Joint Spatial Modeling of Nutrients and Their Ratio in the Sediments of Lake Balaton (Hungary): A Multivariate Geostatistical Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sediment Sampling and Acquired Data on Nutrients
2.2. Variography
2.3. Multivariate Geostatistical Modeling
2.4. Spatial Aggregation
2.5. Quantification of Uncertainty
2.6. Validation
3. Results
3.1. Exploratory Data Analysis
3.2. Variography and Multivariate Geostatistical Modeling
3.3. Spatial Prediction at Point Support
3.4. Performance of Spatial Predictions and Uncertainty Quantifications
3.5. Spatial Aggregation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herodek, S. The eutrophication of Lake Balaton: Measurements, modeling and management. In SIL Proceedings, 1922–2010; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1984; Volume 22, pp. 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatvani, I.G.; Clement, A.; Kovács, J.; Kovács, I.S.; Korponai, J. Assessing water-quality data: The relationship between the water quality amelioration of Lake Balaton and the construction of its mitigation wetland. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istvánovics, V.; Clement, A.; Somlyódy, L.; Specziár, A.; László, G.; Padisák, J. Updating water quality targets for shallow Lake Balaton (Hungary), recovering from eutrophication. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostrom, B.; Pettersson, K. Different patterns of phosphorus release from lake sediments in laboratory experiments. Hydrobiologia 1982, 91, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, G.E. A Treatise on Limnology I.: Geography, Physics and Chemistry; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, R.G. Limnology; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.D.H.; Syers, J.K.; Harris, R.F.; Armstrong, D.E. Fractionation of Inorganic Phosphate in Calcareous Lake Sediments. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1971, 35, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istvanovics, V.; Somlyody, L. Factors influencing lake recovery from eutrophication—The case of Basin 1 of Lake Balaton. Water Res. 2001, 35, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatvani, I.G.; de Barros, V.D.; Tanos, P.; Kovács, J.; Székely Kovács, I.; Clement, A. Spatiotemporal changes and drivers of trophic status over three decades in the largest shallow lake in Central Europe, Lake Balaton. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 151, 105861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istvánovics, V. Seasonal variation of phosphorus release from the sediments of Shallow Lake Balaton (Hungary). Water Res. 1988, 22, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istvánovics, V.; Herodek, S.; Szilágyi, F. Phosphate adsorption by different sediment fractions in Lake Balaton and its protecting reservoirs. Water Res. 1989, 23, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinović, Z.; Tokodi, N.; Backović, D.D.; Šćekić, I.; Kitanović, N.; Simić, S.B.; Đorđević, N.B.; Ferincz, Á.; Staszny, Á.; Dulić, T.; et al. Does the kis-balaton water protection system (Kbwps) effectively safeguard lake balaton from toxic cyanobacterial blooms? Microorganisms 2021, 9, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, M.; Szatmári, G.; Kassai, P.; Kovács, G.; Tóth, J.; Krámer, T.; Torma, P.; Homoródi, K.; Pomogyi, P.; Szeglet, P.; et al. Soluble phosphorus content of Lake Balaton sediments. J. Maps 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, J.A.; McCauley, E. The nitrogen: Phosphorus relationship in lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Présing, M.; Preston, T.; Takátsy, A.; Sprőber, P.; Kovács, A.W.; Vörös, L.; Kenesi, G.; Kóbor, I. Phytoplankton nitrogen demand and the significance of internal and external nitrogen sources in a large shallow lake (Lake Balaton, Hungary). Hydrobiologia 2008, 599, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörös, L.; Göde, P.N. Long term changes of phytoplankton in Lake Balaton (Hungary). Int. Ver. Für Theor. Und Angew.Limnol. Verh. 1993, 25, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, J.; Nagy, M.; Czauner, B.; Kovács, I.S.; Borsodi, A.K.; Hatvani, I.G. Delimiting sub-areas in water bodies using multivariate data analysis on the example of Lake Balaton (W Hungary). J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 110, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magyar, N.; Hatvani, I.G.; Székely, I.K.; Herzig, A.; Dinka, M.; Kovács, J. Application of multivariate statistical methods in determining spatial changes in water quality in the Austrian part of Neusiedler See. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 55, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blix, K.; Pálffy, K.; Tóth, V.R.; Eltoft, T. Remote sensing of water quality parameters over Lake Balaton by using Sentinel-3 OLCI. Water 2018, 10, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Łopata, M.; Popielarczyk, D.; Templin, T.; Dunalska, J.; Wiśniewski, G.; Bigaj, I.; Szymański, D. Spatial variability of nutrients (N, P) in a deep, temperate lake with a low trophic level supported by global navigation satellite systems, geographic information system and geostatistics. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 1834–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, J.M.; Williams, G.P.; Miller, A.W.; Merritt, L.V. Measuring and calculating current atmospheric phosphorous and nitrogen loadings to Utah Lake using field samples and geostatistical analysis. Hydrology 2018, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarah, S.; Jeelani, G.; Ahmed, S. Assessing variability of water quality in a groundwater-fed perennial lake of Kashmir Himalayas using linear geostatistics. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 120, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997; ISBN 9780195115383. [Google Scholar]
- Wackernagel, H. Multivariate Geostatistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cressie, N.A.C. Statistics for Spatial Data; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, R.; Oliver, M.A. Geostatistics for Environmental Scientists, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 0470028580. [Google Scholar]
- Pásztor, L.; Szabó, K.Z.; Szatmári, G.; Laborczi, A.; Horváth, Á. Mapping geogenic radon potential by regression kriging. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, G.; Hermann, T.; Szatmári, G.; Pásztor, L. Maps of heavy metals in the soils of the European Union and proposed priority areas for detailed assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborczi, A.; Bozán, C.; Körösparti, J.; Szatmári, G.; Kajári, B.; Túri, N.; Kerezsi, G.; Pásztor, L. Application of Hybrid Prediction Methods in Spatial Assessment of Inland Excess Water Hazard. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, G.; Pásztor, L. Comparison of various uncertainty modelling approaches based on geostatistics and machine learning algorithms. Geoderma 2019, 337, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somlyódy, L.; van Straten, G. Modeling and Managing Shallow Lake Eutrophication with Application to Lake Balaton; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Tasnim, B.; Fang, X.; Hayworth, J.S.; Tian, D. Simulating nutrients and phytoplankton dynamics in lakes: Model development and applications. Water 2021, 13, 2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istvánovics, V.; Honti, M. Stochastic simulation of phytoplankton biomass using eighteen years of daily data—Predictability of phytoplankton growth in a large, shallow lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 143636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.; Teurlincx, S.; Janse, J.H.; Paerl, H.W.; Mooij, W.M.; Janssen, A.B.G. Exploring how cyanobacterial traits affect nutrient loading thresholds in shallow lakes: A modelling approach. Water 2020, 12, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honti, M.; Gao, C.; Istvánovics, V.; Clement, A. Lessons Learnt from the Long-Term Management of a Large (Re)constructed Wetland, the Kis-Balaton Protection System (Hungary). Water 2020, 12, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goovaerts, P. Sample Support. Encycl. Environ. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistical modelling of uncertainty in soil science. Geoderma 2001, 103, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressie, N. Block kriging for lognormal spatial processes. Math. Geol. 2006, 38, 413–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, G.; Pásztor, L.; Heuvelink, G.B.M. Estimating soil organic carbon stock change at multiple scales using machine learning and multivariate geostatistics. Geoderma 2021, 403, 115356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csermák, K.; Máté, F. A Balaton Talaja; Veszprémi Egyetem Georgikon Kar: Keszthely, Hungary, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Máté, F. A Balaton-meder recens üledékeinek térképezése. Magy. Állami Földtani Intézet Évi Jelentése Az 1985. Évről 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldahl, J. Neue Methode zur Bestimmung des Stickstoffs in organischen Körpern. Z. Für Anal. Chem. 1883, 22, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geiger, J. Some thoughts on the pre- and post-processing in sequential gaussian simulation and their effects on reservoir characterization. In New Horizons in Central European Geomathematics, Geostatistics and Geoinformatics; Geiger, J., Pál-Molnár, E., Malvic, T., Eds.; GeoLitera: Szeged, Hungary, 2012; pp. 17–34. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch, C.V.; Journel, A.G. GSLIB: Geostatistical Software Library and User’s Guide; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998; ISBN 9780195100150. [Google Scholar]
- Matheron, G. Principles of geostatistics. Econ. Geol. 1963, 58, 1246–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.I.-K. A Concordance Correlation Coefficient to Evaluate Reproducibility. Biometrics 1989, 45, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, G.; Bakacsi, Z.; Laborczi, A.; Petrik, O.; Pataki, R.; Tóth, T.; Pásztor, L. Elaborating Hungarian segment of the Global Map of Salt-affected Soils (GSSmap): National contribution to an international initiative. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herodek, S.; Istvánovics, V. Mobility of phosphorus fractions in the sediments of Lake Balaton. Hydrobiologia 1986, 135, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczkó, K.; Ács, É.; Báldi, K.; Pozderka, V.; Braun, M.; Kiss, K.T.; Korponai, J. The first high resolution diatom record from Lake Balaton, Hungary in Central Europe. Limnetica 2019, 38, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagehashi, M.; Sakoda, A.; Suzuki, M. A mathematical model of a shallow and Eutrophic Lake (The Keszthely Basin, Lake Balaton) and simulation of restorative manipulations. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuvelink, G.B.M. Error Propagation in Environmental Modelling with GIS; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1998; ISBN 074840743X. [Google Scholar]
- Chilès, J.-P.; Delfiner, P. Geostatistics: Modeling Spatial Uncertainty, 2nd ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780470183151. [Google Scholar]
- Fehér, Z.Z.; Rakonczai, J. Analysing the sensitivity of Hungarian landscapes based on climate change induced shallow groundwater fluctuation. Hung. Geogr. Bull. 2019, 68, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborczi, A.; Szatmári, G.; Kaposi, A.D.; Pásztor, L. Comparison of soil texture maps synthetized from standard depth layers with directly compiled products. Geoderma 2019, 352, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garamhegyi, T.; Hatvani, I.G.; Szalai, J.; Kovács, J. Delineation of Hydraulic Flow Regime Areas Based on the Statistical Analysis of Semicentennial Shallow Groundwater Table Time Series. Water 2020, 12, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McBratney, A.B.; Webster, R. Optimal interpolation and isarithmic mapping of soil properties. V. Co-regionalization and multiple sampling strategy. J. Soil Sci. 1983, 34, 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeh, I.O.A.; McBratney, A.B.; Chittleborough, D.J. Spatial prediction of soil properties from landform attributes derived from a digital elevation model. Geoderma 1994, 63, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeh, I.O.A.; McBratney, A.B.; Chittleborough, D.J. Further results on prediction of soil properties from terrain attributes: Heterotopic cokriging and regression-kriging. Geoderma 1995, 67, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

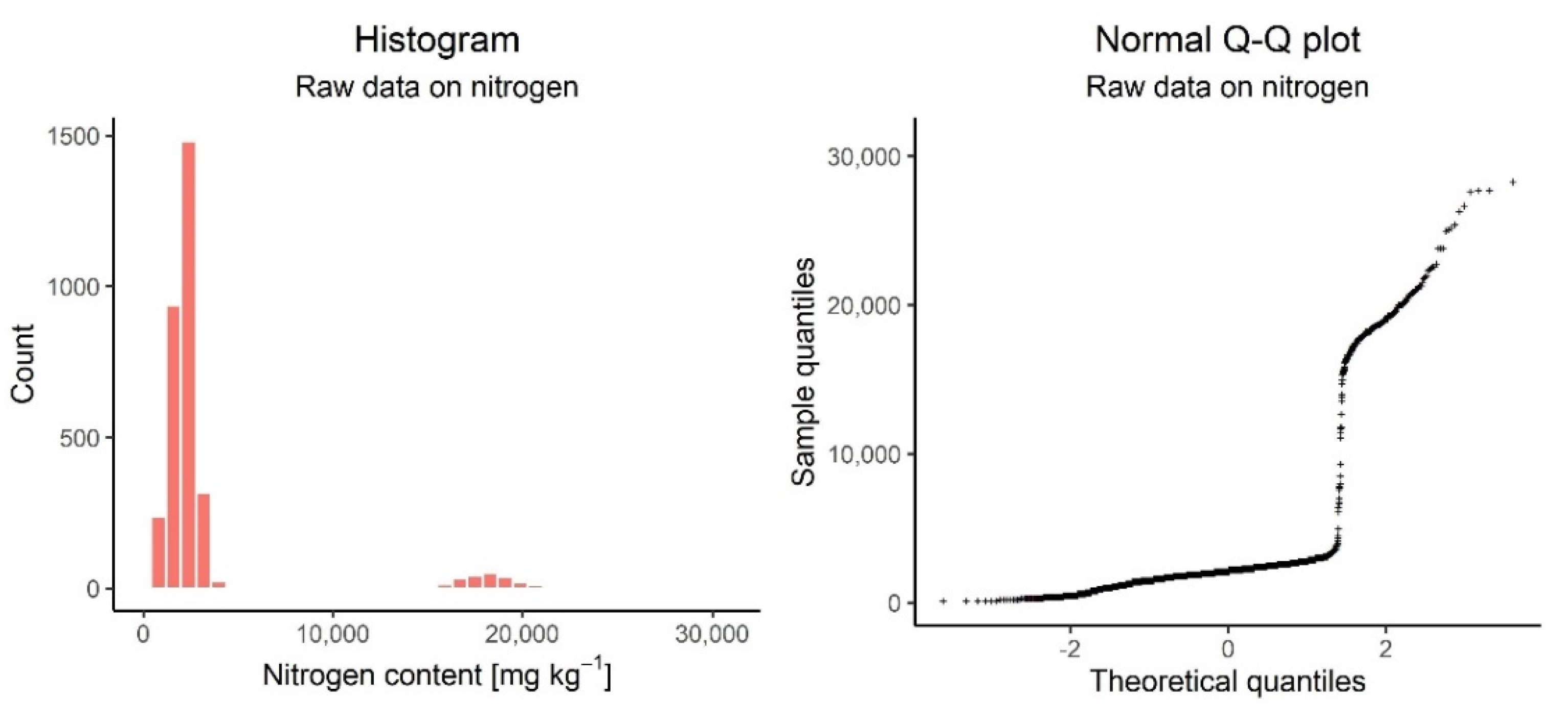
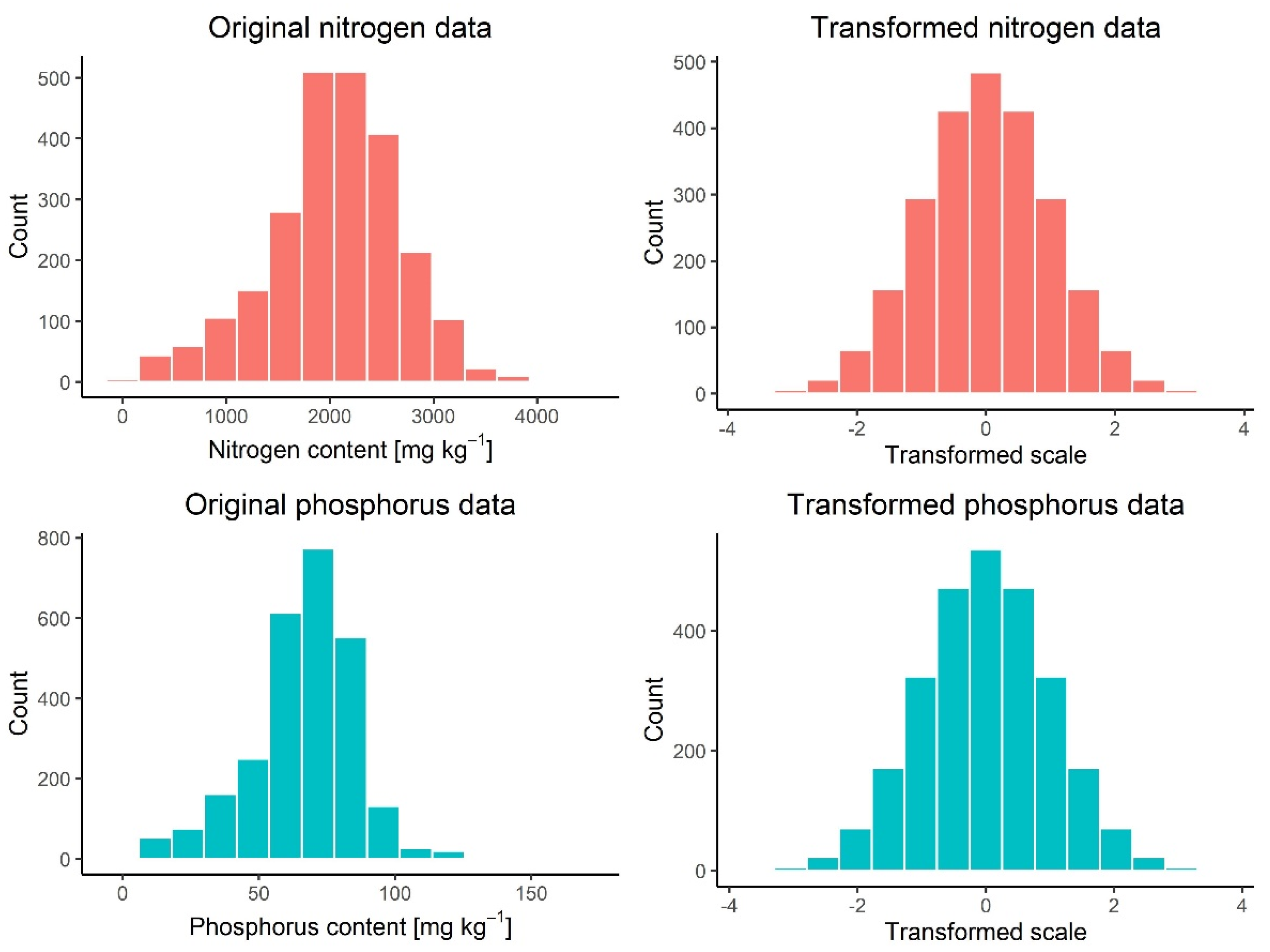




| Nutrient | Unit | n | Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | mg kg−1 | 2426 | 100 | 4500 | 2040 | 2100 | 634.63 |
| Phosphorus | mg kg−1 | 2672 | 3.49 | 170.86 | 66.61 | 68.17 | 19.27 |
| Model Type | Partial Sill | Range [km] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Variogram Nitrogen | Nugget | 0.2726 | 0 |
| Spherical | 0.4199 | 3.5 | |
| Spherical | 0.3845 | 20 | |
| Variogram Phosphorus | Nugget | 0.0723 | 0 |
| Spherical | 0.2835 | 3.5 | |
| Spherical | 0.7612 | 20 | |
| Cross-variogram Nitrogen and Phosphorus | Nugget | 0.0063 | 0 |
| Spherical | 0.0320 | 3.5 | |
| Spherical | 0.3413 | 20 |
| ME | RMSE | CCC | NSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | 7.61 | 463.93 | 0.65 | 0.48 |
| Phosphorus | 0.34 | 8.56 | 0.89 | 0.80 |
| N:P ratio | 0.09 | 12.54 | 0.52 | 0.31 |
| Spatial Average | Spatial Average | Spatial Average | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Phosphorus | N:P Ratio | |
| Keszthely basin | 2383.15 mg kg−1 | 87.56 mg kg−1 | 28.76 |
| [2005.15; 2775.96] | [86.29; 88.87] | [23.77; 33.91] | |
| Szigliget basin | 2389.21 mg kg−1 | 78.74 mg kg−1 | 30.68 |
| [2361.82; 2416.21] | [78.26; 79.20] | [30.30; 31.07] | |
| Szemes basin | 1920.13 mg kg−1 | 59.39 mg kg−1 | 36.63 |
| [1893.33; 1947.10] | [58.84; 59.96] | [35.71; 37.57] | |
| Siófok basin | 1950.68 mg kg−1 | 63.31 mg kg−1 | 32.39 |
| [1927.07; 1971.57] | [62.88; 63.74] | [31.88; 32.86] | |
| Lake Balaton | 2063.51 mg kg−1 | 66.94 mg kg−1 | 33.17 |
| [2035.44; 2092.69] | [66.68; 67.22] | [32.67; 33.70] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szatmári, G.; Kocsis, M.; Makó, A.; Pásztor, L.; Bakacsi, Z. Joint Spatial Modeling of Nutrients and Their Ratio in the Sediments of Lake Balaton (Hungary): A Multivariate Geostatistical Approach. Water 2022, 14, 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030361
Szatmári G, Kocsis M, Makó A, Pásztor L, Bakacsi Z. Joint Spatial Modeling of Nutrients and Their Ratio in the Sediments of Lake Balaton (Hungary): A Multivariate Geostatistical Approach. Water. 2022; 14(3):361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030361
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzatmári, Gábor, Mihály Kocsis, András Makó, László Pásztor, and Zsófia Bakacsi. 2022. "Joint Spatial Modeling of Nutrients and Their Ratio in the Sediments of Lake Balaton (Hungary): A Multivariate Geostatistical Approach" Water 14, no. 3: 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030361
APA StyleSzatmári, G., Kocsis, M., Makó, A., Pásztor, L., & Bakacsi, Z. (2022). Joint Spatial Modeling of Nutrients and Their Ratio in the Sediments of Lake Balaton (Hungary): A Multivariate Geostatistical Approach. Water, 14(3), 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030361







