Application of Activated Seashells and Sand Armor for Disrupting N and P Release from River Sediments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sediments and River Water Sampling
2.2. Preparation of Capping Materials
2.3. Laboratory Scale Incubation Experiments
2.4. Analysis of N and P in Water Samples
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Sequential Extraction of P
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Water and Sediment Properties
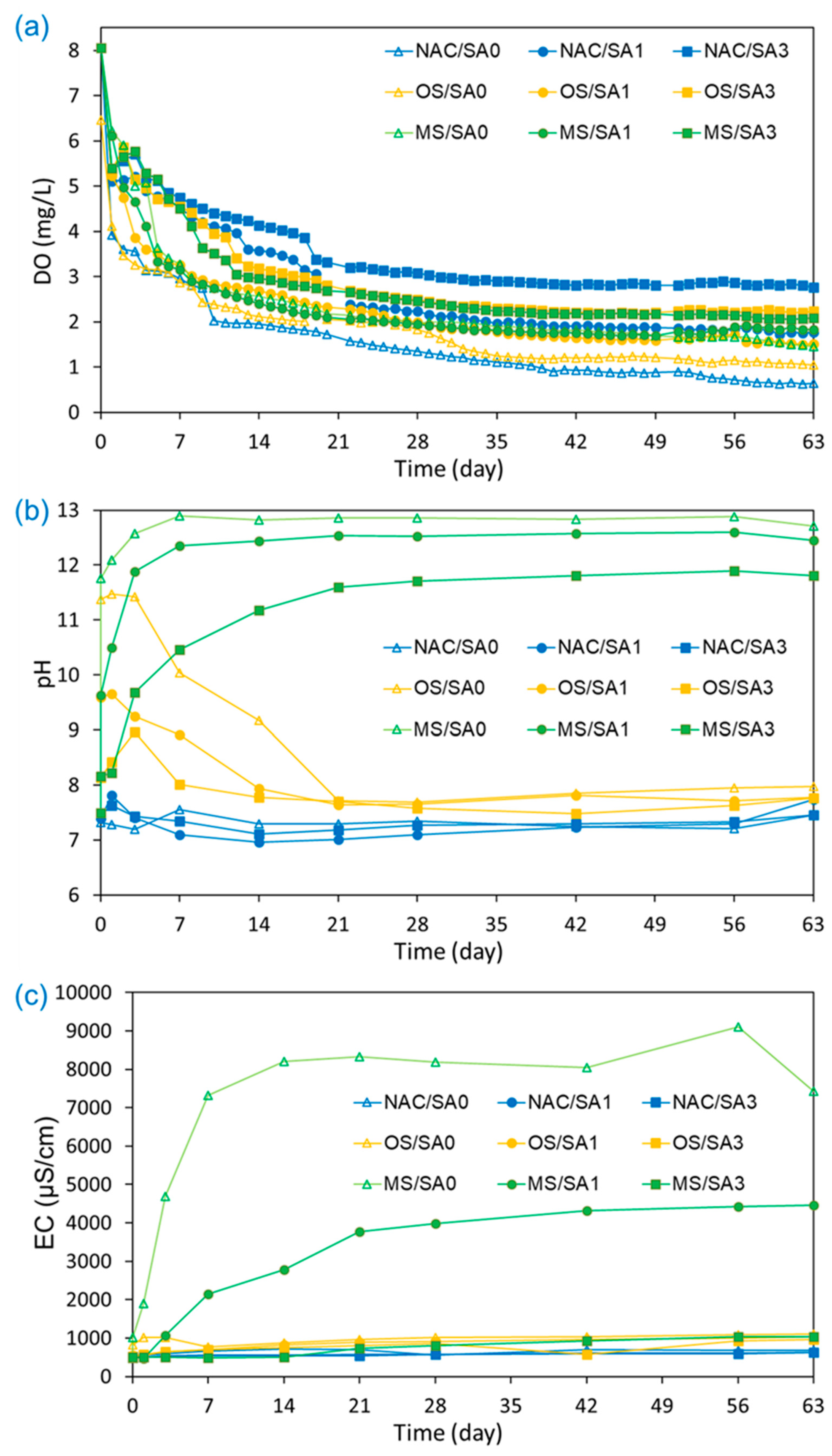
3.2. Effects of Capping Materials on the Water Environment
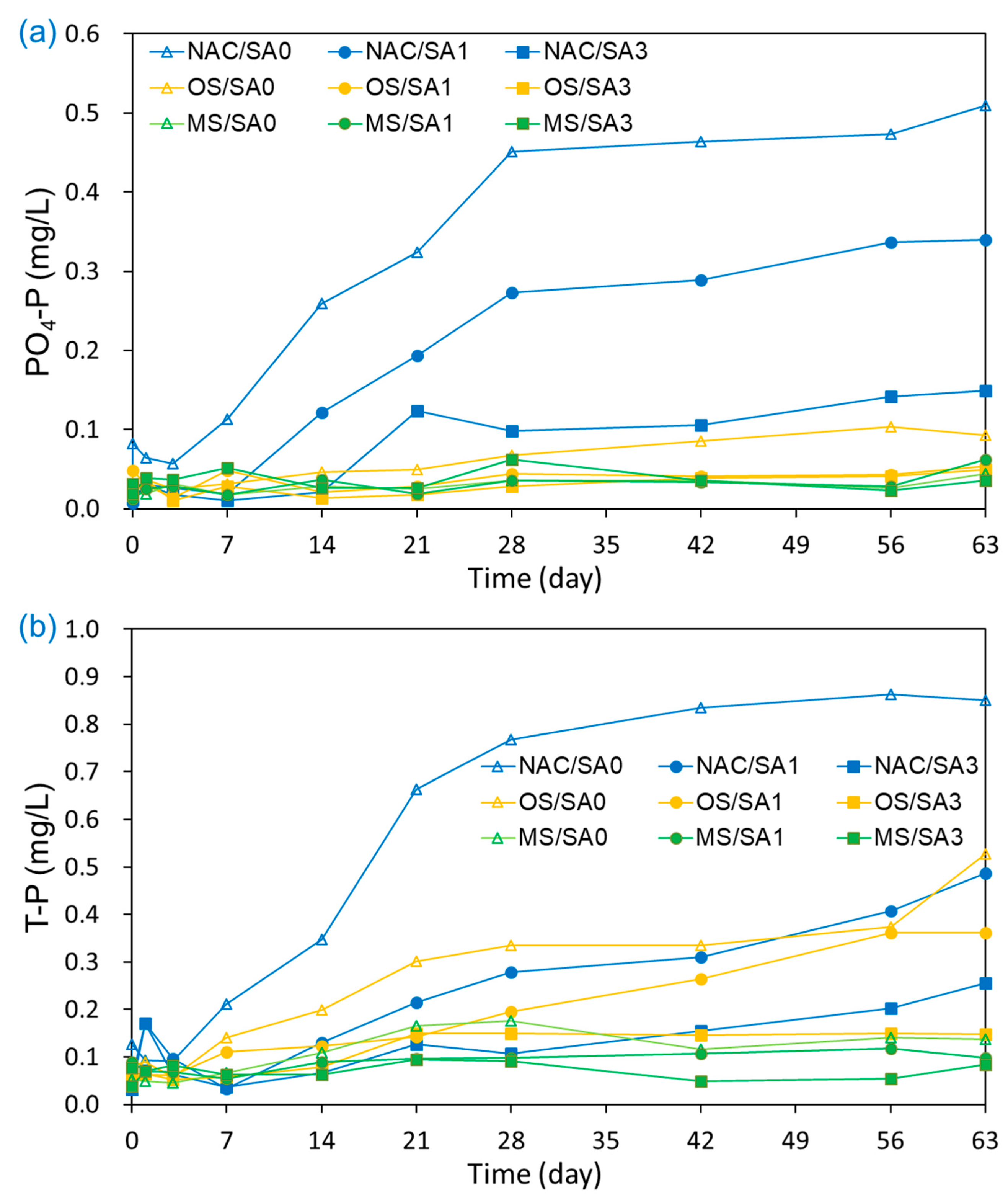
3.3. Impact of Capping on the Release of N and P from Sediments into the Overlying Water
3.4. N and P Fluxes and CE under Uncapped and Capped Conditions
3.5. Phosphorus Fractionation of Sediments under Different Capping Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, D.; Pillai, S.C.; Ho, S.-H.; Zeng, J.; Li, Y.; Dionysiou, D.D. Plasmonic-based nanomaterials for environmental remediation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 237, 721–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabil, B.; Messikh, N.; Bousba, S.; Magri, P.; Faycal, D.; Zaghdoudi, R. Adsorption of Humic Acid from Aqueous Solution on Different Modified Bentonites. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 60, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vikrant, K.; Kim, K.-H.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Tsang, Y.F.; Giri, B.S.; Singh, R.S. Engineered/designer biochar for the removal of phosphate in water and wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 1242–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Viana, P.; Zhao, X.; Rockne, K. Characterization, performance modeling, and design of an active capping remediation project in a heavily polluted urban channel. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3454–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Tang, W.; Jin, X.; Shan, B. Using biochar capping to reduce nitrogen release from sediments in eutrophic lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, U.; Neumann, T.; Donnert, D.; Nüesch, R.; Stüben, D. Sediment capping in eutrophic lakes–efficiency of undisturbed calcite barriers to immobilize phosphorus. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Han, M.; Tang, W. Phosphorus sorption and supply from eutrophic lake sediment amended with thermally-treated calcium-rich attapulgite and a safety evaluation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.-W.; Lee, C.-G.; Lee, T.-G.; Park, S.-J. Evaluation of sediment capping with activated carbon and nonwoven fabric mat to interrupt nutrient release from lake sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599-600, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.; Nybom, I.; Mäenpää, K.; Hale, S.E.; Cornelissen, G.; Akkanen, J. Mixing and capping techniques for activated carbon based sediment remediation – Efficiency and adverse effects for Lumbriculus variegatus. Water Res. 2017, 114, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenborg, K.A.; Steinman, A.D. Impact of sediment dredging on sediment phosphorus flux in a restored riparian wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoplev, A.; Golosov, V.; Wakiyama, Y.; Takase, T.; Yoschenko, V.; Yoshihara, T.; Parenyuk, O.; Cresswell, A.; Ivanov, M.; Carradine, M.; et al. Natural attenuation of Fukushima-derived radiocesium in soils due to its vertical and lateral migration. J. Environ. Radioact. 2018, 186, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dykes, G.A.; Coorey, R.; Ravensdale, J.T.; Sarjit, A. Phosphates. In Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry; Melton, L., Shahidi, F., Varelis, P., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 218–224. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, S.; Ali, Q.; Zahir, Z.A.; Ashraf, S.; Asghar, H.N. Phytoremediation: Environmentally sustainable way for reclamation of heavy metal polluted soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermassi, M.; Valderrama, C.; Moreno, N.; Font, O.; Querol, X.; Batis, N.H.; Cortina, J.L. Fly ash as reactive sorbent for phosphate removal from treated waste water as a potential slow release fertilizer. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, M.; Gabriel, O.; Rutzen, C.; Koschel, R. Lake restoration by hypolimnetic Ca(OH)2 treatment: Impact on phosphorus sedimentation and release from sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1504–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutel, M.W. Inhibition of ammonia release from anoxic profundal sediments in lakes using hypolimnetic oxygenation. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 28, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.R.; MacAskill, D.; Rushton, T.; Thalheimer, A.; Weaver, P. Monitoring effects of remediation on natural sediment recovery in Sydney Harbour, Nova Scotia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8089–8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Lee, C.-G.; Choi, J.-W.; Kim, Y.-K.; Park, S.-J. Evaluation of the use of sea sand, crushed concrete, and bentonite to stabilize trace metals and to interrupt their release from contaminated marine sediments. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Wang, D.; Tam, N.F.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tang, X.; Yang, Y. Enhancement of active thin-layer capping with natural zeolite to simultaneously inhibit nutrient and heavy metal release from sediments. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 119, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.; Gong, J.-L.; Zeng, G.-M.; Yao, F.-B.; Guo, M.; Ou, X.-M. Remediation of organochlorine pesticides contaminated lake sediment using activated carbon and carbon nanotubes. Chemosphere 2017, 177, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, D. Application of synthetic iron-oxide coated zeolite for the pollution control of river sediments. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, P.H.; Förstner, U. Concept of subaqueous capping of contaminated sediments with active barrier systems (ABS) using natural and modified zeolites. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2083–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, Y. Control of internal phosphorus release from sediments using magnetic lanthanum/iron-modified bentonite as active capping material. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, G.; Luo, X.; Li, F.; Wang, Z. Comparison of the ecotoxicological effects of biochar and activated carbon on a marine clam (Meretrix meretrix). J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelo, L.W. Review: In situ and bioremediation of organic pollutants in aquatic sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.-W.; Hong, S.-H.; Lee, C.-G.; Park, S.-J. The feasibility of using bentonite, illite, and zeolite as capping materials to stabilize nutrients and interrupt their release from contaminated lake sediments. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Andserson, B.; Zhao, X.; Wang, D.; Ding, A. Review on utilization of biochar for metal-contaminated soil and sediment remediation. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 63, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lin, J.; Zhan, Y. Interception of phosphorus release from sediments using Mg/Fe-based layered double hydroxide (MF-LDH) and MF-LDH coated magnetite as geo-engineering tools. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, F.; Barjoveanu, G.; De Gisi, S.; Teodosiu, C.; Notarnicola, M. Sustainability assessment of reactive capping alternatives for the remediation of contaminated marine sediments. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 124946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zukri, N.; Khamidun, M.; Sapiren, M.; Abdullah, S.; Rahman, M. Lake Water Quality Improvement by Using Waste Mussel Shell Powder as an Adsorbent. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; p. 012057. [Google Scholar]
- Huh, J.-H.; Choi, Y.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Choi, W.J.; Ramakrishna, C.; Lee, H.-W.; Lee, S.-H.; Ahn, J.-W. The use of oyster shell powders for water quality improvement of lakes by algal blooms removal. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2016, 53, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.I.; Wang, L.Y.; Abeynaike, A.; Patterson, D.A. Utilisation of waste material for environmental applications: Calcination of mussel shells for waste water treatment. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2011, 110, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, C.A.; Krey, G.; Stamatis, N.; Kallianiotis, A. The use of waste mussel shells for the adsorption of dyes and heavy metals. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeynaike, A.; Wang, L.; Jones, M.I.; Patterson, D.A. Pyrolysed powdered mussel shells for eutrophication control: Effect of particle size and powder concentration on the mechanism and extent of phosphate removal. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 6, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Haddad, M.; Regti, A.; Laamari, M.R.; Slimani, R.; Mamouni, R.; El Antri, S.; Lazar, S. Calcined mussel shells as a new and eco-friendly biosorbent to remove textile dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Aziz, H.A.; Isa, M.H.; Ahmad, A.; Van Leeuwen, J.; Zou, L.; Beecham, S.; Umar, M. Orthophosphate removal from domestic wastewater using limestone and granular activated carbon. Desalination 2011, 271, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, P.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Bolan, N.S. Removal and recovery of phosphate from water using sorption. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 847–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-I.; Kang, J.-K.; Hong, S.-H.; Lee, C.-G.; Jeong, S.; Park, S.-J. Thermally treated Mytilus coruscus shells for fluoride removal and their adsorption mechanism. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.I.; Park, S.J. Adsorption characteristics of calcined oyster shell for the removal of fluoride. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2019, 41, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.H.; Mesquita-Guimarães, J.; Henriques, B.; Silva, F.S.; Fredel, M.C. The potential use of oyster shell waste in new value-added by-product. Resources 2019, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-García, C.; González-Fonteboa, B.; Martínez-Abella, F.; Carro-López, D. Performance of mussel shell as aggregate in plain concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 139, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamester, M.R.R.; Balzer, P.S.; Becker, D. Characterization of calcium carbonate obtained from oyster and mussel shells and incorporation in polypropylene. Mater. Res. 2012, 15, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eek, E.; Cornelissen, G.; Kibsgaard, A.; Breedveld, G.D. Diffusion of PAH and PCB from contaminated sediments with and without mineral capping; measurement and modelling. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Environment Korea. Standard Methods for the Analysis of Water and Wastewater; Ministry of Environment Korea: Sejong City, Korea, 2007.
- Lin, J.; Zhan, Y.; Zhu, Z. Evaluation of sediment capping with active barrier systems (ABS) using calcite/zeolite mixtures to simultaneously manage phosphorus and ammonium release. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaanning, M.; Breyholtz, B.; Skei, J. Experimental results on effects of capping on fluxes of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) from historically contaminated sediments. Mar. Chem. 2006, 102, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eek, E.; Godøy, O.; Aagaard, P.; Breedveld, G.D. Experimental determination of efficiency of capping materials during consolidation of metal-contaminated dredged material. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieltjes, A.H.; Lijklema, L. Fractionation of Inorganic Phosphates in Calcareous Sediments; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Liikanen, A.; Murtoniemi, T.; Tanskanen, H.; Väisänen, T.; Martikainen, P.J. Effects of temperature and oxygenavailability on greenhouse gas and nutrient dynamics in sediment of a eutrophic mid-boreal lake. Biogeochemistry 2002, 59, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelheber, D.W.; Pennell, K.D.; Hughes, J.B. Natural attenuation processes during in situ capping. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5306–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, Q.; Gu, S. Thin-layer fine-sand capping of polluted sediments decreases nutrients in overlying water of Wuhan Donghu Lake in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7156–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.-H.; Yan, F.-L.; Ding, Z.; Feng, L.-L.; Zhao, J.-C. Effects and mechanisms of calcium peroxide on purification of severely eutrophic water. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2796–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-G.; Khirul, M.A.; Cho, D.; Kwon, S.-H. The effect of calcium peroxide originating from oyster shell powder on control of phosphorus compounds in oceanic sediment. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, M.M.; Hickey, C.W. Flocculants and Sediment Capping for Phosphorus Management. In Lake Restoration Handbook; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 207–265. [Google Scholar]
- Knox, A.S.; Paller, M.H.; Roberts, J. Active capping technology—New approaches for in situ remediation of contaminated sediments. Remediat. J. 2012, 22, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khirul, M.A.; Kim, B.-G.; Cho, D.; Yoo, G.; Kwon, S.-H. Effect of oyster shell powder on nitrogen releases from contaminated marine sediment. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.-H.; Lee, J.-I.; Lee, C.-G.; Park, S.-J. Effect of temperature on capping efficiency of zeolite and activated carbon under fabric mats for interrupting nutrient release from sediments. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, J.A.; Alonso, Á. Ecological and toxicological effects of inorganic nitrogen pollution in aquatic ecosystems: A global assessment. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 831–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Kankanamge, N.R.; Chow, C.; Welsh, D.T.; Li, T.; Teasdale, P.R. Removing ammonium from water and wastewater using cost-effective adsorbents: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 63, 174–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.-H.; Lee, C.-G.; Park, S.-J. Application of calcium-rich mineral under nonwoven fabric mats and sand armor as cap layer for interrupting N and P release from river sediments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 59444–59455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampert, D.J.; Sarchet, W.V.; Reible, D.D. Assessing the effectiveness of thin-layer sand caps for contaminated sediment management through passive sampling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8437–8443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, C.H. Nutrient Flux Assessment in the Port Waterways; Environment Protection Authority: Parramatta, Australia, 2005.
- Le Tissier, M.; Buddemeier, R.; Parslow, J.; Swaney, D.; Crossland, C.; Smith, S.; Whyte, H.; Dennison, W.; Hills, J.; Kremer, H. The Role of the Coastal Ocean in the Disturbed and Undisturbed Nutrient and Carbon Cycles–A Management Perspective; LOICZ: Geesthacht, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-I.; Oh, J.-S.; Yoo, S.-C.; Jho, E.H.; Lee, C.-G.; Park, S.-J. Removal of phosphorus from water using calcium-rich organic waste and its potential as a fertilizer for rice growth. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Shi, X.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, M.; Guo, Y.; Dong, X.; Guo, R. Modification of oyster shell powder by humic acid for ammonium removal from aqueous solutions and nutrient retention in soil. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Jung, W. Role of sand capping in phosphorus release from sediment. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2010, 14, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, K.L.; Prepas, E.E.; Chambers, P.A. Phosphorus release from sediments in hardwater eutrophic lakes: The effects of redox-sensitive and-insensitive chemical treatments. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 1061–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, Z.; Muhmood, A.; Usman, M.; Kizito, S.; Lu, J.; Dong, R.; Wu, S. Phosphate removal from aqueous solution using iron oxides: Adsorption, desorption and regeneration characteristics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 528, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Guo, Q.; Zhu, B. Phosphorus removal from aqueous solution in parent and aluminum-modified eggshells: Thermodynamics and kinetics, adsorption mechanism, and diffusion process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 14525–14536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
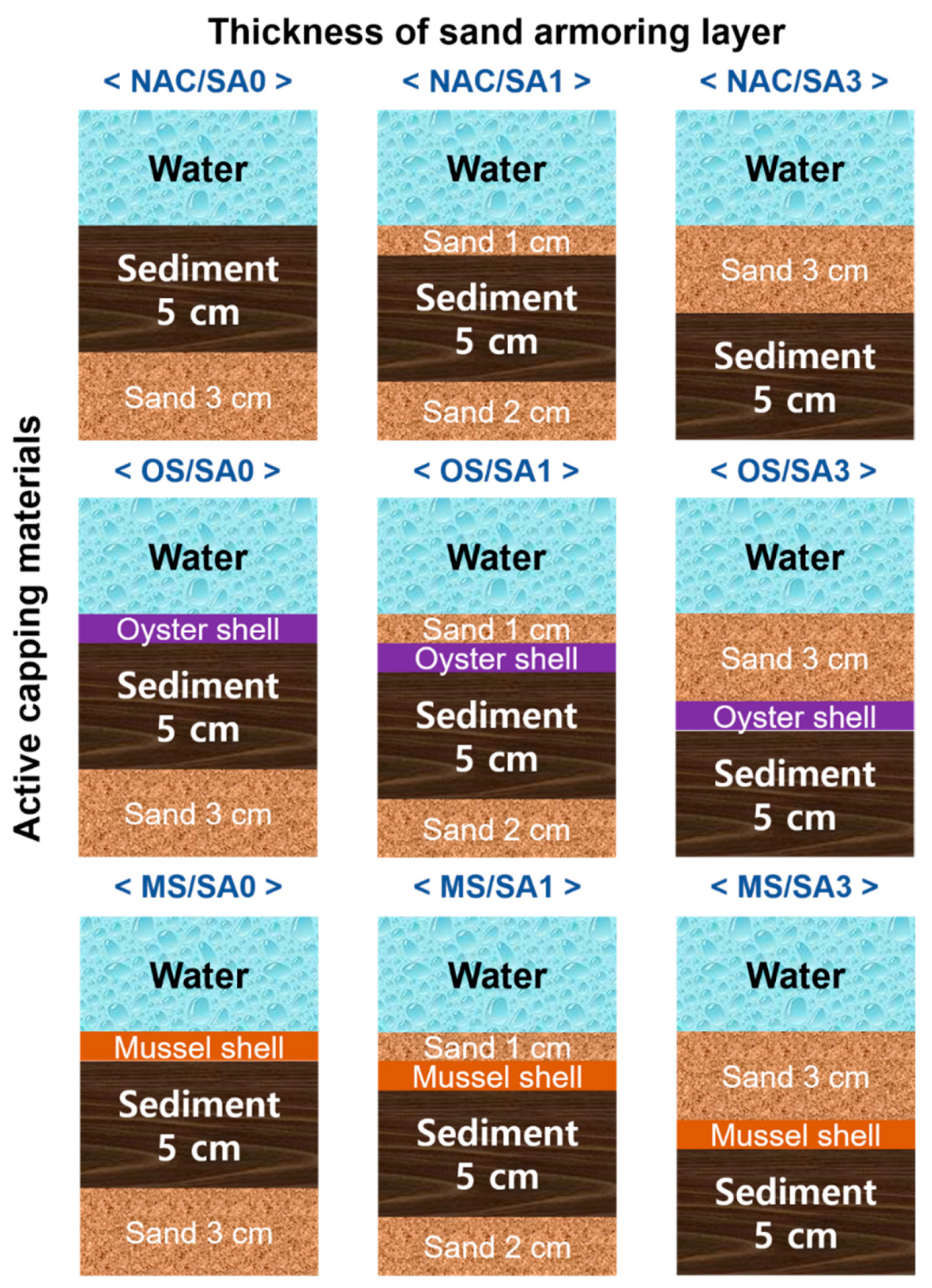



| River Water | Sediment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Property | Value | Property | Value |
| pH | 7.49 | Water contents (%) | 76.43 |
| EC (µS/cm) | 489 | pH | 6.81 |
| DO (mg/L) | 8.06 | EC (µS/cm) | 250 |
| SS (mg/L) | 230 | IL (%) | 9.98 |
| T-N (mg/L) | 3.67 | T-N (mg/kg) | 3269 |
| NH4-N (mg/L) | 0.14 | NH4-N (mg/kg) | 47.39 |
| NO3-N (mg/L) | 3.67 | NO3-N (mg/kg) | 2.97 |
| T-P (mg/L) | 0.07 | T-P (mg/kg) | 915 |
| PO4-P (mg/L) | 0.03 | SRP (mg/kg) | 68.91 |
| ORP (mV) | -30.7 | ORP (mV) | 5.50 |
| NAC/ SA0 | NAC/ SA1 | NAC/ SA3 | OS/ SA0 | OS/ SA1 | OS/ SA3 | MS/ SA0 | MS/ SA1 | MS/ SA3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DO (mg/L) | 1.57 ± 1.17 | 2.72 ± 1.28 | 3.47 ± 1.01 | 1.92 ± 1.22 | 2.26 ± 1.08 | 2.92 ± 1.14 | 2.36 ± 1.22 | 2.32 ± 1.11 | 2.83 ± 1.18 |
| pH | 7.34 ± 0.12 | 7.32 ± 0.28 | 7.36 ± 0.15 | 9.11 ± 1.67 | 8.31 ± 0.85 | 7.91 ± 0.46 | 12.16 ± 1.59 | 11.54 ± 1.66 | 10.37 ± 1.70 |
| EC (μS/cm) | 623 ± 77 | 561 ± 45 | 550 ± 42 | 925 ± 180 | 779 ± 197 | 710 ± 163 | 5882 ± 3259 | 2586 ± 1703 | 684 ± 229 |
| NAC/ SA0 | NAC/ SA1 | NAC/ SA3 | OS/ SA0 | OS/ SA1 | OS/ SA3 | MS/ SA0 | MS/ SA1 | MS/ SA3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4-N | Flux (mg/m2d) CE (%) | 35.9 | 16.0 55.5 | 6.8 81.1 | 9.8 72.8 | 3.0 91.7 | 2.8 92.2 | 60.9 −69.3 | 49.2 −36.8 | 16.2 54.9 |
| T-N | Flux (mg/m2d) CE (%) | 39.1 | 24.3 37.7 | 22.3 43.0 | 36.0 7.9 | 22.6 42.1 | 19.0 51.4 | 82.0 −109.7 | 54.3 −39.0 | 30.0 23.2 |
| PO4-P | Flux (mg/m2d) CE (%) | 1.31 | 0.70 46.8 | 0.21 84.2 | 0.13 90.4 | 0.03 97.9 | −0.02 101.3 | −0.02 101.5 | −0.01 100.8 | 0.02 98.5 |
| T-P | Flux (mg/m2d) CE (%) | 2.17 | 0.75 65.3 | 0.24 89.1 | 0.89 59.1 | 0.52 76.0 | 0.15 93.3 | 0.15 93.0 | 0.06 97.0 | −0.04 102.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quansah, J.O.; Hong, S.-H.; Lee, C.-G.; Park, S.-J. Application of Activated Seashells and Sand Armor for Disrupting N and P Release from River Sediments. Water 2022, 14, 2875. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182875
Quansah JO, Hong S-H, Lee C-G, Park S-J. Application of Activated Seashells and Sand Armor for Disrupting N and P Release from River Sediments. Water. 2022; 14(18):2875. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182875
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuansah, Jude Ofei, Seung-Hee Hong, Chang-Gu Lee, and Seong-Jik Park. 2022. "Application of Activated Seashells and Sand Armor for Disrupting N and P Release from River Sediments" Water 14, no. 18: 2875. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182875
APA StyleQuansah, J. O., Hong, S.-H., Lee, C.-G., & Park, S.-J. (2022). Application of Activated Seashells and Sand Armor for Disrupting N and P Release from River Sediments. Water, 14(18), 2875. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182875








