Abstract
Microplastics (MPs) are widely distributed in the environment. MP pollution has been found in the environment globally, which directly threatens human health. It is of great importance to study the influencing factors and mechanism of MP migration in the vadose zone to evaluate its distribution and environmental risk accurately. Through a literature review, the source, migration, and transformation of MPs in the vadose zone were summarized, and the influencing factors of MP migration in the vadose zone were systematically expounded. The mechanism of MP migration was analyzed, and future research was suggested. The factors affecting the migration of MPs can be divided into chemical, physical, and biological categories. At present, research on the migration of MPs in the vadose zone is in its infancy. In a further study, the migration of MPs at the field scale, the synergistic migration and transformation of MPs with other pollutants and the mutual feedback mechanism, and the use of the properties and biological functions of the vadose zone to study the role and mechanism of MPs in global carbon neutralization are worthy of attention.
1. Introduction
Plastics have accelerated changes in social production and lifestyles. Plastic has become the main raw material for producing daily items such as food packaging, water bottles, single-use medical supplies in the medical industry, personal care products, clothing, and textiles that improve the quality of human life. The name ‘plastic’ derives from the Greek word ‘plastikos’, which means that it can be shaped into miscellaneous forms [1]. Plastic has become one of the most significant pollutants in a diverse environment, and plastic pollution has emerged as an international issue. Therefore, it has received global attention [2]. Indeed, plastic production increased from 2 million tons in the 1950s to 367–381 million tons in the 2020s. The development of high technology and the science of human life has led to the growth of plastic pollution in different ecosystems [3,4,5,6] related to the unlimited sources of plastic waste.
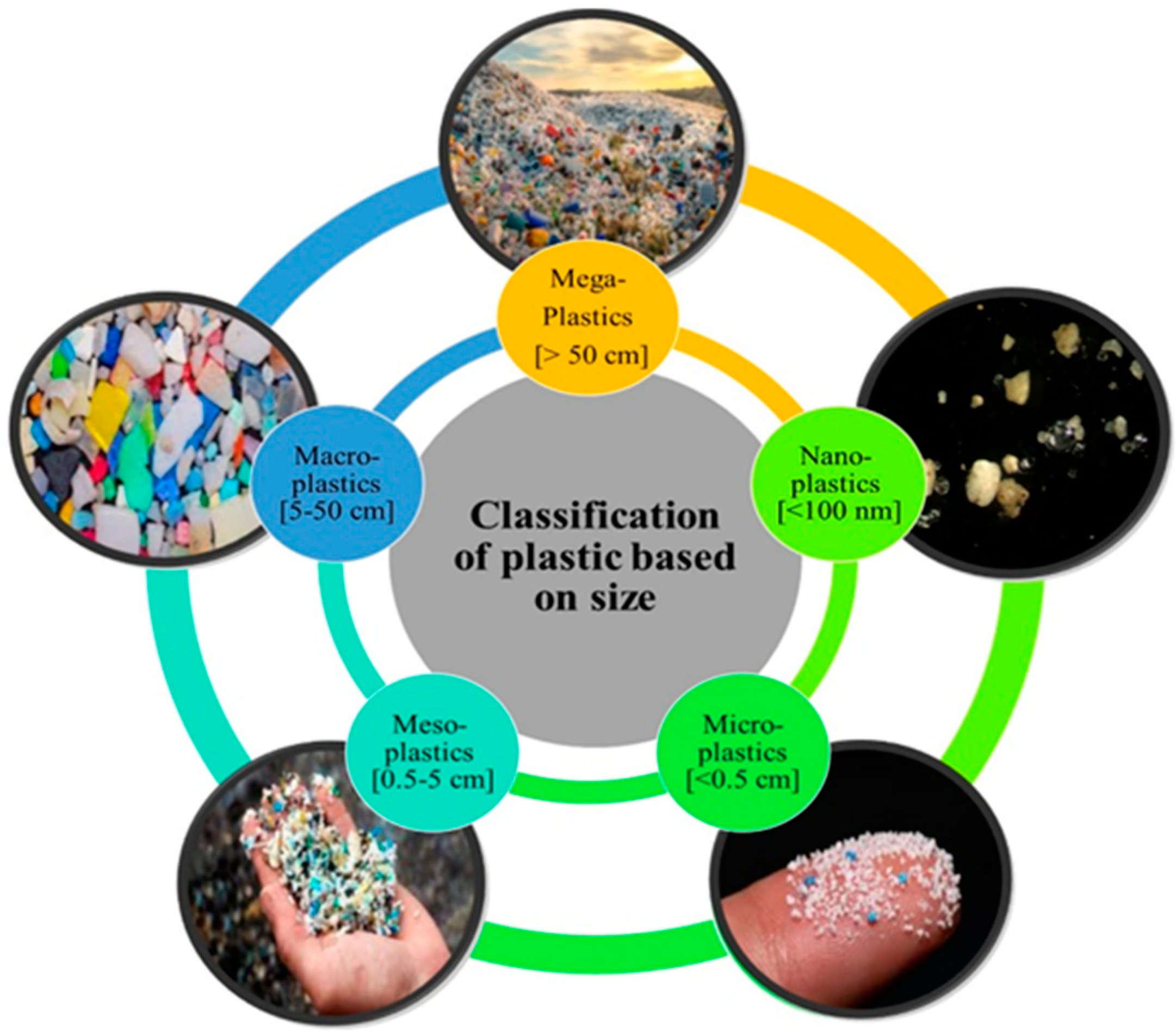
Plastic particles can be classified into five classes according to size (Figure 1): Megaplastics [>50 cm]; Macroplastics [5–50 cm]; Mesoplastics [0.5–5 cm]; Microplastics [<0.5 cm]; Nanoplastics [(NPs) (<100 nm)] [7,8]. This definition does not distinguish between the diverse types, origins, and physical properties of plastic, all of which have a strong influence on their prevalence, transport, and effects on the environment. Additionally, the term “microplastic” [MP] was formally introduced in 2004 by Thompson, who identified the rising pollution problem of plastic discharged into the seas. MPs are defined as plastic fragments (a wide range of multiple colors, polymers, particle sizes, and densities) which are less than 5 mm in any dimension [7], while “nanoplastics” are commonly under 100 nm in any dimension. Nevertheless, previous studies showed discrepancies in the range of MP sizes and the progress of the terms due to their impact [9]. Microplastics are not just one contaminant, which is often misunderstood by some scientists and policymakers [2]. According to the particle shape, MPs display various forms such as fragments, fibers, beads, granules, pellets, and film. In addition to a large amount of significant research, reviews have been carried out on MPs in different environments, including water systems (oceans, estuaries, surface water, freshwater), sediments (beaches, marine sediment), and soils, atmosphere, and the biota in various ecosystems [10].
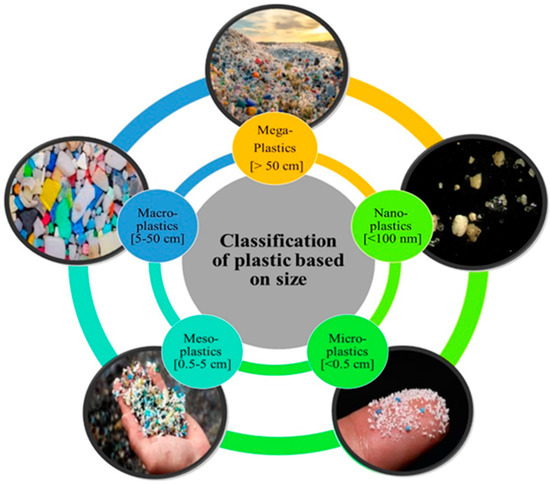
Figure 1.
Classification of plastic based on size.
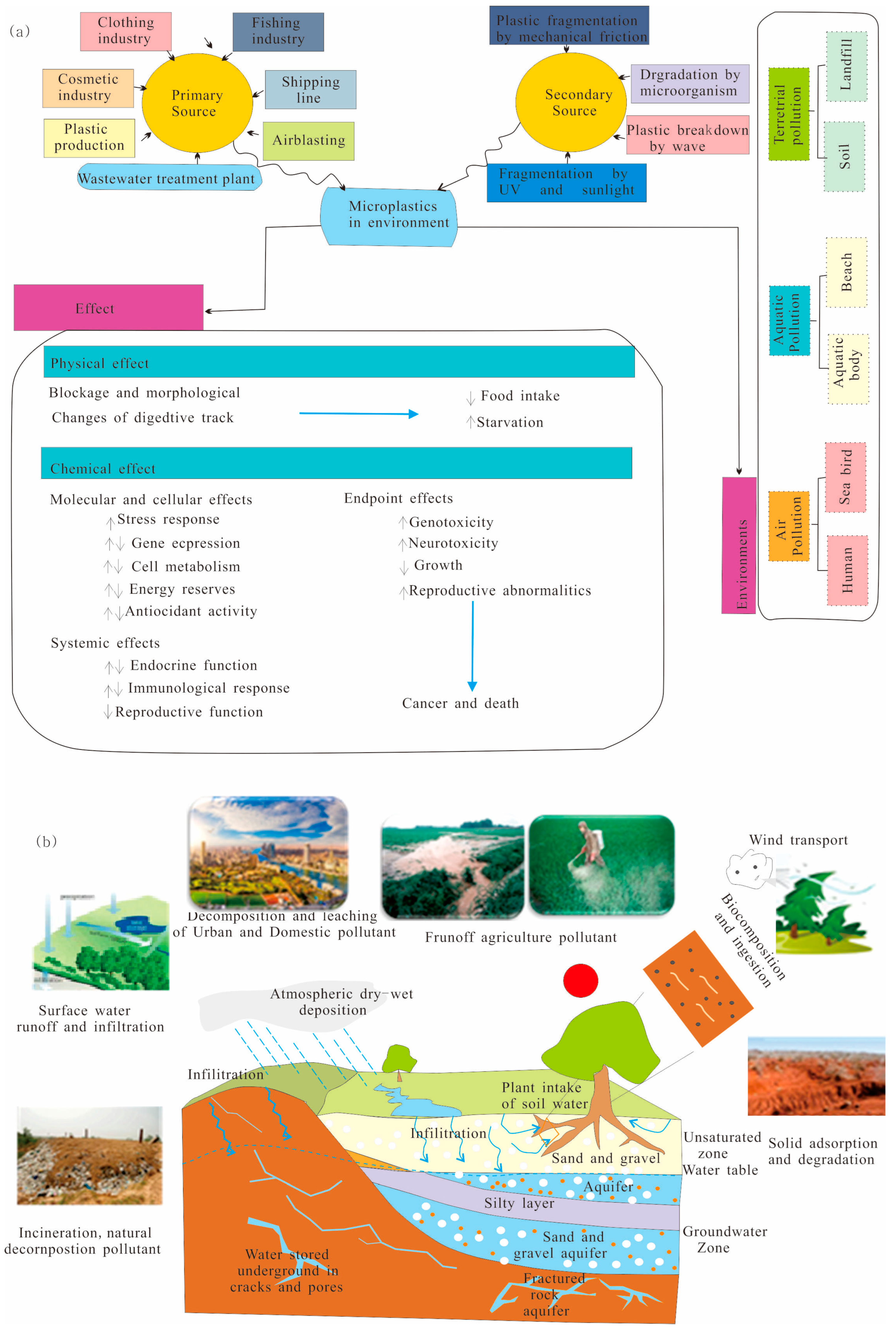
MPs are usually produced by direct industrial production or large plastic cracking. The origin and sources of MPs can be classified into two main groups, primary and secondary microplastics (Figure 2). Primary MPs are small-sized industrially manufactured pellets, microbeads, and fragments used in plastic manufacturing and packing, the product of industrial mixtures used for air-blasting media, sandblasting, shot blasting, abrasive media [11], clothing industry, the fishing industry, shipping line, tires, pharmaceutical drugs, and personal care products (e.g., microbeads, cleaning products such as hand and facial cleansers, toothpaste, and the cosmetics industry), and other chemical products, which enter different environments directly. Secondary MPs are derived by the degradation, decomposition, and fragmentation of larger plastic materials, such as plastic bags, nylon ropes, fibers, fabrics, spandex, acrylics, and polyester produced from laundry and textile factories, and films produced from agrochemical use weathering in various environments [12,13,14]. MPs have physical and chemical effects on the environment and human health. Physical effects include blockage and morphological changes in the digestive tract, which can decrease food intake and increase the degree of starvation. However, the influence of chemical effects is reflected in molecular and cellular effects by systemic effects and endpoint effects. These MP effects, including genotoxicity and neurotoxicity, inhibit the organism’s growth, which further causes harmful effects, for instance, cancer and death.
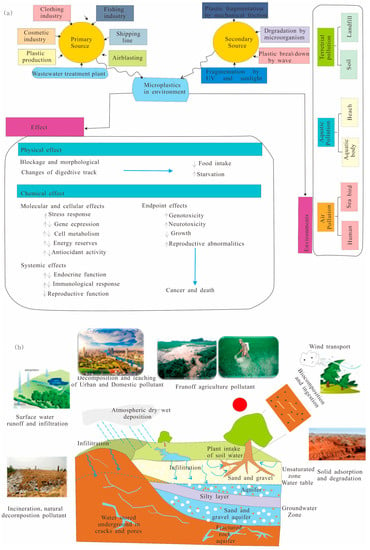
Figure 2.
(a) Sources, environments, and effects of microplastics after [3]. (b) Pollution source and migration of MPs in the vadose zone.
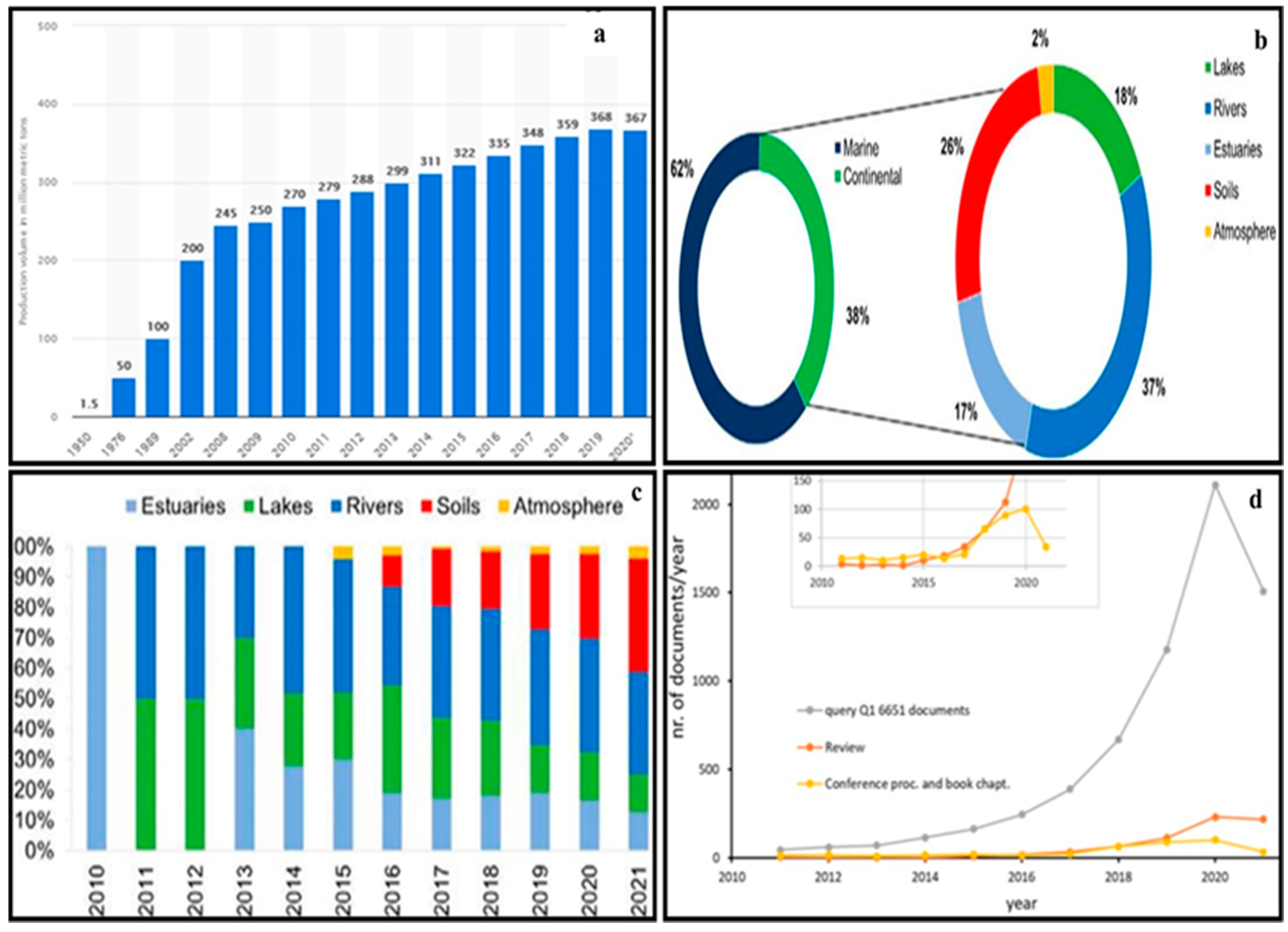
In recent years, the problem of MP pollution has attracted great attention from researchers worldwide and has become a hot research topic due to the increasing use and production rate of plastics. At the Second United Nations Environment Assembly in 2016, MP pollution was included as the second-largest scientific issue in the environment and ecology fields (Figure 3a,b). Furthermore, because MPs do not degrade easily and can exist in the environment for a long time, they pose a potential threat to the ecological environment when the particle size of MPs reaches the nanometer level. In addition, plastic pollution increases because nano-MPs usually exhibit a stronger migration ability and a wider pollution range in the environment. Additionally, the biotoxicity is more pronounced. MPs in the environment can be eaten by animals, enriched layer by layer through the food chain, and finally enter the human body, threatening human health [8,15,16].
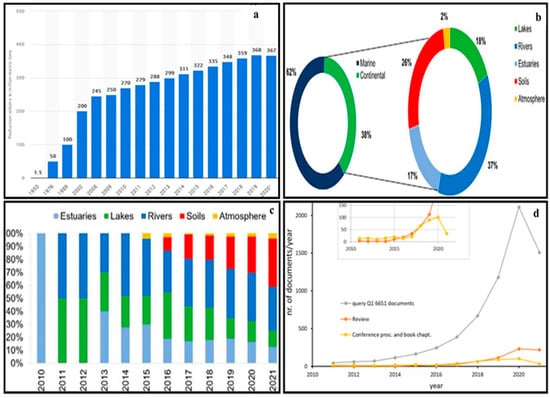
Figure 3.
(a) The percentage of microplastics studied in marine and continental environments, lakes, rivers, estuaries, soils, and the atmosphere. (b) An analysis of European plastics production. (c) Percentage of studies in each type of continental environment per year. (d) The trend of the number of total documents, reviews or conference proceedings, and book chapters published from the year 2010 [5,12,17].
At present, the publication scope includes the sources, occurrence, behavior, distribution patterns, and the best analytical methods for separation, identification, quantification, migration, transformation, and interaction with different environmental constituents and ecosystems (Figure 3) [12]. In addition, many bibliographic reviews have been submitted according to the statistics data analysis of the different types of scientific literature related to the several problems of MPs (Figure 3d); it is derived from social networks combined with specific fields of science, such as the SCOPUS database and Web of Science, by using closely related keywords of ‘microplastic’ and ‘environment’, in addition to using some software such as VOS viewer to extract scientific analysis maps and graph plotting. The research results returned a huge number of published papers around the world. The number of publications is growing exponentially, and the results of the analysis could significantly change over months or even weeks [13]. Researchers studied MP contamination in groundwater because they found plastic fibers in the groundwater in the United States and Germany with a maximum abundance of 7–15,200g/m3 [13]. The vadose zone has an important impact on the environment. The upper interface of the vadose zone is the ground (direct contact with the atmosphere), which is not only the bearing surface of rainfall but also the evaporation surface of soil water (Figure 2b). The lower interface is the surface of the groundwater. After rainfall seeps into the vadose zone, part of it is absorbed by the soil and temporarily stored in the vadose zone to become soil water, and part of it is converted into a middle soil stream and underground runoff. The vadose zone is the transition zone of pollutant migration to groundwater, which plays a key role in the recharge of groundwater by atmospheric precipitation and the evaporation of groundwater through the vadose zone. China is a major producer and emitter of plastic waste, and agricultural soil and the related groundwater environment are seriously threatened by MP pollution [8]. A study on the migration behavior of MPs in the vadose zone has important theoretical significance and practical value for the comprehensive evaluation and prediction of pollution risk in the vadose zone. Most current review articles focus on the environmental behavior and ecological effects of MPs in soil and groundwater, but the mechanism of MP migration in the vadose zone is not fully explained.
This work concentrates on MP pollution in the vadose zone. In general, MP pollution transportation is linked to the water in soils and rocks in the vadose zone. Consequently, quantitative analysis of contaminant transport must first evaluate water fluxes into and through the vadose [18]. This review paper summarizes the existing research progress on the migration of MPs in the vadose zone (unsaturated zone). Furthermore, this paper analyzes the possible sources of MPs in the unsaturated zone, clarifies the chemical, physical, and biological factors that affect the migration of MPs in the unsaturated zone, shows the mechanism that affects the migration of MPs, and finally, recommends prospects and development directions for future research.
2. The Source, Types, and Properties of MPs in the Vadose Zone
2.1. The Source of Microplastics in the Vadose Zone
MPs in the vadose zone come from different environments. Water systems (estuaries, surface water, freshwater), sediments (beaches, marine sediment), soils, and the biota in various ecosystems] (Figure 2b). Primary microplastics from different industrial product mediums can directly enter the area from sewage and wastewater and then go into the vadose zone; secondary microplastics enter the zone indirectly after weathering in various environments [15,16,19]. According to the distribution breadth, the origin can be classified into two main types of sources. The first type is point source pollution (coming from a single point, such as a factory or sewage plant). Point source pollution mainly includes the use of sludge, the application of organic fertilizer, wastewater irrigation, sewage discharge, etc. The second type is non-point source pollution and comes from agricultural plastic film, garbage incineration, garbage landfills, and atmospheric deposition [20]. It is reported that a large number of different types of MP particles (up to 2.2 × 107 particles per day) still exist in the water after tertiary treatment in sewage treatment plants, of which polypropylene is the most abundant, mainly in the form of fiber (67%) and film (18%) [21]. In addition, landfills have also been proven to be a potential source of MPs. A total of 17 types of MPs were detected in 12 leachate samples, of which 99.36% were formed by plastic debris buried in landfills [22]. These MPs are derived from plastic beads in personal care products or detergents, such as masks and gloves, accidental loss of plastic particles in factories and transportation, fiber loss in textiles during washing, etc. [23]. Moreover, there are a large number of MPs particles in farmland wastewater irrigation, and the residuals from plastic film used in agricultural production lead to the continuous enrichment of MPs in soil. Sources of atmospheric MPs include industrial smoke emissions, synthetic textiles, abrasion and corrosion of synthetic rubber tires, plastic debris from building materials, waste incineration, and landfill exposure [24]. Diverse ways of migration and transportation in the vadose zone mean that MPs can also enter the aboveground environment through plant absorption and food chain transmission. MPs can be accumulated in organisms during migration and then transferred in food chain links layer by layer.
2.2. The Main Types and Properties of MPs in the Vadose Zone
Consistent with global production, there are several types and composites of polymer plastic categories depending on their uses (Figure 4). We can summarize them into polyethylene (PE), which includes two types, (1) high-density polyethylene (HDPE), which is used in bottles and containers for drinks, detergent, soap, bags, extruded pipe, and wire covering, and (2) low-density polyethylene (LDPE), used for bags (such as garbage bags), squeeze bottles, container lids, and beverage cups. Polypropylene (PP) is used for food containers, bottles for medicine and caps, and fibers. Polyester, polyamide, and acrylic fibers (PP&A) is used in plastic containers, water bottles, fibers for clothing, and plastic bags. Polystyrene (PS) is used for CD boxes, food containers, plates, cups, bowls, house insulation, coats, medical, foam, and egg cartons. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is used in bottles, cartons, food jars and trays, cloth, films, monofilaments, and carpets. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is used to make pipes, medical tools (bags, tubing), and window frames. PE, PP, and PP&A are the three most common plastic types. There are other plastic polymers, such as poly (vinyl stearate) (PVS), polyepoxide (epoxy resin), ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), paraffin wax, polycaprolactone (a biodegradable polyester), rayon (a semi-synthetic has been used in cigarette filters), personal hygiene products, and clothing, which can enter the ocean through sewage [25]. In China, there is increasing use and production of agricultural films annually. It is reported that the use of agricultural film in China increased by 15% to 30% between 1991 and 2004. On the other hand, it increased from 1.85 × 106 t to 2.60 × 106 t [26] between 2006 and 2015. That means a huge quantity of agricultural films has been used year after year. There are many kinds of interactions between MPs and pollutants. Plastic debris has been detected in air, oceans, soils, sediments, and surface waters worldwide. Because the vadose zone has an intimate relationship with the air, soil, and water in transformation, different experimental approaches have been used to investigate MPs’ deposition kinetics in systems representative of the unsaturated (vadose) and water-saturated zones of the subsurface environment [27].

Figure 4.
Categories of polymer plastic depending on their uses (after https://www.plasticsforchange.org/blog/different-types-of-plastic, accessed on 26 September 2022).
3. Migration Mechanism
After entering the vadose zone environment, MPs may migrate longitudinally along with underground water flow [28]. Likewise, they can degrade and transform in the terrestrial water environment; they can also be absorbed and accumulated by organisms in the vadose zone during the migration process, consequently entering, accumulating, and transferring in different food chain links to form biological transmission. Indeed, the influences affecting the migration of MPs can be divided into three main factors, chemical, physical, and biological categories [29,30,31]. Table 1 summarizes the influencing factors and effects of MP migration in the unsaturated zone.
3.1. Characteristics of Microplastics in the Vadose Zone
The characteristics of MPs include both physical (size, density, color, shape, and crystallinity) and chemical (chemical composition and surface groups) properties. Particle size is the most significant condition for MPs to enter groundwater because large MP fragments may be trapped in the soil through filtration [32]. Hereafter, exceedingly small plastic fragments in the range of nanoparticles or colloids can enter groundwater through large pores and thicker aeration belts. Instead, Horton AA [33] suggests that the plastics in the topsoil are exposed to ultraviolet radiation and transformed into microplastic fragments. UV radiation from the sun oxidizes the polymer matrix and leads to the formation of bond fractures.
3.2. Hydrometeorological Factors
Microplastic transportation into the vadose zone is controlled by rain, snow, surface water, and atmospheric conditions, whereas microplastics deposited in soil are fragmented by gravity and can be transported to water aquifers [34]. Liu suggested that changes in surface water levels promoted the migration of heavy metals [35], whereas the pollution of heavy metals and microplastics appeared to be synergistic [35].
3.3. Effect of Chemical Factors on the Migration of MPs in the Vadose Zone
The main chemical factors include ionic strength and type, pH, and dissolved organic matter (DOM). Other hydrochemical conditions in the vadose zone environment, as well as the chemical properties of the vadose zone medium, are crucial factors affecting the migration of MPs. The effects of DOM and high valence cations on the migration of MPs in the vadose zone medium; therefore, the migration of MPs in the vadose zone decreases with increasing ionic strength [36,37]. Furthermore, migration of MPs in the vadose zone is usually enhanced with increasing pH. The presence of DOM in an unsaturated zone usually improves the migration ability of MPs. DOM can be adsorbed on the surface of vadose media by a covalent (covalent(π-π)) bond and hydrogen bond to enhance the surface electronegativity of the media. Wu et al. concluded that MPs had a high migration ability in sandy soil and black soil, whereas, in red soil, it was very low. In addition, a certain amount of cations (Na +, Mg 2 +, Ca 2 +, and Al 3+) may be released in the vadose zone medium under the condition of pH change or water renewal [38], producing an increase in the concentration and type of cations [39,40,41]. Predominantly, the increase in ion concentrations will lead to an increase in ion strength and will consistently increase the deposition of MPs on the medium surface and reduce their migration ability [35].
3.4. Effect of Hydrogeological Factors on the Migration of MPs in the Vadose Zone
Hydrogeological properties and conditions, such as particle size, saturation, heterogeneity, and flow conditions, unquestionably show a significant effect on the migration behavior of MPs. The migration ability of MPs usually decreases with decreasing particle size of the vadose zone medium [42]. The smaller the particle size of the vadose zone medium, the larger the specific surface area and roughness, causing enhancement of the ability of the medium surface to adsorb MPs. In addition, the smaller the pores and permeability are, the more obvious the filtering effect. More MPs can be deposited in the vadose zone medium during the migration process, hence proving a low migration ability. The migration ability of MPs usually decreases with the decrease in medium saturation in the vadose zone. The frequent alternation of wetting and drying promotes vertical migration of MPs in the vadose zone [37]. Furthermore, the water–air interface has a high capillary attraction for MPs, which can control the migration of MPs in water and deposit them at the water–air interface [43]. Once the unsaturated zone saturation increases, the bubbles decompose, and the water–gas interface disappears; thus, the deposited MPs can be released to the water phase and continue to migrate with the water flow. The unsaturated zone medium usually has strong heterogeneity. Because the permeability of each soil part constituting the heterogeneous medium is often quite different, the unsaturated zone medium generates many advantageous channels and preferential flows. The preferential flow in the dominant channel of heterogeneous medium is often high; therefore, it can dominate the migration behavior of MPs. This means MPs migrate mainly through the dominant channel; moreover, this chief role is usually more obvious with the increase in pore water velocity. The migration ability of MPs in the unsaturated zone generally increases with the increase in the pore water flow rate. With the increase in the pore-water flow rate, the shear and stress of fluid in the migration process of MPs increases due to the shortening of the deposition time on the surface of the medium in the vadose zone, which makes it more difficult to deposit on the surface of the medium in the vadose zone, and the migration ability is significantly improved [31].
3.5. Effect of Biological Factors on the Migration of MPs in the Vadose Zone
Biological life activity is a principal factor affecting the migration of MPs in the soil environment. MP particles in the soil and pore water may adhere to the surface of small animals, microorganisms, bacteria, or feed [44]. These attached or ingested MPs can migrate with the movement of small animals or microorganisms to other areas of the soil and remain there by shedding, excretion, and death. In addition, pores formed by small animal activities, caves caused by the excavation of mammals, and soil fissures caused by plant root development supply dominant pathways, making it easier for MP particles to migrate from the surface soil layer to the deep soil layer under gravity. It is generally believed that the vertical migration of MP particles in the soil is an important source of MP pollutants in groundwater. In the presence of hydrophilic biofilm, the effect of ionic strength on the deposition of MPs on the surface of the vadose zone medium is more obvious, which makes the migration ability of MPs lower under high ionic strength conditions.

Table 1.
Influence factors of MPs migration in unsaturated porous media.
Table 1.
Influence factors of MPs migration in unsaturated porous media.
| Factor | Changes in MPs with Influencing Factors | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MPs | Characteristics of MPs | Particle size, shape, surface morphology, and density of MPs [27] | Smaller MPs and very small plastic fragments within the range of nanometer particles or colloids migrate easily, and large particles may cause blockage; the shape of MPs affects soil aggregate formation and organic decomposition in the soil system. |
| Hydrometeorological factors | Surface runoff, dry and wet deposition, wind and sun exposure | In the event of rain and snow, microplastics deposited in the soil are fragmented by gravity and can be transported further to the aquifer; the change in surface water level promotes the migration of microplastics. | |
| hydrogeology factor | Hydrodynamic condition | Flow;Topographic conditions [45] | MPs in the soils can be released and transported by water flow through the vadose zone to enter the groundwater under various conditions [19]. Microplastics migrate mainly through dominant channels, and this dominant effect is usually more pronounced with an increase in pore water flow velocities [46]. |
| Hydrogeological properties of the surrounding rock | Particle size; surface roughness; heterogeneity; saturation [47] | With increased pore water flow rate, the MPs’ capacity is enhanced; the smaller the medium particle size, the higher the medium roughness, and the smaller the medium saturation are, the lower the MPs’ capability is; MPs migrate mainly through dominant channels; frequent alternation of wetting and drying promotes vertical migration of MPs in the vadose zone [27]. | |
| Chemical factor | Chemical Properties of MPs | Chemical composition; surface functional groups; hydrophobicity; surface charge | The particle surface electronegativity and hydrophilicity are enhanced, and the migration ability in the soil medium is significantly enhanced. Migration ability of MPs with different surface functional groups [36]. The transport of MP particles could be dramatically mitigated with increased hydrophobicity after they enter the vadose zone if they behaved as colloids. |
| Chemical properties of the medium | Medium mineral composition; surface charge; pH, and chemical bond between ions | The higher the Fe/Al oxide content, the lower the migration ability of MPs; the cations released on the medium surface may reduce the MPs’ capacity; the migration ability of MPs decreased with the increase in ionic strength or the presence of high valence cations. | |
| Chemical properties of water flow | pH; organic matter composition; colloid; coexistent pollutants [34] | Increased pH and dissolved organic matter can enhance MPs’ capacity. | |
| Biological factor | Plant response | Plant absorption, root fissure; root exudates [48] | Fractures formed by root development enhance the migration of MPs. |
| Animal effect | Animal feeding and sports activities [19] | Migration of MPs with feeding and movement of small animals. | |
| Microbial effect | The existence of microorganisms and biofilms [49] | Microorganisms exist, and MPs’ capacity decreases. | |
4. Study on Synergistic Migration and Transformation of MPs and Other Pollutants in Inflated Zone
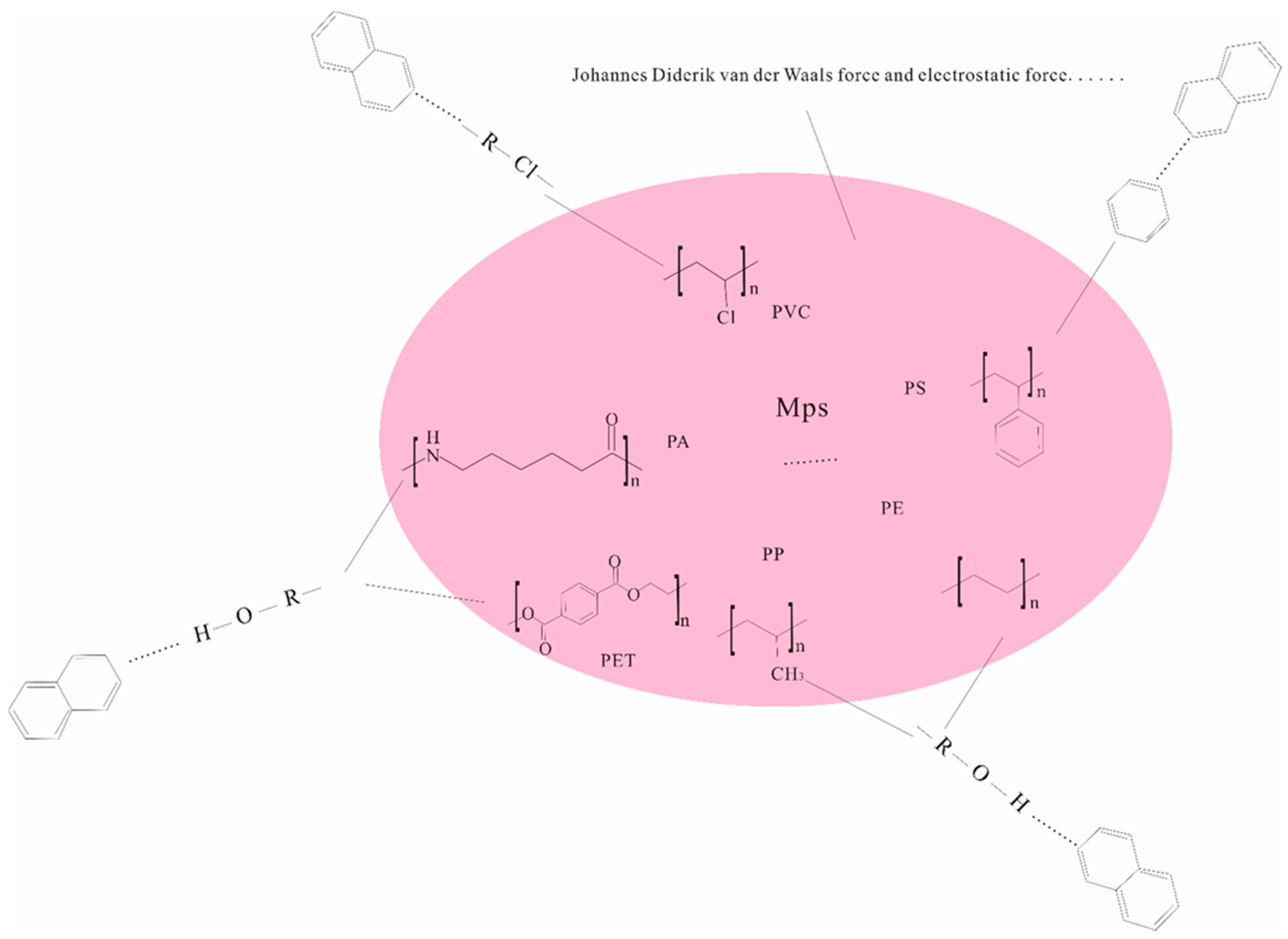
The types of MPs involved in this study mainly include PS, PE, PP, PVC, PA, PET, etc., and there are many kinds of interactions between MPs and pollutants (Figure 2b). The surface of PE and PP is only composed of C-C and C-H. For example, PS shows a stronger adsorption affinity for PCBs than PE due to hydrophobic and π-π interactions. The adsorption ability of PAHs is also stronger than that of non-aromatic polymers such as PE, PP, and PVC. PA-containing amide groups composed of something bonds are easy to form adsorption with contaminants through a hydrogen bond, which makes PA-containing MPs more capable of adsorption than other materials. PA is more hydrophilic and therefore has a higher affinity for hydrophilic organic compounds such as antibiotics [26]. Halogen bonds may be formed between halogen atoms on the surface of PVC and π electrons (as electron donors) of the benzene ring. Halogen bonds may also promote the adsorption of bisphenol compounds on PVC MPs [6] (Figure 5).
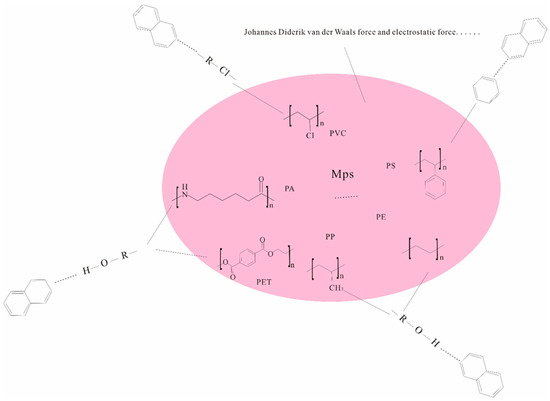
Figure 5.
The main mechanism of interaction between MPs and pollutants.
The co-migration behavior of MPs and other pollutants (such as heavy metals and nonmetals) in the vadose zone is one of the significant environmental behaviors of MPs, likewise, an essential process directly determining the composite effect of MPs and pollutants [50]. MPs have various effects on numerous chemical forms of heavy metals, especially total dissolved solids (TDS), in the vadose zone. The presence of MPs promotes the transformation of heavy metals from bioavailable to stable organic binding and reduces their bioavailability. In general, responses of heavy metals to the addition of MPs in different particle size fractions of vadose zone media are different [51]. Small particles such as clay minerals, metal oxides, hydroxides, humus, and microorganisms in the vadose zone bind organic pollutants and heavy metals in varying degrees through van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonds, ion exchange, and charge transfer, ligand exchange, and cation bridging [52,53]. At present, there are many studies on the adsorption and desorption of MPs with other pollutants, but the common migration with other pollutants is still limited. It is worth noting that the relevant experts’ studies on the synergistic migration between MPs and pollutants mostly focus on the influence of MPs on pollutant migration, the influence of pollutants on the migration and distribution behavior of MPs in porous media, and the mechanism of action need to be further expanded and deepened. The accumulation of MPs can affect the production of greenhouse gases CO2 and NO2 by changing the structure of the vadose zone and microbial function [54].
5. Conclusions and Outlook
In summary, the migration of MPs in the unsaturated zone is affected by many chemical, physical, and biological factors, and it is easy for MPs to absorb other heavy metals and organic pollutants. However, the research on the migration of MPs in the unsaturated zone is still in its infancy, and a complete and comprehensive knowledge system has not yet been formed. In further research, the following issues deserve attention.
(1) At present, most studies on the migration of MPs in the vadose zone are carried out through laboratory tests or in situ shallow soil analysis. Although laboratory tests can well clarify the mechanism of factors affecting the migration of MPs, it is difficult to reflect the complexity of the real vadose zone environment. Therefore, it is urgent to carry out field-scale plastic migration studies.
(2) In-depth study on the enrichment, migration, and transformation mechanism of MPs in the vadose zone, using the properties and biological functions of the vadose zone to study the role and mechanism of MPs in global carbon.
(3) Study of the synergistic migration and transformation of MPs and other pollutants in the vadose zone. There are many kinds of MPs, which have different coupling modes and stability with other pollutants. However, the hydraulic connection in the vadose zone is varied, and the decomposition, adsorption, and migration of MPs in the vadose zone may be affected by various conditions. Therefore, it is also urgent to explore the transformation behavior of MPs and their synergistic pollutants in the vadose zone migration process.
Author Contributions
R.-P.L., F.L. and H.-Q.C. conducted the investigation, experiments, and sampling. R.-P.L. wrote the manuscript. J.-G.J., Y.D., Y.-B.Z. and P.-P.S. helped R.-P.L. conceive the original idea. J.-G.J. and E.-W.R.M. polished the English manuscripts. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the survey projects initiated by the Land and Resources Investigation Project (1212011220224), Basic Research Project of Natural Science in Shaanxi Province in 2015 “2015JM4129”, and Basic Research Project of Scientific Research Business Fee of Central University in 2016 (Open Fund) 310829161128. Investigation on geological environment effect of Qinghai mining industry development (121201011000150022).The Qinghai-Tibet scientific research project “Geological Background Investigation of Freeze-thaw Disaster Development in Permafrost Regions of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (2019QZKK0905)”, Xi’an Geological Safety Investigation Evaluation and Risk Management Demonstration (DD20211317), and Xi’an Multi-factor Urban Geological Survey (DD20189220), Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Program No. 2021ZDLSF05-01.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are also grateful to the experiment and testing lab of Xi’an Center, China Geological Survey, for statistical data analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Rajmohan, K.V.; Ramya, C.; Sunita, V. Plastic pollutants: Effective waste management for pollution control and abatement. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2019, 12, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Xie, Y.; Sun, X.; Du, H.; Wang, J. Identification and Quantification of Microplastics in Aquaculture Environment. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 804208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.-P.; Dong, Y.; Quan, G.-C.; Zhu, H.; Xu, Y.-N.; Elwardany, R.M. Microplastic pollution in surface water and sediments of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Current status and causes. China Geol. 2021, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, S.; Jesuraja, K.; Venkatramanan, S.; Roy, P.D.; Kumari, V.J. Hazardous microplastic characteristics and its role as a vector of heavy metal in groundwater and surface water of coastal south India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 402, 123786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Huang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, F.; Chen, H.; Quan, G.; Yan, J.; Li, T.; et al. Environmental occurrences, fate, and impacts of microplastics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at Sea: Where Is All the Plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmas, S.; Annalisa, V.; Laura, M. Bibliometric Analysis on the Papers Dedicated to Microplastics in Wastewater Treatments. Catalysts 2021, 11, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. The plastic in microplastics: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmeester, H.; Hollman, P.C.H.; Peters, R.J.B. Potential Health Impact of Environmentally Released Micro- and Nanoplastics in the Human Food Production Chain: Experiences from Nanotoxicology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8932–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devriese, L.; De Witte, B.; Vethaak, A.D.; Hostens, K.; Leslie, H.A. Bioaccumulation of PCBs from Microplastics in Norway Lobster Nephrops N: An Experimental Study. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fen, Q.; Du, J.; Gao, J.; Liu, G.Y.; Song, Y.Q.; Yang, A.F.; Wang, H.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Q. Bibliometric Profile of Global Microplastics Research from 2004 to 2019. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panno, S.V.; Kelly, W.R.; Scott, J.; Zheng, W.; McNeish, R.E.; Holm, N.; Hoellein, T.J.; Baranski, E.L. Microplastic contamination in Karst groundwater systems. Groundwater 2019, 572, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Pu, S.; Lv, X.; Gao, Y.; Ge, L. Global trends and prospects in microplastics research: A bibliometric analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 5, 123110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, T.K.; Uddin, E.; Jamal, M. Detection and removal of microplastics in wastewater: Evolution and impact. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 16925–16947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Lambert, S. Microplastics Are Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Freshwater En-vironments: An Overview.in Freshwater Microplastics. Freshw. Microplastics 2018, 58, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkul, M.M.; Özhan, H.O. Microplastic Contamination in Soils: A Review from Geotechnical Engineering View. Polymers 2021, 13, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Su, J.; Xiong, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, C.; Liu, J. Microplastic pollution of lakeshore sediments from remote lakes in Tibet plateau, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lyu, X.; Li, Z.; Gao, B.; Zeng, X.; Wu, J.; Sun, Y. Transport of polystyrene nanoplastics in natural soils: Effect of soil properties, ionic strength and cation type. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 136065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, R.M.; Waldron, S.; Gauchotte-Lindsay, C. Average daily flow of microplastics through a tertiary wastewater treatment plant over a ten-month period. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Chen, L.; Shao, L.; Zhang, H.; Lü, F. Municipal solid waste (MSW) landfill: A source of microplastics? -Evidence of microplastics in landfill leachate. Water Res. 2019, 159, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, E.; Nowack, B.; Mitrano, D.M. Polyester Textiles as a Source of Microplastics from Households: A Mechanistic Study to Understand Microfiber Release during Washing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7036–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Li, X.; Xiao, J. Characteristics of daily extreme wind gusts on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. J. Arid Land 2018, 10, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.K.A.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junhua, H.; Wen-Bing, T.; Hong, Y. Microplastics in soil ecosystem: A review on sources, fate, and ecological impact. Environ. Eng. 2020, 38, 16–27. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, W.; Chen, G.; Bao, J.; Song, M.; Li, Y.; Luo, C. Interactions between microplastics and organic compounds in aquatic environments: A mini review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimi, O.S.; Farner Budarz, J.; Hernandez, L.M.; Tufenkji, N. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Aquatic Environments: Aggregation, Deposition, and Enhanced Contaminant Transport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anika, L.; Eva, F.L.; Maurice, G.; Matthias, C.R. Microplastics have shape and polymer-dependent effects on soil processes. Ecol. Environ. Conserv. 2020, 530, 130054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.L.; Bi, E.P. Effects of dissolved organic matter on the sorption of organic pollutants to soils. Environ. Chem. 2014, 33, 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.M.; Su, C.Y.; Wu, S.M. Effects of PES and 2,4-DPC the on the Extracellular Polymeric Substances and microbial community of anaerobic granular sludge. Environ. Sci. 2020, 42, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Coffin, S.; Sun, C.; Schlenk, D.; Gan, J. Negligible effects of microplastics on animal fitness and HOC bioaccumulation in earthworm Eisenia fetida in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, X. Review on the environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of microplastics in soil-groundwater. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2020, 15, 44–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bläsing, M.; Amelung, W. Plastics in soil: Analytical methods and possible sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.-P.; Xu, Y.-N.; Rui, H.-C.; Rm, E.-W.; Dong, Y. Migration and speciation transformation mechanisms of mercury in undercurrent zones of the Tongguan gold mining area, Shannxi and impact on the environment. China Geol. 2021, 4, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Pan, S.; Li, P.; Wang, L.; Hou, R.; Wu, W.-M.; Luo, J.; Hou, D. Vertical migration of microplastics in porous media: Multiple controlling factors under wet-dry cycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colpaert, R.; Petit dit Grézériat, L.; Louzon, M.; de Vaufleury, A.; Gimbert, F. Polyethylene microplastic toxicity to the terrestrial snail Cantareus aspersus: Size matters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 29258–29267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Rong, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, S.; Yang, M.; Tong, M. Bacteria have different effects on the transport behaviors of positively and negatively charged microplastics in porous media. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Cai, Z.; Jin, H.; Tang, Y. Adsorption mechanisms of five bisphenol analogues on PVC microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 650, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Yi, K.; He, L.; Han, P.; Tong, M. Transport and deposition of microplastic particles in saturated porous media: Co-effects of clay particles and natural organic matter. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Sun, Y.; Gao, B.; Shi, X.; Xu, H.; Wu, J.; Wu, J. Retention and transport of graphene oxide in water-saturated limestone media. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.-P.; Zhu, H.; Liu, F.; Dong, Y.; El-Wardany, R.M. Current situation and human health risk assessment of fluoride enrichment in groundwater in the Loess Plateau: A case study of Dali County, Shaanxi Province, China. China Geol. 2021, 4, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.-P.; Li, Z.-Z.; Liu, F.; Dong, Y.; Jiao, J.-G.; Sun, P.-P.; Rm, E.-W. Microplastic pollution in Yellow River: Current status and research progress of biotoxicological effects. China Geol. 2021, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.P.; Xu, Y.N.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, W.K.; El-Wardany, R.M. The effect of heavy metal pollution on soil and crops in farmland: An example from the Xiaoqinling Gold Belt, China. China Geol. 2020, 3, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.H.; Jia, C.; Xu, Y.L.; Xu, Y.L.; Yu, Z.M.; Yu, W.J. Study on numerical simulation of organic pollutant transport in ground-water northwest of Laixi. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, V.L.; Parlange, J.Y.; Steenhuis, T.S. Are preferentialflow paths perpetuated by microbial activity in the soil matrix: A review. J. Hydrol. 2010, 393, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Johnson, W.P. Excess Colloid Retention in Porous Media as a Function of Colloid Size, Fluid Ve-locity, and Grain Angularity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7725–7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Xu, X.; Lan, L.; Miao, L.; Xu, Y.; You, G.; Liu, Z. Transport behavior of micro polyethylene particles in saturated quartz sand: Impacts of input concentration and physicochemical factors. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Chen, Q.L.; An, X.L.; Yang, X.R.; Christie, P.; Ke, X.; Wu, L.-H.; Zhu, Y.G. Exposure of soil collembolans to microplastics perturbs their gut microbiota and alters their isotopic composition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, G.; Ke, H.; Chen, H.; He, F. Safe Technology of Crops in Reclaimed Farmland of Heavy Metals Tail Slag Field. Northwestern Geol. 2019, 52, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, H.; Li, M.; He, L.; Zhang, M.; Hsieh, L.; Wang, S.; Han, P.; Tong, M. Transport and deposition behaviors of microplastics in porous media: Co-impacts of N fertilizers and humic acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 426, 127787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Xia, J.; Sheng, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Gao, B. Transport characteristics of fragmental polyethylene glycol terephthalate (PET) microplastics in porous media under various chemical conditions. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poritosh, R.; Amar, K.M.; Manjusri, M. Microplastics in ecosystems: Their implications and mitigation pathways. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2022, 1, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, P.; Xi, B.; Tan, W. Metal type and aggregate microenvironment govern the response sequence of speciation transformation of different heavy metals to microplastics in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 752, 141956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).