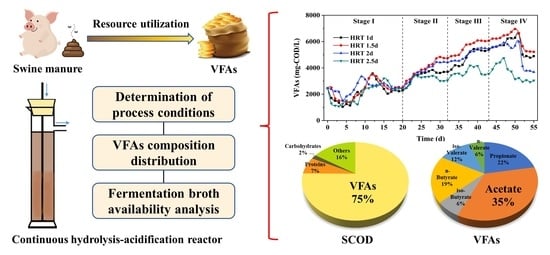
Continuous Production of Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) from Swine Manure: Determination of Process Conditions, VFAs Composition Distribution and Fermentation Broth Availability Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Swine Manure
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analytical Methods
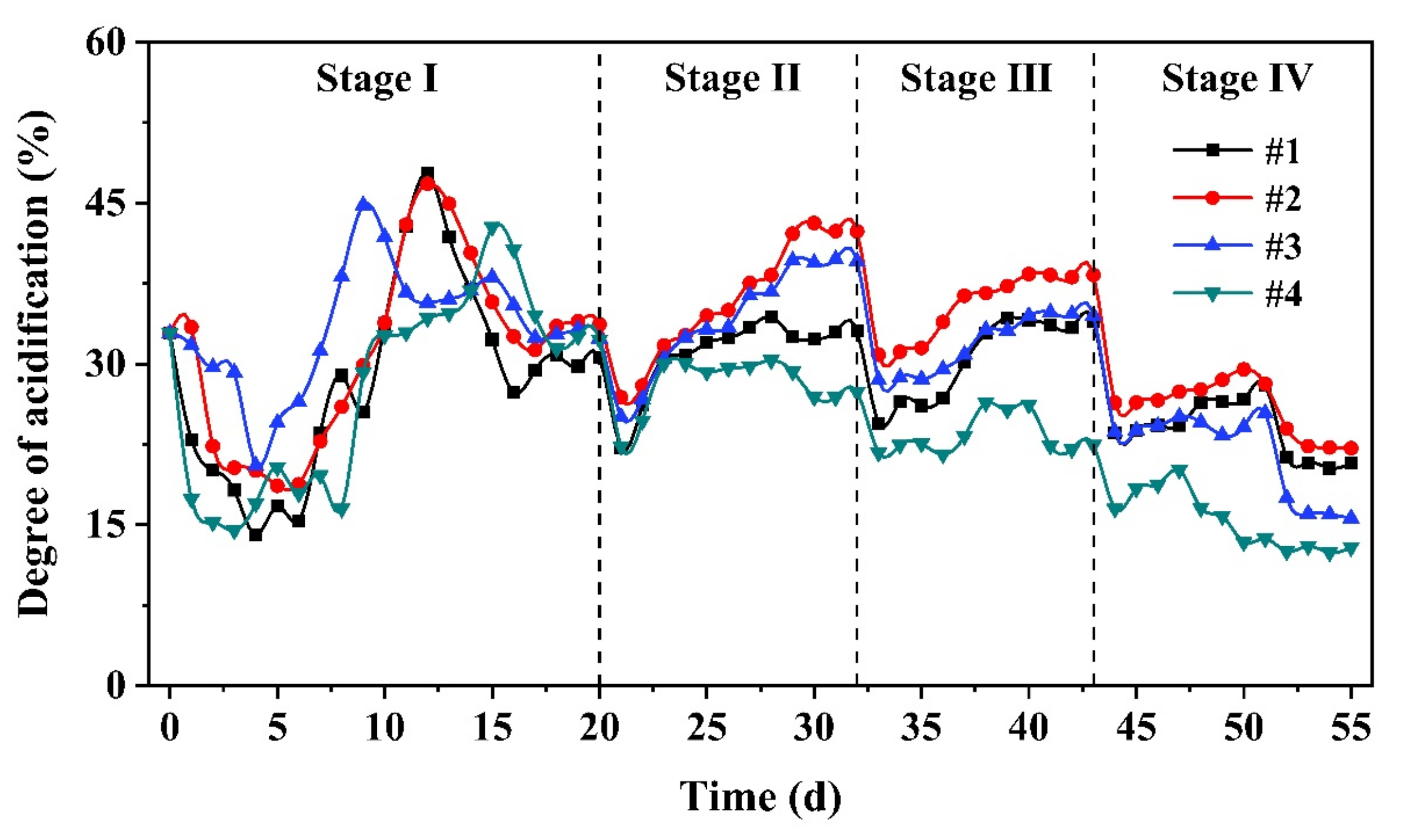
2.4. Calculation Method of Acidification Degree
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
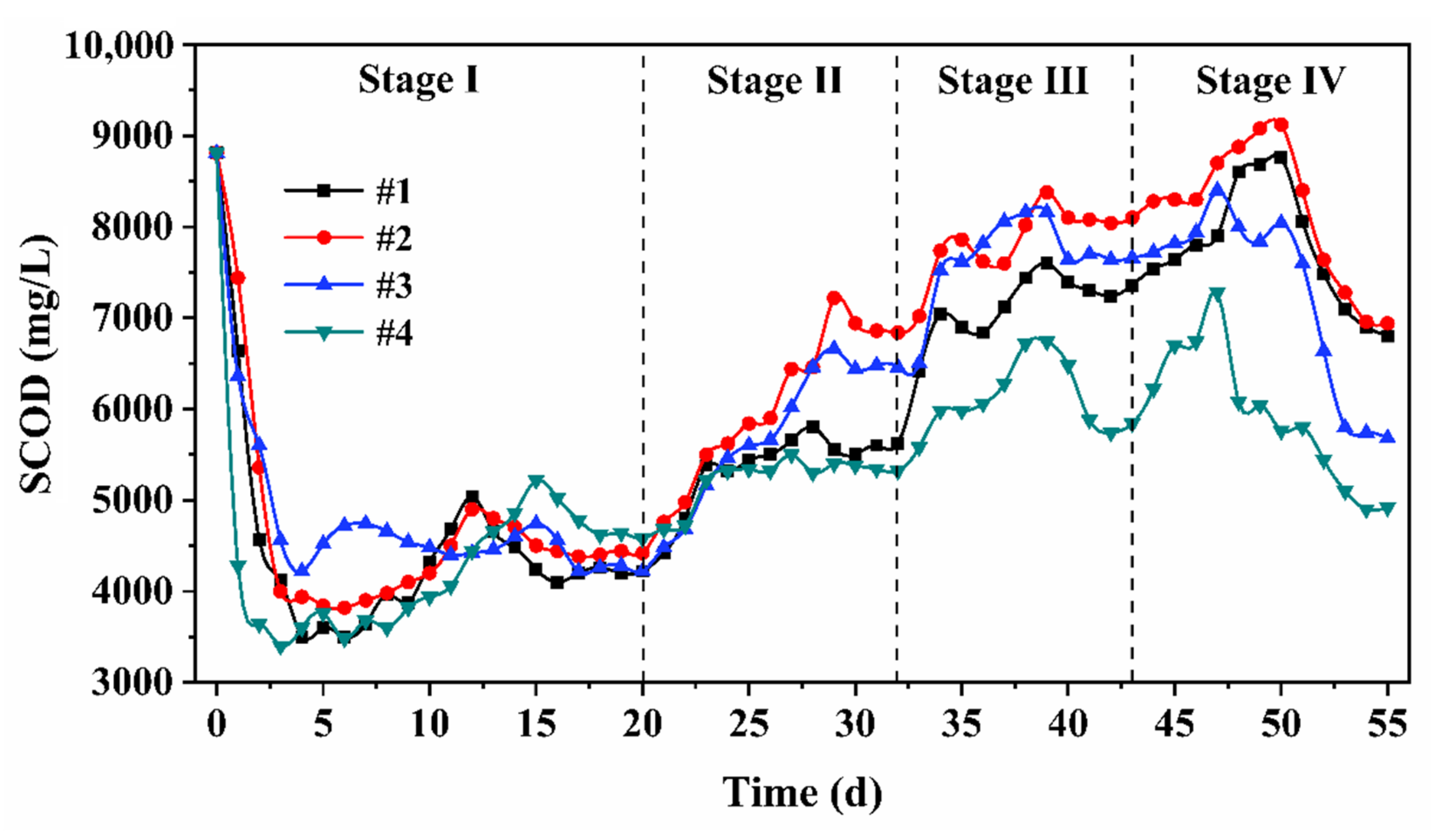
3.1. Hydrolysis-Acidification Effect and Determination of Process Conditions
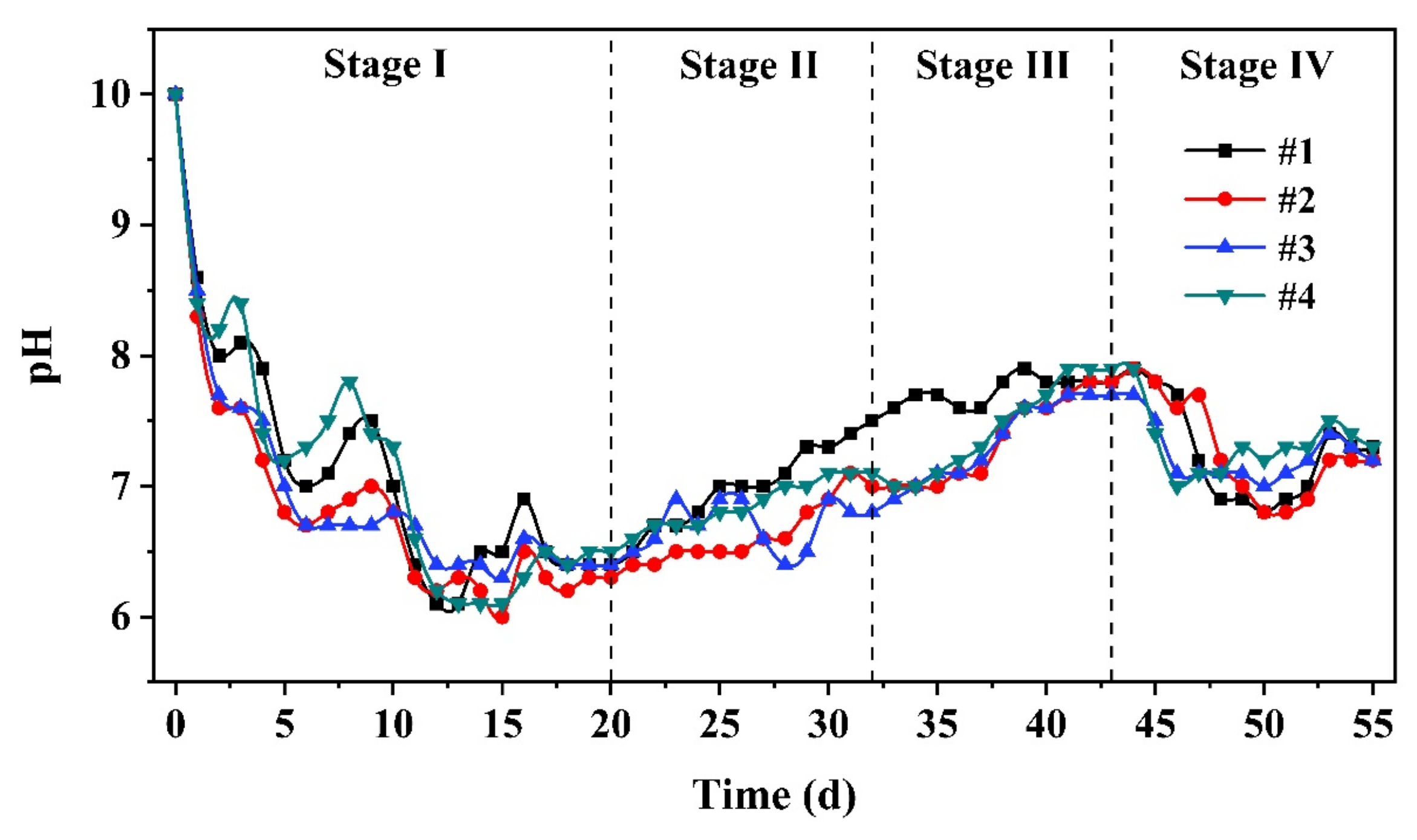
3.1.1. Hydrolysis Performance
3.1.2. Acidification Performance
3.1.3. NH4+-N and PO43−-P Release
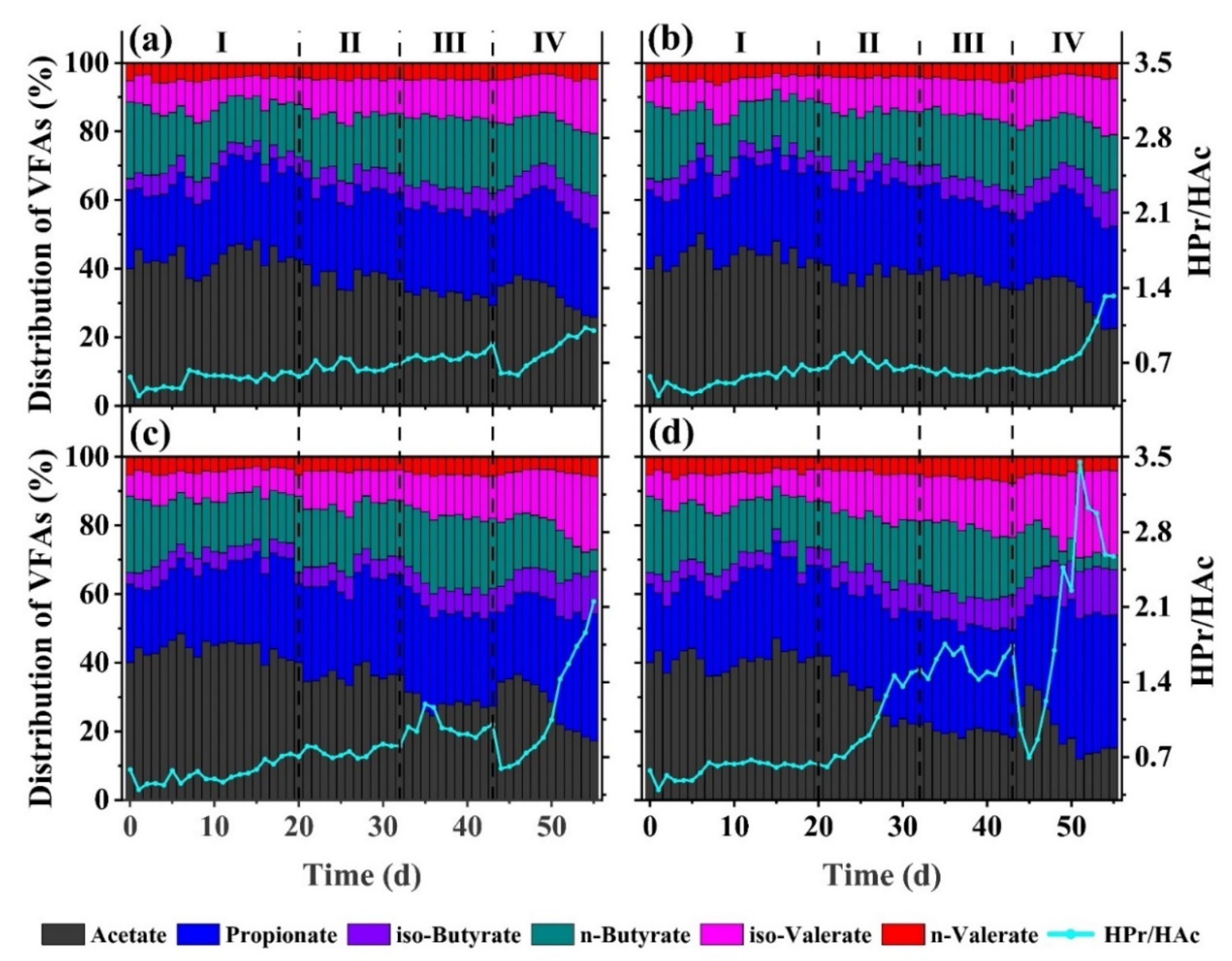
3.2. VFAs Composition Distribution Characteristics
3.3. Application Feasibility Analysis of Fermentation Broth
3.3.1. Distribution of Organic Carbon Sources
3.3.2. Availability Analysis of Fermentation Broth Applied to Enhanced Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Pork Meat Market 2020–2024. Available online: https://www.reportlinker.com/p05144646/Global-Pork-Meat-Market.html (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Cheng, D.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D.; Kumar, S.M. Microalgae biomass from swine wastewater and its conversion to bioenergy. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboudi, K.; Álvarez-Gallego, C.J.; Romero-García, L.I. Semi-continuous anaerobic co-digestion of sugar beet byproduct and pig manure: Effect of the organic loading rate (OLR) on process performance. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 194, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.H.; Narindri, B.; Chu, H.; Whang, L.M. Recent advancement on biological technologies and strategies for resource recovery from swine wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 303, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, G.; Lu, X.; Kato, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.-Y. Overview of pretreatment strategies for enhancing sewage sludge disintegration and subsequent anaerobic digestion: Current advances, full-scale application and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, Z.; Xiong, D.; Wen, Q.; Ji, Y. Oriented acidification of wasted activated sludge (WAS) focused on odd-carbon volatile fatty acid (VFA): Regulation strategy and microbial community dynamics. Water Res. 2018, 142, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychaudhuri, A.; Behera, M. Enhancement of bioelectricity generation by integrating acidogenic compartment into a dual-chambered microbial fuel cell during rice mill wastewater treatment. Process Biochem. 2021, 105, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Kim, J.; Han, J.; Lee, D.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.T.; Cheng, X.; Xu, Y.; Lee, J.; Kwon, E.E. Bioalcohol production from acidogenic products via a two-step process: A case study of butyric acid to butanol. Appl. Energy 2019, 252, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, H.; Ye, J.J.; Luo, J.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, J.Y. Short-chain fatty acids recovery from sewage sludge via acidogenic fermentation as a carbon source for denitrification: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 311, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Q.; Tooker, N.B.; Srinivasan, V.; Li, G.Y.; Fernandez, L.A.; Schauer, P.; Menniti, A.; Maher, C.; Bott, C.B.; Dombrowski, P.; et al. Side-stream enhanced biological phosphorus removal (S2EBPR) process improves system performance—A full-scale comparative study. Water Res. 2019, 167, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perimenis, A.; Nicolay, T.; Leclercq, M.; Gerin, P.A. Comparison of the acidogenic and methanogenic potential of agroindustrial residues. Waste Manag. 2018, 72, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Chua, A.S.M.; Yeoh, H.K.; Ngoh, G.C. A review of the production and applications of waste-derived volatile fatty acids. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 235, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wan, C.; Liu, X.; Lee, D.-J.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tay, J.H. Effect of initial pH on mesophilic hydrolysis and acidification of swine manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Wen, L.; Chen, S.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Wan, C. Effect of alkaline treatment pattern on anaerobic fermentation of swine manure. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Huang, W.; Yuan, T.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Feng, C. Volatile fatty acids (VFAs) production from swine manure through short-term dry anaerobic digestion and its separation from nitrogen and phosphorus resources in the digestate. Water Res. 2016, 90, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Oh, C.; Hwang, S. Optimizing volatile fatty acid production in partial acidogenesis of swine wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 50, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.-J.; Kim, B.J.; Jeong, C.-M.; Choi, J.-d.-r.; Ahn, Y.H.; Chang, H.N. Anaerobic organic acid production of food waste in once-a-day feeding and drawing-off bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7866–7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Hwang, K.; Shin, S.G.; Lee, S.; Hwang, S. Effect of high temperature on bacterial community dynamics in anaerobic acidogenesis using mesophilic sludge inoculum. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, S17–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Shin, S.G.; Lim, J.; Hwang, S. Effect of temperature and hydraulic retention time on volatile fatty acid production based on bacterial community structure in anaerobic acidogenesis using swine wastewater. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 36, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Han, P.; Liu, H.; Zhou, G.; Fu, B.; Zheng, Z. Full-scale production of VFAs from sewage sludge by anaerobic alkaline fermentation to improve biological nutrients removal in domestic wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 260, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Shin, S.G.; Hwang, S.; Lee, C. Continuous fermentation of food waste leachate for the production of volatile fatty acids and potential as a denitrification carbon source. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 207, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C. Waste activated sludge alkaline fermentation liquid as carbon source for biological nutrients removal in anaerobic followed by alternating aerobic-anoxic sequencing batch reactors. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 18, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frison, N.; Di Fabio, S.; Cavinato, C.; Pavan, P.; Fatone, F. Best available carbon sources to enhance the via-nitrite biological nutrients removal from supernatants of anaerobic co-digestion. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215–216, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federation, W.E.; Association, A. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, J.H. The determination of sugar in blood and spinal fluid with anthrone reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1955, 212, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoso-Bravo, A.; Pérez-Elvira, S.; Aymerich, E.; Fdz-Polanco, F. Assessment of the influence of thermal pre-treatment time on the macromolecular composition and anaerobic biodegradability of sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainaina, S.; Awasthi, M.K.; Horváth, I.S.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Anaerobic digestion of food waste to volatile fatty acids and hydrogen at high organic loading rates in immersed membrane bioreactors. Renew. Energy 2020, 152, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, R.; Béline, F. Anaerobic hydrolysis and acidification of organic substrates: Determination of anaerobic hydrolytic potential. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5653–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, C.; Zhou, Q. Effects of pH on the hydrolysis of lignocellulosic wastes and volatile fatty acids accumulation: The contribution of biotic and abiotic factors. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Lian, T.; Wang, S.; Dong, H. Short chain carboxylic acids production and dynamicity of microbial communities from co-digestion of swine manure and corn silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, Q.; Gu, G. Hydrolysis and acidification of waste activated sludge at different pHs. Water Res. 2007, 41, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahring, B.K.; Sandberg, M.; Angelidaki, I. Volatile fatty acids as indicators of process imbalance in anaerobic digestors. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1995, 43, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, H.; Yang, M.; Liu, H. Continuous liquid fermentation of pretreated waste activated sludge for high rate volatile fatty acids production and online nutrients recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owusu-Agyeman, I.; Plaza, E.; Cetecioglu, Z. Production of volatile fatty acids through co-digestion of sewage sludge and external organic waste: Effect of substrate proportions and long-term operation. Waste Manag. 2020, 112, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.; Usack, J.G.; Spirito, C.M.; Angenent, L.T. Long-term n-caproic acid production from yeast-fermentation beer in an anaerobic bioreactor with continuous product extraction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8012–8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Lee, Y.; Yang, K.Y. Maximization of acetic acid production in partial acidogenesis of swine wastewater. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2001, 75, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Behera, S.K.; Kim, J.W.; Park, H.-S. Methane production potential of leachate generated from Korean food waste recycling facilities: A lab-scale study. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, G. Review on research achievements of biogas from anaerobic digestion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, R.; Massé, D.I.; Singh, G. A critical review on inhibition of anaerobic digestion process by excess ammonia. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucisik, A.S.; Henze, M. Biological hydrolysis and acidification of sludge under anaerobic conditions: The effect of sludge type and origin on the production and composition of volatile fatty acids. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3729–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banister, S.S.; Pitman, A.R.; Pretorius, W.A. The solubilisation of N and P during primary sludge acid fermentation and precipitation of the resultant P. Water SA 1998, 24, 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Wild, D.; Kisliakova, A.; Siegrist, H. Prediction of recycle phosphorus loads from anaerobic digestion. Water Res. 1997, 31, 2300–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tan, F.; Ke, L.; Xia, D.; Wang, Y.; He, N.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q. Mass balances and distributions of C, N, and P in the anaerobic digestion of different substrates and relationships between products and substrates. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; An, H.; Xie, T.; Xu, Q.; Deng, Y.; Zeng, G. Effect of initial pH on short chain fatty acid production during the anaerobic fermentation of membrane bioreactor sludge enhanced by alkyl polyglcoside. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 104, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Yan, B.; Wong, J.W.C.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced volatile fatty acids production from anaerobic fermentation of food waste: A mini-review focusing on acidogenic metabolic pathways. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jomnonkhaow, U.; Uwineza, C.; Mahboubi, A.; Wainaina, S.; Reungsang, A.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Membrane bioreactor-assisted volatile fatty acids production and in situ recovery from cow manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 321, 124456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parawira, W.; Murto, M.; Read, J.S.; Mattiasson, B. Volatile fatty acid production during anaerobic mesophilic digestion of solid potato waste. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Kuninobu, M.; Ogawa, H.I.; Kato, Y. Degradation of volatile fatty acids in highly efficient anaerobic digestion. Biomass Bioenergy 1999, 16, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchaim, U.; Krause, C. Propionic to acetic acid ratios in overloaded anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 1993, 43, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.T.; Cobb, S.A.; Bolte, J.P. Using volatile fatty acid relationships to predict anaerobic digester failure. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1987, 30, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland, P. Wichtige messdaten für den prozessablauf und stand der technik in der praxis. Gülzower Fachgespräche 2008, 27, 17–31. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, F.; Huang, W.; Huang, W.; Li, F.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced anaerobic digestion of ammonia-rich swine manure by zero-valent iron: With special focus on the enhancement effect on hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis activity. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Aguirre, J.; Aymerich, E.; de Goñi, J.G.M.; Esteban-Gutiérrez, M. Selective VFA production potential from organic waste streams: Assessing temperature and pH influence. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wan, R.; Huang, H.; Li, M.; Wu, L. Using sludge fermentation liquid to reduce the inhibitory effect of copper oxide nanoparticles on municipal wastewater biological nutrient removal. Water Res. 2016, 99, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.T.T.; Le, V.Q.; Hansen, A.A.; Nielsen, J.L.; Nielsen, P.H. High diversity and abundance of putative polyphosphate-accumulating Tetrasphaera-related bacteria in activated sludge systems. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 76, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elefsiniotis, P.; Wareham, D.G. Utilization patterns of volatile fatty acids in the denitrification reaction. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2007, 41, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehmen, A.; Yuan, Z.; Blackall, L.L.; Keller, J. Comparison of acetate and propionate uptake by polyphosphate accumulating organisms and glycogen accumulating organisms. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 91, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, X.; Oehmen, A.; Keller, J. Anaerobic metabolism of Defluviicoccus vanus related glycogen accumulating organisms (GAOs) with acetate and propionate as carbon sources. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1885–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Zhou, Y. Enhanced biological phosphorus removal with different carbon sources. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4735–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Randall, A.A.; McCue, T. The efficiency of enhanced biological phosphorus removal from real wastewater affected by different ratios of acetic to propionic acid. Water Res. 2004, 38, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| pH | – | 7.1 ± 0.1 |
| Total solids (TS) | % | 26.9 ± 0.1 |
| Volatile solids/total solids (VS/TS) | % | 83.1 ± 0.2 |
| Soluble chemical oxygen demand (SCOD) | mg/L | 71,867 ± 1820 |
| Total chemical oxygen demand (TCOD) | mg/L | 191,822 ± 7705 |
| Soluble proteins | mg/L | 10,073 ± 368 |
| Soluble carbohydrates | mg/L | 2714 ± 93 |
| Ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N) | mg/L | 1954 ± 78 |
| Soluble phosphorus (PO43−-P) | mg/L | 664 ± 41 |
| Reactor | Hydrolysis Degree (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage I | Stage II | Stage III | Stage IV | |
| #1 | 56.5 ± 0.4 | 49.7 ± 0.5 | 46.2 ± 0.4 | 29.4 ± 0.6 |
| #2 | 59.1 ± 0.3 | 62.2 ± 1.6 | 51.0 ± 0.2 | 29.9 ± 0.8 |
| #3 | 56.9 ± 0.4 | 58.1 ± 0.9 | 48.3 ± 0.2 | 24.3 ± 0.3 |
| #4 | 61.7 ± 0.4 | 47.9 ± 0.3 | 37.8 ± 2.1 | 21.1 ± 0.5 |
| Reactor | Stage | Acetate (%) | Propionate (%) | iso-Butyrate (%) | n-Butyrate (%) | iso-Valerate (%) | n-Valerate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | I | 42.6 ± 0.7 | 25.9 ± 0.5 | 4.6 ± 0.1 | 15.0 ± 0.7 | 7.7 ± 0.3 | 4.2 ± 0.1 |
| II | 37.4 ± 1.1 | 25.0 ± 0.4 | 6.0 ± 0.1 | 16.7 ± 1.2 | 10.1 ± 0.0 | 4.8 ± 0.4 | |
| III | 31.2 ± 1.7 | 25.3 ± 0.5 | 6.6 ± 0.1 | 20.5 ± 0.2 | 11.4 ± 0.8 | 5.0 ± 0.2 | |
| IV | 26.7 ± 1.2 | 26.4 ± 0.5 | 9.0 ± 0.6 | 17.7 ± 0.3 | 15.2 ± 0.9 | 4.9 ± 0.4 | |
| #2 | I | 41.6 ± 1.3 | 27.1 ± 0.4 | 4.4 ± 0.2 | 15.9 ± 0.7 | 7.2 ± 0.5 | 3.8 ± 0.2 |
| II | 38.9 ± 0.8 | 25.6 ± 0.2 | 6.0 ± 0.1 | 15.4 ± 0.4 | 10.2 ± 0.1 | 4.0 ± 0.0 | |
| III | 34.8 ± 1.2 | 22.2 ± 0.1 | 6.4 ± 0.3 | 19.4 ± 0.5 | 11.7 ± 1.0 | 5.6 ± 0.3 | |
| IV | 23.7 ± 2.2 | 29.3 ± 0.7 | 10.2 ± 0.6 | 16.4 ± 0.4 | 16.0 ± 1.0 | 4.5 ± 0.3 | |
| #3 | I | 40.9 ± 0.5 | 29.2 ± 0.6 | 4.4 ± 0.1 | 14.4 ± 0.4 | 7.5 ± 0.3 | 3.5 ± 0.2 |
| II | 36.1 ± 0.6 | 29.2 ± 0.2 | 5.5 ± 0.2 | 16.4 ± 0.1 | 9.1 ± 0.4 | 3.9 ± 0.1 | |
| III | 27.7 ± 1.1 | 26.3 ± 1.0 | 7.1 ± 0.3 | 20.8 ± 0.5 | 12.6 ± 0.5 | 5.5 ± 0.3 | |
| IV | 18.5 ± 1.4 | 35.2 ± 1.6 | 12.2 ± 0.8 | 7.1 ± 0.8 | 21.7 ± 0.6 | 5.3 ± 0.4 | |
| #4 | I | 42.6 ± 1.5 | 26.7 ± 0.2 | 5.0 ± 0.4 | 13.0 ± 0.8 | 9.2 ± 0.2 | 3.5 ± 0.3 |
| II | 22.6 ± 1.0 | 32.7 ± 0.6 | 8.0 ± 0.2 | 18.3 ± 0.4 | 13.5 ± 0.1 | 5.0 ± 0.1 | |
| III | 19.1 ± 1.0 | 30.7 ± 1.1 | 9.4 ± 0.7 | 17.4 ± 0.7 | 16.1 ± 0.4 | 7.3 ± 0.4 | |
| IV | 14.6 ± 0.7 | 39.6 ± 1.2 | 13.4 ± 0.2 | 4.0 ± 0.2 | 24.4 ± 0.7 | 4.0 ± 0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, P.; Leng, Y.; Wu, J. Continuous Production of Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) from Swine Manure: Determination of Process Conditions, VFAs Composition Distribution and Fermentation Broth Availability Analysis. Water 2022, 14, 1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121935
Wang Z, Wang W, Li P, Leng Y, Wu J. Continuous Production of Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) from Swine Manure: Determination of Process Conditions, VFAs Composition Distribution and Fermentation Broth Availability Analysis. Water. 2022; 14(12):1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121935
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhiwei, Weiwu Wang, Ping Li, Yaping Leng, and Jinhua Wu. 2022. "Continuous Production of Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) from Swine Manure: Determination of Process Conditions, VFAs Composition Distribution and Fermentation Broth Availability Analysis" Water 14, no. 12: 1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121935
APA StyleWang, Z., Wang, W., Li, P., Leng, Y., & Wu, J. (2022). Continuous Production of Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) from Swine Manure: Determination of Process Conditions, VFAs Composition Distribution and Fermentation Broth Availability Analysis. Water, 14(12), 1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121935