Long-Term Study of Antibiotic Presence in Ebro River Basin (Spain): Identification of the Emission Sources
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Antibiotic Selection
2.3. Sampling, Conditioning and Conservation Procedure
2.4. Antibiotic Quantification
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antibiotics Presence in Surface Waters
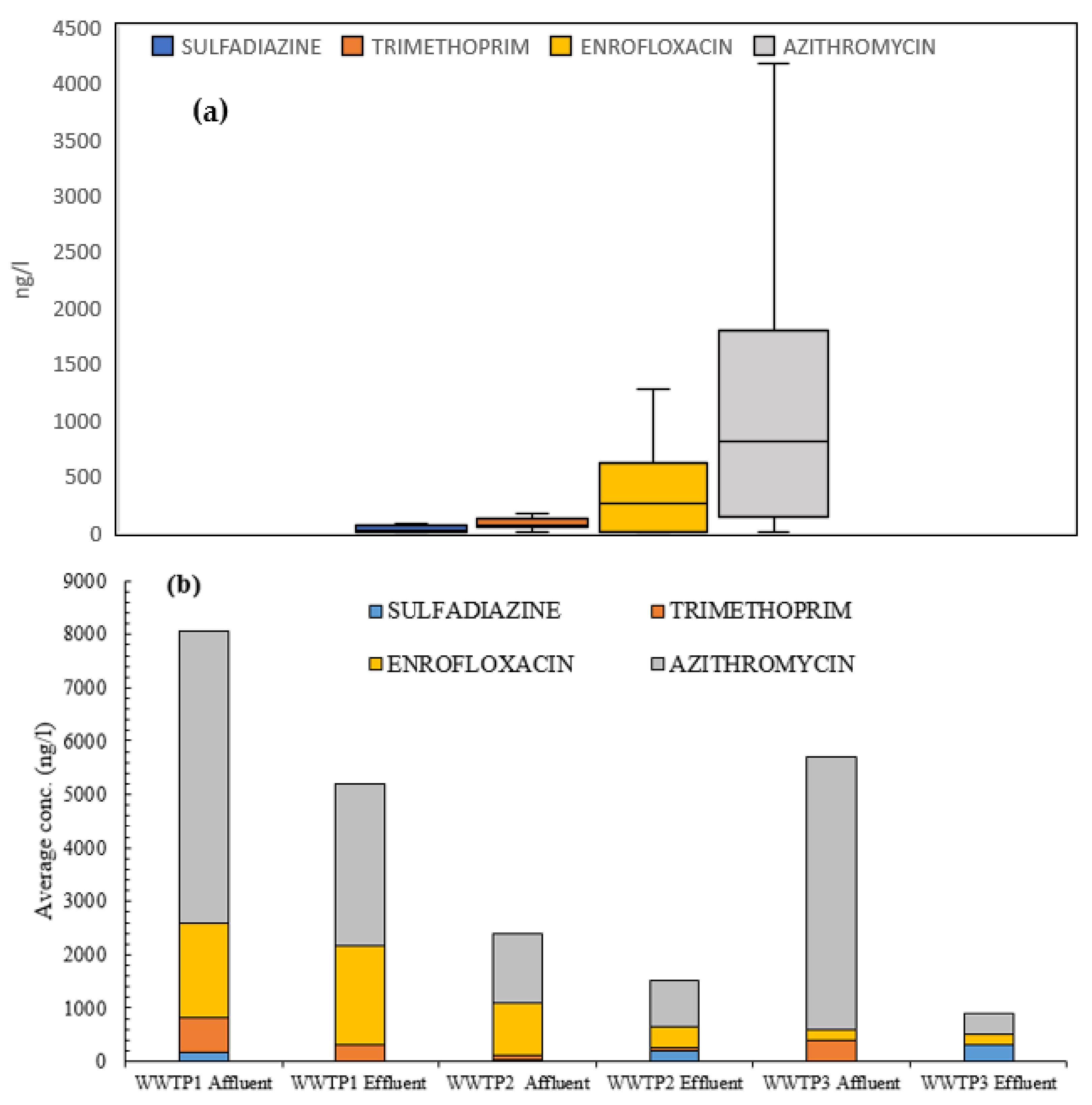
3.2. Antibiotics Presence in Wastewaters
4. Conclusions
- Enrofloxacin and sulfadiazine were present in almost all surface-water control points, which denotes high, direct exposure to these substances, especially in areas that are close to intensive farming. In fact, this fluoroquinolone antibiotic appears at very high concentrations in rivers of the Ebro basin near intensive farming, such as the Segre, Gallego or Cinca Rivers. Significant differences were found between the areas exposed to high livestock pressure and the concentration of enrofloxacin.
- Azithromycin was detected at very high concentrations in WWTPs. Complementarily, trimethoprim and enrofloxacin were detected in wastewaters of the Ebro River basin, especially in areas near large urban cores (>100,000 equivalent inhabitants).
- According to previous studies carried out in Ebro River basin in 2012 and 2010 [32,47], another important finding of this research is an increasing quantitative presence of antibiotics. Consequently, comprehensive studies of antibiotic assessment in Spanish rivers, wastewater, tap water, seawater and groundwater should be continued in order to establish water-quality standards for legislative guidance.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Conde-Cid, M.; Álvarez-Esmorís, C.; Paradelo-Núñez, R.; Nóvoa-Muñoz, J.C.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, E.; Fernández-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Núñez-Delgado, A. Occurrence of tetracyclines and sulfonamides in manures, agricultural soils and crops from different areas in Galicia (NW Spain). J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, R.; Yunesian, M.; Nasseri, S.; Gholami, M.; Jalilzadeh, E.; Shoeibi, S.; Bidshahi, H.S.; Mesdaghinia, A. An optimized SPE-LC-MS/MS method for antibiotics residue analysis in ground, surface and treated water samples by response surface methodology- central composite design. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2017, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, A.; Aceña, J.; Pérez, S.; de Alda, M.L.; Barceló, D.; Gil, A.; Valcárcel, Y. Pharmaceuticals and iodinated contrast media in a hospital wastewater: A case study to analyse their presence and characterise their environmental risk and hazard. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Bao, M.; Barreiro, R.; Miranda, J.M.; Cepeda, A.; Regal, P. Fast HPLC-MS/MS Method for Determining Penicillin Antibiotics in Infant Formulas Using Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2015, 2015, 959675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alygizakis, N.; Gago-Ferrero, P.; Borova, V.L.; Pavlidou, A.; Hatzianestis, I.; Thomaidis, N.S. Occurrence and spatial distribution of 158 pharmaceuticals, drugs of abuse and related metabolites in offshore seawater. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gracia-Lor, E.; Rousis, N.I.; Zuccato, E.; Bade, R.; Lomba, J.A.B.; Castrignanò, E.; Causanilles, A.; Hernández, F.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Kinyua, J.; et al. Estimation of caffeine intake from analysis of caffeine metabolites in wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gothwal, R.; Shashidhar, T. Antibiotic Pollution in the Environment: A Review. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2014, 43, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moles, S.; Mosteo, R.; Gómez, J.; Szpunar, J.; Gozzo, S.; Castillo, J.R.; Ormad, M.P. Towards the Removal of Antibiotics Detected in Wastewaters in the POCTEFA Territory: Occurrence and TiO2 Photocatalytic Pilot-Scale Plant Performance. Water 2020, 12, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegglen, C.; Joss, A.; McArdell, C.S.; Fink, G.; Schlüsener, M.P.; Ternes, T.A.; Siegrist, H. The fate of selected micropollutants in a single-house MBR. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2036–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massé, D.I.; Saady, N.M.C.; Gilbert, Y. Potential of Biological Processes to Eliminate Antibiotics in Livestock Manure: An Overview. Animals 2014, 4, 146–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Della Giustina, S.V.; Llorca, M.; Barceló, D.; Schubert, S.; Berendonk, T.U.; Michael-Kordatou, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Martinez, J.L.; et al. Antibiotic residues in final effluents of European wastewater treatment plants and their impact on the aquatic environment. Environ. Int. 2020, 140, 105733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.O.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Ratola, N.; Hain, E.; Homem, V.; Pereira, M.F.; Blaney, L.; Silva, A. Spatial and seasonal occurrence of micropollutants in four Portuguese rivers and a case study for fluorescence excitation-emission matrices. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1128–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control; European Food Safety Authority; European Medicines Agency. Antimicrobial Consumption and Resistance in Bacteria from Humans and Animals: Third Joint Inter-Agency Report on Integrated Analysis of Antimicrobial Agent Consumption and Occurrence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria from Humans and Food-Producing Animals in the EU/EEA: JIACRA III 2016–2018. European Medicines Agency. 2021. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2900/056892 (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Regulation (EU) 2019/6 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 December 2018 on veterinary medicinal products and repealing Directive 2001/82/EC. Off. J. Eur. Union 2019, L4, 43–167. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency. Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 31 European Countries in 2017; Trends from 2010 to 2017; European Medicines Agency: UK. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/sales-veterinary-antimicrobial-agents-31-european-countries-2017_en.pdf (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- García-Galán, M.J.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Determination of 19 sulfonamides in environmental water samples by automated on-line solid-phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (SPE-LC-MS/MS). Talanta 2010, 81, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelliapan, S.; Wilby, T.; Sallis, P.J. Performance of an up-flow anaerobic stage reactor (UASR) in the treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater containing macrolide antibiotics. Water Res. 2006, 40, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverté-Villarroya, S.; Borrull, F.; Pocurull, E.; Marcé-Recasens, R.M. Determination of antibiotic compounds in water by solid-phase extraction–high-performance liquid chromatography–(electrospray) mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1010, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Davidson, R.; Jones, K.C. Screening the environmental fate of organic contaminants in sewage sludge applied to agricultural soils: II. The potential for transfers to plants and grazing animals. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 185, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggen, T.; Asp, T.N.; Grave, K.; Hormazabal, V. Uptake and translocation of metformin, ciprofloxacin and narasin in forage- and crop plants. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Luo, Y. Occurrence and source analysis of typical veterinary antibiotics in manure, soil, vegetables and groundwater from organic vegetable bases, northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2992–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shi, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, M.E.; Helwig, K.; Hunter, C.; Roberts, J.; Subtil, E.L.; Coelho, L.H.G. Amoxicillin removal by pre-denitrification membrane bioreactor (A/O-MBR): Performance evaluation, degradation by-products, and antibiotic resistant bacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 192, 110258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, N.; Narciso-Da-Rocha, C.; Polo-López, M.I.; Pastrana-Martínez, L.M.; Faria, J.L.; Manaia, C.M.; Fernández-Ibáñez, P.; Nunes, O.; Silva, A.M. Solar treatment (H2O2, TiO2-P25 and GO-TiO2 photocatalysis, photo-Fenton) of organic micropollutants, human pathogen indicators, antibiotic resistant bacteria and related genes in urban wastewater. Water Res. 2018, 135, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Khalil, S.; Bayen, S. Effect of thermal treatments on the degradation of antibiotic residues in food. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3760–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagil, M.; Kumirska, J.; Stolte, S.; Puckowski, A.; Maszkowska, J.; Stepnowski, P.; Białk-Bielińska, A. Development of sensitive and reliable LC-MS/MS methods for the determination of three fluoroquinolones in water and fish tissue samples and preliminary environmental risk assessment of their presence in two rivers in northern Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieuwlaat, R.; Mbuagbaw, L.; Mertz, D.; Burrows, L.L.; Bowdish, D.M.E.; Moja, L.; Wright, G.D.; Schünemann, H.J. Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Antimicrobial Resistance: Parallel and Interacting Health Emergencies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 1657–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagier, J.-C.; Million, M.; Gautret, P.; Colson, P.; Cortaredona, S.; Giraud-Gatineau, A.; Honoré, S.; Gaubert, J.-Y.; Fournier, P.-E.; Tissot-Dupont, H.; et al. Outcomes of 3,737 COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin and other regimens in Marseille, France: A retrospective analysis. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 36, 101791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madero, C.M. Primer año del plan estrategico y de acción para reducir el riesgo de selección y diseminación de resistencia a los antibióticos. Albeitar Public. Vet. Indep. 2016, 194, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Aliste, M.; Garrido, I.; Flores, P.; Hellín, P.; Vela, N.; Navarro, S.; Fenoll, J. Reclamation of agro-wastewater polluted with thirteen pesticides by solar photocatalysis to reuse in irrigation of greenhouse lettuce grown. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 266, 110565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Serna, R.; Jurado, A.; Vázquez-Suñé, E.; Carrera, J.; Petrović, M.; Barceló, D. Occurrence of 95 pharmaceuticals and transformation products in urban groundwaters underlying the metropolis of Barcelona, Spain. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 174, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, M.; Petrovic, M.; Ginebreda, A.; Barceló, D. Sources, Occurrence, and Environmental Risk Assessment of Pharmaceuticals in the Ebro River Basin. Ebro River Basin 2010, 13, 209–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Serna, R.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Development of a fast instrumental method for the analysis of pharmaceuticals in environmental and wastewaters based on ultra high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC)–tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solaun, O.; Franco, J.; Borja, A.; Menchaca, I.; Otaola, J.; Manzanos, A. Análisis de Presiones e Impactos; Confederación Hidrográfica del Ebro: Zaragoza, Spain, 2015; pp. 175–187. Available online: https://www.chebro.es/.../6e31da48-b276-71b0-ec39-d1e50de17939?t=1617716661315 (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- Simon-Sánchez, L.; Grelaud, M.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Ziveri, P. River Deltas as hotspots of microplastic accumulation: The case study of the Ebro River (NW Mediterranean). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1186–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, B.F.; Jelic, A.; López-Serna, R.; Mozeto, A.A.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals in surface water, suspended solids and sediments of the Ebro river basin, Spain. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Galán, M.J.; Blanco, S.G.; Roldán, R.L.; Díaz-Cruz, S.; Barceló, D. Ecotoxicity evaluation and removal of sulfonamides and their acetylated metabolites during conventional wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 437, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamtam, F.; Mercier, F.; Le Bot, B.; Eurin, J.; Dinh, Q.T.; Clément, M.; Chevreuil, M. Occurrence and fate of antibiotics in the Seine River in various hydrological conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 393, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Aukidy, M.; Verlicchi, P.; Jelic, A.; Petrovic, M.; Barcelò, D. Monitoring release of pharmaceutical compounds: Occurrence and environmental risk assessment of two WWTP effluents and their receiving bodies in the Po Valley, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 438, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, A.; Zhang, X.; Dai, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y. Occurrence and removal of quinolone, tetracycline, and macrolide antibiotics from urban wastewater in constructed wetlands. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 30 European Countries in 2015. Seventh ESVAC Report. Seventh ESVAC Rep. 2017. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Report/2017/10/WC500236750.pdf%0Ahttps://bi.ema.europa.eu/analyticsSOAP/saw.dll?PortalPages (accessed on 17 November 2021).
- USEPA. Method 1694: Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Water, Soil, Sediment, and Biosolids by HPLC/MS/MS. EPA Method. 2007. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-10/documents/method_1694_2007.pdf (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- Santos, L.H.M.L.M.; Gros, M.; Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Pena, A.; Barceló, D.; Montenegro, M.C.B.S.M. Contribution of hospital effluents to the load of pharmaceuticals in urban wastewaters: Identification of ecologically relevant pharmaceuticals. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vergeynst, L.; Haeck, A.; De Wispelaere, P.; Van Langenhove, H.; Demeestere, K. Multi-residue analysis of pharmaceuticals in wastewater by liquid chromatography–magnetic sector mass spectrometry: Method quality assessment and application in a Belgian case study. Chemosphere 2015, 119, S2–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujar, P.M.; Kenchannavar, H.H.; Kulkarni, R.; Kulkarni, U.P. Real-time water quality monitoring through Internet of Things and ANOVA-based analysis: A case study on river Krishna. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danner, M.C.; Robertson, A.; Behrends, V.; Reiss, J. Antibiotic pollution in surface fresh waters: Occurrence and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serna, R.L.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Occurrence and distribution of multi-class pharmaceuticals and their active metabolites and transformation products in the Ebro River basin (NE Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 440, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milaković, M.; Vestergaard, G.; Plaza, J.J.G.; Petrić, I.; Simatovic, A.; Senta, I.; Kublik, S.; Schloter, M.; Smalla, K.; Udiković-Kolić, N. Pollution from azithromycin-manufacturing promotes macrolide-resistance gene propagation and induces spatial and seasonal bacterial community shifts in receiving river sediments. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, I.; Muga, I.; Rogríguez, J.; Blanco, M. Contaminantes emergentes en aguas residuales urbanas y efluentes hospi-talarios. Tecnoaqua 2018, 29, 42–54. [Google Scholar]
- Verlicchi, P.; Al Aukidy, M.; Galletti, A.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Hospital effluent: Investigation of the concentrations and distribution of pharmaceuticals and environmental risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 430, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio, V.; Marcé, R.; Pérez, S.; Ginebreda, A.; Cortina, J.L.; Barceló, D. Occurrence and modeling of pharmaceuticals on a sewage-impacted Mediterranean river and their dynamics under different hydrological conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 440, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senta, I.; Terzic, S.; Ahel, M. Occurrence and fate of dissolved and particulate antimicrobials in municipal wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2013, 47, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birošová, L.; Mackuľak, T.; Bodik, I.; Ryba, J.; Škubák, J.; Grabic, R. Pilot study of seasonal occurrence and distribution of antibiotics and drug resistant bacteria in wastewater treatment plants in Slovakia. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Galan, M.J.; Diaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barcelo, D. Occurrence of sulfonamide residues along the Ebro river basin: Removal in wastewater treatment plants and environmental impact assessment. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovko, O.; Kumar, V.; Fedorova, G.; Randak, T.; Grabic, R. Seasonal changes in antibiotics, antidepressants/psychiatric drugs, antihistamines and lipid regulators in a wastewater treatment plant. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berges, J.; Moles, S.; Ormad, M.P.; Mosteo, R.; Gómez, J. Antibiotics removal from aquatic environments: Adsorption of enrofloxacin, trimethoprim, sulfadiazine, and amoxicillin on vegetal powdered activated carbon. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 8442–8452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillossou, R.; Le Roux, J.; Mailler, R.; Pereira-Derome, C.S.; Varrault, G.; Bressy, A.; Vulliet, E.; Morlay, C.; Nauleau, F.; Rocher, V.; et al. Influence of dissolved organic matter on the removal of 12 organic micropollutants from wastewater effluent by powdered activated carbon adsorption. Water Res. 2020, 172, 115487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillossou, R.; Le Roux, J.; Mailler, R.; Vulliet, E.; Morlay, C.; Nauleau, F.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V. Organic micropollutants in a large wastewater treatment plant: What are the benefits of an advanced treatment by activated carbon adsorption in comparison to conventional treatment? Chemosphere 2019, 218, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viana, P.; Meisel, L.; Lopes, A.; de Jesus, R.; Sarmento, G.; Duarte, S.; Sepodes, B.; Fernandes, A.; dos Santos, M.; Almeida, A.; et al. Identification of Antibiotics in Surface-Groundwater. A Tool towards the Ecopharmacovigilance Approach: A Portuguese Case-Study. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2013/11/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council. In Fundamental Texts on European Private Law; Hart Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2016; Volume 2013, pp. 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Unión Europea. Directiva (UE) 2020/2184 del Parlamento Europeo y del Consejo de 16 de diciembre de 2020 relativa a la calidad de las aguas destinadas al consumo humano (versión refundida). D Unión Eur. 2020, 53, 1–62. [Google Scholar]






| River | Location | Sampling Point | Sub-Basin | Livestock Pressure | WWTP Pressure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Segre River | Torres de Segre | 01_ASE | Segre | High | Null |
| Noguera Ribagorzana River | Corbins | 02_ASE | Segre | High | Null |
| Clamor Amarga River | Zaidín | 03_ASE | Cinca | High | High |
| Cinca River | Fraga | 04_ASE | Cinca | High | Null |
| Alcanadre River | Sariñena | 05_ASE | Alcanadre | High | Null |
| Flumen River | Albalatillo | 06_ASE | Alcanadre | High | Null |
| Gállego River | San Mateo de Gállego | 07_ASE | Gallego | Low | Null |
| Arba de Ríquel River | Ejea de los Caballeros | 08_ASE | Ebro | High | Low |
| Aragon Subordan River | Javierregay | 09_ASE | Aragón | Low | Null |
| Aragon River | Caparroso | 10_ASE | Aragón | High | Null |
| Irantzu River | Estella | 11_ASE | Ega | Medium | Null |
| Arakil River | Irañeta | 12_ASE | Arga | High | Null |
| Queiles River | Novallas | 13_ASE | Queiles | High | High |
| Alhama River | Alfaro | 14_ASE | Alhama | High | Null |
| Ega River | Estella | 15_ASE | Ega | Low | Medium |
| Ega River | Downstream Estella | 16_ASE | Ega | Low | High |
| Ega River | Upstream Pamplona | 17_ASE | Arga | Null | Low |
| Arga River | Downstream Pamplona | 18_ASE | Arga | Null | High |
| Ebro River | Upstream Tudela | 19_ASE | Ebro | Low | Low |
| Ebro River | Downstream Tudela | 20_ASE | Ebro | Low | Medium |
| WWTP | Equivalent Inhabitants | Inlet Flow (m3/day) |
|---|---|---|
| WWTP1 | 695.232 | 129.600 |
| WWTP2 | 82.500 | 22.150 |
| WWTP3 | 51.336 | 7.500 |
| Group | Antibiotic | CAS | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Molecular Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfonamide | Sulfadiazine | 26787-78-0 | 365.4 |  |
| Trimethoprim | Trimethoprim | 93106-60-6 | 359.4 | 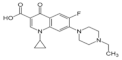 |
| Fluoroquinolone | Enrofloxacin | 738-70-5 | 290.3 |  |
| Macrolide | Azithromycin | 83905-01-5 | 749.0 |  |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moles, S.; Gozzo, S.; Ormad, M.P.; Mosteo, R.; Gómez, J.; Laborda, F.; Szpunar, J. Long-Term Study of Antibiotic Presence in Ebro River Basin (Spain): Identification of the Emission Sources. Water 2022, 14, 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071033
Moles S, Gozzo S, Ormad MP, Mosteo R, Gómez J, Laborda F, Szpunar J. Long-Term Study of Antibiotic Presence in Ebro River Basin (Spain): Identification of the Emission Sources. Water. 2022; 14(7):1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071033
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoles, Samuel, Sebastiano Gozzo, María P. Ormad, Rosa Mosteo, Jairo Gómez, Francisco Laborda, and Joanna Szpunar. 2022. "Long-Term Study of Antibiotic Presence in Ebro River Basin (Spain): Identification of the Emission Sources" Water 14, no. 7: 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071033
APA StyleMoles, S., Gozzo, S., Ormad, M. P., Mosteo, R., Gómez, J., Laborda, F., & Szpunar, J. (2022). Long-Term Study of Antibiotic Presence in Ebro River Basin (Spain): Identification of the Emission Sources. Water, 14(7), 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071033






