Mathematical Modeling-Based Management of a Sand Trap throughout Operational and Maintenance Periods (Case Study: Pengasih Irrigation Network, Indonesia)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
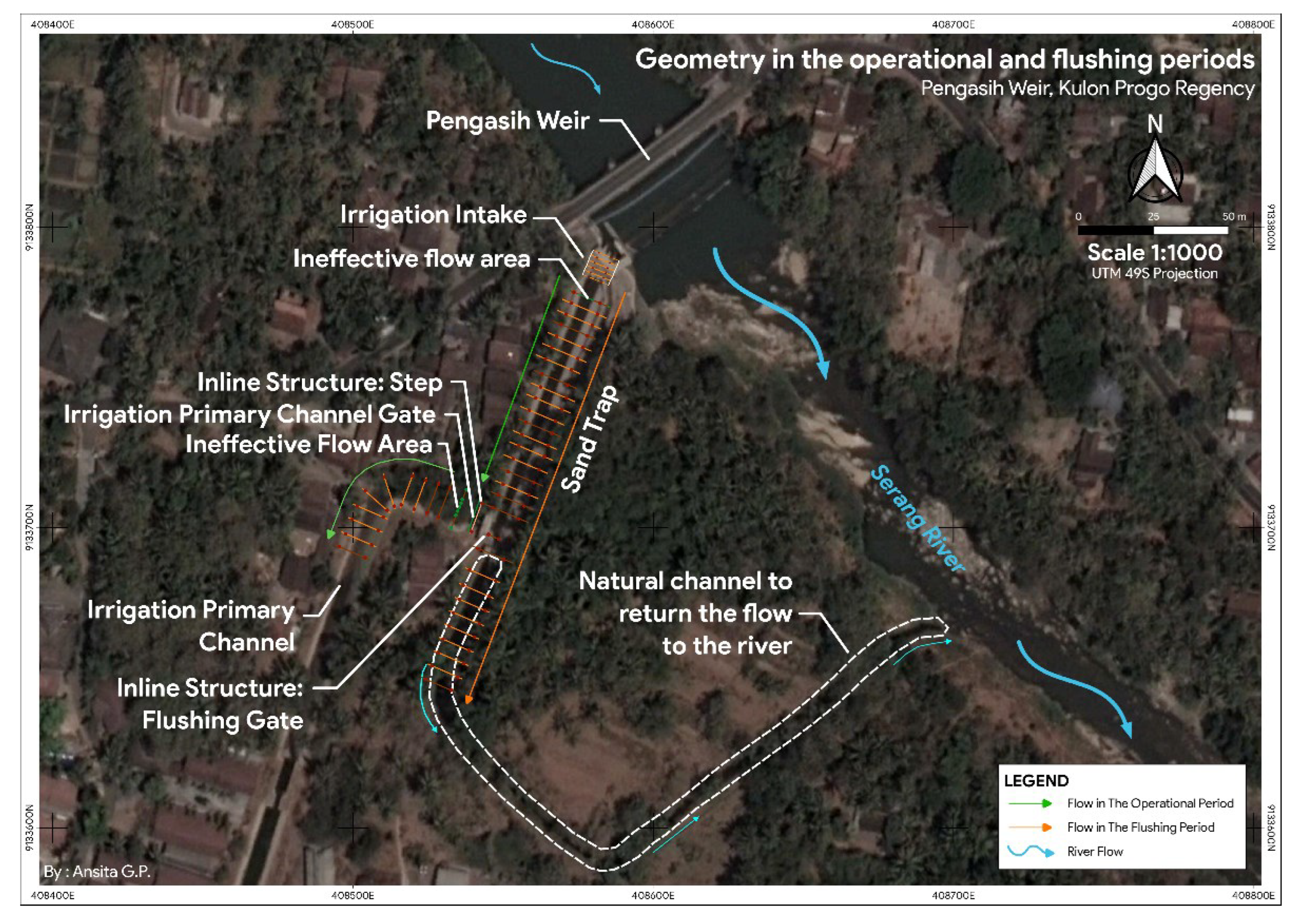
2.1. Scope of Work
2.2. General Description of the Methodology
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. Geometric Measurement
2.3.2. Discharge Measurement
2.3.3. Water Surface Elevation Measurement
2.3.4. Sediment Investigation
2.3.5. Flushing Measurement
2.4. Mathematical Modelling in Irrigation Network
2.5. Performance Indicators
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Data Collection Results
3.2. Preparation of Model
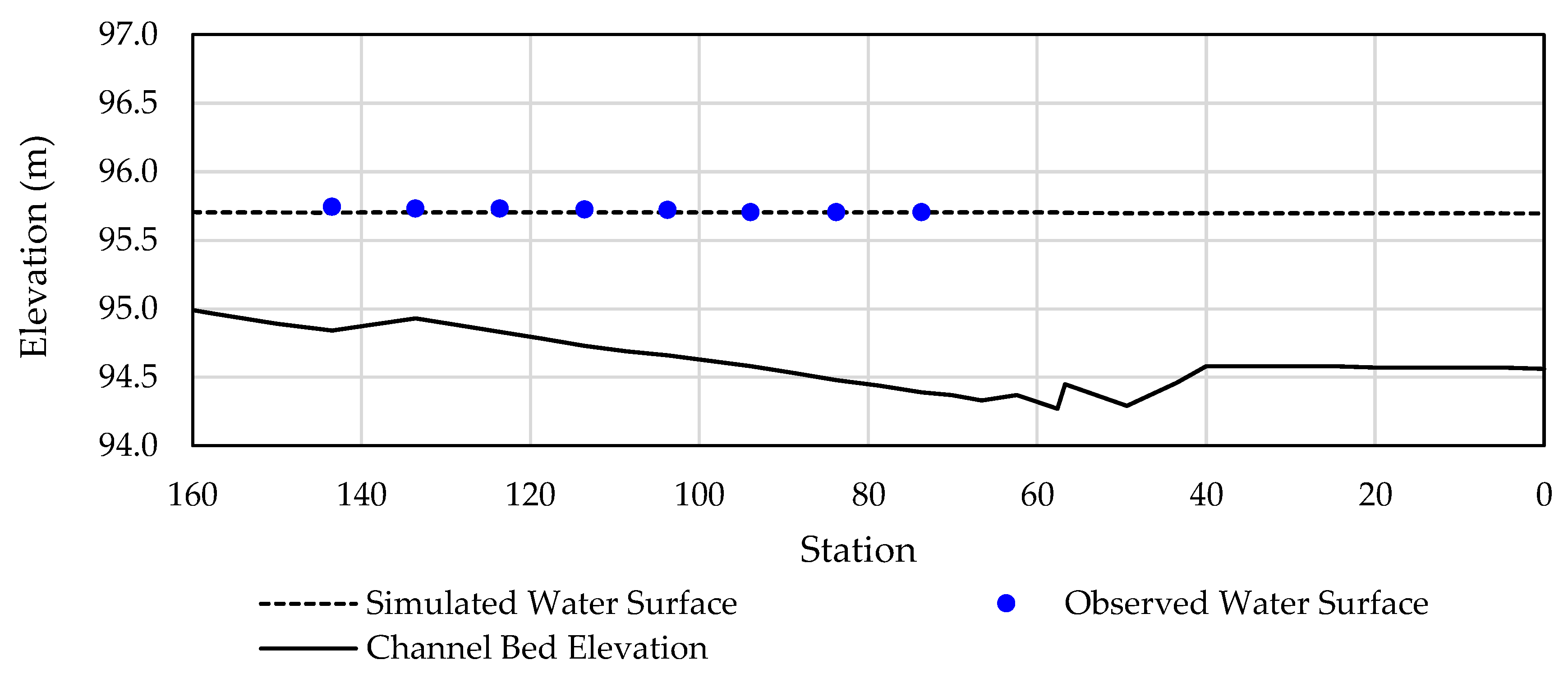
3.3. Hydraulic Calibration and Validation
3.4. Sediment Calibration
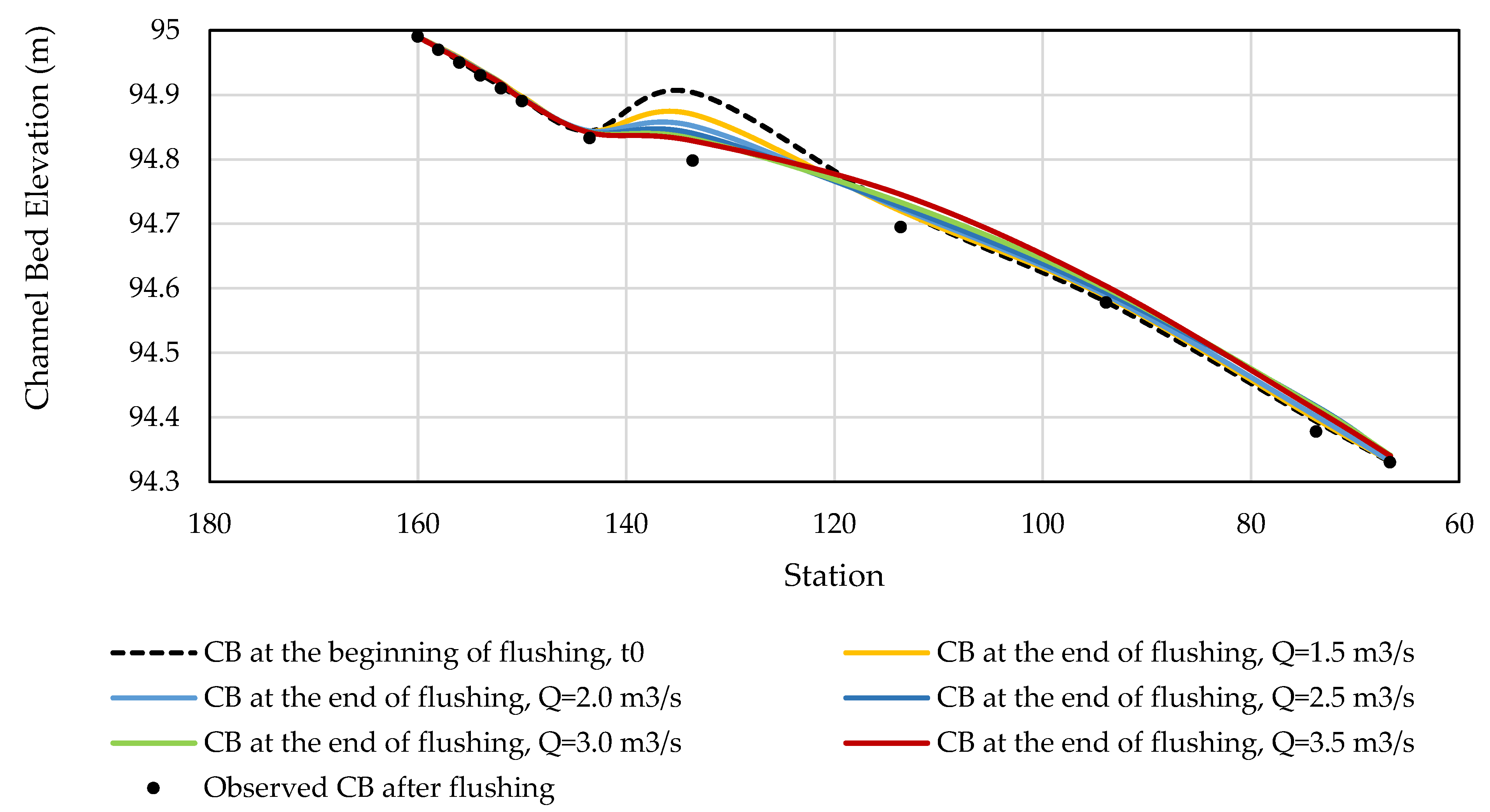
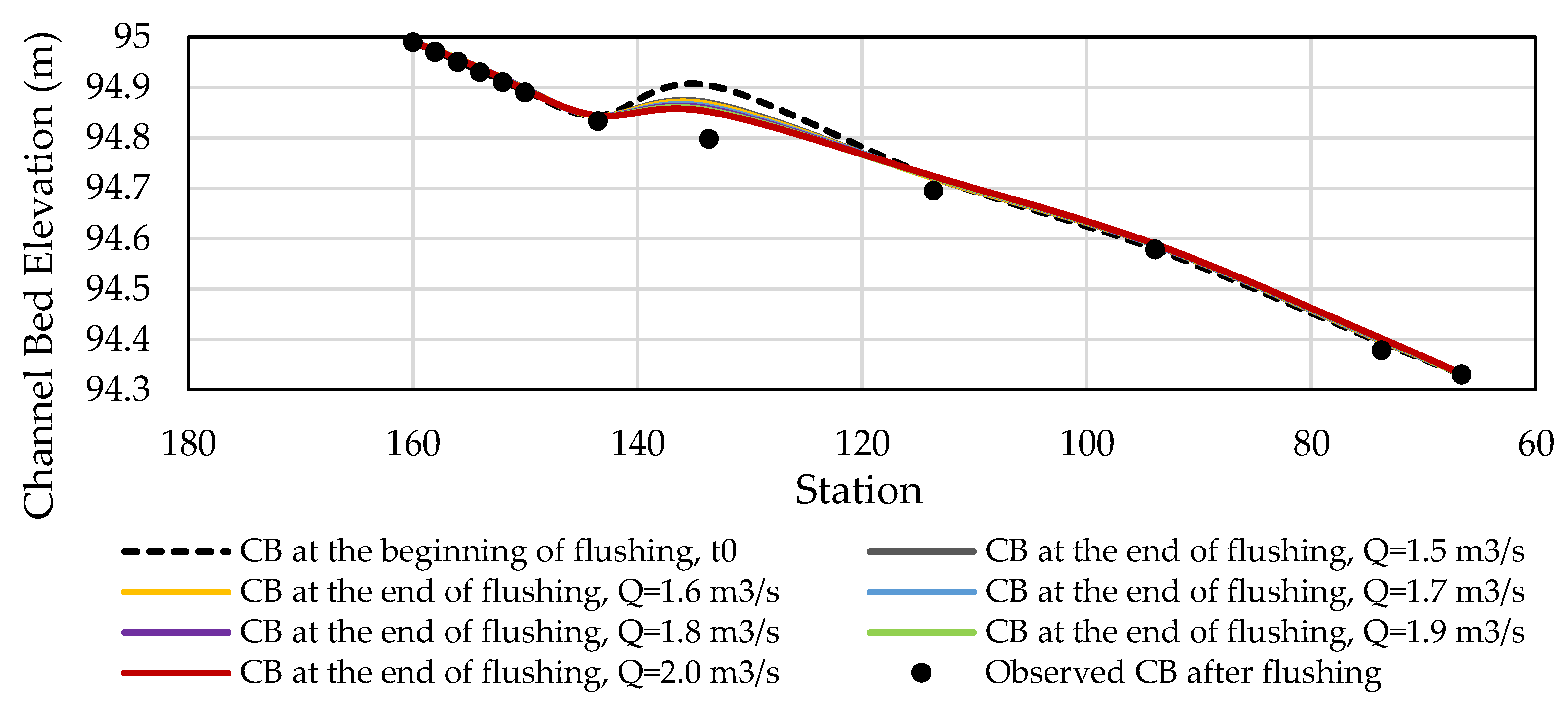
3.5. Simulation of Sand Trap Model in Flushing Period
3.6. Simulation of Sand Trap Model in Operational Period
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loucks, D.P.; van Beek, E. Water Resource Systems Planning and Management: An Introduction to Methods, Models, and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-44234-1. [Google Scholar]
- Pimentel, D.; Houser, J.; Preiss, E.; White, O.; Fang, H.; Mesnick, L.; Barsky, T.; Tariche, S.; Schreck, J.; Alpert, S. Water Resources: Agriculture, the Environment, and Society. Bioscience 1997, 47, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. AQUASTAT Main Database; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Döll, P. Vulnerability to the Impact of Climate Change on Renewable Groundwater Resources: A Global-Scale Assessment. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 035006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Him-Gonzalez, C. Water Resources for Agriculture and Food Production. Water Interact. Energy Environ. Food Agric. 2009, 1, 148–159. [Google Scholar]
- Starr, G.; Levison, J.; Starr, G.; Levison, J. Identification of Crop Groundwater and Surface Water Consumption Using Blue and Green Virtual Water Contents at a Subwatershed Scale. Environ. Process. 2014, 1, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Munir, S. Role of Sediment Transport in Operation and Maintenance of Supply and Demand Based Irrigation Canals. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Delft, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Paudel, K.P. Role of Sediment in the Design and Management of Irrigation Canals. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Delft, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-González, V.; Rojas-Palma, A.; Carrasco-Benavides, M. How Does Irrigation Affect Crop Growth? A Mathematical Modeling Approach. Mathematics 2022, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, S.; Döll, P. Quantifying Blue and Green Virtual Water Contents in Global Crop Production as Well as Potential Production Losses without Irrigation. J. Hydrol. 2010, 384, 198–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, G.; Leung, L.R.; Huang, M. Significant Impacts of Irrigation Water Sources and Methods on Modeling Irrigation Effects in the ACME Land Model. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2017, 9, 1665–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaerts, G.J. Adaptive Policy Implementation: Process and Impact of Indonesia’s National Irrigation Reform 1999–2018. World Dev. 2020, 129, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradipta, A.G.; Murtiningrum, M.; Febriyan, N.W.D.; Rizqi, F.A.; Ngadisih, N. Prioritas Pengembangan Dan Pengelolaan Jaringan Irigasi Tersier Di D.I. Yogyakarta Menggunakan Multiple Attribute Decision Making. J. Irig. 2020, 15, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, S.S.; Pradipta, A.G.; Murtiningrum; Subekti, E.; Sukrasno; Prabowo, A.; Djito; Sidharti, T.S.; Soekarno, I.; Fatah, Z. Toward Modernization of Irrigation from Concept to Implementations: Indonesia Case. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 355, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradipta, A.G.; Maulana, A.F.; Murtiningrum; Arif, S.S.; Tirtalistyani, R. Evaluation of the Sand Trap Performance of the Pengasih Weir during the Operational Period. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 542, 012053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurmu, Z.A.; Ritzema, H.; de Fraiture, C.; Ayana, M. Stakeholder Roles, and Perspectives on Sedimentation Management in Small-Scale Irrigation Schemes in Ethiopia. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukardi, S.; Warsito, B.; Kisworo, H.S. River Management in Indonesia; Directorate General of Water Resources: Jakarta Pusat, Indonesia, 2013.
- De Sousa, L.S.; Wambua, R.M.; Raude, J.M.; Mutua, B.M. Assessment of Water Flow and Sedimentation Processes in Irrigation Schemes for Decision-Support Tool Development: A Case Review for the Chókwè Irrigation Scheme, Mozambique. AgriEngineering 2019, 1, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revel, N.M.T.K.; Ranasiri, L.P.G.R.; Rathnayake, R.M.C.R.K.; Pathirana, K.P.P. Estimation of Sediment Trap Efficiency in Reservoirs—An Experimental Study. Eng. J. Inst. Eng. Sri Lanka 2015, 48, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiere, H.O.; Onyando, J.O.; Kamau, D.N. Simulation of Sediment Transport in the Canal Using the Hec-Ras (Hydrologic Engineering Centre—River Analysis System) In an Underground Canal in Southwest Kano Irrigation Scheme—Kenya. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Invent. 2015, 4, 15–31. [Google Scholar]
- Arif, S.S.; Prabowo, A. Pokok-Pokok Modernisasi Irigasi Indonesia; Direktorat Jenderal Sumber Daya Air; Kementerian Pekerjaan Umum: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2014.
- Pradipta, A.G.; Pratyasta, A.S.; Arif, S.S. Analisis Kesiapan Modernisasi Daerah Irigasi Kedung Putri Pada Tingkat Sekunder Menggunakan Metode K-Medoids Clustering. agriTECH 2019, 39, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.R.; Tariq, A.R.; Rezaur, R.B.; Javed, M. Investigation on Dynamics of Sediment and Water Flow in a Sand Trap. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanics, Fluids, Heat, Elasticity, and Electromagnetic Fields, Venice, Italy, 28–30 September 2013; Volume 14, pp. 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Widaryanto, L.H. Evaluation on Flushing Operation Frequency of Sand Trap of Pendowo and Pijenan Weirs. J. Civ. Eng. Forum 2018, 4, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, W.; Vereide, K.; Mauko, G.; Havrevoll, O.H.; Schneider, J.; Zenz, G. Retrofitting of Pressurized Sand Traps in Hydropower Plants. Water 2021, 13, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulos, T.; Yilma, S.; Ketema, T. Evaluation of the Sand-Trap Structures of the Wonji-Shoa Sugar Estate Irrigation Scheme, Ethiopia. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2006, 20, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large River Basin Organization of Serayu-Opak. A Report: Pola Pengelolaan Sumber Daya Air Wilayah Sungai Progo Opak Serang; Large River Basin Organization of Serayu-Opak Rencana: Special Region of Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2016.
- Arif, N.; Danoedoro, P.; Hartono, H. Remote Sensing and GIS Approaches to a Qualitative Assessment of Soil Erosion Risk in Serang Watershed, Kulonprogo, Indonesia. Geoplan. J. Geomat. Plan. 2017, 4, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, N.; Danoedoro, P. Hartono Analysis of Artificial Neural Network in Erosion Modeling: A Case Study of Serang Watershed. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 98, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Raghuwanshi, N.S.; Singh, R. Development and Application of Hydraulic Simulation Model for Irrigation Canal Network. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2008, 134, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwantoro, D.; Nurrochmad, F. Analisa Pengembangan Daerah Irigasi Baru Di DAS Ngrancah Kabupaten Kulon Progo. Master’s Thesis, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Arif, N.; Danoedoro, P.; Hartono, H.; Mulabbi, A. Erosion Prediction Model Using Fractional Vegetation Cover. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2020, 5, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.; Joko, H.; Susanto, S. Assessment of Watershed Status (Case Study at Serang Sub Watershed). agriTECH 2009, 29, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuningtyas, E.A.; Fahmi, A.; Ilma, N.; Yudha, R.B. Pemetaan Erodibilitas Tanah Dan Korelasinya Terhadap Karakteristik Tanah Di DAS Serang, Kulon Progo. J. Nas. Teknol. Terap. 2018, 1, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabowo, A. Identifikasi Morfometri DAS Serang Dari Citra DEM SRTM. KURVATEK 2022, 7, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serede, I.J.; Mutua, B.M.; Raude, J.M. Hydraulic Analysis of Irrigation Canals Using HEC-RAS Model: A Case Study of Mwea Irrigation Scheme, Kenya. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 989–1005. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/download/63368271/hydraulic-analysis-of-irrigation-canals-using-IJERTV4IS09029420200519-4388-3dnb6n.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Hamzeh Haghiabi, A.; Zaredehdasht, E. Evaluation of HEC-RAS Ability in Erosion and Sediment Transport Forecasting. World Appl. Sci. J. 2012, 17, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, H.S.; Alturfi, U.A.M.; Shlash, M.A. Sediment Transport Capacity in Euphrates River at Al-Abbasia Reach Using HEC-RAS Model. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 919–929. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, D.J.; Ramani, M.; Joshi, M. Application of 1-D Hec-Ras Model in Design of Channels. Int. J. Innov. Res. Adv. Eng. 2014, 1, 1883. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, F.; Ansari, M.A.; Hussain, A.; Jahangeer, J. Model Development for Estimation of Sediment Removal Efficiency of Settling Basins Using Group Methods of Data Handling. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2021, 147, 04020043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Lamichhane, G.R.; Rahaman, M.M.; Kalra, A.; Ahmad, S. Application of HEC-RAS to Study the Sediment Transport Characteristics of Maumee River in Ohio. In World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2019: Hydraulics, Waterways, and Water Distribution Systems Analysis—Selected Papers from the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2019; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2019; pp. 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, G.W.; Gibson, S. Sediment Transport Modeling in HEC RAS. In Impacts of Global Climate Change; American Society of Civil Engineers: Anchorage, AL, USA, 2005; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Traore, V.B.; Bop, M.; Faye, M.; Giovani, M.; Boukhaly Traore, V.; Malomar, G.; Hadj, E.; Gueye, O.; Sambou, H.; Dione, A.N.; et al. Using of Hec-Ras Model for Hydraulic Analysis of a River with Agricultural Vocation: A Case Study of the Kayanga River Basin, Senegal “Using of Hec-Ras Model for Hydraulic Analysis OPV Modelling and Fabrication View Project Modelling for Hydraulic Anal. Am. J. Water Resour. 2015, 3, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serede, I.J.; Mutua, B.M.; Raude, J.M. A Review for Hydraulic Analysis of Irrigation Canals Using HEC-RAS Model: A Case Study of Mwea Irrigation Scheme, Kenya. Hydrology 2014, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ShahiriParsa, A.; Noori, M.; Heydari, M.; Rashidi, M. Floodplain Zoning Simulation by Using HEC-RAS and CCHE2D Models in the Sungai Maka River. Air Soil Water Res. 2016, 9, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisinggih, D.; Wahyuni, S.; Nugroho, R.; Hidayat, F.; Idi Rahman, K. Sediment Transport Functions in HEC-RAS 4.0 and Their Evaluation Using Data from Sediment Flushing of Wlingi Reservoir—Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 437, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USACE. HEC-RAS River Analysis Systems: Hydraulic Reference Manual, Version 4.1; USACE Hydrologic Engineering Center: Davis, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pokrajac, D.; Finnigan, J.J.; Manes, C.; McEwan, I.; Nikora, V. On the Definition of the Shear Velocity in Rough Bed Open Channel Flows. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Fluvial Hydraulics—River Flow 2006, Lisbon, Portugal, 6–8 September 2006; Volume 1, pp. 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Lu, Y. Analysis of the Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) in Assessing Rounding Model. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 324, 012049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, B. The Correlation Coefficient: Its Values Range between 1/1, or Do They. J. Target. Meas. Anal. Mark. 2009, 17, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccuen, R.H.; Knight, Z.; Cutter, A.G. Evaluation of the Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency Index. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2006, 11, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negoro, A.K. Estimasi Nilai Faktor K Daerah Irigasi Sistem Kalibawang Kabupaten Kulon Progo. Undergraduate Thesis, University of Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Peni, S.N. Kualitas Air Di Daerah Waduk Sermo Dan Sekitarnya, Desa Hargowilis, Kabupaten Kulon Progo. Master’s Thesis, Institut Teknologi Nasional Yogyakarta, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
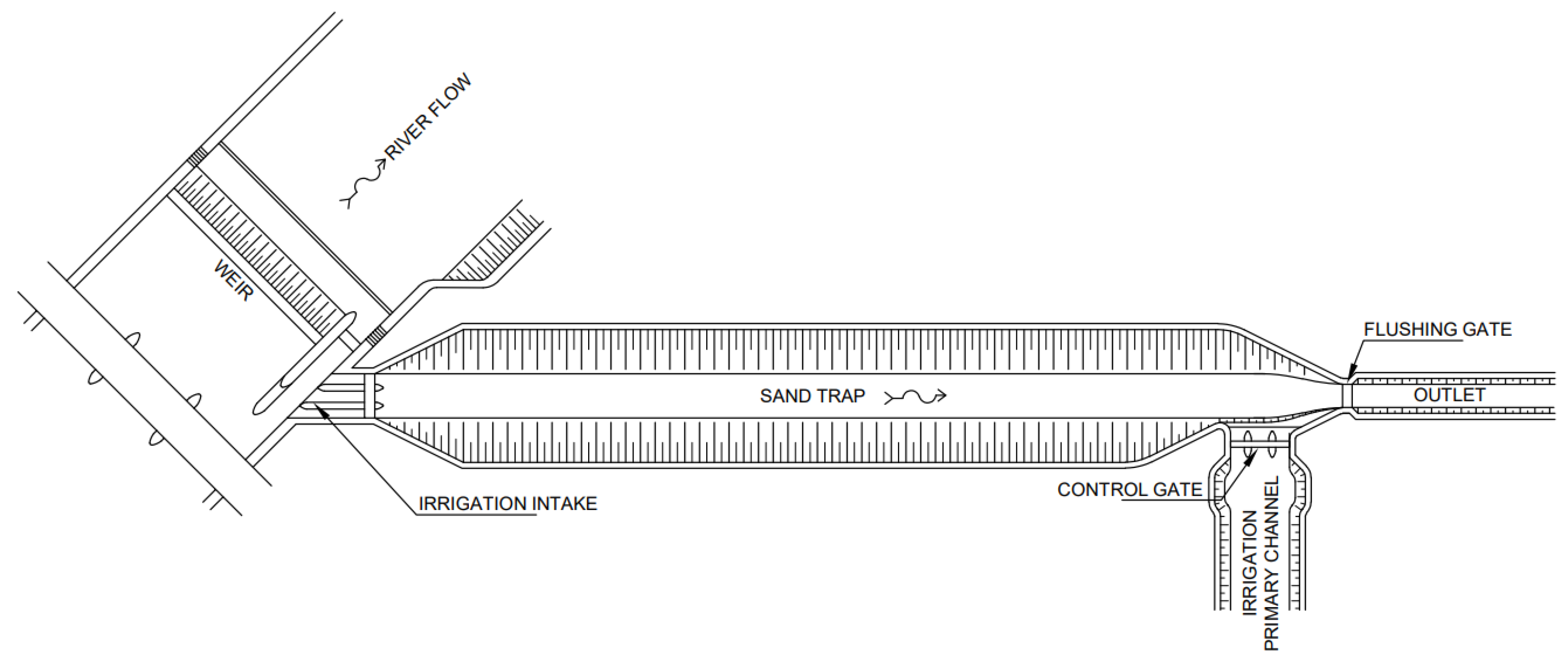

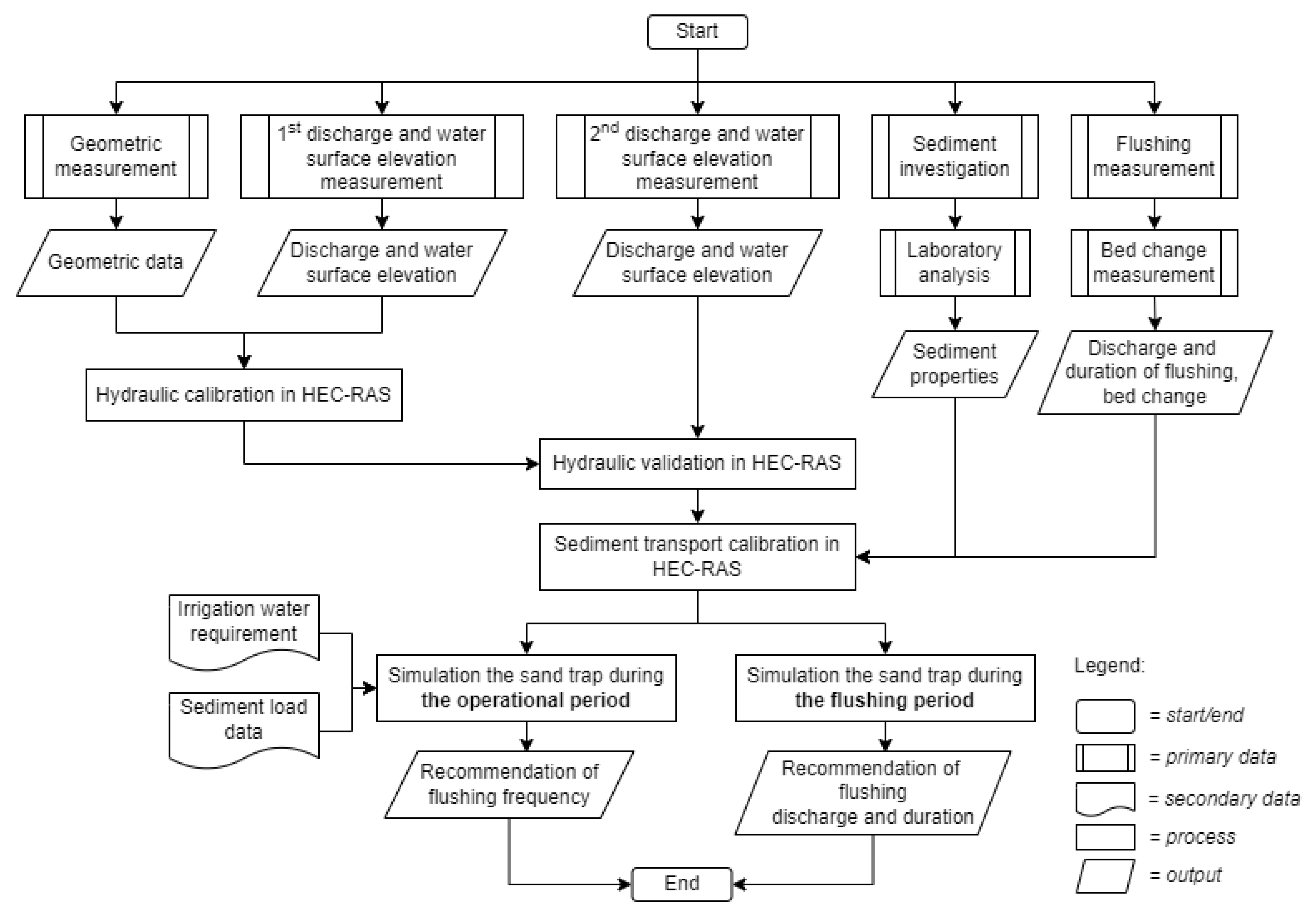
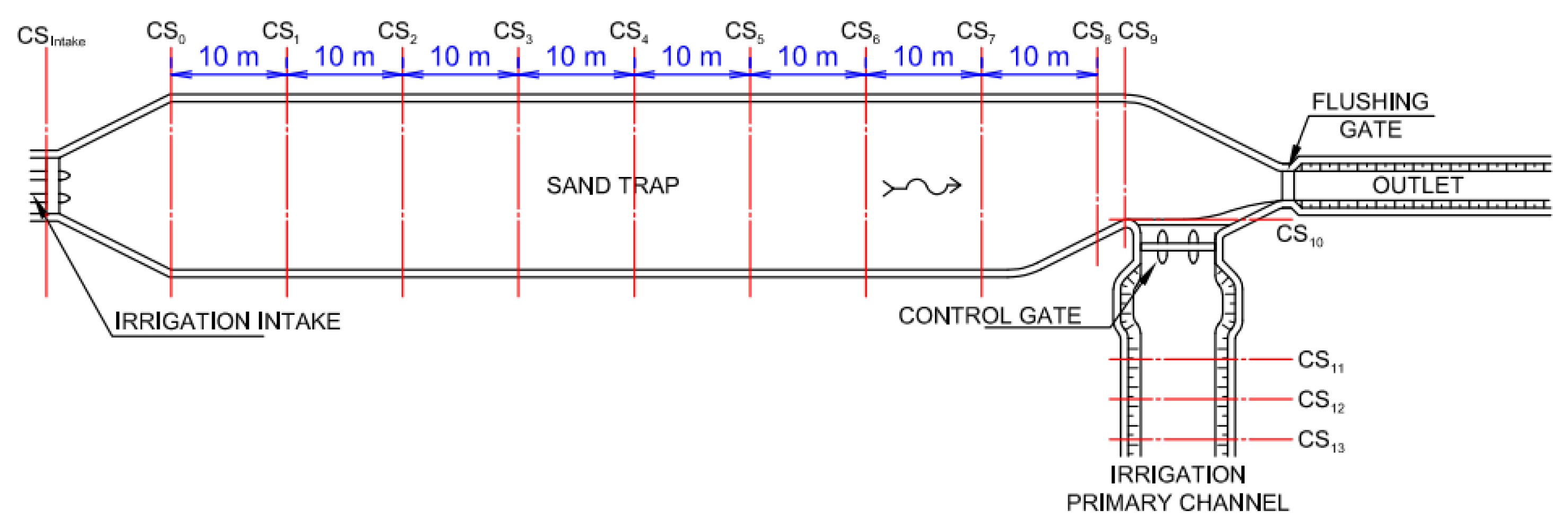
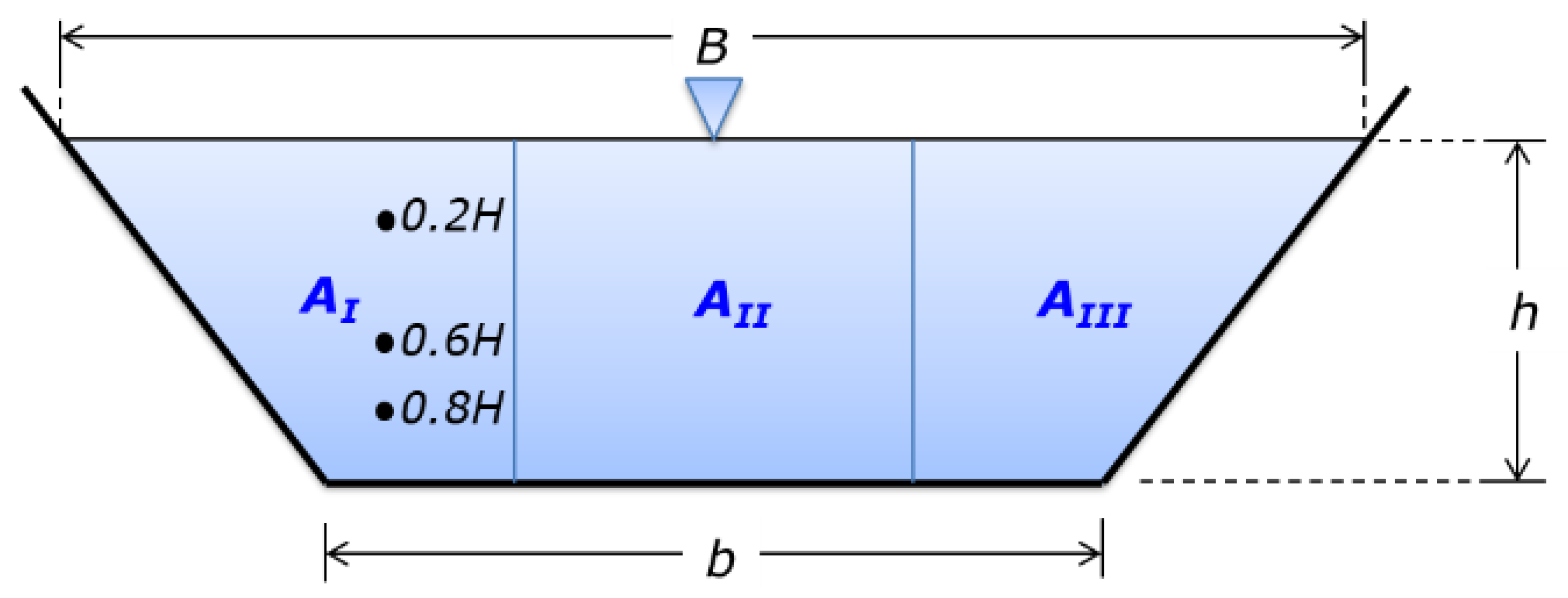





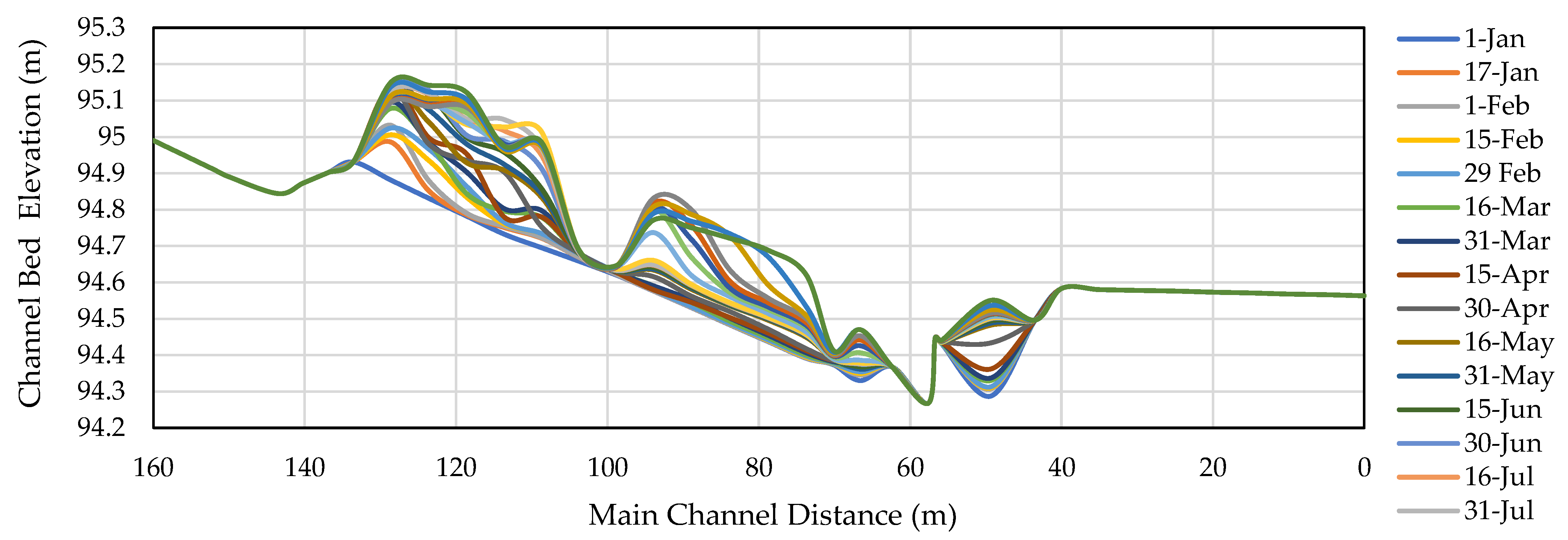
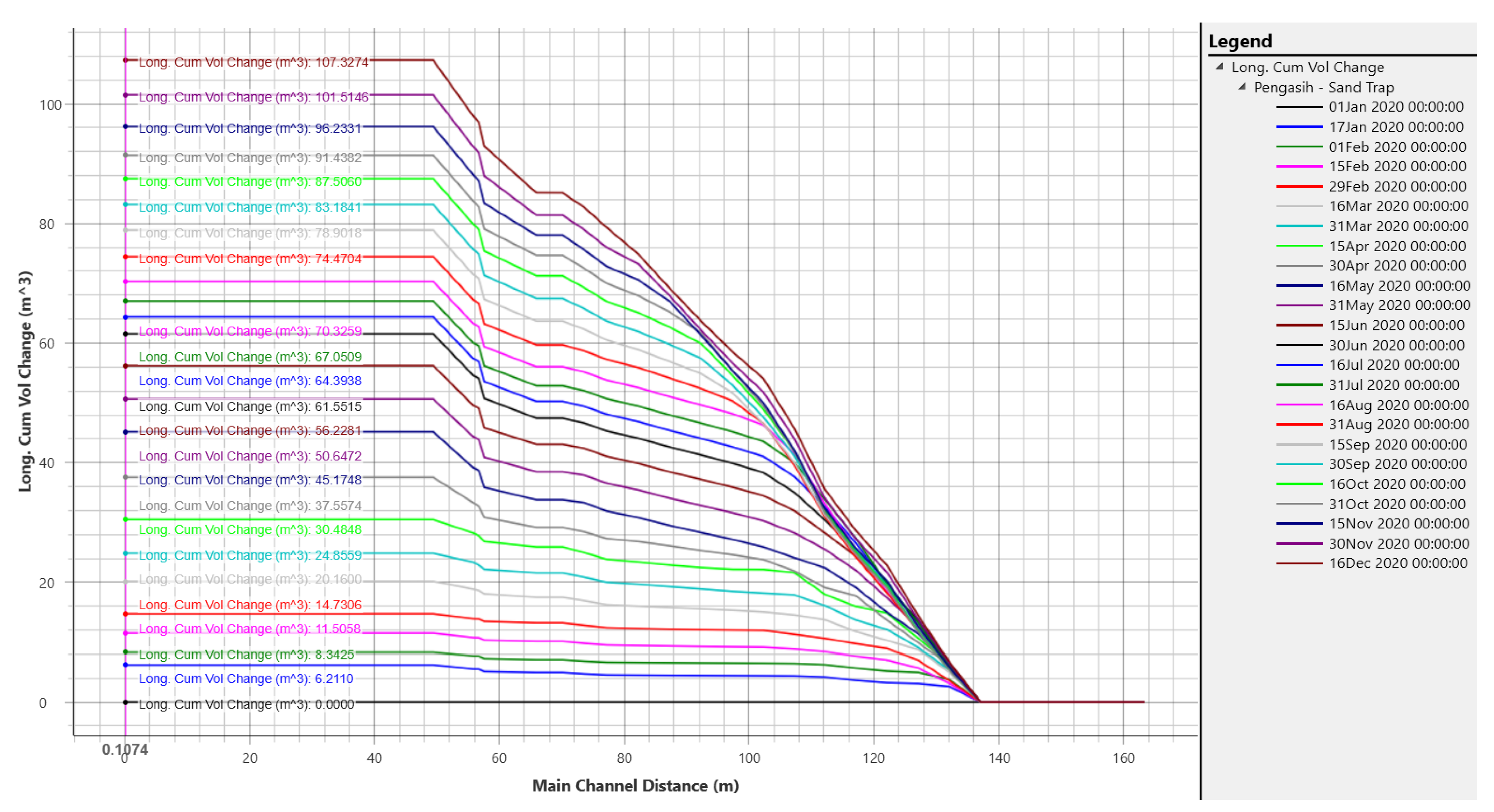

| No. | Type of Data | Results | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Average discharge | ||
| 2.03 m3/s | Average flow depth: 1.56 m; average velocity: 0.19 m/s | |
| 0.53 m3/s | Average flow depth: 1.20 m; average velocity: 0.08 m/s | |
| 2. | Water surface elevation | ||
| 8 values (in meters) | From station 0–70: 96.416, 96.409, 96.401, 96.436, 96.435, 96.384, 96.383, 96.382 | |
| 8 values (in meters) | From station 0–70: 95.741, 95.730, 95.730, 95.724, 95.718, 95.702, 95.702, 95.702 | |
| 3. | Sediment | ||
| 2.66 | Based on pycnometer test | |
| Based on sieve and hydrometer test | ||
| 9 values (in % finer) | VFG: 99.58, VCS: 98.48, CS: 94.49, MS: 76.97, FS: 48.86, VFS: 9.66, CM: 5.59, FM: 2.20, Clay: 0 | |
| 9 values (in % finer) | VFG: 99.08, VCS: 98.81, CS: 98.43, MS: 79.30, FS: 60.11, VFS: 22.16, CM: 13.29, FM: 10.54, Clay: 0 | |
| 9 values (in % finer) | VFG: 95.87, VCS: 91.58, CS: 87.30, MS: 74.41, FS: 60.54, VFS: 18.03, CM: 11.29, FM: 6.92, Clay: 0 | |
| 4. | Discharge and duration of flushing | ||
| 2.08 m3/s | Average flow depth: 0.30 m; average velocity: 1.59 m/s | |
| 90 min | ||
| 6. | Volume of sediment deposited during the operational period at the time of measurement (within 80 days) | 36.51 m3 | based on cross-section measurement |
| 7. | Capacity of sand trap | 84.40 m3 | based on cross-section measurement |
| 8. | Length of sand trap | 100 m |
| No. | Performance Indicator | Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 0.015 | n = 0.020 | n = 0.024 | n = 0.025 | n = 0.026 | n = 0.030 | n = 0.035 | ||
| 1 | Coefficient of Determination (R2) | 0.9379 | 0.9457 | 0.9369 | 0.9522 | 0.9474 | 0.9477 | 0.8051 |
| 2 | Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency Index (NSE) | −282.7061 | −68.1269 | −4.8787 | −0.6402 | −0.5346 | −38.6501 | −166.5715 |
| 3 | Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) | 0.3505 | 0.1730 | 0.0504 | 0.0266 | 0.0258 | 0.1310 | 0.2693 |
| 4 | Mean Absolute Error (MAE) | 0.3497 | 0.1716 | 0.0456 | 0.0216 | 0.0224 | 0.1293 | 0.2685 |
| No. | Performance Indicator | Value, n = 0.025 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Coefficient of Determination (R2) | 0.8479 |
| 2 | Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency Index (NSE) | −0.9833 |
| 3 | Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) | 0.0221 |
| 4 | Mean Absolute Error (MAE) | 0.0168 |
| Scenario | Sediment Transport Parameter | |
|---|---|---|
| Sorting Method | Fall Velocity Method | |
| 1 | Active Layer | Rubey |
| 2 | Active Layer | Toffaleti |
| 3 | Active Layer | Van Rijn |
| 4 | Active Layer | Report 12 |
| 5 | Exner 5 | Rubey |
| 6 | Exner 5 | Toffaleti |
| 7 | Exner 5 | Van Rijn |
| 8 | Exner 5 | Report 12 |
| No. | Performance Indicator | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Coefficient of Determination (R2) | 0.9986 |
| 2 | Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency Index (NSE) | 0.9974 |
| 3 | Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) | 0.0163 |
| 4 | Mean Absolute Error (MAE) | 0.0114 |
| Performance Indicators | Values from the Discharge of | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 m3/s | 2.0 m3/s | 2.5 m3/s | 3.0 m3/s | 3.5 m3/s | |
| R2 | 0.9972 | 0.9981 | 0.9975 | 0.9973 | 0.9968 |
| NSE | 0.9956 | 0.9968 | 0.9954 | 0.9950 | 0.9943 |
| RMSE | 0.0212 | 0.0181 | 0.0217 | 0.0226 | 0.0241 |
| MAE | 0.0127 | 0.0117 | 0.0149 | 0.0156 | 0.0161 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pradipta, A.G.; Loc, H.H.; Nurhady, S.; Murtiningrum; Mohanasundaram, S.; Park, E.; Shrestha, S.; Arif, S.S. Mathematical Modeling-Based Management of a Sand Trap throughout Operational and Maintenance Periods (Case Study: Pengasih Irrigation Network, Indonesia). Water 2022, 14, 3081. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193081
Pradipta AG, Loc HH, Nurhady S, Murtiningrum, Mohanasundaram S, Park E, Shrestha S, Arif SS. Mathematical Modeling-Based Management of a Sand Trap throughout Operational and Maintenance Periods (Case Study: Pengasih Irrigation Network, Indonesia). Water. 2022; 14(19):3081. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193081
Chicago/Turabian StylePradipta, Ansita Gupitakingkin, Ho Huu Loc, Sigit Nurhady, Murtiningrum, S. Mohanasundaram, Edward Park, Sangam Shrestha, and Sigit Supadmo Arif. 2022. "Mathematical Modeling-Based Management of a Sand Trap throughout Operational and Maintenance Periods (Case Study: Pengasih Irrigation Network, Indonesia)" Water 14, no. 19: 3081. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193081
APA StylePradipta, A. G., Loc, H. H., Nurhady, S., Murtiningrum, Mohanasundaram, S., Park, E., Shrestha, S., & Arif, S. S. (2022). Mathematical Modeling-Based Management of a Sand Trap throughout Operational and Maintenance Periods (Case Study: Pengasih Irrigation Network, Indonesia). Water, 14(19), 3081. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193081








