Large-Scale Physical Modeling of Salt-Water Intrusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Methods
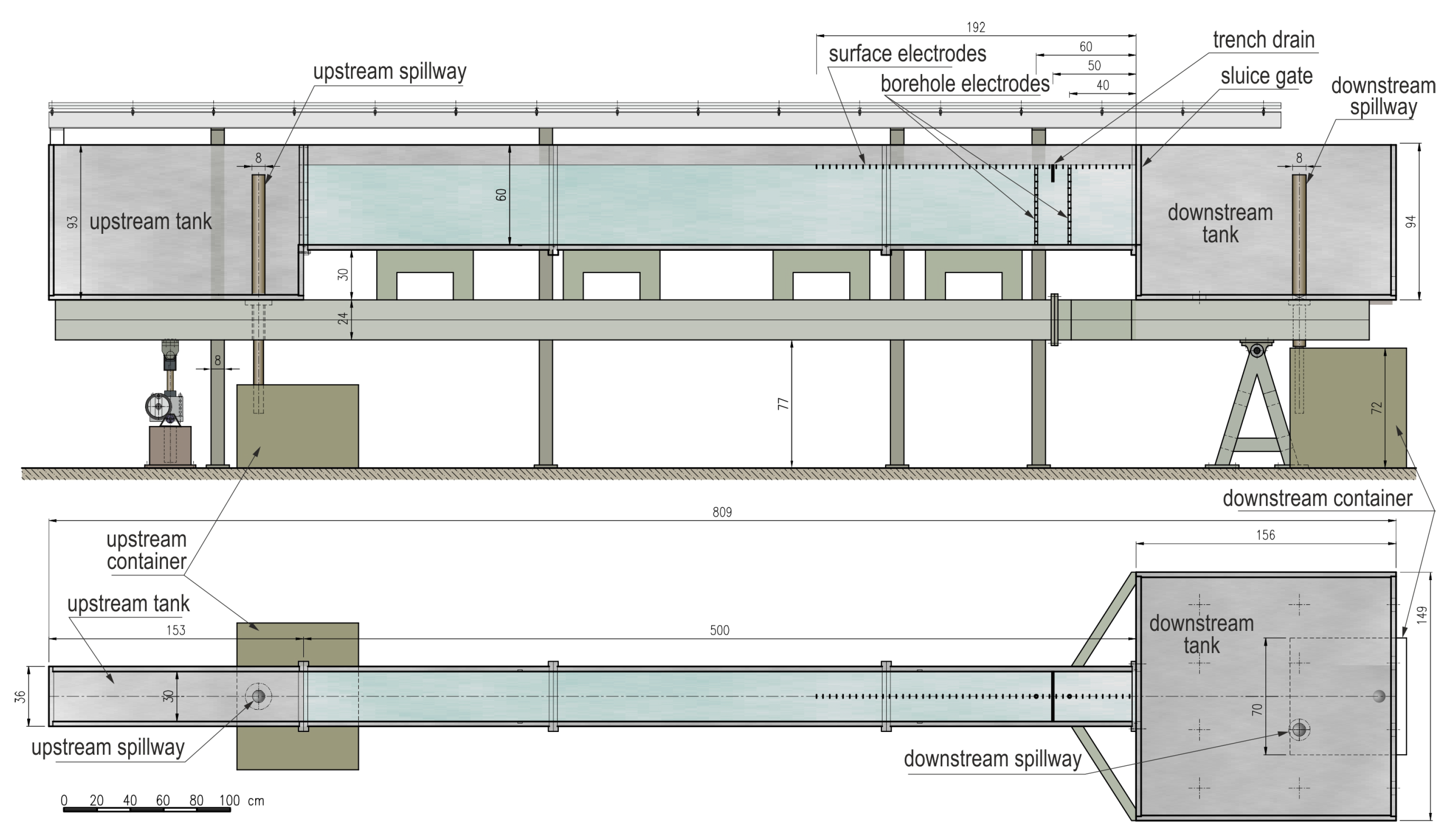
2.1.1. The Sandbox Setup
2.1.2. Monitoring Equipment
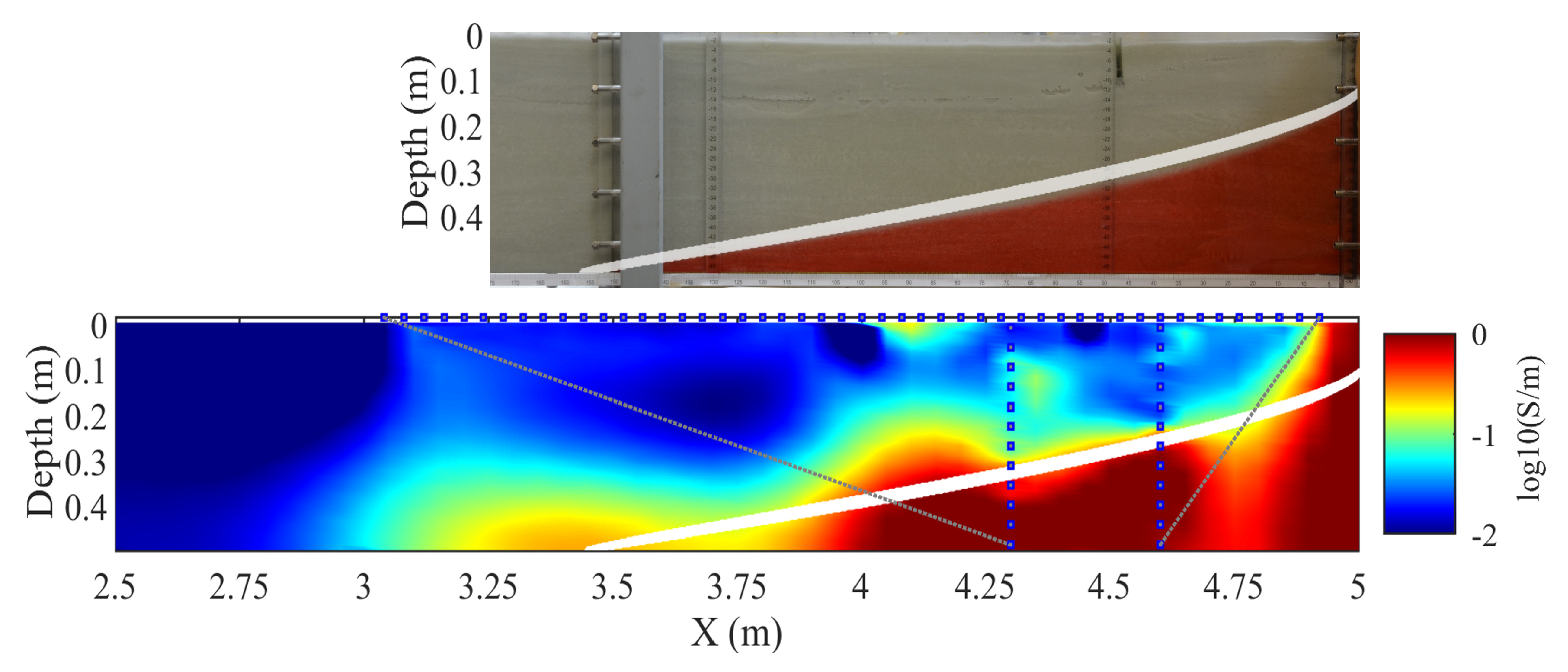
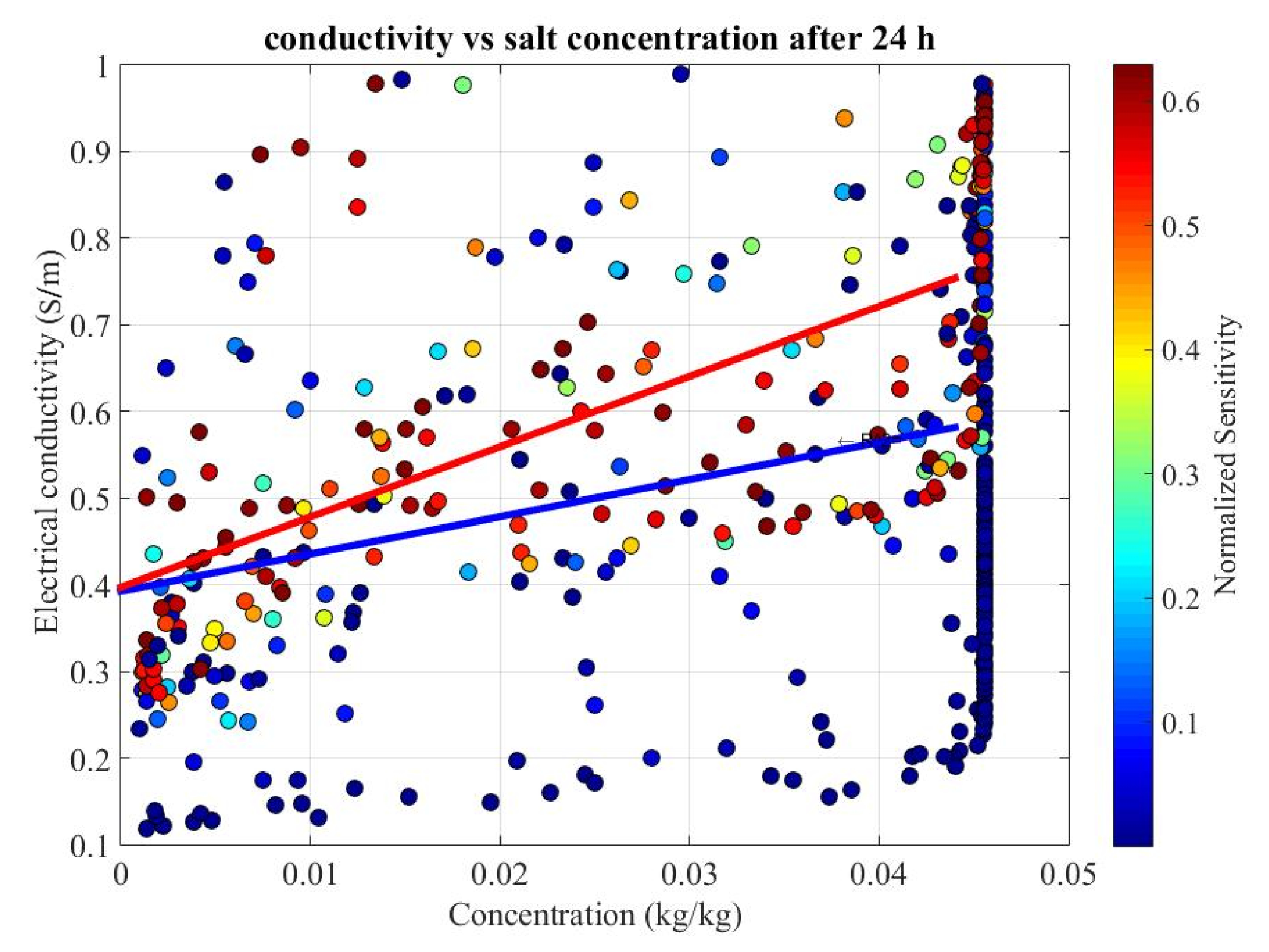
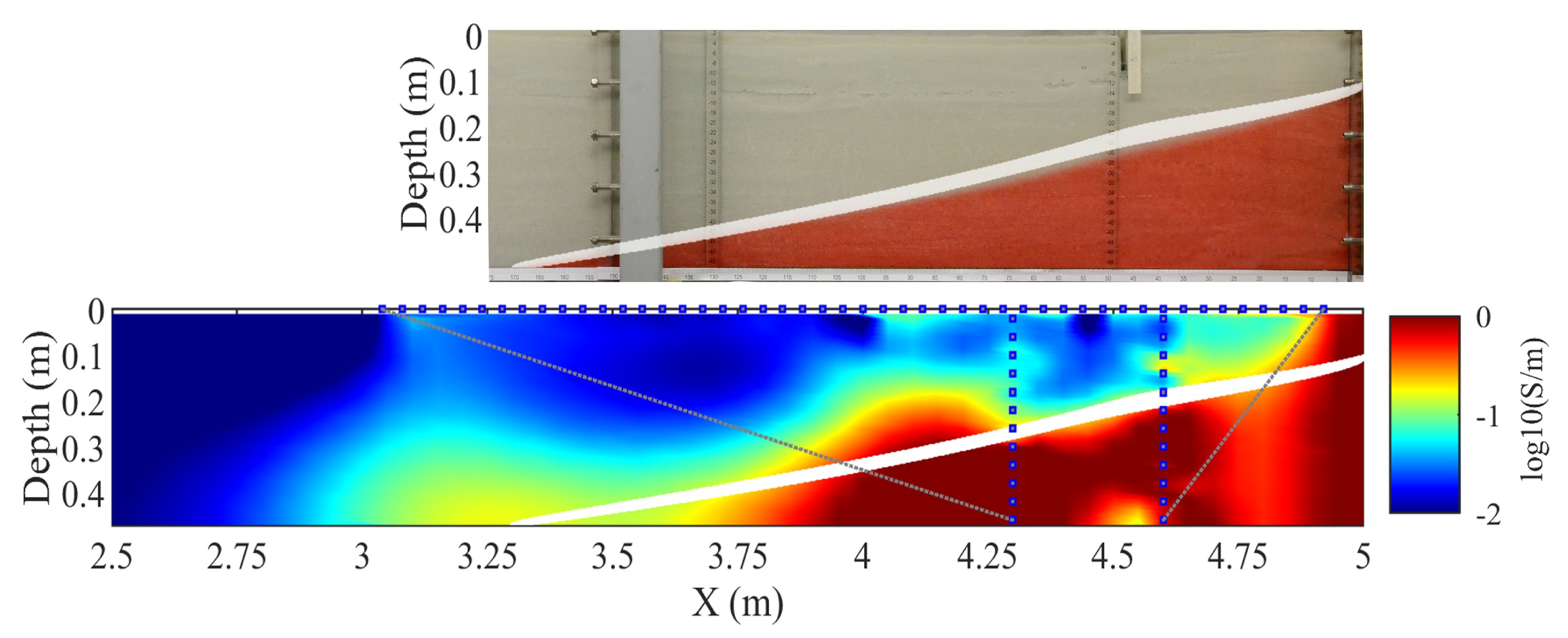
2.1.3. ERT Monitoring and Inversion Modeling
2.1.4. Experiment Set-Up and Initialization
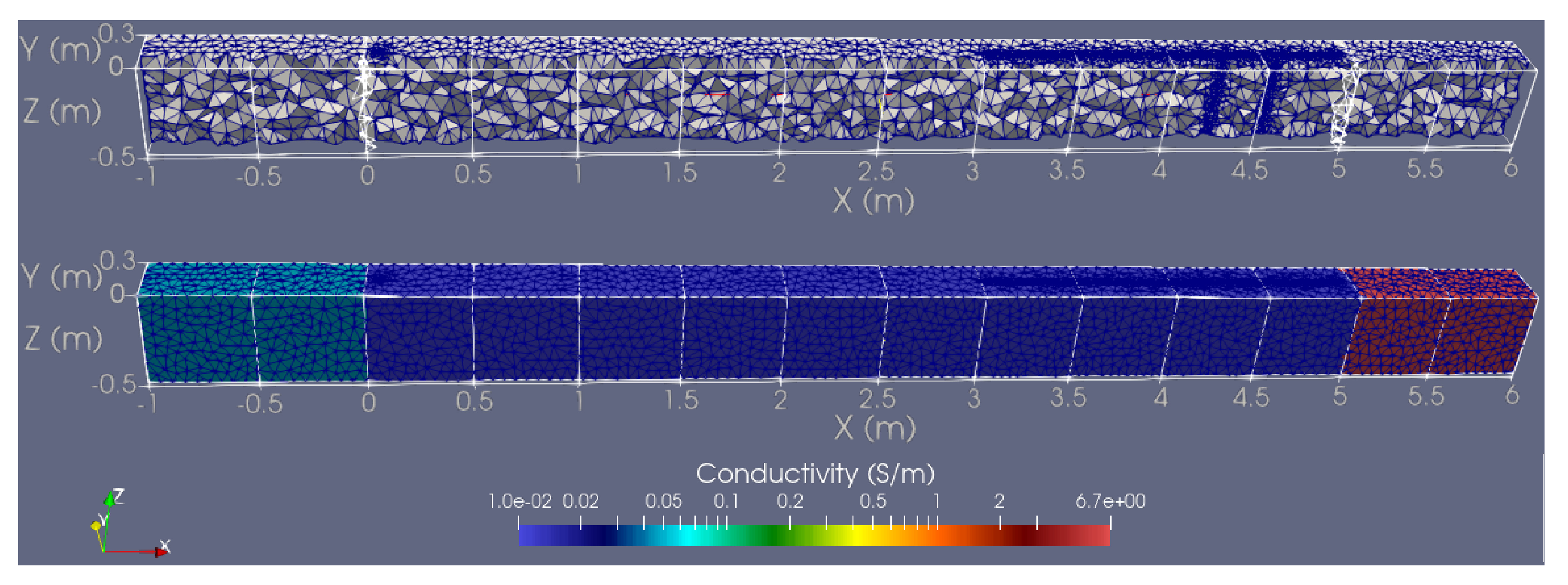
2.2. Numerical Modeling
3. Results
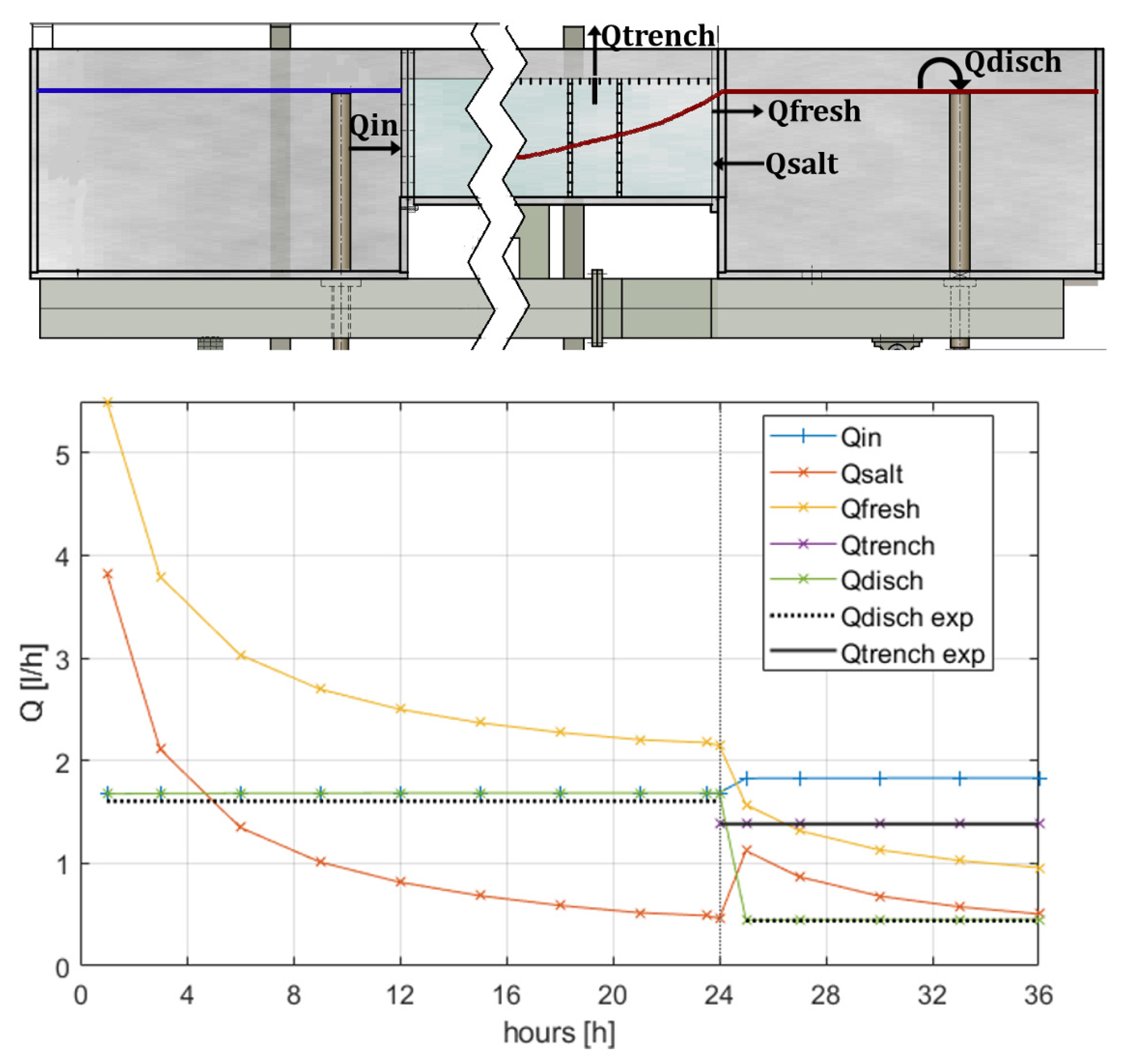
3.1. First Phase: No Pumping
3.2. Second Phase: Pumping from the Channel Drain
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ketabchi, H.; Mahmoodzadeh, D.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T. Sea-level rise impacts on seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: Review and integration. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyun, R.; Momii, K.; Nakagawa, K. Laboratory-scale saltwater behavior due to subsurface cutoff wall. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyun, R.; Momii, K.; Nakagawa, K. Effects of Recharge Wells and Flow Barriers on Seawater Intrusion. Ground Water 2011, 49, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleris, V.K.; Ziogas, A.I. The effect of cutoff walls on saltwater intrusion and groundwater extraction in coastal aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoulhalik, A.; Ahmed, A.; Hamill, G. A new physical barrier system for seawater intrusion control. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armanuos, A.M.; Ibrahim, M.G.; Mahmod, W.E.; Takemura, J.; Yoshimura, C. Analysing the Combined Effect of Barrier Wall and Freshwater Injection Countermeasures on Controlling Saltwater Intrusion in Unconfined Coastal Aquifer Systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 1265–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Cao, H.; Ma, J.; Shi, W.; Rathore, S.S.; Wu, J.; Luo, J. A proof-of-concept study of using a less permeable slice along the shoreline to increase fresh groundwater storage of oceanic islands: Analytical and experimental validation. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 6450–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Zheng, T.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, B.; Sun, Q.; Walther, M. Effect of subsurface dams on saltwater intrusion and fresh groundwater discharge. J. Hydrol. 2019, 576, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanuos, A.M.; Al-Ansari, N.; Yaseen, Z.M. Assessing the effectiveness of using recharge wells for controlling the saltwater intrusion in unconfined coastal aquifers with sloping beds: Numerical study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armanuos, A.M.; Al-Ansari, N.; Yaseen, Z.M. Underground barrier wall evaluation for controlling saltwater intrusion in sloping unconfined coastal aquifers. Water 2020, 12, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, O.P.; Sharma, B.; Stamm, J.; Bhattacharjya, R.K. Groundwater circulation well for controlling saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers: Numerical study with experimental validation. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 3551–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Li, M. Numerical assessment of compressed air injection for mitigating seawater intrusion in a coastal unconfined aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 125964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Volker, R.E.; Lockington, D.A. Experimental investigation of contaminant transport in coastal groundwater. Adv. Environ. Res. 2002, 6, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, R.R.; Clement, T.P. Laboratory-scale investigation of saltwater intrusion dynamics. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W04418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Langevin, C.D. User’s guide to SEAWAT; a computer program for simulation of three-dimensional variable-density ground-water flow. In US Geological Survey Techniques of Water Resources Investigations 6-A7; US Geological Survey: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Jakovovic, D.; Simmons, C.T. Experimental observations of saltwater up-coning. J. Hydrol. 2009, 373, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagan, G.; Bear, J. Solving the problem of local interface upconing in a coastal aquifer by the method of small perturbations. J. Hydraul. Res. 1968, 6, 15–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovovic, D.; Werner, A.D.; Simmons, C.T. Numerical modelling of saltwater up-coning: Comparison with experimental laboratory observations. J. Hydrol. 2011, 402, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.W.; Clement, T.P. Experimental and numerical investigation of saltwater intrusion dynamics in flux-controlled groundwater systems. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W09527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.W.; Clement, T.P. Laboratory and numerical investigation of transport processes occurring above and within a saltwater wedge. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2013, 147, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, L.K.; Stoeckl, L.; Werner, A.D.; Post, V.E. An assessment of seawater intrusion overshoot using physical and numerical modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 6522–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, S.S.; Vafaie, F.; Abolghasemi, H. Assessment of sharp-interface approach for saltwater intrusion prediction in an unconfined coastal aquifer exposed to pumping. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 8345–8355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, J.; Chi, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, X. Study on the influence of seawater density variation on sea water intrusion in confined coastal aquifers. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.; Hamill, G.; Ahmed, A.A. Automated image analysis for experimental investigations of salt water intrusion in coastal aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdoulhalik, A.; Ahmed, A.A. The effectiveness of cutoff walls to control saltwater intrusion in multi-layered coastal aquifers: Experimental and numerical study. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 199, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdollahi-Nasab, A.; Boufadel, M.C.; Li, H.; Weaver, J.W. Saltwater flushing by freshwater in a laboratory beach. J. Hydrol. 2010, 386, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, W.K.; Jin, G.; Xin, P.; Robinson, C.; Gibbes, B.; Li, L. Tidal influence on seawater intrusion in unconfined coastal aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W02502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dose, E.J.; Stoeckl, L.; Houben, G.J.; Vacher, H.; Vassolo, S.; Dietrich, J.; Himmelsbach, T. Experiments and modeling of freshwater lenses in layered aquifers: Steady state interface geometry. J. Hydrol. 2014, 509, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Xin, P.; Lu, C. Seawater intrusion and retreat in tidally-affected unconfined aquifers: Laboratory experiments and numerical simulations. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 132, 103393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerton, C.W.; Wood, P. Effect of walls in modeling flow through porous media. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1988, 114, 1431–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalin, M. Fundamentals of hydraulic physical modelling. In Recent Advances in Hydraulic Physical Modelling; Martins, R., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1989; Volume 165, pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binley, A.; Henry-Poulter, S.; Shaw, B. Examination of Solute Transport in an Undisturbed Soil Column Using Electrical Resistance Tomography. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemna, A.; Vanderborght, J.; Kulessa, B.; Vereecken, H. Imaging and characterisation of subsurface solute transport using electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and equivalent transport models. J. Hydrol. 2002, 267, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontar, E.A.; Ozorovich, Y.R. Geo-electromagnetic survey of the fresh/salt water interface in the coastal southeastern Sicily. Cont. Shelf Res. 2006, 26-7, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Franco, R.; Biella, G.; Tosi, L.; Teatini, P.; Lozej, A.; Chiozzotto, B.; Giada, M.; Rizzetto, F.; Claude, C.; Mayer, A.; et al. Monitoring the saltwater intrusion by time lapse electrical resistivity tomography: The Chioggia test site (Venice Lagoon, Italy). J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 69, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.G.; Rao, G.T.; Surinaidu, L.; Rajesh, R.; Mahesh, J. Geophysical and geochemical approach for seawater intrusion assessment in the Godavari Delta Basin, AP, India. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 217, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pollock, D.; Cirpka, O.A. Fully coupled hydrogeophysical inversion of a laboratory salt tracer experiment monitored by electrical resistivity tomography. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W01505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crestani, E.; Camporese, M.; Salandin, P. Assessment of hydraulic conductivity distributions through assimilation of travel time data from ERT-monitored tracer tests. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 84, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzaglou, V.; Crestani, E.; Salandin, P.; Gloaguen, E.; Camporese, M. Ensemble Kalman filter assimilation of ERT data for numerical modeling of seawater intrusion in a laboratory experiment. Water 2018, 10, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voss, C.I. A Finite-Element Simulation Model for Saturated-Unsaturated, Fluid-Density-Dependent Ground-Water Flow with Energy Transport or Chemically-Reactive Single-Species Solute Transport; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1984; Volume 84.
- Bertorelle, E. Laboratory Experiments on the Saltwater Intrusion Process. Master’s Thesis, University of Padova, Padova, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Felt, E.J. Laboratory methods of compacting granular soils. In Symposium on Application of Soil Testing in Highway Design and Construction; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1959; pp. 89–110. [Google Scholar]
- Loke, M.; Wilkinson, P.; Chambers, J.; Meldrum, P. Rapid inversion of data from 2D resistivity surveys with electrode displacements. Geophys. Prospect. 2018, 66, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, A.; Arsenin, V.Y. Solutions of Ill Posed Problems. In Bulletin (New Series) of the American Mathematical Society; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 1977; Volume 1, pp. 521–524. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, T.C.; Versteeg, R.J.; Ward, A.; Day-Lewis, F.D.; Revil, A. Improved hydrogeophysical characterization and monitoring through parallel modeling and inversion of time-domain resistivity andinduced-polarization data. Geophysics 2010, 75, WA27–WA41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, M.; Knight, R.; Kang, S. Enhancing the resolving ability of electrical resistivity tomography for imaging saltwater intrusion through improvements in inversion methods: A laboratory and numerical study. Geophysics 2021, 86, WB101–WB115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binley, A.; Kemna, A. DC resistivity and induced polarization methods. In Hydrogeophysics. Water Science and Technology Library; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 50, pp. 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonellini, M.; Mollema, P.; Giambastiani, B.; Bishop, K.; Caruso, L.; Minchio, A.; Pellegrini, L.; Sabia, M.; Ulazzi, E.; Gabbianelli, G. Salt water intrusion in the coastal aquifer of the southern Po Plain, Italy. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 1541–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yechieli, Y.; Shalev, E.; Wollman, S.; Kiro, Y.; Kafri, U. Response of the Mediterranean and Dead Sea coastal aquifers to sea level variations. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W12550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca, E.; Carrera, J.; Sánchez-Vila, X.; Dentz, M. Anisotropic dispersive Henry problem. Adv. Water Resour. 2007, 30, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, C.; Provost, A. SUTRA a Model for Saturated-Unsaturated, Variable-Density Ground-Water Flow with Solute or Energy Transport; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2010.
- Oswald, S.; Kinzelbach, W. Three-dimensional physical benchmark experiments to test variable-density flow models. J. Hydrol. 2004, 290, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca, E.; Clement, T.P. A novel approach for characterizing the mixing zone of a saltwater wedge. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L06402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walther, M.; Delfs, J.O.; Grundmann, J.; Kolditz, O.; Liedl, R. Saltwater intrusion modeling: Verification and application to an agricultural coastal arid region in Oman. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2012, 236, 4798–4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosegaard, K. Quest for consistency, symmetry, and simplicity—The legacy of Albert Tarantola. Geophysics 2011, 76, W51–W61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darvini, G.; Salandin, P. Interazione tra acqua dolce e acqua salata in un acquifero costiero. In Proceedings of the XXVIII Convegno di Idraulica e Costruzioni Idrauliche, Potenza, Italy, 16–19 September 2002; Volume 2, pp. 129–138. [Google Scholar]

| Variable or Parameter | Symbol | Value | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porous Medium thickness | B | 0.48 m | measured |
| Hydraulic gradient | 0.0039 | measured | |
| Seaward water depth | 42 cm | measured | |
| Hydraulic conductivity | K | 1.30 m/s | measured |
| Discharged flow rate (first phase) | 1.6 L/h | measured | |
| Discharged flow rate (second phase) | 0.3 L/h | measured | |
| Pumped flow rate | 1.3 L/h | measured | |
| Porosity | n | 0.37 | measured |
| Longitudinal dispersivity | 0.001 m | calibrated | |
| Transversal dispersivity | 0.0001 m | calibrated |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crestani, E.; Camporese, M.; Belluco, E.; Bouchedda, A.; Gloaguen, E.; Salandin, P. Large-Scale Physical Modeling of Salt-Water Intrusion. Water 2022, 14, 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14081183
Crestani E, Camporese M, Belluco E, Bouchedda A, Gloaguen E, Salandin P. Large-Scale Physical Modeling of Salt-Water Intrusion. Water. 2022; 14(8):1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14081183
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrestani, Elena, Matteo Camporese, Enrica Belluco, Abderrezak Bouchedda, Erwan Gloaguen, and Paolo Salandin. 2022. "Large-Scale Physical Modeling of Salt-Water Intrusion" Water 14, no. 8: 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14081183
APA StyleCrestani, E., Camporese, M., Belluco, E., Bouchedda, A., Gloaguen, E., & Salandin, P. (2022). Large-Scale Physical Modeling of Salt-Water Intrusion. Water, 14(8), 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14081183







