Spatial Distribution of Ciliate Assemblages in a Shallow Floodplain Lake with an Anaerobic Zone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
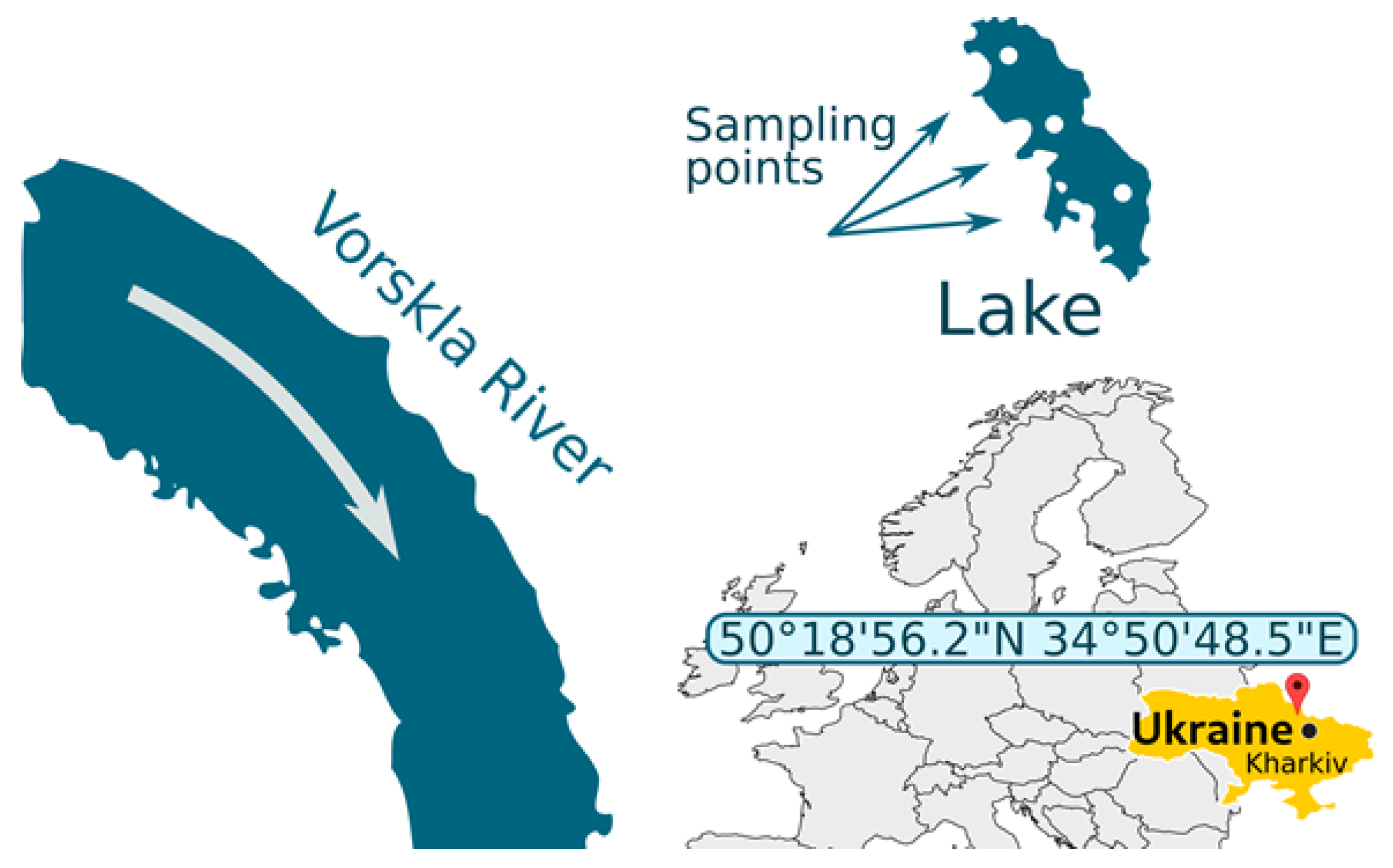
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Habitats
2.3. Data Collection and Sample Processing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
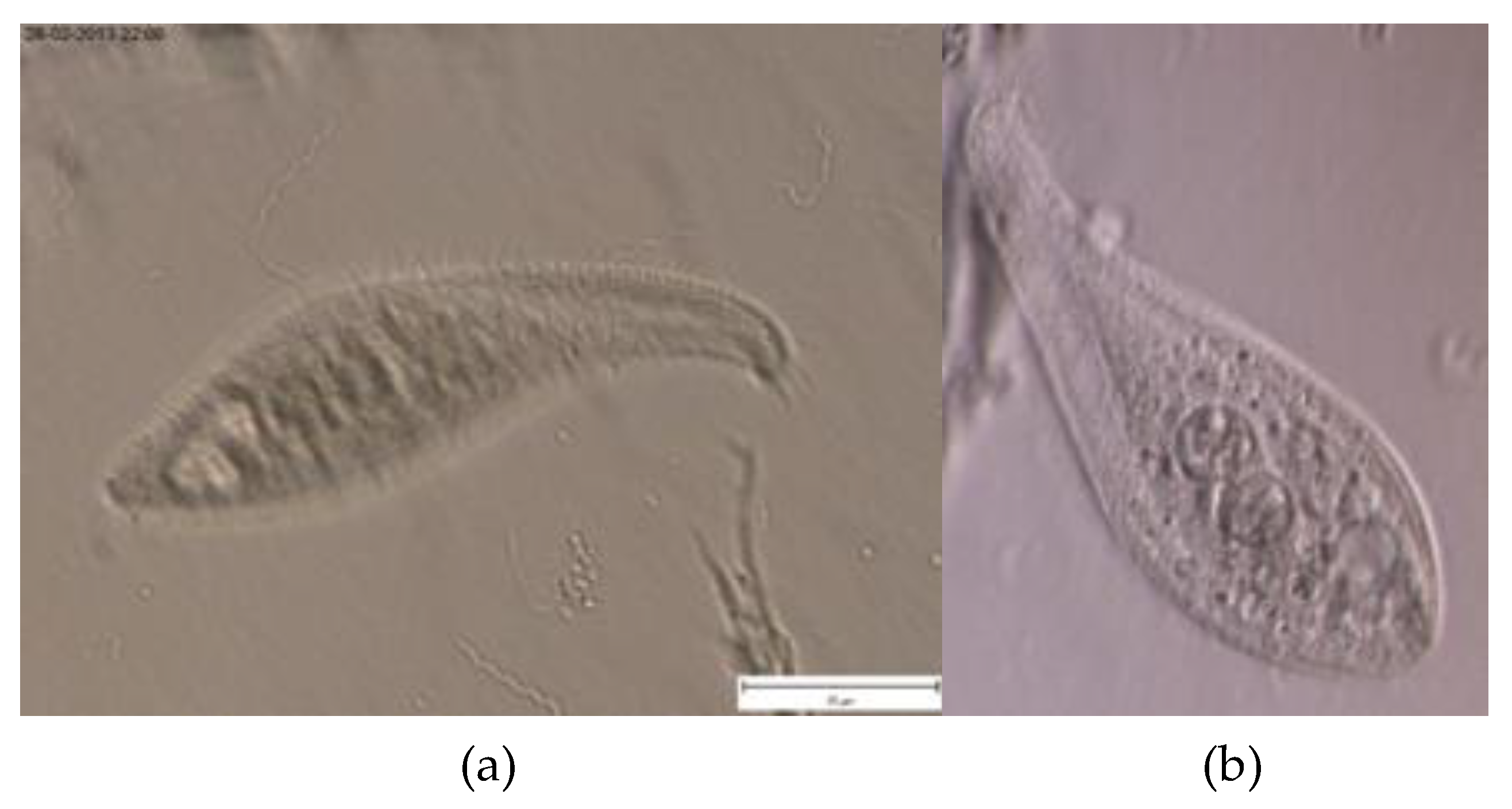
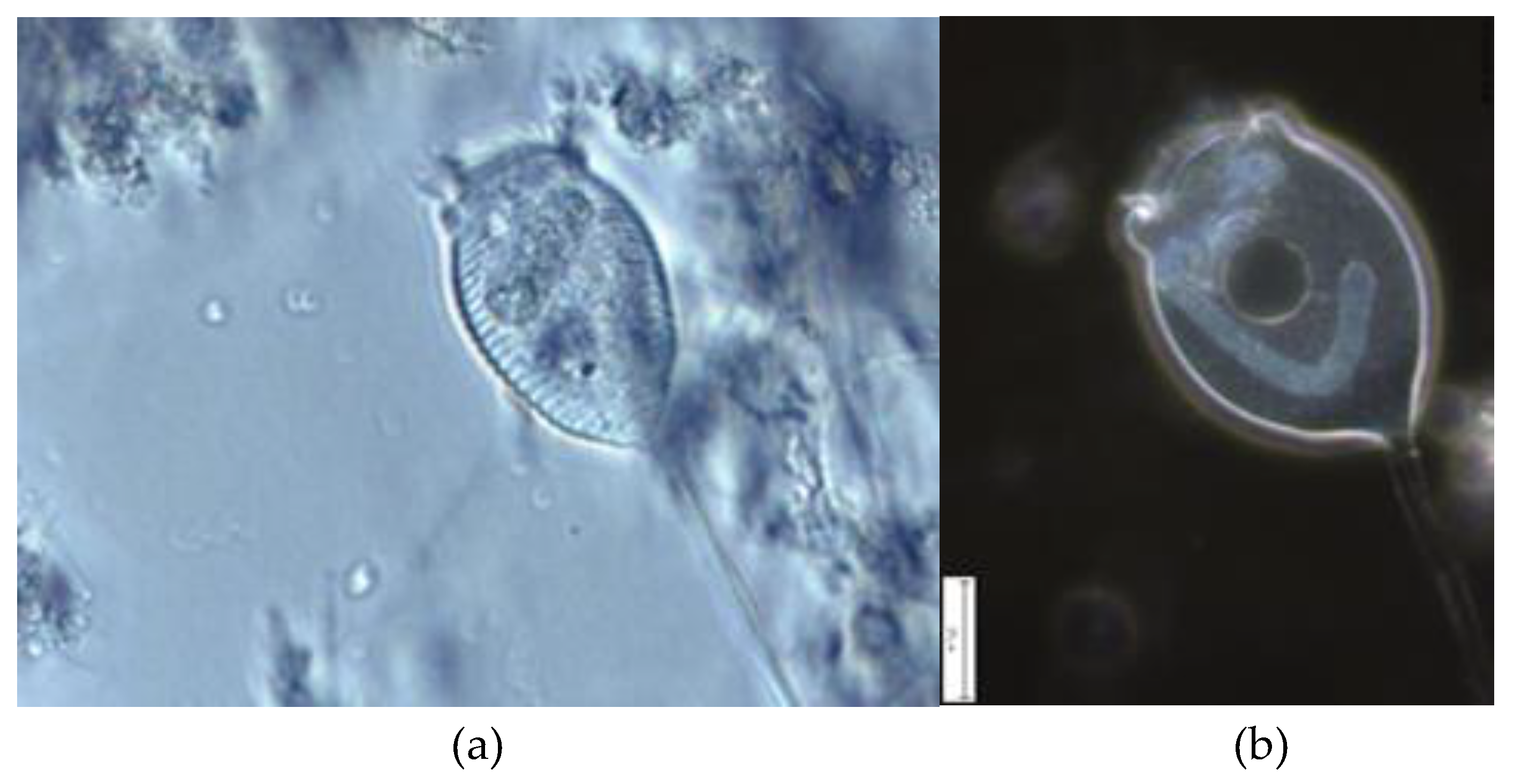
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Acreman, M.; Dunbar, M.J. Defining environmental river flow requirements—A review. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 8, 861–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babko, R.; Kuzmina, T. Effect of dams on hydrological parameters and the structure of benthic molluscs: Case study in Dnieper river Basin. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2009, 9, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Zimmerman, J.K.H. Ecological responses to altered flow regimes: A literature review to inform the science and management of environmental flows. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belletti, B.; Rinaldi, M.; Buijse, A.D.; Gurnell, A.M.; Mosselman, E. A review of assessment methods for river hydromorphology. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 2079–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizzetti, B.; Pistocchi, A.; Liquete, C.; Udias, A.; Bouraoui, F.; Van De Bund, W. Human pressures and ecological status of European rivers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ward, J.V.; Tockner, K.; Schiemer, F. Biodiversity of floodplain river ecosystems: Ecotones and connectivity1. Regul. Rivers Res. Manag. 1999, 15, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weilhoefer, C.L.; Pan, Y.; Eppard, S. The effects of river floodwaters on floodplain wetland water quality and diatom assemblages. Wetlands 2008, 28, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.G.C.; Gurney, S.E.; Goldsborough, L.G. The primary productivity of benthic and planktonic algae in a prairie wetland under controlled water-level regimes. Wetlands 1997, 17, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stromberg, J.C.; Fry, J.; Patten, D.T. Marsh development after large floods in an alluvial, arid-land river. Wetlands 1997, 17, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.J.; Prairie, Y.T.; Caraco, N.F.; McDowell, W.H.; Tranvik, L.J.; Striegl, R.G.; Duarte, C.M.; Kortelainen, P.; Downing, J.A.; Middelburg, J.J.; et al. Plumbing the Global Carbon Cycle: Integrating Inland Waters into the Terrestrial Carbon Budget. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tranvik, L.J.; Downing, J.A.; Cotner, J.B.; Loiselle, S.A.; Striegl, R.G.; Ballatore, T.J.; Dillon, P.; Finlay, K.; Fortino, K.; Knoll, L.B.; et al. Lakes and reservoirs as regulators of carbon cycling and climate. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2298–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastviken, D.; Tranvik, L.J.; Downing, J.A.; Crill, P.M.; Enrich-Prast, A. Freshwater Methane Emissions Offset the Continental Carbon Sink. Science 2011, 331, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grasset, C.; Mendonça, R.; Villamor Saucedo, G.; Bastviken, D.; Roland, F.; Sobek, S. Large but variable methane production in anoxic freshwater sediment upon addition of allochthonous and autochthonous organic matter. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 1488–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobek, S.; Durisch-Kaiser, E.; Zurbrügg, R.; Wongfun, N.; Wessels, M.; Pasche, N.; Wehrli, B. Organic carbon burial efficiency in lake sediments controlled by oxygen exposure time and sediment source. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2243–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobek, S.; Delsontro, T.; Wongfun, N.; Wehrli, B. Extreme organic carbon burial fuels intense methane bubbling in a temperate reservoir. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L01401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finlay, B. An anaerobic protozoon, with symbiotic methanogens, living in municipal landfill material. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1991, 85, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fenchel, T. Methanogenesis in marine shallow water sediments: The quantitative role of anaerobic protozoa with endosymbiotic methanogenic bacteria. Ophelia 1993, 37, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foissner, W.; Berger, H. A user-friendly guide to the ciliates (Protozoa, Ciliophora) commonly used by hydrobiologists as bioindicators in rivers, lakes, and waste waters, with notes on their ecology. Freshw. Biol. 1996, 35, 375–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primc-Habdija, B.; Habdija, I.; Plenković-Moraj, A. Tufa deposition and periphyton overgrowth as factors affecting the ciliate community on travertine barriers in different current velocity conditions. Hydrobiologia 2001, 457, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, S.A.; Nagel, S.; Hillebrand, H. Control of epibenthic ciliate communities by grazers and nutrients. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 35, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, J.; Song, W.; Warren, A. Periphytic ciliate colonization: Annual cycle and responses to environmental conditions. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 39, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mieczan, T. Periphytic ciliates in littoral zone of three lakes of different trophic status. Polish J. Ecol. 2005, 53, 489–501. [Google Scholar]
- Fenchel, T.; Finlay, B. Oxygen and the spatial structure of microbial communities. Biol. Rev. 2008, 83, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenchel, T. Protozoa and oxygen. Acta Protozool. 2014, 53, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babko, R.; Kuzmina, T.; Danko, Y.; Szulzyk-Cieplak, J.; Łagód, G. Oxygen gradients and structure of the ciliate assemblages in floodplain lake. Water 2020, 12, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleigh, M.A.; Baldock, B.M.; Baker, J.H. Protozoan communities in chalk streams. Hydrobiologia 1992, 248, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primc-Habdija, B.; Habdija, I.; Radanović, I. Seasonal changes in trophic structure of periphytic ciliates in relation to discharge regime. SIL Proc. 1922–2010 1998, 26, 1116–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament, C. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Parliam. 2000, L327, 1–82. [Google Scholar]
- Babko, R. Microbenthometer for protistological studies. Hydrobiol. J. 1989, 25, 78–80. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Foissner, W. Basic light and scanning electron microscopic methods for taxonomic studies of ciliated protozoa. Eur. J. Protistol. 1991, 27, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foissner, W.; Blatterer, H.; Berger, H.; Kohmann, F. Taxonomische und Ökologische Revision der Ciliaten des Saprobiensystems. Band I: Cyrtophorida, Oligotrichida, Hypotrichida, Colpodea; Informationsberichte des Bayer; Landesamtes für Wasserwirtschaft: Deggendorf, Germany, 1991; pp. 1–478.
- Foissner, W.; Berger, H.; Kohmann, F. Taxonomische und Ökologische Revision der Ciliaten des Saprobiensystems. Band II: Peritrichida, Heterotrichida, Odontostomatida; Informationsberichte des Bayer; Landesamtes für Wasserwirtschaft: Deggendorf, Germany, 1992; pp. 1–502.
- Foissner, W.; Berger, H.; Kohmann, F. Taxonomische und Ökologische Revision der Ciliaten des Saprobiensystems. Band III: Hymenostomatida, Prostomatida, Nassulida; Informationsberichte des Bayer; Landesamtes für Wasserwirtschaft: Deggendorf, Germany, 1994; pp. 1–548.
- Foissner, W.; Berger, H.; Blatterer, H.; Kohmann, F. Taxonomische und Ökologische Revision der Ciliaten des Saprobiensystems. Band IV: Gymnostomatea, Loxodes, Suctoria; Informationsberichte des Bayer; Landesamtes für Wasserwirtschaft: Deggendorf, Germany, 1995; pp. 1–540.
- Jankowski, A.W. Morphology and evolution of Ciliophora. III. Diagnoses and phylogenesis of 53 sapropelebionts, mainly of the order Heterotrichida. Arch. Protistenkd. 1964, 107, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Kahl, A. Urtiere oder Protozoa I: Wimpertiere oder Ciliata (Infusoria) 1. Allgemeiner Teil und Prostomata. Tierwelt Dtl. 1930, 18, 1–180. [Google Scholar]
- Kahl, A. Urtiere oder Protozoa I: Wimpertiere oder Ciliata (Infusoria) 2. Holotricha außer den im 1. Teil behandelten Prostomata. Tierwelt Dtl. 1931, 21, 181–398. [Google Scholar]
- Kahl, A. Urtiere oder Protozoa I: Wimpertiere oder Ciliata (Infusoria) 3. Spirotricha. Tierwelt Dtl. 1932, 25, 399–650. [Google Scholar]
- Kahl, A. Urtiere oder Protozoa I: Wimpertiere oder Ciliata (Infusoria) 4. Peritricha und Chonotricha. Tierwelt Dtl. 1935, 30, 651–886. [Google Scholar]
- Team R Development Core. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; The R Project for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Volume 2, Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 11 January 2022).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G.E. Visualizing High-Dimensional Data Using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Maaten, L. Accelerating t-SNE using tree-based algorithms. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2015, 15, 3221–3245. [Google Scholar]
- Krijthe, J.H. Rtsne: T-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding Using a Barnes-Hut Implementation. 2016. Available online: https://github.com/jkrijthe/Rtsne (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’Hara, B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.M.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.4-2. Community Ecol. Packag. 2019, 2.5-6, 190. [Google Scholar]
- De Cáceres, M.; Legendre, P. Associations between species and groups of sites: Indices and statistical inference. Ecology 2009, 90, 3566–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindt, R.; Coe, R. Tree Diversity Analysis; A Manual and Software for Common Statistical Methods for Ecological and Biodiversity Studies; World Agroforestry Centre: Nairobi, Kenya, 2005; p. 196. [Google Scholar]
- Lynn, D.H. The Ciliated Protozoa: Characterization, Classification, and Guide to the Literature, 3rd ed.; Lynn, D.H., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; ISBN 9781402082399. [Google Scholar]
- Babko, R.V. Communities of Free-Living Ciliated Protozoa (Chromista, Ciliophora) of Continental Waters. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Hydrobiology, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine, 2019. (In Ukrainian). [Google Scholar]
- Fenchel, T. Ecology of Protozoa; Brock/Springer Series in Contemporary Bioscience; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987; ISBN 978-3-662-06819-9. [Google Scholar]
- Finlay, B.J.; Esteban, G.F. Freshwater protozoa: Biodiversity and ecological function. Biodivers. Conserv. 1998, 7, 1163–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.R.; Swerhone, G.D.W.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Neu, T.R. Effects of selected pharmaceuticals on riverine biofilm communities. Can. J. Microbiol. 2005, 51, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finlay, B.J.; Esteban, G.F.; Fenchel, T. Protozoan diversity: Converging estimates of the global number of free-living ciliate species. Protist 1998, 149, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, B.J.; Esteban, G.F.; Olmo, J.L.; Tyler, P.A. Global distribution of free-living microbial species. Ecography 1999, 22, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolkwitz, R.; Marsson, M. Ökologie der tierischen Saprobien. Beiträge zur Lehre von der biologischen Gewässerbeurteilung. Int. Rev. der Gesamten Hydrobiol. und Hydrogr. 1909, 2, 126–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sládeček, V. System of Water Analysis from the Biologica Point of View. Arch. Fuer Hydrobiol. Beih. 1973, 7, 114–137. [Google Scholar]
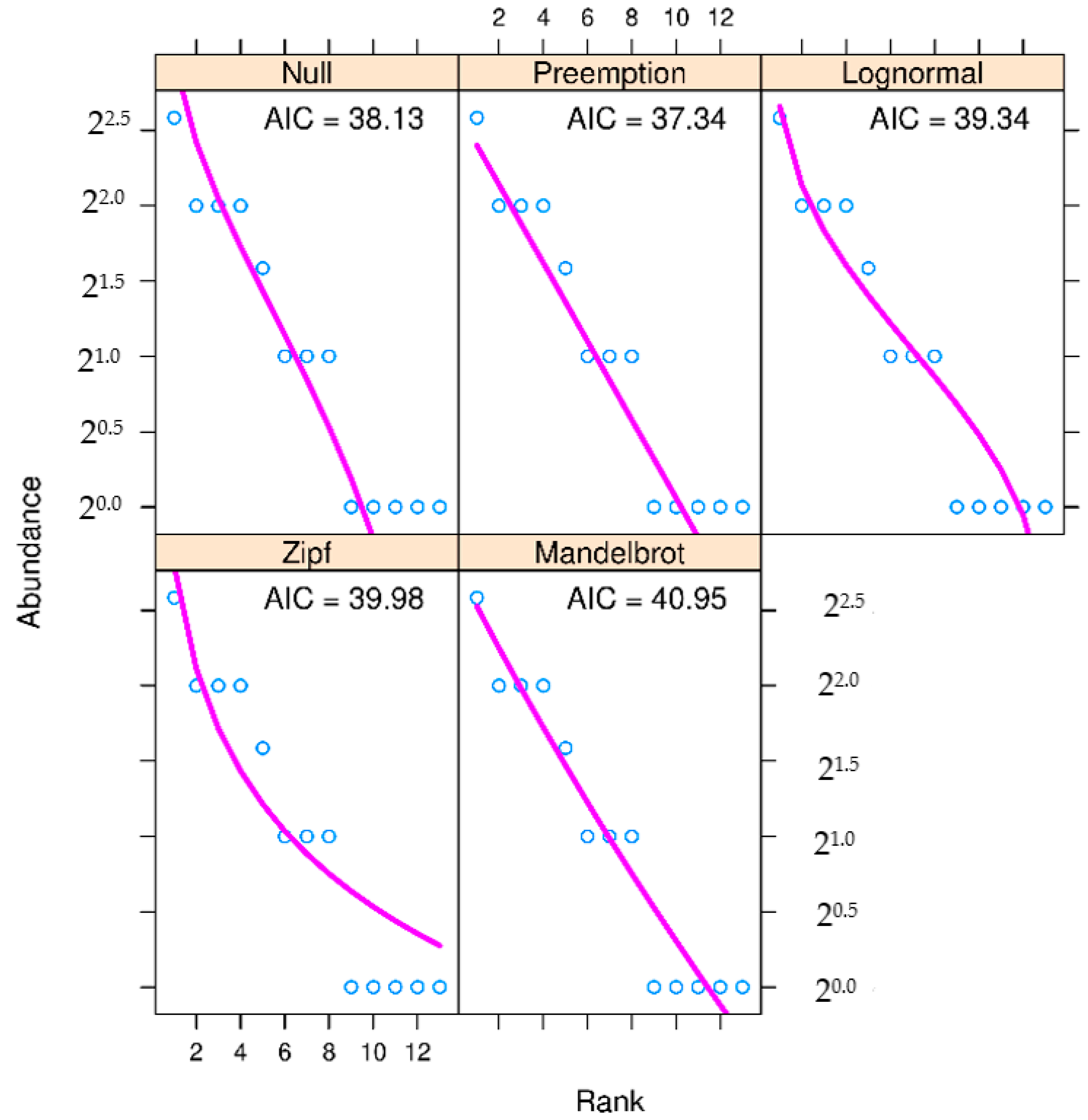
- Su, Q. A general pattern of the species abundance distribution. PeerJ 2018, 2018, e5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
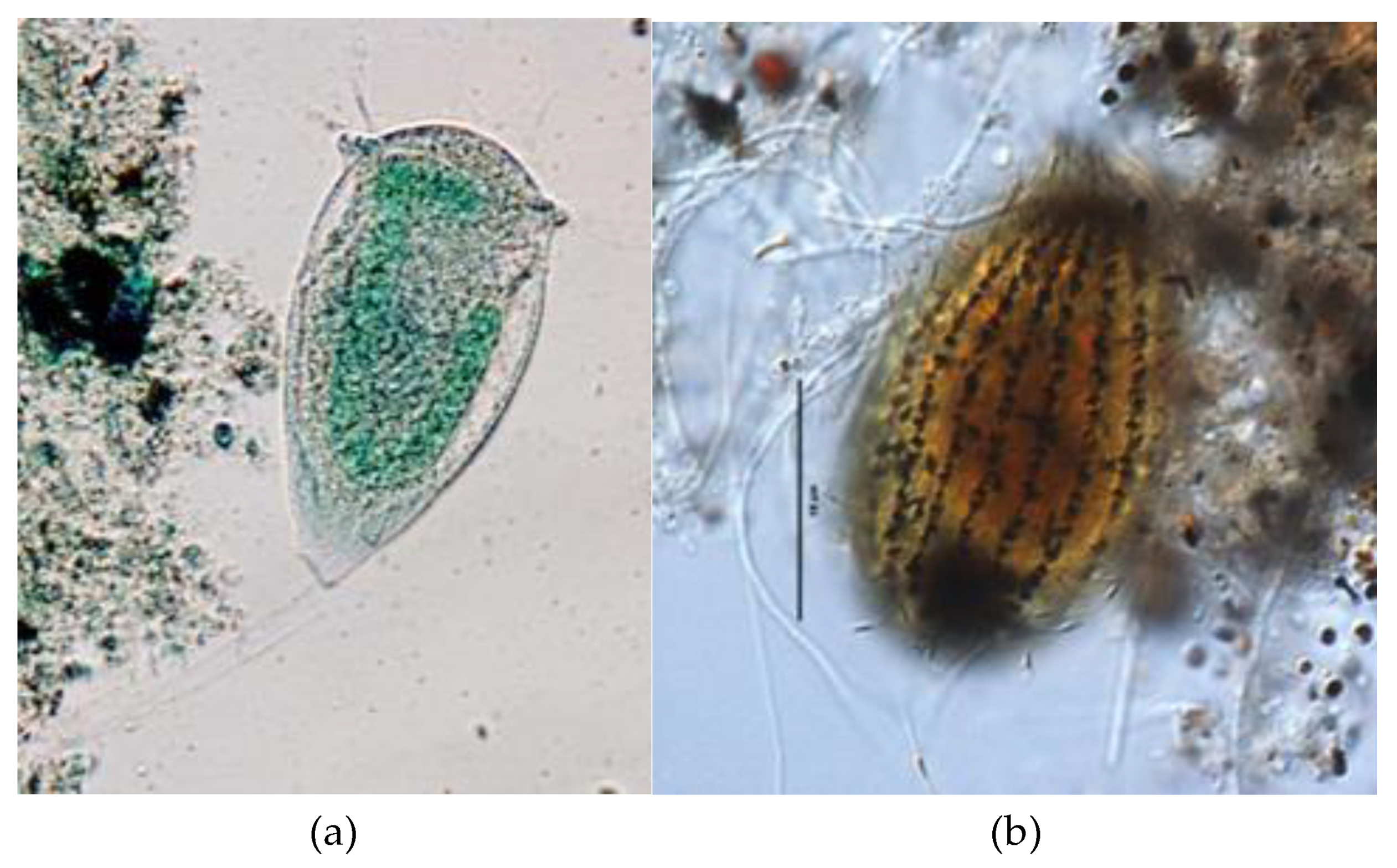



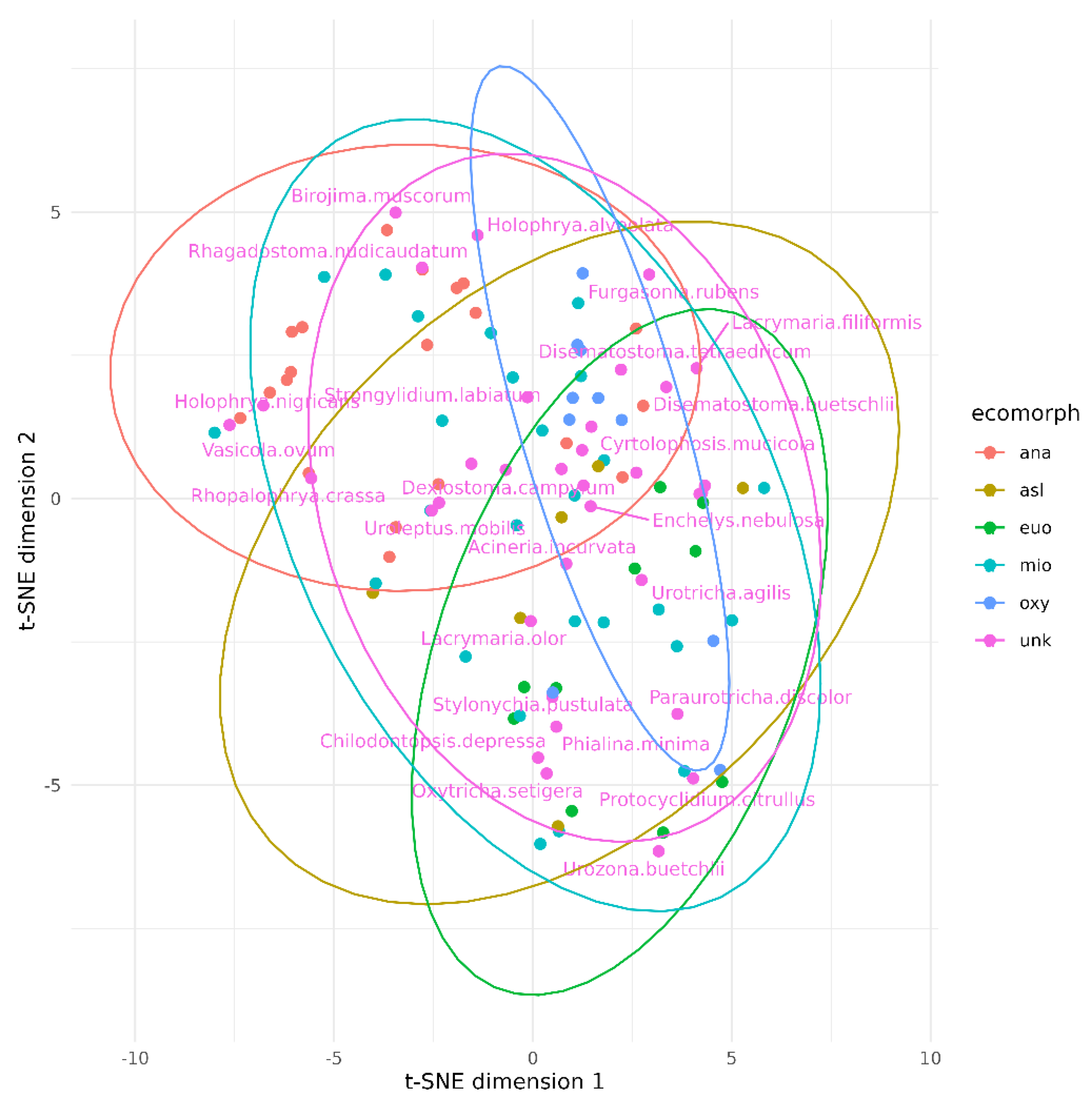

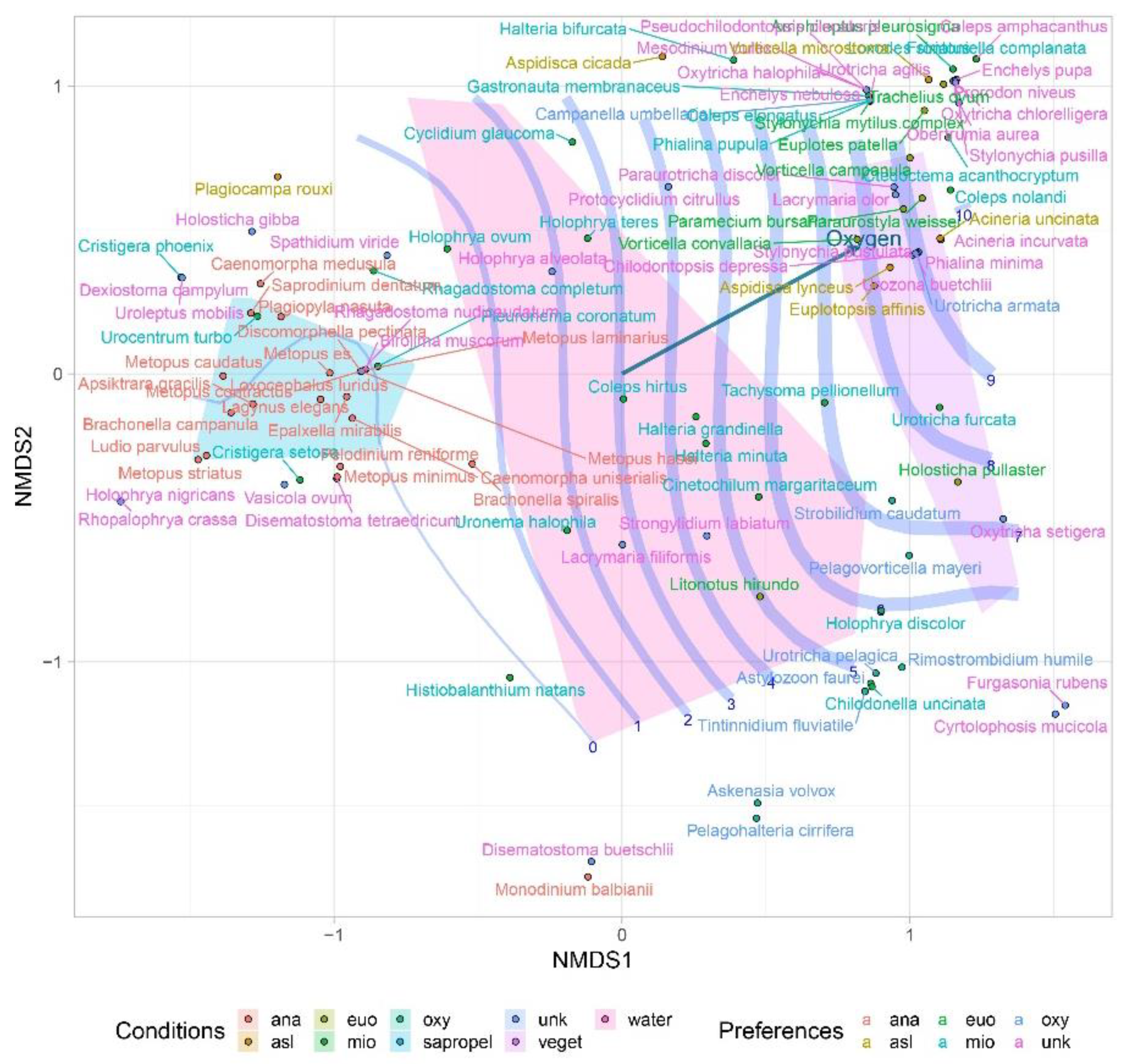
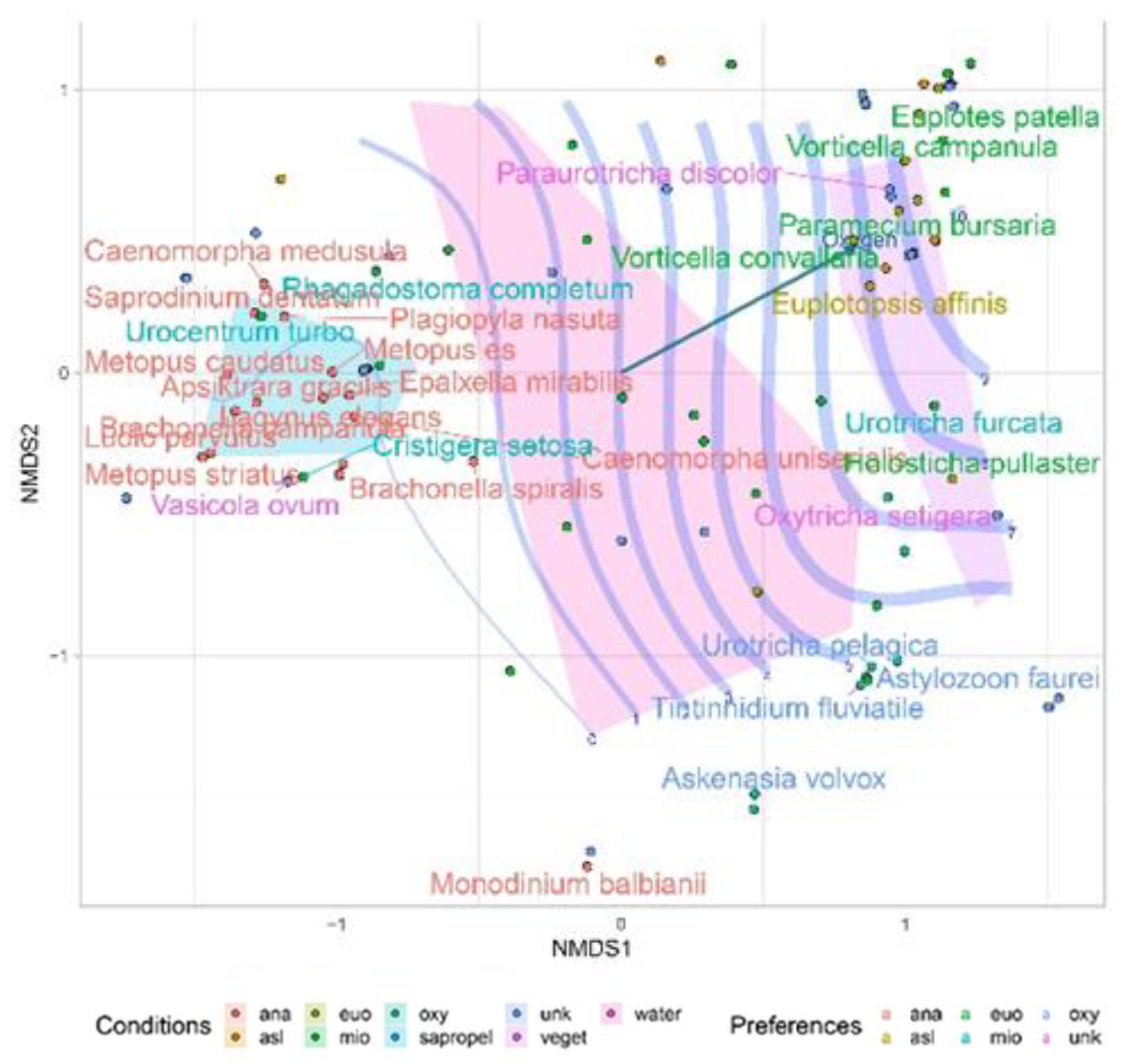
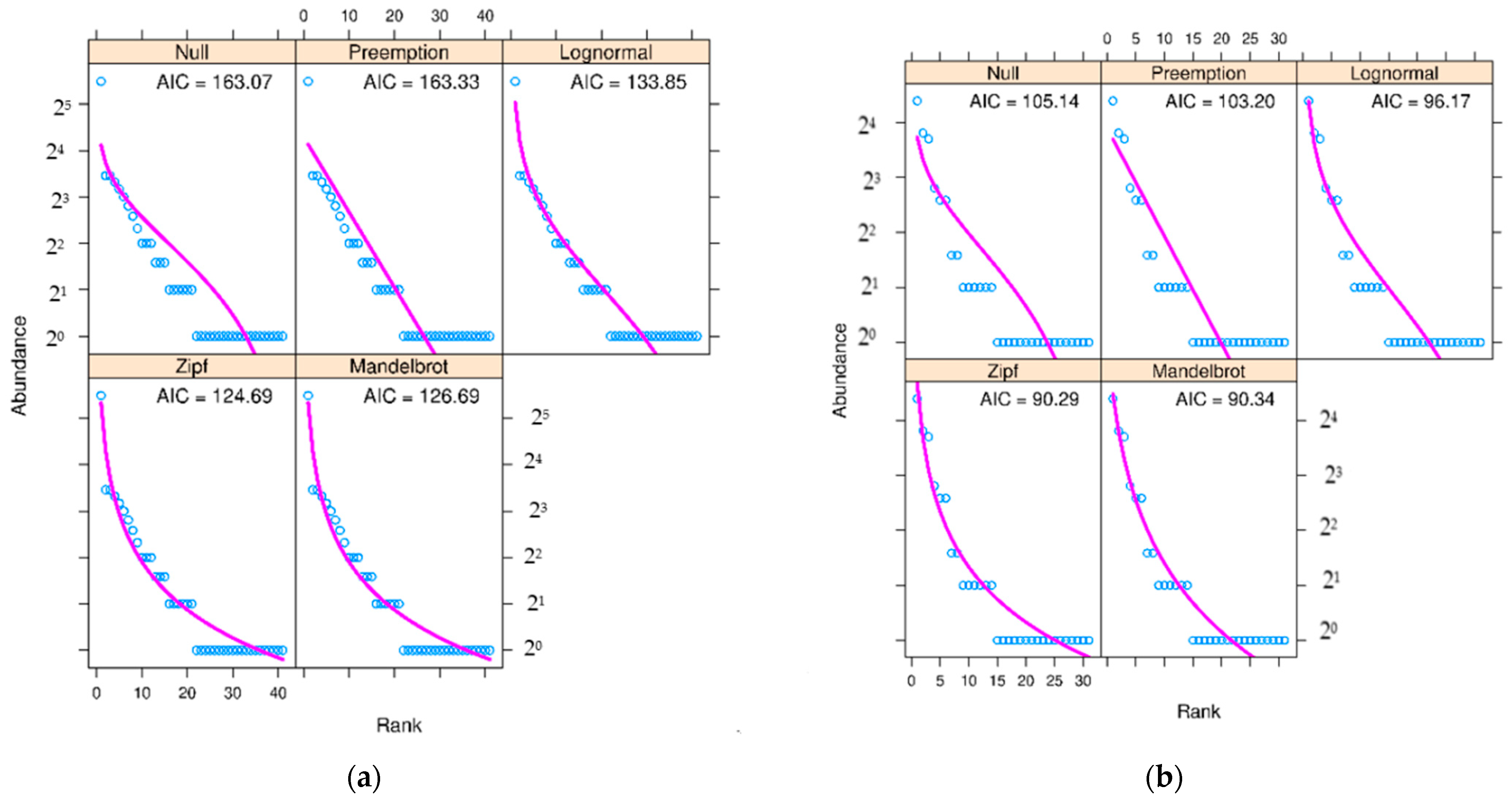
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Area, m2 | 3.006 |
| Length, m | 112.9 |
| Maximum width, m | 33.0 |
| Maximum depth, m | 1.5 |
| Habitats | T, °C | O2, mg/L | PI, mg O2/L |
|---|---|---|---|
| Among duckweed (L. trisulca and L. minor) | |||
| Winter | 0 | 0.0–7.0 | 28.6 ± 1.1 |
| Spring | 5–14 | 4.0–7.0 | 41.1 ± 5.4 |
| Summer | 18.5–25.5 | 7.0–10.3 | 37.4 ± 7.1 |
| Autumn | 2–13 | 2.4–5.7 | 45.4 ± 5.2 |
| Water under a layer of duckweed | |||
| Winter | 0 | 0.0–7.2 | 16.1 ± 1.4 |
| Spring | 5.0–10.1 | 1.0–7.0 | 21.1 ± 2.7 |
| Summer | 10.5–17.0 | 0.0–1.5 | 18.9 ± 2.1 |
| Autumn | 4.0–8.2 | 0.0–0.7 | 19.4 ± 3.6 |
| Sapropel | |||
| Winter | 0 | 0.0 | 48.4 ± 4.1 |
| Spring | 0.0–10.0 | 0.0 | 54.1 ± 3.8 |
| Summer | 9.1–16.0 | 0.0 | 52.0 ± 2.7 |
| Autumn | 4.0–9.2 | 0.0 | 61.7 ± 5.6 |
| Species | A | B | Stat | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sapropel | ||||
| Apsiktrara gracilis | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.001 |
| Brachonella campanula | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.001 |
| Cristigera setosa | 0.9824 | 1 | 0.991 | 0.001 |
| Plagiopyla nasuta | 0.9322 | 1 | 0.966 | 0.001 |
| Epalxella mirabilis | 0.9497 | 0.9231 | 0.936 | 0.001 |
| Rhagadostoma completum | 0.7842 | 1 | 0.886 | 0.001 |
| Metopus caudatus | 1 | 0.7692 | 0.877 | 0.001 |
| Lagynus elegans | 0.9719 | 0.7692 | 0.865 | 0.001 |
| Metopus es | 0.9276 | 0.7692 | 0.845 | 0.001 |
| Caenomorpha medusula | 0.9156 | 0.7692 | 0.839 | 0.001 |
| Vasicola ovum | 0.9921 | 0.6154 | 0.781 | 0.001 |
| Brachonella spiralis | 0.7759 | 0.7692 | 0.773 | 0.001 |
| Saprodinium dentatum | 1 | 0.5385 | 0.734 | 0.001 |
| Urocentrum turbo | 1 | 0.5385 | 0.734 | 0.001 |
| Caenomorpha uniserialis | 1 | 0.4615 | 0.679 | 0.002 |
| Ludio parvulus | 1 | 0.4615 | 0.679 | 0.003 |
| Metopus striatus | 1 | 0.4615 | 0.679 | 0.005 |
| Vegetation | ||||
| Urotricha furcata | 0.8521 | 1 | 0.923 | 0.001 |
| Vorticella campanula | 1 | 0.8 | 0.894 | 0.001 |
| Holosticha pullaster | 0.7633 | 1 | 0.874 | 0.001 |
| Euplotopsis affinis | 0.959 | 0.7333 | 0.839 | 0.001 |
| Vorticella convallaria | 0.8361 | 0.8 | 0.818 | 0.001 |
| Oxytricha setigera | 1 | 0.6 | 0.775 | 0.001 |
| Paramecium bursaria | 1 | 0.6 | 0.775 | 0.001 |
| Paraurotricha discolor | 1 | 0.6 | 0.775 | 0.001 |
| Euplotes patella | 1 | 0.5333 | 0.73 | 0.001 |
| Water | ||||
| Askenasia volvox | 1 | 0.3333 | 0.577 | 0.01 |
| Astylozoon faurei | 1 | 0.3333 | 0.577 | 0.009 |
| Disematostoma buetschlii | 1 | 0.3333 | 0.577 | 0.012 |
| Monodinium balbianii | 1 | 0.3333 | 0.577 | 0.012 |
| Tintinnidium fluviatile | 1 | 0.3333 | 0.577 | 0.009 |
| Urotricha pelagica | 1 | 0.3333 | 0.577 | 0.009 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babko, R.; Kuzmina, T.; Danko, Y.; Pliashechnyk, V.; Szulżyk-Cieplak, J.; Łazuka, E.; Zaburko, J.; Łagód, G. Spatial Distribution of Ciliate Assemblages in a Shallow Floodplain Lake with an Anaerobic Zone. Water 2022, 14, 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060898
Babko R, Kuzmina T, Danko Y, Pliashechnyk V, Szulżyk-Cieplak J, Łazuka E, Zaburko J, Łagód G. Spatial Distribution of Ciliate Assemblages in a Shallow Floodplain Lake with an Anaerobic Zone. Water. 2022; 14(6):898. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060898
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabko, Roman, Tetiana Kuzmina, Yaroslav Danko, Volodymyr Pliashechnyk, Joanna Szulżyk-Cieplak, Ewa Łazuka, Jacek Zaburko, and Grzegorz Łagód. 2022. "Spatial Distribution of Ciliate Assemblages in a Shallow Floodplain Lake with an Anaerobic Zone" Water 14, no. 6: 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060898
APA StyleBabko, R., Kuzmina, T., Danko, Y., Pliashechnyk, V., Szulżyk-Cieplak, J., Łazuka, E., Zaburko, J., & Łagód, G. (2022). Spatial Distribution of Ciliate Assemblages in a Shallow Floodplain Lake with an Anaerobic Zone. Water, 14(6), 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060898








