The Effect of Rough Rigid Apron on Scour Downstream of Sluice Gates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Dimensional Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
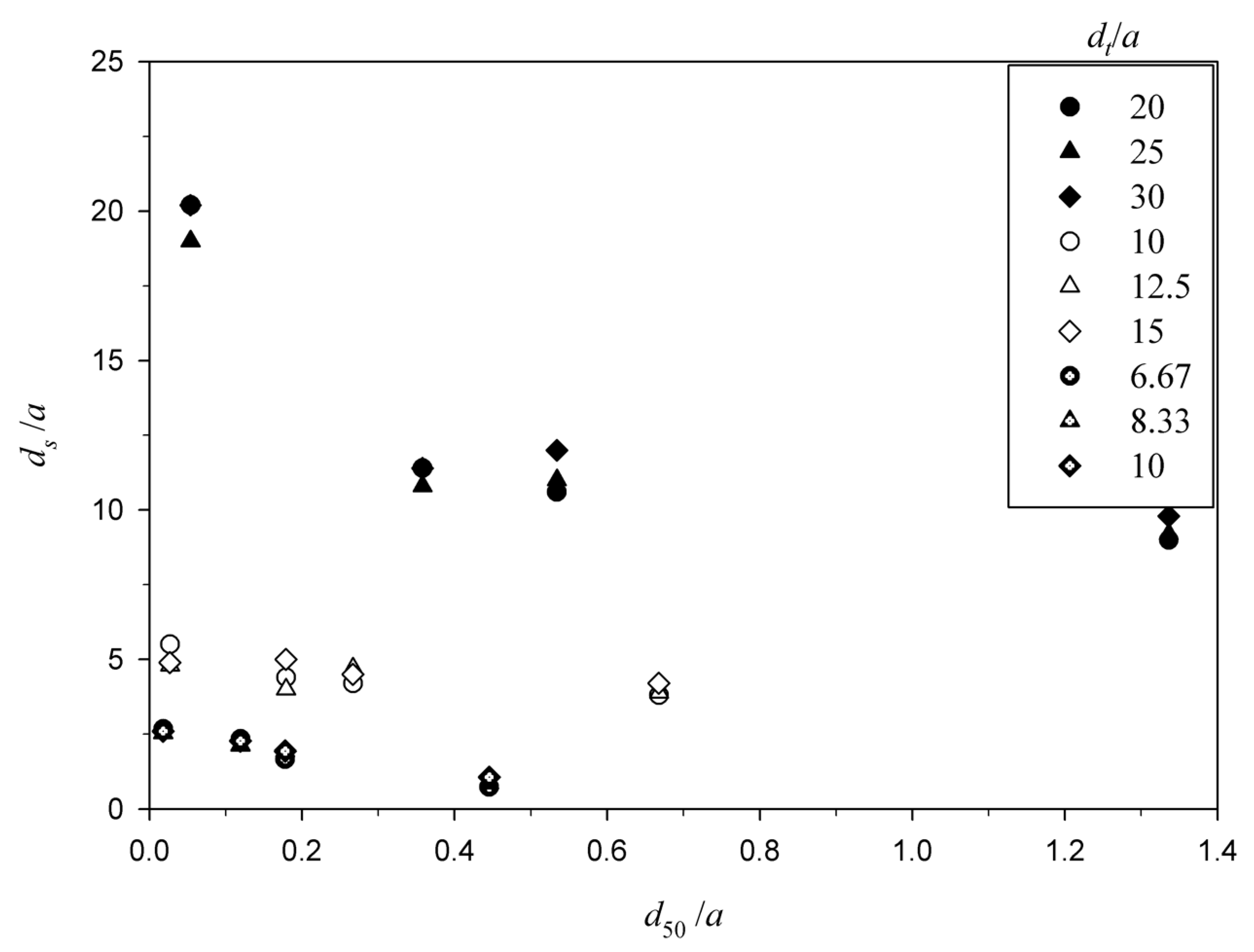
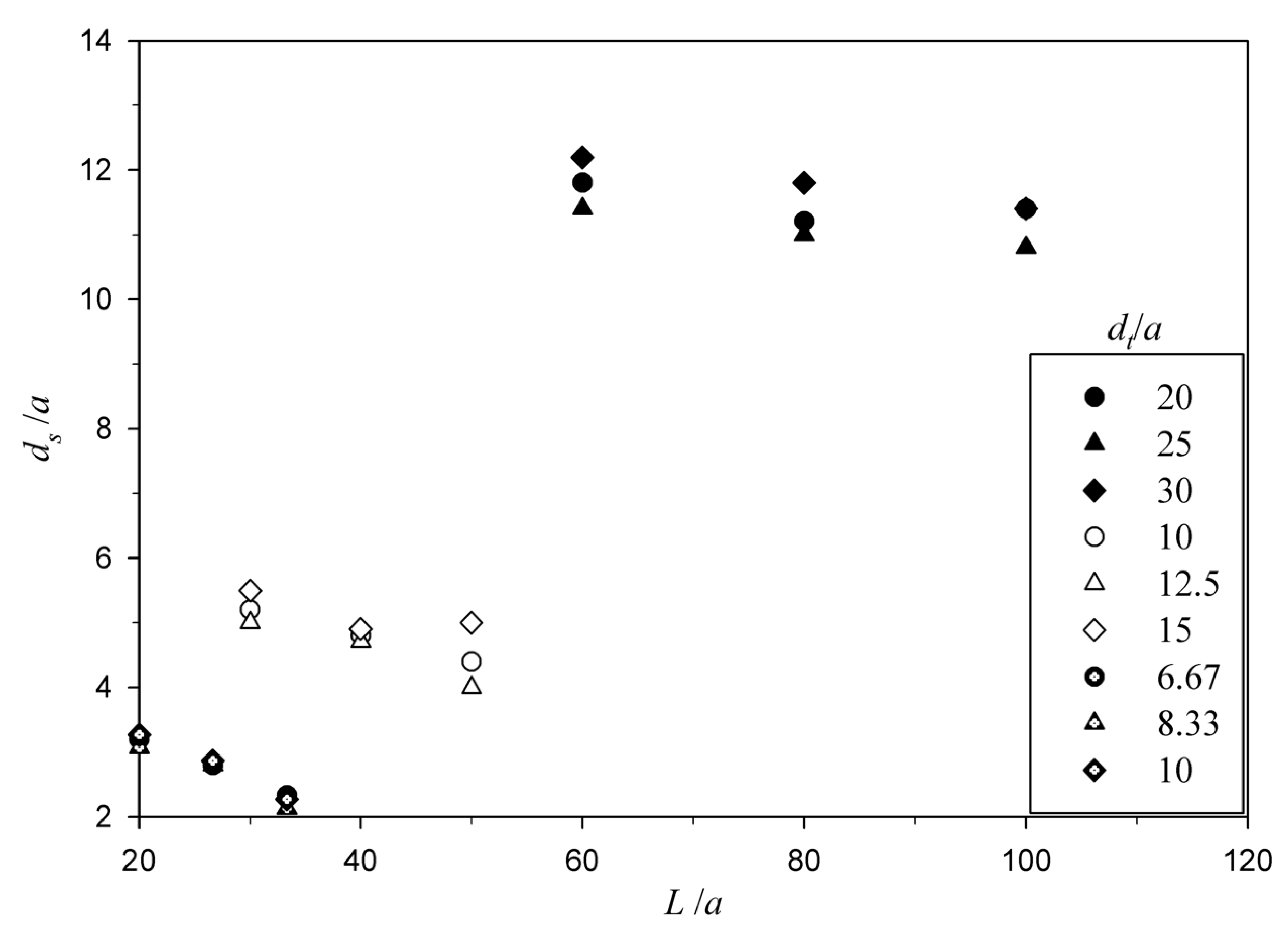
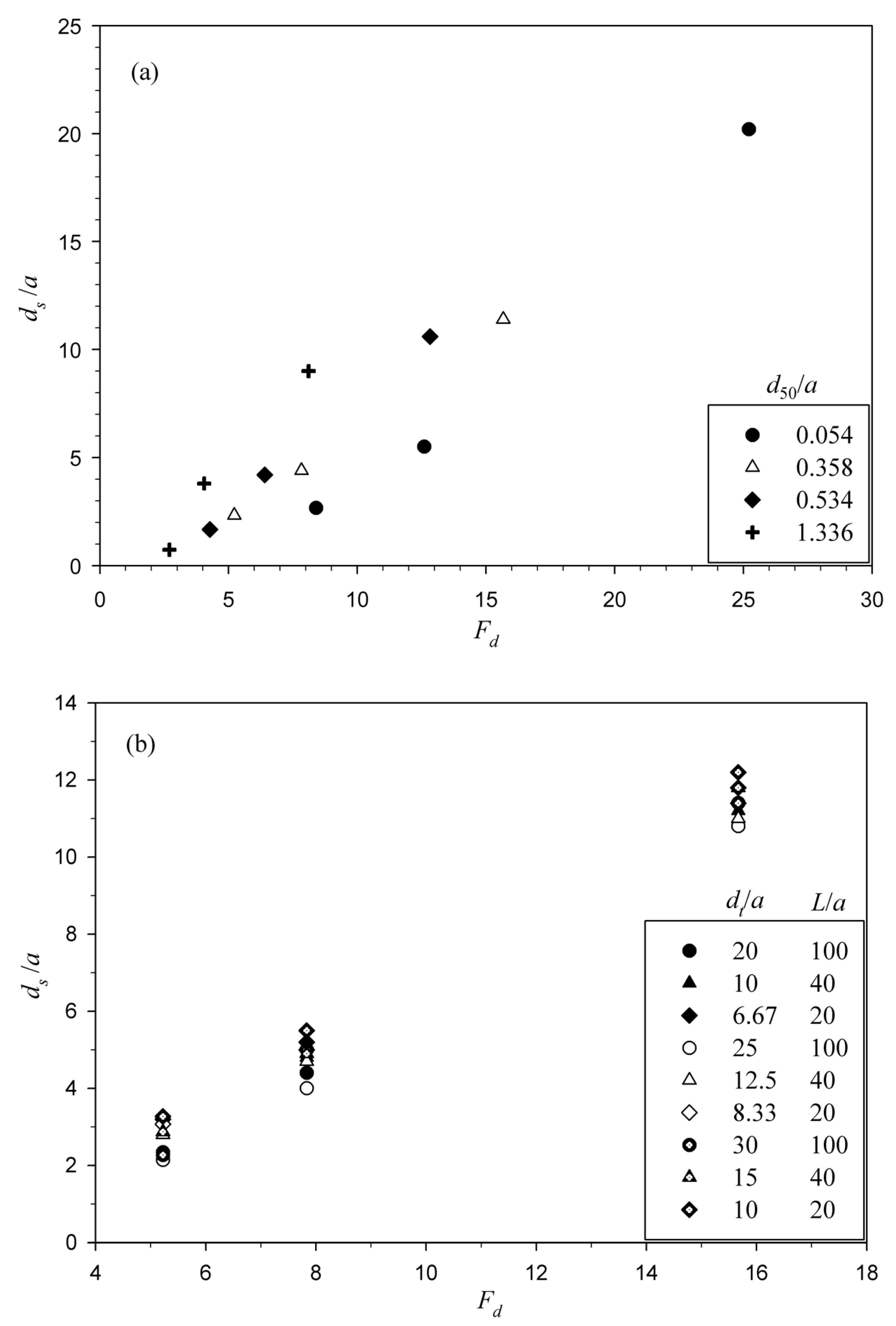
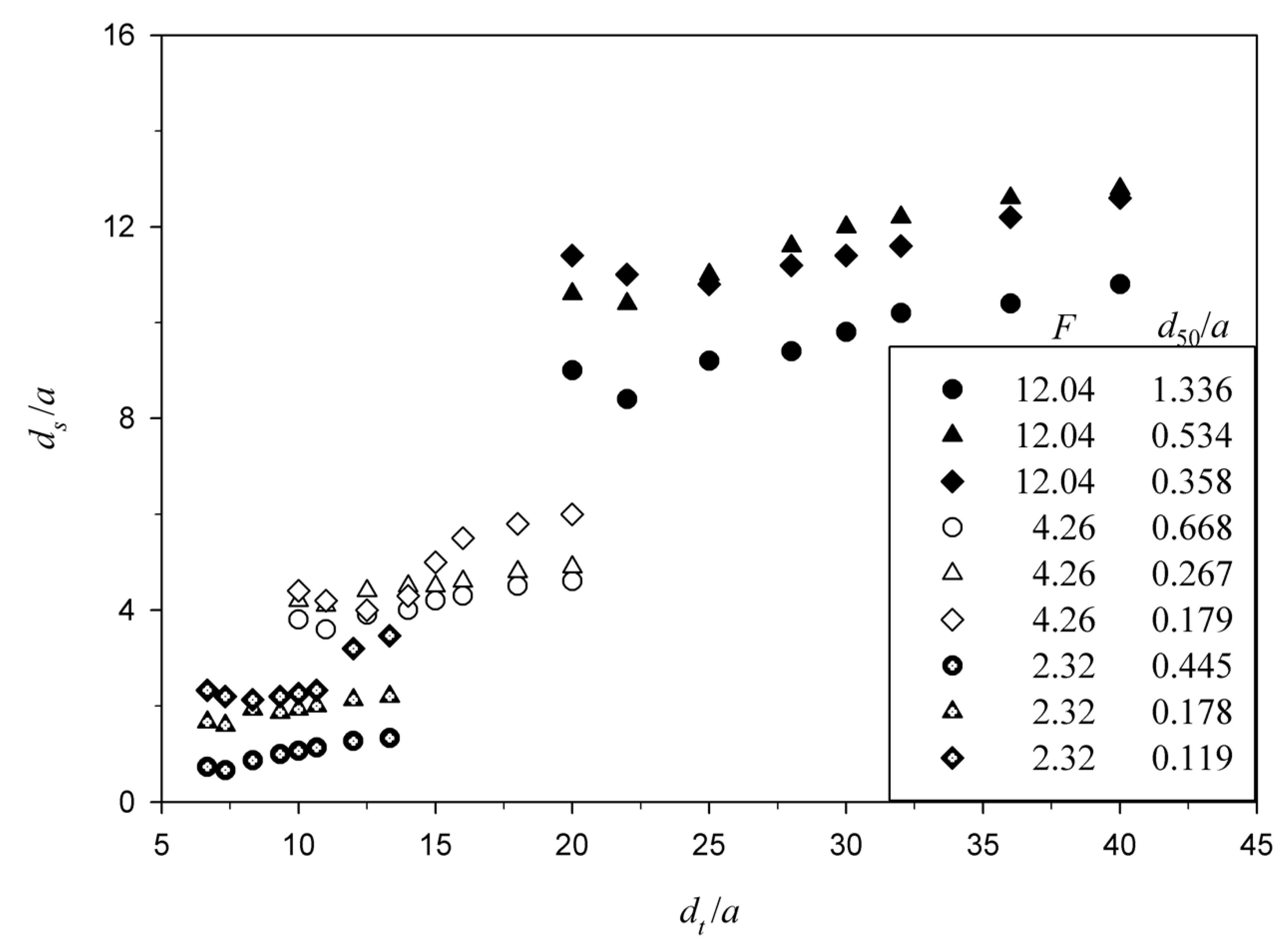
4.1. Effect of Different Parameters on Maximum Scour Depth
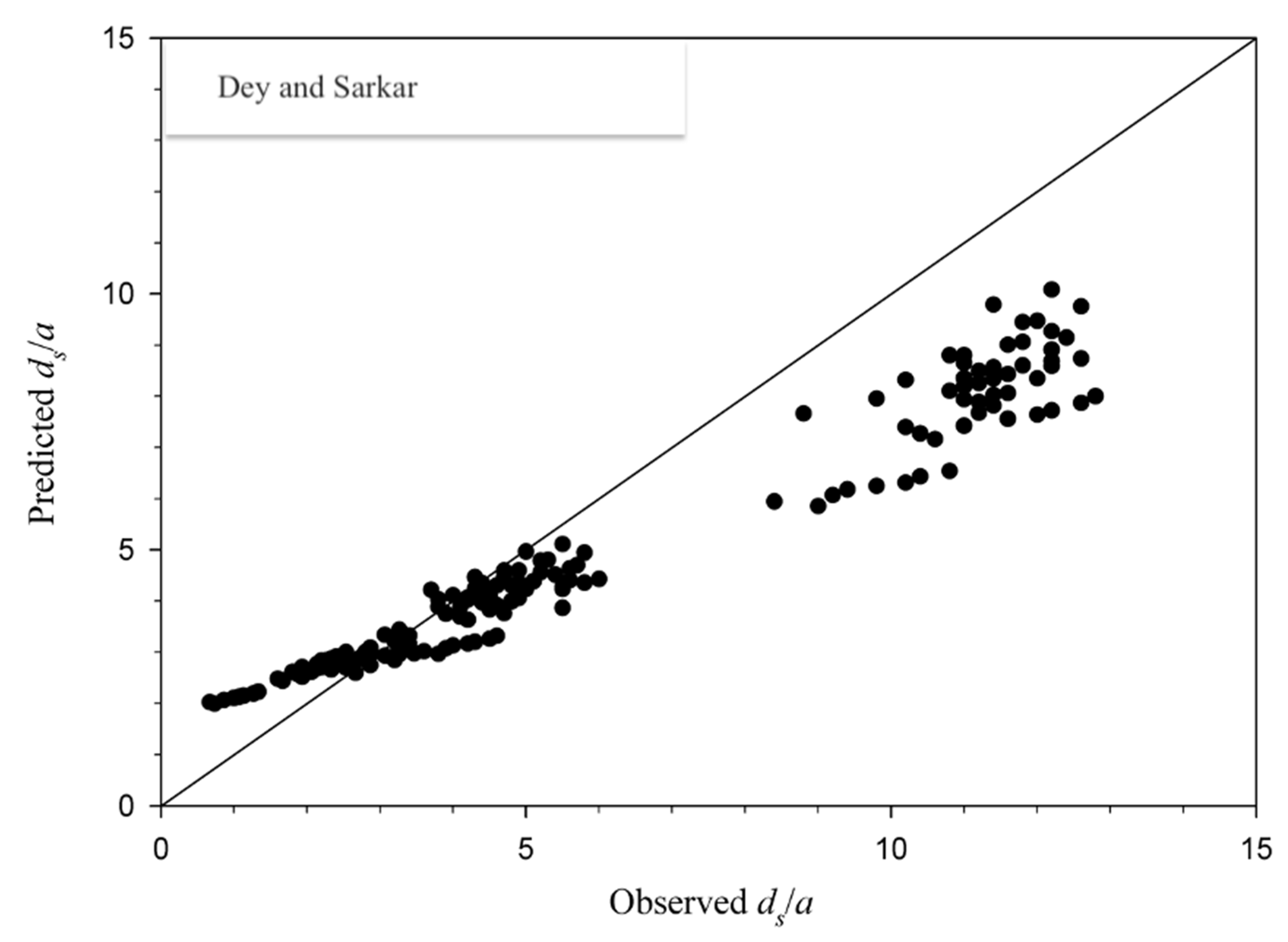
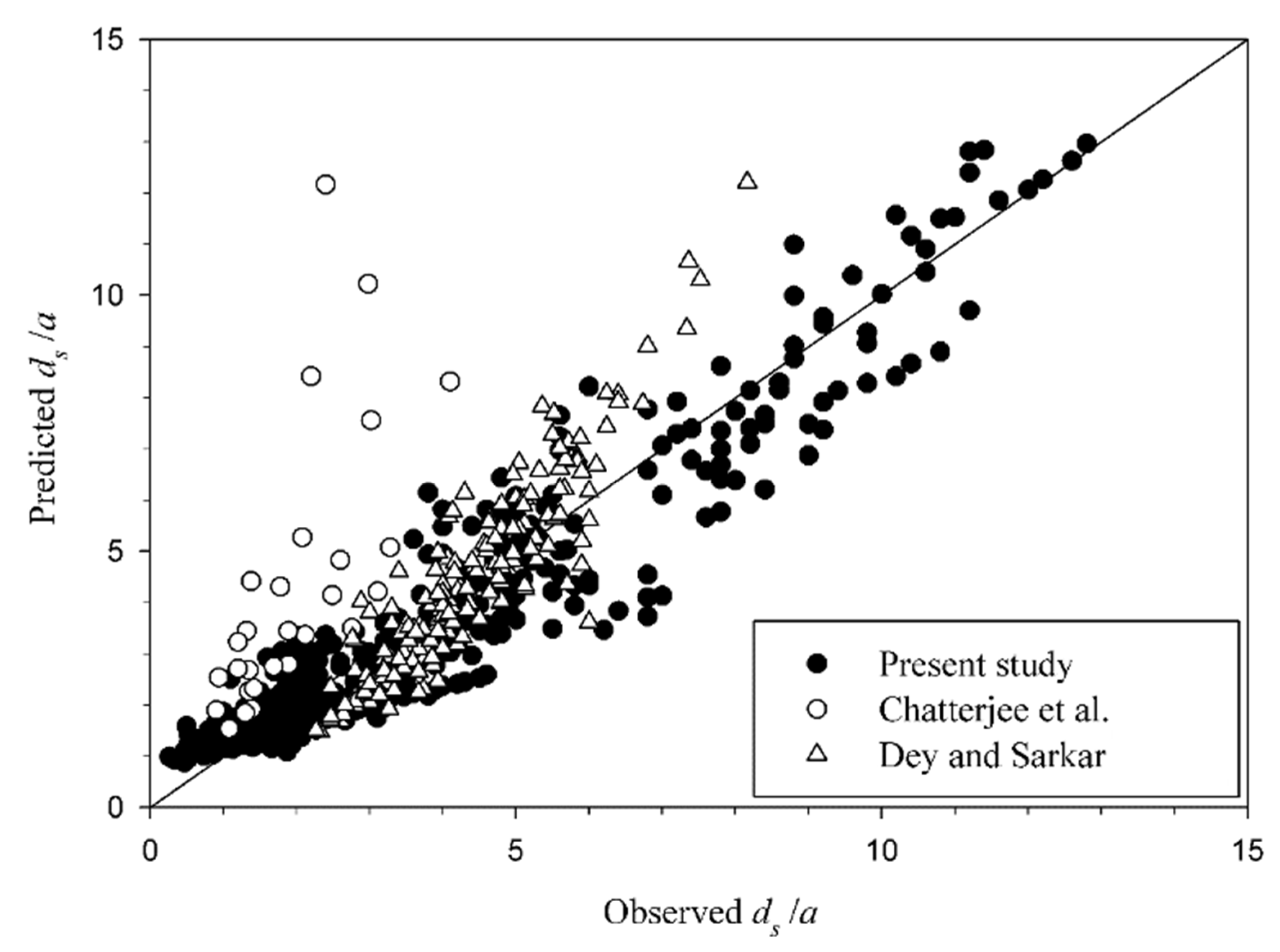
4.2. Estimation of Maximum Scour Depth
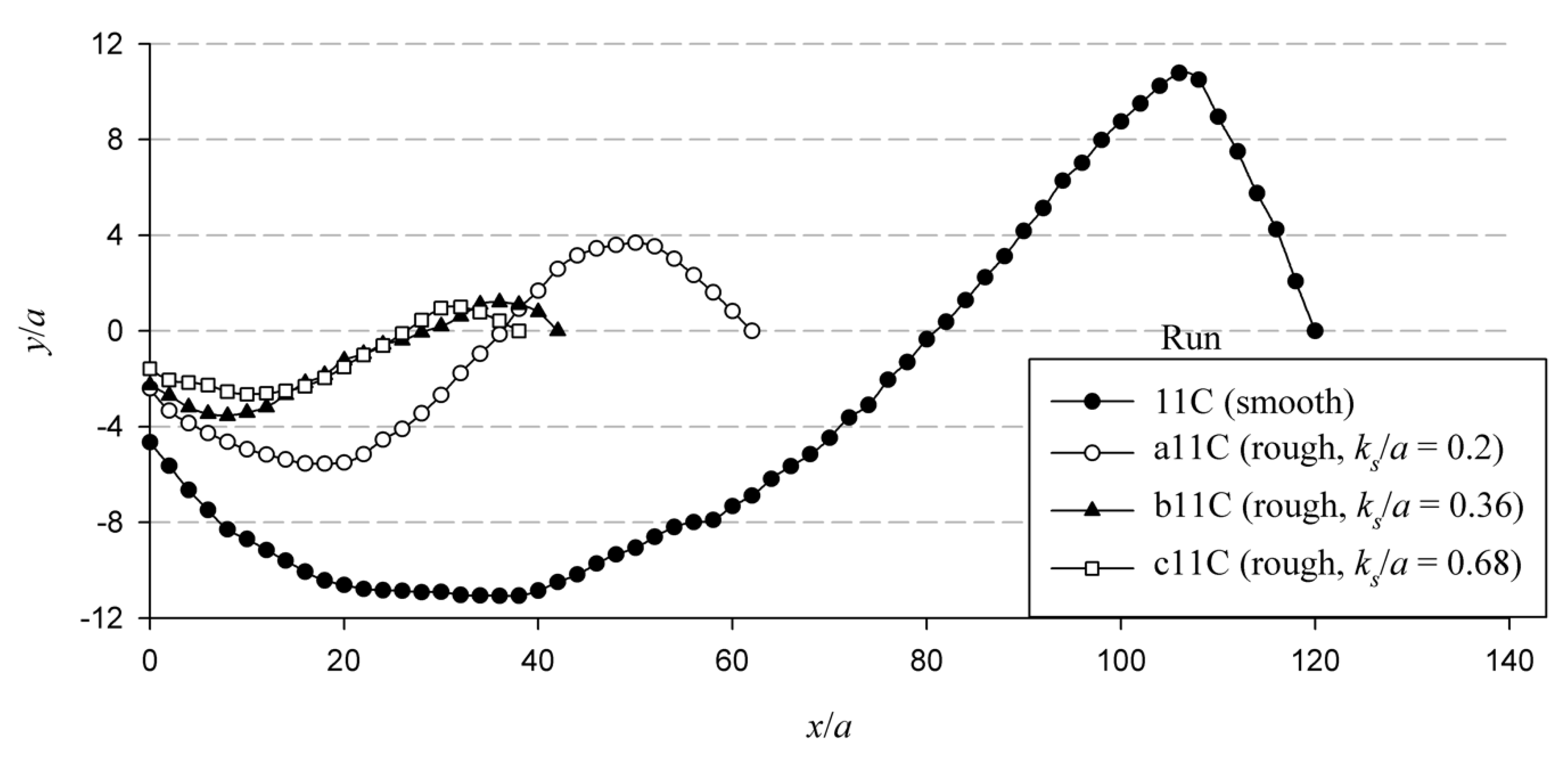
4.3. Scour Profiles
4.4. Temporal Variation of Scour Depth
5. Conclusions
- The maximum scour depth reduces significantly with a rise in the roughness of stiff apron. Further, equilibrium scour depth decreases with increasing sediment size. It is more for a shorter length of the stiff apron than for longer aprons. Also, the maximum depth of scour is higher for smaller slit size of sluice gate a. An increase in the maximum scour depth is observed with increasing densimetric Froude number.
- The influence of depth of tailwater level on maximum scour depth is such that there exists a critical tailwater level conforming with the minimum value of maximum scour depth. Thereafter, an increase in the maximum scour depth is seen with an increase in tailwater level.
- A new empirical equation for the prediction of maximum scour depth under smooth and rough apron is proposed. The proposed equation takes into account the influence of apron roughness on maximum scour depth, while the existing equations do not account for this parameter. Polynomial equations are also proposed for scour profiles under smooth and rough aprons.
- The maximum scour depth predicted using the proposed equation, which is applicable to both smooth and rough aprons, is in conformity with that obtained experimentally.
- The temporal scour profiles at distinct intervals of time obey a particular resemblance in geometry, both in the case of rough and smooth aprons. The scour profiles can be obtained from the proposed polynomial equations, which are satisfactory. The time variation of depth of scour was scaled by an exponential law. There is a linear increase in the time scale with densimetric Froude number.
- There is a significant reduction observed in the maximum scour depth due to roughness, which is in the range of 70–83%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Run | d50 (mm) | a (mm) | ks (mm) | dt (m) | V (m/s) | L (m) | ds (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | 0.27 | 5 | 0 | 0.1 | 1.67 | 0.5 | 10.1 |
| 2A | 0.27 | 5 | 0 | 0.125 | 1.67 | 0.5 | 9.5 |
| 3A | 0.27 | 5 | 0 | 0.15 | 1.67 | 0.5 | 10.1 |
| 4A | 0.27 | 10 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.83 | 0.5 | 5.5 |
| 5A | 0.27 | 10 | 0 | 0.125 | 0.83 | 0.5 | 4.8 |
| 6A | 0.27 | 10 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.83 | 0.5 | 4.9 |
| 7A | 0.27 | 15 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.56 | 0.5 | 4.0 |
| 8A | 0.27 | 15 | 0 | 0.125 | 0.56 | 0.5 | 3.8 |
| 9A | 0.27 | 15 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.56 | 0.5 | 3.9 |
| 10B | 6.70 | 5 | 0 | 0.1 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 4.5 |
| 10B1 | 6.70 | 5 | 0 | 0.11 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 4.2 |
| 11B | 6.70 | 5 | 0 | 0.125 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 4.6 |
| 11B1 | 6.70 | 5 | 0 | 0.14 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 4.7 |
| 12B | 6.70 | 5 | 0 | 0.15 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 4.9 |
| 12B1 | 6.70 | 5 | 0 | 0.16 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 5.1 |
| 12B2 | 6.70 | 5 | 0 | 0.18 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 5.2 |
| 12B3 | 6.70 | 5 | 0 | 0.20 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 5.4 |
| 13B | 6.70 | 10 | 0 | 0.1 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 3.8 |
| 13B1 | 6.70 | 10 | 0 | 0.11 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 3.6 |
| 14B | 6.70 | 10 | 0 | 0.125 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 3.9 |
| 14B1 | 6.70 | 10 | 0 | 0.14 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.0 |
| 15B | 6.70 | 10 | 0 | 0.15 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.2 |
| 15B1 | 6.70 | 10 | 0 | 0.16 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.3 |
| 15B2 | 6.70 | 10 | 0 | 0.18 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.5 |
| 15B3 | 6.70 | 10 | 0 | 0.20 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.6 |
| 16B | 6.70 | 15 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 1.1 |
| 16B1 | 6.70 | 15 | 0 | 0.11 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| 17B | 6.70 | 15 | 0 | 0.125 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 1.3 |
| 17B1 | 6.70 | 15 | 0 | 0.14 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 1.5 |
| 18B | 6.70 | 15 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 1.6 |
| 18B1 | 6.70 | 15 | 0 | 0.16 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 1.7 |
| 18B2 | 6.70 | 15 | 0 | 0.18 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 1.9 |
| 18B3 | 6.70 | 15 | 0 | 0.20 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 2.0 |
| 10C | 2.67 | 5 | 0 | 0.1 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 5.3 |
| 10C1 | 2.67 | 5 | 0 | 0.11 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 5.2 |
| 11C | 2.67 | 5 | 0 | 0.125 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 5.5 |
| 11C1 | 2.67 | 5 | 0 | 0.14 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 5.8 |
| 12C | 2.67 | 5 | 0 | 0.15 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 6.0 |
| 12C1 | 2.67 | 5 | 0 | 0.16 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 6.1 |
| 12C2 | 2.67 | 5 | 0 | 0.18 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 6.3 |
| 12C3 | 2.67 | 5 | 0 | 0.20 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 6.4 |
| 13C | 2.67 | 10 | 0 | 0.1 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.2 |
| 13C1 | 2.67 | 10 | 0 | 0.11 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.1 |
| 14C | 2.67 | 10 | 0 | 0.125 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.7 |
| 14C1 | 2.67 | 10 | 0 | 0.14 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.5 |
| 15C | 2.67 | 10 | 0 | 0.15 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.5 |
| 15C1 | 2.67 | 10 | 0 | 0.16 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.6 |
| 15C2 | 2.67 | 10 | 0 | 0.18 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.8 |
| 15C3 | 2.67 | 10 | 0 | 0.20 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.9 |
| 16C | 2.67 | 15 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 2.5 |
| 16C1 | 2.67 | 15 | 0 | 0.11 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 2.4 |
| 17C | 2.67 | 15 | 0 | 0.125 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 2.9 |
| 17C1 | 2.67 | 15 | 0 | 0.14 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 2.8 |
| 18C | 2.67 | 15 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 2.9 |
| 18C1 | 2.67 | 15 | 0 | 0.16 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 3.0 |
| 18C2 | 2.67 | 15 | 0 | 0.18 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 3.2 |
| 18C3 | 2.67 | 15 | 0 | 0.20 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 3.3 |
| 10D | 1.79 | 5 | 0 | 0.1 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 5.7 |
| 10D1 | 1.79 | 5 | 0 | 0.11 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 5.5 |
| 11D | 1.79 | 5 | 0 | 0.125 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 5.4 |
| 11D1 | 1.79 | 5 | 0 | 0.14 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 5.6 |
| 12D | 1.79 | 5 | 0 | 0.15 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 5.7 |
| 12D1 | 1.79 | 5 | 0 | 0.16 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 5.8 |
| 12D2 | 1.79 | 5 | 0 | 0.18 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 6.1 |
| 12D3 | 1.79 | 5 | 0 | 0.20 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 6.3 |
| 13D | 1.79 | 10 | 0 | 0.1 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.4 |
| 13D1 | 1.79 | 10 | 0 | 0.11 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.2 |
| 14D | 1.79 | 10 | 0 | 0.125 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.0 |
| 14D1 | 1.79 | 10 | 0 | 0.14 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 4.3 |
| 15D | 1.79 | 10 | 0 | 0.15 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 5.0 |
| 15D1 | 1.79 | 10 | 0 | 0.16 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 5.5 |
| 15D2 | 1.79 | 10 | 0 | 0.18 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 5.8 |
| 15D3 | 1.79 | 10 | 0 | 0.20 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 6.0 |
| 16D | 1.79 | 15 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 3.5 |
| 16D1 | 1.79 | 15 | 0 | 0.11 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 3.3 |
| 17D | 1.79 | 15 | 0 | 0.125 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 3.2 |
| 17D1 | 1.79 | 15 | 0 | 0.14 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 3.3 |
| 18D | 1.79 | 15 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 3.4 |
| 18D1 | 1.79 | 15 | 0 | 0.16 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 3.5 |
| 18D2 | 1.79 | 15 | 0 | 0.18 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 4.8 |
| 18D3 | 1.79 | 15 | 0 | 0.20 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 5.2 |
| 19D | 1.79 | 5 | 0 | 0.1 | 2.67 | 0.4 | 5.6 |
| 20D | 1.79 | 5 | 0 | 0.125 | 2.67 | 0.4 | 5.5 |
| 21D | 1.79 | 5 | 0 | 0.15 | 2.67 | 0.4 | 5.9 |
| 22D | 1.79 | 10 | 0 | 0.1 | 1.33 | 0.4 | 4.8 |
| 23D | 1.79 | 10 | 0 | 0.125 | 1.33 | 0.4 | 4.7 |
| 24D | 1.79 | 10 | 0 | 0.15 | 1.33 | 0.4 | 4.9 |
| 25D | 1.79 | 15 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.89 | 0.4 | 4.2 |
| 26D | 1.79 | 15 | 0 | 0.125 | 0.89 | 0.4 | 4.2 |
| 27D | 1.79 | 15 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.89 | 0.4 | 4.3 |
| 28D | 1.79 | 5 | 0 | 0.1 | 2.67 | 0.3 | 5.9 |
| 29D | 1.79 | 5 | 0 | 0.125 | 2.67 | 0.3 | 5.7 |
| 30D | 1.79 | 5 | 0 | 0.15 | 2.67 | 0.3 | 6.1 |
| 31D | 1.79 | 10 | 0 | 0.1 | 1.33 | 0.3 | 5.2 |
| 32D | 1.79 | 10 | 0 | 0.125 | 1.33 | 0.3 | 5.0 |
| 33D | 1.79 | 10 | 0 | 0.15 | 1.33 | 0.3 | 5.5 |
| 34D | 1.79 | 15 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.89 | 0.3 | 4.8 |
| 35D | 1.79 | 15 | 0 | 0.125 | 0.89 | 0.3 | 4.6 |
| 36D | 1.79 | 15 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.89 | 0.3 | 4.9 |
| a10C | 2.67 | 5 | 1.00 | 0.1 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 3.4 |
| a11C | 2.67 | 5 | 1.00 | 0.125 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 2.8 |
| a12C | 2.67 | 5 | 1.00 | 0.15 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 3.6 |
| a13C | 2.67 | 10 | 1.00 | 0.1 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 2.8 |
| a14C | 2.67 | 10 | 1.00 | 0.125 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 2.3 |
| a15C | 2.67 | 10 | 1.00 | 0.15 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 3.1 |
| a16C | 2.67 | 15 | 1.00 | 0.1 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 1.5 |
| a17C | 2.67 | 15 | 1.00 | 0.125 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 1.1 |
| a18C | 2.67 | 15 | 1.00 | 0.15 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 1.8 |
| b10C | 2.67 | 5 | 1.79 | 0.1 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 2.1 |
| b11C | 2.67 | 5 | 1.79 | 0.125 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 1.9 |
| b12C | 2.67 | 5 | 1.79 | 0.15 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 2.4 |
| b13C | 2.67 | 10 | 1.79 | 0.1 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 1.6 |
| b14C | 2.67 | 10 | 1.79 | 0.125 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 1.5 |
| b15C | 2.67 | 10 | 1.79 | 0.15 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 1.8 |
| b16C | 2.67 | 15 | 1.79 | 0.1 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 1.4 |
| b17C | 2.67 | 15 | 1.79 | 0.125 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 1.3 |
| b18C | 2.67 | 15 | 1.79 | 0.15 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 1.5 |
| c10C | 2.67 | 5 | 3.40 | 0.1 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 1.6 |
| c11C | 2.67 | 5 | 3.40 | 0.125 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 1.3 |
| c12C | 2.67 | 5 | 3.40 | 0.15 | 2.67 | 0.5 | 1.6 |
| c13C | 2.67 | 10 | 3.40 | 0.1 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 1.1 |
| c14C | 2.67 | 10 | 3.40 | 0.125 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 0.9 |
| c15C | 2.67 | 10 | 3.40 | 0.15 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 1.3 |
| c16C | 2.67 | 15 | 3.40 | 0.1 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
| c17C | 2.67 | 15 | 3.40 | 0.125 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| c18C | 2.67 | 15 | 3.40 | 0.15 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 0.8 |
References
- Rouse, H. Criteria for similarity in transportation of sediment. In Proceedings of the 1st Hydraulic Conference, Iowa City, IA, USA, 12–15 June 1939; pp. 33–49. [Google Scholar]
- Laursen, E.M. Observations of the Nature of Scour. In Proceedings of the 5th Hydraulic Conference, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, USA, 9–12 June 1952; pp. 179–197. [Google Scholar]
- Tarapore, Z.S. Scour below a submerged sluice gate. Master’s Thesis, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Hogg, A.J.; Huppert, H.E.; Dade, W.B. Erosion by planar turbulent wall jets. J. Fluid Mech. 1997, 338, 317–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carstens, M.R. Similarity laws for localized scour. J. Hydraul. Div. 1966, 92, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.S.; Ghosh, S.N. Submerged horizontal jet over erodible bed. J. Hydraul. Div. 1980, 106, 1765–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.S.; Ghosh, S.N.; Chatterjee, M. Local scour due to submerged horizontal jet. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1994, 120, 973–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaratnam, N. Erosion by plane turbulent jets. J. Hydraul. Res. 1981, 19, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaratnam, N.; Macdougall, R.K. Erosion by plane wall jets with minimum tail water. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1983, 109, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.M.K.N.; Narayanan, R. Local scour downstream of an apron. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1985, 111, 1371–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.H.M.; Lim, S.Y. Local scour caused by submerged wall jets. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. 1986, 81, 607–645. [Google Scholar]
- Aderibigbe, O.; Rajaratnam, N. Effect of sediment gradation on erosion by plane turbulent wall jets. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1998, 124, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidifar, H.; Omid, M.H.; Nasrabadi, M. Scour downstream of a rough rigid apron. World Appl. Sci. J. 2011, 14, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, H.M.; El Gendy, M.M.; Mirdan, A.M.H.; Ali, A.A.M.; Abdelhaleem, F.S.F. Minimizing downstream scour due to submerged hydraulic jump using corrugated aprons. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2014, 5, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Sarkar, A. Scour downstream of an apron due to submerged horizontal jets. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2006, 132, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Dey, S. Scour downstream of aprons caused by sluices. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manag. 2005, 158, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamir, M.; Ahmad, Z. Estimation of scour depth downstream of an apron under 2D horizontal jets. In Proceedings of the HYDRO 2015 International—20th International Conference on Hydraulics, Water Resources and River Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, India, 17–19 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Aamir, M.; Ahmad, Z. Prediction of local scour depth downstream of an apron under wall jets. In Development of Water Resources in India; Garg, V., Singh, V., Raj, V., Eds.; Water Science and Technology Library; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 75, pp. 375–385. [Google Scholar]
- Azamathulla, H.M.; Ahmad, Z. Gene-expression programming for transverse mixing coefficient. J. Hydrol. 2012, 434–435, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azamathulla, H.M.; Deo, M.C.; Deolalikar, P.B. Neural networks for estimation of scour downstream of a ski-jump bucket. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2005, 131, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azamathulla, H.M.; Deo, M.C.; Deolalikar, P.B. Estimation of scour below spillways using neural networks. J. Hydraul. Res. 2006, 44, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azamathulla, H.M.; Ghani, A.A.; Zakaria, N.A.; Guven, A. Genetic programming to predict bridge pier scour. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2010, 136, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashiri, H.; Sharifi, E.; Singh, V.P. Prediction of local scour depth downstream of sluice gates using harmony search algorithm and artificial neural networks. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2018, 144, 06018002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafzadeh, M.; Oliveto, G. More reliable predictions of clear-water scour depth at pile groups by robust artificial intelligence techniques while preserving physical consistency. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 5723–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamir, M.; Ahmad, Z. Review of literature on local scour under plane turbulent wall jets. Phys. Fluids 2016, 28, 105102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, L.; Chanson, H. Singular air entrapment at vertical and horizontal supported jets: Plunging jets versus hydraulic jumps. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2020, 20, 1075–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamir, M.; Ahmad, Z. Effect of apron roughness on flow characteristics and scour depth under submerged wall jets. Acta Geophys. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadollahi, M.; Vaghefi, M.; Akbari, M. Effect of the position of perpendicular pier groups in a sharp bend on flow and scour patterns: Numerical simulation. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2020, 42, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhave, S.; Kumar, S.; Singh, U.K.; Pandey, M.; Ahmad, Z. Experimental investigation of a trench weir with T-shaped bars. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2020, 42, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, D.; Vaghefi, M.; Ghodsian, M. Experimental study of the effect of the length-to-width ratio and skewness angles of the pier installed at the bend on scour pattern. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2021, 43, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Oliveto, G.; Pu, J.H.; Sharma, P.K.; Ojha, C.S.P. Pier scour prediction in non-uniform gravel beds. Water 2020, 12, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghefi, M.; Faraji, B.; Akbari, M.; Eghbalzadeh, A. Numerical investigation of flow pattern around a T-shaped spur dike in the vicinity of attractive and repelling protective structures. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Vaghefi, M.; Solati, S.; Chooplou, C.H. The effect of upstream T-shaped spur dike on reducing the amount of scouring around downstream bridge pier located at a 180° sharp bend. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2021, 19, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestawy, A.; Eltahawy, T.; Alsaluli, A.; Almaliki, A.; Alqurashi, M. Reduction of local scour around a bridge pier by using different shapes of pier slots and collars. Water Supply 2020, 20, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, R.; Kumar, B. Prediction of scour depth and dune morphology around circular bridge piers in seepage affected alluvial channels. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2018, 18, 923–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzi, A.; Shrestha, C.K.; Melville, B.; Khabbaz, H.; Ranjbar-Zahedani, M.; Ball, J. Estimation of maximum scour depths at upstream of front and rear piers for two in-line circular columns. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2018, 18, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Sharma, P.K.; Ahmad, Z.; Singh, U.K. Experimental investigation of clear-water temporal scour variation around bridge pier in gravel. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2018, 18, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamir, M.; Ahmad, Z. Estimation of maximum scour depth downstream of an apron under submerged wall jets. J. Hydroinformatics 2019, 21, 523–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumer, B.M.; Christiansen, N.; Fredsoe, J. Influence of cross section on wave scour around piles. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean. Eng. 1993, 119, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
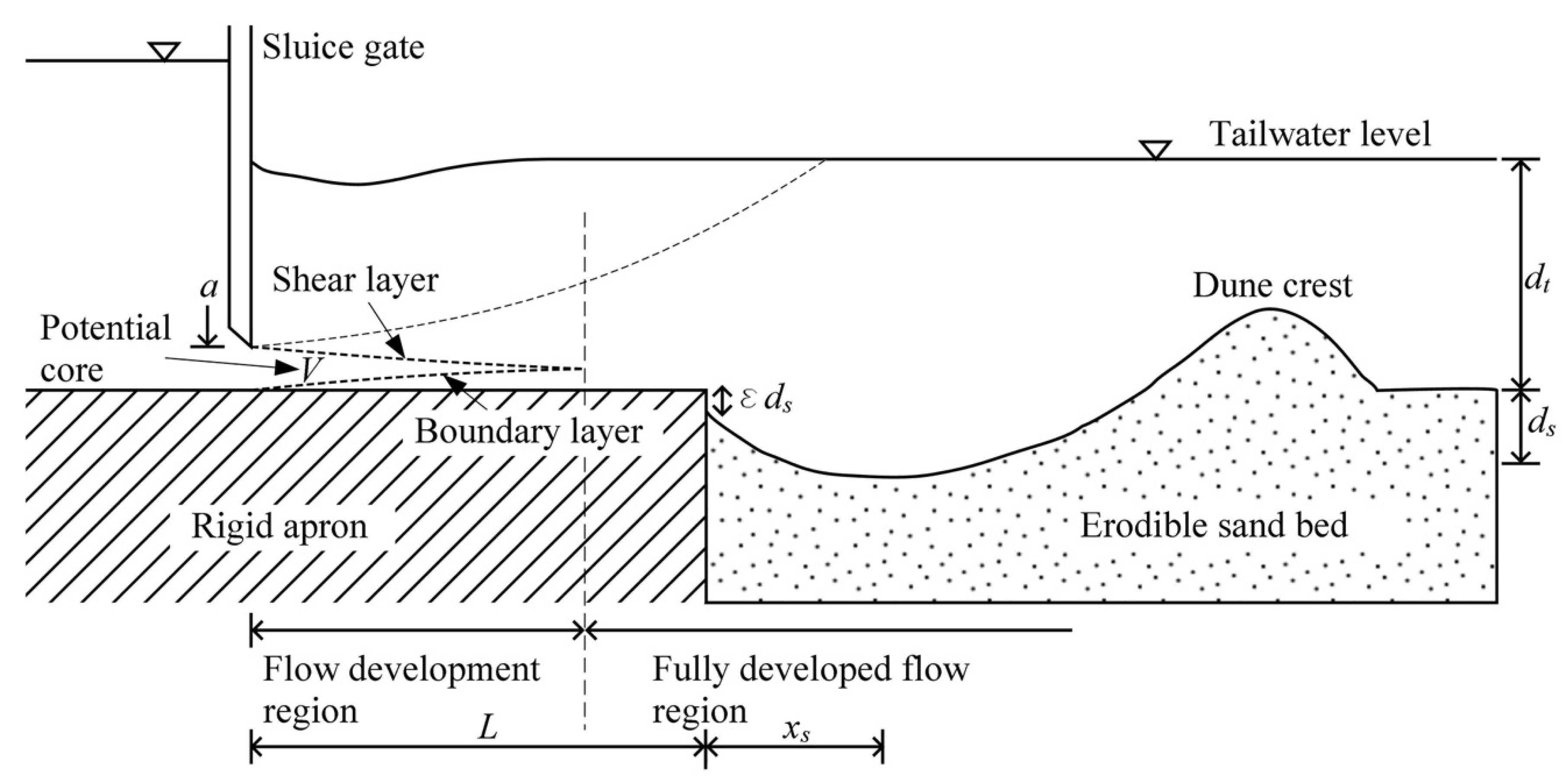
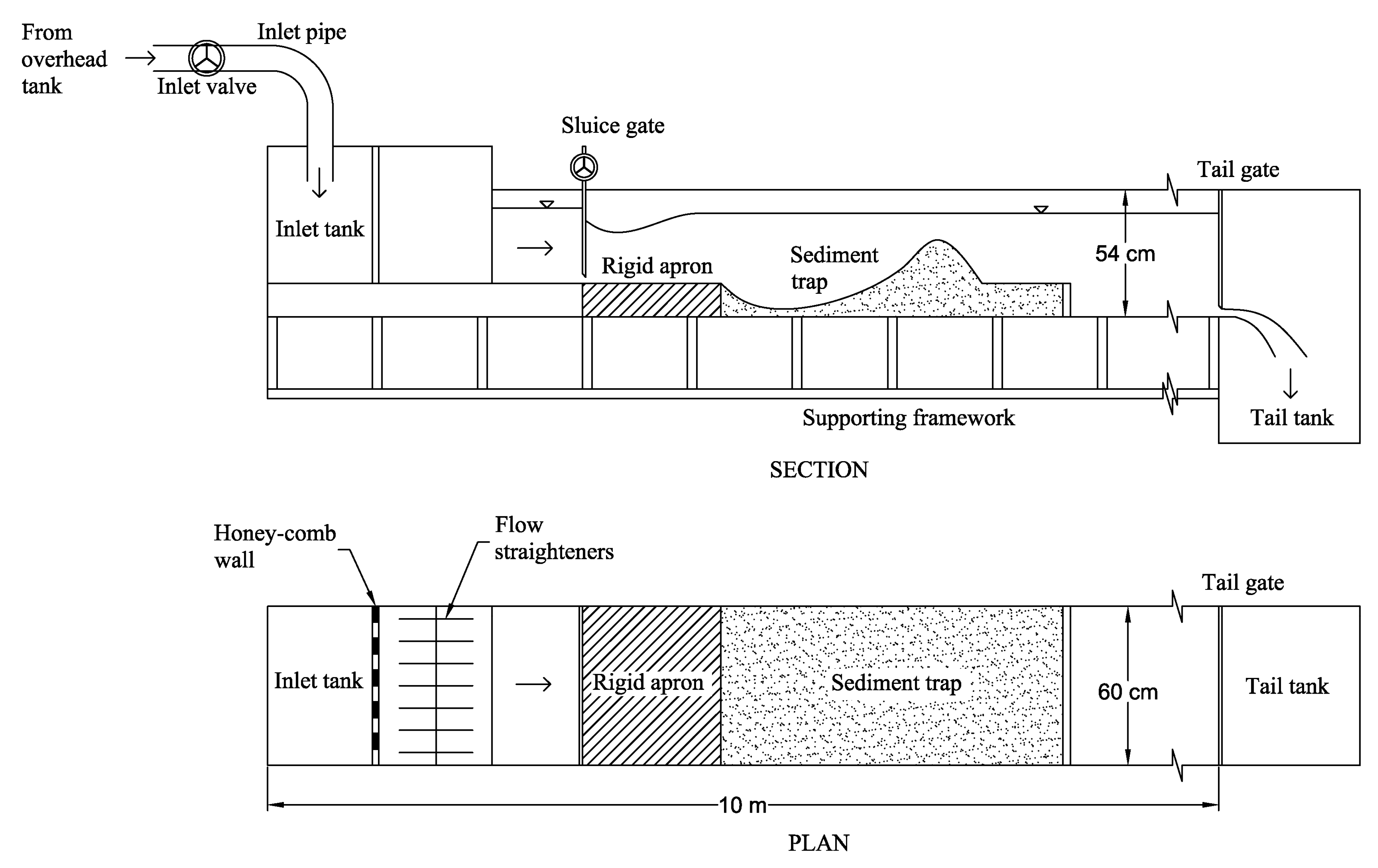
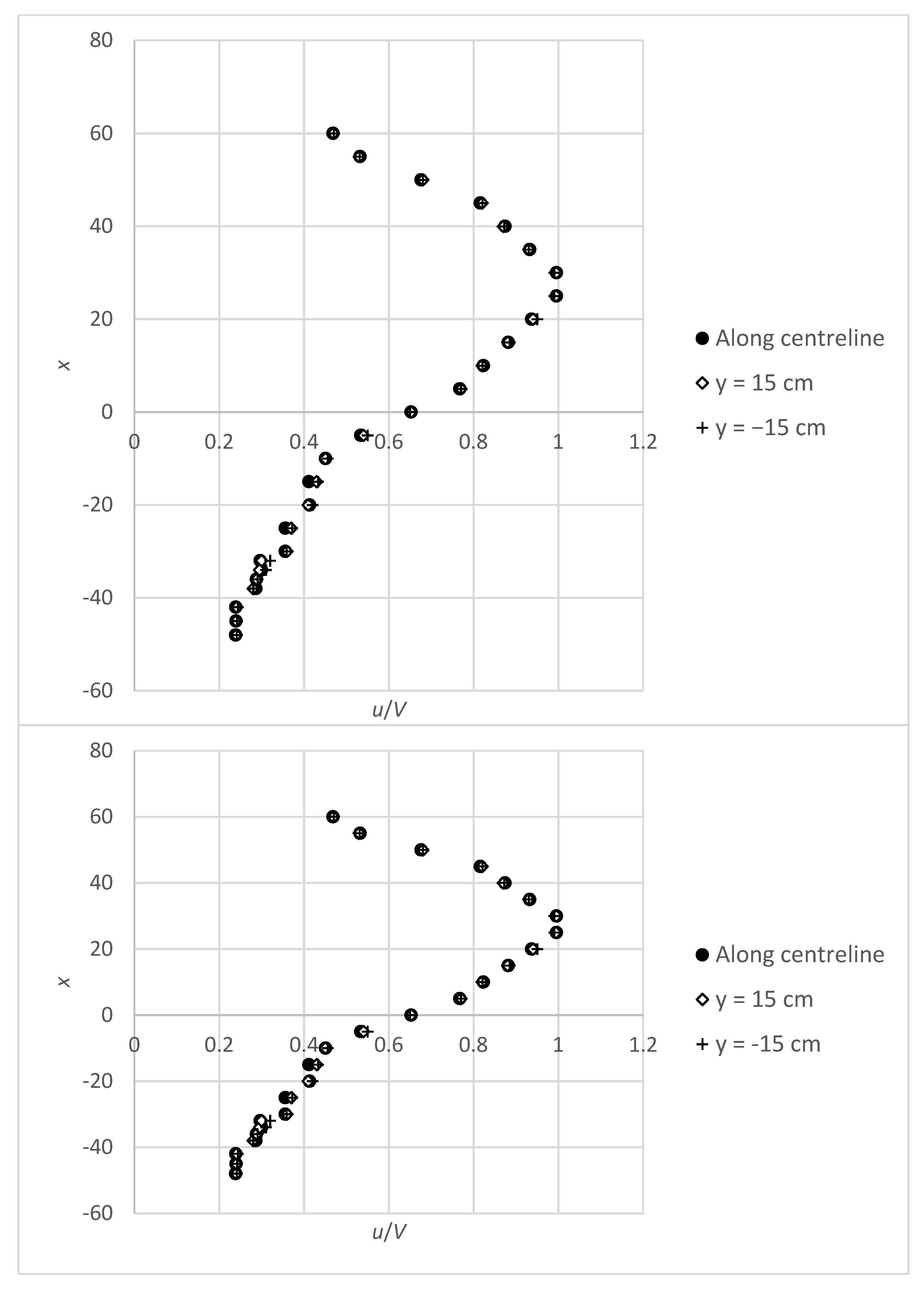
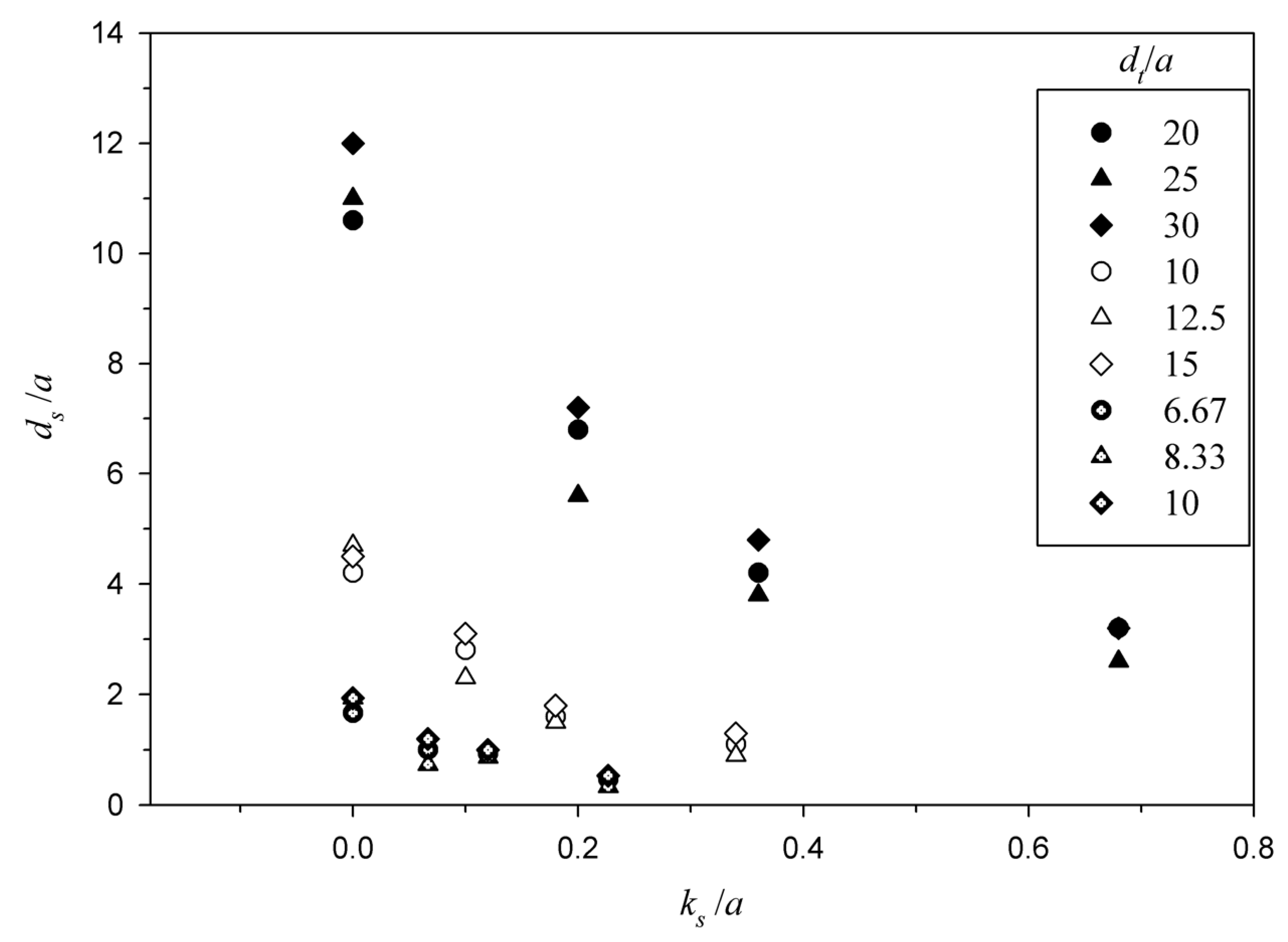


| Median Size d50 (mm) | Geometric Standard Deviation σg | Relative Density s | Angle of Repose ϕ (Degree) | Shields Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.27 | 1.45 | 2.65 | 29 | 0.039 |
| 1.79 | 1.14 | 2.65 | 31.5 | 0.04 |
| 2.67 | 1.11 | 2.65 | 33 | 0.043 |
| 6.70 | 1.26 | 2.65 | 37.5 | 0.055 |
| No. of Experimental Runs | d50 (mm) | a (mm) | ks (mm) | dt (m) | V (m/s) | L (m) | ds (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 126 | 0.27–6.70 | 5–15 | 0–3.40 | 0.1–0.2 | 0.56–2.67 | 0.3–0.5 | 0.5–10.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aamir, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Pandey, M.; Khan, M.A.; Aldrees, A.; Mohamed, A. The Effect of Rough Rigid Apron on Scour Downstream of Sluice Gates. Water 2022, 14, 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142223
Aamir M, Ahmad Z, Pandey M, Khan MA, Aldrees A, Mohamed A. The Effect of Rough Rigid Apron on Scour Downstream of Sluice Gates. Water. 2022; 14(14):2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142223
Chicago/Turabian StyleAamir, Mohammad, Zulfequar Ahmad, Manish Pandey, Mohammad Amir Khan, Ali Aldrees, and Abdullah Mohamed. 2022. "The Effect of Rough Rigid Apron on Scour Downstream of Sluice Gates" Water 14, no. 14: 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142223
APA StyleAamir, M., Ahmad, Z., Pandey, M., Khan, M. A., Aldrees, A., & Mohamed, A. (2022). The Effect of Rough Rigid Apron on Scour Downstream of Sluice Gates. Water, 14(14), 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142223







