Sustainable Restoration as a Tool for the Improvement of Water Quality in a Shallow, Hypertrophic Lake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- changes of individual physico-chemical and biological parameters (chlorophyll-a content and plankton abundance) in time and space;
- (2)
- differences in the functioning of the lake ecosystem in both study periods (before and during the treatments);
- (3)
- identification of the most important factors influencing changes taking place in the ecosystem as a result of sustainable restoration treatments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area

2.2. Restoration Treatments of Raczyńskie Lake
2.3. Field and Laboratory Research
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
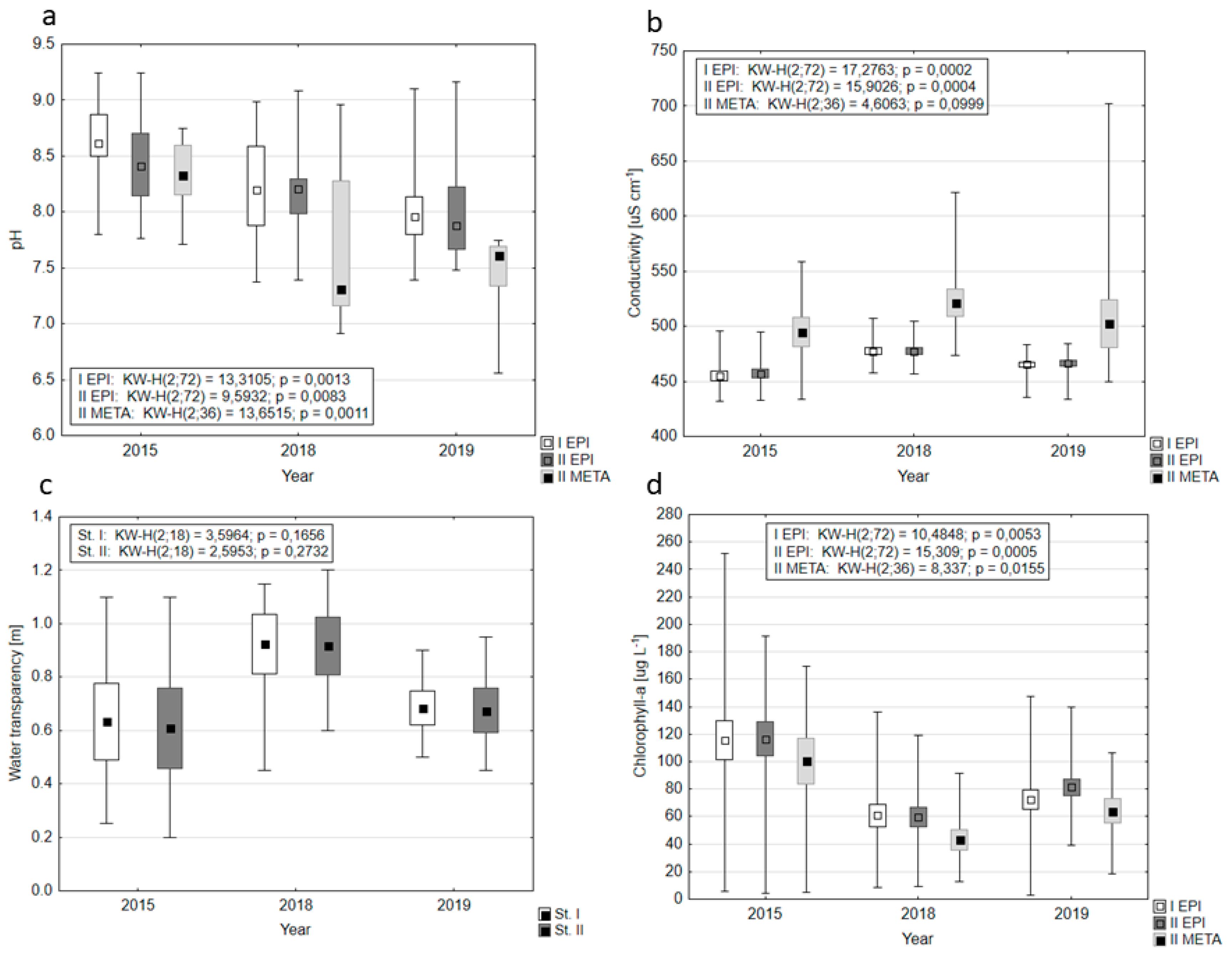
3.1. Water Chemistry
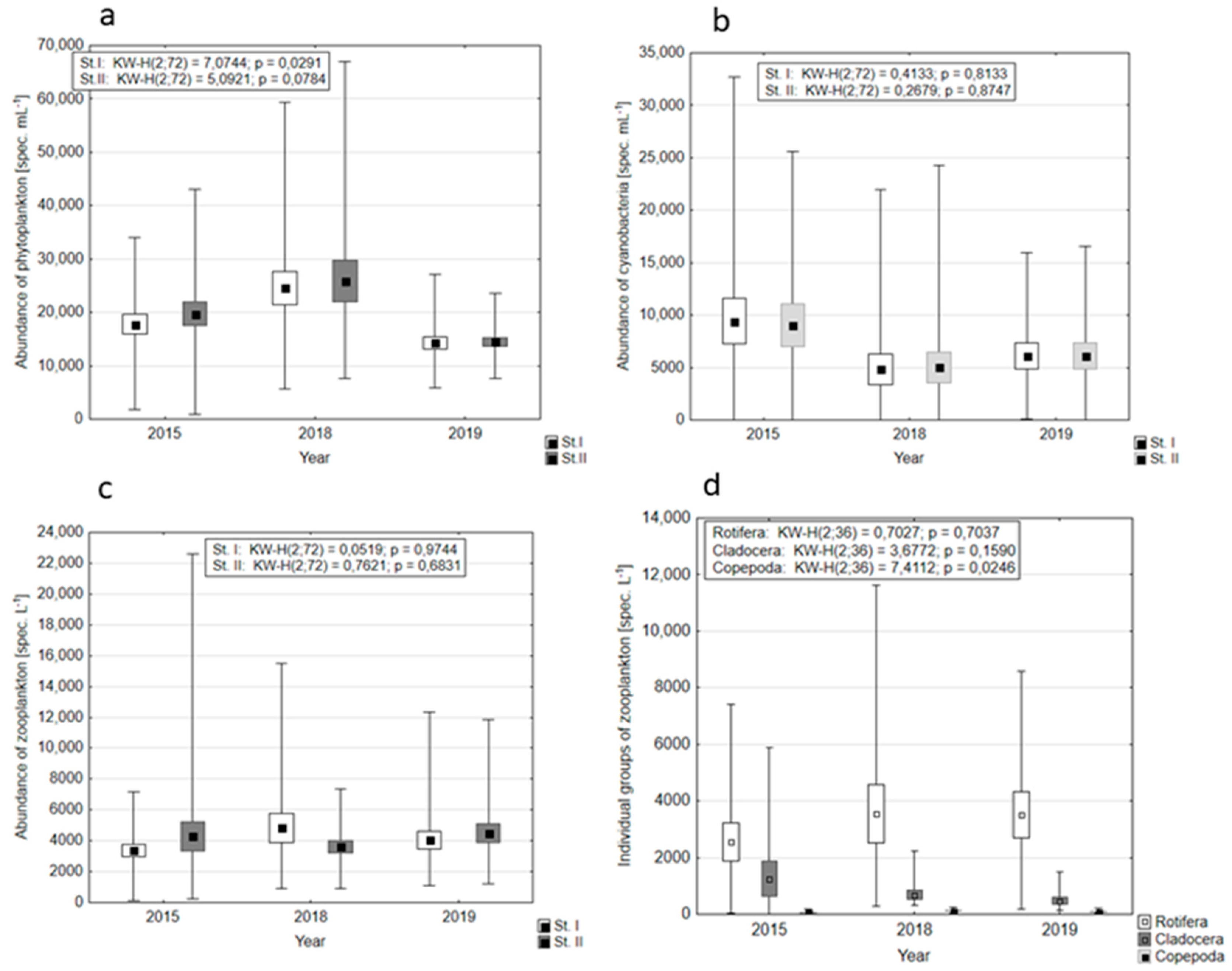
3.2. Plankton Abundance
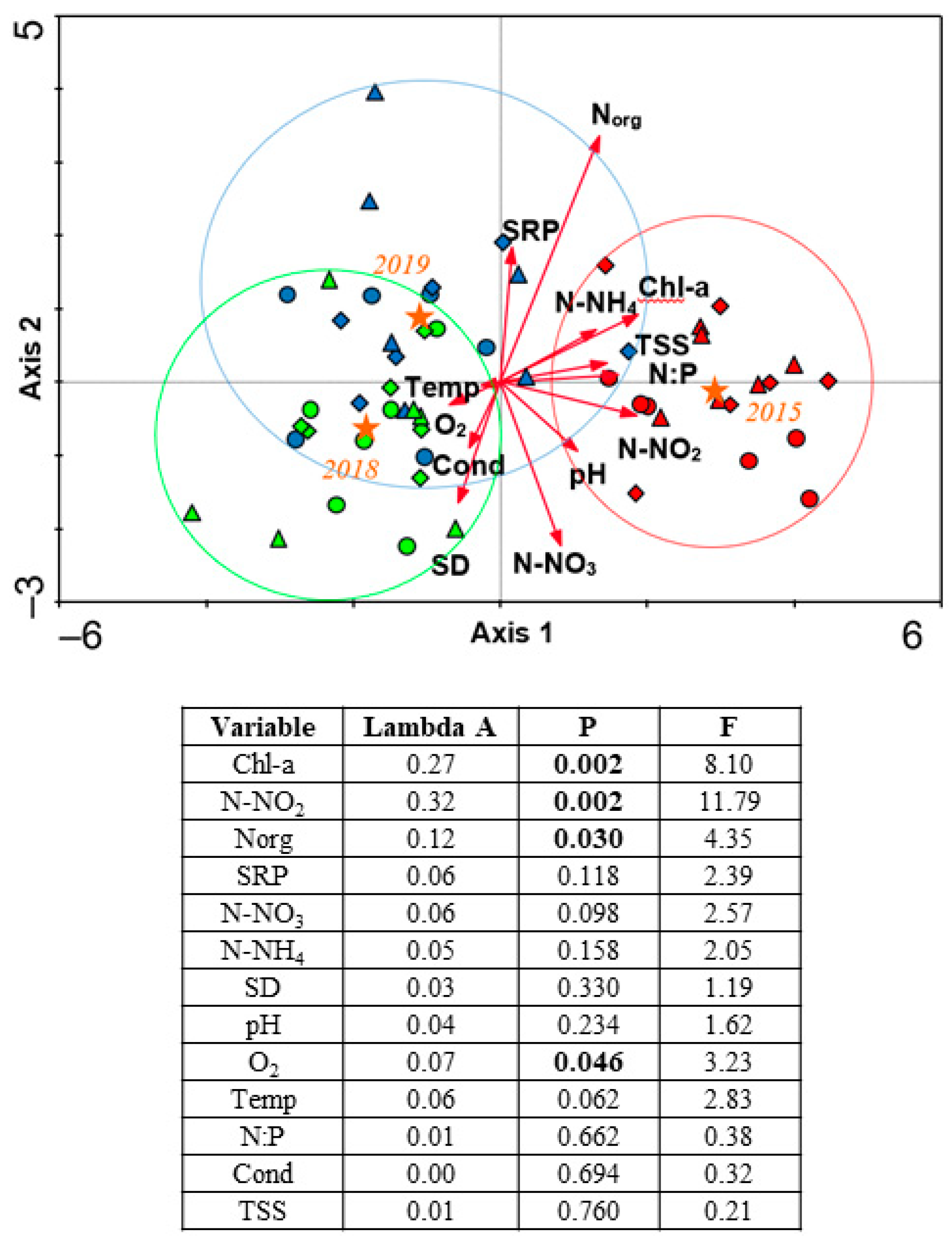
3.3. CVA Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. The Impact of Restoration on the Basic Variables of Water Quality
4.2. Influence of Chemicals Used on Nitrogen Concentration
4.3. Influence of Chemicals Used on Phosphorus Concentrations
4.4. Influence of Biomanipulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dokulil, M.T.; Teubner, K. Cyanobacterial dominance in lakes. Hydrobiologia 2000, 438, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merel, S.; Walker, D.; Chicana, R.; Snyder, S.; Baures, E.; Thomas, O. State of knowledge and concerns on cyanobacterial blooms and cyanotoxins. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, B.; Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Liu, Z. Nitrogen, macrophytes, shallow lakes and nutrient limitation: Resolution of a current controversy? Hydrobiologia 2013, 710, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barałkiewicz, D.; Chudzińska, M.; Szpakowska, B.; Świerk, D.; Gołdyn, R.; Dondajewska, R. Storm water contamination and its effect on the quality of urban surface waters. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 6789–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dondajewska, R.; Gołdyn, R.; Messyasz, B.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Cerbin, S. A shallow lake in an agricultural landscape—Water quality, nutrient loads, future management. Limnol. Rev. 2019, 19, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, S.; Chen, M.; Gong, M.; Fan, X.; Qin, B.; Xu, H.; Gao, S.S.; Jin, Z.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Zhang, C. Internal phosphorus loading from sediments causes seasonal nitrogen limitation for harmful algal blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a frame-work for Community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Community 2000, L327, 1–72.
- Gołdyn, R.; Podsiadłowski, S.; Dondajewska, R.; Kozak, A. The sustainable restoration of lakes—Towards challenges of the water framework directive. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2014, 14, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalewski, M.; McClain, M.; Eslamian, C.S. Ecohydrology—The background for the integrative sustainability science. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2016, 16, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Cottingham, K.L. Resilience and restoration of lakes. Conserv. Ecol. 1997, 1, 2. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/26271648 (accessed on 17 January 2022). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dondajewska-Pielka, R.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Kozak, A.; Budzyńska, A.; Gołdyn, R.; Messyasz, B.; Podsiadłowski, S. Sustainable lake restoration as a long-term strategy for water quality improvement. In Water Ecosystems: Functioning, Importance, Protection and Restoration; Budzyńska, A., Dondajewska-Pielka, R., Rosińska, J., Kozak, A., Kowalczewska-Madura, K., Eds.; Bogucki Press: Poznań, Poland, 2019; pp. 105–117. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Paul, W.J.; Hamilton, D.P.; Gibbs, M.M. Low-dose alum application trialled as a management tool for internal nutrient loads in Lake Okaro, New Zealand. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2008, 42, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Podsiadłowski, S. Method of precise phosphorus inactivation in lake waters. Limnol. Rev. 2008, 8, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Rosińska, J.; Kozak, A.; Dondajewska, R.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Gołdyn, R. Water quality response to sustainable restoration measures—Case study of urban Swarzędzkie Lake. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Rosińska, J.; Dondajewska-Pielka, R.; Gołdyn, R.; Kaczmarek, L. The effects of limiting restoration treatments in a shallow urban Lake. Water 2020, 12, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Jensen, J.P.; Sondergaard, M. Response of phytoplankton, zooplankton and fish to re-oligotrophication: An 11 year study of 23 Danish lakes. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2002, 5, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immers, A.K.; Vendrig, K.; Ibelings, B.W.; van Donk, E.; Ter Heerdt, G.N.J.; Geurts, J.J.M.; Bakker, E.S. Iron addition as a measure to restore water quality: Implications for macrophyte growth. Aquat. Bot. 2014, 116, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R. Limnology. Lake and River Ecosystems, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gulati, R.D.; Pires, L.M.D.; van Donk, E. Lake restoration studies: Failures, bottlenecks and prospects of new ecotechnological measures. Limnologica 2008, 38, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuczyńska-Kippen, N.; Messyasz, B.; Nagengast, B.; Celewicz, S.; Klimko, M. A comparative study of periphyton communities on reed complex and Chara tomentosa in three shallow lakes of Wielkopolska area, Poland. Biol. Sect. Bot. 2005, 60, 349–355. [Google Scholar]
- Hilt, S.; Gross, E.M.; Hupfer, M.; Morscheid, H.; Mählmann, J.; Melzer, A.; Poltz, J.; Sandrock, S.; Scharf, E.M.; Schneider, S.; et al. Restoration of submerged vegetation in shallow eutrophic lakes—Guideline and state of the art in Germany. Limnologica 2006, 36, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Søndergaard, M.; Jeppesen, E.; Lauridsen, L.; Skov, C.; Nes, E.; Roijackers, R.; Lammens, E.; Portielje, R. Lake restoration: Successes, failures and long-term effects. J. Appl. Ecol. 2007, 44, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunalska, J.A.; Grochowska, J.; Wiśniewski, G.; Napiórkowska-Krzebietke, A. Can we restore badly degraded urban lakes? Ecol. Eng. 2015, 82, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunalska, J. Abiotic-biotic method of water treatment in a shore of lake—A new strategy for protection of urban lakes. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2018, 18, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špoljar, M.; Zhang, C.; Drazina, T.; Zhao, G.X.; Lajtner, J.; Radonic, G. Development of submerged macrophyte and epiphyton in a flow-through system: Assessment and modelling predictions in interconnected reservoirs. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 75, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurczak, T.; Wagner, I.; Kaczkowski, Z.; Szklarek, S.; Zalewski, M. Hybrid system for the purification of street stormwater runoff supplying urban recreation reservoirs. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 110, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liquete, C.; Udias, A.; Conte, G.; Grizzetti, B.; Masi, F. Integrated valuation of a nature-based solution for water pollution control. Highlighting hidden benefits. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 22, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, Y.; Dimitriou, E. A large-scale nature-based solution in agriculture for sustainable water management: The Lake Karla case. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jańczak, J. The Atlas of Polish Lakes; Bogucki Scientific Publisher: Poznań, Poland, 1996. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Pułyk, M.; Tybiszewska, E. Report of the State of the Environment in Wielkopolska in 2001; Biblioteka Monitoringu Środowiska: Poznań, Poland, 2002. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Rosińska, J.; Gołdyn, R. Response of vegetation to growing recreational pressure in the shallow Raczyńskie Lake. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2018, 419, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pułyk, M.; Buczyńska, E. Surface Water Quality in the Kopla River Catchment Based on Monitoring Studies; Biblioteka Monitoringu Środowiska: Poznań, Poland, 1997. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Tybiszewska, E.; Szulczyńska, M. Water Quality of Raczyńskie Lake in 2001; WIOS: Poznań, Poland, 2002. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Pułyk, M.; Koziarska, M. Information of the State of the Environment and Control Activities of the Wielkopolska Inspector Provincial Environmental Protection in Średzki District in 2013; WIOS: Poznań, Poland, 2014. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Elbanowska, H.; Zerbe, J.; Siepak, J. Physicochemical Water Analyses; AMU Press: Poznań, Poland, 1999. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, R.G.; Likens, G.E. Limnological Analyses; Springer: New York, NY, USA; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Šmilauer, P. CANOCO Reference Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide. Software for Canonical Community Ordination (Version 4.5); Biometris: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dondajewska, R.; Kozak, A.; Budzyńska, A.; Gołdyn, R.; Podsiadłowski, S.; Tomkowiak, A. The response of a shallow hypertrophic lake to innovative restoration measures—Uzarzewskie Lake case study. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 121, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondajewska, R.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Gołdyn, R.; Kozak, A.; Messyasz, B.; Cerbin, S. Long-term water quality changes as a result of a sustainable restoration—A case study of dimictic Durowskie Lake. Water 2019, 11, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grochowska, J.; Augustyniak, R.; Łopata, M. How durable is the improvement of environment al conditions in a lake after the termination of restoration treatments. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 104, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horppila, J. Sediment nutrients, ecological status and restoration of lakes. Water Res. 2019, 160, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, J. Current beliefs regarding dominance of blue-greens: The case for the importance of CO2 and pH. Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 1990, 24, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomqvist, P.; Pettersson, A.; Hyenstrand, P. Ammonium—Nitrogen: A key of non-nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria in aquatic systems. Archiv Für Hydrobiol. 1994, 132, 141–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S. Ecology of Phytoplankton; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Havens, K.E.; Xu, H.; Zhu, G.; McCarthy, M.J.; Newell, S.E.; Scott, J.T.; Hall, N.S.; Otten, T.G.; Qin, B. Mitigating eutrophication and toxic cyanobacterial blooms in large lakes: The evolution of a dual nutrient (N and P) reduction paradigm. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 4359–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korchef, A.; Saidou, H.; Ban Amor, M. Phosphate recovery through struvite precipitation by CO2 removal: Effect of magnesium, phosphate and ammonium concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wever, D.A.; Muylaert, K.; Langlet, D.; Alleman, L.; Descry, J.P.; Andre, L.; Cocquyt, C.; Vyverman, W. Differential response of phytoplankton to additions of nitrogen, phosphorus and iron in Lake Tanganyika. Freshwat. Biol. 2007, 53, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadegh, A.S.; Sidoumou, Z.; Dia, M.; Pinchetti, J.L.G.; Bouaïcha, N. Impacts of phosphorus loads on the water quality and the proliferation of harmful cyanobacteria in Foum-Gleita Reservoir (Mauritania). Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Lim. 2021, 57, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, M.-L.; Hosper, H. Effects of biomanipulation in the large and shallow Lake Wolderwijd, The Netherlands. Hydrobiologia 1997, 342, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosińska, J.; Rybak, M.; Gołdyn, R. Patterns of macrophyte community recovery as a result of the restoration of a shallow lake. Aquat. Bot. 2017, 138, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WeatherOnline. Available online: www.weatheronline.pl (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Donis, D.; Mantzouki, E.; McGinnis, D.F.; Vachon, D.; Gallego, I.; Grossart, H.P.; de Senerpont Domis, L.N.; Teurlincx, S.; Seelen, L.; Lürling, M.; et al. Stratification strength and light climate explain variation in chlorophyll a at the continental scale in a European multilake survey in a heatwave summer. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 4314–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppensen, E. Retention and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow, eutrophic lakes. Sci. World 2001, 1, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malerba, M.E.; Connolly, S.R.; Heimann, K. Nitrate–nitrite dynamics and phytoplankton growth: Formulation and experimental evaluation of a dynamic model. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 1555–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donald, D.B.; Bogard, M.J.; Finlay, K.; Leavit, P.R. Comparative effects of urea, ammonium, and nitrate on phytoplankton abundance, community composition, and toxicity in hypereutrophic freshwaters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 2161–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Yao, X.; Zhao, Z.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, L. Internal loop sustains cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic lakes: Evidence from organic nitrogen and ammonium regeneration. Water Res. 2021, 206, 117724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmański, K.; Trzebiatowski, M. Organic matter removal from surface water by coagulation and sorption onto powdered active carbon. Ochr. Sr. 2009, 31, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zamparas, M.; Zacharias, I. Restoration of eutrophic freshwater by managing internal nutrient loads. A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparas, M.; Gavriil, G.; Coutelieris, F.A.; Zacharias, I. A theoretical and experimental study on the P-adsorption capacity of PhoslockTM. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 335, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gophen, M. Biomanipulation: Retrospective and future development. Hydrobiologia 1990, 200, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Meerhoff, M.; Jacobsen, B.A.; Hansen, R.S.; Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Mazzeo, N.; Branco, C.W.C. Restoration of shallow lakes by nutrient control and biomanipulation—the successful strategy varies with lake size and climate. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triest, L.; Stiers, I.; van Onsem, S. Biomanipulation as a nature-based solution to reduce cyanobacterial blooms. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 461–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.Y.; Hanazato, T.; Chang, K.H.; Jeong, K.S.; Kim, D.-K. Assessment of the lake biomanipulation mediated by piscivorous rainbow trout and herbivorous daphnids using a self-organizing map: A case study in Lake Shirakaba, Japan. Ecol. Inform. 2015, 29, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, M.L.; de Boois, I.; Scheffer, M.; Portielje, R.; Hosper, H. Biomanipulation in shallow lakes in the Netherlands: An evaluation of 18 case studies. Hydrobiologia 1999, 408, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Sortkjoær, O.; Mortensen, E.; Kristensen, P. Interactions between phytoplankton, zooplankton and fish in a shallow, hypertrophic lake: A study of phytoplankton collapses in Lake Søbygård, Denmark. Hydrobiologia 1990, 191, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczyńska-Kippen, N.; Pronin, M. Diversity and zooplankton species associated with certain hydroperiods and fish state in field ponds. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basińska, A.M.; Kuczyńska-Kippen, N.; Świdnicki, K. The body size distribution of Filinia longiseta (Ehrenberg) in different types of small water bodies in the Wielkopolska region. Limnetica 2010, 29, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basińska, A.M.; Antczak, M.; Świdnicki, K.; Jassey, V.E.J.; Kuczyńska-Kippen, N. Habitat type as strongest predictor of the body size distribution of Chydorus sphaericus (O. F. Müller) in small water bodies. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2014, 99, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofir, E.; Heymans, J.J.; Shapiro, J.; Goren, M.; Spanier, E.; Gal, G. Predicting the impact of lake biomanipulation based on food-web modelling—Lake Kinneret as a case study. Ecol. Model. 2017, 348, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.L.M.; Ibelings, B.W.; Brehm, M.; van Donk, E. Comparing grazing on lake seston by Dreissena and Daphnia: Lessons for biomanipulation. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 50, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobos, J.; Błaszczyk, A.; Hohlfeld, N.; Toruńska-Sitarz, A.; Krakowiak, A.; Hebel, A.; Sutryk, K.; Grabowska, M.; Toporowska, M.; Kokociński, M.; et al. Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins in Polish freshwater bodies. Ocean. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2013, 42, 358–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabowska, M.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Vertical distribution of cyanobacteria biomass and cyanotoxin production in the polymictic Siemianówka Dam Reservoir (eastern Poland). Arch. Pol. Fish. 2014, 22, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołdyn, R.; Messyasz, B.; Domek, P.; Windhorst, W.; Hugenschmidt, C.; Nicoara, M.; Plavan, G. The response of Lake Durowskie ecosystem to restoration measures. Carpath. J. Earth Environ. 2013, 8, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Kozak, A.; Gołdyn, R.; Dondajewska, R.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Holona, T. Changes in phytoplankton and water quality during sustainable restoration of an urban lake used for recreation and water supply. Water 2017, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozak, A.; Rosińska, R.; Gołdyn, R. Changes in the phytoplankton structure due to prematurely limited restoration treatments. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, A.; Budzyńska, A.; Dondajewska-Pielka, R.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Gołdyn, R. Functional groups of phytoplankton and their relationship with environment al factors in the restored Uzarzewskie Lake. Water 2020, 12, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Year | TSI (SD) | TSI (TP) | TSI (ChL) | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 76.90 | 68.91 | 80.13 | 75.31—Hypereutrophy |
| 2018 | 66.21 | 75.34 | 73.80 | 71.78—Hypereutrophy |
| 2019 | 70.29 | 73.10 | 75.32 | 72.90—Hypereutrophy |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Kozak, A.; Kuczyńska-Kippen, N.; Dondajewska-Pielka, R.; Gołdyn, R. Sustainable Restoration as a Tool for the Improvement of Water Quality in a Shallow, Hypertrophic Lake. Water 2022, 14, 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071005
Kowalczewska-Madura K, Kozak A, Kuczyńska-Kippen N, Dondajewska-Pielka R, Gołdyn R. Sustainable Restoration as a Tool for the Improvement of Water Quality in a Shallow, Hypertrophic Lake. Water. 2022; 14(7):1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071005
Chicago/Turabian StyleKowalczewska-Madura, Katarzyna, Anna Kozak, Natalia Kuczyńska-Kippen, Renata Dondajewska-Pielka, and Ryszard Gołdyn. 2022. "Sustainable Restoration as a Tool for the Improvement of Water Quality in a Shallow, Hypertrophic Lake" Water 14, no. 7: 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071005
APA StyleKowalczewska-Madura, K., Kozak, A., Kuczyńska-Kippen, N., Dondajewska-Pielka, R., & Gołdyn, R. (2022). Sustainable Restoration as a Tool for the Improvement of Water Quality in a Shallow, Hypertrophic Lake. Water, 14(7), 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071005









