Algae and Hydrophytes as Potential Plants for Bioremediation of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
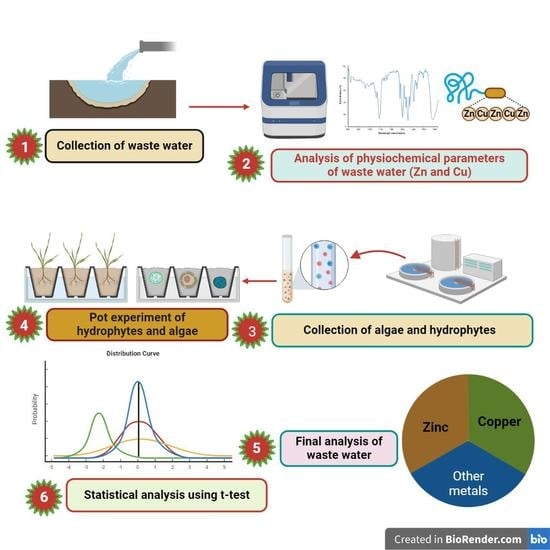
2. Materials and Methods
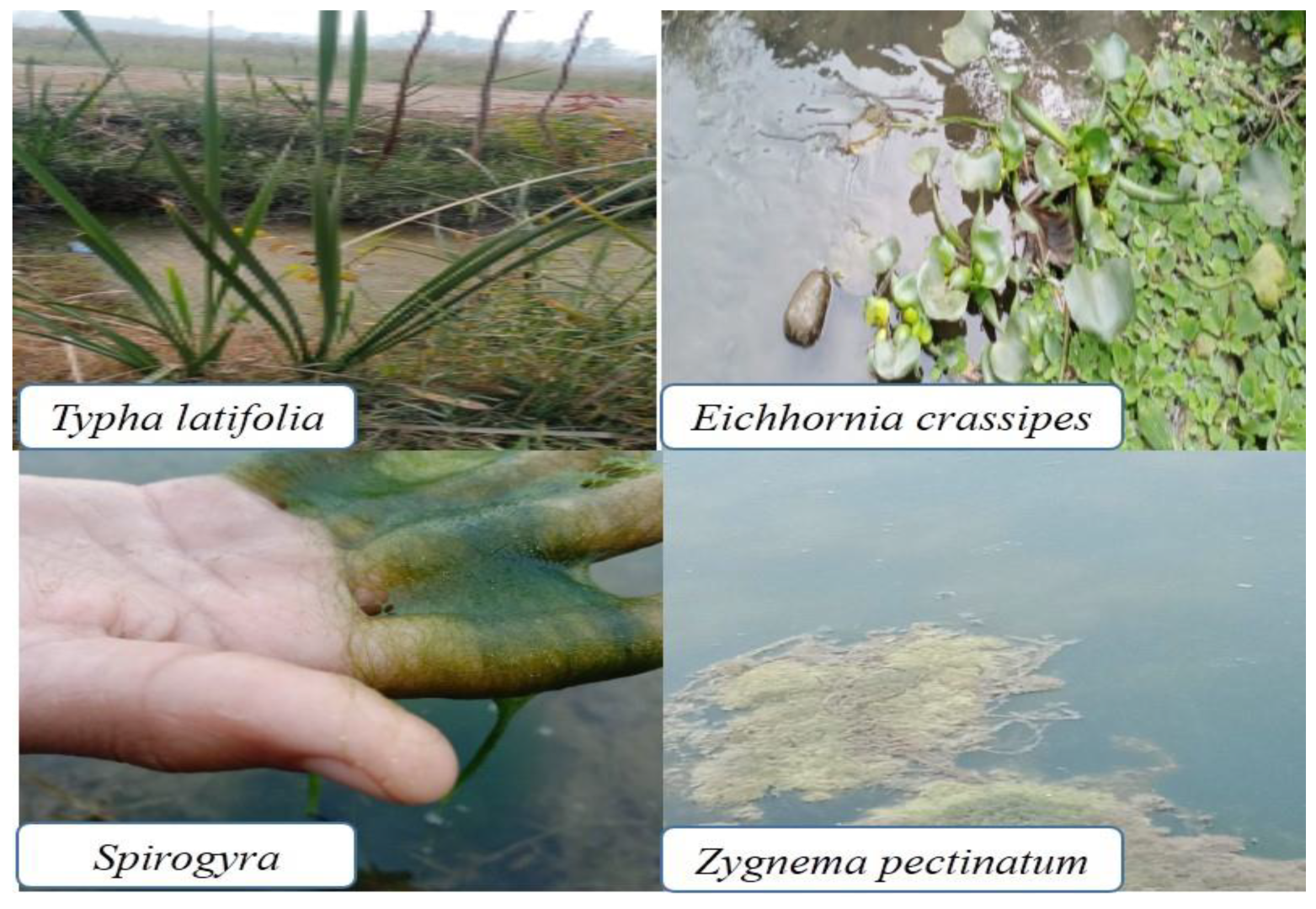
2.1. Algae and Hydrophyte Collection and Transplantation
2.2. Collection and Analysis of IWW
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Sampling and Analysis of Sediment
2.5. Sampling, Preparation, and Analysis of Hydrophyte
2.6. Formula
2.6.1. Bioconcentration Factor
2.6.2. Translocation Factor
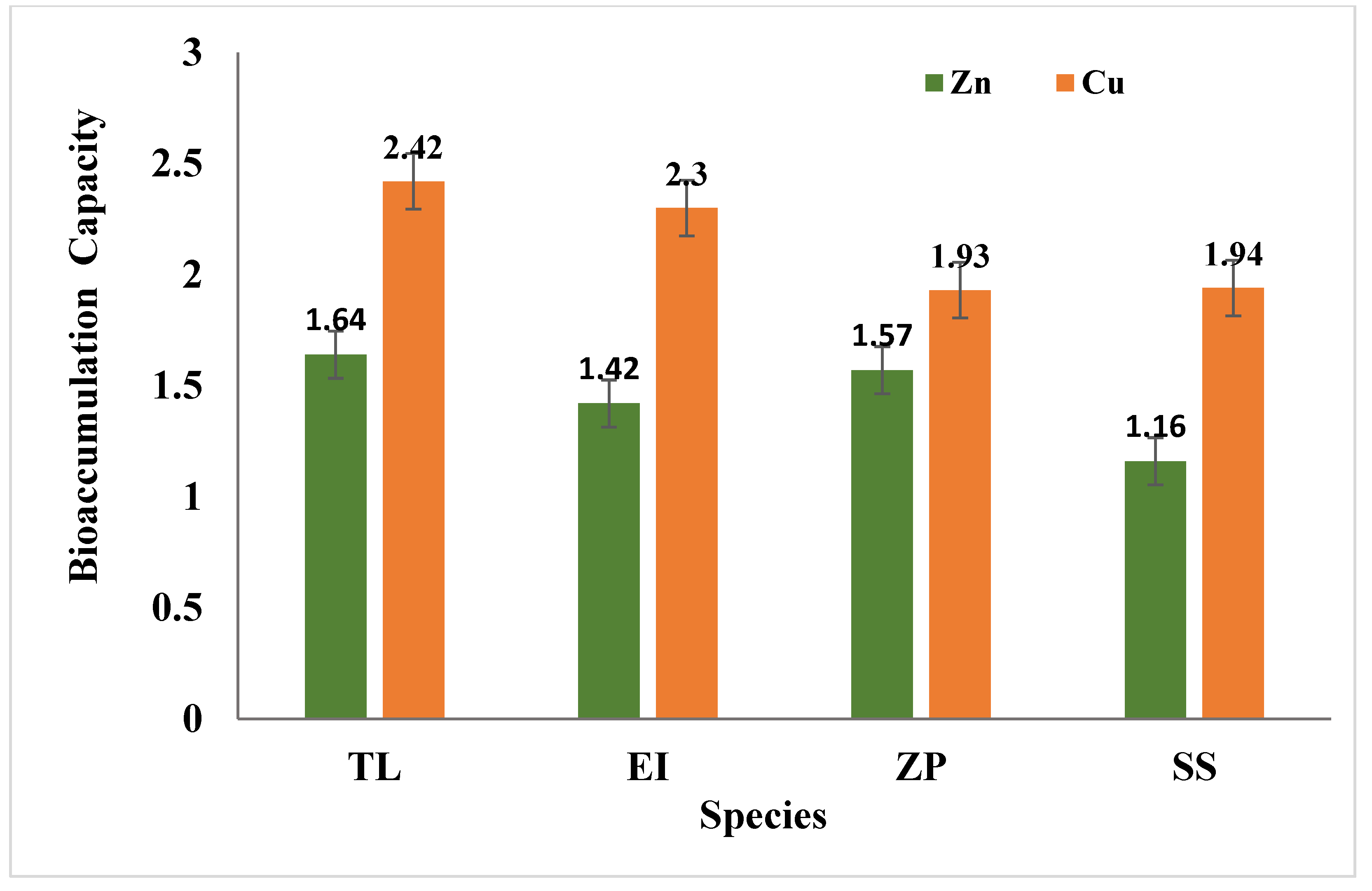
2.6.3. Bioaccumulation Measurement
2.6.4. Bioremoval Efficiency
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of Sediment Sample
3.2. Characteristics and Pollution Load of IWW
3.3. Effect of Hydrophytes and Algal Species on Physicochemical Parameters
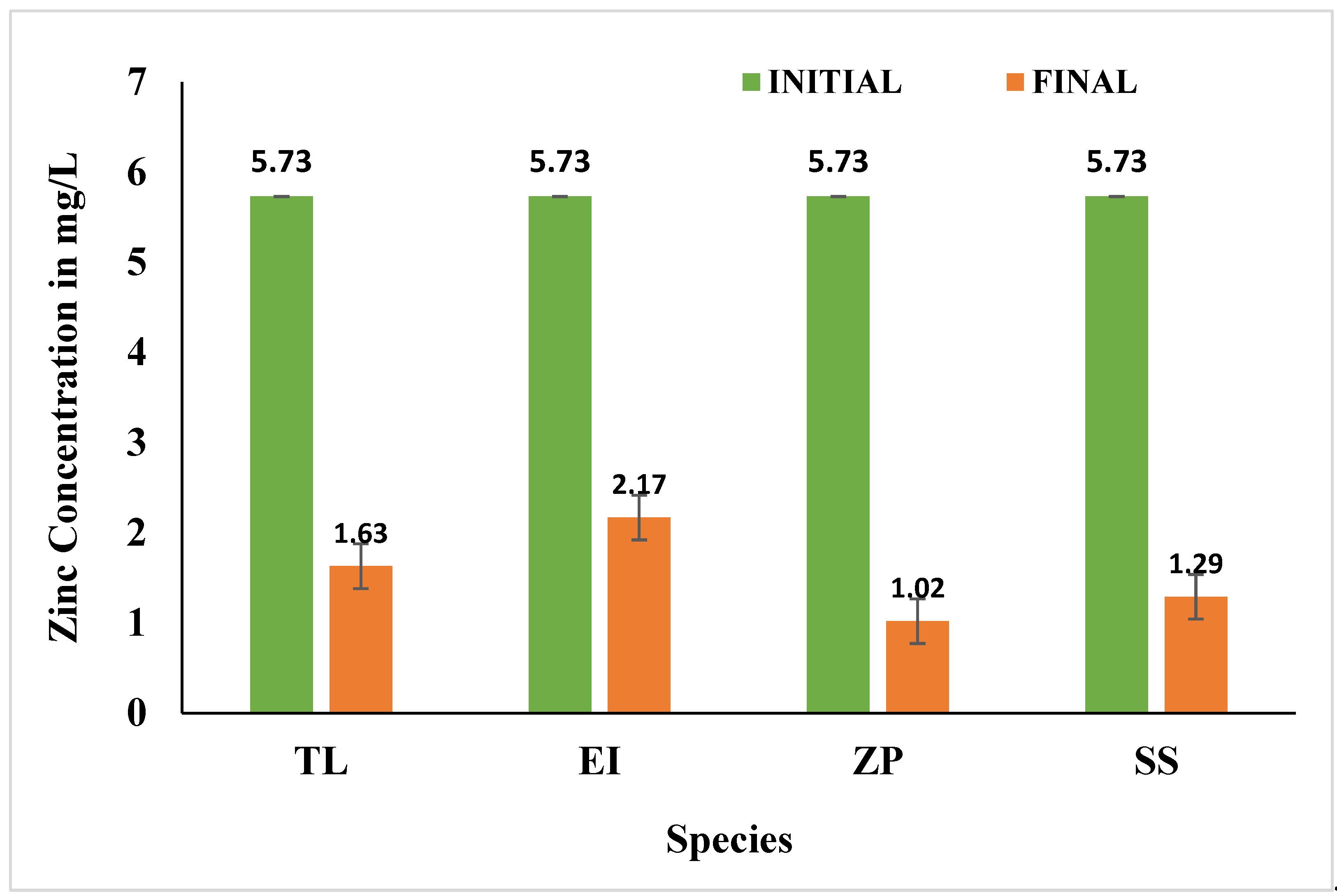
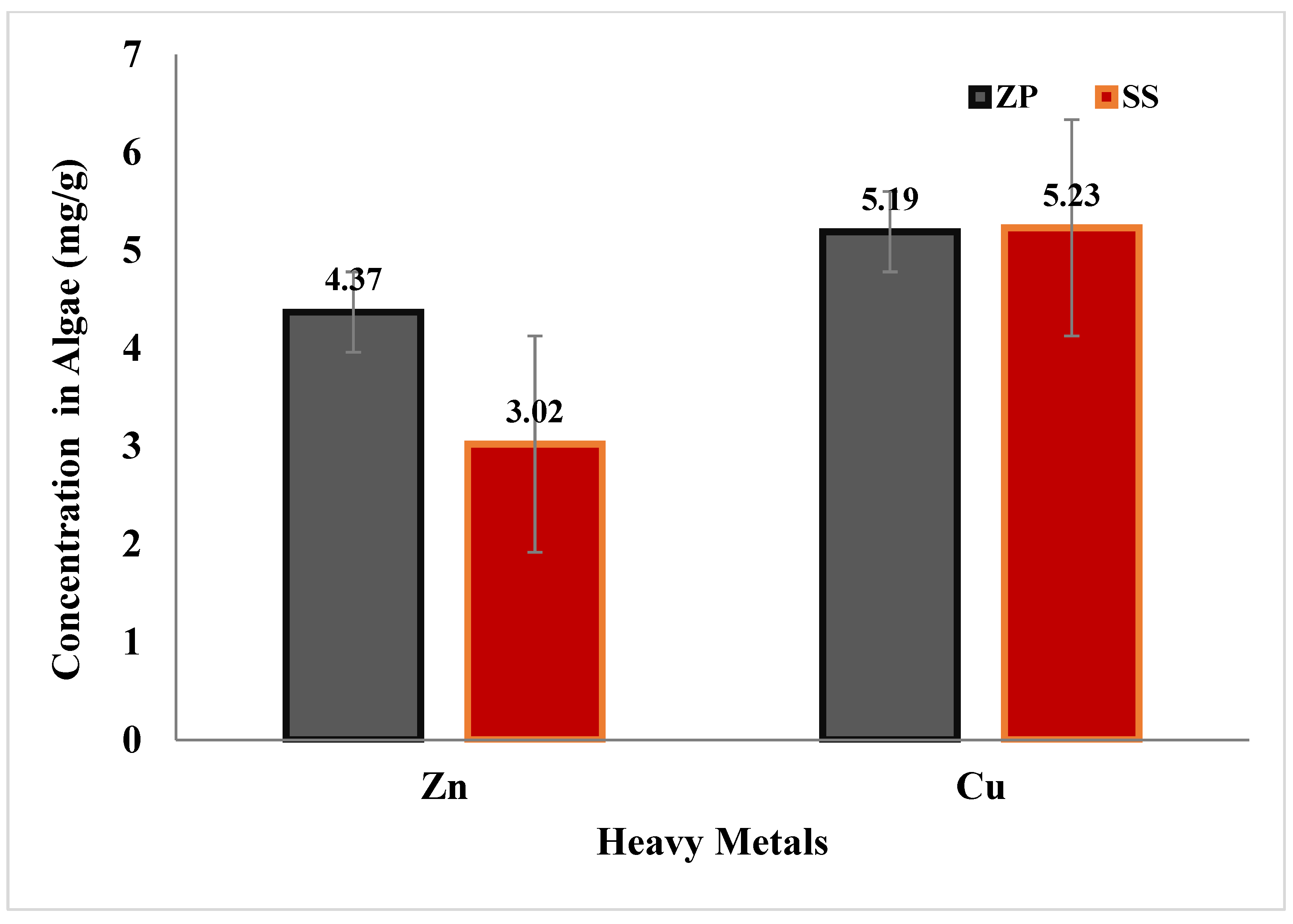
3.4. Effects of Selected Species on Heavy Metals
3.4.1. Zinc (Zn)
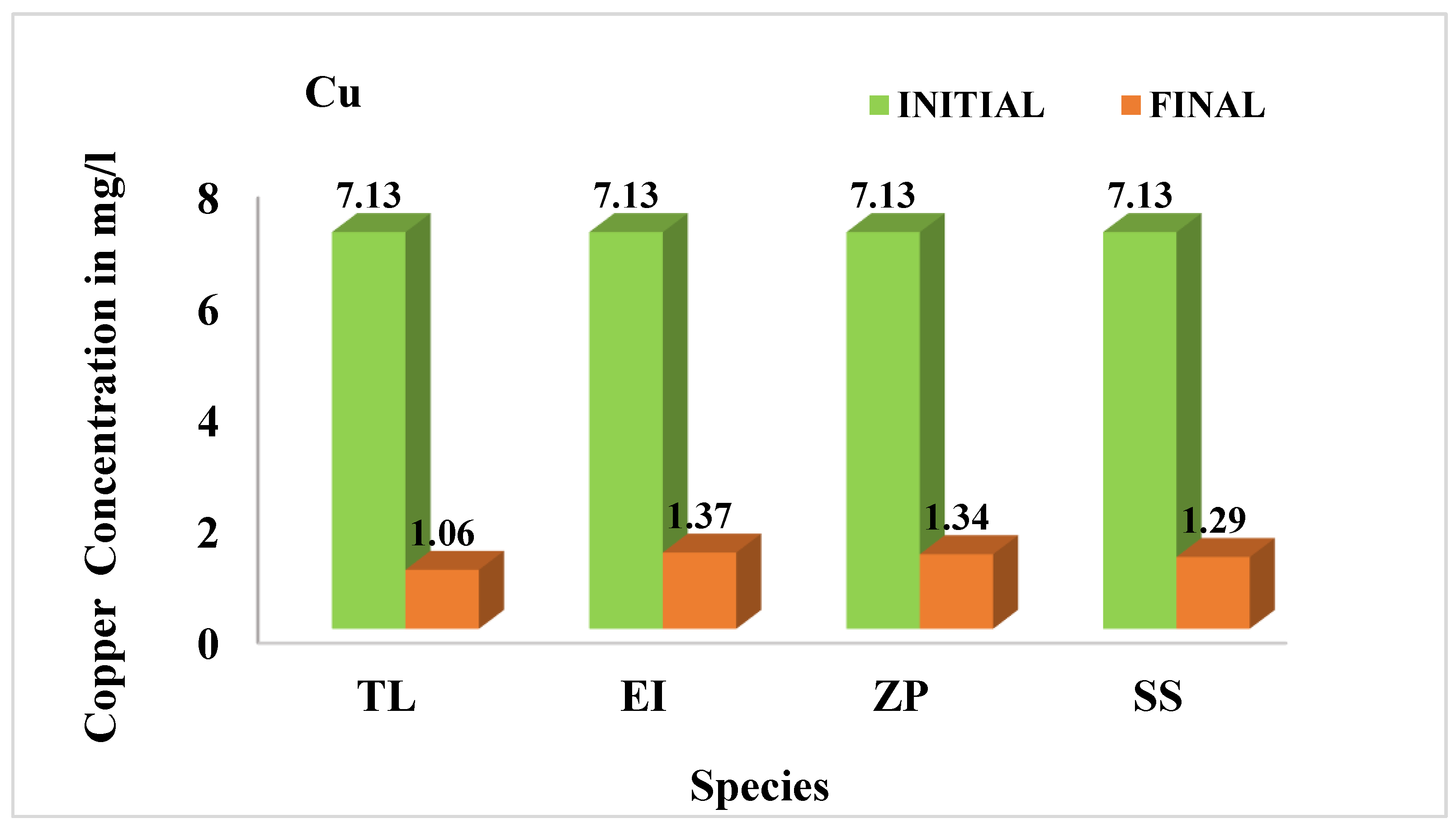
3.4.2. Copper (Cu)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goutam, S.P.; Saxena, G.; Singh, V.; Yadav, A.K.; Bharagava, R.N. Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using leaf extract of Jatropha curcas L. for photocatalytic degradation of tannery wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 336, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.O.; Ndukwe, A.O.; Asadu, C.O. Application of activated biomass waste as an adsorbent for the removal of lead (II) ion from wastewater. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, B.; Akpınar, I. A comparative study of heavy metals removal using agricultural waste biosorbents. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 15, 100719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Chung, J.; Lee, Y.W. Use of TiO2 media by sputtering and peroxy gel method for wastewater reuse in the electronics industry. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2019, 11, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis and Characterization of Zeolite A Obtained from Coal Gangue for the Adsorption of F–in Wastewater. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2019, 11, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Niu, B.; Yu, Q.; Guo, X.; Guo, Z.; Wen, J.; Wang, N. Photoinduced multiple effects to enhance uranium extraction from natural seawater by black phosphorus nanosheets. Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheela, T.; Sadasivam, S.K. Dye degradation potential and its degradative enzymes synthesis of Bacillus cereus SKB12 isolated from a textile industrial effluent. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, T.A.; Mustaqeem, M.; Khaled, M. Water treatment technologies in removing heavy metal ions from wastewater: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshoodeh, R.; Alavi, N.; Oldham, C.; Santos, R.M.; Babaei, A.A.; Vymazal, J.; Paydary, P. Constructed wetlands for landfill leachate treatment: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 146, 105725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Chen, H.; Reinhard, M.; Yi, X.; He, Y.; Gin, K.Y.H. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances removal in a full-scale tropical constructed wetland system treating landfill leachate. Water Res. 2017, 125, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DalCorso, G.; Fasani, E.; Manara, A.; Visioli, G.; Furini, A. Heavy metal pollutions: State of the art and innovation in phytoremediation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.N.; Faisal, M. Phytoremediation of industrial wastewater by hydrophytes. Phytoremediation Manag. Environ. Contam. 2018, 6, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, S.K.; Meravi, N.; Singh, S. Phytoremediation of Chromium and Cobalt using Pistia stratiotes: A sustainable approach. Proc. Int. Acad. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2012, 2, 136. [Google Scholar]
- Demim, S.; Drouiche, N.; Aouabed, A.; Benayad, T.; Couderchet, M.; Semsari, S. Study of heavy metal removal from heavy metal mixture using the CCD method. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, T.; Khan, S.; Khan, A.Z.; Lei, M.; Alam, M. Remediation of industrial wastewater using four hydrophyte species: A comparison of individual (pot experiments) and mix plants (constructed wetland). J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezania, S.; Taib, S.M.; Din, M.F.M.; Dahalan, F.A.; Kamyab, H. Comprehensive review on phytotechnology: Heavy metals removal by diverse aquatic plants species from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 318, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ahmad, I.; Shah, M.T.; Rehman, S.; Khaliq, A. Use of constructed wetland for the removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3451–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndeddy Aka, R.J.; Babalola, O.O. Effect of bacterial inoculation of strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Alcaligenesfeacalis and Bacillus subtilis on germination, growth and heavy metal (Cd, Cr, and Ni) uptake of Brassica juncea. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2016, 18, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, F.Z.; Archana, K.M.; Krishnaswamy, V.G.; Rajagopal, R. Remediation of heavy metals (Cr, Zn) using physical, chemical and biological methods: A novel approach. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katarzyna, H.; Baum, C. Application of microorganisms in bioremediation of environment from heavy metals. In Environmental Deterioration and Human Health; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Malaviya, P. Bioremediation of tannery wastewater by Aspergillus flavus SPFT2. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, S.; Singh, V. Phytoremediation approaches for heavy metal pollution: A review. J. Plant Sci. Res. 2015, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ajayan, K.V.; Selvaraju, M.; Unnikannan, P.; Sruthi, P. Phycoremediation of tannery wastewater using microalgae Scenedesmus species. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2015, 17, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshad, I.; Khan, S.; Waqas, M.; Ahmad, N.; Ur-Rehman, K.; Khan, K. Removal and bioaccumulation of heavy metals from aqueous solutions using freshwater algae. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 71, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, B.; Thanasekaran, K. Copper biosorption on Lyngbyaputealis: Application of response surface methodology (RSM). Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska-Niczyporuk, A.; Bajguz, A.; Talarek, M.; Bralska, M.; Zambrzycka, E. The effect of lead on the growth, content of primary metabolites, and antioxidant response of green alga Acutodesmus obliquus (Chlorophyceae). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 19112–19123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ye, Z.H.; Wei, Z.J.; Wong, M.H. Root porosity and radial oxygen loss related to arsenic tolerance and uptake in wetland plants. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ge, F.; Liu, N.; Wong, M. A pH-dependent enhancement effect of co-cultured Bacillus licheniformis on nutrient removal by Chlorella vulgaris. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 75, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Hu, R.; Yao, X.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, T. Towards high-quality biodiesel production from microalgae using original and anaerobically-digested livestock wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 128578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, J.; Dong, W.; Zhang, X.; Tyagi, R.D.; Drogui, P.; Surampalli, R.Y. The potential of microalgae in biodiesel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 90, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Kumar, M.; Usman, M.; Li, J.; Tsang, D.C. Bioremediation of water containing pesticides by microalgae: Mechanisms, methods, and prospects for future research. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 136080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshad, I.; Khan, S.; Waqas, M.; Asma, M.; Nawab, J.; Gul, N.; Li, G. Heavy metal uptake capacity of fresh water algae (Oedogonium westti) from aqueous solution: A mesocosm research. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2016, 18, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter 2016, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, W.E. Determination of carbonate and organic matter in calcareous sediments and sedimentary rocks by loss on ignition; comparison with other methods. J. Sediment. Res. 1974, 44, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Rehman, S.; Khan, A.Z.; Khan, M.A.; Shah, M.T. Soil and vegetables enrichment with heavy metals from geological sources in Gilgit, northern Pakistan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association. APHA Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination, 3rd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; pp. 105–119, 325–367, 371–415, 451–469, 637–658. [Google Scholar]
- Basílico, G.; Faggi, A.; de Cabo, L. Tolerance to metals in two species of fabaceae grown in riverbank sediments polluted with chromium 2020, copper, and lead. In Phytoremediation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Pyatt, F.B. Heavy metal bioaccumulation by the important food plant, Olea europaea L.; in an ancient metalliferous polluted area of Cyprus. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 78, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flouty, R.; Estephane, G. Bioaccumulation and biosorption of copper and lead by a unicellular algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in single and binary metal systems: A comparative study. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 111, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadad, H.R.; Maine, M.A.; Bonetto, C.A. Macrophyte growth in a pilot-scale constructed wetland for industrial wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 1744–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mays, P.A.; Edwards, G.S. Comparison of heavy metal accumulation in a natural wetland and constructed wetlands receiving acid mine drainage. Ecol. Eng. 2001, 16, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fito, J.; Tefera, N.; Kloos, H.; Van Hulle, S.W. Physicochemical properties of the sugar industry and ethanol distillery wastewater and their impact on the environment. Sugar Tech. 2019, 21, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asia, I.O.; Akporhonor, E.E. Characterization and physicochemical treatment of wastewater from rubber processing factory. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2007, 2, 061–067. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.B.; Islam, M.N.; Alam, M.S.; Hossen, M.Z. Industrialisation scenario at Sreepur of Gazipur, Bangladesh and physico-chemical properties of wastewater discharged from industries. Asian J. Environ. Ecol. 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniyikaiye, T.E.; Oluseyi, T.; Odiyo, J.O.; Edokpayi, J.N. Physico-chemical analysis of wastewater discharge from selected paint industries in Lagos, Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Shamshad, I.; Waqas, M.; Nawab, J.; Ming, L. Remediating industrial wastewater containing potentially toxic elements with four freshwater algae. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Singh, V.; Agnihotri, A.K. Study of textile effluent in and around Ludhiana district in Punjab, India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 3, 1271. [Google Scholar]
- Abrha, B.H.; Chen, Y. Analysis of physico-chemical characteristics of effluents from beverage industry in Ethiopia. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2017, 5, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, M.I.; Wahaab, R.A.; El-Kalliny, A.S. Fenton-biological treatment processes for the removal of some pharmaceuticals from industrial wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.A.; Chavan, S.K.; Khambe, S.D. Studies on characterization of textile industrial waste water in Solapur city. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2012, 10, 635–642. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, G.K.; Khan, S.A.; Shrivastava, M.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, S.; Malav, L.C.; Dubey, S.K. Bioremediation of sewage wastewater through microalgae (Chlorella minutissima). Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 90, 2024–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okpozu, O.O.; Ogbonna, I.O.; Ikwebe, J.; Ogbonna, J.C. Phycoremediation of cassava wastewater by Desmodesmus armatus and the concomitant accumulation of lipids for biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagy, L.E.; Johnson, B.M.; Castle, J.W.; Rodgers, J.H., Jr. Design and performance of a pilot-scale constructed wetland treatment system for natural gas storage produced water. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzakis, S.; Fountoulakis, M.S.; Georgaki, I.; Albantakis, D.; Sabathianakis, I.; Karathanasis, A.D.; Manios, T. Constructed wetlands treating highway runoff in the central Mediterranean region. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, P.C.; Bhosle, A.B. Bioremoval of some metals by living algae Spirogyra sp. and Spirullina sp. from aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Resour. 2012, 6, 571–576. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, A.; Lall, A.M.; Rao, K.P.; John, S.A.; Chattree, A. Phycoremediation of Pb, Cd, and of Cu by Spirogyra cummins from wastewater. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2019, 7, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, M.; Tripathi, B.D. Efficiency of Phragmites australis and Typha latifolia for heavy metal removal from wastewater. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 112, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victor, K.K.; Ladji, M.; Adjiri, A.O.; Cyrille, Y.D.A.; Sanogo, T.A. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals from wastewaters (Pb, Zn, Cd, Cu and Cr) in water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) and water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes). Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 2016, 9, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Galal, T.M.; Eid, E.M.; Dakhil, M.A.; Hassan, L.M. Bioaccumulation and rhizofiltration potential of Pistia stratiotes L. for mitigating water pollution in the Egyptian wetlands. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2018, 20, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Parameters (n = 3) | Samples * | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| pH | Initial | 8.09 ± 0.03 |
| Final | 8.02 ± 0.03 | |
| EC (mS/cm) | Initial | 341.5 ± 2.14 |
| Final | 94.0 ± 2.85 | |
| MC (mg/m3) | Initial | 0.62 ± 0.03 |
| Final | 0.85 ± 0.013 | |
| TOM (mg/kg) | Initial | 3.24 ± 0.03 |
| Final | 3.81 ± 0.03 | |
| TOC (mg/kg) | Initial | 1.78 ± 0.013 |
| Final | 2.39 ± 2.011 | |
| Zn (mg/kg) | Initial | 5.30 ± 3.17 |
| Final | 7.47 ± 2.70 | |
| Cu (mg/kg) | Initial | 19.07 ± 4.01 |
| Final | 20.82 ± 4.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farid, N.; Ullah, A.; Khan, S.; Butt, S.; Khan, A.Z.; Afsheen, Z.; El-Serehy, H.A.; Yasmin, H.; Ayaz, T.; Ali, Q. Algae and Hydrophytes as Potential Plants for Bioremediation of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater. Water 2023, 15, 2142. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122142
Farid N, Ullah A, Khan S, Butt S, Khan AZ, Afsheen Z, El-Serehy HA, Yasmin H, Ayaz T, Ali Q. Algae and Hydrophytes as Potential Plants for Bioremediation of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater. Water. 2023; 15(12):2142. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122142
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarid, Naila, Amin Ullah, Sara Khan, Sadia Butt, Amir Zeb Khan, Zobia Afsheen, Hamed A. El-Serehy, Humaira Yasmin, Tehreem Ayaz, and Qurban Ali. 2023. "Algae and Hydrophytes as Potential Plants for Bioremediation of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater" Water 15, no. 12: 2142. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122142
APA StyleFarid, N., Ullah, A., Khan, S., Butt, S., Khan, A. Z., Afsheen, Z., El-Serehy, H. A., Yasmin, H., Ayaz, T., & Ali, Q. (2023). Algae and Hydrophytes as Potential Plants for Bioremediation of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater. Water, 15(12), 2142. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122142