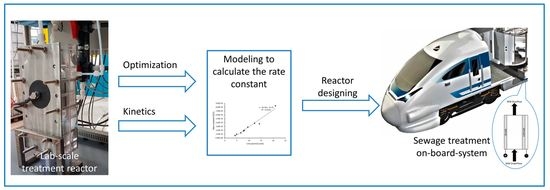
The Electrochemical Reaction Kinetics during Synthetic Wastewater Treatment Using a Reactor with Boron-Doped Diamond Anode and Gas Diffusion Cathode
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
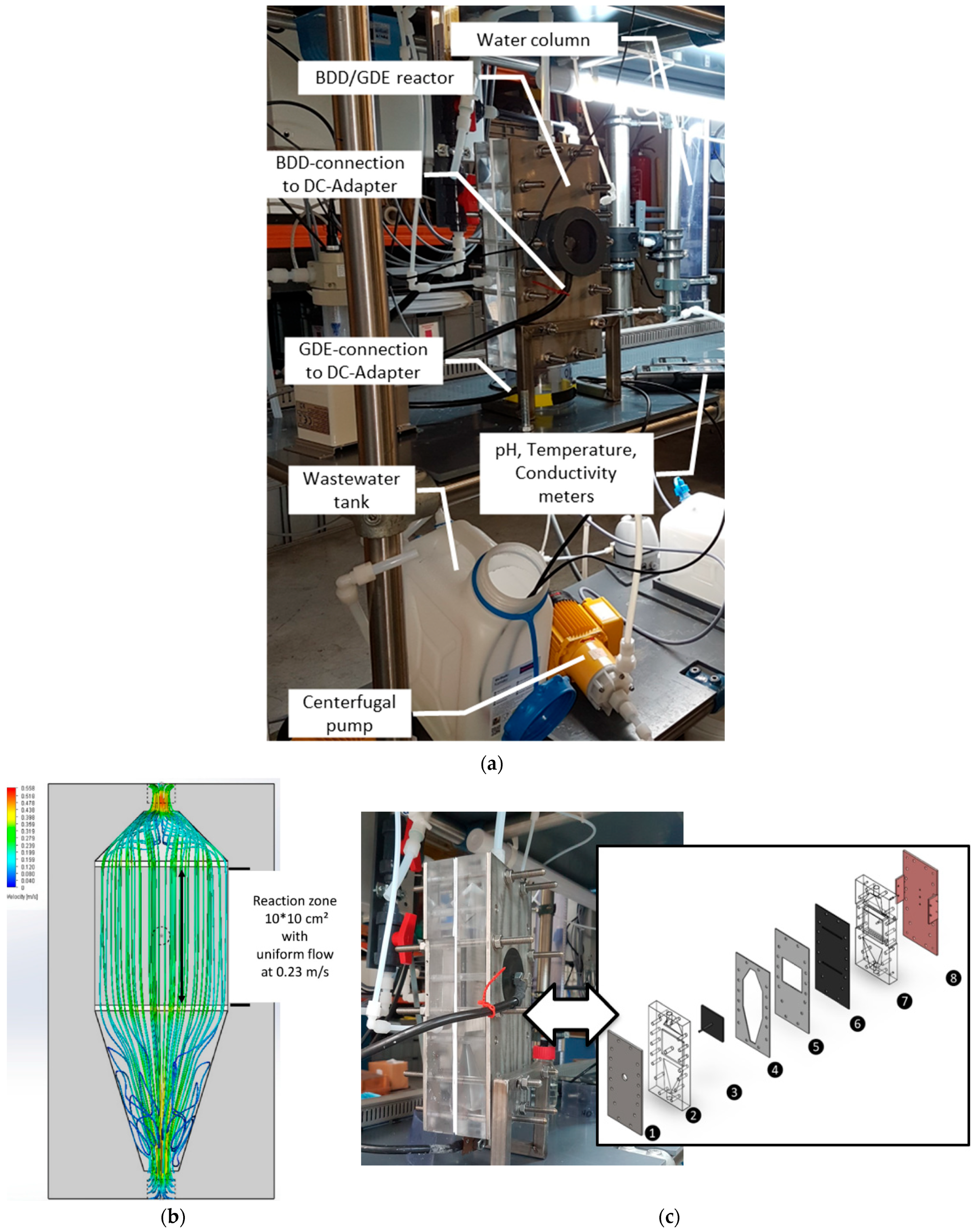
2.1. Experimental Set-Up
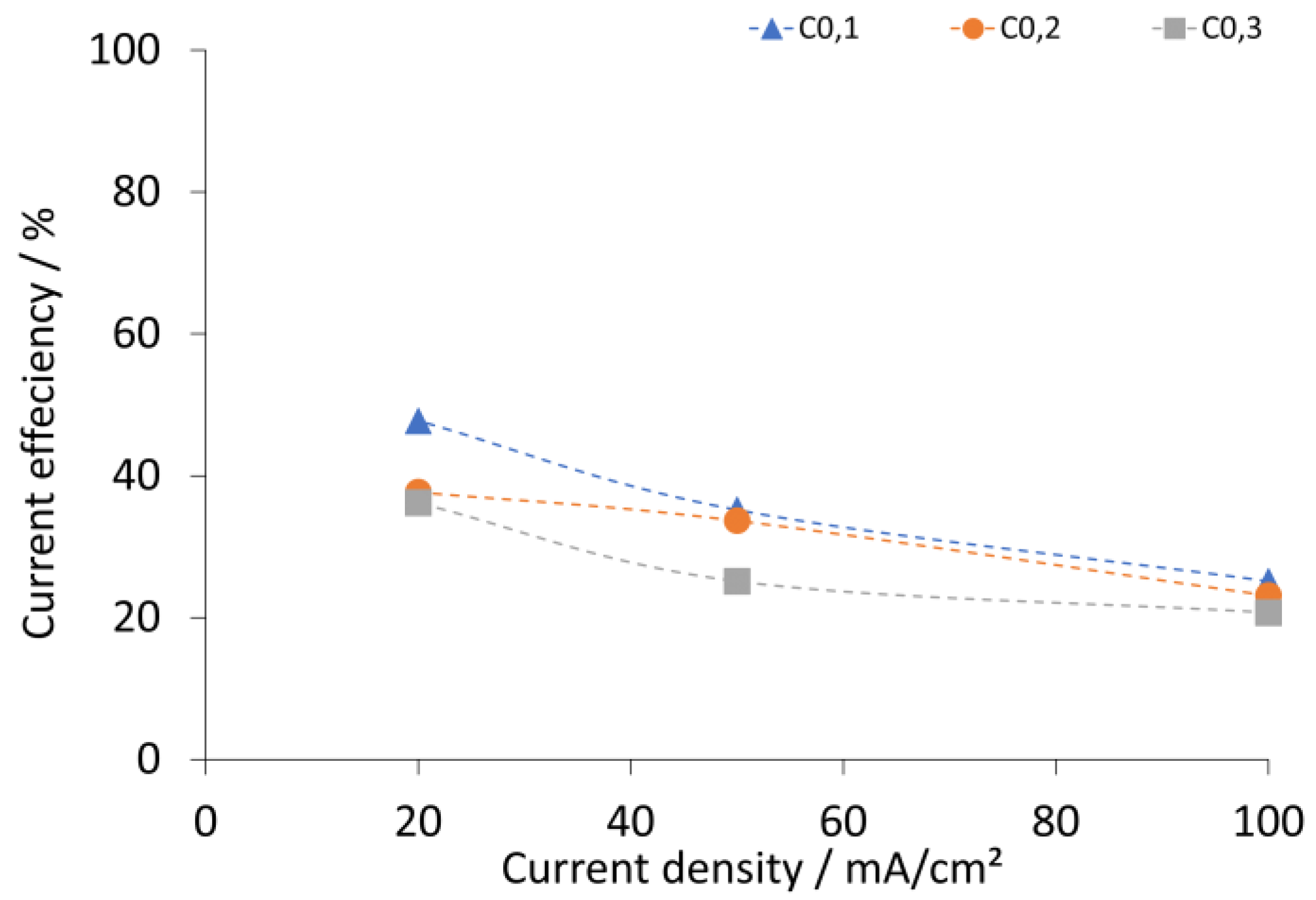
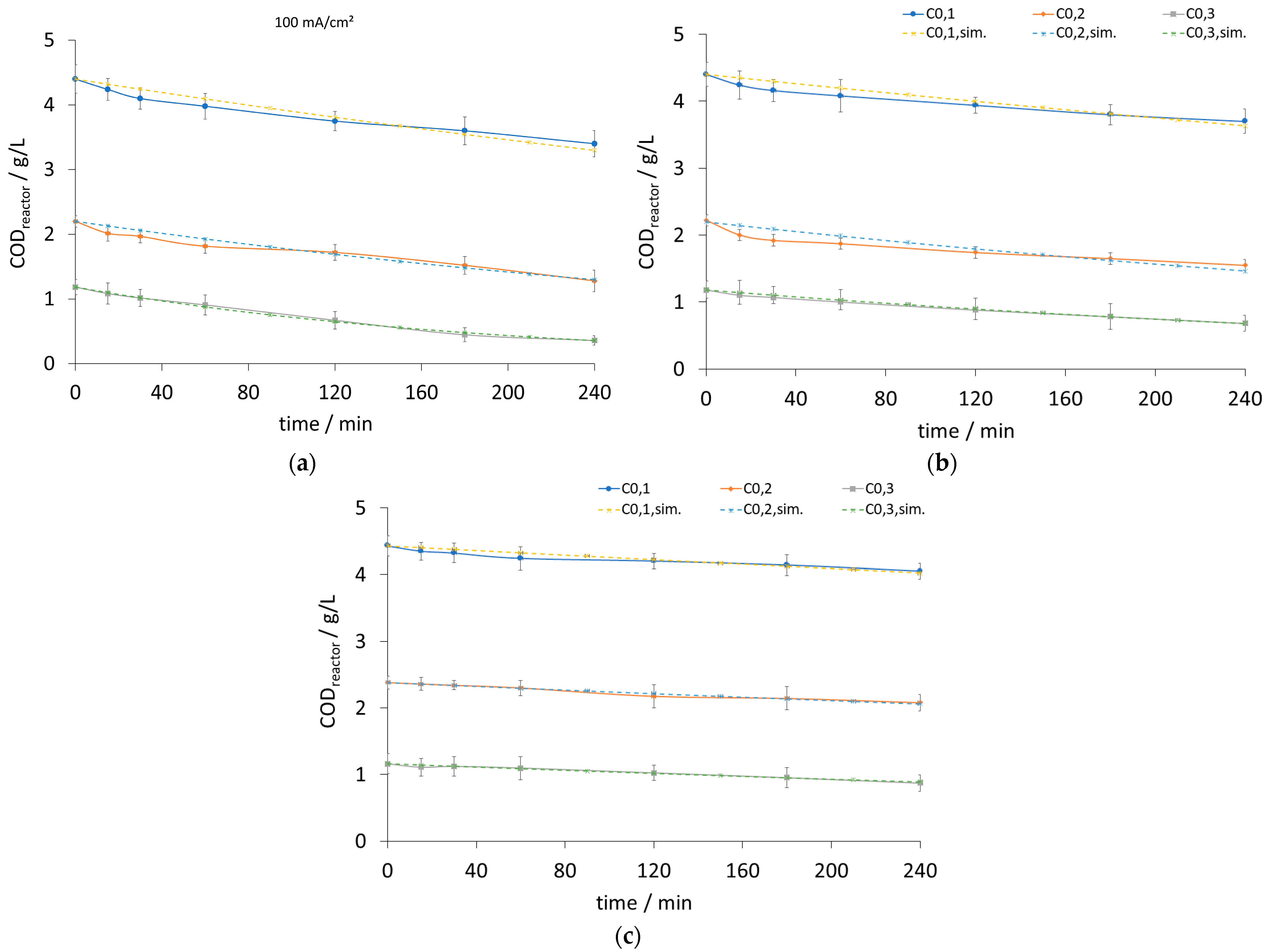
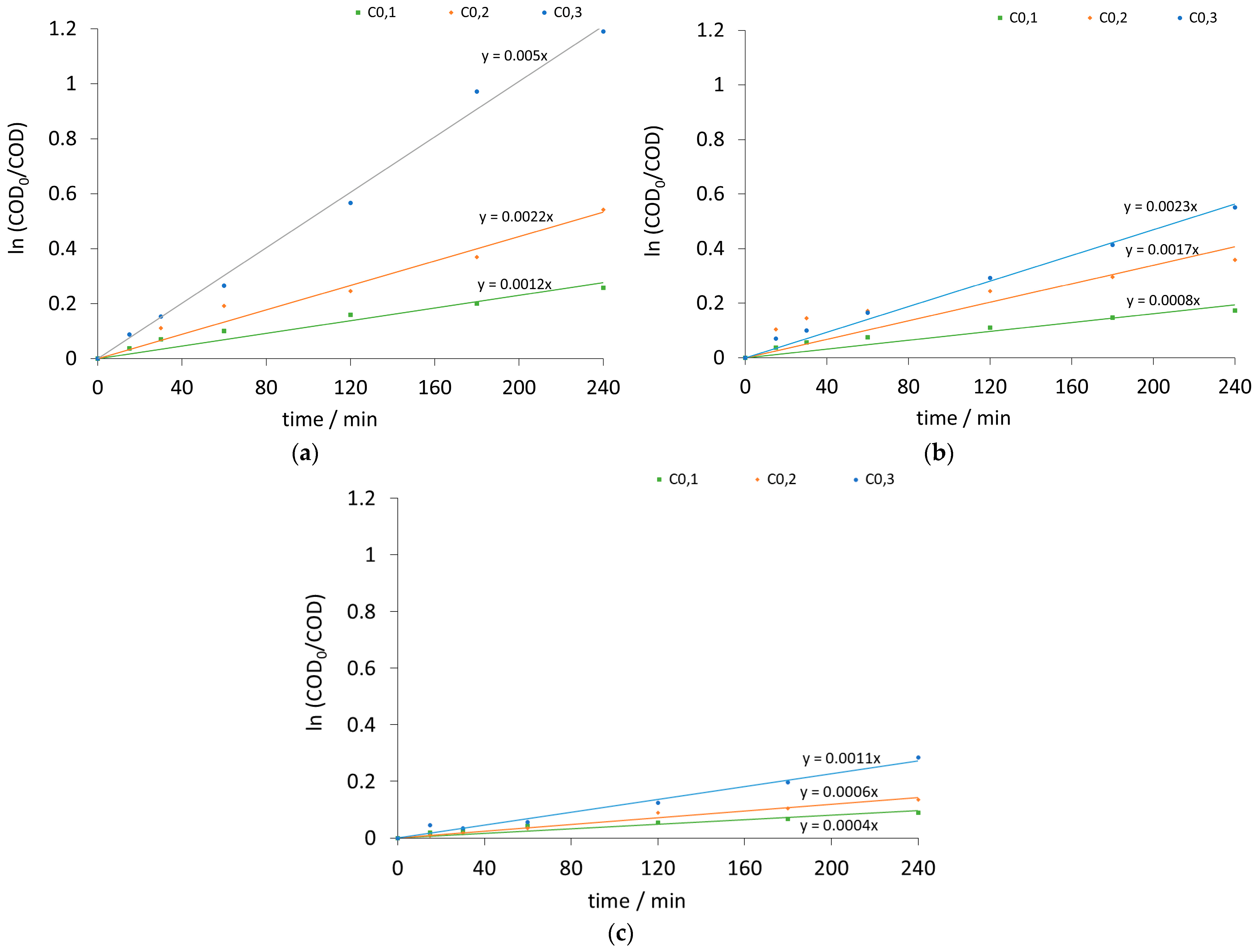
2.2. Analysis and Calculations
2.3. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Viessman, W.; Hammer, M. Water Supply and Pollution Control; Pearson Education Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Frontistis, Z.; Brebou, C.; Venieri, D.; Mantzavinos, D.; Katsaounis, A. BDD anodic oxidation as tertiary wastewater treatment for the removal of emerging micro-pollutants, pathogens and organic matter. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2011, 86, 1233–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco Mj Santos, V.; Ciríaco, L.; Lopes, A. Electrochemical degradation of aromatic amines on BDD electrodes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabaaoui, N.; Saad, M.E.K.; Moussaoui, Y.; Allagui, M.S.; Bedoui, A.; Elaloui, E. Anodic oxidation of o-nitrophenol on BDD electrode: Variable effects and mechanisms of degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250–251, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, G. Anodic oxidation of Orange II on Ti/BDD electrode: Variable effects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 48, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtiaga, A.; Fernandez-Castro, P.; Gómez, P.; Ortiz, I. Remediation of wastewaters containing tetrahydrofuran. Study of the electrochemical mineralization on BDD electrodes. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 239, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klidi, N.; Clematis, D.; Delucchi, M.; Gadri, A.; Ammar, S.; Panizza, M. Applicability of electrochemical methods to paper mill wastewater for reuse. Anodic oxidation with BDD and TiRuSnO2 anodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 815, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazouani, M.; Akrout, H.; Bousselmi, L. Nitrate and carbon matter removals from real effluents using Si/BDD electrode. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9895–9906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlin, P.; Grelot, J. Abklärungen Verfahrenseignung Ozonung; Empfehlung: Glattbrugg, Switerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Lin, H.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Huang, W. Recent developments and advances in boron-doped diamond electrodes for electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 802–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, D.; Muddemann, T.; Kunz, U.; Sievers, M. Evaluation of a new electrochemical concept for vacuum toilet wastewater treatment—Comparison with ozonation and peroxone processes. Electrochem. Commun. 2019, 101, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muddemann, T.; Neuber, R.; Haupt, D.; Graßl, T.; Issa, M.; Bienen, F.; Enstrup, M.; Möller, J.; Matthée, T.; Sievers, M.; et al. Improving the Treatment Efficiency and Lowering the Operating Costs of Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes. Processes 2021, 9, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjenovic, J.; Petrovic, M. Sulfate-mediated electrooxidation of X-ray contrast media on boron-doped diamond anode. Water Res. 2016, 94, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G.; Berardinelli, S.; Resini, C.; Arrighi, L. Technologies for the removal of phenol from fluid streams: A short review of recent developments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 265–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, M. Advanced Oxidation Processes. Treatise Water Sci. 2011, 4, 377–408. [Google Scholar]
- Bokare, A.D.; Choi, W. Singlet-Oxygen Generation in Alkaline Periodate Solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14392–14400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Hoffmann, M.R. Substrate oxidation enhances the electrochemical production of hydrogen peroxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, S.K. Chemical Kinetics and Reaction Dynamics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Segura, S.; Keller, J.; Brillas, E.; Radjenovic, J. Removal of organic contaminants from secondary effluent by anodic oxidation with a boron-doped diamond anode as tertiary treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Coetsier, C.; Causserand, C.; Groenen Serrano, K. On the role of salts for the treatment of wastewaters containing pharmaceuticals by electrochemical oxidation using a boron doped diamond anode. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 231, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Y.P.; Chen, R.L.; Wang, C.N.; Li, H.D.; Huang, W.M.; Lin, H.B. Electrochemical oxidation of substituted phenols on a boron doped diamond electrode. Wuli Huaxue Xuebao/Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2017, 33, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar]
- Comninellis, C.; Chen, G. Electrochemistry for the Environment; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cañizares, P.; Louhichi, B.; Gadri, A.; Nasr, B.; Paz, R.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Saez, C. Electrochemical treatment of the pollutants generated in an ink-manufacturing process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizza, M.; Cerisola, G. Application of diamond electrodes to electrochemical processes. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 51, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EVAC. Wastewater Treatment. 2022. Available online: https://evac.com/solutions/wastewater-treatment/ (accessed on 21 September 2022).
- Wasielewski, S.; Morandi, C. Impacts of blackwater co-digestion upon biogas production in pilot-scale UASB and CSTR reactor. In Proceedings of the 13th IWA Specialized Conference on Small Water and Wastewater Systems & 5th IWA Specialized Conference on Resources-Oriented Sanitation, Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 13–17 September 2020; IWA Publishing Allianceto: Athen, Greece, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Issa, M. Optimierung Eines Aeroben Membran-Bioreaktor-Systems mit Querstrom-Membranabtrennung; Papierflieger: Clausthal-Zellerfeld, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Englehardt, J.D. A new method for removal of hydrogen peroxide interference in the analysis of chemical oxygen demand. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2291–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groele, J.; Foster, J. Hydrogen Peroxide Interference in Chemical Oxygen Demand Assessments of Plasma Treated Waters. Plasma 2019, 2, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, M.; Muddemann, T.; Haupt, D.R.; Kunz, U.; Sievers, M. Simple Catalytic Approach for Removal of Analytical Interferences caused by Hydrogen Peroxide in a Standard Chemical Oxygen Demand Test. J. Environ. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, M.; Bahadir, M.; Teichgräber, B. Determination of chemical oxygen demand (COD) using an alternative wet chemical method free of mercury and dichromate. Water Res. 2017, 122, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizza, M.; Cerisola, G. Electrochemical degradation of gallic acid on a BDD anode. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.M. Elektrochemische Verfahrenstechnik; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk, C.; Libra, J.A.; Saupe, A. Ozonation of Water and Waste Water: A Practical Guide to Understanding Ozone and Its Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Rong, F.; Fu, D. Electrochemical degradation of ethidium bromide using boron-doped diamond electrode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 107, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad Mek Rabaaoui, N.; Elaloui, E.; Moussaoui, Y. Mineralization of p-methylphenol in aqueous medium by anodic oxidation with a boron-doped diamond electrode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 171, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muddemann, T.; Haupt, D.R.; Sievers, M.; Kunz, U. Improved Operating Parameters for Hydrogen Peroxide-Generating Gas Diffusion Electrodes. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2020, 92, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, K.; Han, W.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Shen, J.; Wang, L. Improved electrochemical oxidation of tricyclazole from aqueous solution by enhancing mass transfer in a tubular porous electrode electrocatalytic reactor. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 189, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Yu, Z.; Wei, Q.; Long, H.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y. Electrochemical oxidation of biological pretreated and membrane separated landfill leachate concentrates on boron doped diamond anode. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 377, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velegraki, T.; Balayiannis, G.; Diamadopoulos, E.; Katsaounis, A.; Mantzavinos, D. Electrochemical oxidation of benzoic acid in water over boron-doped diamond electrodes: Statistical analysis of key operating parameters, kinetic modeling, reaction by-products and ecotoxicity. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savéant, J.M. Molecular catalysis of electrochemical reactions. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2348–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, L.; Du, A.; Gao, G.; Chen, J.; Yan, X.; Christopher, L.; Brown, X.Y. Defect Graphene as a Trifunctional Catalyst for Electrochemical Reactions. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 95432–99538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Long, Y.; Zhu, X.; Tian, Y.; Ye, J. Influencing factors and chlorinated byproducts in electrochemical oxidation of bisphenol A with boron-doped diamond anodes. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 246, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtiaga, A.; Ortiz, I.; Anglada, A. Kinetic modeling of the electrochemical removal of ammonium and COD from landfill leachates. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2012, 42, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Shi, S.; Wei, J.; Lv, F.; Zhao, H.; Kong, J.; He, Q.; Ni, J. Electrochemical oxidation characteristics of p-substituted phenols using a boron-doped diamond electrode. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6541–6546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Current Density (mA/cm2) | k [1/s] | Initial Potential V0 [volt] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conductivity [mS/cm] | Conductivity [mS/cm] | |||||
| 8.58 ± 0.24 | 4.62 ± 0.12 | 2.49 ± 0.06 | 8.58 ± 0.24 | 4.62 ± 0.12 | 2.49 ± 0.06 | |
| 100 | 2.00 × 10−5 | 3.67 × 10−5 | 8.33 × 10−5 | 8.03 | 14.3 | 20.9 |
| 50 | 1.33 × 10−5 | 2.83 × 10−5 | 3.83 × 10−5 | 6.59 | 9.51 | 12.3 |
| 20 | 0.67 × 10−5 | 1.00 × 10−5 | 1.83 × 10−5 | 4.24 | 4.85 | 7.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Issa, M.; Haupt, D.; Muddemann, T.; Kunz, U.; Sievers, M. The Electrochemical Reaction Kinetics during Synthetic Wastewater Treatment Using a Reactor with Boron-Doped Diamond Anode and Gas Diffusion Cathode. Water 2022, 14, 3592. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223592
Issa M, Haupt D, Muddemann T, Kunz U, Sievers M. The Electrochemical Reaction Kinetics during Synthetic Wastewater Treatment Using a Reactor with Boron-Doped Diamond Anode and Gas Diffusion Cathode. Water. 2022; 14(22):3592. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223592
Chicago/Turabian StyleIssa, Mohammad, Dennis Haupt, Thorben Muddemann, Ulrich Kunz, and Michael Sievers. 2022. "The Electrochemical Reaction Kinetics during Synthetic Wastewater Treatment Using a Reactor with Boron-Doped Diamond Anode and Gas Diffusion Cathode" Water 14, no. 22: 3592. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223592
APA StyleIssa, M., Haupt, D., Muddemann, T., Kunz, U., & Sievers, M. (2022). The Electrochemical Reaction Kinetics during Synthetic Wastewater Treatment Using a Reactor with Boron-Doped Diamond Anode and Gas Diffusion Cathode. Water, 14(22), 3592. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223592