence of rainfall infiltration on slopes by physical model test. J. Geotech. Eng. 2009, 3, 589–594. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, S.; Lee, K.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y. Analysis of Rainfall-Induced Landslide on Unsaturated Soil Slopes. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aleotti, P. A warning system for rainfall-induced shallow failures. Eng. Geol. 2004, 73, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.M.; Wang, G.L.; Gu, X.W. Centrifuge modeling for instability of excavated slope inexpansive soil due to water in-filtration. J. Geotech. Eng. 2006, 2, 270–273. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Sassa, K. Factors affecting rainfall-induced flowslides in laboratory flume tests. Géotechnique 2001, 7, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohari, A.; Nishigaki, M.; Komatsu, M. Laboratory Rainfall-Induced Slope Failure with Moisture Content Measurement. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2007, 133, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-C.; Lo, C.-L.; Jang, J.-S.; Hwu, L.-K. Internal soil moisture response to rainfall-induced slope failures and debris discharge. Eng. Geol. 2008, 101, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, I.; Karacan, E. A Landslide in Clayey Soils: An Example from the Kızıldag Region of the Sivas-Erzincan Highway (Sivas-Turkey). Environ. Geosci. 2008, 9, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benn, J.L. Landslide events on the West Coast, South Island, 1867–2002. N. Z. Geogr. 2005, 61, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Benoy, G.; Chow, T.L.; Rees, H.W.; Bourque, C.P.-A.; Meng, F.-R. A Watershed-scale Assessment of Cost-Effectiveness of Sediment Abatement with Flow Diversion Terraces. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Yang, J.; Zhao, C.Y. Runoff and sediment from orchard terraces in southeastern china. Land Degrad. Dev. 2012, 25, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Gao, J.E.; Zhang, Y.X. Analysis of Yan’an extreme rainfall characteristics and impacts of erosion disasters on terraces. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 6, 79–84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Stavi, I.; Rozenberg, T.; Al Ashhab, A.; Argaman, E.; Groner, E. Failure and Collapse of Ancient Agricultural Stone Terraces: On-Site Effects on Soil and Vegetation. Water 2018, 10, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, D.S. The design of the cross-sections of terrace in the loess plateau of china. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1987, 02, 28–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.Q. Analysis of the stability of terrace soil edge in sandy mountains. Soil Water Conserv. 1999, 7, 32–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Han, T.C.; Dou, H.Q.; Ma, S.G. Research on slope stability of terrace based on crop irrigation infiltration. J. Sichuan Univ. 2014, S1, 79–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Li, G.L.; Wei, Z. Teat on expansion ratio and mechanical property of terrace soil ridges of southern shaanxi. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 5, 40–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.L.; Tian, J.; Zheng, T.T. Optimized design of loess terrace based on slope stability. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 4, 21–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire, E. Geological hazards in loess terrain, with particular reference to the loess regions of China. Earth Sci. Rev. 2001, 1–3, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.j.; Chen, Y. Rb and Sr Geochemical Characterization of the Chinese Loess Stratigraphy and Its Implications for Palaeomonsoon Climate. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2010, 74, 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, F.-L.; Huang, C.-H.; Norton, L.D. Vertical Hydraulic Gradient and Run-On Water and Sediment Effects on Erosion Processes and Sediment Regimes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Hong, B.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Lei, H. Erosion characteristics of loess tunnels on the Loess Plateau: A field investigation and experimental study. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2020, 45, 1945–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xu, X.; Zheng, F.; Qin, C.; He, X. Gully morphological characteristics in the loess hilly-gully region based on 3D laser scanning technique. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, Z.-L.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, B.; Liu, J.; Nan, S. Modelling the process of soil detachment by rill flow on steep loessial hillslopes. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2020, 45, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Ni, J.R.; Li, T.H. Headcut and bank landslip in rill evolution. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 2002, 2, 115–125. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, G.; Cochrane, T.A. Rainfall induced shallow landslides on sandy soil and impacts on sediment discharge: A flume based investigation. In Proceedings of the 12th Conference of International Association for Computer Methods and Advances in Geomechanics, Goa, India, 1–6 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Q.M.; Chen, S.S.; Mei, S.A. Breach Mechanism and Breach Process Simulation of Homogeneous Cohesive Earthen Dam Due to Overtopping. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2019, 51, 25–32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.W.; Hassan, M.A.A.M.; Vaskinn, K.A. Breach formation: Field test and la-boratory experiments. J. Hydraul. Res. 2007, 45, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, G.J.; Cook, K.R.; Hunt, S.L. Physical modeling of overtopping erosion and breach formation of cohesive embankments. Trans. ASAE 2005, 48, 1783–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Wang, G.; Wu, L.Z. Physical model experiments for shallow failure in rain-fall-triggered loess slope, Northwest China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 4363–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.P.; Lei, T.W.; Guo, S.Y. Study on spatial variation of infiltration rates for small watershed in loess plateau. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2001, 10, 88–92. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Y.; Wang, F.G.; Yang, S.T. Study on harmony equilibrium between water re-sources and economic society development. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 45, 793–800. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X. Effects of rainfall intensity, underlying surface and slope gradient on soil infiltration under simulated rainfall experiments. Catena 2013, 104, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Zhu, J. Infiltration Model Based on Traveling Characteristics of Wetting Front. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2018, 82, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S. Indoor Model Test Study on Fill Slope under Earthquake and Rainfull. Pearl River 2019, 40, 61–70. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Guan, Y. Assessing the Impact of Terraces and Vegetation on Runoff and Sediment Routing Using the Time-Area Method in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Water 2019, 11, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.J.; Su, X.; Meng, X.M. Characteristics and Origin of Loess Landslides on Loess Terraces at Heifangtai, Gansu Province, China. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 694, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnoletti, M.; Errico, A.; Santoro, A.; Dani, A.; Preti, F. Terraced Landscapes and Hydrogeological Risk. Effects of Land Abandonment in Cinque Terre (Italy) during Severe Rainfall Events. Sustainability 2019, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, R. Determination of the critical slip surface in slope stability computations. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 1980, 4, 333–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, J.Q.; Li, J. The Influence of Water Content on the Strength of Unsaturated Loess. J. Northwest Agric. Univ. 1996, 1, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, J.Q.; Li, J. The structural strength and shear strength of unsaturated loess. Shuili Xuebo 2001, 7, 0079-05. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Luo, Y.S.; Wu, C.P. The Laboratory Model Test Sdudy of Loess Slope uder the Artificial Rainfall. China Rural Water Hydropower 2013, 5, 100–104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]












| Great Group | Natural Density (g.cm−3) | Natural Water Content (%) | Dry Density (g.cm−3) | Cohesion (Kpa) | Internal Friction Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcic Cambisols | 1.32 | 7.86 | 1.21 | 13.85 | 20.10 |
| Soil Dry Density (g/cm−3) | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1.2 | 37.67 | 1.602 |
| 1.3 | 42.3 | 1.615 |
| 1.4 | 79.33 | 1.782 |
| 1.5 | 108.901 | 1.795 |
| 1.6 | 56.687 | 1.503 |
| Soil Dry Density (g/cm−3) | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| soil water content | 7% | 20.8 | 21 | 21.1 | 21.6 | 22.6 |
| 9% | 20.4 | 20.7 | 20.9 | 21.5 | 22.5 | |
| 11% | 20.1 | 20.3 | 20.7 | 21.3 | 22.3 | |
| 13% | 19.8 | 20 | 20.5 | 21.2 | 22.1 | |
| 15% | 19.6 | 19.6 | 20.3 | 20.9 | 21.9 | |
| 17% | 19.3 | 19.4 | 20.1 | 20.8 | 21.6 | |
| 19% | 18.9 | 19.2 | 19.9 | 20.8 | 21.4 | |
| 21% | 18.6 | 19 | 19.7 | 20.5 | 21.2 | |
| 23% | 18.2 | 18.8 | 19.5 | 20.4 | 21.1 | |
| 25% | 17.9 | 18.6 | 19.3 | 20.2 | 21 | |
| 27% | 17.6 | 18.4 | 19.1 | 20.2 | 20.9 | |
| 29% | 17.2 | 18.2 | 18.9 | 20 | 20.8 | |
| 31% | 16.8 | 18 | 18.7 | 19.9 | 20.6 | |
| 33% | 16.5 | 17.8 | 18.5 | 19.8 | 20.5 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, Y.; Gao, P.; Mu, X.; Li, M.; Su, Y.; Wang, H. Experimental Study on Landslides in Terraced Fields in the Chinese Loessial Region under Extreme Rainfall. Water 2021, 13, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030270
Wen Y, Gao P, Mu X, Li M, Su Y, Wang H. Experimental Study on Landslides in Terraced Fields in the Chinese Loessial Region under Extreme Rainfall. Water. 2021; 13(3):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030270
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Yongfu, Peng Gao, Xingmin Mu, Mengzhen Li, Yongjun Su, and Haixing Wang. 2021. "Experimental Study on Landslides in Terraced Fields in the Chinese Loessial Region under Extreme Rainfall" Water 13, no. 3: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030270
APA StyleWen, Y., Gao, P., Mu, X., Li, M., Su, Y., & Wang, H. (2021). Experimental Study on Landslides in Terraced Fields in the Chinese Loessial Region under Extreme Rainfall. Water, 13(3), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030270






