Abstract
The adsorption and electroadsorption of bromide from natural water has been studied in a filter-press electrochemical cell using a commercial granular activated carbon as the adsorbent. During electroadsorption experiments, different voltages were applied (2 V, 3 V and 4 V) under anodic conditions. The presence of the electric field improves the adsorption capacity of the activated carbon. The decrease in bromide concentration observed at high potentials (3 V or 4 V) may be due to the electrochemical transformation of bromide to Br2. The anodic treatment produces a higher decrease in the concentration of bromide in the case of cathodic electroadsorption. Moreover, in this anodic electroadsorption, if the system is again put under open circuit conditions, no desorption of the bromide is produced. In the case of anodic treatment in the following adsorption process after 24 h of treatment at 3 V, a new decrease in the bromide concentration is observed as a consequence of the decrease in bromide concentration after the electrochemical stage. It can be concluded that the electroadsorption process is effective against the elimination of bromide and total bromine in water, with a content of 345 and 470 µg L−1, respectively, reaching elimination values of 46% in a single-stage electroadsorption process in bromide and total bromine. The application of the electric field to the activated carbon with a positive polarization (anodic electroadsorption) increases the adsorption capacity of the activated carbon significantly, achieving a reduction of up to 220 µg L−1 after 1 h of contact with water. The two stage process in which a previous electrochemical oxidation is incorporated before the electroadsorption stage significantly increased the efficiency from 46% in a single electroadsorption step at 3 V, to 59% in two stages.
1. Introduction
Disinfection and elimination of pathogens is a fundamental part of water treatment for human consumption, with chlorination being the most widespread method in the world due to its low cost, among other favorable conditions. To ensure water quality, a concentration between 0.2 and 1 mg L−1 of free residual chlorine is necessary in the entire drinking water distribution network. When chlorine is combined with some contaminants present in the water, disinfection by-products can be generated. These water disinfection by-products (DBPs) are substances that are formed as a result of the reaction between disinfectants and some compounds present in water, such as natural organic matter. Organic matter dissolved in raw water is one of the main causes of the formation of DPBs, since it reacts with chlorine giving rise to the formation of halogenated trihalomethanes [1]. Trihalomethanes are disinfection by-products (DBPs) formed by the reaction of chlorine derivatives in drinking water with their precursors, which can be organic matter or bromide. The most common THMs are chloroform trichloromethane (CHCl3), bromodichloromethane (CHBrCl2), dibromochloromethane (CHBr2Cl), bromoform, and tribromomethane (CHBr3) [2].
Environmental legislation regarding the presence of trihalomethanes (THMs) in drinking water is becoming increasingly restrictive. In accordance with current regulations, the need to control the concentration of these compounds in water for human consumption is established, since their presence can cause serious damage to human health [3].
In this sense, drinking water, or sources of water intended for human consumption (potable and/or pre-potable), usually have a low concentration of bromide. However, sometimes they can be generated during the purification process and lead to compounds of high toxicity for humans [4,5,6,7].
The presence of bromide is of special interest because, unlike chloride, bromide favors the formation of THMs, producing compounds such as bromoform (CHBr3), bromodichloromethane (CHCl2Br) or chlorodibromomethane (CHCIBr2), among others. [8,9]. Bromide is found naturally in seawater and in coastal areas, which is a problem of special interest in the waters for human consumption in the Mediterranean basin.
Conventional water treatment processes (coagulation, flocculation, and sedimentation) remove organic precursors from water in the range of 20%–60% [10,11,12], but they are not effective in removing inorganic precursors [13,14,15,16,17]. Bromide, arsenic, phosphate, nitrite and selenium are available in water as anions. Therefore, the removal is strongly dependent on the hydrophobic character of the sorbent (in essence it is about the isolectric point and/or point of zero charge) and the properties of the anions (in this sense, the speciation that encompasses the charge and the changes are important with respect to electrostatic interaction with the adsorbent). Thus, adsorption is favored in hydrophobic materials, such as activated carbons, for hydrated anions with a low degree of hydration, when comparing anions with the same charge [18,19]. In this study, we focus on the removal of bromide in waters with elevated bromide levels. This results in an increase in the Br-/DOC ratio and promotes the formation of brominated DBPs with higher toxicity [20]. Thus, new and advanced treatment technologies are needed to remove inorganic precursors.
Until now, the existing treatment systems for the removal of Br−, I−, and Cl− ions are based on the use of different types of ion exchange resins, although they are not very efficient due to their high cost and the low selectivity of the exchange process [21,22,23,24,25]. Activated carbons are the alternative for the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from polluted waters due to the combination of high surface area, chemical and physical stability, adjustable surface chemistry and reduced production costs. Thus, adsorption treatments using these porous carbon materials are known to combine a high degree of efficiency with a reasonable cost [26,27].
GAC has a number of properties, such as high surface area, large porosity, well developed internal pore structure consisting of micro-, meso- and macropores, as well as a wide spectrum of functional groups present on the surface of AC, which makes it a versatile material that has numerous applications in many areas, but mainly in the environmental field [28]. The efficiency of ACs as adsorbents for diverse types of pollutants is well reported [29,30]. It is well known that activated carbon has been found to be very efficient in removing organic compounds than metals and other inorganic pollutants. Efforts are ongoing to substantially improve the potential of carbon surface by using different chemicals or suitable treatment methods [31], which will enable AC to enhance its potential for the removal of specific contaminants from the aqueous phase. The use of granular activated carbons in organic DBP precursors removal has been widely reported. [32] However, the influence of carbon surface tailoring on Br removal has not been extensively investigated, and very few studies have explored Br removal by the tailored AC surface at practical adsorbent doses [33], along with the control of brominated DBPs in natural waters.
In this sense, activated carbon treatments with silver ions deposited on their surface have been used for selective adsorption of Br−, I−, and Cl− anions, although their adsorption efficiency is not very important due to the dissolution of silver during the process [34,35]. The use of granular activated carbon (GAC) adsorption is beneficial from a standpoint of controlling disinfection by-product (DBP) formation and associated toxicity in water impacted by bromide and iodide. GAC has been used as an effective material to control DBP formation on a large range of bromide (20–1000 μg L−1) and iodide (<5–100 μg L−1) concentrations [36]. There are many reports in the literature on the use of carbon adsorbents for the removal of metals and metal compounds, but generally not for low μg L−1 levels [34,35,37], which is mainly a consequence of its hydrophobic nature. Moreover, composite materials based on activated carbons have been used in the removal of inorganic compounds in water [18,19,38].
More particularly, remediation of metallic ions in concentrations in the range of parts per million (mg L−1) using activated carbon as the adsorbent has proved to be feasible [39,40,41]. Interestingly, under certain conditions, the effectiveness of activated carbons can be significantly improved by the application of an electric field during the adsorption/desorption process (electrosorption/electrodesorption), which may enhance their capacity [42,43]. In those cases, the application of a controlled electric potential to the adsorbent can enhance adsorption by enabling the formation of an electric double layer in the surface of the activated carbon in contact with the solution. This phenomenon shares the same fundamentals as the energy storage in supercapacitors [44] and the capacitive deionization for water purification [42,45], and it is only possible in porous materials with adequate pore size distribution and acceptable conductivity, such as activated carbons. However, most of the electroadsorption studies have been done for organic compounds [43,46,47], although it has also been used in the elimination of inorganic salts in water [48,49]; however, this electroadsorption methodology has not been used for the elimination of bromide in water in a low concentration level of µg L−1. The electroadsorption process, under appropriate conditions, may be effective for the removal of a low concentration of pollutants, and in addition, it is a non-destructive procedure.
This research studies the removal of Br− ion and total bromine in water by electroadsorption and the combination of this process with an electrochemical treatment under anodic conditions using an activated carbon filter in an electrochemical cell, thus suppressing the possible formation of these brominated compounds. In this sense, the main objective of this work is to study the reduction in the concentration of bromide and total bromine in a solution that allows, in subsequent investigations, it to develop/optimize a procedure for the elimination of bromide to comply with current regulations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of Granular Activated Carbon
In this study, the activated carbon used was a Granular Activated Carbon (GAC), available from Waterlink Suctliffe Carbons (Lancashire, UK). It is a high porosity material whose adsorption was characterized using the Autosorb-6 equipment (Quantachrome, Boynton Beach, FL, USA). For this, the adsorption-desorption analyses of N2 were performed at a temperature of −196 °C and CO2 adsorption at a temperature of 0 °C. Previously, the sample was degassed under a vacuum for 4 h at a temperature of 250 °C. To determine the apparent surface area SBET, the BET equation was applied to the adsorption isotherm of N2 under the relative pressures region between 0.05 and 0.20. Similarly, for the determination of the total volume of micropores, the Dubinin Radushkevich equation (DR) was applied on the adsorption isotherm of N2 in the range of relative pressures between 0.005 and 0.10. Regarding the narrow volume of micropores, it was determined by means of the CO2 adsorption isotherm [50]. Table 1 shows the textural properties of the GAC.

Table 1.
Characterization of the porosity of Activated Carbon PQ-0602-04.
Granular activated carbon was thoroughly washed using distilled water, filtered and dried at 110 °C in order to clean its internal surface before its characterization and further use as bromide adsorbent.
2.2. Water Characterization, Bromide and Total Bromine Determination
The drinking water used in this study is a real sample that came from the Alicante seawater desalination plant (Alicante, Spain). The bromide concentration (Br−) was 345 µg L−1, and this concentration was analyzed by ion chromatography. The Br− and total bromine (Br) concentrations during the different experiments were measured using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) with Perkin-Elmer 4300 DV equipment (Waltham, MA, USA). For the ICP-MS measurements, each sample was dissolved in 0.5 M HNO3, followed by filtration using a nylon membrane filter (pore diameter ~350 nm). The total bromine concentration includes all Br-containing species present in the water.
The water characterization is detailed in the following table (Table 2).

Table 2.
Water characterization.
2.3. Electrochemical Filter-Press Cell
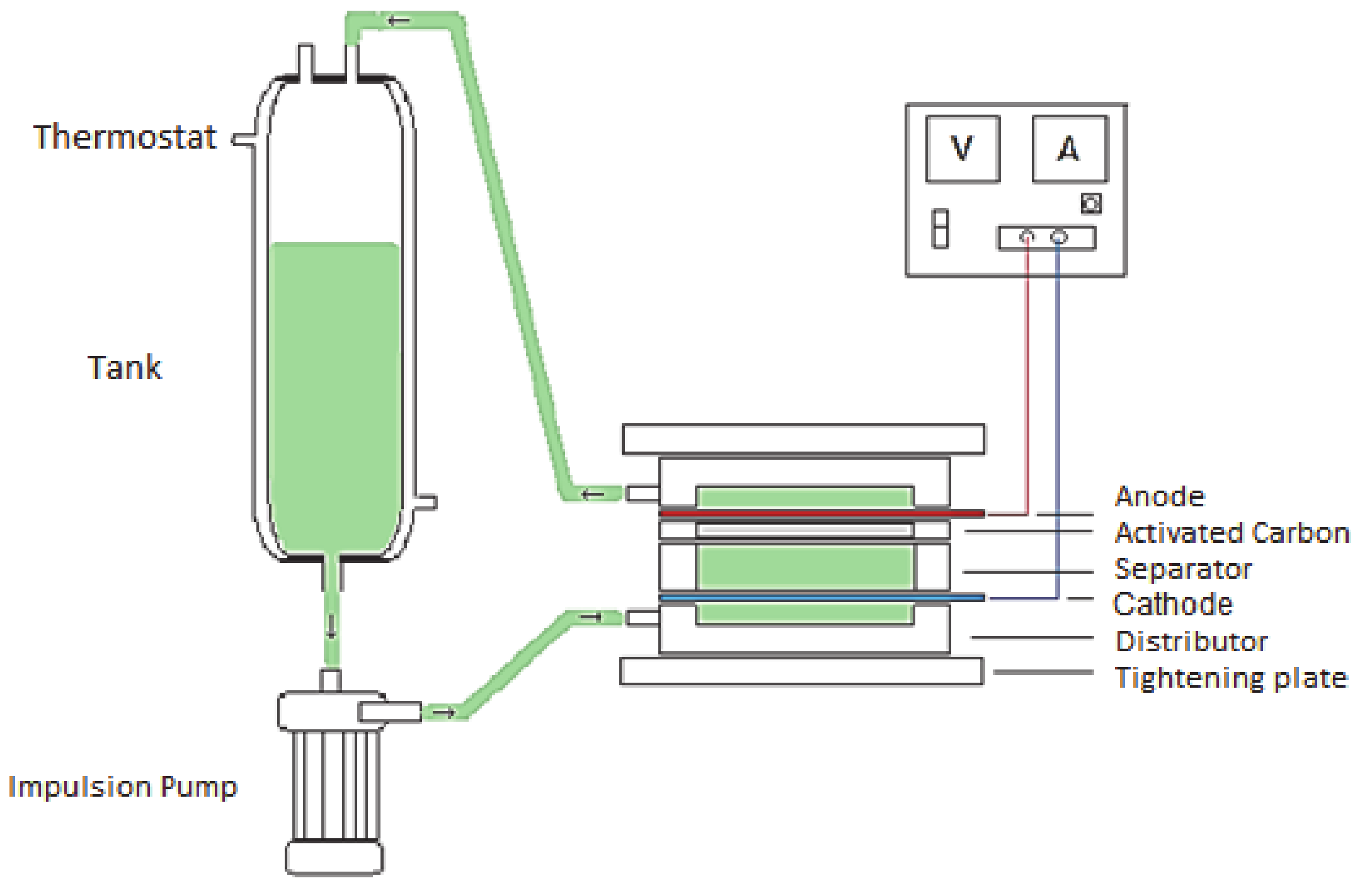
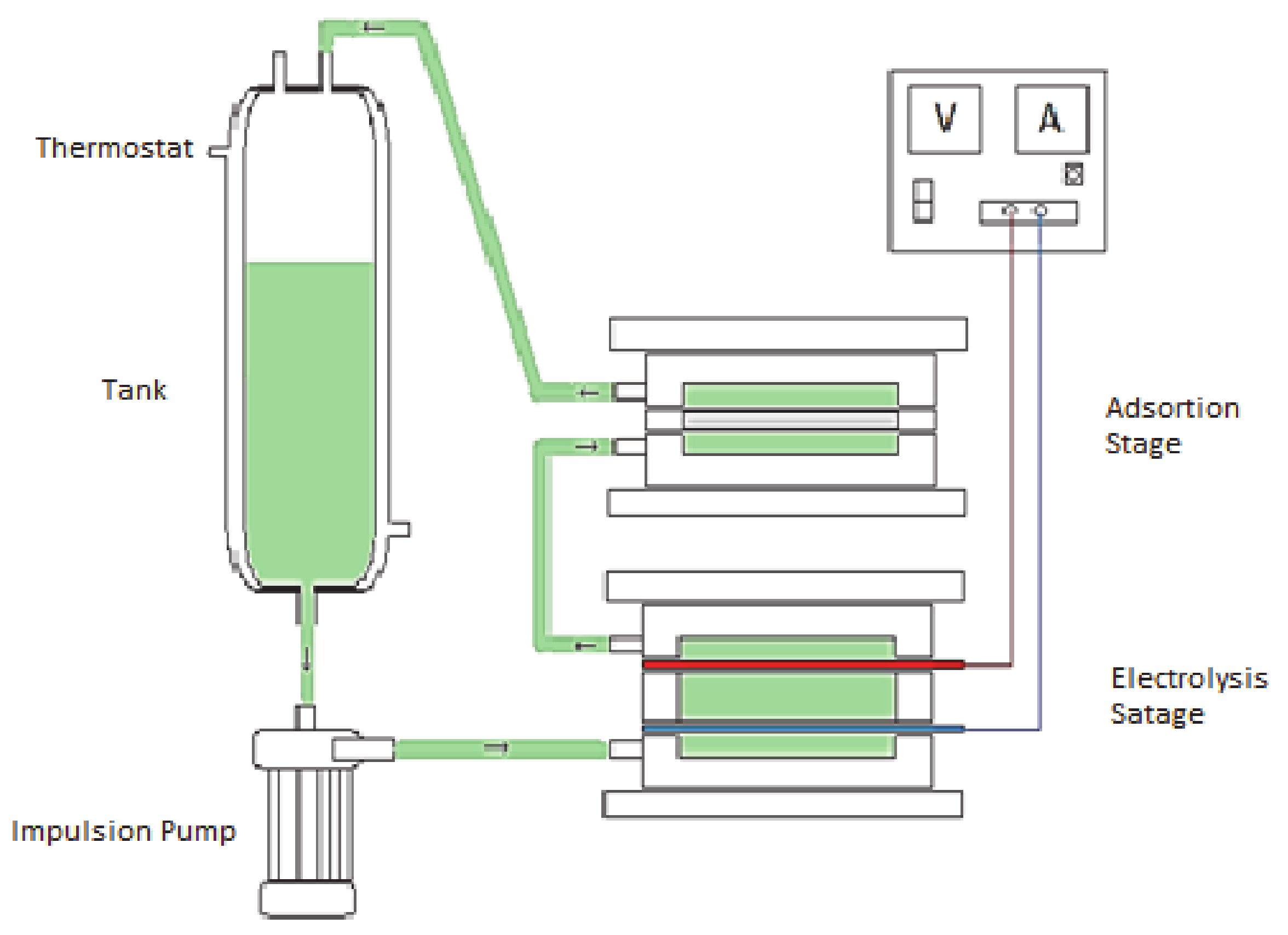
In this study, the filter press electrochemical cell for the electroadsorption of bromide has been developed. The electrochemical cell has been modified in order to put it in contact with the contaminated water with a wider activated carbon bed [51]. During the experiment, the water was circulated by means of a centrifugal pump between the anode and the cathode and passing through the activated carbon that is found as a bed. In this way, information can be obtained on the adsorption kinetics in this batch reactor, as well as the amount adsorbed at the equilibrium. This last data is very important to know the possible improvement in the adsorption capacity of the activated carbon as a consequence of the applied potential. Figure 1 shows a diagram of the electrochemical cell and the device used for the electroadsorption process.
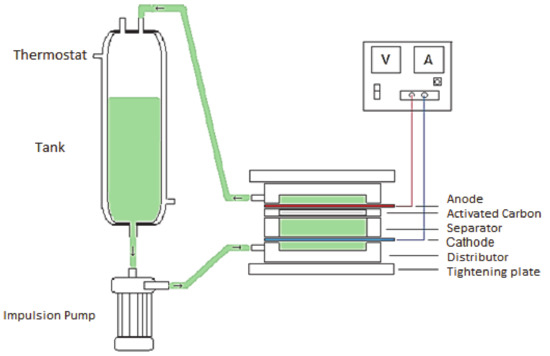
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the electroadsorption experiments in which the electrochemical chemical cell together with the current source, water tank and impulsion pump are included.
It is divided into two compartments that are herein referred to as the anolyte and catholyte, and each one being composed by (i) a flow distributor with one nozzle that can be used as a water inlet or outlet, (ii) a mesh for keeping the activated carbon particles and the electrode pressed altogether, (iii) a joint that provides volume for allocating the activated carbon particles, and (iv) an electrode. The compartments are tightly connected together by means of (v) two screwed stainless steel plates, with (vi) a final joint being displayed between anode and cathode. In this work, the electrochemical filter-press cell was disposed horizontally without compartment separation (i.e., no selective ionic membrane was used between the compartments). The cell has a plane electrode area of 20 cm2. The width of each compartment is 0.9 cm, resulting in a volume of 18 cm3. The external DC Power supply was Blausonic FA-325 (Promax Test & Measurement, Barcelona, Spain), 30 V, and 2.5 A.
2.4. Operational Conditions
In this study, the following operational conditions were carried out with 4 g of the washed GAC placed near the cathode or near the anode for the cathodic or anodic electroadsorptions, respectively, and contacted with 400 mL of water [52]. While the contact between the GAC particles and the electrode was slightly loose, in previous research it was proved that, for a configuration similar to that used in this study, a polarization of carbon particles is achieved [53]. The adsorption experiments were initiated when real Br-containing water started circulating inside the electrochemical cell for 24 h in the absence of current, which was enough time to ensure the adsorption equilibrium (around 250 µg L−1). In order to analyze the effect of the voltage, different values have been used in different experiments, with new water, during 24 h in order to reach the equilibrium conditions at each voltage. Anodic cathodic conditions in other experiments, after the adsorption in the absence of voltage, at three different voltages, 2.0, 3.0, and 4.0 V, were sequentially applied. Each voltage step was imposed for 24 h before proceeding to the next electroadsorption stage in order to reach the equilibrium conditions. In this case, no additional water is used for electroadsorption in order to achieve the simplest possible bromide removal treatment. In order to analyze the reversibility of Br− removal in the electroadsorption experiments, one last step was carried out in the absence of voltage during 24 h. The analysis of the bromide and bromine were determined, as exposed above, and 1 mL of solution was periodically taken from the electrochemical cell.
3. Results
The selection of this material, GAC, and the real natural water sample used will allow us to demonstrate the validity of this method at conditions very close to those available in a real water treatment plant. The most relevant surface properties of the GAC were assessed by N2 and CO2 adsorption–desorption isotherms. In this sense, the micropore volume obtained from CO2 adsorption, compared to the N2 one, indicates that most of the microporosity has a size of about 0.5 nm (the micropore volumes from N2 and CO2 adsorptions are similar (see Table 1) [50]. Thus, from the point of view of textural properties, it can be concluded that the selected GAC has a well-developed porous texture, which makes it a good choice for water treatment.
3.1. Effect of Voltage in the Anodic Electroadsorption
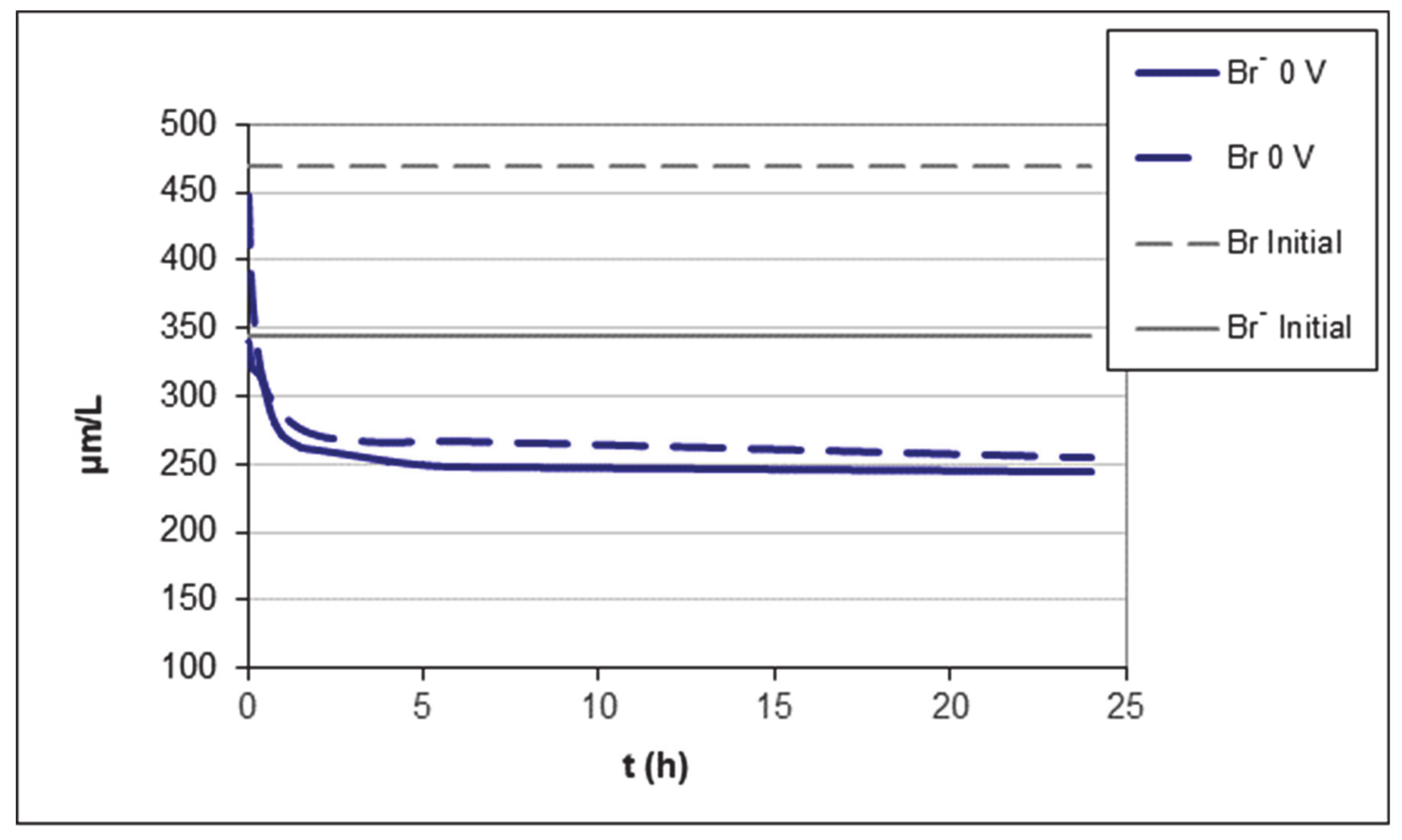
In order to initially identify the amount adsorbed by the activated carbon in the absence of voltage, and thus check if the presence of electric field produces an increase in the amount adsorbed, the water (400 mL) was put in contact in the filter-press cell with activated carbon (4 g) and allowed to reach the adsorption equilibrium for 24 h Figure 2 shows the variation of the concentration with time; in this figure, the initial concentration of bromide and total bromine are also represented.
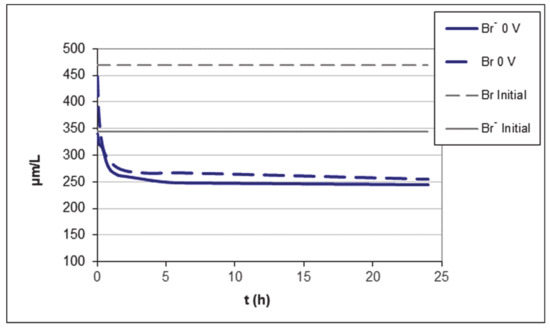
Figure 2.
Variation of bromide and total bromine concentration in the absence of voltage. Filter press.
It is observed that the concentration of bromide and total bromine decreases as a consequence of adsorption on activated carbon until reaching an equilibrium concentration of approximately 250 µg L−1 for the bromide. Figure 2 also shows the presence of two regions in the adsorption process. In the first region, the adsorption is very fast, and it is mainly due to either mass transfer through the stationary liquid boundary layer that appears over the external surface of the particle or restricted pore diffusion of the adsorbate in the wider porosity of the carbon particle. A second region is distinguished after 7 h, where adsorption is slower due to surface diffusion of adsorbed molecules within narrower pores. The appearance of two zones on the adsorption graph of an activated carbon is very characteristic of these materials [54,55].
The initial Br- concentration is 345 µg L−1, and the equilibrium concentration reached is 250 µg L−1. Therefore, the adsorption capacity of the activated carbon in these conditions is 9.5 µg g−1, which corresponds to a removal efficiency of 29% (Table 3).

Table 3.
Bromide concentration at the end of the experiment, % removal and amount adsorbed at the equilibrium on activated carbon in different electroadsorption experiments at different voltages.
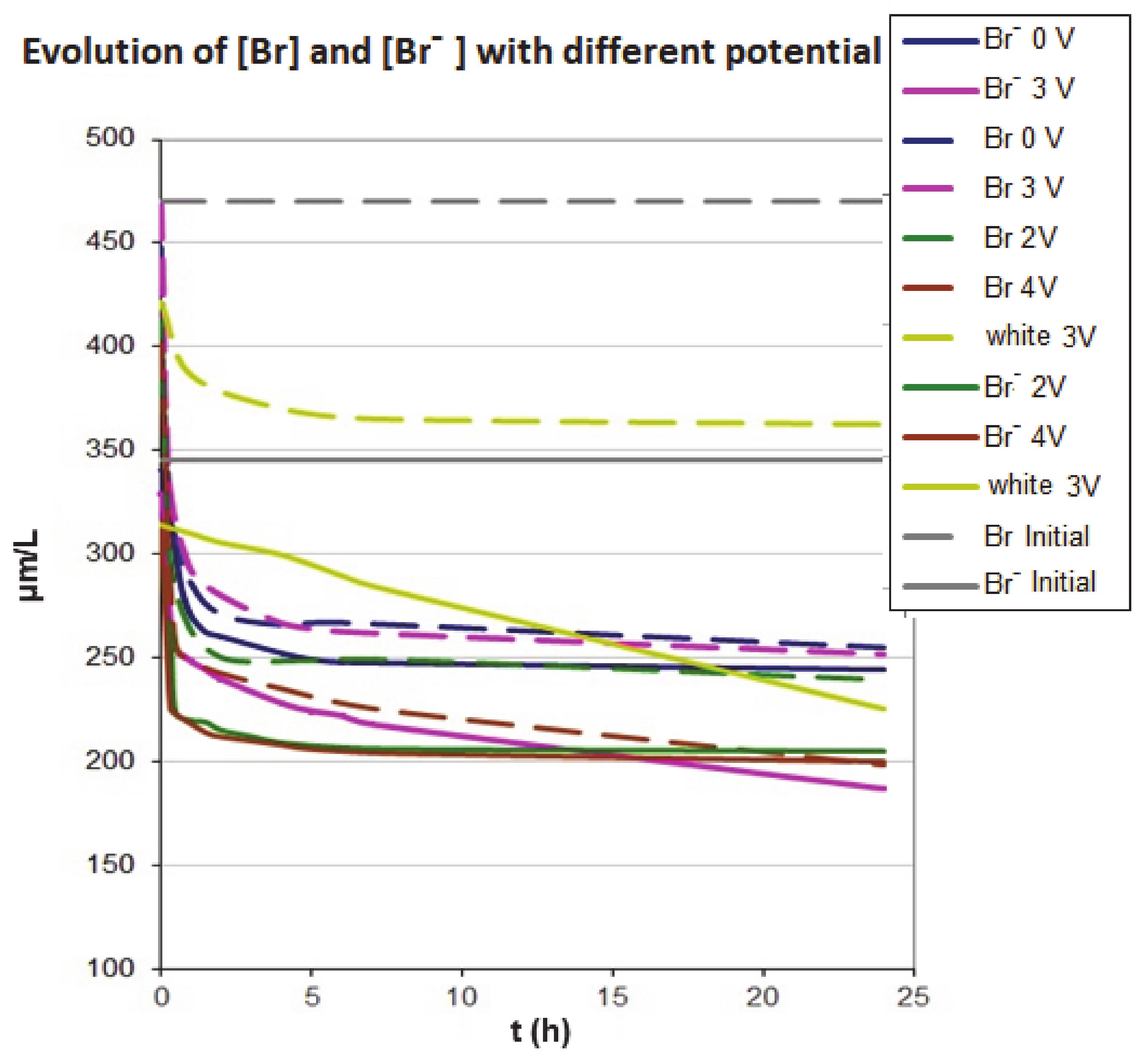
Figure 3 shows the bromide and total bromine concentration during electroadsorption when different voltages are applied (2 V, 3 V and 4 V) under anodic conditions. It can be observed that the concentrations of bromide and total bromine decrease with time for all voltages used and lower values are reached than those obtained in the absence of the voltage (0 V in Figure 3). These results indicate that the presence of the electric field increases the amount of bromide and total bromine removal, improving the adsorption capacity of the activated carbon.
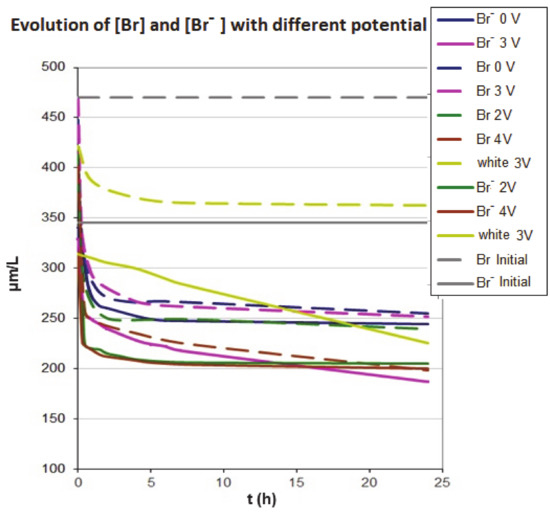
Figure 3.
Variation of the bromide and total bromine at different voltages (2 V, 3 V and 4 V) under anodic conditions. The adsorption in the absence of voltage is also included. The dashed line corresponds to the total bromine and full line to the bromide.
We can also observe that, in the case of 4 V, the bromide and total bromine concentrations decrease significantly and with a much higher rate than in the absence of potential, achieving a reduction of the bromide concentration by 29% after 0.5 h of contact with the activated carbon. In the absence of voltage, the reduction in concentration after 0.5 h is 14 %. The bromide concentration after equilibrium is 200 µg L−1, which corresponds to an adsorption capacity of the activated carbon of 14.5 µg g−1 and to a reduction of the bromide concentration of 42%.
At high potentials, bromide ions can be oxidized to Br2 according to Equation (1), and the decrease in concentration observed at high potentials (3 V or 4 V) may be due to the electrochemical transformation of bromide to bromine. At these voltages, values higher than the standard potential of this reaction are reached in the anode, making the oxidation of bromide possible. It should be noted that the adsorption of Br2 on activated carbon is a very favorable process, unlike the anion.
Br2 + 2e− → 2 Br− E0 = 1.08V/ENH
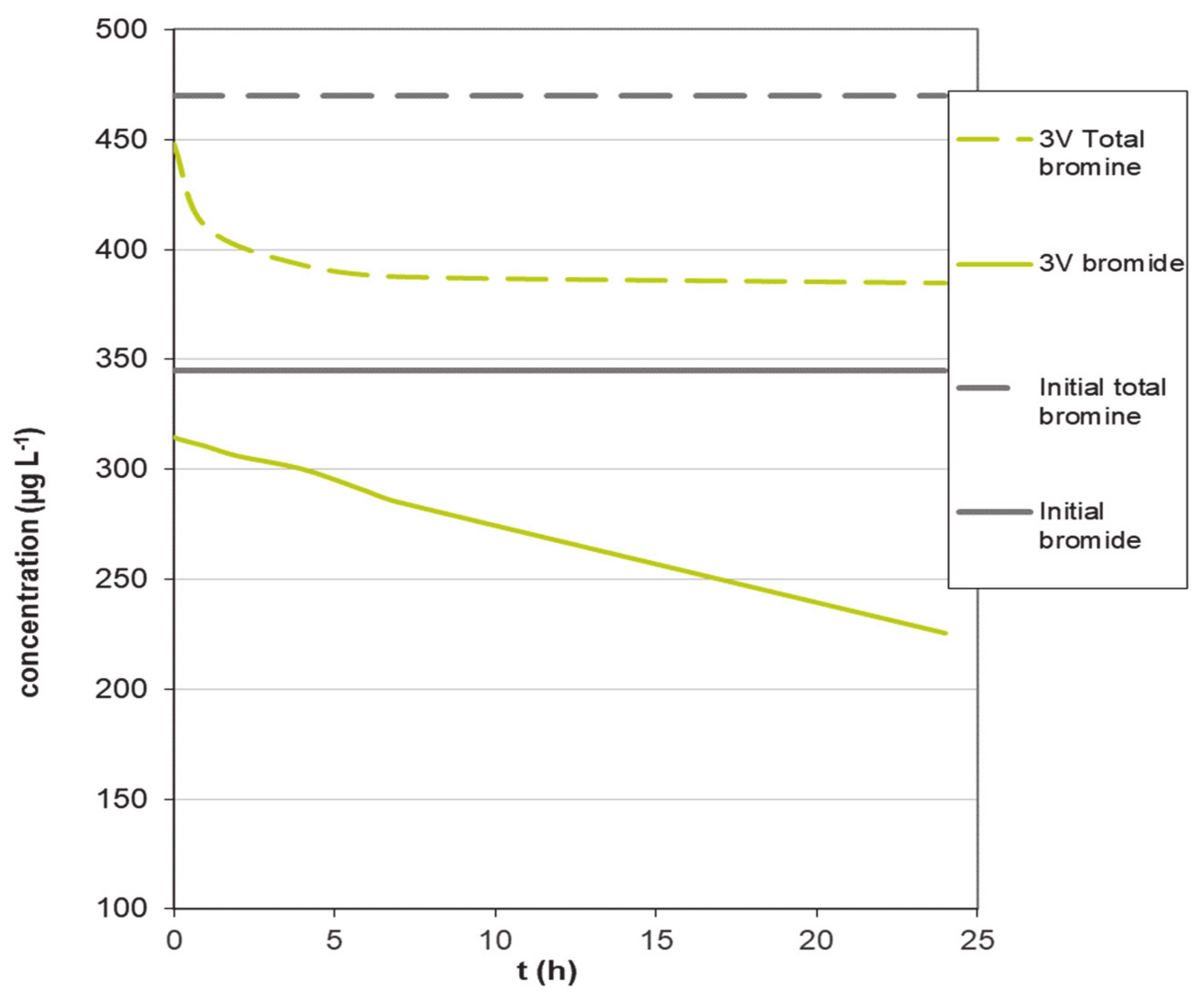
To verify this result, a pure electrochemical treatment experiment in the absence of activated carbon in the electrochemical cell was carried out by applying a voltage of 3 V, and the result is shown in Figure 4. This voltage is selected in order to avoid the formation of bubbles on the electrode.
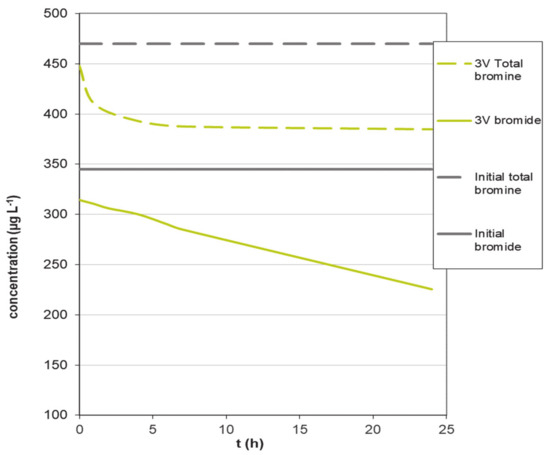
Figure 4.
Variation of bromide concentration in an experiment in the absence of activated carbon at 3 V.
It can be observed, in Figure 4, that the bromide concentration decreases continuously over time, indicating that it is oxidized on the electrode, thus decreasing its concentration in the solution; however, the total bromine after an initial decrease, probably due to some volatilization, remains constant with time, indicating the conversion of bromide into Br2 according to Equation (1). This oxidation reaction, once the constant value of bromine is reached, is not producing a change in the total bromine in solution, but an interconversion of one species into another.
Table 3 and Table 4 compare the final bromide and final total bromine concentration values obtained in the adsorption and electroadsorption experiments after 24 h at different voltages. The tables also include the percentages of bromide removal and total bromine removal (with respect to the initial concentration). In addition, the amount adsorbed by the activated carbon of both bromide and total bromine is shown.

Table 4.
Total bromine concentration at the end of the experiment, % removal and amount adsorbed at equilibrium on activated carbon in different electroadsorption experiments.
We can see that the bromide concentration decreases in the absence of potential by 29% [33] and we managed to increase the percentage of elimination by 41% and 46% in the presence of the electric field, which is 12% and 17% more than just in a process of adsorption (open circuit conditions). However, the value of total bromine content in adsorption and electroadsorption is similar (Table 4) to the applied voltage up to 3 V.
However, when the voltage increases to values where the electrode potential reaches the oxidation of bromide to bromine (4 V), the percentage of total bromine removal increases, which indicates that the adsorption of bromine is more favorable on the activated carbon increasing the adsorption capacity. However, at this voltage, the formation of gas on the electrode surface is clearly observed, mainly due to water oxidation. Then, in order to avoid the formation of bubbling on the electrode, the effect of polarity on the electroadsorption, a voltage of 3 V has been selected.
Energy Consumption of Electrochemical Removal of Bromide
The Energy Consumption (EC) per unit volume of treated water was calculated according to Equation (2):
where U is the voltage of the electrochemical cell (V), I is the average current (A), t is the treatment time (h) and V is the volume of treated water (L).
EC(kWh L−1) = (U·I·t)/(V·1000)
Then, the EC during the removal of bromide in this laboratory scale is between 1 and 2 kWh L−1.
3.2. Effect of the Polarity of the Electrode (Anodic Electroadsorption and Cathodic Electroadsorption)
In order to study the effect of the polarity of the electroadsorption experiments, the comparison between the performance of an anodic electroadsorption (the activated carbon is located in the anode compartment in which the activated carbon is subjected to a positive polarity) and the cathodic electroadsorption (the activated carbon is located in the cathode compartment, in which the activated carbon is subjected to a negative polarity) has been done. In these experiments, the following consecutive steps have been done: (i) adsorption at open circuit conditions during 24 h, (ii) application a voltage of 3 V during 24 h and (iii) again open circuit potential during 24 h in order to analyze the reversibility of the electroadsorption step.
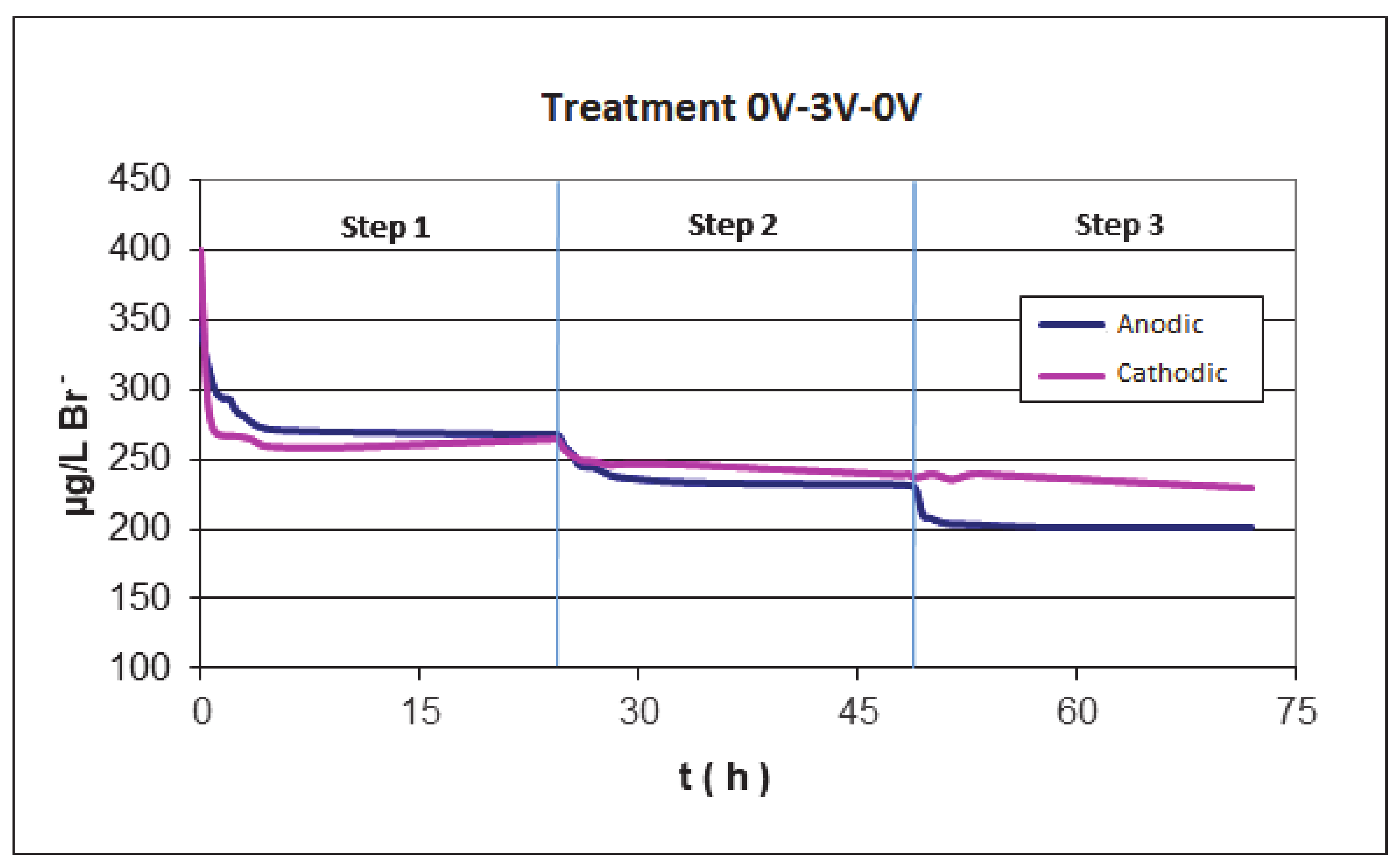
Figure 5 shows the evolution of the bromide concentration during these experiments at cathodic and anodic conditions during the second step. It can be observed that, after the adsorption at the open circuit potential (step 1 in Figure 5), the amount of bromide is similar in both cases; however, after the electroadsorption, the anodic treatment produces a higher decrease in the concentration of bromide that, in the case of cathodic electro-adsorption (step 2 in Figure 5). These results can be as a consequence of two processes: the electroadsorption of the bromide that is favored at a positive polarization of the active carbon and the oxidation of bromide on the anode according to Equation (1). Moreover, after the electroadsorption step, if the system is again put at open circuit conditions, no desorption of the bromide is produced in both polarities, indicating the irreversibility of the electroadsorption processes.
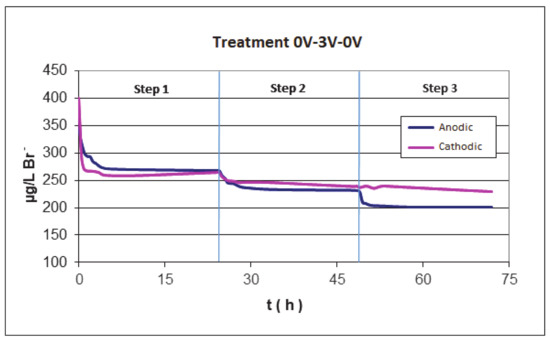
Figure 5.
Bromide concentration during three steps experiment, the second corresponds to anodic and cathodic electroadsorption experiments for 24 h at 3 V. 3 V is applied for 24 h in the second step and then it is left at open circuit again for 24 h.
It can be also seen that, after the anodic electroadsorption treatment (24 h of treatment at 3 V), in the following adsorption process at open circuit potential (step 3 in Figure 5), a new decrease in the bromide concentration is observed. These results seem to indicate that the bromide has been oxidized in anodic conditions to Br2 and a new adsorption equilibrium of bromide is again reached as a consequence of the different concentration of bromide in solution.
3.3. Adsorption after an Electrochemical Oxidation Process: Two-Stages Electroadsorption
In order to improve the bromide removal, the following experiment in two stages was designed: in the first, an electrochemical treatment during 24 h takes place in the absence of activated carbon (electrolysis stage). During this stage, the bromide is oxidized to Br2, which can be easily adsorbed on the activated carbon. Then, after this electrochemical oxidation stage, the water is passed to another electrochemical cell in which a second adsorption stage during 24 h in the presence of activated carbon is done, but in the absence of potential (adsorption stage). The water is continuously circulated between both electrochemical cells and the concentration is taken over time. Figure 6 shows a scheme of the electrochemical device used.
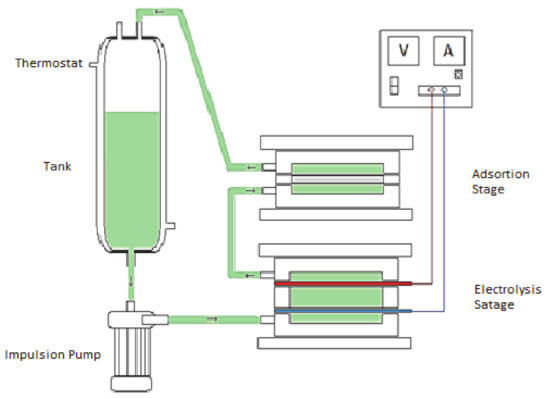
Figure 6.
Scheme of the two electroadsorption stages.
The data obtained after the total treatment are shown in Table 5. We can see that the concentration of bromide reaches a value similar to that obtained in the pure electroadsorption experiment in the same conditions of voltage (Table 3); however, the total bromine falls below 200 µg L−1 and the percentage of elimination of this total bromine increases with respect to that obtained in an electroadsorption process (Table 4). Then, using two stages in comparison to only the electroadsorption stage, it is possible to reduce both concentrations, bromide and total bromine, from the water.

Table 5.
Bromide concentration, bromine and percent removal and amount adsorbed by activated carbon in a two-stage experiment at the end of the treatment.
4. Conclusions
It can be concluded that the electroadsorption process is effective against the elimination of bromide and total bromine in water with a content of 345 µg L−1 and 470 µg L−1, respectively, reaching elimination values of around 46 % in a single-stage electroadsorption process in both bromide and total bromine. It has been studied that the better conditions for removal of bromide in water with a concentration is the application of the electric field to the activated carbon that produces a positive polarization (anodic electroadsorption). This treatment increases the adsorption capacity of the activated carbon significantly, achieving a reduction of bromide of up to 220 µg L−1 after 1 h of contact with water. The removal percentage of bromide increases from 29% in the absence of voltage (adsorption) to 46% at 3 V (electroadsorption). When the process is carried out in two stages in which a previous electrochemical oxidation to the adsorption stage is introduced, similar values of removal of bromide are achieved. In this previous electrochemical oxidation stage, the oxidation of bromide to Br2, which is easily adsorbed on the activated carbon, is produced, and the total bromine content of the water is reduced by 59% in the two stages of the experiment, with this value significantly increased from 46% in a single electroadsorption step at 3 V.
Author Contributions
D.R.: Investigation, Writing—Original Draft; E.M.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—Review & Editing; D.C.-A.: Investigation, Writing—Original Draft; Data Curation; F.O.: Conceptualization, Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision; M.J.G.-R.: Conceptualization, Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gopal, K.; Tripathy, S.S.; Bersillon, J.L.; Dubey, S.P. Chlorination byproducts, their toxicodynamics and removal from drinking water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 140, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symons, J.M.; Stevens, A.; Clark, R.M.; Geldreich, E.E.; Love, O.T., Jr.; DeMarco, J. Treatment Techniques for Controlling Trihalomethanes in Drinking Water; EPA/600/2-81/156 (NTIS PB82163197); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Villanueva, C.M.; Cordier, S.; Font-Ribera, L.; Salas, L.A.; Levallois, P. Overview of disinfection by-products and associated health effects. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2015, 2, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, C.; Marcos, R. Genotoxicity of disinfection byproducts and disinfected waters: A review of recent literature. Mutat. Res./Toxicol. Environ. Mutagenesis 2018, 831, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liviac, D.; Wagner, E.D.; Mitch, W.A.; Altonji, M.J.; Plewa, M.J. Genotoxicity of Water Concentrates from Recreational Pools after Various Disinfection Methods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3527–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plewa, M.J.; Wagner, E.D.; Richardson, S.D.; Thruston, A.D.; Woo, Y.-T.; McKague, A.B. Chemical and biological char-acterization of newly discovered iodoacid drinking water disinfection byproducts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4713–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plewa, M.; Wagner, E. Risks of Disinfection Byproducts in Drinking Water: Comparative Mammalian Cell Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity. In Encyclopedia of Environmental Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 5, pp. 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beita-Sandí, W.; Selbes, M.; Kim, D.; Karanfil, T. Removal of N-nitrosodimethylamine precursors by cation exchange resin: The effects of pH and calcium. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyluoglu, M.; Ersan, M.S.; Ateia, M.; Karanfil, T. Removal of bromide from natural waters: Bromide-selective vs. conventional ion exchange resins. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, L.; Flora, J.R.; Park, Y.-G.; Badawy, M.; Saleh, H.; Yoon, Y. Removal of natural organic matter from potential drinking water sources by combined coagulation and adsorption using carbon nanomaterials. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 95, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainudin, F.M.; Abu Hasan, H.; Abdullah, S.R.S. An overview of the technology used to remove trihalomethane (THM), trihalomethane precursors, and trihalomethane formation potential (THMFP) from water and wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 57, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpää, M.; Ncibi, M.C.; Matilainen, A.; Vepsäläinen, M. Removal of natural organic matter in drinking water treatment by coagulation: A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 54–71. [Google Scholar]
- Ates, N.; Yilmaz, L.; Kitis, M.; Yetis, U. Removal of disinfection by-product precursors by UF and NF membranes in low-SUVA waters. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 328, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiana, I.; Joll, C.; Heitz, A. Powdered activated carbon coupled with enhanced coagulation for natural organic matter removal and disinfection by-product control: Application in a Western Australian water treatment plant. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, P.C.; Bilyk, K. Enhanced coagulation using a magnetic ion exchange resin. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4009–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiao, R.; Liu, H.; Wang, D.; Chow, C.W.K.; Drikas, M. Hybrid treatment process of using MIEX and high per-formance composite coagulant for DOM and bromide removal. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; He, M.; Zhi, Y.; Chang, S.X.; Gu, B.; Liu, X.; Xu, J. An integrated analysis on source-exposure risk of heavy metals in agricultural soils near intense electronic waste recycling activities. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabiul, M. Efficient phosphate removal from water for controlling eutrophication using novel composite adsorbent. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Rabiul, M.; Munjur, M.; Asiri, A.; Rahma, M. Cleaning the arsenic (V) contaminated water for safe-guarding the public health using novel composite material. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 171, 294–301. [Google Scholar]
- Phetrak, A.; Lohwacharin, J.; Sakai, H.; Murakami, M.; Oguma, K.; Takizawa, S. Simultaneous removal of dissolved organic matter and bromide from drinking water source by anion exchange resins for controlling disinfection by-products. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, T.H.; Singer, P.C. Bench-scale testing of a magnetic ion exchange resin for removal of disinfection by-product precursors. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.; Singer, P.C. Removal of bromide and natural organic matter by anion exchange. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2133–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, P.; Schäfer, A. Magnetic ion exchange: Is there potential for international development? Desalination 2009, 248, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, K.M.; Boyer, T.H. Long-term performance of bicarbonate-form anion exchange: Removal of dissolved organic matter and bromide from the St. Johns River, FL, USA. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2875–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiul, M.; Jyo, A.; El-Safty, S.; Tamada, M.; Seko, N. A weak-base fibrous anion exchanger effective for rapid phosphate removal from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 164–171. [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire, F.; Jagtoyen, M.; Andrews, R.; Rao, A.; Martín-Gullón, I.; Grulke, E. Carbon materials in environmental applications. In Chemistry and Physics of Carbon; Radovic, L.R., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 27, pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Radovic, L.R.; Moreno-Castilla, C.; Rivero Utrilla, J. Carbon materials as adsorbents in aqueous solutions. Chem. Phys. Carbon 2000, 27, 227–405. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Hogland, W.; Marques, M.; Sillanpää, M. An overview of the modification methods of activated carbon for its water treatment applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, J.W.; Cheremisinoff, P.N. Carbon Adsorption Handbook; Ann Arbor Science: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.T. Adsorbents: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Monser, L.; Adhoum, N. Modified activated carbon for the removal of copper, zinc, chromium and cyanide from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2002, 26, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.M. Removal of DBP Precursors by GAC Adsorption; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, K.; Farré, M.J.; Knight, N. Comparing a silver-impregnated activated carbon with an unmodified activated carbon for disinfection by-product minimisation and precursor removal. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 542, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanayak, J.; Mondal, K.; Mathew, S.; Lalvani, S.B. Aparametric eval-cuation of the removal of As(V) and As(III) by carbon based adsorbents. Carbon 2000, 38, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babic, B.M.; Milonjic, S.K.; Polovina, M.J.; Cupic, S.; Kaludjerovic, B.V. Adsorption of zinc, cadmium and mercury ions from aqueous solution sonan activated carbon cloth. Carbon 2002, 40, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Maness, J.C.; Cuthbertson, A.A.; Kimura, S.Y.; Liberatore, H.K.; Richardson, S.D.; Stanford, B.D.; Sun, M.; Knappe, D.R. Treating water containing elevated bromide and iodide levels with granular activated carbon and free chlorine: Impacts on disinfection byproduct formation and calculated toxicity†. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasivayam, C.; Kadirvelu, K. Uptake of mercury (II) from wastewater by activated carbon from an unwanted agri-cultural solid by-product: Coirpith. Carbon 1999, 37, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiul, M. A novel facial composite adsorbent for enhanced copper(II) detection and removal from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 266, 368–375. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, S.E.; Olin, T.J.; Bricka, R.; Adrian, D. A review of potentially low-cost sorbents for heavy metals. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, S.; Kurniawan, T.A. Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals up take from contaminated water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobya, M.; Demirbas, E.; Senturk, E.; Ince, M. Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by activated carbon prepared from a pricot stone. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1518–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, A.; Schäfer, A.; Wendt, H. Fundamentals of electrosorption on activated carbon for wastewater treatment of industrial effluents. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1998, 28, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Bernabeu, S.; Ruiz-Rosas, R.; Quijada, C.; Montilla, F.; Morallón, E. Enhanced removal of 8-quinolinecarboxylic acid in an activated carbon cloth by electroadsorption in aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Lee, Y.H. Carbon-Based Electrochemical Capacitors. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 480–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noked, M.; Avraham, E.; Soffer, A.; Aurbach, D. The rate determining step of electroadsorption processes into na-noporous carbon electrodes related to water desalination. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 21319–21327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisinger, R.S.; Alkire, R.C. Electrosorption of β-naphthol on graphite. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1980, 112, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkire, R.C.; Eisinger, R.S. Separation by Electrosorption of Organic Compounds in a Flow-Through Porous Electrode: I. Mathematical Model for One-Dimensional Geometry. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1983, 130, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabelich, C.J.; Tran, T.D.; Suffet, I.H. “Mel” Electrosorption of Inorganic Salts from Aqueous Solution Using Carbon Aerogels. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3010–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A. Adsorption and electrosorption of nitrate and nitrite on high-area carbon cloth: An approach to purification of water and waste-water samples. Carbon 2003, 41, 1309–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Alcañiz-Monge, J.; De La Casa-Lillo, M.A.; Linares-Solano, A. CO2As an Adsorptive to Characterize Carbon Molecular Sieves and Activated Carbons. Langmuir 1998, 14, 4589–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenguer, R.; Marco-Lozar, J.; Quijada, C.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Morallón, E. Electrochemical regeneration and porosity recovery of phenol-saturated granular activated carbon in an alkaline medium. Carbon 2010, 48, 2734–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beralus, J.-M.; Ruiz-Rosas, R.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Morallón, E. Electroadsorption of Arsenic from Natural Water in Granular Activated Carbon. Front. Mater. 2014, 1, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenguer, R.; Lozar, J.P.M.; Quijada, C.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Morallon, E. Effect of electrochemical treatments on the surface chemistry of activated carbon. Carbon 2009, 47, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.; KookLee, W. Intraparticle diffusion inliquid phase adsorp tion of phenols with activated carbon infinite batch adsorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1983, 96, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Al-Duri, B. Kinetic model in gof liquid phase adsorption bofre active dyeson activated carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 287, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).