Assessment of Aquatic Ecosystem Health with Indices of Biotic Integrity (IBIs) in the Ganjiang River System, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Surveys and Environmental Variable Measurements
2.3. Development of F-IBI, B-IBI, and P-IBI
2.3.1. Selection of Reference Sites
2.3.2. Selection of Metrics
2.3.3. Calculation of the IBI and Assessment of Ecosystem Health
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Community Structure
3.1.1. Fish Community Structure
3.1.2. Benthic Macroinvertebrate Community Structure
3.1.3. Phytoplankton Community Structure
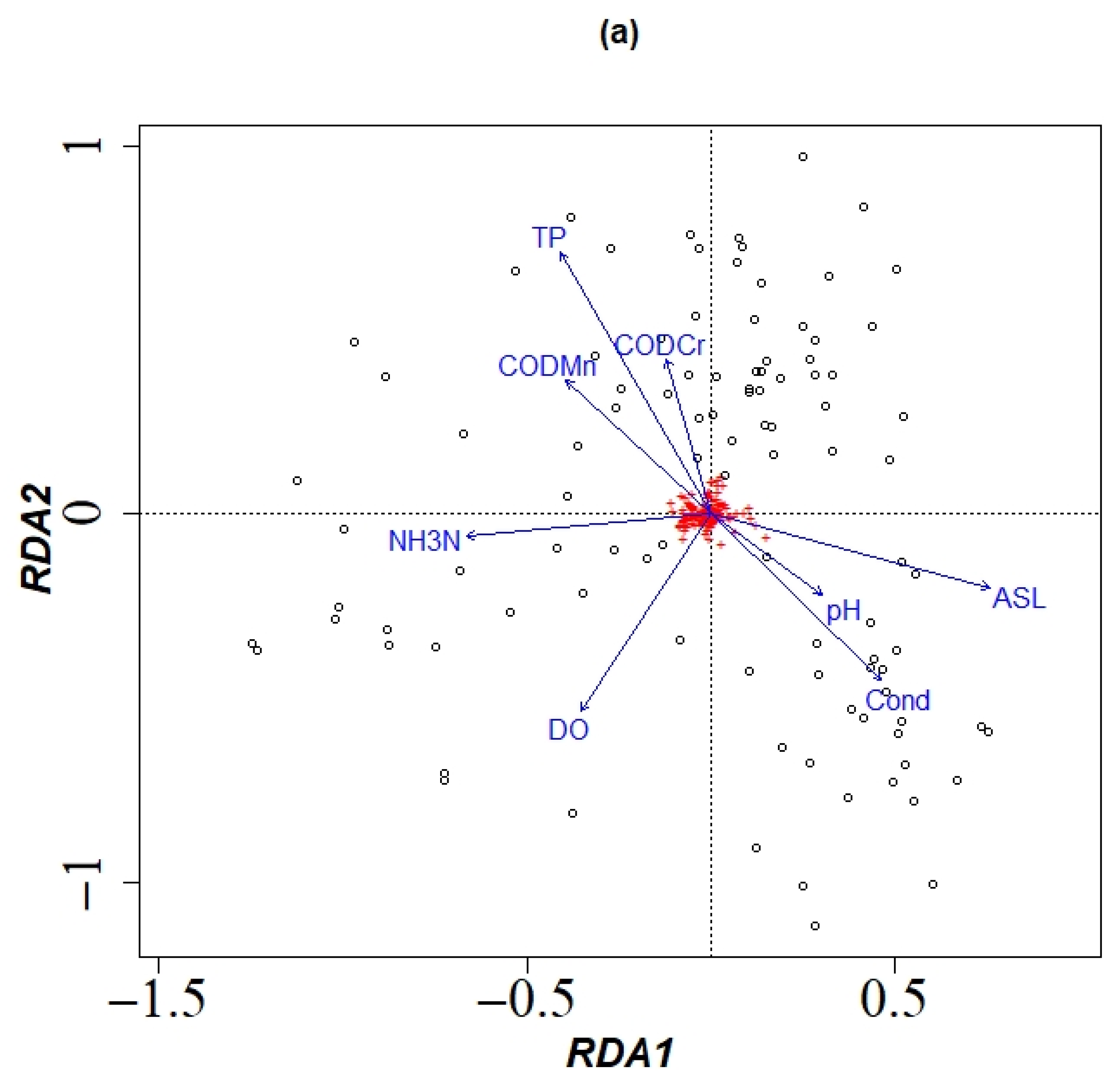
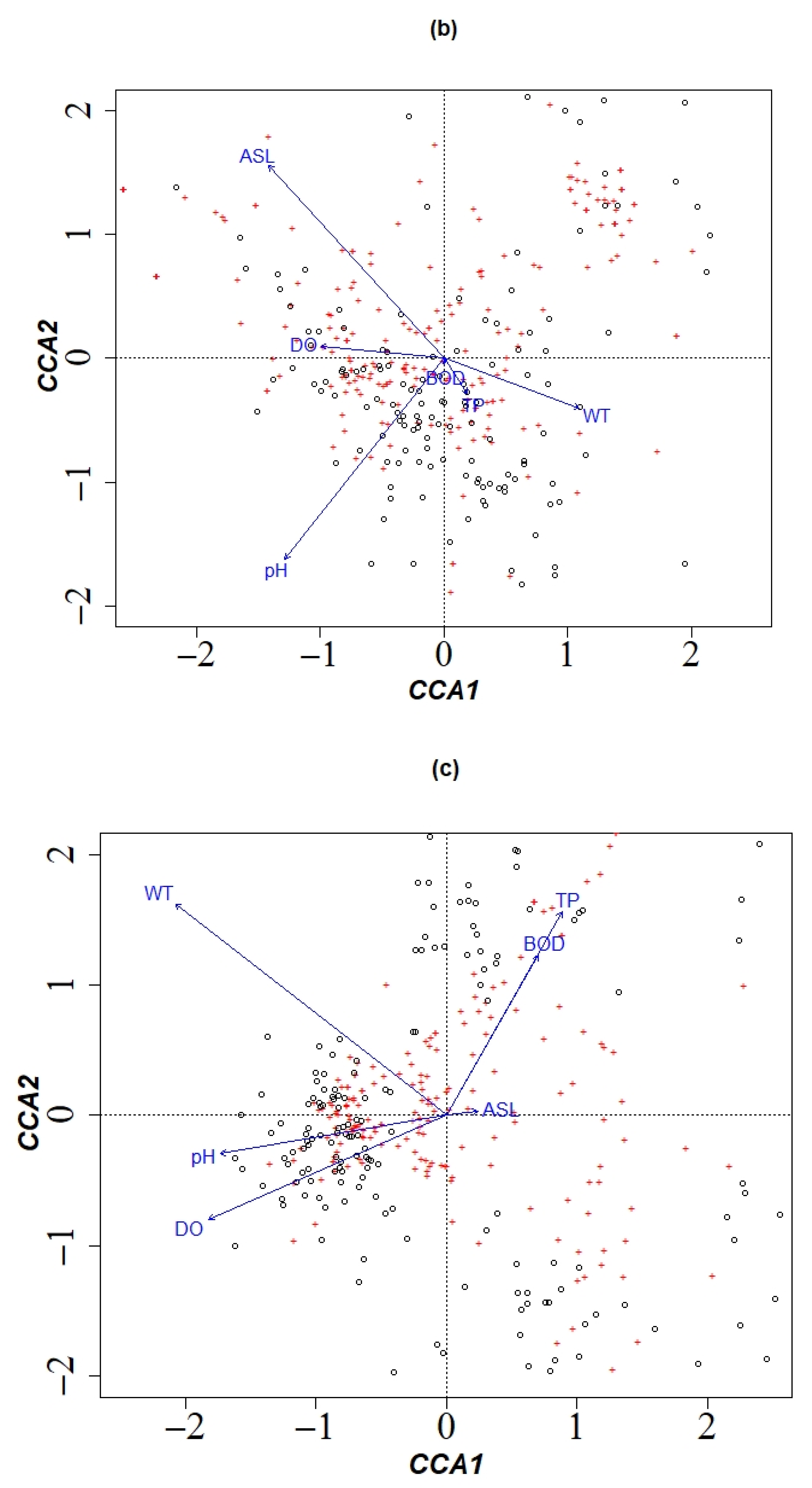
3.1.4. Dominant Environmental Factors Affecting Community Structure
3.2. Selection of Core Metrics and Establishment of the F-IBI, B-IBI, and P-IBI
4. Discussion
4.1. Community Structure Analysis
4.2. Evaluation of Assessment Results Obtained Based on the F-IBI, B-IBI, and P-IBI
4.3. Temporal Heterogeneity of the F-IBI, B-IBI, and P-IBI
4.4. Spatial Heterogeneity of the F-IBI, B-IBI, and P-IBI
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gonino, G.; Benedito, E.; Cionek, V.d.M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Oliveira, J.M. A fish-based index of biotic integrity for neotropical rainforest sandy soil streams—Southern Brazil. Water 2020, 12, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Stanley, E.H.; Vander Zanden, M.J. State of the world’s freshwater ecosystems: Physical, chemical, and biological changes. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2011, 36, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, Y.S.; Hwang, S.J. Ecological monitoring, assessment, and management in freshwater systems. Water 2016, 8, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veach, A.M.; Troia, M.J.; Cregger, M.A. Assessing biogeographic survey gaps in bacterial diversity knowledge: A global synthesis of freshwaters. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapport, D.J.; Costanza, R.; McMichael, A.J. Assessing ecosystem health. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1998, 13, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R. Ecosystem health and ecological engineering. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 45, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Z.; He, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Guo, X. Ecosystem health assessment based on ecological integrity and ecosystem services demand in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 144837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Chen, J. River health assessment: Proposing a comprehensive model based on physical habitat, chemical condition and biotic structure. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 103, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, R.H.; Thoms, M.C. What is river health? Freshw. Biol. 1999, 41, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shan, C.; Dong, Z.; Lu, D.; Xu, C.; Wang, H.; Ling, Z.; Liu, Q. Study on river health assessment based on a fuzzy matter-element extension model. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Sanches, B.; Becker, B.; Hughes, R.M.; Petesse, M.L.; Ribeiro, J.R.; Santos, G.B. Fish-based multimetric index for evaluating land use effects on large neotropical reservoirs. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2019, 35, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi, H.; Schinegger, R.; Melcher, A.; Moder, K.; Mielach, C.; Schmutz, S. A new fish-based multi-metric assessment index for cyprinid streams in the Iranian Caspian Sea Basin. Limnologica 2015, 51, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emery, E.B.; Simon, T.P.; McCormick, F.H.; Angermeier, P.L.; Deshon, J.E.; Yoder, C.O.; Sanders, R.E.; Pearson, W.D.; Hickman, G.D.; Reash, R.J.; et al. Development of a Multimetric Index for Assessing the Biological Condition of the Ohio River. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2003, 132, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neachell, E. A multimetric macroinvertebrate index for the implementation of the European Water Framework Directive in French Guiana, East Amazonia. River Res. Applic. 2014, 30, 132–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallottini, M.; Goretti, E.; Selvaggi, R.; Cappelletti, D.; Dedieu, N.; Céréghino, R. An efficient semi-quantitative macroinvertebrate multimetric index for the assessment of water and sediment contamination in streams. Inl. Waters 2017, 7, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondy, C.P.; Villeneuve, B.; Archaimbault, V.; Usseglio-Polatera, P. A new macroinvertebrate-based multimetric index (I 2M 2) to evaluate ecological quality of French wadeable streams fulfilling the WFD demands: A taxonomical and trait approach. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacouture, R.V.; Johnson, J.M.; Buchanan, C.; Marshall, H.G. Phytoplankton index of biotic integrity for Chesapeake Bay and its tidal tributaries. Estuaries Coasts 2006, 29, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longphuirt, S.N.; McDermott, G.; O’Boyle, S.; Wilkes, R.; Stengel, D.B. Decoupling abundance and biomass of phytoplankton communities under different environmental controls: A new multi-metric index. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lugoli, F.; Garmendia, M.; Lehtinen, S.; Kauppila, P.; Moncheva, S.; Revilla, M.; Roselli, L.; Slabakova, N.; Valencia, V.; Dromph, K.M.; et al. Application of a new multi-metric phytoplankton index to the assessment of ecological status in marine and transitional waters. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 338–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.R. Assessment of Biotic Integrity Using Fish Communities. Fisheries 1981, 6, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, A.; Bricker, S.B.; Dauer, D.M.; Demetriades, N.T.; Ferreira, J.G.; Forbes, A.T.; Hutchings, P.; Jia, X.; Kenchington, R.; Marques, J.C.; et al. Overview of integrative tools and methods in assessing ecological integrity in estuarine and coastal systems worldwide. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1519–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayon, N.; Bertrand, A.; Leroy, D.; Malbrouck, C.; Mandiki, S.N.M.; Silvestre, F.; Goffart, A.; Thomé, J.P.; Kestemont, P. Multiscale approach of fish responses to different types of environmental contaminations: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 715–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, S.; Rocher, V. Influence of the water quality improvement on fish population in the Seine River (Paris, France) over the 1990-2013 period. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Tang, G.; Zhao, P.; Hong, Y.; Gou, Y.; Yang, K. Statistical assessment and hydrological utility of the latest multi-satellite precipitation analysis IMERG in Ganjiang River basin. Atmos. Res. 2017, 183, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poikane, S.; Kelly, M.; Cantonati, M. Benthic algal assessment of ecological status in European lakes and rivers: Challenges and opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Schmalz, B.; Fohrer, N. Development and testing of a phytoplankton index of biotic integrity (P-IBI) for a German lowland river. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 13, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Kong, M.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, K. Index of biotic integrity based on phytoplankton and water quality index: Do they have a similar pattern on water quality assessment? A study of rivers in Lake Taihu Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, N.; Feng, B.; Zhang, M.; He, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z. Impact of industrial production, dam construction, and agriculture on the Z-IBI in river ecosystems: A case study of the wanan river basin in China. Water 2021, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poikane, S.; Johnson, R.K.; Sandin, L.; Schartau, A.K.; Solimini, A.G.; Urbanič, G.; Arbačiauskas, K.S.; Aroviita, J.; Gabriels, W.; Miler, O.; et al. Benthic macroinvertebrates in lake ecological assessment: A review of methods, intercalibration and practical recommendations. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Wu, H. Development of a microbial community-based index of biotic integrity (MC-IBI) for the assessment of ecological status of rivers in the Taihu Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; You, Q.; Fang, N.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, N.; Ni, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Yang, T.; et al. Assessment of wetland health status of Poyang Lake using vegetation-based indices of biotic integrity. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de paiva Silva, D.; De Marco, P.; Resende, D.C. Adult odonate abundance and community assemblage measures as indicators of stream ecological integrity: A case study. Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Huang, X.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X. Assessment of ecosystem health of the Yellow River with fish index of biotic integrity. Hydrobiologia 2018, 814, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; An, K.G. Integrative restoration assessment of an urban stream using multiple modeling approaches with physical, chemical, and biological integrity indicators. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 62, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.J.; Li, F.; Kwon, Y.S.; Chung, N.; Choi, H.; Hwang, S.J.; Park, Y.S. Concordance of diatom, macroinvertebrate and fish assemblages in streams at nested spatial scales: Implications for ecological integrity. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 47, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.S.; Yang, H.N.; Huang, D.J.; Liu, S.M.; Huang, Y.H.; Chiang, C.T.; Liu, J.W. Using benthic macroinvertebrate and fish communities as bioindicators of the Tanshui river basin around the greater Taipei area—Multivariate analysis of spatial variation related to levels of water pollution. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 7116–7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Mao, R.; Li, M.; Xia, J.; Song, J.; Cheng, D.; Sun, H. Assessment of aquatic ecological health based on determination of biological community variability of fish and macroinvertebrates in the Weihe River Basin, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 267, 110651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paavola, R.; Muotka, T.; Virtanen, R.; Heino, J.; Jackson, D.; Mäki-Petäys, A. Spatial scale affects community concordance among fishes, benthic macroinvertebrates, and bryophytes in streams. Ecol. Appl. 2006, 16, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.K.; Daniel, H. Spatial congruency of benthic diatom, invertebrate, macrophyte, and fish assemblages in European streams. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 978–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolph, C.L.; Huff, D.D.; Chizinski, C.J.; Vondracek, B. Implications of community concordance for assessing stream integrity at three nested spatial scales in Minnesota, U.S.A. Freshw. Biol. 2011, 56, 1652–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, B.; Qin, T.; Nie, H.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Shen, Z. Assessment of hydrological changes and their influence on the aquatic ecology over the last 58 years in Ganjiang Basin, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, P.; Jiang, T.; Tu, X.; Chen, X. Patrons spatio-temporels des processus hydrologiques et de leurs réponses aux activités humaines dans le bassin du Lac Poyang, Chine. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2011, 56, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, S. Evaluating the TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis for Extreme Precipitation and Streamflow in Ganjiang River Basin, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2017, 2017, 2902493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Liu, X.; Ao, X.; Qin, J.; Wu, X.; Ouyang, S. Fish diversity in the middle and lower reaches of the Ganjiang River of China: Threats and conservation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.J.; Duan, J.J.; Junaid, M.; Cao, T.W.; Ding, S.M.; Pei, D.S. Recent status of fishes in the Yangtze river and its ecological health assessment. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 12, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capmourteres, V.; Rooney, N.; Anand, M. Assessing the causal relationships of ecological integrity: A re-evaluation of Karr’s iconic Index of Biotic Integrity. Ecosphere 2018, 9, e02168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffith, M.B.; Hill, B.H.; McCormick, F.H.; Kaufmann, P.R.; Herlihy, A.T.; Selle, A.R. Comparative application of indices of biotic integrity based on periphyton, macroinvertebrates, and fish to southern Rocky Mountain streams. Ecol. Indic. 2005, 5, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-La-Ossa-Carretero, J.A.; Lane, M.F.; Llansó, R.J.; Dauer, D.M. Classification efficiency of the B-IBI comparing water body size classes in Chesapeake Bay. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 63, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, M.C.; Gold, A.J.; Heltshe, J.F.; Buffum, H.W. A method to identify estuarine macroinvertebrate pollution indicator species in the Virginian Biogeographic Province. Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, M.T.; Gerritsen, J.; Griffith, G.E.; Frydenborg, R.; Mccarron, E.; White, J.S.; Bastian, M.L. A framework for biological criteria for Florida streams using benthic macroinvertebrates. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1996, 15, 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Son, M.; Kim, D.; Choi, H.W.; Kim, Y.O. Assessing the ecosystem health status of Korea gwangyang and jinhae bays based on a planktonic index of biotic integrity (P-IBI). Ocean. Sci. J. 2014, 49, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ban, X.; Li, E.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, F. Evaluating ecological health in the middle-lower reaches of the Hanjiang River with cascade reservoirs using the Planktonic index of biotic integrity (P-IBI). Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, D.D.; Gordon, S.I.; Munawar, M.; Charlton, M.N.; Culver, D.A. The Planktonic Index of Biotic Integrity (P-IBI): An approach for assessing lake ecosystem health. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 1234–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Duan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, M.; Tian, W.; Wang, H.; Huang, H. Freshwater lake ecosystem health assessment and its response to pollution stresses based on planktonic index of biotic integrity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 35240–35252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Dong, S.; Peng, M.; Yang, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, C. Effects of damming on the biological integrity of fish assemblages in the middle Lancang-Mekong River basin. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Yang, W.; Jian, M.; Hu, Q. A comparison of metric scoring and health status classification methods to evaluate benthic macroinvertebrate-based index of biotic integrity performance in Poyang Lake wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 144112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.R. Defining and measuring river health. Freshw. Biol. 1999, 41, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Hu, X.D.; Wu, P.P.; Chen, W.M.; Wu, S.S.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhu, L.; Xi, Y.L.; Huang, R. Development and testing of the phytoplankton biological integrity index (P-IBI) in dry and wet seasons for Lake Gehu. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutter, F.M. An empirical biotic index of the quality of water in south African streams and rivers. Water Res. 1972, 6, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.X.; Yang, L.F. A study on tolerance values of benthic macroinvertebrate taxa in Eastern China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2004, 24, 2768–2775. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Yang, M.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, F. Tolerance values of benthic macroinvertebrates and bioassessment of water quality in the Lushan Nature Reserve. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2003, 9, 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Hurd, T.M.; Jesic, S.; Jerin, J.L.; Fuller, N.W.; Miller, D. Stable isotope tracing of trout hatchery carbon to sediments and foodwebs of limestone spring creeks. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 405, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyväsjärvi, J.; Immonen, H.; Högmander, P.; Högmander, H.; Hämäläinen, H.; Karjalainen, J. Can lake restoration by fish removal improve the status of profundal macroinvertebrate assemblages? Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, R.; Thakur, R.K.; Singh, U.B.; Ahluwalia, A.S. Phytoplankton dynamics and species diversity in a shallow eutrophic, natural mid-altitude lake in Himachal Pradesh (India): Role of physicochemical factors. Chem. Ecol. 2014, 30, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornés, E.; Mor, J.R.; Mandaric, L.; Sabater, S. Diatom responses to sewage inputs and hydrological alteration in Mediterranean streams. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fausch, K.D.; Karr, J.R.; Yant, P.R. Regional Application of an Index of Biotic Integrity Based on Stream Fish Communities. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1984, 113, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, A.; Siegel, V.; Pakhomov, E.; Rothery, P. Long-term decline in krill stock and increase in salps within the Southern Ocean. Nature 2004, 432, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful Cyanobacterial Blooms: Causes, Consequences, and Controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoddard, J.L.; Herlihy, A.T.; Peck, D.V.; Hughes, R.M.; Whittier, T.R.; Tarquinio, E. A process for creating multimetric indices for large-scale aquatic surveys. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2008, 27, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, J. Are indicator groups and cross-taxon congruence useful for predicting biodiversity in aquatic ecosystems? Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Metrics and Groups | ||
|---|---|---|
| F-IBI | B-IBI | P-IBI |
| Species Composition | Species Composition | Species Composition |
| M1 Total taxa% (↓) | M’1 Total taxa (↓) | M’’1 Total taxa (↓) |
| M2 Cypriniformes taxa% (↑) | M’2 EPT taxa (↓) | M’’2 Cyanobacteria taxa (↑) |
| M3 Cyprinidae taxa% (↑) | M’3 Ephemeroptera taxa (↓) | M’’3 Chlorophyta taxa (↓) |
| M4 Gobioninae taxa% (↑) | M’4 Trichoptera taxa (↓) | M’’4 Bacillariophyta taxa (↑) |
| M5 Culterinae taxa% (↓) | M’5 Diptera taxa (↓) | M’’5 Except Bacillariophyta taxa (↓) |
| M6 Rhodeinae taxa% (↓) | M’6 Coleoptera taxa (↓) | |
| M7 Barbinae taxa% (↑) | M’7 Plecoptera taxa (↓) | M’’6 Total density (↓) |
| M8 Cobitidae taxa% (↑) | M’8 Crustacea + Molluscs taxa (↓) | Relative abundance |
| M9 Perciformes taxa% (↓) | M’9 Aquatic insect taxa (↓) | M’’7 Chlorophyta taxa% (↓) |
| M10 Serranidae taxa% (↓) | M’10 Chironomidae taxa (↑) | M’’8 Bacillariophyta taxa% (↑) |
| M11 Siluriformes taxa% (↑) | Relative abundance | |
| M12 Bagridae taxa% (↓) | M’11 EPT % (↓) | M’’9 Achnanthes taxa% (↓) |
| Ecological types | M’12 EpheMeroptera % (↓) | M’’10 Cymbella taxa% (↓) |
| M13 Migration fishes taxa% (↓) | M’13 Trichoptera % (↓) | M’’11 Nitzschia taxa% (↑) |
| M14 Freshwater fishes taxa% (↓) | M’14 Diptera % (↑) | M’’12 Naviculataxa% (↑) |
| M15 Settled fishes taxa% (↑) | M’15 Coleoptera % (↓) | M’’13 Cyanobacteria taxa% (↑) |
| Nutrition structure | M’16 Plecoptera % (↓) | |
| M16 Epipelagic fishes% (↓) | M’17 Chironomidae % (↑) | Biodiversity Index |
| M17 Mesopelagic fishes% (↓) | M’18 Crustacea + Molluscs % (↑) | M’’14 Shannon–Wiener index (↓) |
| M18 Demersal fishes% (↓) | M’19 Oligochaeta % (↑) | M’’15 Simpson index (↓) |
| M19 Predatory fishes% (↓) | M’20 Oligochaetes/Hirudinea (↑) | M’’16 Margalef index (↓) |
| M20 Herbivorous fishes% (↓) | M’21 Tubificidae % (↑) | M’’17 Pielou index (↓) |
| M21 Omnivorous fishes% (↑) | Dominant group | Nutrition structure |
| Breeding group | M’22 Dominant taxon % (↑) | M’’18 Cyanobacteria density% (↑) |
| M22 Fish species spawning adhesive eggs% (↑) | M’23 Top 3 dominant taxon % (↑) | |
| Pollution tolerance | M’’19 Chlorophyta density% (↓) | |
| M23 Fish species spawning drifting eggs% (↓) | M’24 Tolerant taxa (↑) | |
| M’25 Tolerant % (↑) | M’’20 Bacillariophyta density% (↑) | |
| M24 Fish species spawning demersal eggs% (↓) | M’26 Intolerant taxa (↓) | |
| M’27 Intolerant % (↓) | M’’21Cyanobacteria+ Chlorophyta density% (↓) | |
| M25 Fish species with special spawning types% (↓) | M’28 Biotic index [59,60,61] (↑) | |
| Functional feeding group | M’’22 Chlorophyta+ Bacillariophyta density% (↓) | |
| Pollution tolerance | M’29 Collect-Gatherers % (↑) | |
| M26 Sensitive taxa% (↓) | M’30 Filterers % (↑) | M’’23 Diatom quotient (↓) |
| M27 Sensitive % (↓) | M’31 Scrapers % (↓) | M’’24 Cocconeis+ Nitzschia+ Synedra% (↑) |
| M28 Tolerant taxa% (↑) | M’32 Predators % (↓) | |
| M29 Tolerant% (↑) | M’33 Shredders % (↓) | Ecological types |
| Resources and health condition | Habitat quality | M’’25 Mobile diatom percentage (↑) |
| M30 Individual number (↓) | M’34 Clingers taxa (↓) | |
| M31 Shannon-Wiener index% (↓) | M’35 Clingers % (↓) | |
| M32 Simpson index (↓) | Biodiversity Index | |
| M33 Margalef index (↓) | M’36 Shannon-Wiener index (↓) | |
| M34 Pielou index (↓) | M’37 Simpson index (↓) | |
| M35 Alien species% (↑) | M’38 Margalef index (↓) | |
| M36 Deformity and disease% (↑) | M’39 Pielou index (↓) | |
| Dominant Species | Dominance Index |
|---|---|
| Fish | |
| Acrossocheilus parallens | 0.05 |
| Saurogobio dabryi | 0.02 |
| Squalidus argentatus | 0.05 |
| Benthic macroinvertebrate | |
| Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri | 0.05 |
| Corbicula fluminea | 0.03 |
| Phytoplankton | |
| Navicula simplex | 0.06 |
| Ankistrodesmus angustus | 0.03 |
| Crucigenia apiculata | 0.02 |
| Cyclotella meneghiniana | 0.02 |
| Main Stream | Branches of the Upstream | Branches of the Midstream | Branches of the Downstream | Chi-Square Test (χ2) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASL(m) | 61.4 ± 42.3 | 197.2 ± 49.1 | 150.3 ± 151 | 77.9 ± 8.8 | 114.546 | <0.001 * |
| WT(℃) | 22.3 ± 6.8 | 22.4 ± 7.1 | 22.2 ± 7 | 22.7 ± 7.3 | 0.346 | 0.951 |
| pH | 8.14 ± 0.92 | 7.96 ± 0.72 | 8.07 ± 0.81 | 7.98 ± 0.83 | 1.004 | 0.800 |
| DO(mg/L) | 10.11 ± 1.59 | 9.95 ± 1.6 | 10.31 ± 1.2 | 9.73 ± 1.54 | 1.19 | 0.755 |
| CODMn(mg/L) | 3.46 ± 2.65 | 2.9 ± 2.9 | 3.36 ± 2.72 | 3.82 ± 2.74 | 22.23 | <0.001 * |
| BOD(mg/L) | 1.44 ± 0.57 | 0.89 ± 0.54 | 1.36 ± 0.43 | 2.03 ± 0.75 | 50.339 | <0.001 * |
| NH3-N(mg/L) | 0.49 ± 0.49 | 0.24 ± 0.24 | 0.43 ± 0.37 | 0.76 ± 0.68 | 21.356 | <0.001 * |
| TP(mg/L) | 0.09 ± 0.1 | 0.06 ± 0.09 | 0.09 ± 0.05 | 0.12 ± 0.04 | 21.488 | <0.001 * |
| CODCr(mg/L) | 8.27 ± 6.18 | 6.57 ± 4.68 | 6.2 ± 4.09 | 7.93 ± 5.43 | 5.096 | 0.165 |
| Cond(s/cm) | 77.79 ± 43.92 | 71.64 ± 50.51 | 61.83 ± 36.31 | 63.06 ± 34.04 | 7.03 | 0.071 |
| Healthy | Good | Fair | Poor | Extremely Poor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-IBI | ≥3.14 | 2.36–3.14 | 1.57–2.36 | 0.79–1.57 | <1.57 |
| B-IBI | ≥3.22 | 2.42–3.22 | 1.61–2.42 | 0.81–1.61 | <0.81 |
| P-IBI | ≥2.38 | 1.79–2.38 | 1.19–1.79 | 0.60–1.19 | <0.60 |
| Constant | ASL | WT | pH | DO | CODMn | BOD | NH3-N | TP | CODCr | Cond | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-IBI | 3.642 | −0.004 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| B-IBI | −1.348 | 0.006 | −0.059 | 0.447 | 2.318 | 0.000 | ||||||
| P-IBI | 5.514 | 0.038 | −0.163 | −0.87 | 2.237 | 0.064 | 0.000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, B.; Guan, X.; Li, J. Assessment of Aquatic Ecosystem Health with Indices of Biotic Integrity (IBIs) in the Ganjiang River System, China. Water 2022, 14, 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030278
Huang X, Xu J, Liu B, Guan X, Li J. Assessment of Aquatic Ecosystem Health with Indices of Biotic Integrity (IBIs) in the Ganjiang River System, China. Water. 2022; 14(3):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030278
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xueyan, Jing Xu, Bo Liu, Xiao Guan, and Junsheng Li. 2022. "Assessment of Aquatic Ecosystem Health with Indices of Biotic Integrity (IBIs) in the Ganjiang River System, China" Water 14, no. 3: 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030278
APA StyleHuang, X., Xu, J., Liu, B., Guan, X., & Li, J. (2022). Assessment of Aquatic Ecosystem Health with Indices of Biotic Integrity (IBIs) in the Ganjiang River System, China. Water, 14(3), 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030278





