Chemical and Ecotoxicological Assessment of Agricultural Drainage Water from a Maize Crop Area: A Case Study in the Tejo Basin (Portugal)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
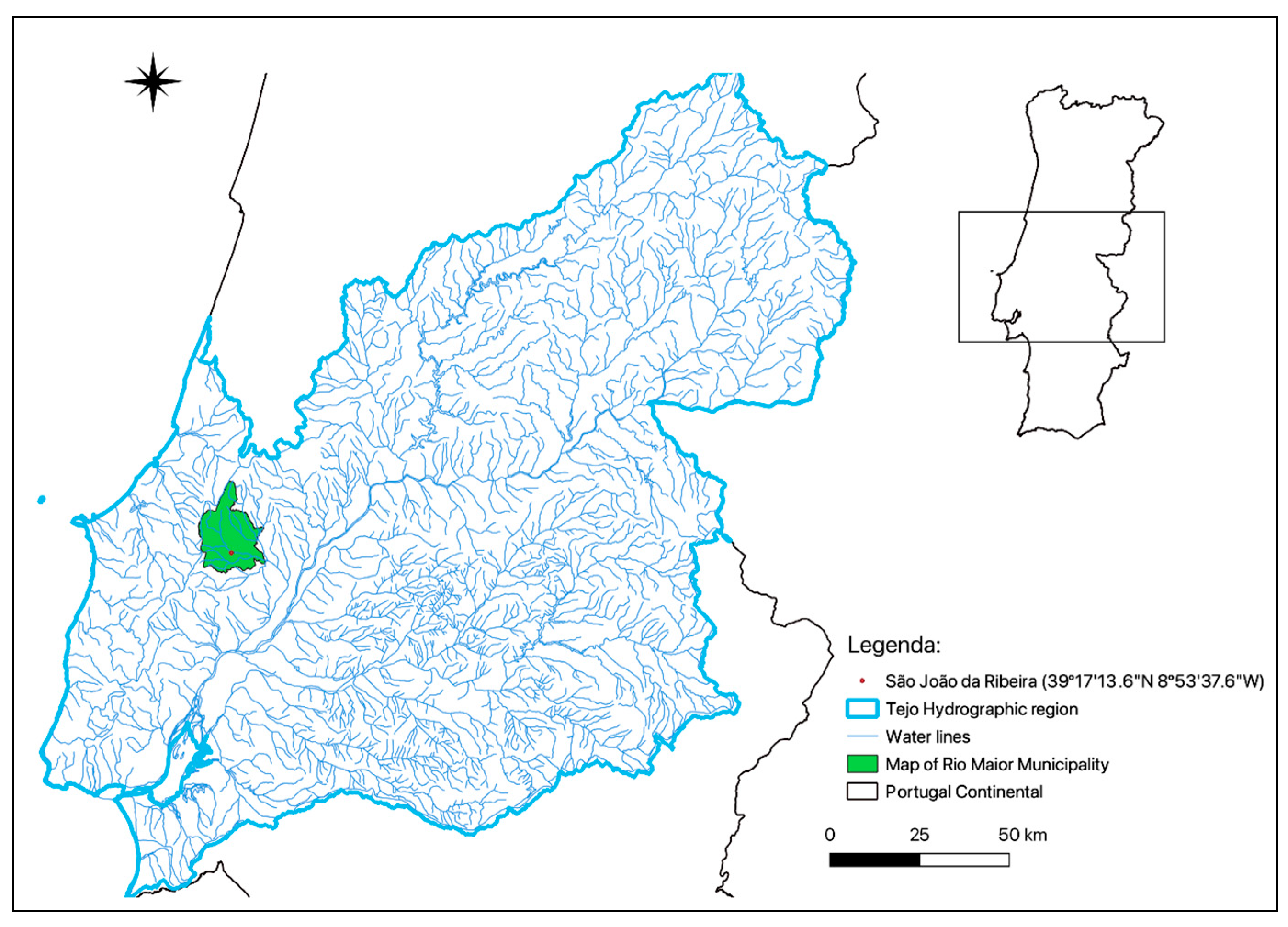
2.1. Site Description and Sampling Characterization
2.2. Physicochemical Parameters and Pesticides Analysis
2.3. Assessment of AWD Quality for Irrigation
2.4. Ecotoxicological Assessment
2.4.1. Luminescence Inhibition of V. fisheri
2.4.2. Growth Inhibition of the Green Microalgae P. subcapitata
2.4.3. Mortality Test with T. platyurus
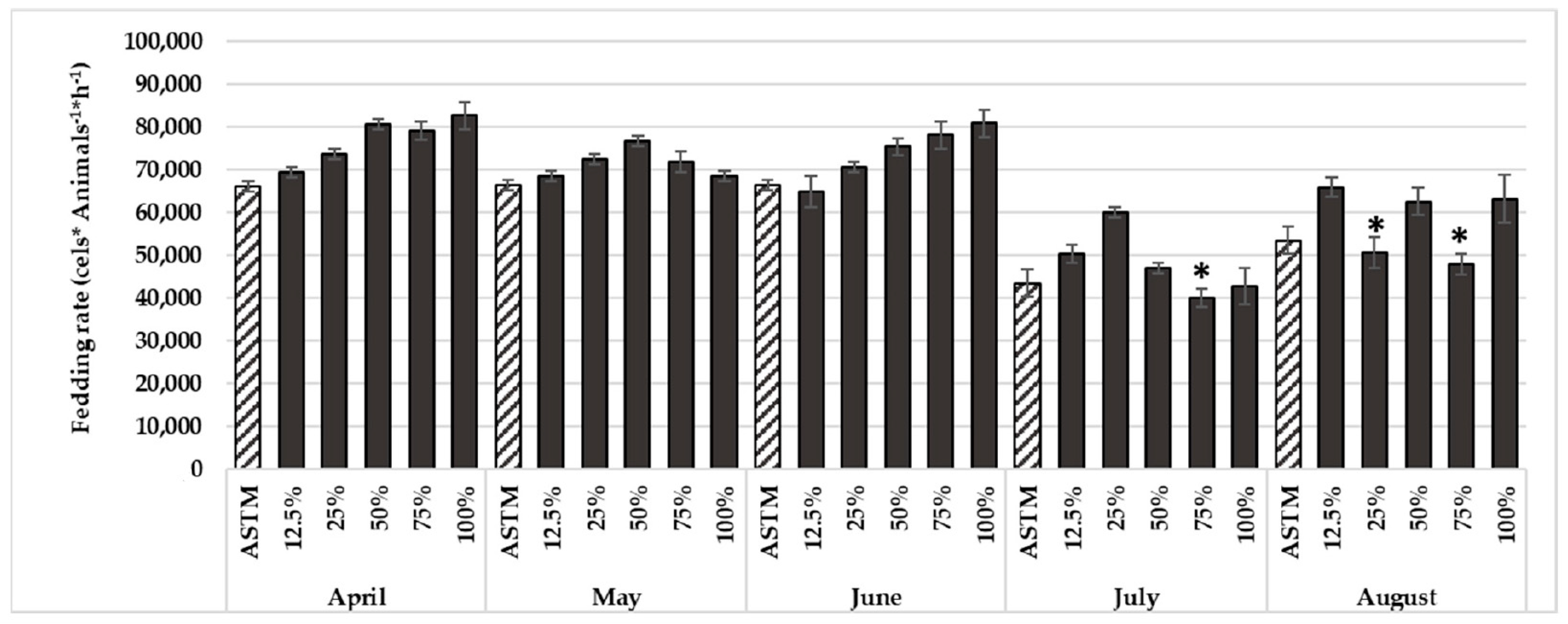
2.4.4. Feeding Assay with D. magna
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization, Pesticides Analysis, and Quality of ADW Samples for Irrigation
3.2. Ecotoxicological Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foley, J.A.; Ramankutty, N.; Brauman, K.A.; Cassidy, E.S.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Mueller, N.D.; O’Connell, C.; Ray, D.K.; West, P.C.; et al. Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature 2011, 478, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameira, M.; Mota, M. Nitrogen Related Diffuse Pollution from Horticulture Production—Mitigation Practices and Assessment Strategies. Horticulturae 2017, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.; Daam, M.A.; Cerejeira, M.J. Aquatic risk assessment of priority and other river basin specific pesticides in surface waters of Mediterranean river basins. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willison, R.S.; Nelson, K.A.; Abendroth, L.J.; Chighladze, G.; Hay, C.H.; Jia, X.; Kjaersgaard, J.; Reinhart, B.D.; Strock, J.S.; Wikle, C.K. Corn yield response to subsurface drainage water recycling in the midwestern United States. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 1865–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraouf, R.E.; Marwa, M.A.; Dewedar, O.M.; El-Shafie, A.F. Smart Techniques for Improving Water Use Under the Conditions of Arid and Semi-Arid Environmental Areas: A Review. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama, J.R.; Jorgensen, D.B.G.; Diamantopoulos, E. Bucheli, T.D. Hansen, H.C.B.; Strobel, B.W. Indole and quinolizidine alkaloids from blue lupin leach to agricultural drainage water. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 834, 155283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Nelson, K.A.; Singh, G.; Veum, K.S.; Davis, M.P.; Udawatta, R.P.; Kaur, G. Drainage water management impacts soil properties in floodplain soils in the midwestern, USA. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 279, 108193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN. United Nations Decade on Ecosystem Restoration (2021–2030). 2019, pp. 1–6. Available online: undocs.org/A/RES/73/284 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- European Commission. Commission Staff Working Document: European Overview–River Basin Management Plans 296; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Helmecke, M.; Fries, E.; Schulte, C. Regulating water reuse for agricultural irrigation: Risks related to organic micro-contaminants. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Serrano, A.; Ibáñez, C.; Lacorte, S.; Barata, C. Ecotoxicological effects of rice field waters on selected planktonic species: Comparison between conventional and organic farming. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 1523–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SCHEER. Scientific Committee on Health, Environmental and Emerging Risks. Scientific Advice on Proposed EU Minimum quality Requirements for Water Reuse in Agricultural Irrigation and Aquifer Recharge; European Union: Luxembourg, 2017; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Rand, G.M. Fundamentals of Aquatic Toxicology: Effects, Environmental Fate, and Risk Assessment, 2nd ed.; Taylor and Francis: Bristol, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarenga, P.; Martins, M.; Ribeiro, H.; Mota, M.; Guerra, I.; Cardoso, H.; Silva, J.L. Evaluation of the fertilizer potential of Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus obliquus grown in agricultural drainage water from maize fields. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APA (Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente). Plano de Gestão de Região Hidrográfica 2016/2021. Parte 2. Caracterização e Diagnóstico; Anexo IV; APA: Amadora, Portugal, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- SNISOLOS. Sistema Nacional de Informação dos Solos. Available online: https://snisolos.dgadr.gov.pt (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- DGADR. Direção-Geral de Agricultura e Desenvolvimento Rural. Nota Explicativa da Carta dos Solos de Portugal e da Carta de Capacidade de Uso do Solo. Available online: https://dgadr.gov.pt (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- INIAV (Instituto Nacional de Investigação Agrária e Veterinária, I.P.). Manual de Fertilização das Culturas; INIAV: Oeiras, Portugal, 2022; ISBN 978-972-579-063-2. [Google Scholar]
- IPMA. Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera. Monitorização Diária. Available online: https://www.ipma.pt/pt/oclima/monitoriza.dia/ (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environmental Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- DGAV. SIFITO—Sistema de Gestão das Autorizações de Produtos Fitofarmacêuticos. 2021. Available online: https://sifito.dgav.pt (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- DIN 38407-36:2014-09, German Standard Methods for the Examination of Water, Waste Water and Sludge—Jointly Determinable Substances (Group F)—Part 36: Determination of Selected Active Substances of Plant Protection Products and Other Organic Substances in Water—Method Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometric Detection (HPLC-MS/MS or -HRMS) after Direct Injection (F 36). Deutsches Institut für Normung e. V. Available online: https://www.beuth.de/en/standard/din-38407-36/208008665 (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- PPDB. Pesticide Properties DataBase. Available online: https://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/index.htm (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Decreto-Lei nº 236/98, de 1 Agosto. Diário da República no. 176/1998—I Série A. 1998, pp. 3676–3722. Available online: https://diariodarepublica.pt/dr/detalhe/decreto-lei/236-1998-430457 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Decreto-Lei n.o 119/2019, de 21 de agosto. Diário da República n.o 159/2019. 2019, pp. 21–44. Available online: https://dre.tretas.org/dre/3824634/decreto-lei-119-2019-de-21-de-agosto (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1985; ISBN 978-92-5-102263-4. [Google Scholar]
- Tomaz, A.; Palma, P.; Fialho, S.; Lima, A.; Alvarenga, P.; Potes, M.; Costa, M.J.; Salgado, R. Risk assessment of irrigation-related soil salinization and sodification in Mediterranean areas. Water 2020, 12, 3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 11348-2; Determination of Inhibitory Effect of Water Samples on the Light Emission of Vibrio Fischeri (Luminescent Bacteria Test). Part 2: Method Using Liquid-dried Bacteria. International Organization for Standardisation: Geneve, Switzerland, 1998.
- OCDE (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development). OCDE 211, Daphnia Magna Reproduction Test; OCDE: Paris, France, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Persoone, G. THAMNOTOXKIT FTM—Crustacean Toxicity Screening Test for Fresh-water. Standard Operational Procedure. Belgium. 1999. Available online: https://www.microbiotests.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/thamnocephalus-toxicity-test_thamnotoxkit-f_standard-operating-procedure.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- McWilliam, R.A.; Baird, D.J. Postexposure feeding depression: A new toxicity endpoint for use in laboratory studies with Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002, 21, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, Y.; Calow, P.; Baird, D. A mechanistic model of contaminant-induced feeding inhibition in Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1995, 14, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, D.J. Probit Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis; Prentice-Hall International: Englewood Cliff, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Cui, S.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Hough, R.; An, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Transport of neonicotinoid insecticides in a wetland ecosystem: Has the cultivation of different crops become the major sources? J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 339, 117838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaz, A.; Palma, P.; Alvarenga, P.; Gonçalves, M.C. Soil salinity risk in a climate change scenario and its effect on crop yield, Chapter 13. In Climate Change and Soil Interactions; Prasad, M.N.V., Pietrzykowski, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 351–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APA, Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente. Critérios para a Classificação das Massas de Água—Ficha Técnica, DRH/DEQA. 2021. Available online: https://apambiente.pt/sites/default/files/_Agua/DRH/ParticipacaoPublica/PGRH/2022-2027/3_Fase/PGRH_3_SistemasClassificacao.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- EPCEU (European Parliament and the Council of the European Union). Directive 2013/39/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 August 2013 amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as regards priority substances in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Union 2013, 226, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Palma, P.; Penha, A.M.; Novais, M.H.; Fialho, S.; Lima, A.; Catarino, A.; Mourinha, C.; Alvarenga, P.; Iakunin, M.; Rodrigues, G.; et al. Integrative toolbox to assess the quality of freshwater sediments contaminated with potentially toxic metals. Environ. Res. 2022, 217, 114798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, P.; Palma, P. Gonçalves, A.P. Fernandes, R.M. de Varennes, A. Vallini, G. Duarte, E. Cunha-Queda, A.C. Organic residues as immobilizing agents in aided phytostabilization: (II) Effects on soil biochemical and ecotoxicological characteristics. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, S.; Mohammad, A.W.; Hilal, N.; Abdullah, P.; Jaafar, O. Comparative study of NF and RO membranes in the treatment of produced water II: Toxicity removal efficiency. Desalination 2013, 315, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, P.; Bonnemoy, F.; Charvy, J.C.; Bohatier, J.; Mallet, C. Toxicity assessment of the maize herbicides S-metolachlor, benoxacor, mesotrione and nicosulfuron, and their corresponding commercial formulations, alone and in mixtures, using the Microtox(®) test. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2444–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Meng, F.L.; Hu, Y.Y.; Habibul, N.; Sheng, G.P. Concentration- and nutrient-dependent cellular responses of microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa to perfluorooctanoic acid. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polazzo, F.; dos Anjos, T.B.O.; Arenas-Sánchez, A.; Romo, S.; Vighi, M.; Rico, A. Effect of multiple agricultural stressors on freshwater ecosystems: The role of community structure, trophic status, and biodiversity-functioning relationships on ecosystem responses. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diogo, B.S.; Rodrigues, S.; Silva, N.; Pinto, I.; Antunes, S.C. Evidence for Links between Feeding Behavior of Daphnia magna and Water Framework Directive Elements: Case Study of Crestuma-Lever Reservoir. Water 2022, 14, 3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, I.; Rodrigues, S.; Lage, O.M.; Antunes, S.C. Assessment of water quality in Aguieira reservoir: Ecotoxicological tools in addition to the Water Framework Directive. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, B.D.; Frankenberger, J.R.; Hay, C.H.; Helmers, M.J. Simulated water quality and irrigation benefits from drainage water recycling at two tile-drained sites in the US Midwest. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 223, 105699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenberger, J.; Reinhart, B.; Nelson, K.; Bowling, L.; Hay, C.; Youssef, M.; Allred, B. Questions and Answers about Drainage Water Recycling for the Midwest. 2017. Available online: https://www.extension.purdue.edu/extmedia/ABE/ABE-156-W.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2022).

| Type of Product | Dose | Composition | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fertilizers | Basal | 300 kg ha−1 | Phosphorus/ Potassium binary fertilizer (0N-12P-30K) |
| 200 kg ha−1 | Nitrogen/Phosphorus binary fertilizer (15N-35P-0K) | ||
| Top-dressing | 850 kg ha−1 | Liquid Nitrogen (32%; w/v) | |
| Herbicides | 4 L ha−1 | A suspo-emulsion containing: Mesotrione: 37.5 g L−1 (3.39%; w/w) S-metolachlor: 312.5 g L−1 (28.2%; w/w) Terbuthylazine: 187.5 g L−1 (16.9%; w/w) | |
| 2 L ha−1 | An oil dispersion containing: Isoxadifen-ethyl: 22 g L−1 Tembotrione: 44 g L−1 | ||
| 1.5 L ha−1 | Pyridate: 600 g L−1 | ||
| Insecticides | 0.75 L ha−1 | Lambda-cyhalothrin: 100 g L−1 or 9.5% (w/w) | |
| Month | T min. (°C) | T max. (°C) | Acummulated Precipitation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| March | 4.6 | 29.1 | 52.2 |
| April | 6.7 | 27.2 | 111.5 |
| May | 6.1 | 30.9 | 23.3 |
| June | 10.8 | 39.4 | 12.6 |
| July | 12.8 | 41.9 | 0.3 |
| August | 12.1 | 38.8 | 0.3 |
| Solubility in Water (mg L−1) a | DT50 (Water) at 20 °C; pH 7 b | Log Kow c | Soil Sorption Koc (mL g−1) d | DT50 (Soil) e | GUS Leaching Potential Index f | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herbicide | ||||||
| Glyphosate | 100,000 | nd | −6.28 | 1424 | 16.11 | 0.21 |
| Nicosulfuron | 7500 | nd | 0.61 | 30 | 26 | 3.44 |
| S-metolachlor | 480 | 9.9 | 3.05 | - | 51.8 | 2.32 |
| Tembotrione | 71,000 | 88 | −1.09 | - | 14.5 | 0.95 |
| Terbuthylazine | 6.6 | 65 | 3.4 | - | 72 | 2.19 |
| Herbicide metabolite | ||||||
| Aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA, glyphosate metabolite) | 1,466,561 | Stable | −1.63 | 2002 | 234 | 0.04 |
| Desethy-terbuthylazine (terbuthylazine metabolite) | 327.1 | 6 | 2.3 | - | 54 | 3.07 |
| Pyridafol (pyridate metabolite) | 23.80 | nd | 0.56 | 104 | 2.2 | 4.73 |
| Insecticide | ||||||
| Lambda-cyalothryn | 0.005 | 9.9 | 5.5 | 283,707 | 175 | −2.09 |
| Parameters | April | May | June | July | August |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.70 ± 0.07 b | 7.96 ± 0.01 a | 7.62 ± 0.02 b | 7.65 ± 0.01 b | 7.22 ± 0.05 c |
| ECw (μS cm−1) | 813.0 ± 0.1 e | 1042.7 ± 2.5 a | 1014.0 ± 0.2 b | 945.0 ± 0.4 c | 843.5 ± 0.3 d |
| Na (mg L−1) | 47.9 ± 1.2 d | 59.5 ± 1.3 c | 69.5 ± 0.4 a | 59.5 ± 0.4 c | 63.0 ± 0.5 b |
| K (mg L−1) | 7.3 ± 0.2 c | 7.6 ± 0.1 c | 13.7 ± 1.9 b | 23.6 ± 0.2 a | 6.7 ± 0.3 c |
| Ca (mg L−1) | 95.2 ± 2.1 b | 112.5 ± 2.8 a | 84.1 ± 1.0 c | 115.5 ± 1.5 a | 98.9 ± 0.1 b |
| Mg (mg L−1) | 12.8 ± 0.3 d | 17.8 ± 0.4 c | 18.0 ± 0.1 c | 18.9 ± 0.1 b | 19.7 ± 0.1 a |
| P (mg L−1) | 0.31 ± 0.01 b,c | 0.33 ± 0.02 b | 0.23 ± 0.06 c | 1.76 ± 0.02 a | 0.27 ± 0.01 b,c |
| S (mg L−1) | 9.40 ± 0.06 c | 13.62 ± 0.08 a | 11.50 ± 0.41 b | 14.26 ± 1.57 a | 15.49 ± 0.21 a |
| Fe (mg L−1) | 0.83 ± 0.04 b | 1.85 ± 0.05 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 d | 0.02 ± 0.00 d | 0.11 ± 0.01 c |
| Cu (mg L−1) | 0.020 ± 0.001 a | 0.010 ± 0.001 b | 0.009 ± 0.001 b | 0.009 ± 0.001 b | 0.010 ± 0.002 b |
| Zn (mg L−1) | 0.047 ± 0.006 b | 0.013 ± 0.006 c | <0.010 | <0.010 | 0.080 ± 0.001 a |
| Mn (mg L−1) | 0.267 ± 0.023 b | 0.757 ± 0.006 a | 0.003 ± 0.000 c | 0.006 ± 0.001 c | 0.010 ± 0.000 c |
| B (mg L−1) | 0.027 ± 0.006 b,c | 0.020 ± 0.002 c | 0.036 ± 0.003 a | 0.035 ± 0.000 a,b | 0.042 ± 0.001 a |
| Cl− (mg L−1) | 74 ± 4 d | 113 ± 4 a | 118 ± 2 a | 91 ± 1 c | 105 ± 4 b |
| COD (mg O2 L−1) | 22.3 ± 0.1 a | 12.6 ± 0.1 a | 19.8 ± 0.1 a | 19.8 ± 0.2 a | 14.9 ± 0.3 a |
| NO3− (mg NO3− L−1) | 25.6 ± 0.4 d | 42.6 ± 1.7 b | 39.6 ± 0.5 c | 98.9 ± 1.1 a | 26.5 ± 0.4 d |
| NH4+ (mg NH4+ L−1) | 1.36 ± 0.03 b | 1.40 ± 0.05 a,b | 1.43 ± 0.01 a,b | 1.43 ± 0.02 a | 0.35 ± 0.02 c |
| SAR | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 1.5 |
| Concentration (μg L−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active Substance | April | May | June | July | August |
| Herbicide | |||||
| S-metolachlor | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.19 ± 0.10 | 0.74 ± 0.37 | 0.33 ± 0.17 | 0.65 ± 0.33 |
| Tembotrione | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.19 ± 0.10 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| Terbuthylazine | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.48 ± 0.24 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | <0.05 |
| Herbicide metabolite | |||||
| AMPA | 0.11 ± 0.06 | <0.05 | 0.15 ± 0.08 | 0.36 ±0.18 | <0.05 |
| Pyridafol | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.14 ± 0.07 | 0.22 ± 0.11 |
| Months | V. fisheri 30 min-EC50 (%; v/v) | T. platyurus 24 h-EC50 (%; v/v) |
|---|---|---|
| April | n.t. | n.t. |
| May | n.t. | n.t. |
| June | n.t. | n.t. |
| July | n.t. | n.t. |
| August | 25.2 ± 0.3 | n.t. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palma, P.; Catarino, A.; Silva, E.; Alvarenga, P. Chemical and Ecotoxicological Assessment of Agricultural Drainage Water from a Maize Crop Area: A Case Study in the Tejo Basin (Portugal). Water 2023, 15, 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132434
Palma P, Catarino A, Silva E, Alvarenga P. Chemical and Ecotoxicological Assessment of Agricultural Drainage Water from a Maize Crop Area: A Case Study in the Tejo Basin (Portugal). Water. 2023; 15(13):2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132434
Chicago/Turabian StylePalma, Patrícia, Adriana Catarino, Emília Silva, and Paula Alvarenga. 2023. "Chemical and Ecotoxicological Assessment of Agricultural Drainage Water from a Maize Crop Area: A Case Study in the Tejo Basin (Portugal)" Water 15, no. 13: 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132434
APA StylePalma, P., Catarino, A., Silva, E., & Alvarenga, P. (2023). Chemical and Ecotoxicological Assessment of Agricultural Drainage Water from a Maize Crop Area: A Case Study in the Tejo Basin (Portugal). Water, 15(13), 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132434








