Spatial–Temporal Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Microplastics in the Shiwuli River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Methods
2.1. Profile of the Sampling Points
2.2. Sample Methods
2.3. Experimental Scheme
2.3.1. Microplastics Separation and Extraction
2.3.2. Observation and Identification
2.4. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial–Temporal Distribution of Microplastics
3.1.1. Abundance Distribution
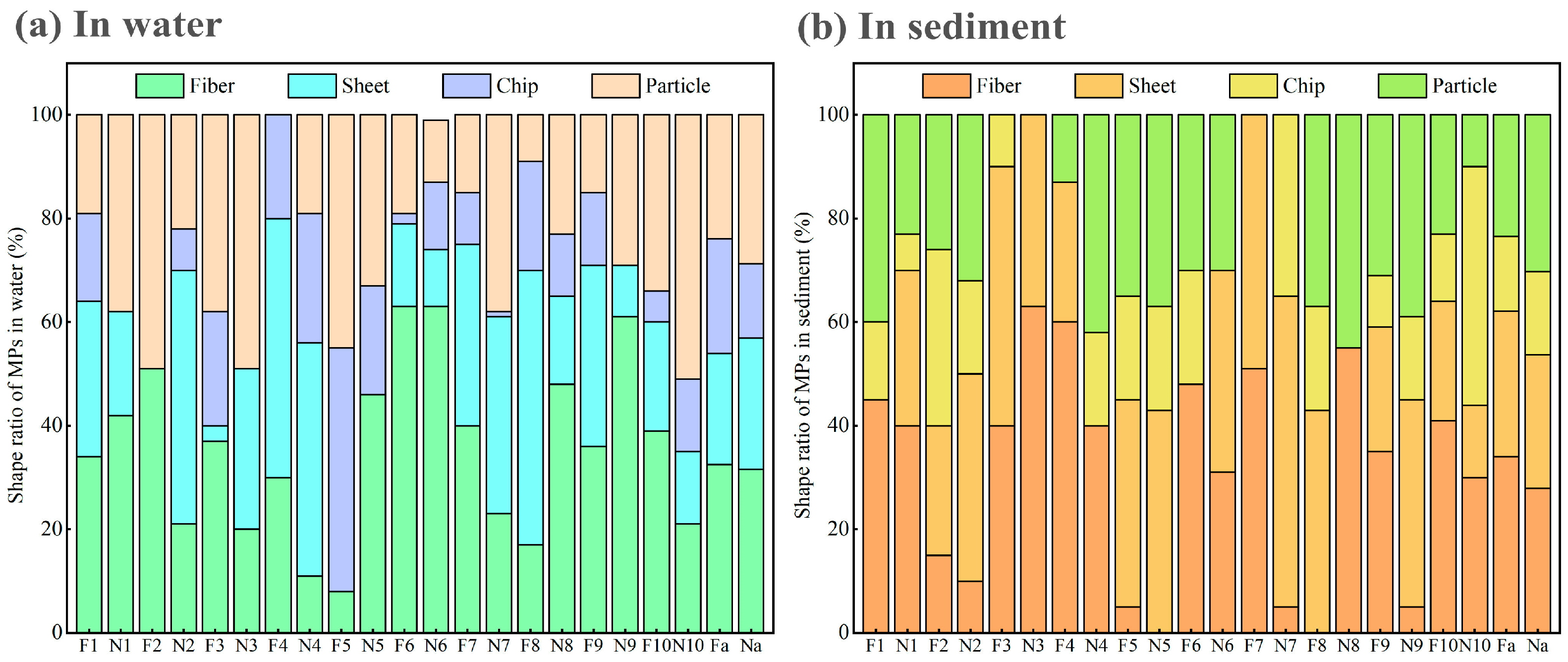
3.1.2. Shape Characteristics
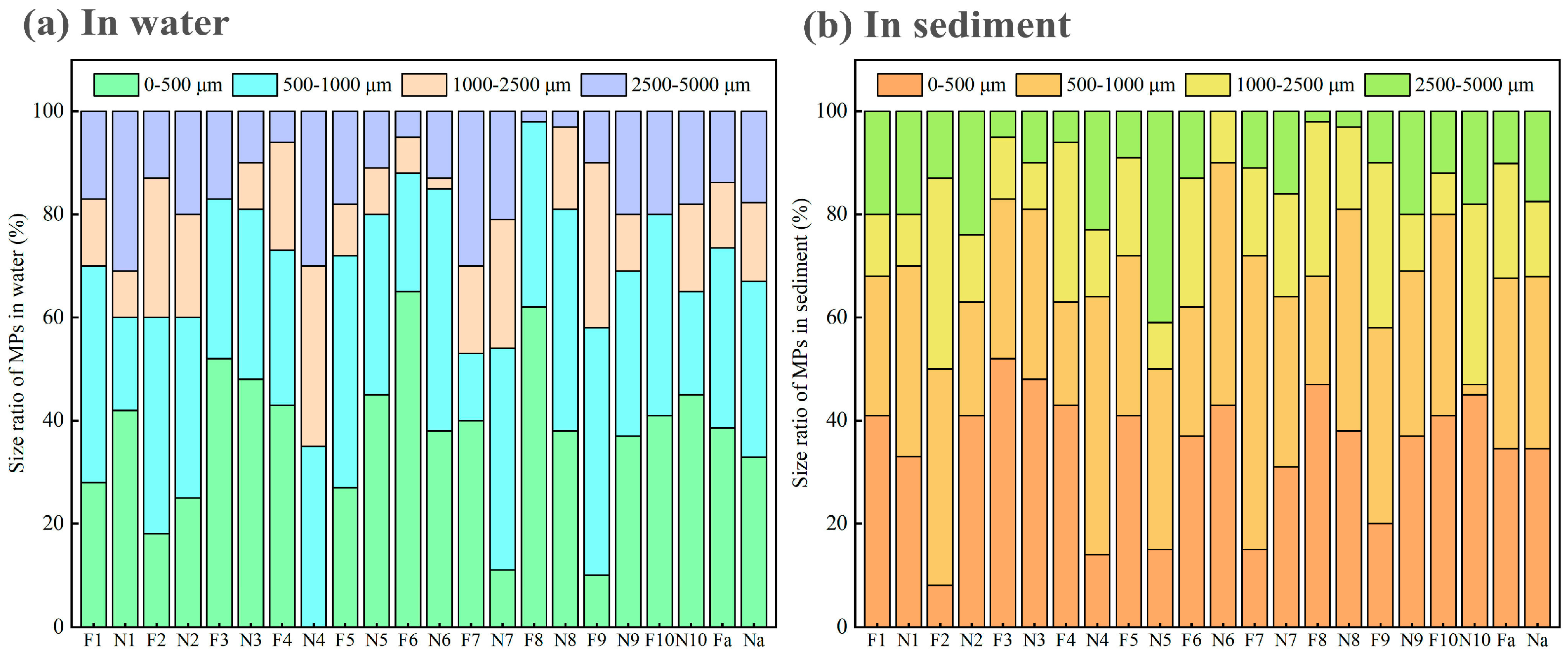
3.1.3. Size Characteristics of MPs
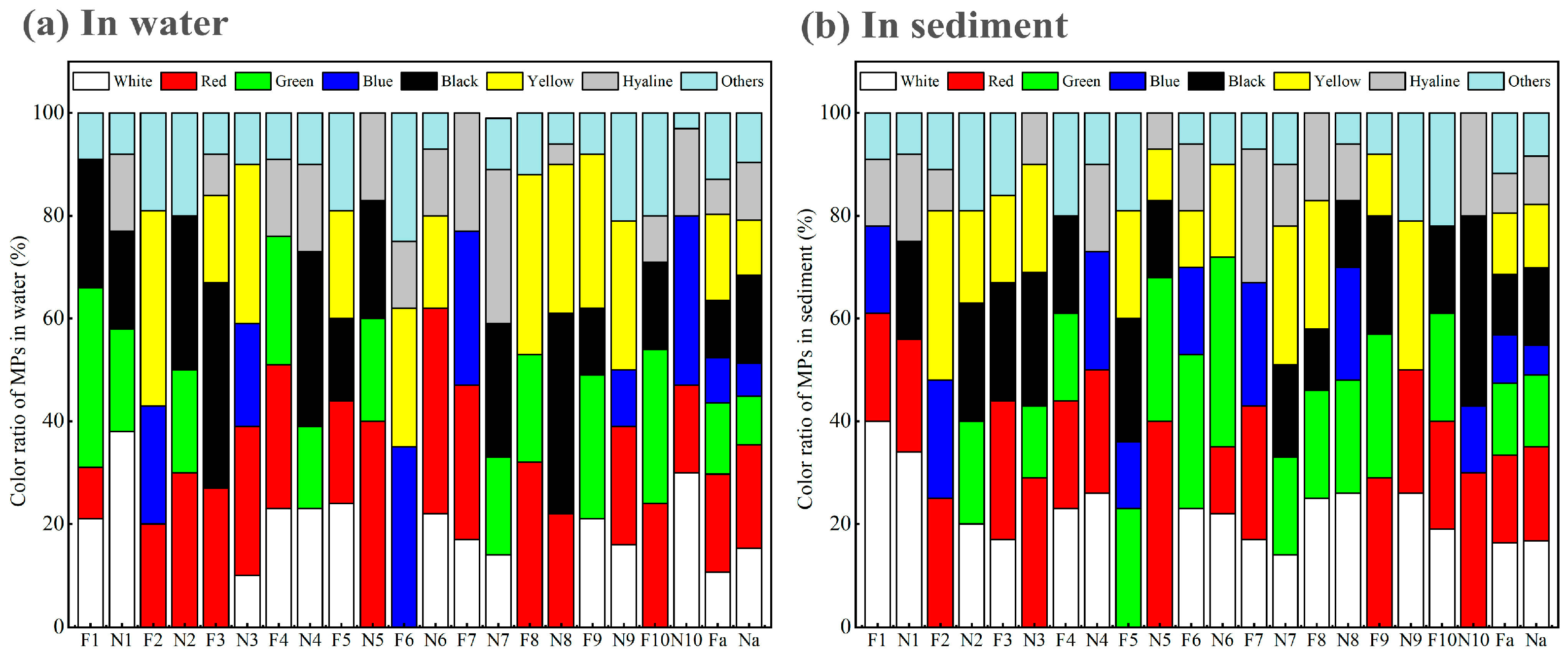
3.1.4. Colour Characteristics
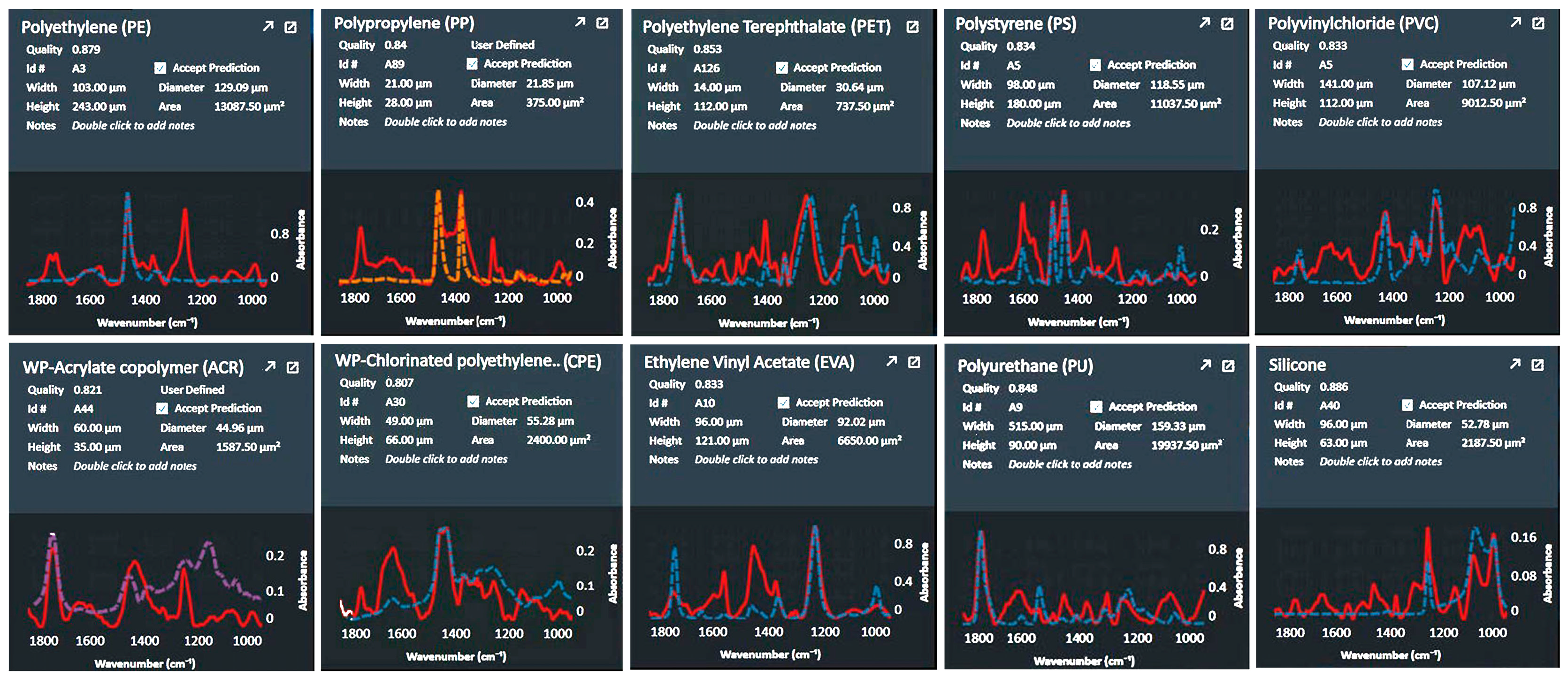
3.1.5. Composition Characteristics
3.2. Pollution Risk Assessment of Microplastics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, R.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.; Davis, A.; Russell, A. Supporting online material, lost at sea, where is all the plastic, material and methods. Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhao, X.; Cao, J. 7-Advanced Nanomaterials for Degrading Persistent Organic Pollutants. In Advanced Nanomaterials for Pollutant Sensing and Environmental Catalysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 249–305. [Google Scholar]
- Alimi, O.S.; Farner Budarz, J.; Hernandez, L.M.; Tufenkji, N. Microplastics and nanoplastics in aquatic environments, aggregation, deposition, and enhanced contaminant transport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, S.; Jung, S.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. Potential toxicity of polystyrene microplastic particles. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Powell, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, P. Microplastics as contaminants in the soil environment, a mini-review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Hamid, A.K.; Krebsbach, S.A.; He, J.; Wang, D. Critical review of microplastics removal from the environment. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, K.N.; Zhang, H. Adsorption of antibiotics on microplastics. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, S.; Takizawa, R.; Okuda, K.; Kanehiro, H.; Ogi, H.; Yamashita, R.; Date, T. Concentration of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in beached resin pellets, variability among individual particles and regional differences. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Tu, C.; Fu, C.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y. Characteristics and distribution of microplastics in the coastal mangrove sediments of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 703, 134807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.P. Microplastics in freshwater systems, a review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection. Water Res. 2018, 137, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Jin, T.; Zou, T.; Xu, L.; Xi, B.; Xu, D.; He, J.; Xiong, L.; Tang, C.; Peng, J.; et al. Current progress on plastic/microplastic degradation, Fact influences and mechanism. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 304, 119159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Mu, J.; Wang, P.; Lin, X.; Ma, D. Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Bohai Sea, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wolanski, E.; Dai, Z.; Lambrechts, J.; Tang, C.; Zhang, H. Trapping of plastics in semi-enclosed seas, insights from the Bohai Sea, China. Mar Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Guo, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, X.; Zou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Cai, S.; Huang, J. Microplastics in the northwestern Pacific, abundance, distribution, and characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 650, 1913–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miloloža, M.; Bule, K.; Prevarić, V.; Cvetnić, M.; Ukić, Š.; Bolanča, T.; Kučić Grgić, D. Assessment of the influence of size and concentration on the ecotoxicity of microplastics to microalgae scenedesmus sp., Bacterium Pseudomonas putida and Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Polymers 2022, 14, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Naushad, M.; Lima, E.C.; Zhang, S.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J. Global soil pollution by toxic elements: Current status and future perspectives on the risk assessment and remediation strategies—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, T.; Hurley, R.; Nizzetto, L.; Rico, A.; Vighi, M. Spatio-temporal distribution of microplastics in a Mediterranean river catchment, the importance of wastewater as an environmental pathway. J. Hazard. Mat. 2021, 420, 126481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ouyang, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhao, X.; Wu, R.; Zhang, C.; Lin, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, X. Distribution and characteristics of microplastics in the basin of Chishui River in Renhuai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 806, 145591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Busquets, R.; Nematollahi, M.J.; Javid, R.; Gobert, S. Effect of land use on microplastic pollution in a major boundary waterway, the Arvand River. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabinski, T.L.; de Carvalho, D.G.; Gaylarde, C.C.; Lourenço, M.F.P.; Machado, W.T.V.; da Fonseca, E.M.; da Silva, A.L.C.; Baptista Neto, J.A. Microplastics in freshwater fiver in Rio de Janeiro and its role as a source of microplastic pollution in Guanabara Bay, SE Brazil. Micro 2023, 3, 208–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradit, S.; Noppradit, P.; Sengloyluan, K.; Suwanno, P.; Tanrattanakul, V.; Sornplang, K.; Nuthammachot, N.; Jitkaew, P.; Nitiratsuwan, T. Occurrence of microplastics in river water in southern Thailand. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zuo, L.; Peng, J.; Cai, L.; Fok, L.; Yan, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, X. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in an urban river: A case study in the Pearl River along Guangzhou city, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, H.; An, Y.J. Species sensitivity distributions of micro- and nanoplastics in soil based on particle characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, R.; Li, W.; Sun, X.; Lin, H.; Jiang, S.; Huang, H. Microplastic pollution and ecological risk assessment in an estuarine environment: The Dongshan Bay of China. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjani, M.; Veerasingam, S.; Venkatachalapathy, R.; Mugilarasan, M.; Andrei, B.; Mukhanov, V.; Vethamony, P. Assessment of potential ecological risk of microplastics in the coastal sediments of India: A meta-analysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Wang, D.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Xing, M. Microplastics pollution and risk assessment in water bodies of two nature reserves in Jilin province: Correlation analysis with the degree of human activity. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Dai, J.; Wu, X.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J. Characteristics, occurrence and fate of non-point source microplastic pollution in aquatic environments. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 341, 130766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Bao, T.; Hong, L.; Wu, K. Occurrence Characterization and Contamination Risk Evaluation of Microplastics in Hefei’s Urban Wastewater Treatment Plant. Water 2023, 15, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, L.; Gareb, F.; Zimmermann, T.; Klein, O.; Kerstan, A.; Emeis, K.C.; Pröfrock, D. Spatial distribution of microplastics in the tropical Indian Ocean based on laser direct infrared imaging and microwave-assisted matrix digestion. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivokonsky, M.; Cermakova, L.; Novotna, K.; Peer, P.; Cajthaml, T.; Janda, V. Occurrence of microplastics in raw and treated drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithner, D.; Larsson, A.; Dave, G. Environmental and health hazard ranking and assessment of plastic polymers based on chemical composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3309–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgolnder Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di, M.; Wang, J. Microplastics in surface waters and sediments of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 1620–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zou, L.; Duan, T.; Qin, L.; Qi, Z.; Sun, J. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in surface water and sediments in china’s inland water systems, a critical review. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 331, 129968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M.F.M.; Ascer, L.G.; Custodio, M.R.; Moreira, F.T.; Turra, A. Microplastic contamination in natural mussel beds from a brazilian urbanized coastal region, rapid evaluation through bioassessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Zhu, L.; An, L.; Peng, G.; Li, D. Estimation and prediction of plastic waste annual input into the sea from china. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Hu, H.; Ao, H.; Wu, C. Transport and fate of microplastics in constructed wetlands: A microcosm study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helcoski, R.; Yonkos, L.T.; Sanchez, A.; Baldwin, A.H. Wetland soil microplastics are negatively related to vegetation cover and stem density. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhu, L.; Wang, T.; Li, D. Suspended microplastics in the surface water of the yangtze estuary system, china, first observations on occurrence, distribution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yuan, W.; Di, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Transfer and fate of microplastics during the conventional activated sludge process in one wastewater treatment plant of China. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Yang, W.; Ren, Y.; Jin, H.; Wang, A. Occurrence, effect, and fate of residual microplastics in anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge: A state-of-the-art review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 331, 125035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, L.; Mei, Q.; Dong, B.; Dai, X.; Ding, G.; Zeng, E.Y. Microplastics in sewage sludge from the wastewater treatment plants in China. Water Res. 2018, 142, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperi, J.; Gromaire, M.C.; Kafi, M.; Moilleron, R.; Chebbo, G. Contributions of wastewater, runoff and sewer depositerosion to wet weather pollutant loads in combined sewersystems. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5875–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessens, M.; Clerck, K.D.; Landuyt, L.V.; Meester, S.D.; Janssen, C.R. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in marine sediments along the Belgian coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, H.; Fischer, F.; Lenz, R.; Fischer, D.; Labrenz, M. Identification and quantification of microplastic particles in drinking water treatment sludge as an integrative approach to determine microplastic abundance in a freshwater river. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, F.; Ewins, C.; Carbonnier, F.; Quinn, B. Wastewatertreatment works (WwTW) as a source of microplastics in theaquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5800–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senathirajah, K.; Attwood, S.; Bhagwat, G.; Carbery, M.; Wilson, S.; Palanisami, T. Estimation of the mass of microplastics ingested—A pivotal first step towards human health risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404 Pt B, 124004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueiras, A.V.; Gago, J.; Campillo, J.A.; León, V.M. Microplastic distribution in surface sediments along the spanish mediterranean continental shelf. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 21264–21273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vibhatabandhu, P.; Srithongouthai, S. Influence of seasonal variations on the distribution characteristics of microplastics in the surface water of the Inner Gulf of Thailand. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Miao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jiao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Cao, L. Effectively and efficiency of best management practices based on a survey and SWAPP model of the Xiangxi River Basin. Water. 2021, 13, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.A.M.; Badr-ElDin, A.M. Ecological risk assessment of surficial sediment by heavy metals from a submerged archaeology harbor, south Mediterranean Sea, Egypt. Acta Geochim. 2020, 39, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoldi, C.; Lara, L.Z.; Mizushima, F.; Martins, F.; Fernandes, A.N. First evidence of microplastic contamination in the freshwater of Lake Guaíba, Porto Alegre, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 759, 143503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, L.; Wen, D. Prevalence of small-sized microplastics in coastal sediments detected by multipoint confocal micro-raman spectrum scanning. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolívar-Subirats, G.; Rivetti, C.; Cortina-Puig, M.; Barata, C.; Lacorte, S. Occurrence, toxicity and risk assessment of plastic additives in Besos River, spain. Chemosphere 2020, 263, 128022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, S.; Liang, Y.; Kim, M.; Byun, J.; Choi, H. Microplastics with adsorbed contaminants: Mechanisms and treatment. Environ. Chall. 2021, 3, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Lu, J.; Li, W.; Ning, J.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Xiayihazi, N. Seasonal variation and risk assessment of microplastics in surface water of the Manas River Basin, China. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2021, 208, 111477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahian, S.; Rakib, M.R.; Kumar, R.; Haider, S.; Sharma, P.; Idris, A.M. Distribution, characteristics, and risk assessments analysis of microplastics in shore sediments and surface water of Moheshkhali channel of bay of Bengal, Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Sampling Points | Locations | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | Administrative and commercial areas | Starting section, estuary of Swan Lake |
| S2 | Urban residential areas | Beside main streets of urban traffic, outlet below the Overpass of Jinzhai Road |
| S3 | Urban residential areas | Outlet of the Hudaying Sewage Treatment Plant |
| S4 | Ecological landscape areas | Intersection with the tributary Xingfu Channel, next to the industrial development zone |
| S5 | Ecological landscape areas | Intersection with the tributary Wangniangou, the planned large ecological park area |
| S6 | Ecological landscape areas | Intersection with the tributary Xuxiaohe, the planned large ecological park area |
| S7 | Ecological landscape areas | Outlet of the Shiwulihe Sewage Treatment Plant |
| S8 | Agricultural areas | Intersection with the tributary Xuxi River, agricultural planting and aquaculture |
| S9 | Wetland ecological protection areas | Large water area |
| S10 | Wetland ecological protection areas | Terminal section, estuary of Chaohu Lake |
| Model (Indexes) | Risk Category | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (Very Low Hazard) | II (Low Hazard) | III (Medium Hazard) | IV (High Hazard) | |
| RI (H value) | <10 | 10~100 | 100~1000 | >1000 |
| PLI (PLIzone value) | <10 | 10~20 | 20~30 | >30 |
| PE | PP | PET | PA | PS | PVC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sn [31] | 11 | 1 | 30 | 50 | 871 | 30 | ||||||
| (hazard score, highest level) | ||||||||||||
| Seasons | f. | n.-f. | f. | n.-f. | f. | n.-f. | f. | n.-f. | f. | n.-f. | f. | n.-f. |
| (f.: flood; n.-f.: non-flood) | ||||||||||||
| Pn (%) | ||||||||||||
| Water | 21.6 | 19.3 | 14.9 | 16.8 | 12.4 | 11.7 | 12.3 | 9.9 | 15.6 | 12.5 | 15.1 | 15.5 |
| Sediments | 16.5 | 23.2 | 22.7 | 21.8 | 13.5 | 18.1 | 11.9 | 4.8 | 9.6 | 9.9 | 15.4 | 12.2 |
| H value | ||||||||||||
| Water | 2.38 | 2.12 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 3.72 | 3.51 | 6.15 | 4.95 | 135.88 | 108.88 | 4.53 | 4.65 |
| Sediments | 1.82 | 2.55 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 4.05 | 5.43 | 5.95 | 2.40 | 83.62 | 86.23 | 4.62 | 3.66 |
| Risk level | ||||||||||||
| Water | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | III | III | I | I |
| Sediments | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | II | II | I | I |
| PLIzone | ||||||||||||
| Water | PLIzone (f.) value is 2.24 (heavy pollution); PLIzone (n.-f.) value is 1.66 (moderate pollution) | |||||||||||
| Sediments | PLIzone (f.) value is 2.34 (heavy pollution); PLIzone (n.-f.) value is 1.91 (heavy pollution) [32] | |||||||||||
| Research Object | Country | Abundance | Assessment Models | Results of Assessment | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coast of India | India | 12.22–439 items/kg in sediment | Pollution load index (PLI) | PLI of west coast of India: 3.03–15.5 (heavy pollution) PLI of east coast of India: 1–6.14 (moderate to heavy pollution) | [21] |
| Chagan lake and Xianghai lake | China | Chagan Lake: 3.61 ± 2.23 particles/L; Xianghai lake: 0.29 ± 0.11 particles/L | Risk index (RI) | Levels-III (heavy pollution) in Chagan Lake and Xianghai Lake | [22] |
| Manas River Basin | China | 17 ± 4 items/L (April) 14 ± 2 items/L (July) | Risk index (RI) | Most of the study areas: Level-III (heavy pollution) | [56] |
| Pollution load index (PLI) | All the sampling sites: slightly polluted | ||||
| Moheshkhali channel of Bangladesh | Bangladesh | Sediment: 138.33 items/m2 Water: ~0.1 items/m3 | Pollution load index (PLI) | PLIsediments: 2.51 (heavy pollution) PLIsurface water: 1.67 (moderate pollution) | [57] |
| Shiwuli River (this study) | China | Water: Flood season (f.): 8.4 ± 2.5 particles/L Non-flood season (n.-f.): 5.8 ± 1.7 particles/L; Sediment: Flood season (f.): 78.9 ± 8.3 particles/kg Non-flood season (n.-f.): 63.9 ± 7.1 particles/kg. | Risk index (RI) | PS: Level-III in water and Level-II in sediments; Other polymers: Level-I | - |
| Pollution load index (PLI) | Water: PLIzone (f.): 2.24 (heavy pollution); PLIzone (n.-f.): 1.66 (moderate pollution) Sediments: PLIzone (f.): 2.34 (heavy pollution); PLIzone (n.-fl.): 1.91 (heavy pollution) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, L.; Meng, X.; Bao, T.; Liu, B.; Wang, Q.; Jin, J.; Wu, K. Spatial–Temporal Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Microplastics in the Shiwuli River. Water 2023, 15, 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132330
Hong L, Meng X, Bao T, Liu B, Wang Q, Jin J, Wu K. Spatial–Temporal Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Microplastics in the Shiwuli River. Water. 2023; 15(13):2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132330
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Lei, Xiangwu Meng, Teng Bao, Bin Liu, Qun Wang, Jie Jin, and Ke Wu. 2023. "Spatial–Temporal Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Microplastics in the Shiwuli River" Water 15, no. 13: 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132330
APA StyleHong, L., Meng, X., Bao, T., Liu, B., Wang, Q., Jin, J., & Wu, K. (2023). Spatial–Temporal Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Microplastics in the Shiwuli River. Water, 15(13), 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132330









