Characterization of Marine-Surface-Dissolved Organic Matter via Amino Acid Enantiomers and Its Implications Based on Diel and Seasonal Observations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Background
2.2. Field Sampling
2.3. Laboratory Measurements
2.4. The AA-Based Molecular Indicators and Propagated Error Quantification
3. Results
3.1. Time-Series Observations
3.1.1. Physical Parameters, Nutrients, and Bacteria
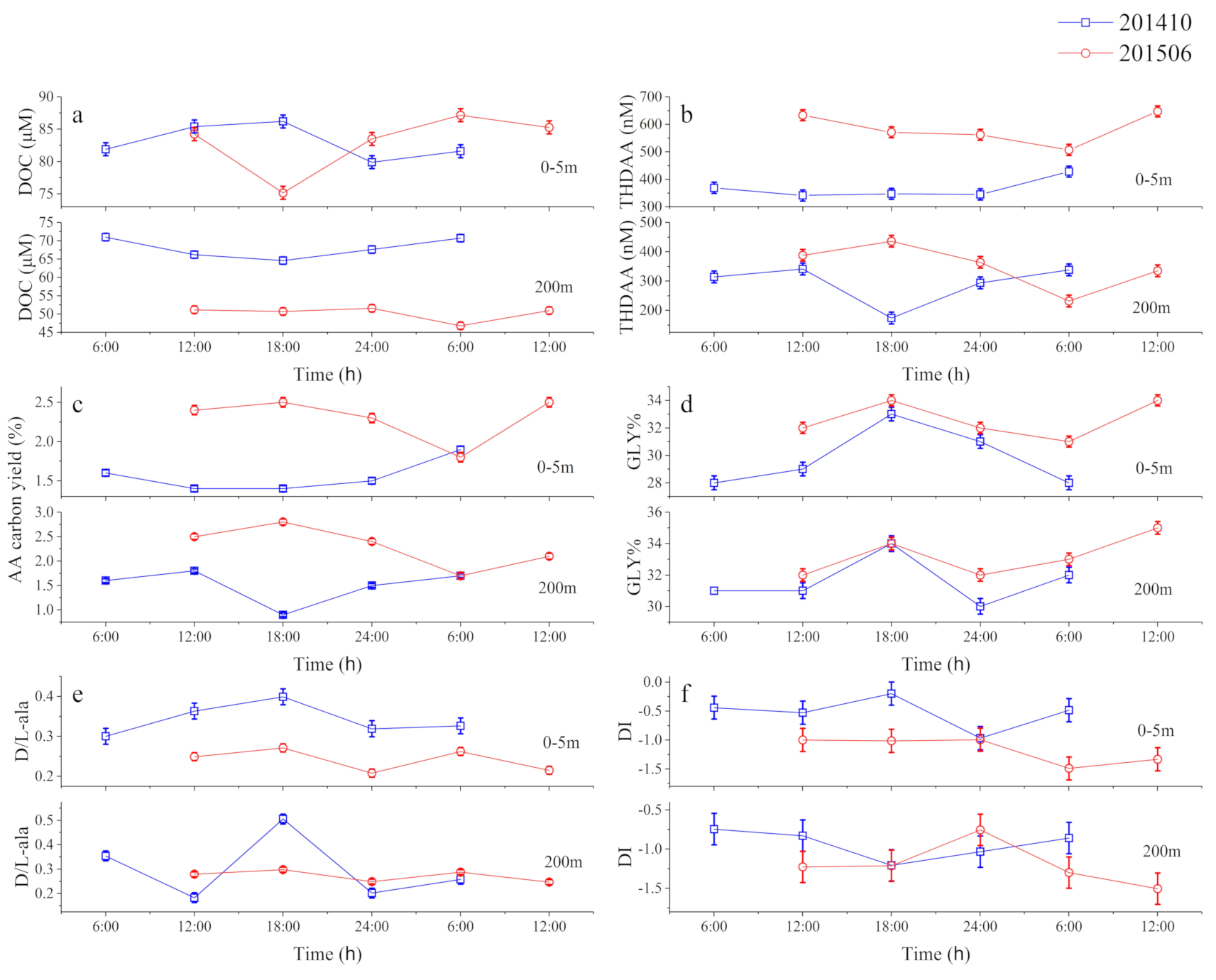
3.1.2. Temporal Variability of DOM over 24 h
3.1.3. Temporal Variations in DOM
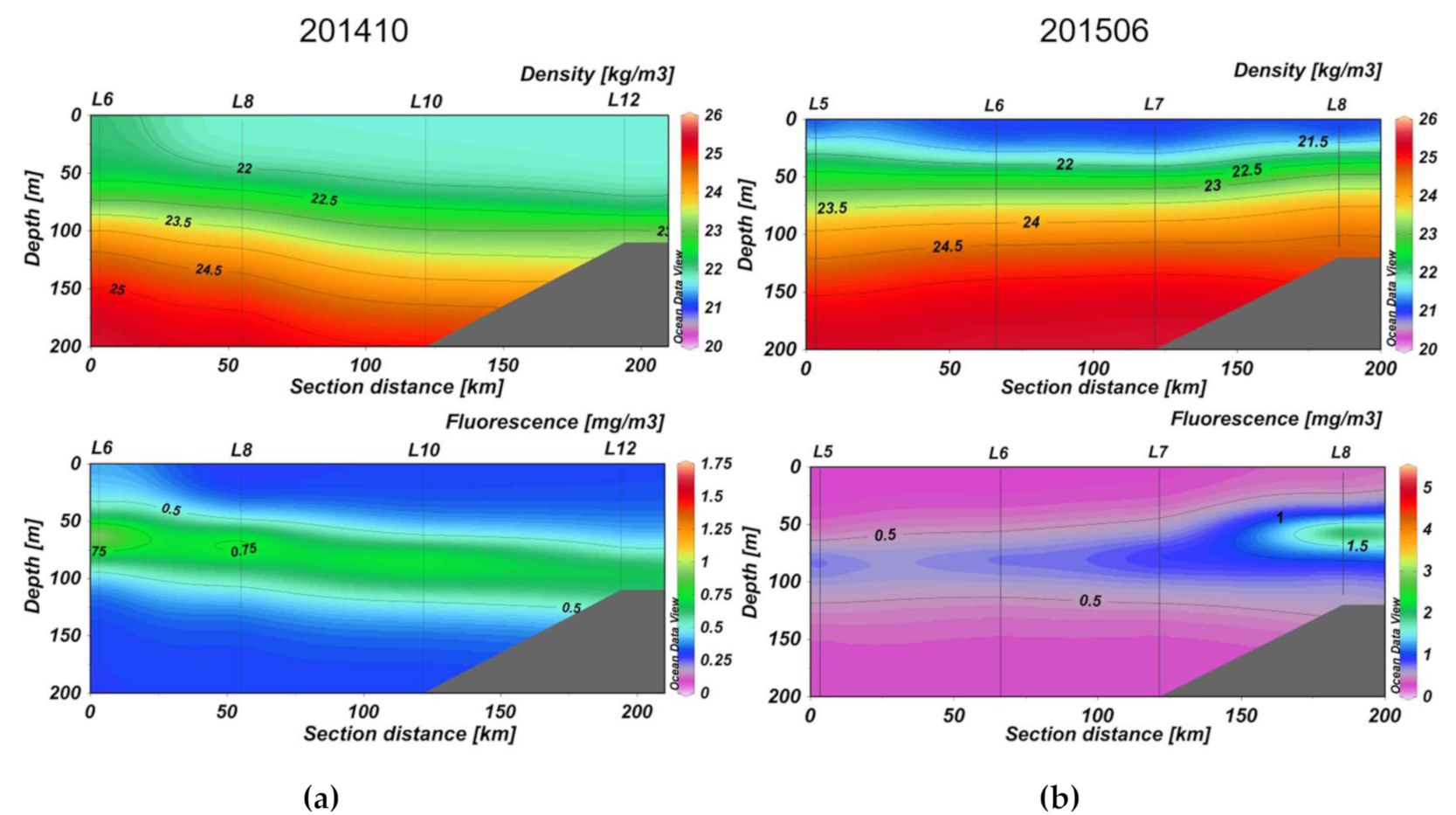
3.2. Section Observations
4. Discussion
4.1. Solid Short-Term Changes of AA-Based Molecular Indicators
4.2. Seasonal DOM Composition Difference and Its Implications
5. Conclusion and Perspective
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hedges, J.I.; Cowie, G.L.; Richey, J.E.; Quay, P.D.; Benner, R.; Mike, S.; Forsberg, B.R. Origins and processing of organic matter in the Amazon River as indicated by carbohydrates and amino acids. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1994, 39, 743–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Dang, H.Y.; Azam, F.; Benner, R.; Legendre, L.; Passow, U.; Polimene, L.; Robinson, C.; Suttle, C.A.; Jiao, N.Z. Evolving paradigms in biological carbon cycling in the ocean. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 481–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S.J.; Ball, G.I.; Allen, B.C.; Schladow, S.G.; Simpson, A.J.; Masoom, H.; Soong, R.; Graven, H.D.; Aluwihare, L.I. Refractory dissolved organic nitrogen accumulation in high-elevation lakes. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertkorn, N.; Benner, R.; Frommberger, M.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Witt, M.; Kaiser, K.; Kettrup, A.; Hedges, J.I. Characterization of a major refractory component of marine dissolved organic matter. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 2990–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broek, T.A.B.; Bour, A.L.; Ianiri, H.L.; Guilderson, T.P.; McCarthy, M.D. Amino acid enantiomers in old and young dissolved organic matter: Implications for a microbial nitrogen pump. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 247, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingalls, A.E.; Liu, Z.; Lee, C. Seasonal trends in the pigment and amino acid compositions of sinking particles in biogenic CaCO3 and SiO2 dominated regions of the Pacific sector of the Southern Ocean along 170° W. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2006, 53, 836–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ittekkot, V. Variations of dissolved organic matter during a plankton bloom: Qualitative aspects, based on sugar and amino acid analyses. Mar. Chem. 1982, 11, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Benner, R. Organic matter transformations in the upper mesopelagic zone of the North Pacific: Chemical composition and linkages to microbial community structure. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, W.; Gerhard, J.H.; Markus, G.W. Diel cycles in viral infection of bacterioplankton in the North Sea. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 35, 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Gasol, J.M.; Doval, M.D.; Pinhassi, J.; Calderon-Paz, J.I.; Nuria, G.B.; Vaque, D.; Pedros-Alio, C. Diel variations in bacterial heterotrophic activity and growth in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 164, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylward, F.O.; Eppley, J.M.; Smith, J.M.; Chavez, F.P.; Scholin, C.A.; DeLong, E.F. Microbial community transcriptional networks are conserved in three domains at ocean basin scales. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5443–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottesen, E.A.; Young, C.R.; Gifford, S.M.; Eppley, J.M.; Marin, R.; Schuster, S.C.; Scholin, C.A.; DeLong, E.F. Multispecies diel transcriptional oscillations in open ocean heterotrophic bacterial assemblages. Science 2014, 345, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansell, D.A. Recalcitrant Dissolved Organic Carbon Fractions. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2013, 5, 421–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mopper, K.; Lindroth, P. Diel and depth variations in dissolved free amino acids and ammonium in the Baltic Sea determined by shipboard HPLC analysis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1982, 27, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronk, D.A.; Glibert, P.M. Contrasting patterns of dissolved organic nitrogen release by two size fractions of estuarine plankton during a period of rapid NH4+ consumption and NO2− production. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 96, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loick-Wilde, N.; Weber, S.C.; Eglite, E.; Liskow, I.; Schulz-Bull, D.; Wasmund, N.; Wodarg, D.; Montoya, J.P. De novo amino acid synthesis and turnover during N2 fixation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 1076–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, M.R.; Bronk, D.A.; Capone, D.G. Dinitrogen fixation and release of ammonium and dissolved organic nitrogen by Trichodesmium IMS101. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 37, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, A.F.; Craven, D.B.; Henrichs, S.M. Diel Production and Microheterotrophic Utilization of Dissolved Free Amino Acids in Waters Off Southern California. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1984, 48, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiene, R.P.; Williams, L.P.H. Glycine betaine uptake, retention, and degradation by microorganisms in seawater. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 1592–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Kaiser, K.; Benner, R. Amino acid and amino sugar yields and compositions as indicators of dissolved organic matter diagenesis. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Benner, R. Biochemical composition and size distribution of organic matter at the Pacific and Atlantic time-series stations. Mar. Chem. 2009, 113, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, H.; Amagai, Y.; Kolke, I.; Kaiser, K.; Benner, R. Production of refractory dissolved organic matter by bacteria. Science 2001, 292, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee Chen, Y.-L.; Chen, H.-Y. Seasonal dynamics of primary and new production in the northern South China Sea: The significance of river discharge and nutrient advection. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2006, 53, 971–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.Q.; Hu, J.; Xu, H.Z.; Cao, Z.R.; Wang, D.X. Phytoplankton community at warm eddies in the northern South China Sea in winter 2003/2004. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 1792–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Smith, W.O. Introduction to the special issue on living-resources and ecosystem dynamics on the slope (LEDS) of the South China Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2019, 167, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.W.; Yang, C.H.; Xu, D.F.; Xu, M.Q. Observed hydrographical features and circulation with influences of cyclonic-anticyclonic eddy-pair in the northern slope of the South China Sea during June 2015. J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 34, 10–19, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, X.; Zheng, S.; Zhu, M.; Liang, J.; Du, J.; Yang, C. Plankton abundance, biovolume, and normalized biovolume size spectra in the northern slope of the South China Sea in autumn 2014 and summer 2015. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2019, 167, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xie, L.; Xu, L.; He, Y.; Xiao, X.; Xu, J. Diurnal variations of the microbial community in mesopelagic fish habitats of the northern slope of the south China sea. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2019, 167, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.M.; Wenger, F.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.F. Organic carbon flux and particulate organic matter composition in Arctic valley glaciers: Examples from the Bayelva River and adjacent Kongsfjorden. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, K.J.; Williams, P.M.; Bada, J.L. Acid hydrolysis of dissolved combined amino acids in seawaters: A precautionary note. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1987, 32, 996–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.T.; Sherr, E.B.; Sherr, B.F. DAPI direct counting underestimates bacteria abundances and average cell size compared to AO direct counting. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1993, 38, 1566–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauwe, B.; Middelburg, J.J. Amino acids and hexosamines as indicators of organic matter degradation state in North Sea sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 782–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, S.; Shen, Y.; Kaiser, K.; Benner, R.; Durisch-Kaiser, E. Bioavailability and diagenetic state of dissolved organic matter in riparian groundwater. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2012, 117, G04006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauwe, B.; Middelburg, J.J.; Herman, P.M.J.; Heip, C.H.R. Linking diagenetic alteration of amino acids and bulk organic matter reactivity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.; Qi, L.; Xu, M.; Yang, C.; Wang, X. Impact of the migration behavior of mesopelagic fishes on the compositions of dissolved and particulate organic carbon on the northern slope of the South China Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2019, 167, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amon, R.M.W.; Fitznar, H.P.; Benner, R. Linkages among the bioreactivity, chemical composition, and diagenetic state of marine dissolved organic matter. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, L.; Lechtenfeld, O.J.; Benner, R.; Middelboe, M.; Stedmon, C.A. Production and transformation of dissolved neutral sugars and amino acids by bacteria in seawater. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 5349–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, T.; Meon, B.; Kirchman, D.L. Microbial degradation of peptidoglycan in seawater. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-L.; Liu, Z.-F.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; He, B.-Y.; Wu, K.; Gu, S.; Jiang, P.; Huang, B.-Q.; Dai, M.-H. Production and Transformation of Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter as Indicated by Amino Acids in the Pearl River Estuary, China. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2018, 123, 3523–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecky, R.E.; Mopper, K.; Kilham, P.; Degens, E.T. The amino acid and sugar composition of diatom cell-walls. Mar. Biol. 1973, 19, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleifer, K.H.; Kandler, O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol. Rev. 1972, 36, 407–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, N.G.; Middelboe, M. Occurrence and bacterial cycling of D amino acid isomers in an estuarine environment. Biogeochemistry 2006, 81, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Benner, R. Major bacterial contribution to the ocean reservoir of detrital organic carbon and nitrogen. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, G.L.; Hedges, J.I. Biochemical indicators of diagenetic alteration in natural organic matter mixtures. Nature 1994, 369, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Name | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| Total hydrolysable dissolved amino acids | THDAAs |
| Alanine | Ala |
| Arginine | Arg |
| Asparagine | Asx |
| Aspartic acid | |
| Glutamine | Glx |
| Glutamic acid | |
| Glycine | Gly |
| Isoleucine | Ile |
| Leucine | Leu |
| Lysine | Lys |
| Methionine | Met |
| Phenylalanine | Phe |
| Serine | Ser |
| Threonine | Thr |
| Tyrosine | Tyr |
| Valine | Val |
| γ–aminobutyric acid | GABA |
| 2–aminobutyric acid | Aba |
| Ammonium | Nitrite | Nitrate | DIP | Silicate | DIN | DIN/DIP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201410 b | 5 m | Mean | 0.1 | bdla | bdla | 2.1 | 0.03 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| sd c | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | ||||
| Min | 0.08 | 2.0 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.04 | ||||
| Max | 0.1 | 2.1 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.06 | ||||
| 200 m | Mean | 0.06 | 0.01 | 11.2 | 14 | 0.8 | 11 | 0.8 | |
| sd c | 0.01 | 0 | 1.3 | 2.7 | 0.1 | 1.3 | 0.05 | ||
| Min | 0.05 | 0.01 | 10 | 12 | 0.7 | 10 | 0.7 | ||
| Max | 0.07 | 0.01 | 13 | 17 | 1.0 | 13 | 0.8 | ||
| 201506 | 5 m | Mean | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 2.0 | 0.3 | 7.6 |
| sd c | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.2 | 0.01 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 4.3 | ||
| Min | 0.1 | bdl a | bdl a | 0.03 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 4 | ||
| Max | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.4 | 0.05 | 2.4 | 0.6 | 12 | ||
| 200 m | Mean | 0.2 | 0.02 | 14 | 0.8 | 20 | 15 | 18 | |
| sd c | 0.2 | 0.01 | 2.1 | 0.2 | 5 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Min | 0.1 | 0.01 | 11 | 0.55 | 13 | 12 | 17 | ||
| Max | 0.5 | 0.04 | 17 | 1.0 | 26 | 17 | 22 |
| Month | Eddy Effect a | Chlorophyll a b | DIN/DIP | Bacteria | Short Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μg L−1 | Surface | Bottom | ×107 Cell L−1 | |||
| October | no | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.8 | 23 | strong nitrogen limit throughout top 200 m; low chla/high bacteria |
| June | weak upwelling | 0.3 (0.12–0.48) | 7.6 | 18 | 2.3 | weak (or no) nitrogen limit over top 200 m, high chla/low bacteria |
| DOC | THDAAs | AA Carbon Yield | Gly | Thr | Ser | GABA | D/L Ala | DI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μM | nM | % | % | % | % | % | |||||
| October 2014 | 5 m | mean | 83 | 366 | 1.6 | 30 | 3.7 | 14.0 | 1.1 | 0.34 | −0.52 |
| sd* | 3 | 37 | 0.2 | 2 | 0.4 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 0.04 | 0.28 | ||
| min | 80 | 341 | 1.4 | 28 | 3.0 | 12.3 | 0.5 | 0.30 | −0.97 | ||
| max | 86 | 428 | 1.9 | 33 | 4.0 | 15.1 | 1.9 | 0.40 | −0.20 | ||
| 200 m | mean | 68 | 292 | 1.5 | 32 | 3.7 | 13.1 | 1.0 | 0.30 | −0.93 | |
| sd* | 3 | 69 | 0.4 | 2 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.13 | 0.18 | ||
| min | 65 | 174 | 0.9 | 30 | 2.9 | 11.7 | 0.3 | 0.18 | −1.21 | ||
| max | 71 | 341 | 1.8 | 34 | 5.3 | 14.2 | 1.5 | 0.50 | −0.75 | ||
| June 2015 | 5 m | mean | 83 | 584 | 2.3 | 33 | 4.6 | 18.9 | 0.8 | 0.24 | −1.17 |
| sd* | 5 | 57 | 0.3 | 2 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.03 | 0.23 | ||
| min | 75 | 507 | 1.8 | 31 | 3.1 | 18.1 | 0.5 | 0.21 | −1.49 | ||
| max | 87 | 647 | 2.5 | 34 | 5.5 | 20.2 | 1.0 | 0.27 | −0.99 | ||
| 200 m | mean | 50 | 351 | 2.3 | 33 | 3.7 | 19.1 | 0.7 | 0.27 | −1.20 | |
| sd* | 2 | 76 | 0.4 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.02 | 0.27 | ||
| min | 47 | 232 | 1.7 | 32 | 3.0 | 18.2 | 0.4 | 0.25 | −1.51 | ||
| max | 52 | 436 | 2.8 | 35 | 4.3 | 19.9 | 0.9 | 0.30 | −0.76 |
| THDAA(nM) | D/L Ala | Gly% | GABA% | DI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| October 2014 | 252 (181–317) | 0.53 (0.44–0.72) | 30 (26–35) | 1.6 (1.1–2.5) | 0.20 (−1.02–2.24) |
| June 2015 | 452 (257–596) | 0.43 (0.34–0.64) | 24 (17–31) | 1.0 (0.4–1.9) | 0.49 (−1.02–2.40) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.-Y.; Zhou, Y.-C.; Ma, W.-C.; Wu, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, S.-M.; Xu, X.-W.; Zhou, M. Characterization of Marine-Surface-Dissolved Organic Matter via Amino Acid Enantiomers and Its Implications Based on Diel and Seasonal Observations. Water 2021, 13, 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13050685
Zhu Z-Y, Zhou Y-C, Ma W-C, Wu Y, Li M, Liu S-M, Xu X-W, Zhou M. Characterization of Marine-Surface-Dissolved Organic Matter via Amino Acid Enantiomers and Its Implications Based on Diel and Seasonal Observations. Water. 2021; 13(5):685. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13050685
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zhuo-Yi, Ying-Chun Zhou, Wen-Chao Ma, Ying Wu, Ming Li, Su-Mei Liu, Xue-Wei Xu, and Meng Zhou. 2021. "Characterization of Marine-Surface-Dissolved Organic Matter via Amino Acid Enantiomers and Its Implications Based on Diel and Seasonal Observations" Water 13, no. 5: 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13050685
APA StyleZhu, Z.-Y., Zhou, Y.-C., Ma, W.-C., Wu, Y., Li, M., Liu, S.-M., Xu, X.-W., & Zhou, M. (2021). Characterization of Marine-Surface-Dissolved Organic Matter via Amino Acid Enantiomers and Its Implications Based on Diel and Seasonal Observations. Water, 13(5), 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13050685







