Structural Diversity of Bacterial Communities and Its Relation to Environmental Factors in the Surface Sediments from Main Stream of Qingshui River
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
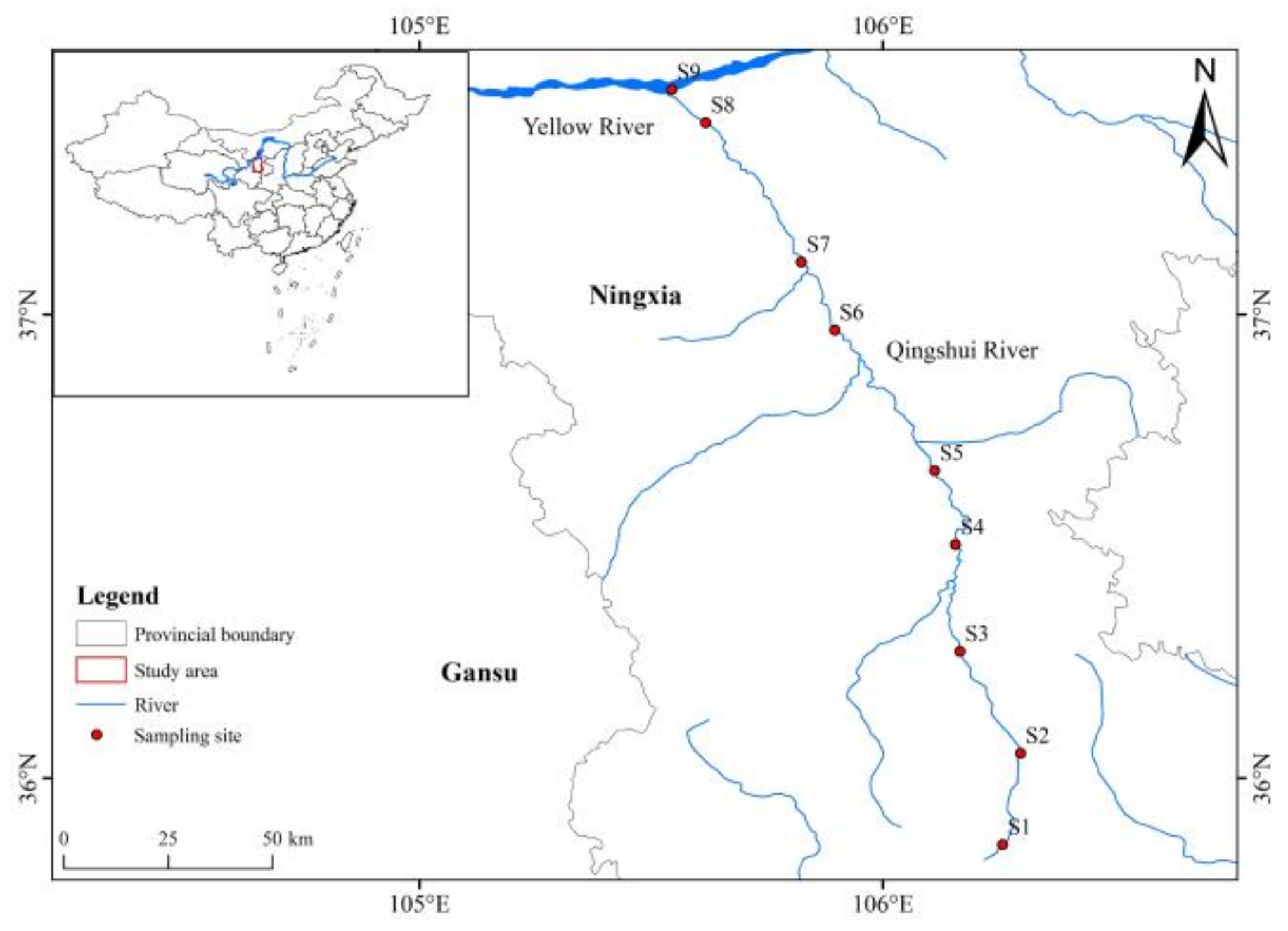
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Pretreatment
2.3. Analysis of Physical-Chemical Properties and Heavy Metals in Sediments
2.4. 16S rDNA High-Throughput Sequencing
2.5. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
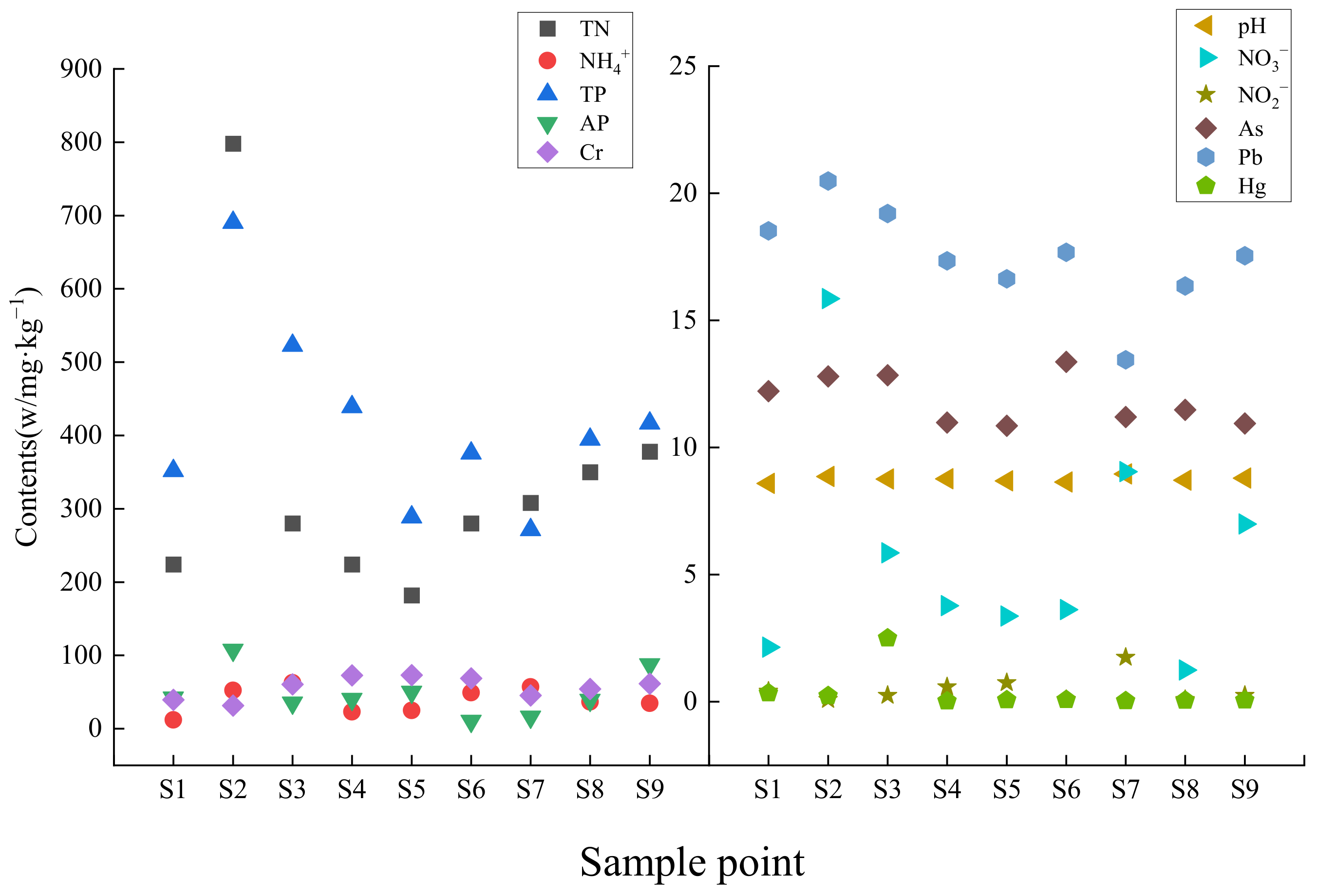
3.1. Physico-Chemical Properties and Heavy Metal Content
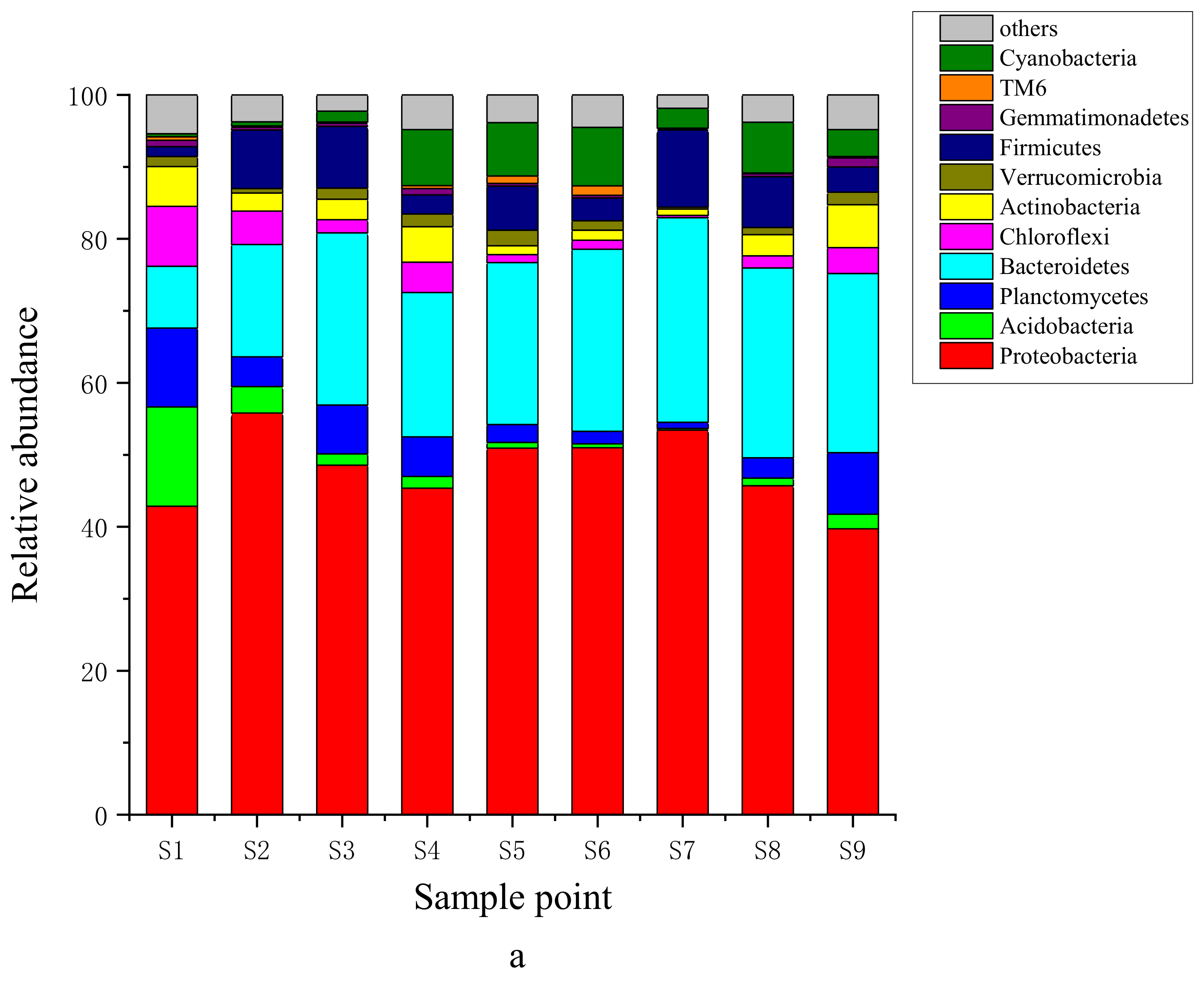
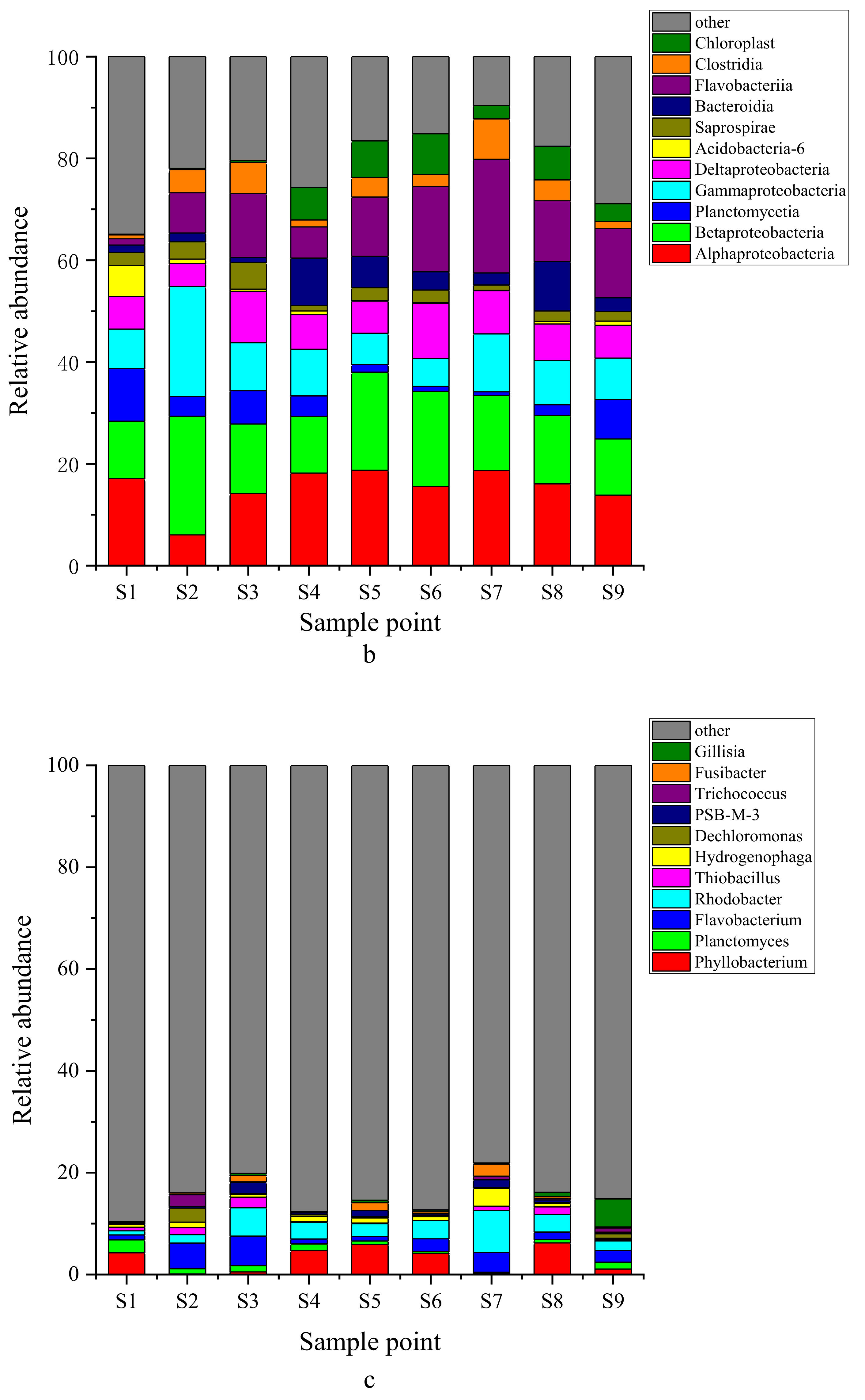
3.2. Structural Characteristics of Bacteria in Surface Sediments
3.3. Analysis of Bacterial Community Diversity in Sediment
3.4. Effects of Environmental Factors on Microbial Community Structure and Diversity
4. Discussion
4.1. Composition and Function of Dominant Bacteria in Sediments
4.2. Correlation between the Structure and Diversity of Bacterial Community and Environmental Factors in Qingshui River Sediments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, B.; Jiang, B.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C. Effects of environmental factors on phosphorus adsorption capacity and release risk in lake sediments. Plant Soil Environ. 2022, 68, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Han, G.L.; Zhang, S.T.; Zhang, Q. Suspended Sediments Quality Assessment in a Coastal River: Identification of Potentially Toxic Elements. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Han, G.L.; Zhang, S.T.; Liang, B.; Qu, R.; Liu, M.; Liu, J.K. Potentially toxic elements in cascade dams-influenced river originated from Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Qian, B.; Niu, L.; Wang, P.; Gu, J.; Yang, N. How fluvial inputs directly and indirectly affect the ecological status of different lake regions: A bio-assessment framework. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, J.I. Ecosystem processes and interactions in a morass of diversity. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 81, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevin, P.; Feris, P.W.R.M.; James, E.; Gannon, A.W.E.H. Determining Rates of Change and Evaluating Group-Level Resiliency Differences in Hyporheic Microbial Communities in Response to Fluvial Heavy-Metal Deposition. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2004, 70, 4756–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, K.; Hu, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, T.; Li, L.; Tao, J.; Liu, D.; et al. Distinct assembly mechanisms of microbial sub-communities with different rarity along the Nu River. J. Soil Sediment 2022, 22, 1530–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaki, Y.; Hattori, K.; Yamashita, Y. Factors Controlling the Spatial Distribution of Dissolved Organic Matter with Changes in the C/N Ratio From the Upper to Lower Reaches of the Ishikari River, Japan. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesner-Friedman, C.; Beattie, R.E.; Stewart, J.R.; Hristova, K.R.; Serre, M.L. Characterizing Differences in Sources of and Contributions to Fecal Contamination of Sediment and Surface Water with the Microbial FIT Framework. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 4231–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Y.Y.; He, G.Y.; Hu, Y.S.; Gao, D.D.; Dai, Y.H.; Li, Q.Y.; Zhang, H. Ecological risk assessment and identification of the distinct microbial groups in heavy metal-polluted river sediments. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Zhang, H.Y.; Guo, Y.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Huang, T.S. Temporal and Spatial Patterns of Sediment Microbial Communities and Driving Environment Variables in a Shallow Temperate Mountain River. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, B.; Yuan, R.Q.; Li, C.Q.; Li, Y. Characteristics of aquatic bacterial community and the influencing factors in an urban river. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Najjar, P.; Pfaffl, M.; Ouaini, N.; Abdel Nour, A.; El Azzi, D. Water and sediment microbiota diversity in response to temporal variation at the outlet of the Ibrahim River (Lebanon). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.D.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, B.B.; Wu, B.; Lu, G.H. Structural Characteristics of Microbial Communities in the Sediments of the Niyang River in Tibet. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 3249–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Xia, X.H.; Liu, T.; Hu, L.J.; Zhu, B.T.; Zhang, X.T.; Dong, J.W. Characteristics of bacterial community in the water and surface sediment of the Yellow River, China, the largest turbid river in the world. J. Soil Sediment 2014, 14, 1894–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, X.L. Study on Environmental Behavior and Health Risk of Heavy Metals and Organochlorine Pesticides in Qingshui River; Ningxia University: Ningxia, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kai, X.L.; Zhang, W.J.; Qiu, X.C.; Chu, J.D.; Zhang, Y.Z. Health risk evaluation of children caused by water pollutants in Qingshui River. Environ. Chem. 2018, 37, 2809–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Lee, S.L.; Qiu, X.C.; Yang, Y.Y.; Lei, X.B. Analysis and Assessment of Water Quality in Qingshui River Basin. Admin. Techol. Environ. Monit. 2021, 33, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Zhao, Z.F.; Qiu, X.C.; Ouyang, H.; Wu, Y.L. Spatial-temporal Characteristics of Water Environmental Quality in Mainstream of Qingshui River. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 3, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.F.; Shi, W.; Qiu, X.C.; OuYang, H.; Wang, S.Q.; Sun, X.Y.; Lee, S.L. Distribution Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Five Heavy Metals in the Water of Qingshui River Basin. Admin. Techol. Environ. Monit. 2021, 33, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.L.; Zhao, Z.F.; Qiu, X.C.; Guo, Q.; Wu, Y.L. Distribution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Qingshui River Basin of Ningxia. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage. J. Irrig. Drain 2020, 39, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.R.; Shi, W.; Qiu, X.C.; Wang, X.Y. Plant Community Structure and Diversity in the Riparian Zone of the Qingshui River Basin. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2020, 48, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Duan, J.R.; Qiu, X.C.; Wang, X.Y. Study on community structure and diversity of zooplankton in Qingshui river. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2021, 60, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.F.; Wang, Y.J.; Xu, Y.; Duan, G.Q.; Huang, M.S.; Peng, J.F. Adaptive Variations of Sediment Microbial Communities and Indication of Fecal-Associated Bacteria to Nutrients in a Regulated Urban River. Water-Sui 2020, 12, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.M.; Wang, S.M.; Chen, Y.P.; Wu, J.H.; Xue, L.G.; Fan, T.T. Pollution status of the Yellow River tributaries in middle and lower reaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, G.Z.; Yang, X.N.; Wu, F.P.; Zhao, W. 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing was used to study the microbial community structure and diversity in rainwater harvesting cellar water. Environ. Sci. 2017, 04, 1704–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.C.; Miao, Y.; Wu, B.; Ye, L.; Yu, H.Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.X. Correlation between microbial community structure and biofouling as determined by analysis of microbial community dynamics. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansola, G.; Arroyo, P.; Saenz De Miera, L.E. Characterisation of the soil bacterial community structure and composition of natural and constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Shen, T.; Guo, W.; Wang, R. Shifts in microbial community function and structure along the successional gradient of coastal wetlands in Yellow River Estuary. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2012, 49, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Xia, X.; Zhu, B.; Zheng, S.; Zhuang, J. Bacterial diversity and community structure in the sediment of the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, the largest turbid river in the world. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 71, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Xie, S.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal variation of planktonic and sediment bacterial assemblages in two plateau freshwater lakes at different trophic status. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2016, 100, 4161–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Jiang, X. Profiling of Sediment Microbial Community in Dongting Lake before and after Impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Gonzalez, A.; Marques, S. Bacterial diversity in oil-polluted marine coastal sediments. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 2016, 38, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, N.; Robeson, M.S.I.; Castro, H.F.; Fortney, J.L.; Techtmann, S.M.; Joyner, D.C.; Paradis, C.J.; Pfiffner, S.M.; Hazen, T.C. Microbial community composition and diversity in Caspian Sea sediments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Hao, J.; Wang, S.; Lin, Y.; Guan, H.; Zhang, J.; Jian, S.; et al. Composition and Functional Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Bacterioplankton Community in the Huangshui River, China. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Ruan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R. Illumina sequencing-based analysis of sediment bacteria community in different trophic status freshwater lakes. Microbiologyopen 2017, 6, e00450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz de Miera, L.; Gutierrez-Gonzalez, J.J.; Arroyo, P.; Falagan, J.; Ansola, G. Prokaryotic community diversity in the sediments of saline lagoons and its resistance to seasonal disturbances by water level cycles. J. Soil Sediment 2021, 21, 3169–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Q.; Gu, Q.; Sun, M.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal changes in bacterial community and microbial activity in a full-scale drinking water treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Xiong, Y.; Ge, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhong, X.; Ou, Z.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, M.; Mo, Y.; et al. Composition of gut and oropharynx bacterial communities in Rattus norvegicus and Suncus murinus in China. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffredi, S.K.; Orphan, V.J. Bacterial community shifts in taxa and diversity in response to localized organic loading in the deep sea. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 344–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.Y.; Ham, J.H. Comparative analysis of the microbial community in the sediments of two constructed wetlands differentially influenced by the concentrated poultry feeding operations. J. Soil Sediment 2016, 17, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhou, H.; Xie, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Jia, L.; Wei, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Z.; Ma, Y. Effects of floodgates operation on nitrogen transformation in a lake based on structural equation modeling analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Liao, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, B.; Li, A. Metagenomic insights into salinity effect on diversity and abundance of denitrifying bacteria and genes in an expanded granular sludge bed reactor treating high-nitrate wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 277, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Xie, S.; Liu, Y. Distribution of sediment bacterial and archaeal communities in plateau freshwater lakes. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2015, 99, 3291–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, C.H.T.; Chun, S.; Seo, S.; Cui, Y.; Ahn, C.; Oh, H. Bacterial community enhances flocculation efficiency of Ettlia sp. by altering extracellular polymeric substances profile. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabil, B.; André, P.; Nadia, A.; Claude-Olivier, S.; Hocine, G.; Nabil, M. Enhancement of the denitrification performance of an activated sludge using an electromagnetic field in batch mode. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, D. Gastrointestinal microbiota imbalance is triggered by the enrichment of Vibrio in subadult Litopenaeus vannamei with acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ren, H.; Shen, L.; Lou, L.; Tan, G.; Zheng, P.; Hu, B. pH levels drive bacterial community structure in sediments of the Qiantang River as determined by 454 pyrosequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, B.; Rosi-Marshall, E.; Kelly, J.J. Wastewater Treatment Effluent Reduces the Abundance and Diversity of Benthic Bacterial Communities in Urban and Suburban Rivers. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2013, 79, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Wang, R.F.; Zhong, W.; Ma, Q.L.; Zong, K.J.; Zhao, C.C.; Wang, Q. Advance in Structural Characteristics and Influence Factors of Functional Microbial Communities in the Soils of the Wetlands in the Yellow River Delta. Wetl. Sci. 2022, 20, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, H.E.; Martiny, J.B.H. Microbial composition affects the functioning of estuarine sediments. ISME J. 2013, 7, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh Roy, S.; Wimpee, C.F.; McGuire, S.A.; Ehlinger, T.J. Responses of Bacterial Taxonomical Diversity Indicators to Pollutant Loadings in Experimental Wetland Microcosms. Water-Sui 2022, 14, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Sun, L.Y.; Chu, R.H.; Qian, J. On the characteristic of sediments microbial community structure of urban polluted river. Adv. Water Sci. 2013, 24, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Fang, D.X.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y. Bacterial diversity in surface sediments of Baiyangdian lake and its influencing factors. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2021, 15, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, X.; Chao, L.; Zhang, W.; You, T.; Zhang, J. Diversity change of microbial communities responding to zinc and arsenic pollution in a river of northeastern China. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B 2014, 15, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | ACE | Chao1 | Observed Species | Shannon | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 2196.95 | 2359.70 | 1855 | 9.230 | 0.007 |
| S2 | 6313.38 | 6072.76 | 3693 | 8.877 | 0.010 |
| S3 | 2669.74 | 2694.02 | 2109 | 8.097 | 0.010 |
| S4 | 1677.40 | 1756.59 | 1281 | 8.583 | 0.007 |
| S5 | 1612.06 | 1720.42 | 1271 | 7.743 | 0.023 |
| S6 | 1582.64 | 1678.85 | 1198 | 7.577 | 0.027 |
| S7 | 2521.76 | 2508.33 | 1818 | 7.773 | 0.013 |
| S8 | 1675.04 | 1775.64 | 1340 | 7.950 | 0.017 |
| S9 | 2880.12 | 2995.85 | 2290 | 9.030 | 0.010 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Zhao, R.; Qiu, X.; Wan, Y.; Lee, L. Structural Diversity of Bacterial Communities and Its Relation to Environmental Factors in the Surface Sediments from Main Stream of Qingshui River. Water 2022, 14, 3356. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213356
Zhao Z, Zhao R, Qiu X, Wan Y, Lee L. Structural Diversity of Bacterial Communities and Its Relation to Environmental Factors in the Surface Sediments from Main Stream of Qingshui River. Water. 2022; 14(21):3356. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213356
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zengfeng, Ruizhi Zhao, Xiaocong Qiu, Yongpeng Wan, and Lin Lee. 2022. "Structural Diversity of Bacterial Communities and Its Relation to Environmental Factors in the Surface Sediments from Main Stream of Qingshui River" Water 14, no. 21: 3356. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213356
APA StyleZhao, Z., Zhao, R., Qiu, X., Wan, Y., & Lee, L. (2022). Structural Diversity of Bacterial Communities and Its Relation to Environmental Factors in the Surface Sediments from Main Stream of Qingshui River. Water, 14(21), 3356. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213356






