Arsenic Occurrence and Cycling in the Aquatic Environment: A Comparison between Freshwater and Seawater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sources of Arsenic in the Aquatic Environment
2.1. Natural Sources of Arsenic
2.2. Anthropogenic Sources of Arsenic
3. Arsenic Occurrence in Freshwater
3.1. Arsenic Concentration and Forms in Freshwater
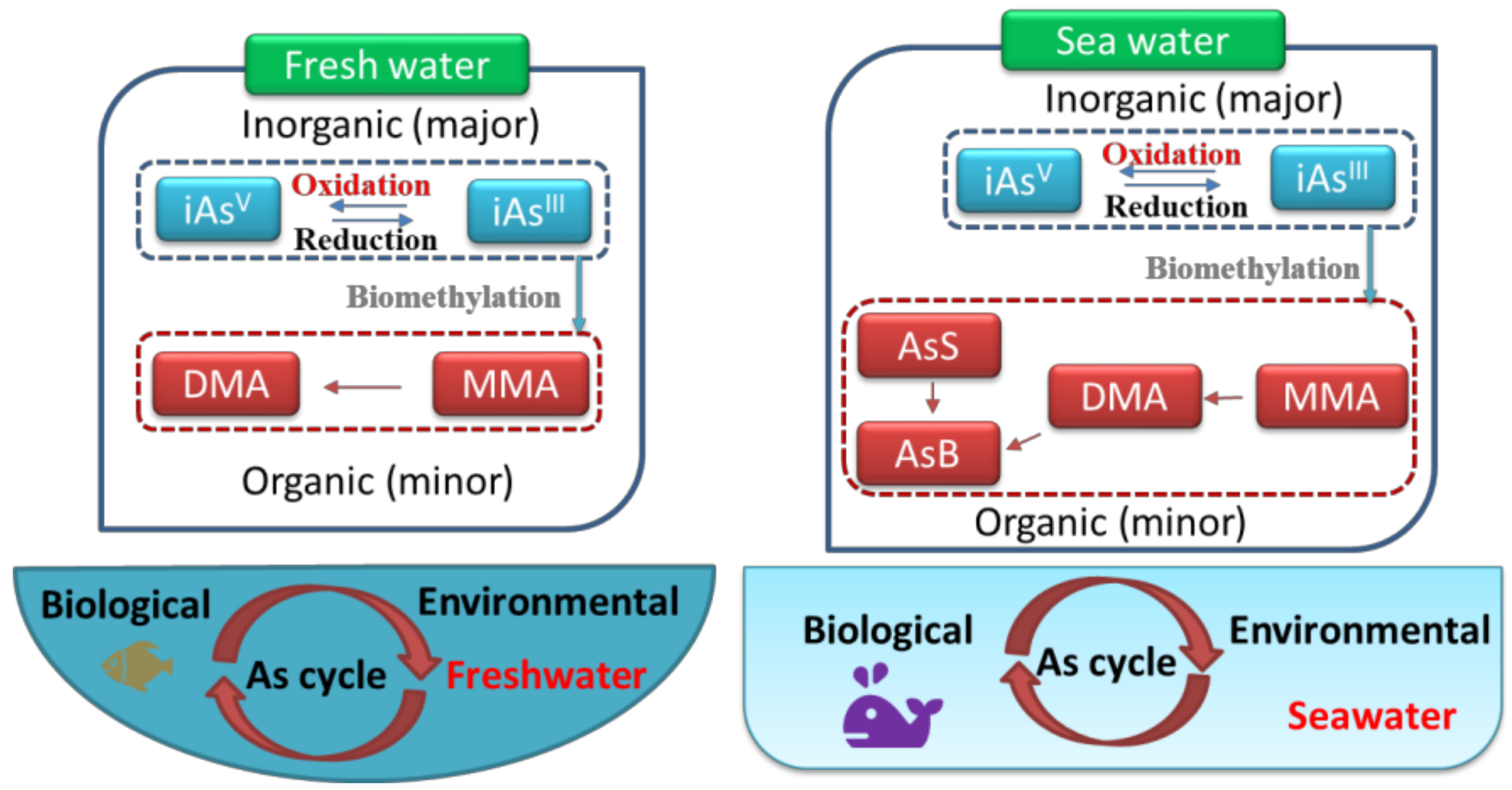
3.2. Cycle of Arsenic in Freshwater
4. Arsenic Occurrence in Seawater
4.1. Arsenic Concentration and Speciation in Seawater
4.2. Cycle of Arsenic in Seawater
4.3. Comparison of the Differences in Occurrence between Freshwater and Seawater
5. Arsenic Occurrence in Freshwater and Seawater Sediments
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Phillips, D. Arsenic in aquatic organisms: A review, emphasizing chemical speciation. Aquat. Toxicol. 1990, 16, 151–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.F.; Beck, B.D.; Chen, Y.; Lewis, A.S.; Thomas, D.J. Arsenic Exposure and Toxicology: A Historical Perspective. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 123, 305–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Straif, K.; Benbrahimtallaa, L.; Baan, R.; Grosse, Y.; Secretan, B.; Ghissassi, F.E.; Bouvard, V.; Guha, N.; Freeman, C.; Galichet, L. WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph Working Group. A review of human carcinogens--part C: Metals, arsenic, dusts, and fibres. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundschuh, J.; Schneider, J.; Alam, M.A.; Niazi, N.K.; Herath, I.; Parvez, F.; Tomaszewska, B.; Guilherme, L.R.G.; Maity, J.P.; López, D.L.; et al. Seven potential sources of arsenic pollution in Latin America and their environmental and health impacts. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 780, 146274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidone, E.; Castilhos, Z.; Cesar, R.; Santos, M.C.; Sierpe, R.; Ferreira, M. Hydrogeochemistry of arsenic pollution in watersheds influenced by gold mining activities in Paracatu (Minas Gerais State, Brazil). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 8546–8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Tang, X.; Yang, S.; Shen, Z. Effect of indigenous bacteria on geochemical behavior of arsenic in aquifer sediments from the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia: Evidence from sediment incubations. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3267–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaescusa, I.; Bollinger, J.-C. Arsenic in drinking water: Sources, occurrence and health effects (a review). Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio. 2008, 7, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkel, L.H.E.; Trang, P.T.K.; Lan, V.M.; Stengel, C.; Amini, M.; Ha, N.T.; Viet, P.H.; Berg, M. Arsenic pollution of groundwater in Vietnam exacerbated by deep aquifer exploitation for more than a century. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahar, M.M.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Toxicity, transformation and accumulation of inorganic arsenic species in a microalga Scenedesmus sp isolated from soil. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Moogouei, R.; Gupta, D.K. Arsenic Accumulation in Rice and Probable Mitigation Approaches: A Review. Agronomy 2017, 7, 4–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Planer-Friedrich, B.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Y. Arsenic and thioarsenic species in the hot springs of the Rehai magmatic geothermal system, Tengchong volcanic region, China. Chem. Geol. 2017, 453, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, I.; Vithanage, M.; Seneweera, S.; Bundschuh, J. Thiolated arsenic in natural systems: What is current, what is new and what needs to be known. Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 370–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, G.; Cai, Y. Thiolated arsenicals in arsenic metabolism: Occurrence, formation, and biological implications. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 49, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordstrom, D.K. Worldwide Occurrences of Arsenic in Ground Water. Science 2002, 296, 2143–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamgir, R.F.; Allan, D.L.; Rosen, C.J.; Sadowsky, M.J. Arsenic Availability from Chromated Copper Arsenate (CCA)-Treated Wood. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, A.H.; Lico, M.S.; Hughes, J.L. Arsenic in Ground Water of the Western United States. Groundwater 1988, 26, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.G. Arsenic geochemistry in Chesapeake Bay: Dependence upon anthropogenic inputs and phytoplankton species composition. Mar. Chem. 1985, 17, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, S.; Langston, W.J.; Whitfield, M.; Turner, D.R.; Liddicoat, M.I. Statistical analysis of estuarine profiles: II application to arsenic in the Tamar estuary (S.W. England). Estuar. Coast. Shelf. S. 1984, 18, 623–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatpanahi, M.; Anderson, A.C.; Abdelghani, A.A.; Englande, A.J.; Hughes, J.; Wilkinson, R.F. Biotransformation of the pesticide sodium arsenate. J. Environ. Sci. Health B. 1981, 16, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J.F.; Gavis, J. A review of the arsenic cycle in natural waters. Water. Res. 1972, 6, 1259–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, W.M.; Wai, C.M. Distribution and mobilization of arsenic species in the creeks around the Blackbird mining district, Idaho. Water. Res. 1989, 23, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, P.L.; Kinniburgh, D.G. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Geochem. 2002, 17, 517–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garelick, H.; Jones, H.; Dybowska, A.; Valsami-Jones, E. Arsenic pollution sources. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 197, 18–51. [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty, M.M.; Lai, V.W.M.; Koch, I.; Cui, L.; Combs, C.; Krupp, E.M.; Feldmann, J.; Cullen, W.R.; Reimer, K.J. Speciation and toxicity of arsenic in mining-affected lake sediments in the Quinsam watershed, British Columbia. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, R.W.; Jonasson, I.R. The geochemistry of arsenic and its use as an indicator element in geochemical prospecting. J. Geochem. Explor. 1973, 2, 251–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janga, Y.C.; Somannaa, Y.; Kimb, H. Source, Distribution, Toxicity and Remediation of Arsenic in the Environment–A review. Int. J. Appl. Environ. Sci. 2016, 11, 559–581. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Xing, Y.; Xia, J.; Feng, X. Immobilization of mercury and arsenic in a mine tailing from a typical Carlin-type gold mining site in southwestern part of China. Int. J. Appl. Environ. S 2016, 11, 559–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldschmidt, V.M. Geochemistry; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Belkin, H.E.; Zheng, B.; Zhou, D.; Finkelman, R.B. Chronic Arsenic Poisoning from Domestic Combustion of Coal in Rural China: A Case Study of the Relationship between Earth Materials and Human Health. In Environmental Geochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 401–420. [Google Scholar]
- Breuer, C.; Pichler, T. Arsenic in marine hydrothermal fluids. Chem. Geol. 2013, 348, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.K.; Suzuki, K.T. Arsenic round the world: A review. Talanta: Int. J. Pure Appl. Anal. Chem. 2002, 58, 201–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, S.; Frankenberger, W.T. Environmental biochemistry of arsenic. Rev. Environ. Contam. T 1992, 124, 79–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne, J.M.; Moore, J.N. Arsenic geochemistry in geothermal systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.E. Magmatic, connate, and metamorphic waters. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1957, 68, 1659–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkle, P.; Bundschuh, J.; Sracek, O. Mechanisms of arsenic enrichment in geothermal and petroleum reservoirs fluids in Mexico. Water. Res. 2010, 44, 5605–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, S.C.; Blum, J.D.; Klaue, B.; Karagas, M.R. Arsenic Occurrence in New Hampshire Drinking Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Rasool, A.; Junaid, M.; Zhang, H. A comprehensive review on current status, mechanism, and possible sources of arsenic contamination in groundwater: A global perspective with prominence of Pakistan scenario. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 737–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, F.H.; Hawkins, D.B. Arsenic in streams, stream sediments, and ground water, fairbanks area, alaska. Environ. Geol. 1978, 2, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.G.; Nordstrom, D.K.; Smith, K.S. Transport and Natural Attenuation of Cu, Zn, As, and Fe in the Acid Mine Drainage of Leviathan and Bryant Creeks. In Environmental Geochemistry of Sulfide Oxidation; ACS Symposium Series; ACS: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; Volume 550, pp. 244–260. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhu, X.; Qi, X.; Li, K.; Wei, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, J.; Hui, X.; Zhang, X. Pyrolysis of arsenic-bearing gypsum sludge being substituted for calcium flux in smelting process. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 130, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Qu, Z.; Yan, N. Surface nano-traps of Fe0/COFs for arsenic(III) depth removal from wastewater in non-ferrous smelting industry. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysiak, A.; Karczewska, A. Arsenic Extractability in Soils in The Areas of Former Arsenic Mining and Smelting, SW Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 379, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschullat, J. Arsenic in the geosphere—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 249, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peshut, P.J.; Morrison, R.J.; Brooks, B.A. Arsenic speciation in marine fish and shellfish from American Samoa. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilvers, D.C.P.P.J. J. Global cycling of arsenic. In Lead, Mercury, Cadmium and Arsenic in the Environment; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 279–301. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasia, F.B.; Kender, W.J. The Influence of Soil Arsenic on the Growth of Lowbush Blueberry. J. Environ. Qual. 1973, 2, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodroad, L.L.; Caldwell, A.C. Effects of Phosphorus Fertilizer and Lime on the As, Cr, Pb, and V Content of Soils and Plants. J. Environ. Qual. 1979, 8, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levander, O.A. Metabolic interrelationships between arsenic and selenium. Environ. Health Perspect. 1997, 19, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobrowicz, P.; Wysocki, R.; Owsianik, G.; Goffeau, A.; Ułaszewski, S. Isolation of Three Contiguous Genes, ACR1, ACR2 and ACR3, Involved in Resistance to Arsenic Compounds in the Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 1997, 13, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednar, A.J.; Garbarino, J.R.; Ferrer, I.; Rutherford, D.W.; Wershaw, R.L.; Ranville, J.F.; Wildeman, T.R. Photodegradation of roxarsone in poultry litter leachates. Sci. Total. Environ. 2003, 302, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, D.W.; Bednar, A.J.; Garbarino, J.R.; Needham, R.; Staver, K.W.; Wershaw, R.L. Environmental fate of roxarsone in poultry litter-Part II: Mobility of arsenic in soils amended with poultry litter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, L.; Hernandez, A.H.; Pessoa, G.S.; Arruda, M.Z.; Rezende-Filho, A.T.; Almeida, R.D.; Menezes, H.A.; Valles, V.; Barbiero, L.; Fostier, A.H. Dissolved arsenic in the upper Paraguay River basin and Pantanal wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundschuh, J.; Litter, M.I.; Parvez, F.; Román-Ross, G.; Nicolli, H.B.; Jean, J.-S.; Liu, C.-W.; López, D.; Armienta, M.A.; Guilherme, L.R.G.; et al. One century of arsenic exposure in Latin America: A review of history and occurrence from 14 countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 429, 2–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusicanqui, H.; Mahon, W.A.J.; Ellis, A.J. The geochemistry of the El Tatio geothermal field, northern Chile. In Proceedings of the Second United Nations Symposium on the Development and Use of Geothermal Resources, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–29 May 1975; Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Demirel, Z.; Yildirim, N. Boron pollution due to geothermal wastewater discharge into the Buyuk Menderes river, Turkey. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 18, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogdu, M.S.; Bayari, C.S. Environmental impact of geothermal fluids on surface water, groundwater and streambed sediments in the Akarcay Basin, Turkey. Environ. Geol. 2005, 47, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, Z.; Ding, S.; Hao, C.; Xiu, W.; Hou, W. Arsenate reduction and mobilization in the presence of indigenous aerobic bacteria obtained from high arsenic aquifers of the Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 203, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimick, D.A.; Moore, J.N.; Dalby, C.E.; Savka, M.W. The fate of geothermal arsenic in the Madison and Missouri Rivers, Montana and Wyoming. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 3051–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonnalagadda, S.B.; Nenzou, G. Studies on arsenic rich mine dumps: I. Effect on the surface soil. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 1996, 31, 8–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.; Tempel, R.N. Arsenic in the waters and sediments of the Humboldt River, North-Central Nevada, USA: Hydrological and mineralogical investigation. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rango, T.; Vengosh, A.; Dwyer, G.; Bianchini, G. Mobilization of arsenic and other naturally occurring contaminants in groundwater of the Main Ethiopian Rift aquifers. Water. Res. 2013, 47, 5801–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serfor-Armah, Y.; Nyarko, B.J.B.; Dampare, S.B.; Adomako, D. Levels of Arsenic and Antimony in Water and Sediment from Prestea, A Gold Mining Town in Ghana and its Environs. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2006, 175, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcue, J.M.; Nriagu, J.O. Impact of Abandoned Mine Tailings on the Arsenic Concentrations in Moira Lake, Ontario. J. Geochem. Explor. 1995, 52, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Rahman, M.A.; Kitahara, K.; Itaya, Y.; Maki, T.; Ueda, K. Seasonal changes of arsenic speciation in lake waters in relation to eutrophication. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1684–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maest, A.S.; Pasilis, S.P.; Miller, L.G.; Nordstrom, D.K. Redox Geochemistry of Arsenic and Iron in Mono Lake, California, USA. Water-Rock Interact. 1992, 1, 507–511. [Google Scholar]
- Houben, A.J.; D’Onofrio, R.; Kokelj, S.V.; Blais, J.M. Factors Affecting Elevated Arsenic and Methyl Mercury Concentrations in Small Shield Lakes Surrounding Gold Mines near the Yellowknife, NT, (Canada) Region. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smedley, P.L.; Edmunds, W.M.; Pelig-Ba, K.B. Mobility of arsenic in groundwater in the Obuasi gold-mining area of Ghana: Some implications for human health. Geo. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1996, 113, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sprague, D.D.; Vermaire, J.C. Legacy Arsenic Pollution of Lakes Near Cobalt, Ontario, Canada: Arsenic in Lake Water and Sediment Remains Elevated Nearly a Century After Mining Activity Has Ceased. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizur Rahman, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Peter Lim, R. Bioaccumulation, biotransformation and trophic transfer of arsenic in the aquatic food chain. Environ. Res. 2012, 116, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, H.; Sohrin, Y.; Matsui, M.; Hojo, M.; Kawashima, M. Speciation of Arsenic in Natural Waters by Solvent Extraction and Hydride Generation Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 3247–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, K.A.; Edmonds, J.S. Arsenic and marine organisms. Adv. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 44, 147–189. [Google Scholar]
- Caumette, G.; Koch, I.; Reimer, K.J. Arsenobetaine formation in plankton: A review of studies at the base of the aquatic food chain. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 2841–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Choi, S.-D.; Khim, J.S. Arsenic speciation in environmental multimedia samples from the Youngsan River Estuary, Korea: A comparison between freshwater and saltwater. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, G.; Calas, G. Arsenic in soils, mine tailings, and former industrial sites. Elements 2006, 2, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senn, D.B.; Hemond, H.F. Nitrate controls on iron and arsenic in an urban lake. Science 2002, 296, 2373–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crecelius, E.A. The geochemical cycle of arsenic in Lake Washington and its relation to other elements. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1975, 20, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, T.; Kawashima, M.; Koyama, M. The role of Mn2+-rich hydrous manganese oxide in the accumulation of arsenic in lake sediments-ScienceDirect. Water. Res. 1985, 19, 1029–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, K.A. Current Perspectives in Arsenic Environmental and Biological Research. Environ. Chem. 2005, 2, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.-X.; Li, Y.; Deng, X.-H.; Miao, A.-J.; Ji, R.; Yang, L.-Y. Toxicity and bioaccumulation kinetics of arsenate in two freshwater green algae under different phosphate regimes. Water. Res. 2013, 47, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, L.; Wang, W.-X. Arsenic bioaccumulation in a marine juvenile fish Terapon jarbua. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 105, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.C.D.; Bruland, K.W. Biogeochemistry of arsenic in natural waters: The importance of methylated species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O. Distribution and speciation of arsenic in natural waters and some marine algae. Deep Sea Res. 1978, 25, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braman, R.S.; Foreback, C.C. Methylated Forms of Arsenic in the Environment. Science 1973, 182, 1247–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H. The Behavior of Trivalent and Pentavalent Methylarsenicals in Lake Biwa. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1997, 11, 305–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G.; Arbab-Zavar, M.H.; Apte, S. Seasonal variability of biological arsenic methylation in the estuary of the River Beaulieu. Mar. Chem. 1982, 11, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, W.R.; Reimer, K.J. Arsenic speciation in the environment. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 713–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sohrin, Y.; Matsui, M.; Kawashima, M.; Hojo, M.; Hasegawa, H. Arsenic Biogeochemistry Affected by Eutrophication in Lake Biwa, Japan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2712–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Rahman, M.A.; Matsuda, T.; Kitahara, T.; Maki, T.; Ueda, K. Effect of eutrophication on the distribution of arsenic species in eutrophic and mesotrophic lakes. Sci. Total Envrion. 2009, 407, 1418–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanders, J.G.; Riedel, G.F. Trace element transformation during the development of an estuarine algal bloom. Estuaries 1993, 16, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, S.; Inoue, R.; Kozono, T.; Tokuda, T.; Ohki, A.; Takeshita, T. Arsenic metabolism in a freshwater food chain. Chemosphere 1990, 20, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, S.; Ohki, A.; Kusadome, K.; Kuroiwa, T.; Yoshifuku, I.; Naka, K. Bioaccumulation of arsenic and its fate in a freshwater food chain. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1992, 6, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, S.; Mawatari, K.; Ohki, A.; Naka, K. Arsenic metabolism in a freshwater food chain: Blue–green alga (Nostoc sp.)→ shrimp (Neocaridina denticulata)→ carp (Cyprinus carpio). Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1993, 7, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroiwa, T.; Ohki, A.; Naka, K.; Maeda, S. Biomethylation and biotransformation of arsenic in a freshwater food chain: Green alga (chlorella vulgaris)→shrimp (neocaridina denticulata)→killifish (oryzias iatipes). Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1994, 8, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G.; Comber, S.D.W.; Kifle, D.; Antai, E.E.; Purdie, D.A. Arsenic Speciation and Seasonal Changes in Nutrient Availability and Micro-plankton Abundance in Southampton Water, U.K. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1995, 40, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Andreae, T.W. Dissolved arsenic species in the Schelde estuary and watershed, Belgium. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1989, 29, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batley, G.E. Heavy Metals and Tributyltin in Australian Coastal and Estuarine Waters: State of the Marine Environment Report for Australia; Technical Annex 2; Department of the Environment, Sports and Territories: Canberra, Australia, 1996; pp. 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone, A.M.; Butler, E.C.V.; O’Grady, B.V. Meridional distribution of arsenic species in the subantarctic zone of the Southern Ocean, south of Australia. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 31657–31667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santosa, S.J.; Mokudai, H.; Takahashi, M.; Tanaka, S. The Distribution of Arsenic Compounds in the Ocean: Biological Activity in the Surface Zone and Removal Processes in the Deep Zone. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1996, 10, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosa, S.J.; Wada, S.; Tanaka, S. Distribution and cycle of arsenic compounds in the ocean. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1994, 8, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyler, P.; Martin, J.-M. Arsenic and selenium in a pristine river-estuarine system: The Krka (Yugoslavia). Mar. Chem. 1991, 34, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisler, R. A review of arsenic hazards to plants and animals with emphasis on fishery and wildlife resources. In Arsenic in the Environment; Nriagu, J.O., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 185–260. [Google Scholar]
- Cutter, G.A. Kinetic controls on metalloid speciation in seawater. Mar. Chem. 1992, 40, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, K.A.; Edmonds, J.S. Arsenic in the sea. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1993, 31, 111–151. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, J.G. Arsenic cycling in marine systems. Mar. Environ. Res. 1980, 3, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anninou, P.; Cave, R.R. How conservative is arsenic in coastal marine environments? A study in Irish coastal waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 82, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, D.M.; Rubinos, D.A.; Piñeiro, V.; Díaz-Fierros, F.; Barral, M.T. Influence of epipsammic biofilm on the biogeochemistry of arsenic in freshwater environments. Biogeochemistry 2016, 129, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O. Arsenic speciation in seawater and interstitial waters: The influence of biological-chemical interactions on the chemistry of a trace element. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1979, 24, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutter, G.A.; Cutter, L.S. Behavior of dissolved antimony, arsenic, and selenium in the Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Chem. 1995, 49, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waslenchuk, D.G.; Windom, H.L. Factors controlling the estuarine chemistry of arsenic. Estuar. Coast. Mar. Sci. 1978, 7, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, W.; Butler, E. Arsenic in the marine environment. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1988, 2, 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.T. The seasonal cycle of arsenic in estuarine and nearshore waters of the South Atlantic Bight. Mar. Chem. 1988, 25, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Moogoui, R.; Gupta, D.K. Arsenic: Source, Occurrence, Cycle, and Detection. In Arsenic Contamination in the Environment: The Issues and Solutions; Gupta, D.K., Chatterjee, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 13–35. [Google Scholar]
- Cullen, W.R.; Harrison, L.G.; Li, H.; Hewitt, G. Bioaccumulation and excretion of arsenic compounds by a marine unicellular alga, polyphysa peniculus. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1994, 8, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, J.M. Ecotoxicology of arsenic in the marine environment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1996, 16, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrench, J.J.; Addison, R.F. Reduction, Methylation, and Incorporation of Arsenic into Lipids by the Marine Phytoplankton Dunaliella tertiolecta. Can. J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 1981, 38, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Klumpp, D.W. Biosynthesis and release of organoarsenic compounds by marine algae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1979, 13, 738–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glabonjat, R.A.; Raber, G.; Van Mooy, B.A.S.; Francesconi, K.A. Arsenobetaine in Seawater: Depth Profiles from Selected Sites in the North Atlantic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goessler, W.; Pavkov, M. Accurate quantification and transformation of arsenic compounds during wet ashing with nitric acid and microwave assisted heating. Analyst 2003, 128, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaoka, K.I.; Yamamoto, H.; Kawashima, K.; Tagawa, S.; Kaise, T. Ubiquity of arsenobetaine in marine animals and degradation of arsenobetaine by sedimentary micro-organisms. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1988, 2, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaoka, K.I.; Tagawa, S.; Kaise, T. The fate of organoarsenic compounds in marine ecosystems. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1992, 6, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaoka, K.i.; Kaise, T.; Kai, N.; Kawasaki, Y.; Miyasita, H.; Kakimoto, K.; Tagawa, S. Arsenobetaine-decomposing Ability of Marine Microorganisms Occurring in Particles Collected at Depths of 1100 and 3500 Meters. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1997, 1, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inskeep, W.P.; McDermott, T.R.; Fendorf, S.E. Arsenic (V)/(III) cycling in soils and natural waters: Chemical and microbiological processes. In Environmental Chemistry of Arsenic; Frankenberger, W.F., Jr., Macy, J.M., Eds.; Marcell Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 183–216. [Google Scholar]
- Millward, G.E.; Ebdon, L.; Walton, A.P. Seasonality in estuarine sources of methylated arsenic. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1993, 7, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, K.; Khambholja, D.B. Arsenic Contents and Its Biotransformation in the Marine Environment-ScienceDirect. Handb. Arsen. Toxicol. 2015, 26, 675–700. [Google Scholar]
- Byrd, J.T. Comparative geochemistries of arsenic and antimony in rivers and estuaries. Sci. Total Environ. 1990, 97–98, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Kwon, H.-O.; Choi, S.-D.; Lee, J.-S.; Khim, J.S. Arsenic speciation in water, suspended particles, and coastal organisms from the Taehwa River Estuary of South Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 108, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, K.A. Arsenic species in seafood: Origin and human health implications. Pure Appl. Chem. 2010, 82, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, W.A.; Foster, S.; Krikowa, F.; Duncan, E.; John, A.S.; Hug, K.; Moreau, J.W. Thio arsenic species measurements in marine organisms and geothermal waters. Microchem. J. 2013, 111, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaise, T.; Ogura, M.; Nozaki, T.; Saitoh, K.; Sakurai, T.; Matsubara, C.; Watanabe, C.; Hanaoka, K. Biomethylation of Arsenic in an Arsenic-rich Freshwater Environment. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1998, 11, 4–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, S.; Ohki, A. Bioaccumulation and Biotransformation of Arsenic, Antimony, and Bismuth Compounds by Freshwater Algae. In Wastewater Treatment with Algae; Wong, Y.-S., Tam, N.F.Y., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 73–92. [Google Scholar]
- Rita, M.; Rosen, B.P.; Phung, L.T.; Simon, S. Microbial arsenic: From geocycles to genes and enzymes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 26, 311–325. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, L.; Wang, W.X. Biotransformation and detoxification of inorganic arsenic in a marine juvenile fish Terapon jarbua after waterborne and dietborne exposure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 221–222, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, Z.; Song, D.; Du, S.; Zhang, L. Arsenic speciation in wild marine organisms and a health risk assessment in a subtropical bay of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, R.; Francesconi, K.A.; Kienzl, N.; Soeroes, C.; Fodor, P.; Váradi, L.; Raml, R.; Goessler, W.; Kuehnelt, D. Arsenic speciation in freshwater organisms from the river Danube in Hungary. Talanta 2006, 69, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmann, D.; Krumholz, L.R.; Hemond, H.F.; Lovley, D.R.; Morel, F.M.M. Microbial mobilization of arsenic from sediments of the Aberjona Watershed. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2923–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-G.; Yoshinaga, M.; Zhao, F.-J.; Rosen, B.P. Earth Abides Arsenic Biotransformations. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet Sci. 2014, 42, 443–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, J.W.; Ramamoorthy, S. Heavy Metals in Natural Waters: Applied Monitoring and Impact Assessment; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Boström, K.; Valdes, S. Arsenic in ocean floors. Lithos 1969, 2, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-Y.; Su, J.-Q.; Sun, G.-X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, J.; Chen, Y.-S.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, G.; Rensing, C.; et al. Land scale biogeography of arsenic biotransformation genes in estuarine wetland. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 2468–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Song, J.; Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Li, N. Spatio-temporal distribution and environmental risk of arsenic in sediments of the East China Sea. Chem. Geol. 2013, 340, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeyens, W.; Mirlean, N.; Bundschuh, J.; de Winter, N.; Baisch, P.; da Silva, F.M.R.; Gao, Y. Arsenic enrichment in sediments and beaches of Brazilian coastal waters: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 681, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aston, S.R.; Thornton, I.; Webb, J.S.; Milford, B.L.; Purves, J.B. Arsenic in stream sediments and waters of South West England. Sci. Total. Environ. 1975, 4, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, W.J. Arsenic in U.K. estuarine sediments and its availability to benthic organisms. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 1980, 60, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.H.; Lamothe, P.J. Heavy metal anomalies in the Tinto and Odiel River and estuary system, Spain. Estuaries 1993, 16, 495–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnin, R.C.; Quaresma, V.S.; Chaillou, G.; Franco, T.; Bastos, A.C. Arsenic enrichment in sediment on the eastern continental shelf of Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, F.; Machado, E.D.C.; Angulo, R.J.; Brandini, N. Arsenic and heavy metals in sediment near Paranaguá Port. J. Coast. Res. 2006, 39, 1066–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, D.; Bellato, C.; Marques Neto, J.; Fontes, M. Trace elements in river waters and sediments before and after a mining dam breach. Quim Nova 2018, 41, 857–866. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, L.; Alonso, H.; Campano, P.; Fanfani, L.; Cidu, R.; Dadea, C.; Keegan, T.; Thornton, I.; Farago, M. Arsenic enrichment in waters and sediments of the Rio Loa (Second Region, Chile). Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 1399–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.d.C.; Paoloni, J.D.; Morrás, H.J.M.; Fiorentino, C.E.; Sequeira, M. Content and distribution of arsenic in soils, sediments and groundwater environments of the southern Pampa region, Argentina. Environ. Toxicol. 2006, 21, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalley, C.; Rowlatt, S.; Bennett, M.; Lovell, D. Total Arsenic in Sediments from the Western North Sea and the Humber Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1999, 38, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anawar, H.M.; Akai, J.; Mihaljevic, M.; Sikder, A.M.; Ahmed, G.; Tareq, S.M.; Rahman, M.M. Arsenic Contamination in Groundwater of Bangladesh: Perspectives on Geochemical, Microbial and Anthropogenic Issues. Water 2011, 3, 1050–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezende, P.S.; Costa, L.M.; Windmöller, C.C. Arsenic mobility in sediments from Paracatu River Basin, MG, Brazil. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 68, 588–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, G.F.; Sanders, J.G.; Osman, R.W. Biogeochemical control on the flux of trace elements from estuarine sediments: Effects of seasonal and short-term hypoxia. Mar. Environ. Res. 1999, 47, 349–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, P.M.; Hull, E.A.; Burkart, K.; Taylor, V.F.; Jackson, B.P.; Gawel, J.E.; Neumann, R.B.; Ohargrave, M.J. Contrasting arsenic cycling in strongly and weakly stratified contaminated lakes: Evidence for temperature control on sediment-water arsenic fluxes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2019, 64, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamindy-Pajany, Y.; Hurel, C.; Géret, F.; Galgani, F.; Battaglia-Brunet, F.; Marmier, N.; Roméo, M. Arsenic in marine sediments from French Mediterranean ports: Geochemical partitioning, bioavailability and ecotoxicology. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 2730–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gorny, J.; Billon, G.; Lesven, L.; Dumoulin, D.; Madé, B.; Noiriel, C. Arsenic behavior in river sediments under redox gradient: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaillou, G.; Schäfer, J.; Anschutz, P.; Lavaux, G.; Blanc, G. The behaviour of arsenic in muddy sediments of the Bay of Biscay (France). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 2993–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, D.; Mahoney, J.; MacDonald, A.; Rowson, J. Predicting arsenic concentrations in the porewaters of buried uranium mill tailings. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 3379–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H. Seasonal Changes in Methylarsenic Distribution in Tosa Bay and Uranouchi Inlet. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1996, 10, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorny, J.; Billon, G.; Noiriel, C.; Dumoulin, D.; Lesven, L.; Madé, B. Redox behaviour of arsenic in the surface sediments of the Marque River (Northern France). J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 188, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, E.A.; Bostick, B.C.; Li, G.; Fendorf, S. Kinetics of Arsenate Reduction by Dissolved Sulfide. Environ. Sci Technol. 2000, 34, 4714–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kim, H.; Townsend, T. Methodology for assessing thioarsenic formation potential in sulfidic landfill environments. Chemosphere 2014, 107, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolz, J.F.; Basu, P.; Santini, J.M.; Oremland, R.S. Arsenic and Selenium in Microbial Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 107–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamamura, N.; Itai, T.; Liu, Y.; Reysenbach, A.-L.; Damdinsuren, N.; Inskeep, W.P. Identification of anaerobic arsenite-oxidizing and arsenate-reducing bacteria associated with an alkaline saline lake in Khovsgol, Mongolia. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niggemyer, A.; Spring, S.; Stackebrandt, E.; Rosenzweig, R.F. Isolation and characterization of a novel As(V)-reducing bacterium: Implications for arsenic mobilization and the genus Desulfitobacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 5568–5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, X.-C.; Yang, Y.; Shi, W.; Peng, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y. Microbially Mediated Methylation of Arsenic in the Arsenic-Rich Soils and Sediments of Jianghan Plain. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanaoka, K.I.; Tagawa, S.; Kaise, T. Conversion of arsenobetaine to dimethylarsinic acid by arsenobetaine-decomposing bacteria isolated from coastal sediment. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1991, 5, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, E.G.; Maher, W.A.; Foster, S.D.; Mikac, K.M.; Krikowa, F. The influence of bacteria on the arsenic species produced by laboratory cultures of the marine phytoplankton Dunaliella tertiolecta. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 2129–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannon, J.M.; Patrick, W.H. Fixation, transformation, and mobilization of arsenic in sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1987, 21, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loring, D.H. Geochemical factors controlling the accumulation and dispersal of heavy metals in the Bay of Fundy sediments: Loring, D.H. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1982, 19, 930–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasmund, K.; Mußmann, M.; Loy, A. The life sulfuric: Microbial ecology of sulfur cycling in marine sediments. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2017, 9, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Water Body and Location | Arsenic Concentrations (Average or Range) |
|---|---|
| Rivers from upper Paraguay River basin, USA | 0.05–1.69 |
| Bowron Lake, Canada | <0.2 |
| Lowhee Creek, Canada | 0.2–2.0 |
| Lake Biwa, Japan | 0.6–1.7 |
| Dordogne, France | 0.7 |
| Youngsan River, Korea | 1.5 (1.3–1.7) |
| Lakes in Yellowknife, Canada | 2–136 |
| Rivers of Poopó basin, Bolivia | 10–11,140 |
| Humboldt River, USA | 12–60 |
| Xiaoqing River, China | 13.9–58.9 |
| Moira Lake, Ontario, Canada | 22.0–47.0 |
| Contaminated lake near Cobalt, Canada | 23.6–972 |
| Madison and Missouri rivers, USA | 44 (19–67) |
| Lakes in the Ziwaye-Shala basin, Ethiopia | 165 (2.39–566) |
| Ashanti, Ghana | 284 (<2–7900) |
| Lakes in the Town of Cobalt, Canada | 431 (2.2–972) |
| Rivers of Rio Loa basin, Chile | 1400–21,000 |
| Mono Lake, USA | 10,000–20,000 |
| Marine Water | Arsenic Concentration (µg/L) (Average or Range) |
|---|---|
| China Sea | 0.6 |
| Atlantic Ocean | 0.6–1.6 |
| Indian Ocean | 0.8–1.1 |
| Atlantic Ocean | 0.94–1.56 |
| Pacific Ocean | 1.0 |
| Unpolluted seawater | 1.0–2.0 |
| Atlantic Ocean | 1.0–1.8 |
| Pacific Ocean | 1.2–1.6 |
| Coastal Australia | 1.3 (1.1–1.6) |
| Rhône estuary, France | 1.3–3.7 |
| Southern Tasman Sea | 1.4 |
| Galway Bay, Ireland | 1.7 |
| Southern Ocean | 1.7–1.8 |
| Krka estuary, Yugoslavia | 1.8 |
| Scheldt estuary, Belgium | 1.8–4.9 |
| Marine hydrothermal fluids | 24.0–5850 |
| Marine Sediment | Arsenic Concentration (µg/g) (Average or Range) |
| Paranagua Bay, Brazil Western North Sea | 0.1–81.5 <0.2–135 |
| Uncontaminated marine sediments | 5.0–15 |
| UK estuarine sediments Rio Lao basin, Chile Doce River mouth, Brazil | 7.0–950 7–11,000 8.2–232.3 |
| Carnon/Restronguet Estuary | 9.0–5000 |
| East China Sea | 11.5 (1.7–22.1) |
| Baltimore Harbor, USA | 25.0–41.1 |
| Deep-sea sediments | 40 |
| French Mediterranean Estaque port | 107–220 |
| Tinto and Odiel River and Estuary | 200–3000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Ye, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, W. Arsenic Occurrence and Cycling in the Aquatic Environment: A Comparison between Freshwater and Seawater. Water 2023, 15, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010147
Wang N, Ye Z, Huang L, Zhang C, Guo Y, Zhang W. Arsenic Occurrence and Cycling in the Aquatic Environment: A Comparison between Freshwater and Seawater. Water. 2023; 15(1):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010147
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ningxin, Zijun Ye, Liping Huang, Chushu Zhang, Yunxue Guo, and Wei Zhang. 2023. "Arsenic Occurrence and Cycling in the Aquatic Environment: A Comparison between Freshwater and Seawater" Water 15, no. 1: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010147
APA StyleWang, N., Ye, Z., Huang, L., Zhang, C., Guo, Y., & Zhang, W. (2023). Arsenic Occurrence and Cycling in the Aquatic Environment: A Comparison between Freshwater and Seawater. Water, 15(1), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010147






