Photosynthetic Responses of Two Woody Halophyte Species to Saline Groundwater Irrigation in the Taklimakan Desert
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
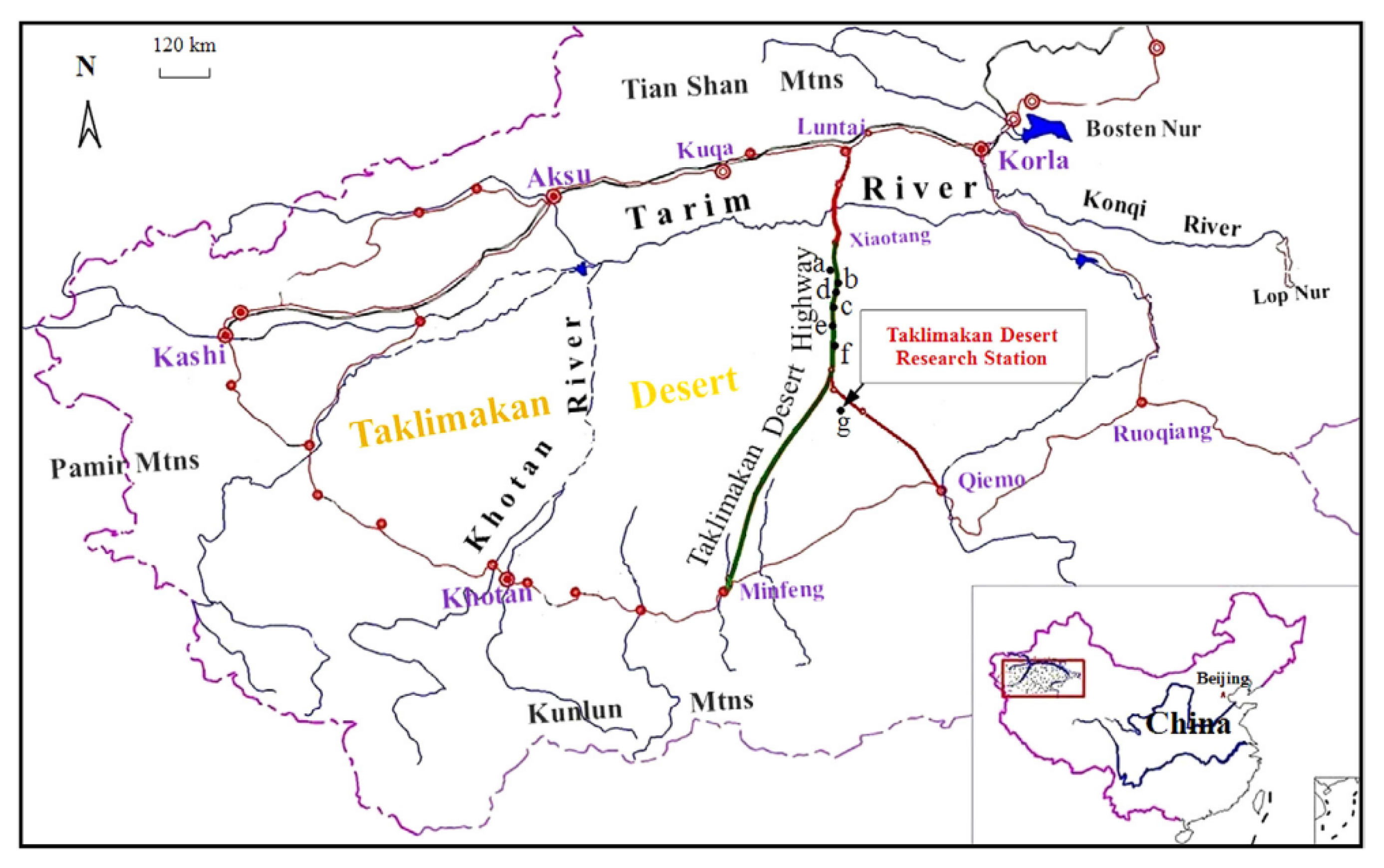
2.1. Environmental Conditions of the Study Area
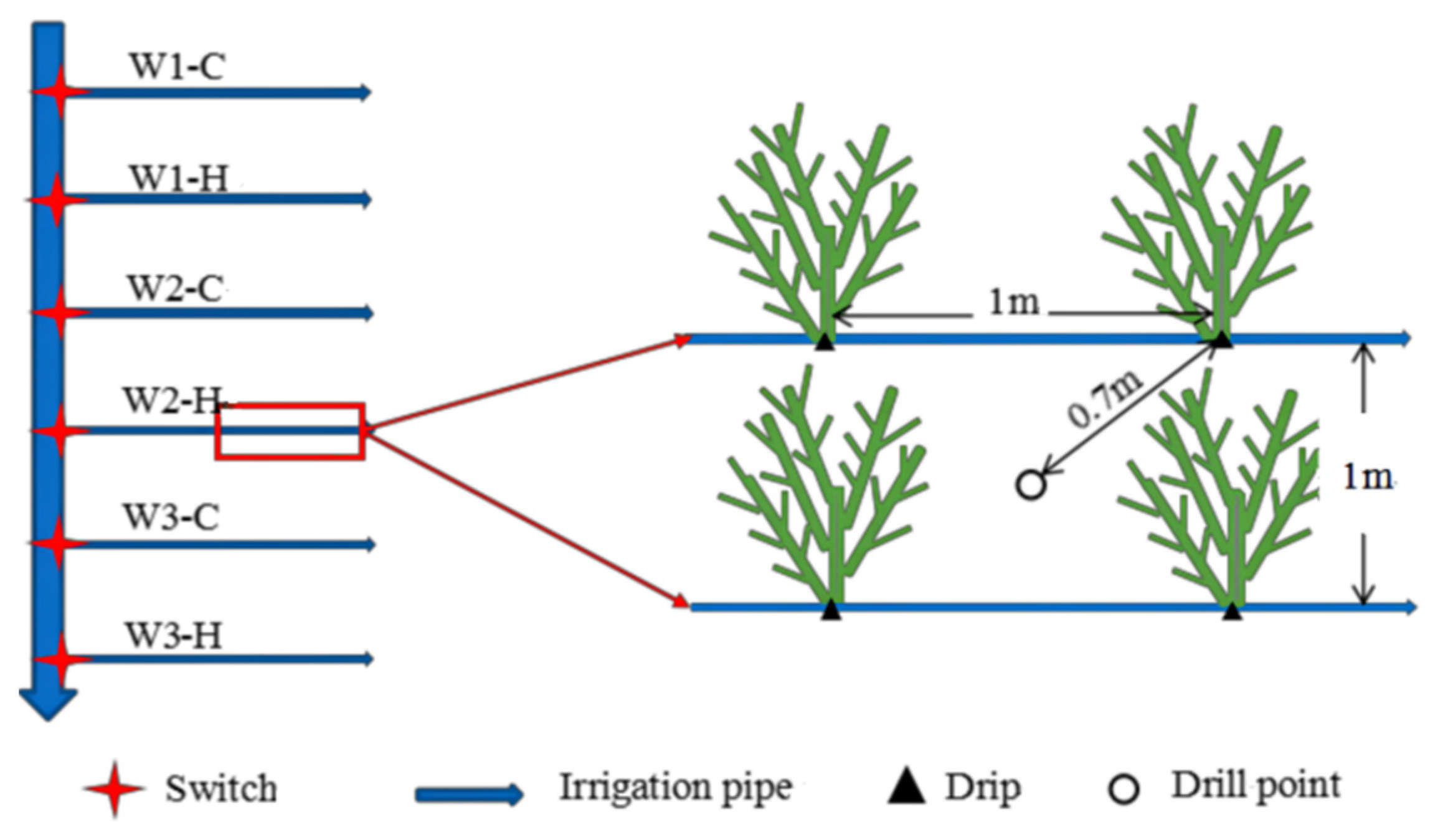
2.2. Difference in Irrigation Management
2.3. Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
2.4. Photosynthesis Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
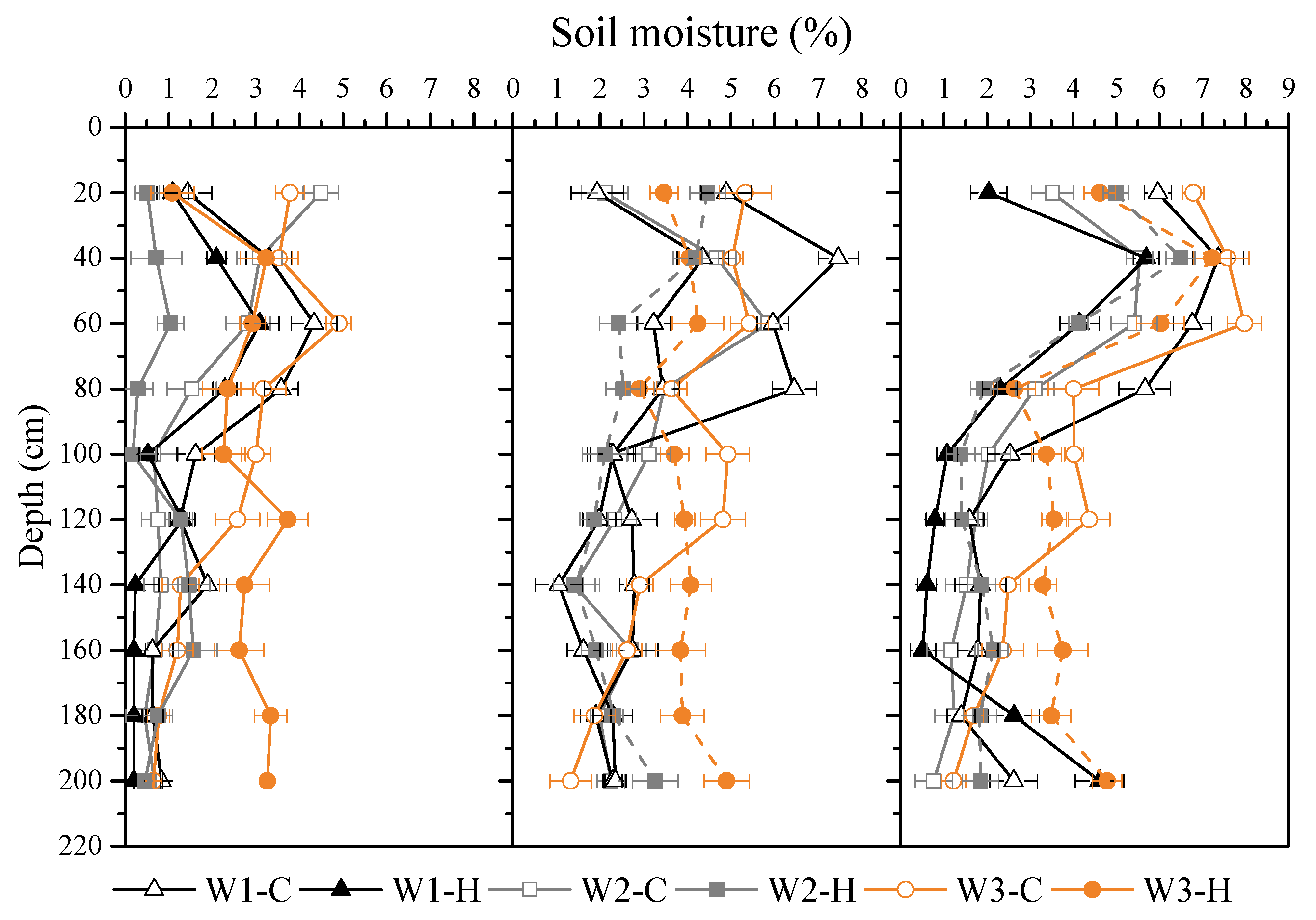
3.1. Soil Moisture Content
3.2. Daily Changes in the Meteorological Factors for the Different Months
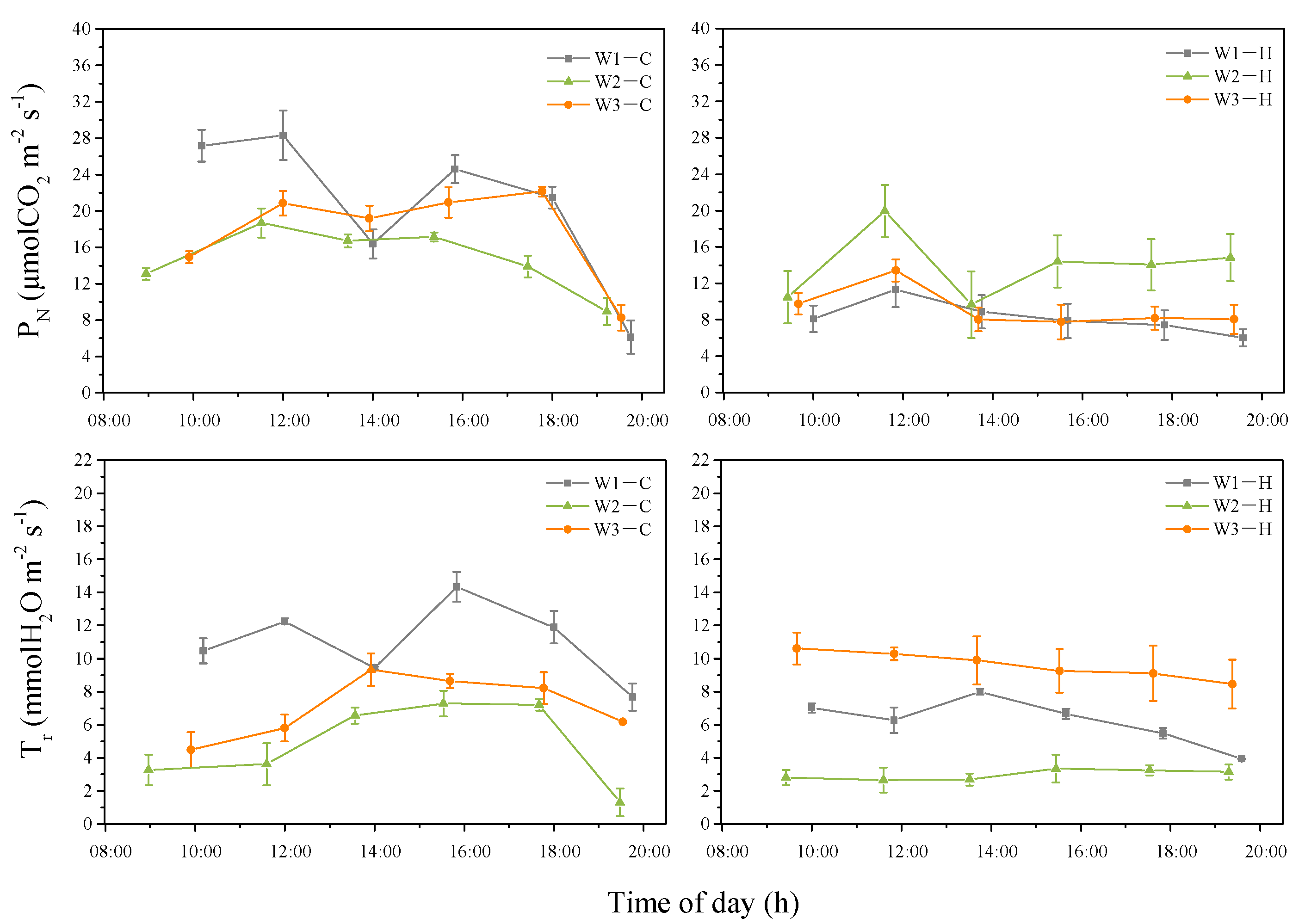
3.3. Diurnal Changes of the Photosynthetic Rate under the Different Irrigation Levels
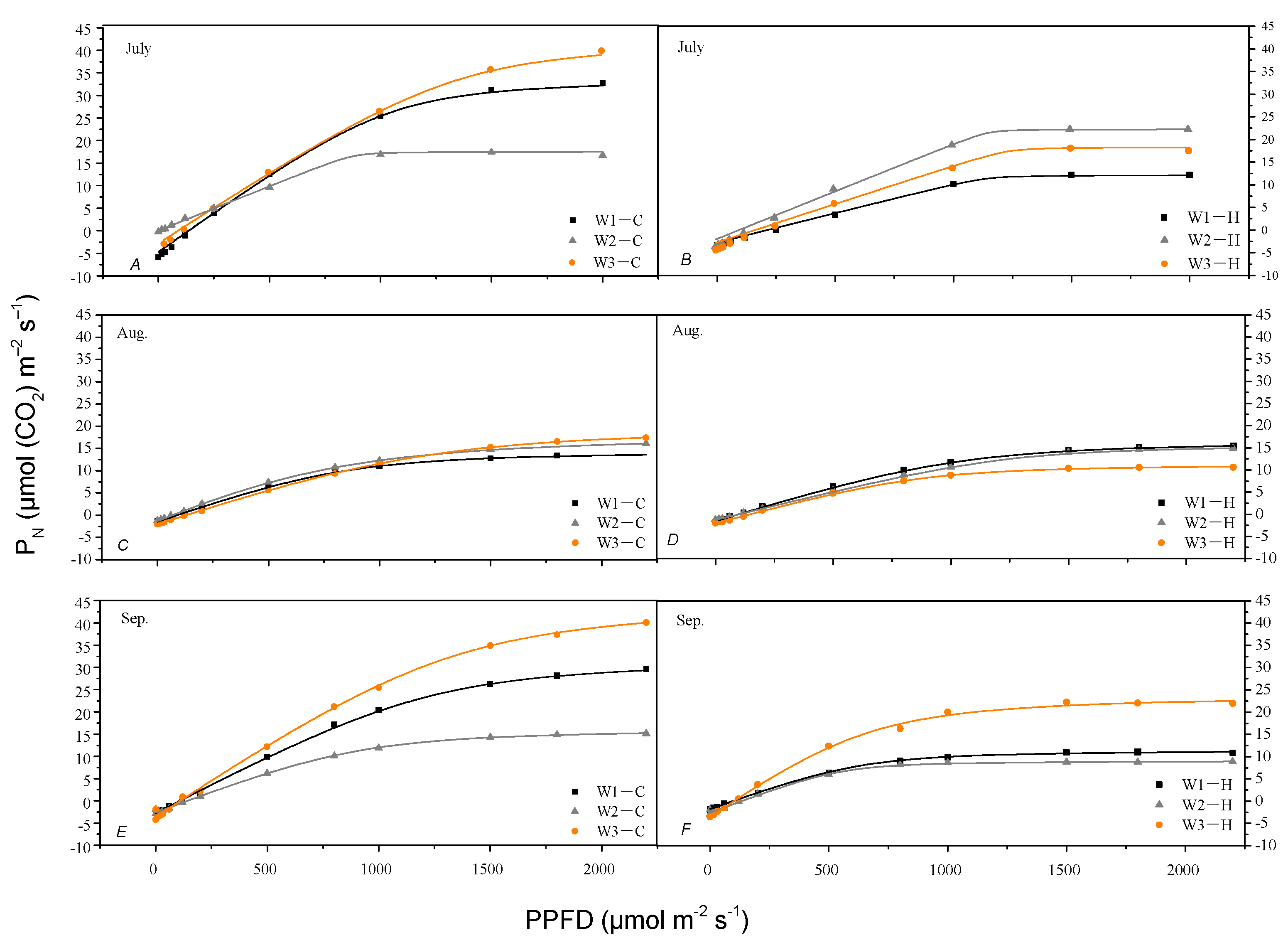
3.4. The Response of PN to Photosynthetic Photon Flux Density (PPFD) under Different Irrigation Levels
4. Discussion
4.1. The Limiting Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
4.2. Plants’ Adaptation Strategy to Drought Stress
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Ivans, S.; Hipps, L.; Leffler, A.J.; Ivans, C.Y. Response of water vapor and CO2 fluxes in semiarid lands to seasonal and intermittent precipitation pulses. J. Hydrometeorol. 2006, 7, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resco, V.; Ignace, D.D.; Sun, W.; Huxman, T.E.; Weltzin, J.F.; Williams, D.G. Chlorophyll fluorescence, predawn water potential and photosynthesis in precipitation pulse-driven ecosystems—Implications for ecological studies. Funct. Ecol. 2008, 22, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Cheng, G.; Yan, Q.; Liu, X. Photosynthetic regulation of C4 desert plant Haloxylon ammodendron under drought stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2007, 51, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R. Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, P.; Yan, Q. Photosynthetic characteristics of C4 desert species Haloxylon ammodendron and Calligonum mongolicm under different moisture conditions. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, A.C.; Lüttge, U. Midday depression in savanna trees: Coordinated adjustments in photochemical efficiency, photorespiration, CO₂ assimilation and water use efficiency. Oecologia 2002, 131, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.W.; Cornic, G. Photosynthetic carbon assimilation and associated metabolism in relation to water deficits in higher plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.L.; Kolb, T.E.; Hart, S.C. Leaf gas exchange characteristics differ among Sonoran Desert riparian tree species. Tree Physiol. 2001, 21, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, W. Responses of leaf stomatal conductance and gas exchange of Haloxylon ammodendron to typical precipition event in the Hexi Corridor. J. Desert Res. 2014, 34, 419–425. [Google Scholar]
- Zan, D.; Zhuang, L. Drought resistance analysis based on anatomical structure of assimilating shoots of Haloxylon ammodendron from Xinjiang. J. Arid Land Res. Environ. 2017, 31, 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Levitt, J. Chilling, Freezing, and High Temperature Stresses. In Responses of Plants to Environmental Stress; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.D.; Devitt, D.A.; Sala, A.; Cleverly, J.R.; Busch, D.E. Water relations of riparian plants from warm desert regions. Wetlands 1998, 18, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, N.; Shan, H.; Wang, X. Responses characteristics of C4 desert shrubs in Minqin under drought stress. Arid Land Geogr. 2016, 39, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Liu, S.; Kang, C.; Delu, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, X. Effects of drought stress on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of Picea mongolica. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2017, 31, 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Fan, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, X.; Fan, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Z. Photosynthetic characteristics and response of Haloxylon ammodendron to drought stress in Hinterland of the Lop Nur. Arid Zone Res. 2018, 35, 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Jin, M.; Nimmo, J.R.; Yang, L.; Wang, W. Estimating groundwater recharge in Hebei Plain, China under varying land use practices using tritium and bromide tracers. J. Hydrol. 2008, 356, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, A.; Li, W.; Chen, H. Chen comparison of d 13C values and gas exchange of assimilating shoots of desert plants H. ammodendron and C. mongolicum with other plants. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 2004, 52, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezara, W.; Marín, O.; Rengifo, E.; Martínez, D. Photosynthesis and photoinhibition in two xerophytic shrubs during drought. Photosynthetica 2005, 43, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maina, N.J.; Wang, Q. Seasonal Response of Chlorophyll a/b Ratio to Stress in a Typical Desert Species: Haloxylon ammodendron. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2015, 29, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Li, Y. Photosynthetic response of desert plants to small rainfall events in the Junggar Basin, northwest China. Photosynthetica 2016, 54, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.G.; Xu, X.; Lei, J.Q.; Sun, S.G.; Fan, J.L.; Li, S.; Gu, F.; Qiu, Y.Z.; Xu, B. The salt accumulation at the shifting aeolian sandy soil surface with high salinity groundwater drip irrigation in the hinterland of the Taklimakan Desert. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lei, J.; Li, S.; Fan, D.; Zhou, H. Classification and regionalization of the forming environment of windblown sand disasters along the Tarim Desert Highway. Chin. Sci. Bull 2008, 53, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Cao, L.; Yimitb, H.; Xu, X.W. Optimization of the saline groundwater irrigation system along the Tarim Desert Highway Ecological Shelterbelt Project in China. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 40, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornley, J.H.M. Instantaneous canopy photosynthesis: Analytical expressions for sun and shade leaves based on exponential light decay down the canopy and an acclimated non-rectangular hyperbola for leaf photosynthesis. Ann. Bot. 2002, 89, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.G.; Lei, J.Q.; Wang, Y.D.; Xu, X.W. Survival and growth of three afforestation species under high saline drip irrigation in the Taklimakan Desert. Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, G.D.; Sharkey, T.D. Stomatal conductance and photosynthesis. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1982, 33, 317–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Li, D.; Zhao, M.; He, Y.; Ma, Q.; Guo, S. Photosynthetic characteristics of Chilopsis linearis under soil water stress. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2007, 27, 2531–2539. [Google Scholar]
- Casper, B.B.; Forseth, I.N.; Wait, D.A. A stage-based study of drought response in Cryptantha flava (Boraginaceae): Gas exchange, water use efficiency, and whole plant performance. Am. J. Bot. 2006, 93, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.R.; Zhao, A.F.; Huang, Y.M.; Zhang, X.S.; Zhang, C.L. Water relations, gas exchange, photochemical efficiency, and peroxidative stress of four plant species in the Heihe drainage basin of northern China. Photosynthetica 2006, 44, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhi, V.; Samson, R.; Lemeur, R.; van Damme, P. Photosynthetic gas exchange characteristics in three different almond species during drought stress and subsequent recovery. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 59, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H. Photosynthetic characteristics responses of three plants to drought stress in Tarim Desert Highway Shelterbelt. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 2519–2528. [Google Scholar]
- Escalona, J.M.; Flexas, J.; Medrano, H. Stomatal and no-stomatal limitation of photosynthesis under water stress in field-grown grapevines. Austral J. Plant Physiol. 1999, 26, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhou, T. Ecophysiological response and morphological adjustment of two Central Asian desert shrubs towards variation in summer precipitation. Plant Cell Environ. 2007, 30, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayup, M.; Hao, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Su, R. Changes of xylem hydraulic efficiency and native embolism of Tamarix ramosissima Ledeb. seedlings under different drought stress conditions and after rewatering. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2011, 78, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wei, X.; Yu, Q.; Deng, J.; Wang, G. Photosynthetic characteristics of Nitraria tangutorum and Haloxylon ammodendron in the ecotone between oasis and desert in Minqin, Region, Country. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 25, 1908–1913. [Google Scholar]
- Sugaya, N.; Kuzushima, K. Increased leaf photosynthesis caused by elevated stomatal conductance in a rice mutant deficient in SLAC1, a guard cell anion channel protein. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 5635–5644. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Taxiplat, T.; Xu, G. Gas Exchange of Haloxylon ammodendron and H. persicum. Arid Zone Res. 2014, 31, 542–549. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Yao, S. Responses of Calligonum arborescens photosynthesis to water atress in Tarim Highway Shelterbelt. J. Desert Res. 2007, 27, 460–465. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, N.; Batra, N.G.; Sharma, V. Photosynthetic performance and drought-induced changes in activity of antioxidative enzymes in different varieties of Vigna radiata. Agric. Res. 2018, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila-Lovera, E.; Zerpa, A.J.; Santiago, L.S. Stem photosynthesis and hydraulics are coordinated in desert plant species. New Phytol. 2017, 216, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simkin, A.J.; Faralli, M.; Ramaoorthy, S.; Lawson, T. Photosynthesis in non-foliartissues: Implications for yield. Plant J. 2020, 101, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.L.; Liu, R.; Ma, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Kong, L. Photosynthetic characteristics and influncing factors of Haloxylon persicun stems (different diameter classes) in Gurbantonggut desert. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 9784–9785. [Google Scholar]


| LCP [μmol m−2 s−1] | LSP [μmol m−2 s−1] | Φ [mol mol−1] | Rd [μmol m−2 s−1] | Pmax [μmol(CO2) m−2 s−1] | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | July | Aug. | Sep. | July | Aug. | Sep. | July | Aug. | Sep. | July | Aug. | Sep. | July | Aug. | Sep. |
| W1-C | 146.87 | 90.68 | 108.65 | 1113.77 | 1131.84 | 1497.70 | 0.040 | 0.016 | 0.025 | 4.714 | 1.510 | 2.739 | 38.78 | 16.14 | 35.00 |
| W2-C | 49.52 | 71.01 | 138.94 | 1109.12 | 1195.87 | 1043.97 | 0.023 | 0.018 | 0.021 | 1.511 | 1.344 | 2.661 | 23.84 | 19.91 | 19.10 |
| W3-C | 214.07 | 128.94 | 100.56 | 1482.02 | 1528.18 | 1252.68 | 0.040 | 0.016 | 0.042 | 7.339 | 2.041 | 3.583 | 50.72 | 22.11 | 48.50 |
| W1-H | 244.13 | 97.25 | 95.74 | 1869.86 | 1213.77 | 811.68 | 0.013 | 0.016 | 0.019 | 6.036 | 1.574 | 1.804 | 21.78 | 18.31 | 13.39 |
| W2-H | 130.17 | 97.09 | 123.69 | 1096.40 | 1371.49 | 618.06 | 0.025 | 0.013 | 0.024 | 1.744 | 1.302 | 2.624 | 24.35 | 17.08 | 11.77 |
| W3-H | 169.02 | 163.86 | 100.51 | 1082.83 | 1281.61 | 871.18 | 0.023 | 0.012 | 0.036 | 2.615 | 2.038 | 3.570 | 21.11 | 13.41 | 27.67 |
| Plant Species | PN | Tr | Ci | Ls | gs | PPFD | Ta | RH | WUE | Tl | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PN | C H | 1.00 1.00 | |||||||||
| Tr | C H | 0.76 ** 0.80 ** | 1.00 1.00 | ||||||||
| Ci | C H | −0.66 ** −0.34 | −0.25 −0.45 | 1.00 1.00 | |||||||
| Ls | C H | 0.65 ** 0.34 | 0.24 0.45 | −0.99 ** −.99 ** | 1.00 1.00 | ||||||
| gs | C H | 0.69 ** 0.76 ** | 0.72 ** 0.80 ** | −0.23 −0.44 | 0.21 0.44 | 1.00 1.00 | |||||
| PPFD | C H | 0.66 ** 0.29 | 0.51* 0.22 | −0.69 ** −0.34 | 0.69 ** 0. 34 | 0.13 −0.04 | 1.00 1.00 | ||||
| Ta | C H | 0.04 −0.10 | 0.20 −0.07 | −0.05 −0.19 | 0.08 0.21 | −0.44 −0.37 | 0.42 0.49 ** | 1.00 1.00 | |||
| RH | C H | −0.30 −0.01 | −0.31 0.06 | 0.15 0.28 | −0.17 −0.29 | 0.25 0.35 | −0.54 * −0.55 * | −0.91 ** −0.94 ** | 1.00 1.00 | ||
| WUE | C H | 0.55 * −0.19 | −0.09 −0.69 ** | −0.73 ** 0.41 | 0.73 ** −0.42 | 0.12 −0.51 * | 0.41 −0.06 | −0.13 0.08 | −0.13 −0.01 | 1.00 1.00 | |
| Tl | C H | 0.31 −0.03 | 0.46 0.13 | −0.19 −0.28 | 0.21 0.30 | −0.18 −0.26 | 0.68 0.59 ** | 0.89 ** 0.86 ** | −0.87 ** −0.82 ** | −0.09 −0.33 | 1.00 1.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sial, T.A.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Photosynthetic Responses of Two Woody Halophyte Species to Saline Groundwater Irrigation in the Taklimakan Desert. Water 2022, 14, 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14091385
Liu J, Zhao Y, Sial TA, Liu H, Wang Y, Zhang J. Photosynthetic Responses of Two Woody Halophyte Species to Saline Groundwater Irrigation in the Taklimakan Desert. Water. 2022; 14(9):1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14091385
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiao, Ying Zhao, Tanveer Ali Sial, Haidong Liu, Yongdong Wang, and Jianguo Zhang. 2022. "Photosynthetic Responses of Two Woody Halophyte Species to Saline Groundwater Irrigation in the Taklimakan Desert" Water 14, no. 9: 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14091385
APA StyleLiu, J., Zhao, Y., Sial, T. A., Liu, H., Wang, Y., & Zhang, J. (2022). Photosynthetic Responses of Two Woody Halophyte Species to Saline Groundwater Irrigation in the Taklimakan Desert. Water, 14(9), 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14091385








