Abstract
Chemical oxygen demand (COD) is one of the indicators used to monitor the level of pollution in surface water. To recycle agricultural water resources, it is crucial to monitor, in a timely manner, whether COD in surface water exceeds the agricultural water control standard. A diagnostic model of surface water pollution was developed using visible near-infrared spectroscopy (Vis-NIR) combined with partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS–DA). A total of 127 surface water samples were collected from Guangzhou, Guangdong, China. The COD content was measured using the potassium dichromate method. The spectra of the surface water samples were recorded using a Vis-NIR spectrometer, and the spectral data were pre-processed using four different methods. To improve the accuracy and simplicity of the model, the synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE) and the competitive adaptive reweighted sampling (CARS) algorithm were used to enhance model performance. The best PLS–DA model achieved an accuracy of 88%, and the SMOTE–PLS–DA model had an accuracy of 94%. The SMOTE algorithm could improve the accuracy of the model despite the sampling imbalance. The CARS–SMOTE–PLS–DA model achieved 97% accuracy, and the CARS band selection technique improved the simplicity and accuracy of the discrimination model. The CARS–SMOTE–PLS–DA model improved the discrimination accuracy by 9% over that of the PLS–DA model. This method can not only save human and material resources but is also a new way for real-time online discrimination of COD in surface water.
1. Introduction
Sustainable development of the ecological environment is the common demand for the survival of all mankind, and the recycling of agricultural water resources is urgent. Surface water is one of the main sources of water for agricultural irrigation and an important factor affecting the quality of crops [1,2]. With the rapid advancement of industrialization in modern society, the random discharge of industrial wastewater has become an increasingly serious environmental problem. Extensive domestic garbage and industrial chemical residues flow into surface water, resulting in the deposition of a variety of harmful chemicals. This poses a serious threat to the recycling of agricultural water resources [3,4]. Accurate judgment of surface water pollution is one of the means to ensure the quality of agricultural cultivation.
Surface water pollutants are mainly organic and are generally quantitatively indicated by the chemical oxygen demand (COD). Conventional methods to test COD include the dichromate method and the permanganate index method. These methods not only require chemical reagents but also have the shortcomings of complex chemical reactions and long time periods. Moreover, they are likely to cause secondary pollution if the chemical reagents are not handled properly [5]. Hence, to protect and recycle surface water resources, it is necessary to develop a rapid, effective, and eco-friendly detection technology to accurately evaluate the degree of surface water pollution [6].
Visible near-infrared spectroscopy (Vis-NIR) is a green, non-destructive, and rapid detection technique. It is widely used in fields such as the ecological environment and medicine through a combination of statistical modeling and chemometric methods [7]. This analytical technique not only provides rich qualitative and quantitative information on substances but also has the advantages of being non-destructive and easy to apply. Therefore, this technique is widely used to detect various water pollution indicators [8]. The analytical method of this technique mainly involves the establishment of a calibration model using the spectra and conventional values of the target components. Linear discriminant models such as partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS–DA) are commonly used in spectral modeling owing to their simple structure and ease of operation [9]. PLS–DA is a classification technique based on partial least squares. Its mathematical basis is principal component analysis, and the regression model between the independent variable and the categorical variable of the training sample is mainly established by the information of the samples in the process of features selection, and then the characteristic variables related to the classification are effectively extracted [10].
On the one hand, the accuracy and stability of the model will be affected by less representative sample data and the skewed distribution of sample categories [11]. Uneven distribution can easily occur when collecting samples. Therefore, the key factor affecting the performance of the classification model is the quantity distribution of the samples in different categories. Common machine learning algorithms adopt a balanced training set, where all categories are represented equally [12]. However, such treatment leads to a certain error in the prediction of categories with a large number of samples, whereas categories with a small number of samples are prone to misclassification [13]. On the other hand, the accuracy and stability of the model will suffer from redundancy in the spectral data. If the entire Vis-NIR band is used to train the model, it is often too complex and may produce inefficient models [14]. Some spectral variables may contain irrelevant or even noise information, which may distort the true relationship between the sample information and Vis-NIR predictors. Spectral selection algorithms are applied to overcome the drawbacks of spectral analysis. The competitive adaptive reweighted sampling (CARS) algorithm is one of the most commonly used band selection strategies [15]. This algorithm eliminates unimportant spectral variables when extracting the optimal subset of such variables according to the regression coefficients. However, it has not been validated whether this algorithm can effectively discriminate if the COD of surface water exceeds the threshold through Vis-NIR.
In our last article, we achieved quantitative predictions for surface water, but not very good predictions for COD greater than 120 mg/L [16]. In this experiment, samples that were more seriously polluted and whose COD was greater than 600 mg/L were added, and the method of qualitative discrimination was tried to achieve high-accuracy COD online discrimination, which provided new ideas for surface water quality management.
The purpose of this study was to explore the best comprehensive modeling approach of Vis-NIR to diagnose whether the COD of surface water exceeds its management value. The following objectives were considered: (1) to understand the effect of spectral pre-processing methods on the discrimination results of surface water COD; (2) to improve the distribution of sample categories using the synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE) algorithm; (3) to develop a CARS-SMOTE-PLS-DA model for rapid determination of COD in surface water using the CARS band selection algorithm and the SMOTE algorithm; and (4) to determine the important wavelengths for the discrimination of surface water COD and the relevant components of surface water pollution.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
The samples for this study were provided by the South China Research and Monitoring Analysis Center, South China Institute of Environmental Sciences, Ministry of Ecology and Environment. These samples were from Guangzhou, Guangdong, China. Surface water was collected from an inland river in Guangzhou that was often used as the water source for agricultural irrigation and the daily life of residents. A total of 127 samples were collected from 15 July to 15 October 2021. They were placed in sealed test tubes and labeled in the sampling order, and then delivered to the laboratory at room temperature on 16 October 2021. The COD value of each sample was determined in all experiments using the conventional permanganate index method [17]. The measured COD values were used for the calibration and validation of spectral analysis.
2.2. Chemical Analysis and Contamination Assessment
To determine the COD content of surface water, a known amount of potassium dichromate solution was added to 127 surface water samples with silver salts as the catalyst in a strong acid medium. After boiling and refluxing, the unreduced potassium dichromate in the samples was titrated with ferrous ammonium sulfate using the ferroin indicator solution as the indicator. The mass concentration of oxygen consumed was calculated based on the amount of potassium dichromate consumed, which was the specific value of COD.
The collected surface water samples were divided into two categories according to the COD threshold value (40 mg/L) required for Class V in the environmental quality standards for surface water (GB3838-2002), which is applicable to surface water for agricultural use and in the general landscape. They were further coded as binary 0 or 1 to indicate the COD content of each water sample as below or above the threshold, respectively [18].
2.3. Spectrum Acquisition and Pre-Processing
An XDS Rapid Content liquid grating Vis-NIR spectrometer (with a transmission attachment and a 2 mm quartz cuvette) from FOSS, Denmark was used for this study. The spectra were collected in the range of 400–2500 nm, including most of the NIR region. The wavelength sampling interval was 2 nm. An appropriate amount of sample was placed in a quartz cuvette with an optical path of 2 mm to collect the spectra. Each sample was scanned thrice in the NIR spectrometer. Then, the average spectrum of the three scans was taken as the acquisition spectrum. At the end of each acquisition, the quartz cuvette was cleaned with distilled water and dried with filter paper. The spectrum of each sample was measured at room temperature (24 ± 1 °C) and humidity (46% ± 1% RH).
The measured spectrum was inevitably affected by instrument noise and the ambient environment. Therefore, four spectral pre-processing methods were used for the spectra of the water samples: first derivative (FD), second derivative (SD), multiplicative scatter correction (MSC), and standard normal variate (SNV) [19].
2.4. Sample Set Partitioning and Model Evaluation Parameters
The sample set partitioning based on joint X-Y distance (SPXY) [20,21] was used. The training and test sets were partitioned with a ratio of 3:1. The training set could identify different classes of spectral patterns upon fitting the classification model, whereas the test set was used to evaluate the performance of the model. The specific partitioning results with the surface water sample information are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Statistics of surface water COD values and partitioning of sample set.
2.5. Evaluation of the Model Performance
The accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity were used to evaluate the overall performance of the classification models. The classification accuracy refers to the ratio of the number of samples correctly discriminated to the total number of samples in the classification model when testing the established model using the prediction set. Sensitivity and specificity are two key metrics for the classification model that indicate the percentage of positive and negative samples correctly classified, respectively. When the accuracy, specificity, and sensitivity are closer to 1, the classification model has better performance.
where denotes the number of positive samples in the predication set correctly classified by the mode; denotes the number of positive samples in the test set incorrectly classified by the model; denotes the number of negative samples in the test set incorrectly classified by the model; and denotes the number of negative samples in the test set correctly classified by the model.
2.6. Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique
When modeling algorithms are applied directly to data with uneven and unbalanced sample distribution, samples in the categories with smaller quantities are prone to misclassification, which reduces the overall accuracy [22]. Therefore, improving the discrimination accuracy of minority samples in discriminant analysis is a key issue. The numbers of collected surface water samples with COD values below and above the threshold were quite different; the number of samples with COD values above the threshold was small. Therefore, the oversampling method of the SMOTE algorithm was used to improve the sample distribution. New surface water categories were generated in the training set such that below-threshold and above-threshold samples obtained balanced observations (equal number of samples per category in the training set). The SMOTE algorithm proposed by Chawla et al. [23] is an efficient oversampling technique that can be used to avoid the overfitting that arises from the direct replication of a small quantity of samples. The SMOTE technique runs the oversampling difference by introducing synthetic examples into the spectral space and adding K-nearest neighbors. The K value was set to five to control the newly generated examples. For the original dataset, the sample training set corresponding to each pre-processing method generated a SMOTE-processed training set.
2.7. Competitive Adaptive Reweighted Sampling
CARS is a wavelength selection method that adopts the Darwinian evolution theory of “survival of the fittest”. The key wavelengths selected are those with relatively large absolute coefficients in the multiple linear regression model. This selection method conducts a wavelength selection based on the exponential decay function (EDF) and then selects the key wavelengths based on the competitive wavelength selection of adaptive reweighted sampling [24,25]. The algorithm implementation is divided into the following four steps:
- (1)
- Perform monte carlo sampling and select a certain proportion of samples to build a calibration model;
- (2)
- Use EDF to remove the number of wavelengths with low absolute values of regression coefficients;
- (3)
- Calculate the root mean square error cross-validation (RMSECV) and filter out significant wavelengths using adaptive reweighted sampling (ARS);
- (4)
- Select the subset with the lowest RMSECV as the best wavelength combination.
EDF can realize the rapid elimination and selection of wavelengths. In each sampling process, the wavelength ratio to be retained is calculated by using EDF. The calculation formula of the wavelength ratio is as follows:
Among them, is related to two fast constants, which are related to the number of spectral wavelengths and the number of sampling runs in CARS.
After forced wavelength reduction by EDF, ARS is used to imitate the principle of survival of the fittest, and wavelengths are eliminated in a competitive manner. In ARS, variables will be randomly weighted and sampled, and variables with larger weights will be selected.
The aforementioned algorithms were run in MATLAB (R2018a, Math Works, Inc., Natick, MA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
The statistics of the COD values for surface water samples measured in the laboratory and the partitioning of the sample set are shown in Table 1. The PH of these samples ranges from 5.63 to 8.92. The COD values of all surface water samples varied between 4 and 688 mg/L, with a mean value of 61.98 mg/L and a median value of 27 mg/L. It was also evident that the number of samples with a COD value below the threshold value far exceeded that of samples with a COD value above the threshold value. Samples with a COD value larger than the threshold value may be influenced by human activities and natural factors related to landscape changes, such as domestic wastewater discharge. The training and test sets were divided using the SPXY method with a ratio of 3:1. A total of 95 and 32 samples in the dataset were divided into the training and test sets, respectively. The results of the division are shown in Table 1.
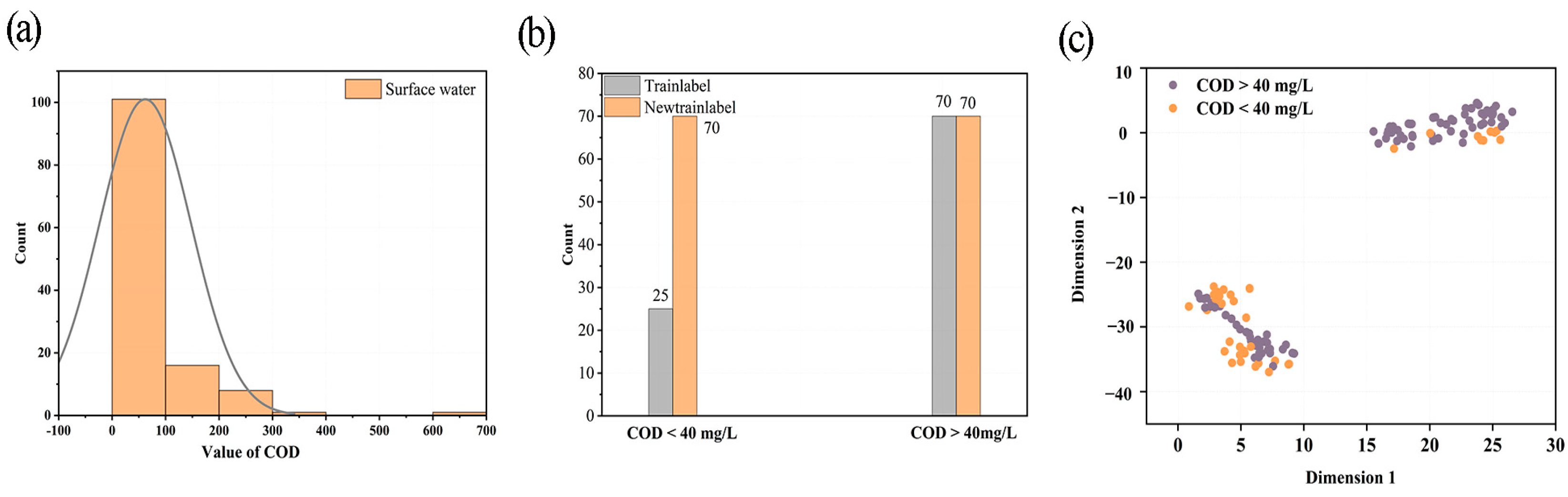
Figure 1a shows the distribution of COD content of surface water samples. Most COD values were between 1 and 100 mg/L. Samples with COD values greater than 40 mg/L were designated as contaminated samples and those with COD values less than 40 mg/L were uncontaminated samples. A total of 25 samples in the training set were contaminated and 70 samples were uncontaminated, whereas 14 samples in the test set were contaminated and 18 samples were uncontaminated. This indicated a large gap between the number of uncontaminated and contaminated samples in the training set, which was likely to affect the modeling results. Therefore, in the subsequent analysis, the SMOTE algorithm was used to generate new surface water categories in the training set, so that the uncontaminated and contaminated samples achieved balanced observations. The impact of the excessive gap between the number of categories on the modeling was examined by comparing this with the modeling results without using the SMOTE algorithm. Additionally, the feasibility of the SMOTE algorithm was verified. With the application of the SMOTE algorithm, the uncontaminated samples (<40 mg/L) in the training set increased from 25 to 70, forming a new training set. The numbers of uncontaminated and contaminated samples in the training set are shown in Figure 1b.

Figure 1.
(a) Histogram of surface water COD value distribution, (b) distribution of training set samples before and after SMOTE expansion, (c) t−SNE visualization results plot.
The Vis-NIR spectral data were mapped into two-dimensional space using the t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) visualization algorithm. Thus, the variability and inherent characteristics of the Vis-NIR spectral datasets of the uncontaminated and contaminated samples could be understood more intuitively. During visualization, the t-SNE method can preserve the nonlinear structure of the spectral dataset [26]. In contrast to principal component analysis, t-SNE searches for the data structure based on a random probability distribution over the domain graph [27]. The visualization results of the surface water sample dataset upon using the t-SNE algorithm are shown in Figure 1c. The dataset forms two distinct clusters, wherein each point represents a sample, and the axes represent the first two dimensions of the t-SNE features. These t-SNE visualization results further validate the feasibility of using the Vis-NIR spectral technique for discriminant analysis of surface water COD.
3.2. Spectral Absorption Characteristics
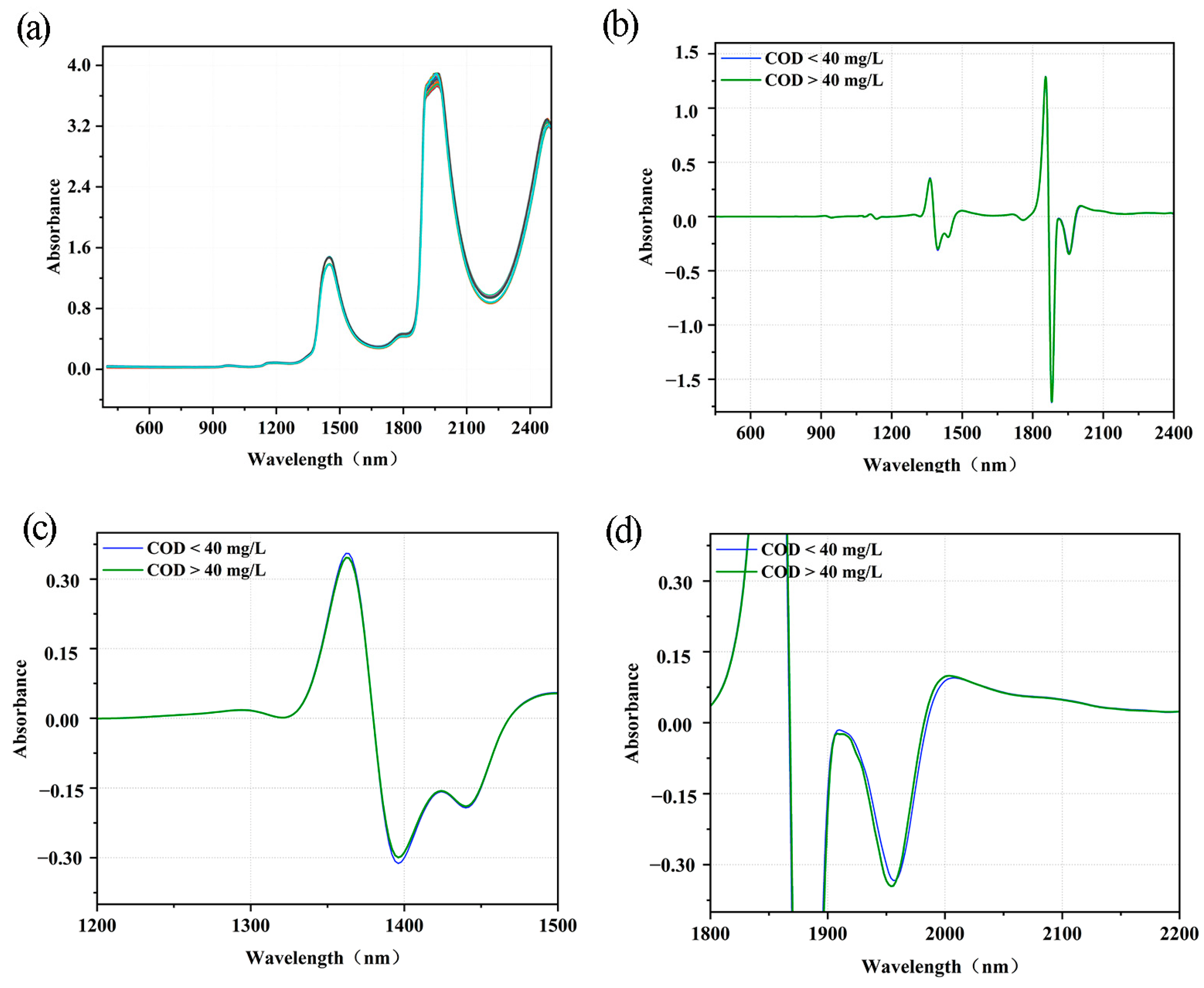
Figure 2a–d present the original spectra of surface water and those after SD pre-processing for 400–2500, 1200–1500, and 1800–2200 nm, respectively. In Figure 2a, the spectra of uncontaminated and contaminated samples show similar trends and shapes. However, after SD pre-processing, the spectra show multiple peaks and troughs. Since there are large peaks and troughs near 1800 nm, the spectra after SD pre-processing were locally amplified to obtain Figure 2c,d. These figures show more pronounced absorptions at 1400, 1450, and 1980 nm, which may be caused by the stretching vibrations of the O-H, C-H, and N-H bonds, respectively [28,29,30]. They also show that the uncontaminated and contaminated samples exhibited large differences in these three bands.
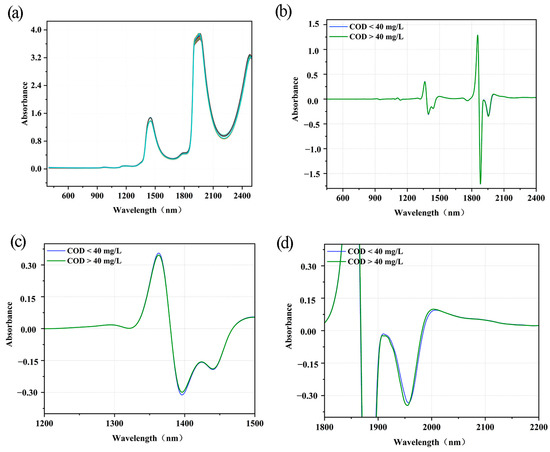
Figure 2.
Visible near-infrared spectroscopy plots of surface water samples: (a) raw spectra; (b) second derivative (SD) (400–2500 nm); (c) SD (1200–1500 nm); (d) SD (1800–2200 nm).
3.3. Correlation Analysis between Wave Bands
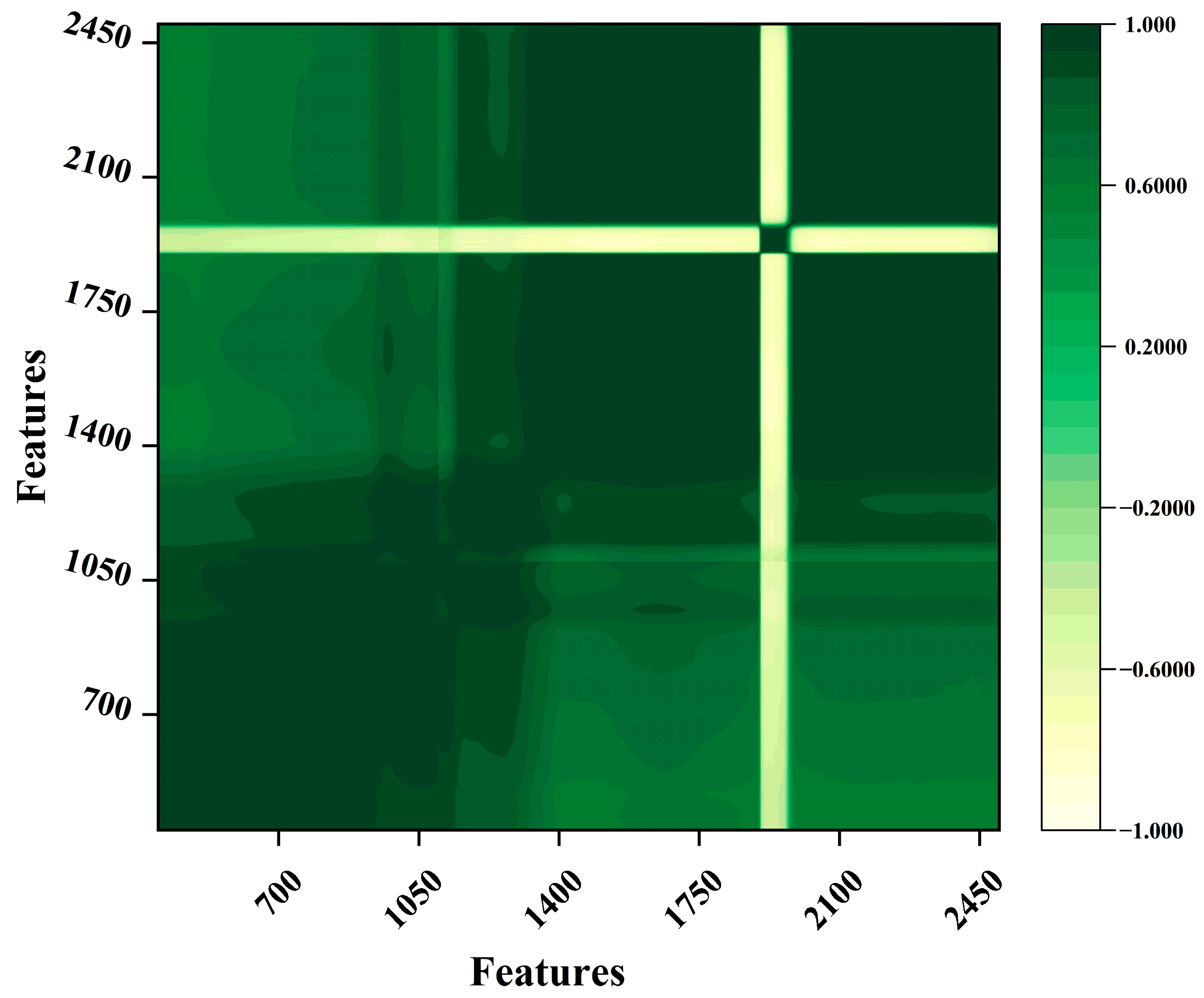
Figure 3 shows the correlation between wavelength points. Vis-NIR is an indirect technique for rapid measurement and discrimination that requires a small amount of prepared samples and does not use harmful chemicals. It can qualitatively discriminate COD contamination in surface water using spectral absorption characteristics [31]. However, interference of instrument noise and high coincidence of information bands of various components occur during measurement. Vis-NIR also has a wide wavelength range. Therefore, there is extensive irrelevant band information. Figure 3 shows that the correlation between the 1050 wavelength points is different, with some features showing a strong correlation and others showing a weak correlation. Therefore, it is necessary to choose the appropriate wavelength band for modeling and obtain a model with high performance by removing non-informative bands.
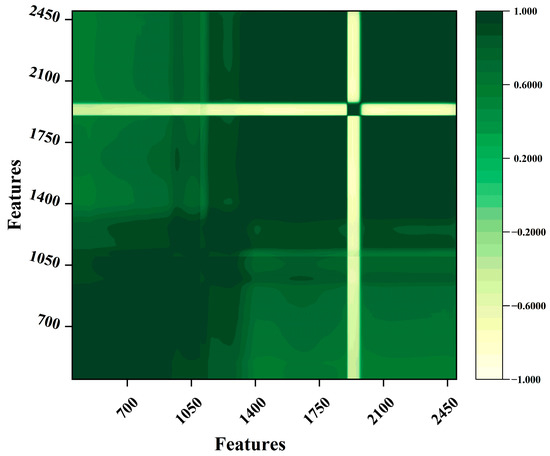
Figure 3.
Correlation between 1050 wavelength points.
3.4. Comparison of Classification Results
The discrimination results of the PLS–DA, SMOTE–PLS–DA, and CARS–SMOTE–PLS–DA models with different pre-processing methods for surface water samples are summarized in Table 2. The sample sets were divided using the SPXY method and saved as the training and test sets. The raw spectra were pre-processed differently. In the PLS–DA model, the spectral pre-processing had different effects on surface water pollution discrimination. FD and SD had positive impacts on the accuracy of the model. The model achieved the best prediction results after SD pre-processing. The accuracy of the training set and the accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of the test set of the PLS–DA model were 0.88, 0.88, 0.83, and 0.93, respectively. However, the MSC and SNV pre-processing methods had a negative impact on the accuracy of the model. With either pre-processing method, the accuracy of the modeling results decreased compared to that with the original spectra. The pre-processed training and test sets were saved separately. The training set was SMOTE-processed to obtain a new training set, which was then subjected to PLS–DA. The SMOTE–PLS–DA modeling results are shown in Table 2. Compared with those of the PLS–DA model, the SMOTE–PLS–DA model accuracy with the FD, SD and MSC pre-processing methods was improved. Among them, for the FD pre-processing method, the training and test set accuracies of the model improved by 7% and 7%. For the SD method, the training and test set accuracies of the model improved by 9% and 6%. For the MSC method, the training and test set accuracies of the model improved by 12% and 3%. However, the accuracy of the SMOTE–PLS–DA model of the SNV pre-processing method was not improved, but the sensitivity of the model was greatly improved.

Table 2.
Summary of discrimination results of partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS–DA), synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE)–PLS–DA, and competitive adaptive reweighted sampling (CARS)–SMOTE–PLS–DA models with different pre-processing methods for surface water.
To simplify the model and further improve its prediction performance, the raw spectra were pre-processed using four different methods and subjected to feature selection. Then, the training set was processed using the SMOTE algorithm to obtain the results of CARS–SMOTE–PLS–DA, as shown in Table 2. The accuracy of the model improved after CARS feature selection. After SD pre-processing, the training and test set accuracies of the model improved by 11% and 9%, respectively, compared to those of the PLS–DA model. The sensitivity and specificity were greatly enhanced. The simplicity of the model also improved, with 1050 wavelength points being reduced to 38. The CARS algorithm further improved the model performance and simplified the model, compared to the SMOTE–PLS–DA model. The training set accuracy of the model improved and the sensitivity and specificity increased to a greater extent.
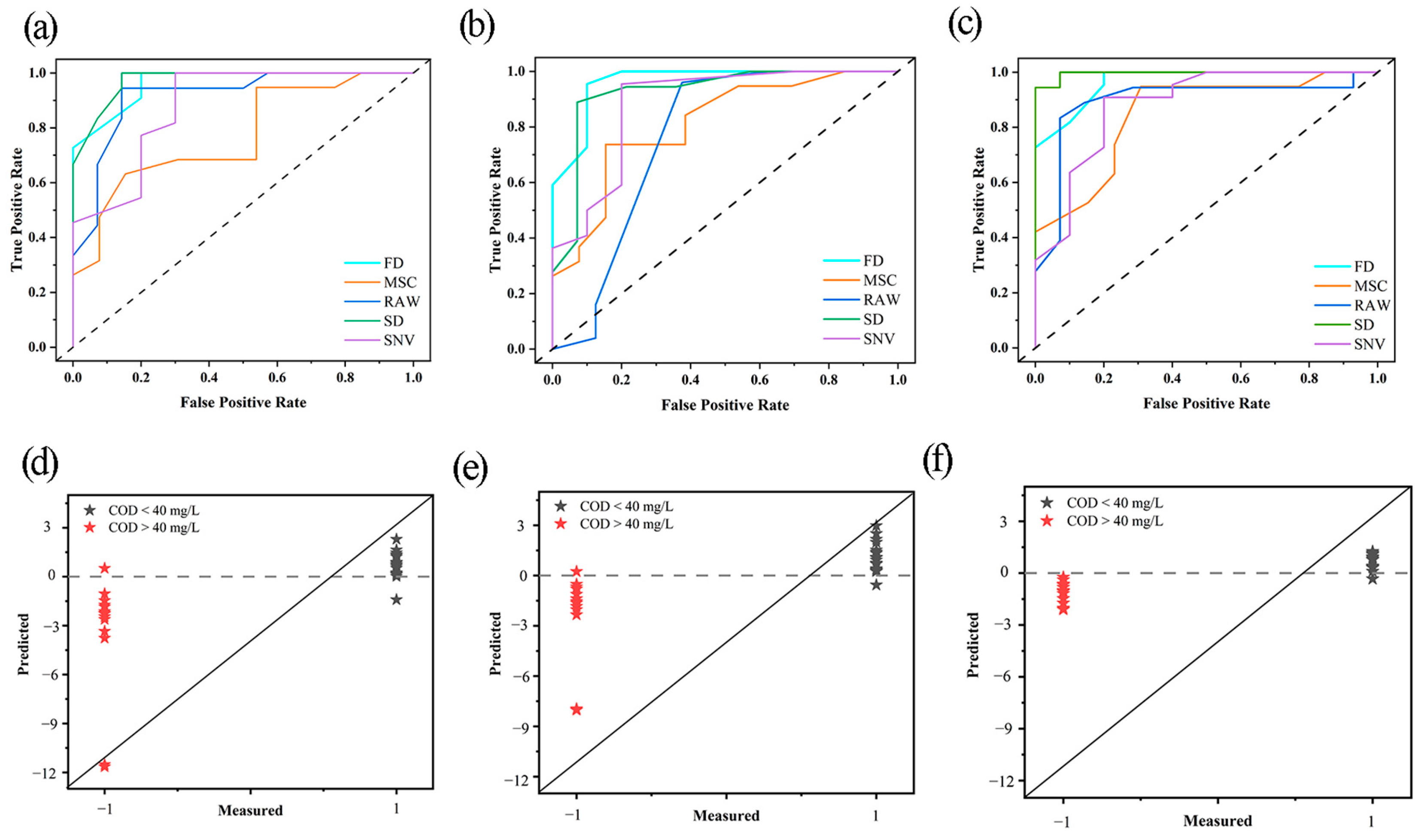
To further investigate the performance of the three models, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of the four different pre-processing methods and surface water score map were plotted and analyzed, the ROC is a comprehensive evaluation index reflecting the continuous variables of the sensitivity and specificity in the classification problem [32], as shown in Figure 4. The points of each curve in Figure 4c are closer to the upper left corner than those in Figure 4a,b, indicating that the prediction accuracy corresponding to each pre-processing method improved with the application of CARS and SMOTE algorithms. However, for the PLS–DA model, the ROC curve is closer to the dashed line after pre-processing with MSC and SNV. In other words, the model performance was reduced. For the SMOTE–PLS–DA model, the ROC curve of the original spectra is closer to the dashed line, i.e., the model performance was poorer. For the CARS–SMOTE–PLS–DA model, compared with Figure 4a, all five curves are closer to the upper left corner, whereas the ROC curves of MSC and SNV are below that of the original spectra. In other words, the MSC and SNV pre-processing methods reduced the model performance. Moreover, the ROC curve of SD is closer to the upper left corner, i.e., the modeling effect with SD pre-processing was better.
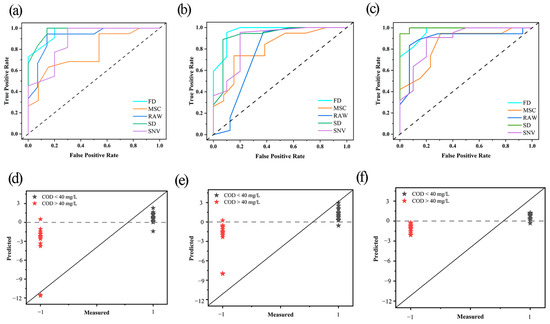
Figure 4.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and surface water score map: (a,d) partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS–DA) model, (b,e) synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE)–PLS–DA model, (c,f) competitive adaptive reweighted sampling (CARS)–SMOTE–PLS–DA model. FD: first derivative; SD: second derivative; MSC: multiple scattering correction; SNV: standard normal variate.
In Figure 4d, it can be seen that a large number of samples with a label value of 1 have scores below 0 and a number of samples are misclassified; in Figure 4e, after SMOTE, it can be seen that for samples with the label value of 1, the score has improved significantly, but there are still a number of samples with scores below 0. In order to further improve the score, we used the CARS algorithm to improve the performance of the model. In Figure 4f, we can see that only two samples with the sample label of 1 have scores below 0, at the same time, the scores of the samples with the label −1 are all located below 0, and the model prediction was greatly improved.
4. Discussion
4.1. Band Analysis by CARS Algorithm
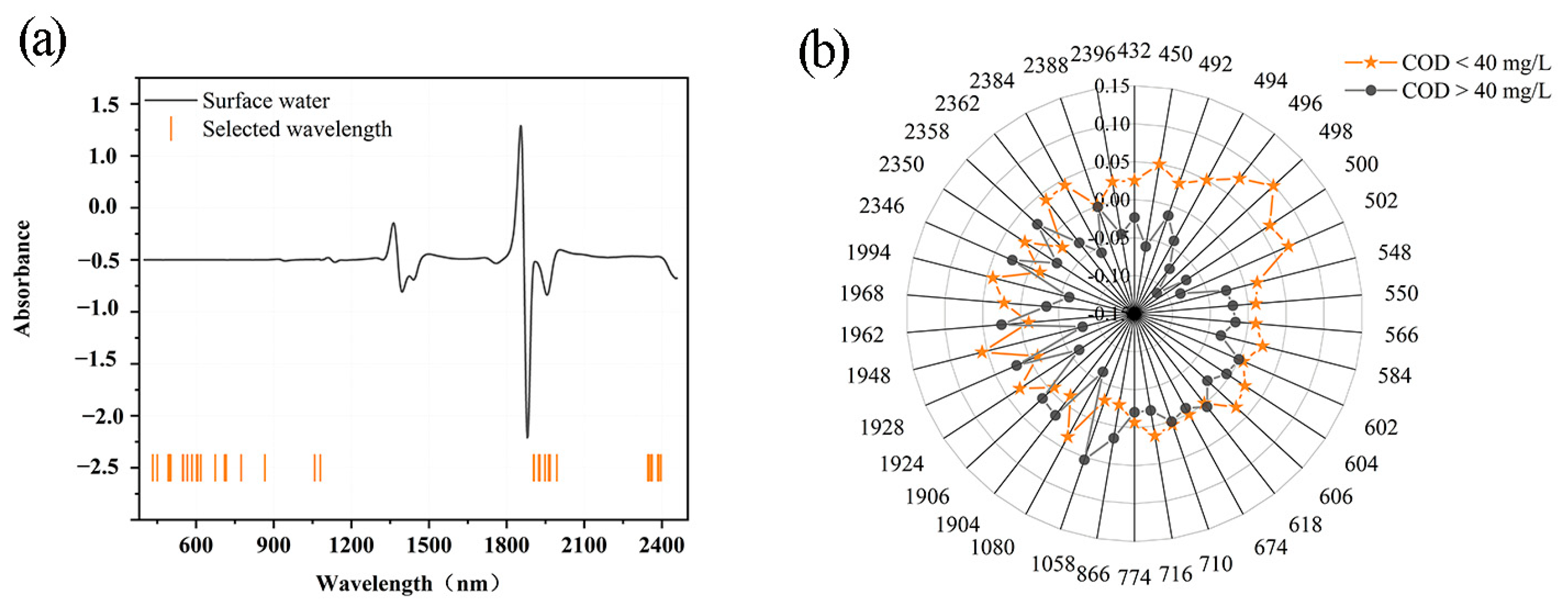
The results of the CARS feature selection of the SD pre-processed spectra are shown in Figure 5a. A total of 38 bands were selected as key variables from 1050 wavelength points, mainly located near 430–500, 550–600, 700–860, 1050–1080, 1900–2000, and 2350–2400 nm. To verify whether the selected 38 bands could represent the variability between uncontaminated and contaminated surface water samples, the scores of the bands were plotted, as shown in Figure 5b. There was large variability in the scores of the 38 bands; this also proved the feasibility of these bands selected by CARS. The greatest variability in the scores was found near 498 nm; this may be caused by C-H bond vibrations of aromatic hydrocarbons in the vicinity [28,33].
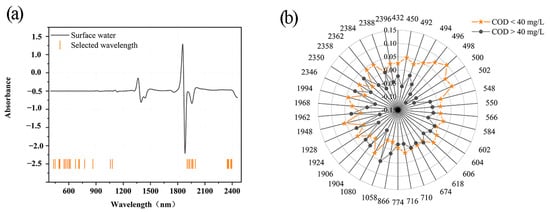
Figure 5.
(a) Feature bands selected by competitive adaptive reweighted sampling (CARS) after second derivative (SD) pre-processing, (b) score plot of the feature bands.
The chemical bonds corresponding to the main bands of the Vis-NIR region screened by CARS and the possible corresponding contamination components are shown in Table 3. The band most screened by CARS was near 400–860 nm; this may arise from the vibration of C-H and N-H chemical bonds, such as those in aromatic hydrocarbons [28,34].

Table 3.
Basic chemical bonds, absorption wavelengths, and possible associated water pollution components of main spectral bands screened by competitive adaptive reweighted sampling (CARS) for visible near-infrared region.
4.2. Implication of Proposed Strategy
The CARS–SMOTE–PLS–DA modeling approach proposed in this paper not only improves the discrimination accuracy of the PLS–DA model but also simplifies the model input variables. When using Vis-NIR as the input for the PLS–DA model, most spectral variables may be redundant; on the other hand, fewer spectral input variables may result in the loss of COD-related information. A spectral selection algorithm can solve both problems, and the optimal number of input spectra for a balanced model can be found using spectral variable selection. The modeling effect can reduce due to the large difference between the number of contaminated and uncontaminated surface water samples collected. To solve this problem, the feasibility of the SMOTE algorithm in solving the problem of uneven sample distribution was explored. The feasibility of PLS–DA and SMOTE–PLS–DA was experimentally verified before conducting CARS–SMOTE–PLS–DA. The discrimination accuracy improved after SMOTE solved the problem of the uneven sample distribution. Finally, the Vis-NIR spectra of surface water were subjected to band selection after the pre-processing with four different methods. Combining the CARS selection algorithm with the SMOTE algorithm not only improved the discrimination accuracy of the model but also reduced the input of the discrimination model.
In this study, the surface water samples were collected for a total of 4 months, covering both the rainy and non-rainy seasons in Guangzhou. Changes in the rainy season will lead to changes in COD because the runoff generated by the rainfall in the rainy season will cause pollutants from land sources to enter the water, resulting in an increase in COD. From the principle of COD chemical detection, these pollutants are all aerobic substances. The aerobic substances in the surface water during the rainy season and non-rainy season have a general law and there will be no major changes in components due to the rainy season. We carried out Vis-NIR detection on a large number of samples and used a surface water model to grasp the quantitative relationship between all aerobic substances and COD values as much as possible. We used the CARS–SMOTE–PLS–DA model to realize the online monitoring of large COD values, which provides a new way of discriminating for the management of seriously polluted surface water.
5. Conclusions
This study employed a new approach with CARS–SMOTE–PLS–DA and Vis-NIR to judge whether surface water can meet the COD standard (40 mg/L) for agricultural use and the general landscape. It demonstrated the feasibility and effectiveness of introducing the CARS band selection technique and the SMOTE algorithm into Vis-NIR analysis. The CARS–SMOTE–PLS–DA modeling approach not only had a higher overall accuracy but also produced a more simplified model. The optimal pre-processing method for all three modeling methods was SD, with PLS–DA yielding an accuracy of 88% with the input of 1050 wavelength points. Compared to the PLS–DA model, the CARS–SMOTE–PLS–DA model exhibited an 11% improvement in accuracy and a 96% reduction in wavelength input. The CARS–SMOTE–PLS–DA model experienced a 5% improvement in accuracy and a 96% reduction in wavelength input compared to the SMOTE–PLS–DA model. Overall, the surface water COD discrimination method (CARS–SMOTE–PLS–DA model) proposed in this paper has the advantages of novelty, eco-friendliness, simplicity, and broad prospects. It is a novel method for real-time online surface water COD discrimination, which is conducive to the management and development of surface water resources.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.H., J.M. and W.J.; methodology, X.H., J.M., J.C. and Y.Y.; visualization, X.H., J.C., B.X. and W.Y.; sampling, X.C.; writing—original draft, X.H.; writing—review and editing, X.C., D.X. and F.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61975069), the Guangzhou science and technology project (202103000095), the Key-Area Research and Devel-opment Program of Guangdong Province (2020B090922006), and the Free Exploration Project of Special Research Funds for the Central Public-Interest Scientific Institution (PM-zx703-202112-338).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors. The data are not publicly available due to the continuation of a follow-up study by the authors.
Acknowledgments
The support provided by South China Institute of Environmental Sciences, Ministry of Ecology and Environment, State Environ-ment Protection Key Laboratory of Water Environmental Simulation and Pollution Control, Guangzhou 510655, China.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Suri, M.R.; Dery, J.L.; Pérodin, J.; Brassill, N.; He, X.; Ammons, S.; Gerdes, M.E.; Rock, C.; Goldstein, R.E.R. U.S. farmers’ opinions on the use of nontraditional water sources for agricultural activities. Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, B.; Gong, J. Impact of transferred water on the hydrochemistry and water quality of surface water and groundwater in Baiyangdian Lake, North China. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotir, J.H.; Smith, C.; Brown, G.; Marshall, N.; Johnstone, R. A system dynamics simulation model for sustainable water resources management and agricultural development in the Volta River Basin, Ghana. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Yang, Y. The Water Pollution Policy Regime Shift and Boundary Pollution: Evidence from the change of water pollution levels in C. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Fan, B.; Bai, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, S.; Han, D.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Development of a fast and ultrasensitive black phosphorus-based colorimetric/photothermal dual-readout immunochromatography for determination of norfloxacin in tap water and river water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghanam, A.H.; Nourani, V.; Aslani, H.; Taghipour, H. Spatiotemporal variation of water pollution near landfill site: Application of clustering methods to assess the admissibility of LWPI. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.P.; Rodrigues, D.P.; Klepacz-Smolka, A.; Martins, R.C.; Quina, M.J. Comparative analysis of methods and models for predicting biochemical methane potential of various organic substrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohman, A.; Nugroho, A.; Lukitaningsih, E. Sudjadi Application of vibrational spectroscopy in combination with chemometrics techniques for authentication of herbal medicine. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2014, 49, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Dai, L. PLS-DA and Vis-NIR spectroscopy based discrimination of abdominal tissues of female rabbits. Spectrochim. Acta A 2022, 271, 120887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, B.; Li, H.; Shen, M.; Tian, S.; Zhang, H.; Ren, X.; Xing, L.; Zhao, J. Determination of bagged ‘Fuji’ apple maturity by visible and near-infrared spectroscopy combined with a machine learning algorithm. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 111, 103529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.-L.; Li, A.-B. Identification of soil profile classes using depth-weighted visible–near-infrared spectral reflectance. Geoderma 2018, 325, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, N.; Maiti, A.; Chakravarty, D.; Das, B.S. Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy based rapid coal rank estimation: A machine learning enabled framework. Spectrochim. Acta A 2021, 263, 120150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharififar, A.; Sarmadian, F.; Minasny, B. Mapping imbalanced soil classes using Markov chain random fields models treated with data resampling technique. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 159, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohland, M.; Ludwig, M.; Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Ludwig, B. Determination of soil properties with visible to near- and mid-infrared spectroscopy: Effects of spectral variable selection. Geoderma 2014, 223–225, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Fang, S.; Zhao, Y. Heavy metal Hg stress detection in tobacco plant using hyperspectral sensing and data-driven machine learning methods. Spectrochim. Acta A 2021, 245, 118917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Xie, D.; Song, H.; Ma, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, F. Estimation of chemical oxygen demand in different water systems by near-infrared spectroscopy. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2022, 243, 113964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tie, Z.; Zhou, M.; Wang, N.; Cao, X.; Xie, Y. Accurate determination of low-level chemical oxygen demand using a multistep chemical oxidation digestion process for treating drinking water samples. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 3839–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China (CNMEE): Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese)
- Hong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, H. Application of fractional-order derivative in the quantitative estimation of soil organic matter content through visible and near-infrared spectroscopy. Geoderma 2019, 337, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvao, R.K.; Araujo, M.C.; Jose, G.E.; Pontes, M.J.; Silva, E.C.; Saldanha, T.C. A method for calibration and validation subset partitioning. Talanta 2005, 67, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Goodacre, R. On splitting training and validation Set: A comparative study of cross-validation, bootstrap and systematic sampling for estimating the generalization performance of supervised learning. J. Anal. Test. 2018, 2, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharififar, A.; Sarmadian, F.; Malone, B.P.; Minasny, B. Addressing the issue of digital mapping of soil classes with imbalanced class observations. Geoderma 2019, 350, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Guo, L.; Huang, F.; Zhao, H. Determination of 10-Hydroxy-2-Decenoic acid of royal jelly using near-infrared spectroscopy vombined with chemometrics. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2458–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Cao, D. Key wavelengths screening using competitive adaptive reweighted sampling method for multivariate calibration. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 648, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, N.; Yang, X.; Sun, C.; Xing, B.; Han, J.; Zhao, C. Visualization of vibrational spectroscopy for agro-food samples using t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding. Food Control 2021, 126, 107812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Huang, W.; Fan, S.; Zhao, F.; Liang, D.; Tian, X. Non-destructive discrimination of the variety of sweet maize seeds based on hyperspectral image coupled with wavelength selection algorithm. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 109, 103418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, H.; He, Y. Theory and application of near infrared reflectance spectroscopy in determination of food quality. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2007, 18, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossel, R.A.V.; Behrens, T. Using data mining to model and interpret soil diffuse reflectance spectra. Geoderma 2010, 158, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Hong, Y.; Wei, Y.; Guo, L.; Shi, T.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Fei, T.; Liu, Y.; Mouazen, A.M.; et al. Estimation of organic carbon in anthropogenic soil by VIS-NIR spectroscopy: Effect of variable selection. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu-Rodríguez, J.; Pérez-Espinosa, A.; Pérez-Murcia, M.D.; Moral, R.; Agulló, E.; Ferrández-Villena, M.; Ferrández-García, M.T.; Bustamante, M.A. Near infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS) for the assessment of biomass production and C sequestration by arundo donax L. in salt-affected environments. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 183, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M.; Guerra, R.; Brázio, A.; Rodrigues, D.; Cavaco, A.M.; Antunes, M.D.; Valente de Oliveira, J. Feature discovery in NIR spectroscopy based Rocha pear classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 177, 114949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shen, R.; Chen, S.; Xu, G.; Cheng, H.; Guo, L.; Wei, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Diagnosis of cadmium contamination in urban and suburban soils using visible-to-near-infrared spectroscopy. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzolino, D.; Smyth, H.E.; Gishen, M. Feasibility study on the use of visible and near-infrared spectroscopy together with chemometrics to discriminate between commercial white wines of different varietal origins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7703–7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).